PBS* 1.2: Master the Morgue
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/42
Last updated 5:18 AM on 10/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
Morgue
A place where the bodies of dead persons are kept temporarily pending identification or release for burial or autopsy.

2
New cards
Autopsy
A postmortem evaluation to determine cause of death.
3
New cards
Cause of death
The specific injury, trauma, or disease that directly caused the victim's death
4
New cards
Mechanism of death
What happens physiologically (inside the body) to result in death
5
New cards
Manner of death
The circumstances that result in death, which are designated as natural or unnatural. Unnatural deaths are further categorized as an accident, as a homicide or as undetermined.
6
New cards
Medical examiner
A physician who performs an autopsy when a death might have been caused accidentally or intentionally. In some jurisdictions, the Medical Examiner may also serve as the coroner.

7
New cards
Organ systems
A group of organs in a body that work together to perform a specific function.
8
New cards
Physiological time of death
The time when the decedent's vital functions actually ceased
9
New cards
Estimated time of death
The time the medical examiner estimates that the death occurred
10
New cards
Legal time of death
The time of death recorded on the death certificate; based on when the body was found or physically pronounced dead
11
New cards
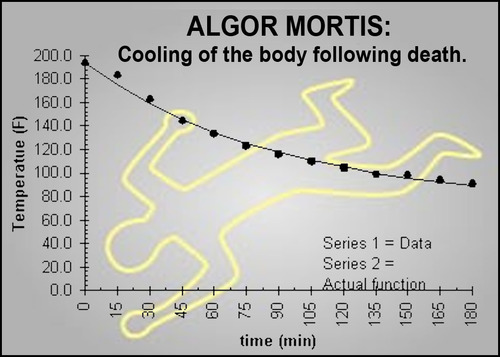
Algor mortis
the change in body temperature after death
12
New cards
Rigor mortis
the stiffening of joints and muscles after death

13
New cards
Livor mortis
pooling of the body following death that causes a purplish red discoloration of the skin; also referred to as lividity
14
New cards
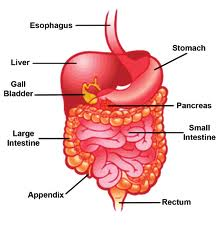
Digestive system
An organ system that breaks down food to extract energy and nutrients and then evacuates remaining waste.
15
New cards
Nutrient
A substance that the body needs to maintain life and health, such as proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals.

16
New cards
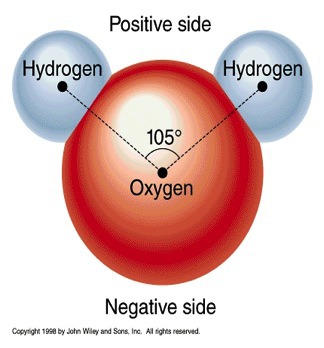
Molecules
A group of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
17
New cards
Chemical reaction
A process where atoms and/or molecules are rearranged to transform matter.
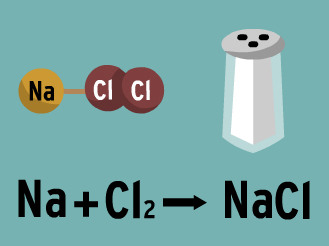
18
New cards
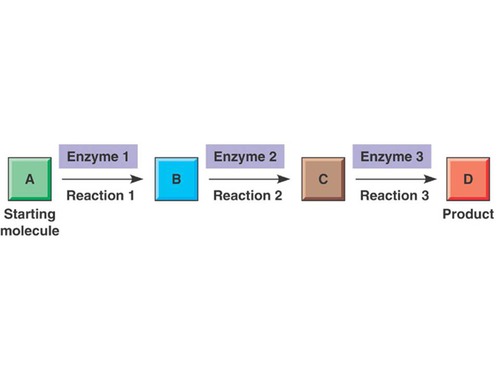
Metabolism
The chemical reaction processes of breaking down molecules for energy and of using simple building blocks to build up more complex molecules needed for growth and repair.
19
New cards
Forensic chemistry
A field of chemistry that tests non-biological samples, such as powders, pills, and other substances, to identify or quantify them.

20
New cards
Personal Protection Equipment (PPE)
Specialized clothing or equipment that a person wears for protection against laboratory hazards, such as infectious materials and chemicals.

21
New cards
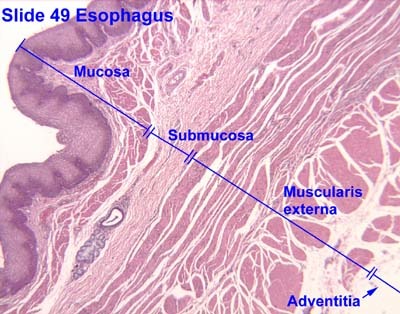
Histology
The study of the microscopic anatomy of tissues. Also known as microanatomy.
