Forces + weight + stopping distance + terminal velocity + Hooke’s law
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the differences and similarities of vector and scalar quantities?
They both have magnitudes but vector quantities also have direction.
What are examples of scalar quantities?
distance, speed, mass, area, time, temperature.
What are examples of vector quantities?
displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, weight.
What do we represent the direction and the magnitude of a vector quantity on paper?
Direction of arrow
Length of arrow
What are forces measured in? What do we do if forces act in the same direction? In opposite directions?
Newtons
We add them
We subtract them
Forces are either or _
A push or a pull
What are examples of contact and non-contact forces?
Contact: friction, tension, normal contact forces, air resistance.
Non-contact: weight due to gravity, magnetic force, electrostatic force.
Forces can cause objects to:
Change speed, change direction, change shape.
When forces are balanced, objects…
Stay still or move at a steady speed.
There must be ZERO resultant force for a object to travel at a constant speed, so they DON'T NEED a constant overall force.
When forces are unbalanced (resultant force), objects…
Accelerate (or decelerate) in the direction of the unbalanced force
These also include stopping, starting and changing direction.
Friction/drag/air resistance is a force that opposes___
Motion
What is the equation for resultant/unbalanced force? Force equation
Force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration (m/s^2)
Equation for weight
Weight (N) = mass (kg) x gravitational field strength (N/kg)
W = m x g
- An apple with mass of 100g falls from a tree on Earth.
What is its weight?
m = 100g/1000
= 0.1 kg
W = mg
= 0.1 x 10 (or 9.8)
= 1N
A machine has a weight of 17N on Mars (g = 3.7 N/Kg). What would its weight be on the moon (g = 1.6 N/Kg)?
Find mass = 17/3.7
= 4.594…
w = 4.594… x 1.6
= 7.4
1 d.p because worst precision data is to 1 d.p
What is Newton's first law?
An object stays at a constant velocity (including at rest) and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced/resultant force.
What is Newton's second law?
Force = mass x acceleration
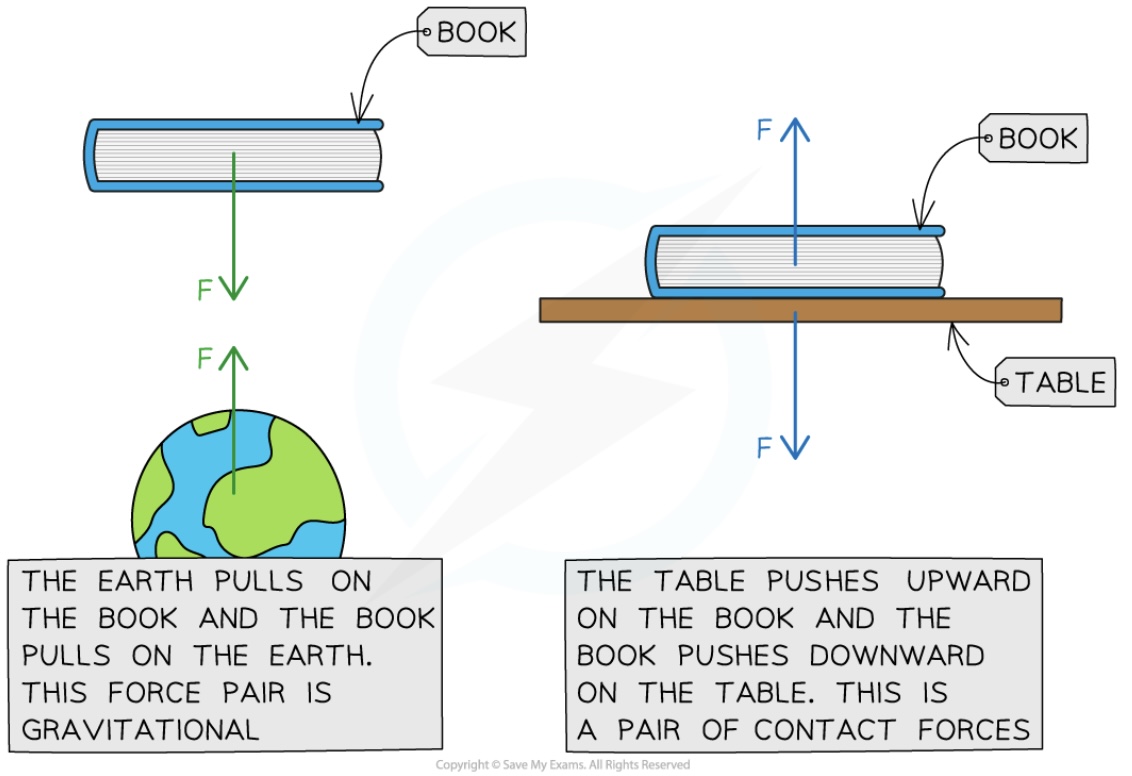
What is Newton's third law? How can you recognize this in a diagram?
Whenever 2 objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal (in magnitude) and opposite (in direction).
