Phase 1
1/292
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
293 Terms
what degenerative joint disease is only found in the cervical spine
uncovertebral joint arthrosis
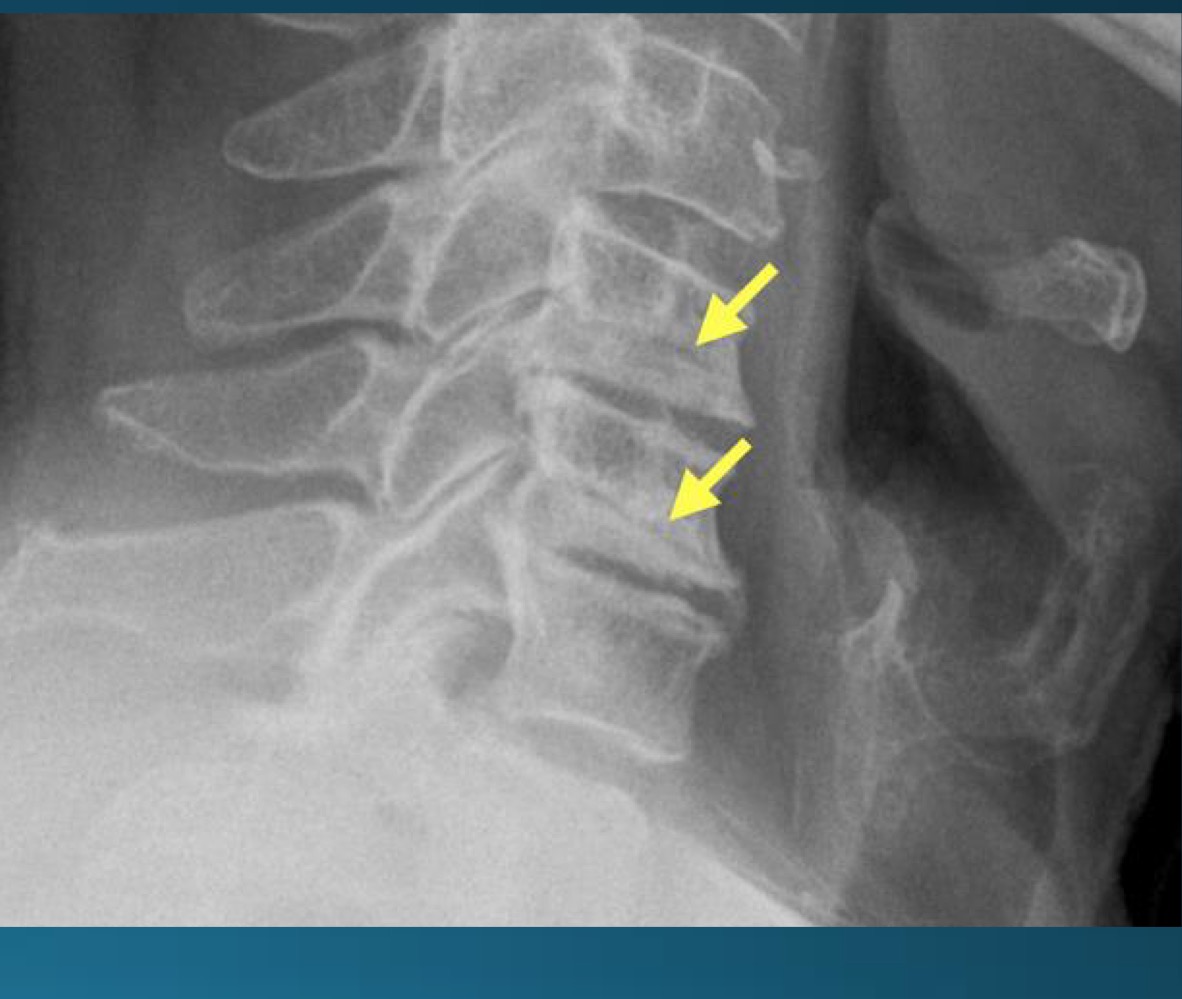
what are the findings in this image?