22
New cards
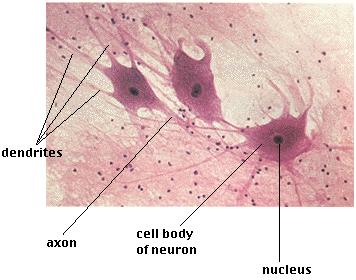
Tissue
An integrated group of cells with a common function and/or structure.
23
New cards
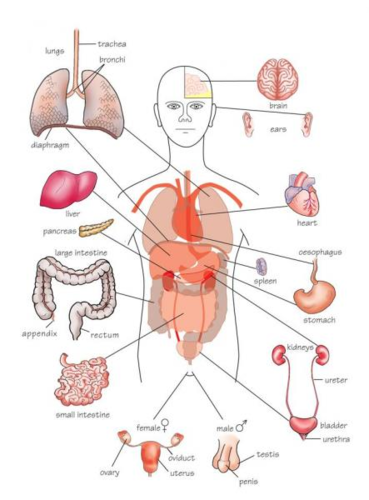
Organ
A collection of tissues in an organism that performs a specific function, such as the heart, brain, skin, and liver.
24
New cards
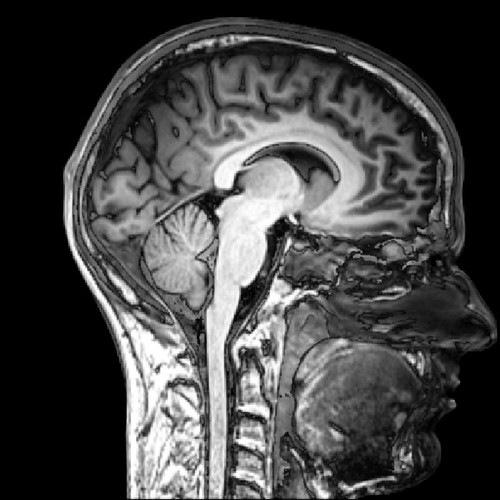
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
A medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to take pictures of the soft tissues of the body.
25
New cards
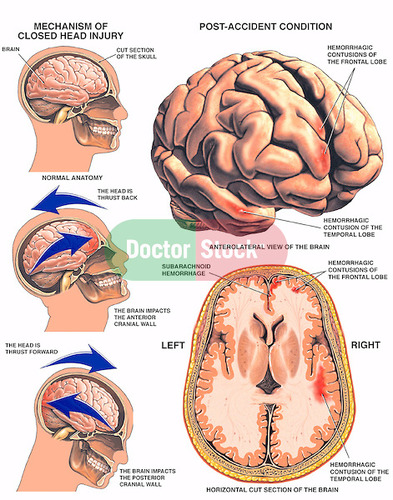
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
A brain dysfunction caused by an outside force to the head.
26
New cards
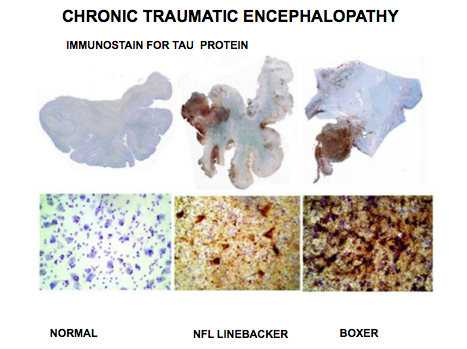
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
A progressive degeneration, and/or death, of nerve cells caused by repeated head injuries, such as repeated concussions.
27
New cards
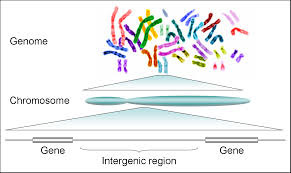
Genome
A complete set of the genes in one organism.
28
New cards
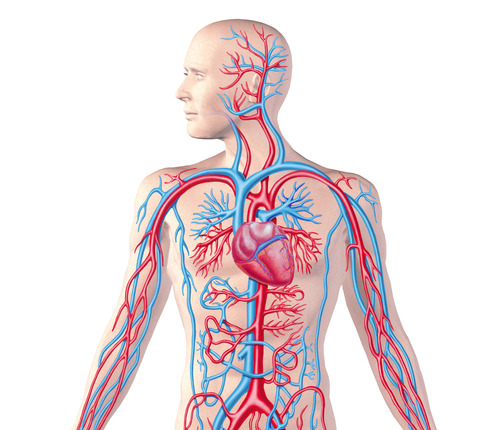
Cardiovascular system
The transport system of the body responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes; composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
29
New cards
Atrium
An upper chamber of the heart where blood enters. The heart has two atria: the left atrium connects to the lungs and the right atrium connects to the veins.