- The two forces act on different objects
- The two forces always are equal in magnitude but act in opposite directions
- The tow forces are always the same type: weight, reaction force, etc
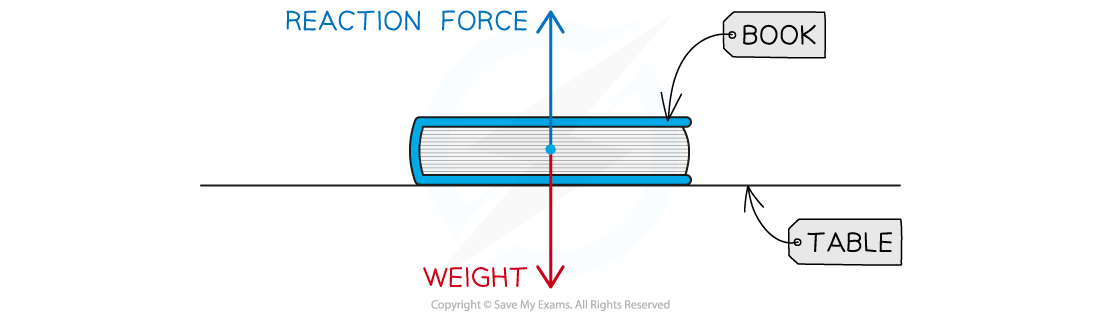
In this diagram is this an example of Newton's third law? Explain
No, because even though they have same magnitude and opposite direction, they are TWO different types of forces (weight and normal contact force) that are acting on ONE object (the book).
If one arrow originated from the book (weight) and the other one from the table (reaction force) it would be third law. The book pushes downward on the table and the table pushes upwards on the book and both these forces are contact forces
What is the stopping distance?
Is the total distance travelled during the time between the driver first spotting a hazard and the car to one to complete stop
How do you calculate stopping distance?
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
y = thinking distance/ x = braking distance
|
|—————-\
| ¡ \
| y ¡ x \
|¡_
What is the thinking distance? Braking distance?
The distance travelled in the time it takes for the driver to react and PREPARE to stop (applying brakes).
The distance travelled under the braking force (brakes are being applied) in meters during its deceleration
What are factors that affect thinking distance?
The initial speed of the vehicle.
- increasing the speed would increase the thinking distance.
REACTION TIME:
Intoxication, ie. consumption of alcohol or drugs.
- alcohol and some drugs would increase the thinking distance by increasing reaction time.
- caffeine can decrease the thinking distance by making you more alert (reducing the reaction time). However, too much caffeine can increase thinking distance by making you distracted which would increase reaction time.
Distractions, i.e using phone, rain
distractions would increase the thinking distance by increasing the reaction time.
tiredness would increase the thinking distance by increasing reaction time.
old age increases thinking distance.
What are factors that affect braking distance?
- speed
Condition of
brakes, tyres, road (wet or icy roads make the breaks less effective and the vehicle travels further as it comes to a stop)
force applied on brakes
vehicle mass (more mass = more distance before it comes to a stop)
What is a factor that affects both the braking and thinking distance?
- Speed of vehicle (x-axis speed/y-axis distance):
Thinking: reaction time is the same but would have travelled a greater distance before braking if faster.
Braking: the grater the speed the greater the braking d. will be because brakes will need to do more work to bring the vehicle to a stop (more time before actually stopping)
|
|—————\
| \
|—————\ \
|___
Describe and explain the motion of the skydiver in terms of acceleration and forces when:
- The instant they step out of the plane
- The only force on them is the weight so there is an unbalanced force downwards.
- The resultant force is equal to the weight.
- The skydiver accelerates downwards at max acceleration as there is no air resistance because speed is 0.
Skydiver continues falling (between second 1-30)
Velocity time graph is a straight line going upwards
- As velocity increases so does the drag force.
- There is still a downwards resultant force but less than before as resultant force = weight - air resistance (drag)
- Skydiver still accelerates downwards but the acceleration decreases.
After 30 seconds.
Graph curves
- As the skydiver's acceleration decreases, it's speed increases at a slower and slower rate.
Graph is a straight line
- Eventually, the skydiver reaches a speed at which drag force is equal to the weight force.
- Forces are balanced so no resultant force.
- Meaning that it stops accelerating and falls at a constant velocity, reaching terminal velocity.
The skydiver opens the parachute.
Sudden drop in velocity in graph (steep line going downwards)
- Drag greatly increases because of the large surface area of the parachute.
- Hence, resultant force is large and upwards (resultant force = drag - weight)
- and upwards acceleration (deceleration) is large as resultant force F = ma
- so velocity also decreases
During first 30 seconds with open parachute.
Curved line on graph
- As velocity decreases, so does the drag force
- therefore the unbalanced force upwards is smaller and the rate of deceleration decreases.
After 30 seconds.
Straight horizontal line on graph.
- The velocity has decreased until the drag force is again equal to the downwards force of weight.
- Forces are balanced so a new slower than before terminal velocity is reached.
Explain how the terminal velocity now compares to when there wasn't a parachute (3).
- Terminal velocity now is slower because there is more drag force
- due to the surface area of the parachute so less velocity is needed to balance out the skydiver's weight force.
- This is because drag increases as velocity increases.
Suggest how terminal velocity would change is the mass of the skydiver was bigger
- Terminal velocity increases
- because more mass requires more drag force to balance out the weight force (W = m x g)
- therefore the diver would have to travel at a greater velocity because drag increases as velocity increases.
What is the elastic behavior?
The ability of a material to return to its original shape after the forces causing deformation have been removed.
What does Hooke's law state?
The extension of a spring is proportional to the applied force until it reaches its elastic limit. Force past the elastic limit will make the spring permanently stretched.
What are the independent and dependent variables of the experiment?
Independent (what you change): force
Dependent (what you measure): extension.
Force on y axis
Extension on x axis
How could you make this experiment more reliable? More accurate?
To avoid errors:
- Avoid parallax error by aligning your eye perpendicularly to the measurement scale (ruler)/use a set square
- Ignore anomalous results
- Repeat several times and find the mean
Accuracy
- Use a millimeter ruler instead of a cm.
A graph with a "S" shaped curve.
Explain how the graph shows that the rubber band does not obey Hooke's Law
Extension is directly proportional to force up to limit of proportionality/elastic limit.
Line is not straight so force and extension can't be directly proportional.