uncovertebral joint arthrosis
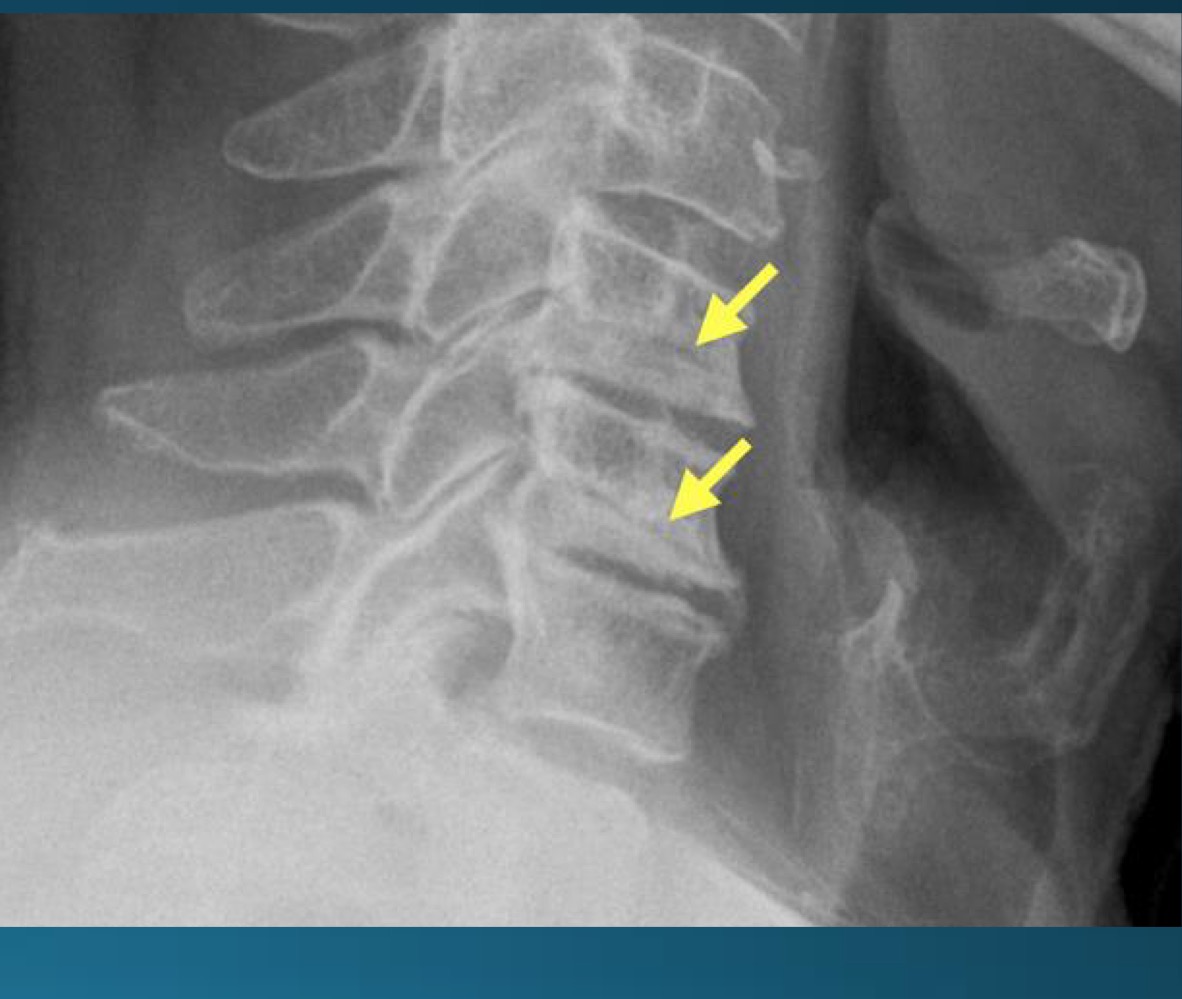
what do you call the radiographic feature commonly seen in uncovertebral joint arthrosis
pseudofracture

what are the findings in this image?