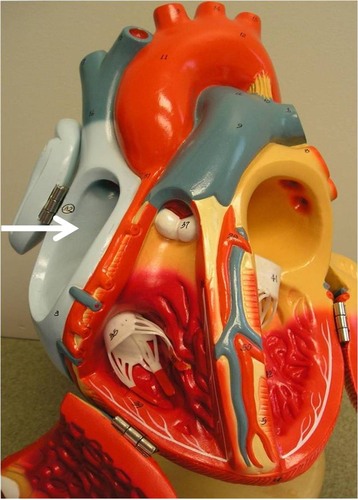
30
New cards
Ventricle
A lower chamber of the heart where blood exits. The heart has two ventricles: the left ventricle connects to the aorta and the right ventricle connects to the main pulmonary artery (or pulmonary trunk).
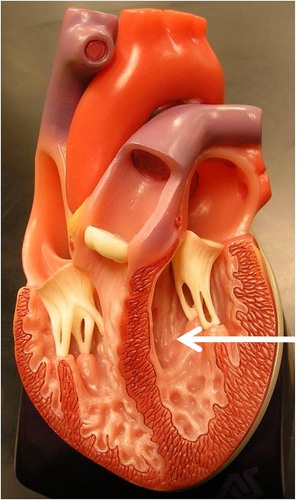
31
New cards
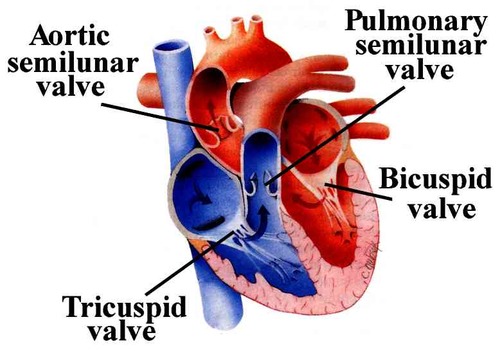
Valve
A body structure that temporarily closes a passage or orifice, or permits movement of fluid in only one direction.
32
New cards
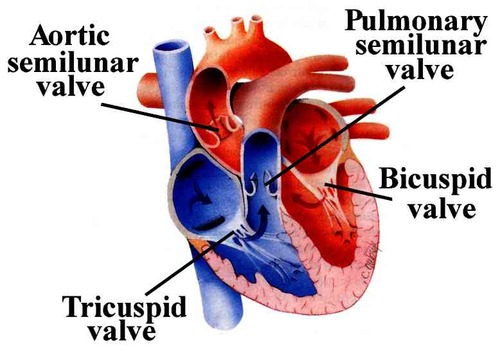
Tricuspid valve
Separates the right atrium from the right ventricle
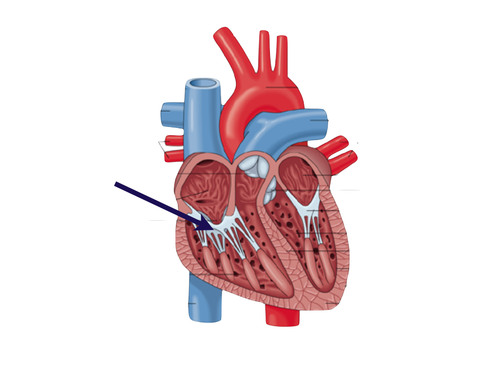
33
New cards
Pulmonary valve
Permits blood to flow into the pulmonary artery from the right ventricle
34
New cards
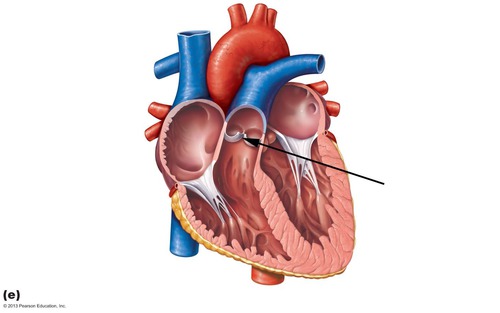
Mitral or Bicuspid valve
Separates the left atrium from the left ventricle
35
New cards
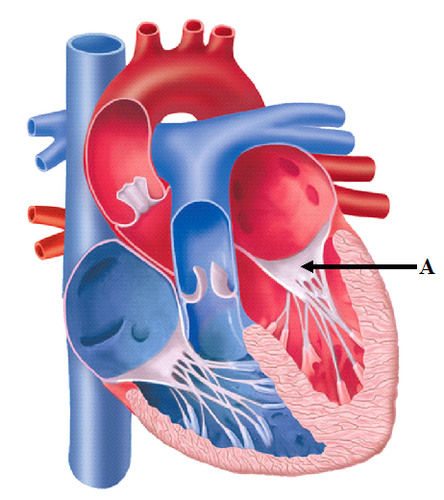
Aortic valve
Permits blood to flow into the aorta from the left ventricle
36
New cards
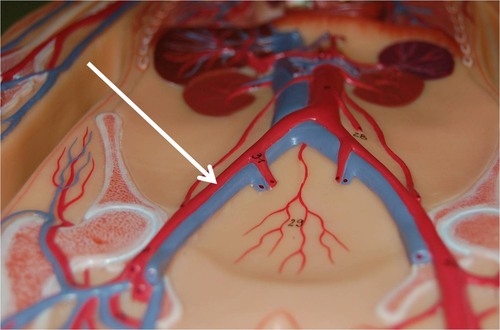
Artery
A type of vessel that carries blood from the heart through the body; part of the circulatory system.
