BIS 2C Midterm 1
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms

What are the letters highlighted in purple?
taxa
a description of the evolutionary history of relationships among organisms (or their parts)
phylogeny
a diagram showing a phylogeny; contains taxa, nodes, and branches
phylogenetic tree
any single entity or group for which we designate a name on a phylogenetic tree (singular)
taxon
Rotated trees do not change in meaning and essentially convey the same information. (T/F)
T
a taxon in the past, the most recent common ancestor of the taxa “above” it; points atwhich a branch splits from one lineage into more
node
The __________ node is the MCRA of all taxa in the tree. It represents a point of the earliest split in the tree.
root
What is used to represent the evolution of taxa over time? (singular)
branch
_____________ branches lead to modern taxa. _______________ branches lead to nodes and connect taxa to it, showing evolution from node to taxa. The ____________ branch leads to the MCRA of all taxa in the tree.
terminal, internal, root
node with more than two branches coming out of it; indicates ambiguity—multiple possible relationships for a particular tree
polytomy
_____________________ and __________ transfer lead to node complications. Proteobacteria evolved into the mitochondria and cyanobacteria evolved into the chloroplast, showing a “ring” of life rather than a tree.
endosymbiosis, gene
Are populations usually shown in a phylogentic tree? (Y/N)
N
Every single branch and taxa are shown in phylogenetic trees. (T/F)
F
Each node in a tree can be rotated/spun around without changing the meaning. This is known as “______________ rotation”.
branch

Do these two trees have the same phylogeny? (Y/N)
Y
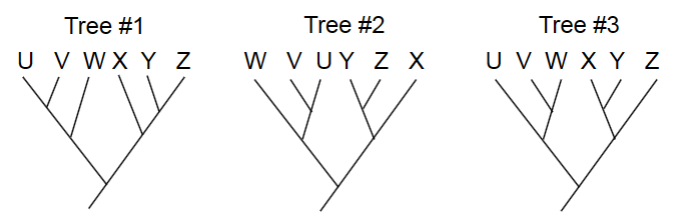
Which of these statements is true?
A. tree 1 = tree 2
B. tree 1 = tree 3
C. all three trees are equivalent
D. all three trees are different
A
A taxon/group’s closest relatives is the taxon or group with which it shares a _________.
MCRA

Answer the questions in this order:
1. Is c more closely related to a or b?
A. a
B. b
C. equivalent
2. What is the closest relative of e?
A. h
B. g
C. h + g
D. f
E. d
F. h+g and f
3. What is the closest relative of g?
A. f
B. e
C. h
D. h and f
E. h, f, and e
C, F, C
a group of taxa consisting of a single node and all its descendants and nothing else
monophyletic group
A monophyletic group can be used interchangeably with _________.
clade
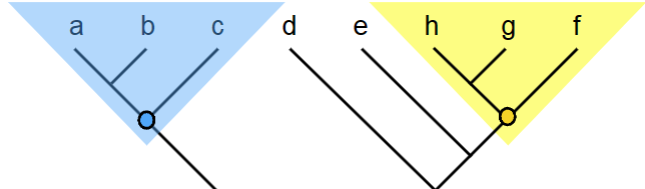
What are a, b, c and h, g, f called?
monophyletic group
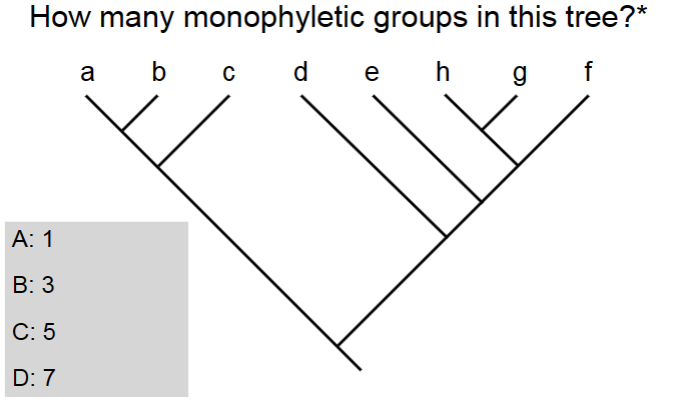
How many monophyletic groups are in this tree?
A. 1
B. 3
C. 5
D. 7
D
The number of nodes is (different/equal) to the number of monophyletic groups in a tree.
equal
a group consisting of their MRCA but excluding some of its descendants; non-natural grouping
paraphyletic group