facet arthrosis
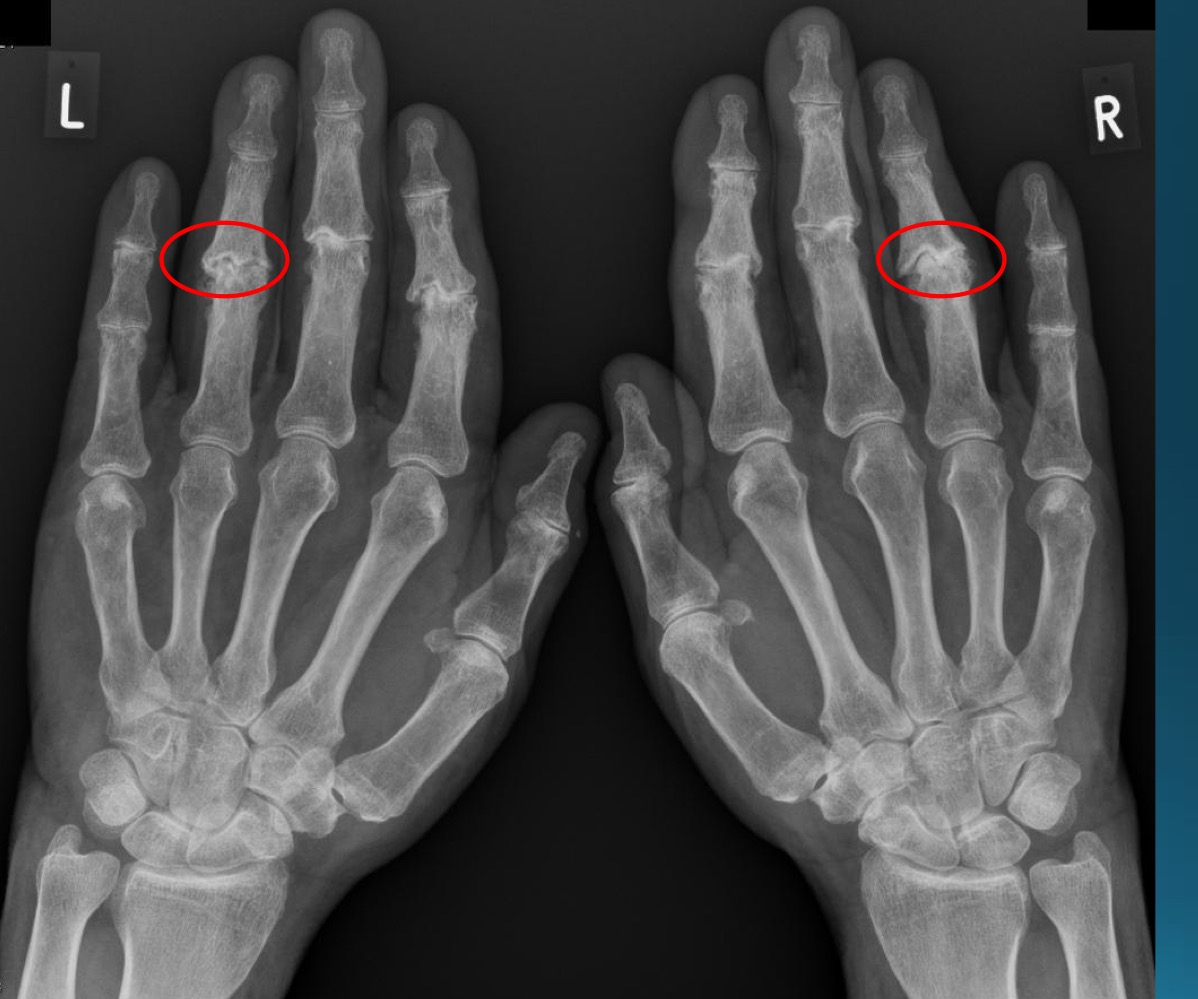
what are the findings in this image?
erosive osteoarthritis
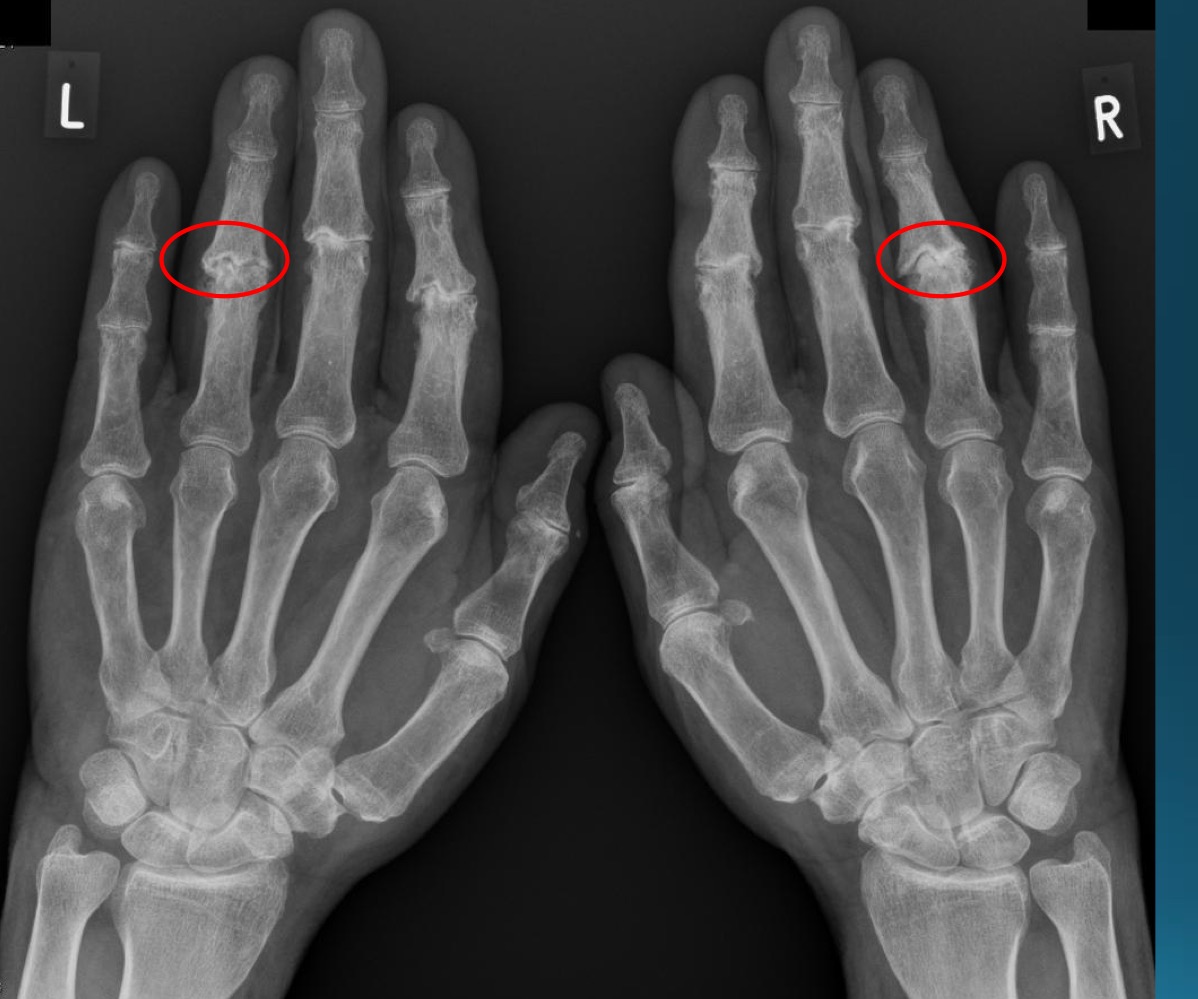
waht are the features denoting erosive osteoarthritis on radiograph?