37
New cards
Vein
A vessel that returns blood—typically deoxygenated—to the heart.
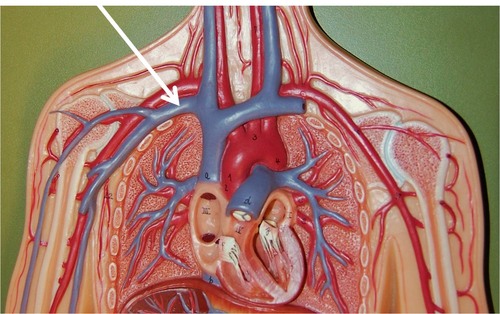
38
New cards
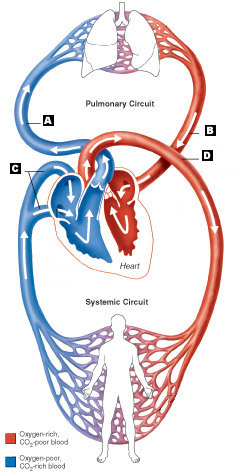
Pulmonary circulation
Part of the circulatory system in which deoxygenated blood moves from the right atrium of the heart to the lungs (through arteries) to become oxygenated and then returns to the left side of the heart (through veins).
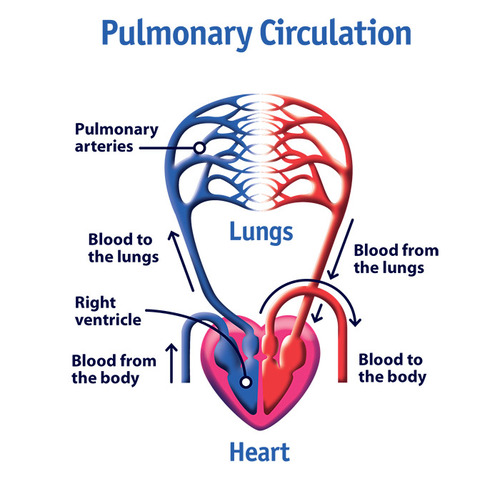
39
New cards
Systemic circulation
The series of vessels that bring oxygenated blood from the heart to tissues and return deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart.
40
New cards
Aorta
The largest artery in the body, the aorta carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the rest of the body.
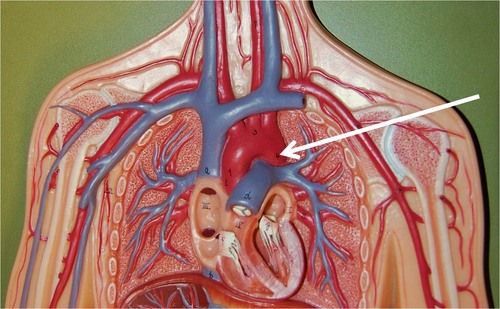
41
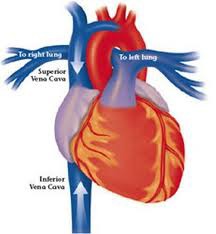
New cards
Superior vena cava
The second largest vein in the human body. The superior vena cava returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from the upper half of the body.
42
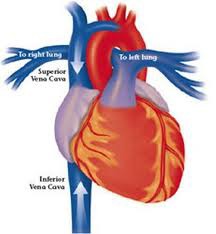
New cards
Inferior vena cava
The largest vein in the human body, the inferior vena cava returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from body parts below the diaphragm.
43
New cards
Digestive system
An organ system that breaks down food to extract energy and nutrients and then evacuates remaining waste.