What is the group highlighted in red called?
paraphyletic group

For this group to be monophyletic, what must be included?
birds
polyphyletic group consisting of birds and mammals
homeotherms
Names of groups that are not ______________ should use quotes.
monophyletic
a group of organisms that excludes the MCRA of the group and usually excludes some of the descendants of the MCRA
polyphyletic group

What is the group highlighted in green called?
polyphyletic

For this group to be monophyletic, what must be included?
lizards, turtles, dinos
Polyphyly should not be grouped because it is the result of ______________, which means they are not closely related by common ancestry.
homoplasy
phylogenetic tree type; shows relative branching order, branch length no meaning
cladogram
phylogenetic tree type; shows relative branching order, branch length is proportional to amount of character change
phylogram
phylogenetic tree type; shows relative branching order, branch length is proportional to time
chronogram
A character _____________ is a heritable feature of an organism.
trait
A character _________ is the particular form that a character takes.
state
Traits that are shared between taxa due to being inherited from a common ancestor are _________________.
homologous
common ancestry
homology
taxa changing over time and become different from their ancestors and other taxa/lineages
divergence
When character states change, the trait will never be homologous. (T/F)
F
character state that is the same as that seen in the ancestor of the group under consideration
ancestral state
character state that is different from that seen in the ancestor of the group under consideration
derived state
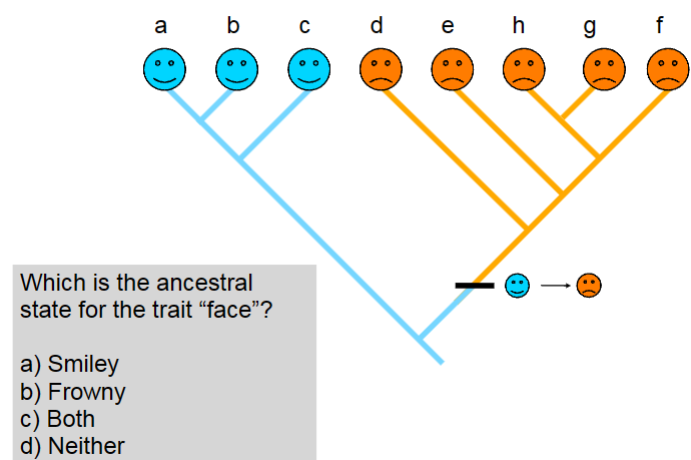
Which is the ancestral state for the trait “face”?
A. smiley
B. frowny
C. both
D. neither
A