central erosions creating gull wing sign
EOA likes what joints?
DIP, PIP, 1st CMC
what referral should you make with EOA
rheumatologist
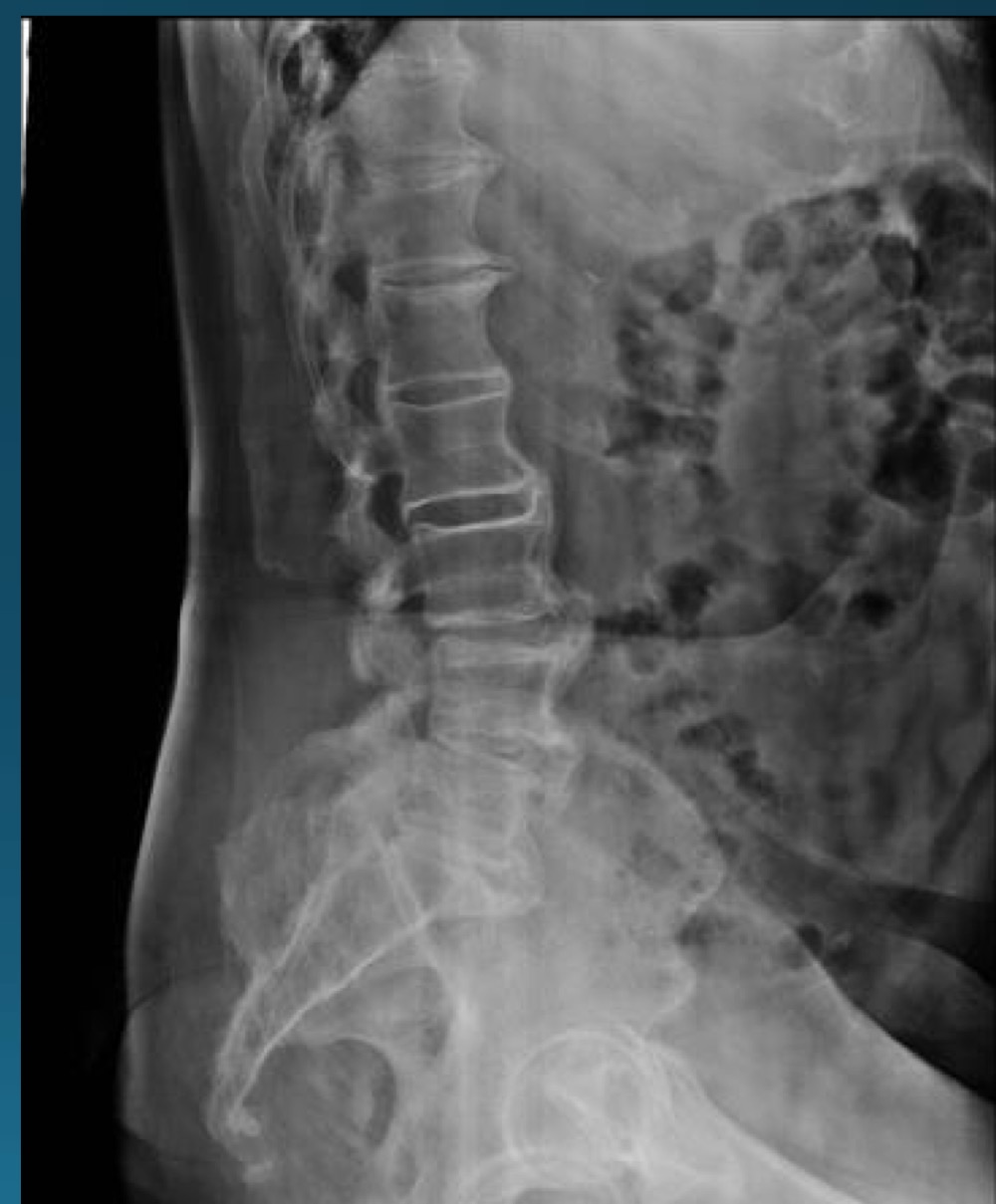
what are the findings in this image?
DISH
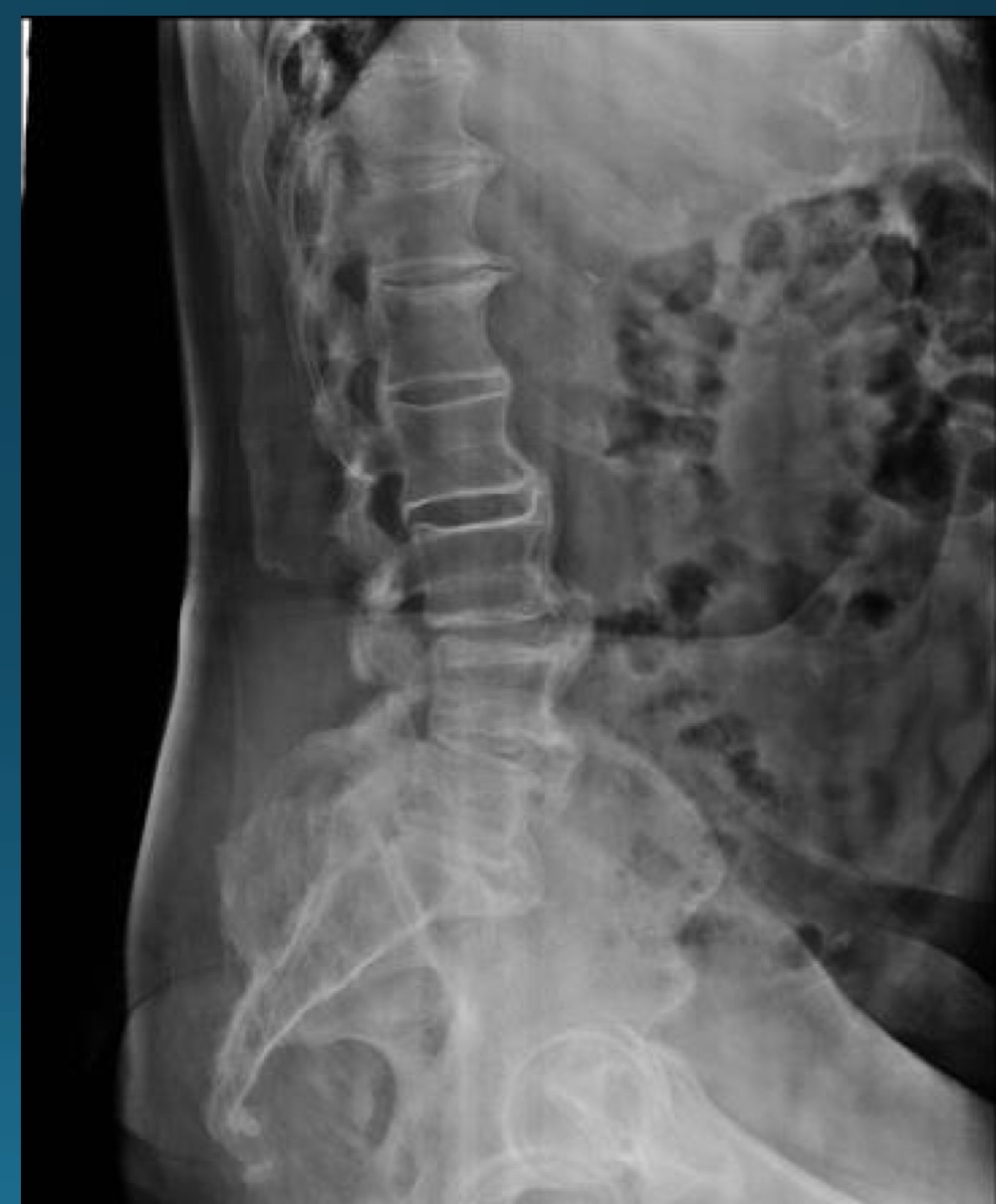
what are the 3 diagnostic criteria of DISH?
flowing calcification of at least 4 contiguous vertebral bodies
relative preservation of disc height
abense of facet joint ankylossi and sacroilitis, sclerosis, or intra articular osseous fusion
DISH is the ossification of what ligament
ALL
where is DISH most common?