Which is the derived state for the trait “face”?
A. smiley
B. frowny
C. both
D. neither
B
A “shared, derived state” is known as a __________________.
synapomorphy
a derived trait (or state) that is shared by a clade
synapomorphy
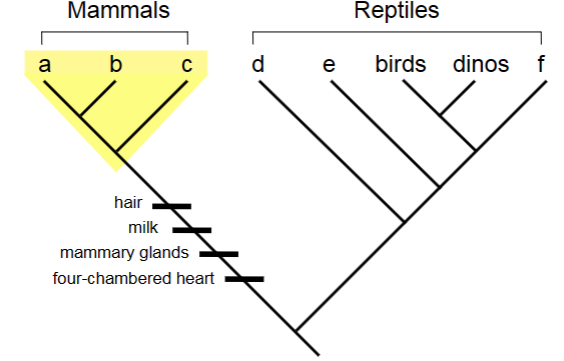
a, b, and c are a ________________ of mammals.
synapomorphy
character state independently evolved; statement of similar traits not caused by common ancestry
homoplasy
independently evolved traits subjected to similar selection pressures may become similar
convergent evolution
Character state __________________ methods allow one to infer the most likely history of state and state changes.
reconstruction
the simplest of two (or more) competing theories is to be preferred (assuming all else is equal)
parsimony
terrorism involving release of biological agents (intentionally)
bioterrorism
After further research, it was determined that the form of __________ used in the bioterrorism attack of 2001 was a lab/research strain used by biological weapons/defense researchers.
anthrax
________________ is caused by microbial eukaryotes and in the group of Apicomplexans. The apical complex helps the parasite enter the host’s cells through a mass of organelles at one tip.
malaria
________________ is responsible for the mitochondria developing in a eukaryotic cell.
proteobacteria
_________________ is responsible for the chloroplast developing in a plant cell.
cyanobacteria
____________________ are strange, non-photosynthetic chloroplasts.
apicoplasts
Apicoplasts were caused by a eukaryotic cell (without chloroplast) engulfing a plant cell. The plant cell acts as an _______________ and the mitochondria + nucleus are removed.
organelle
Apicomplexans all have a mass of organelles at one tip and the ____________ _________ helps parasites enter the host’s cell.
apical complex
_______________ are absorptive heterotrophs and get energy + cell components by degrading organic compounds and organisms. They were once classified as fungi, but not closely related to them.
oomcyetes
seeing more in a microscope than you can culture and grow
Great Plate Count Anomaly
A solution to the Great Plate Count Anomaly and a cheaper/less extensive approach is to take __________, read the sequence, and compare.
DNA
community of microbes
microbiome
Phylogenetic trees can be used to solve forensic science cases. (T/F)
T
organisms scientists use to compare with other organisms
model organisms
________________ are sister to animals and used as a ____________ organism. Some are colonial and resemble a type of cell found in ____________ (relating to multicellularity).
choanoflagellates, model, sponges
making a hypothesis about the phylogeny for a set of taxa
phylogenetic inference
To infer a phylogenetic tree, which two key issues will be decide:
Rooted or unrooted trees?
What scoring scheme do we use?
rooted, parsimony
How many rooted trees are there for four taxa?
15
a clade of taxa under study
ingroup
one or more taxa that are related to but are outside the ingroup; equally related to all members of ingroup
outgroup
How many rooted trees can be developed for three taxa?
3
With three nodes that each have two possible character states, how many possible patterns are there?
8
The minimum number of changes will always be a pattern where the MRCA has the same state as the ___________.
outgroup
If there is only one different character from the rest, how many changes will there be in the tree?
1
_____________ characters are uninformative because they are uniform across the taxa (i.e. all states are “T”)
invariant
Parsimony-______________ characters give us the same number of steps regardless of the tree.
uninformative
How many possible unrooted trees are there for four taxa?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
C
How many possible rootings are there for an unrooted tree with four taxa?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
B
Another method of “scoring” is more accurate, computationally costly, and allows for branches to be different lengths, traits to count differently and types of changes to be modeled compared to parsimony is…
statistical
To test two hypotheses regarding life on Earth, we can look at the _____________ traits.
universal
Which of the following is NOT a universal trait of all life?
A. made up of a cells
B. carry out transcription and translation
C. extract energy from the environment
D. universal molecular code to make proteins
E. contain genomes inside a nucleus
E
The existence of universal traits found in common across all of life proves all life has common ancestry. (T/F)
F
For studies of universal traits, for each trait ask:
What is the probability that such a trait could have been invented in separate lineages that do not share common ancestry?
If (high/low) probability, then that particular trait cannot be used as evidence for common ancestry.
If the probability is (high/low), then that particular trait is evidence for the common ancestry of all life.
high, low
Can we use universal traits to infer phylogenetic relationships? (Y/N)
N
Carl _________ discovered that all organisms have homologous ____________. The sequences of the individual components have changed slowly over time (they can be used to compare).
Woese, ribosomes
___________ archaea were found to be more closely related to eukarya than archaea,
asgard
Asgard archaea and eukarya are in a ________________ group.
monophyletic
Are “prokaryotes” monophyletic? (BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA) (Y/N)
N
Are just “archaea” monophyletic? (Y/N)
N
The groups “prokaryotes” and “archaea” are _____________ groups.
paraphyletic
Archaea and eukarya share a common ancestor that are exclusive to bacteria. (T/F)
T
Asgard archaea and eukaryotes are ____________.
sisters
The overall structure of the tree of life has been determined by analysis of ______________ sequence data. This is particularly important for placing most ________ into the tree of life.
molecular, microbes
It is important to include DNA from organisms that have not been cultured (so using culture-independent methods) to add on to the view of the tree of life. (T/F)
T
The ____________ _______________ Common Ancestor is the MCRA of all organisms.
Last Universal
LUCA most likely had the trait found in ______________ due to parsimony.
prokaryotes
Some features thought to be “eukaryotic” innovations were likely present in the Eukaryote-____________ ancestor.
asgard
Asgard archaea also had ____________ for DNA and a complex _____________, similar to eukaryotic features, which made these features thought to be older than they seemed to be.
chromatin, cytoskeleton