T7-T11 on right side due to pulsatile descending aorta
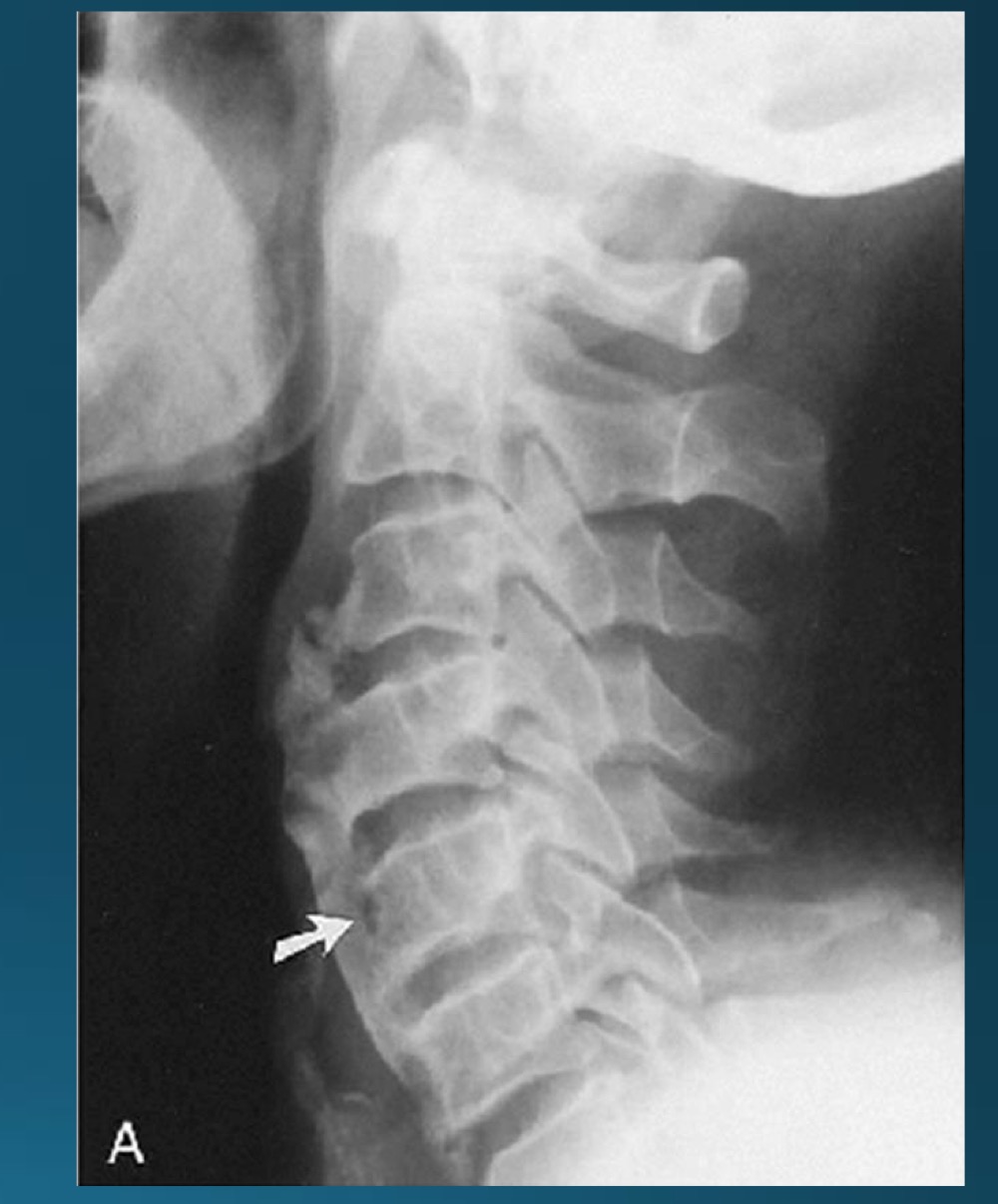
what symptoms would you potentially expect with this radiograph?
asymptomatic or stiffness, dysphagia, or joint/tendon pain
what health state has some co-occurence with DISH?
diabetes mellitus
extraspinal DISH might have effects at what sights?
ligamentous and tendionous attachments
is DISH a contraindication to adjusting? if so, what kind?
yes, relative contraindication
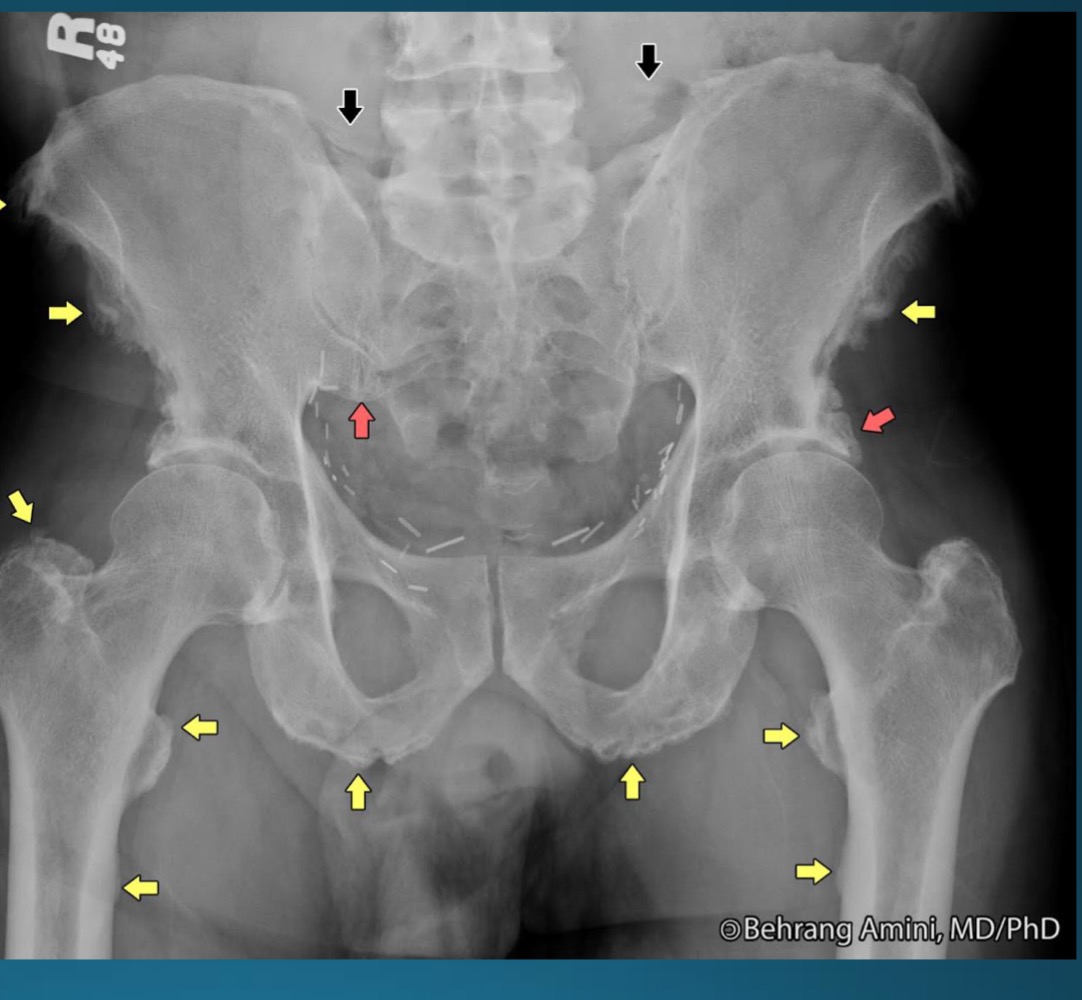
what is this radiographic feature associated with?
DISH
what is this radiographic feature associated with?
DISH
cause of neuropathic arthropathy in ankle/feet
diabetes
neuropathic arthropathy aka
charcot’s joint
cause of neuropathic arthropathy in lumbar spine/knee/ankle
syphilis
cause of neuropathic arthropathy in shoulder, elbow or wrist
syringomyelia
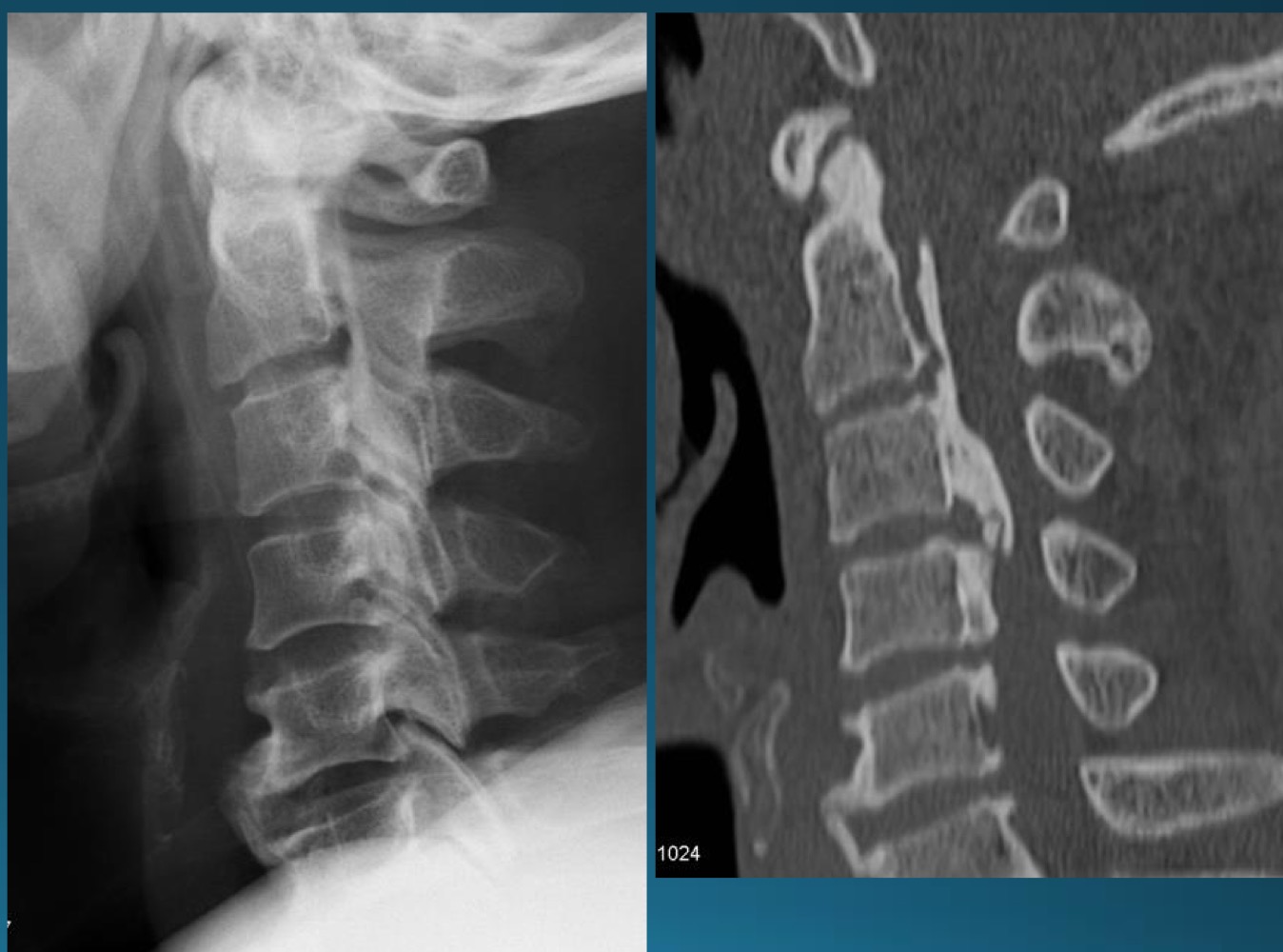
what is the finding in this radiograph? AKA?
OPLL/japanese disease
OPLL might present with what kind of issues? what symptoms would this cause?
neurological disturbance causing
heavy feeling legs
inability to walk and brisk pace
deterioration of fine motor skills
intermittent shooting pains into arms and legs
most common site of OPLL
cervical spine
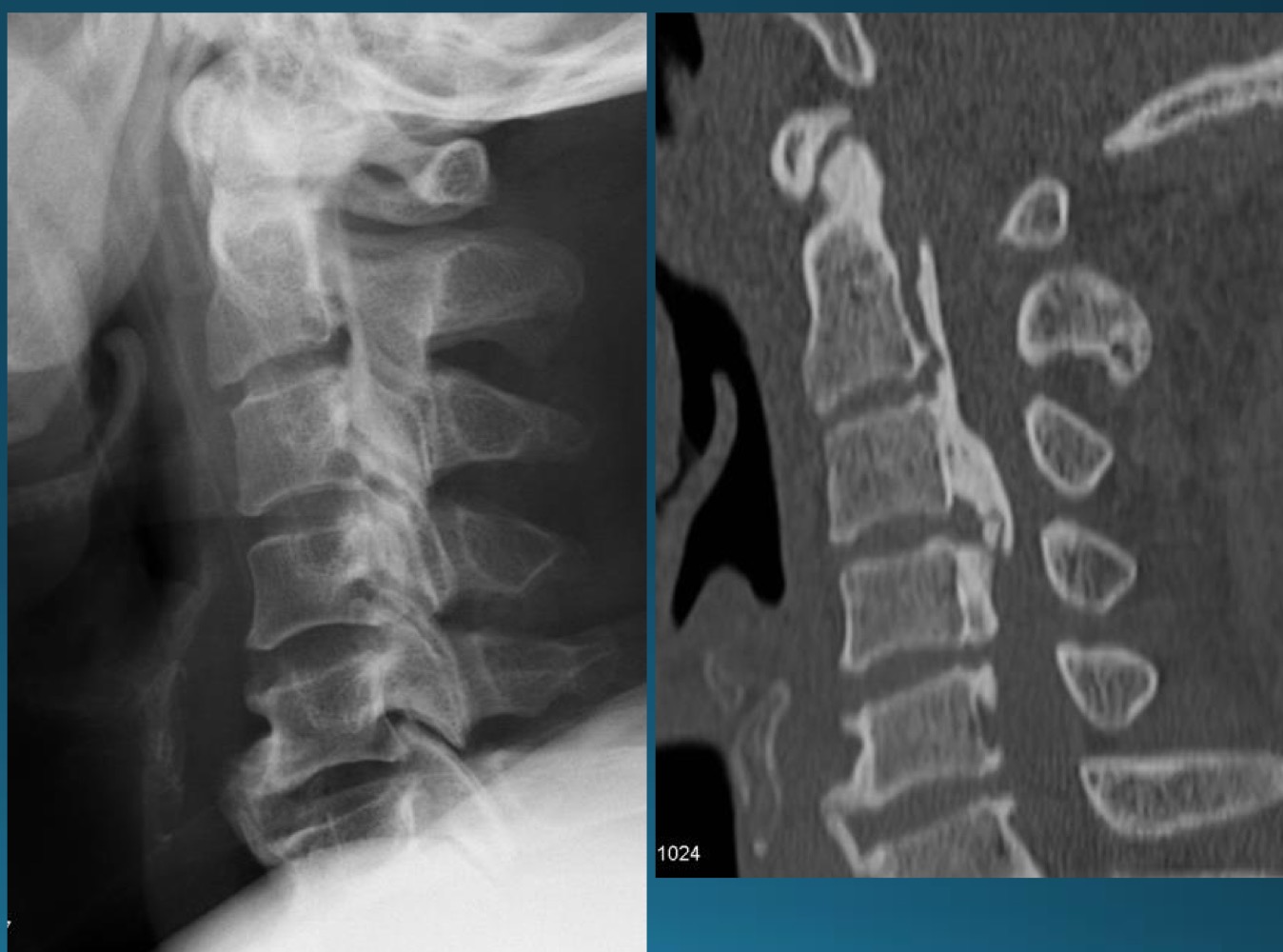
is this a contraindication to adjusting? if so, what kind?
yes, absolute contraindication
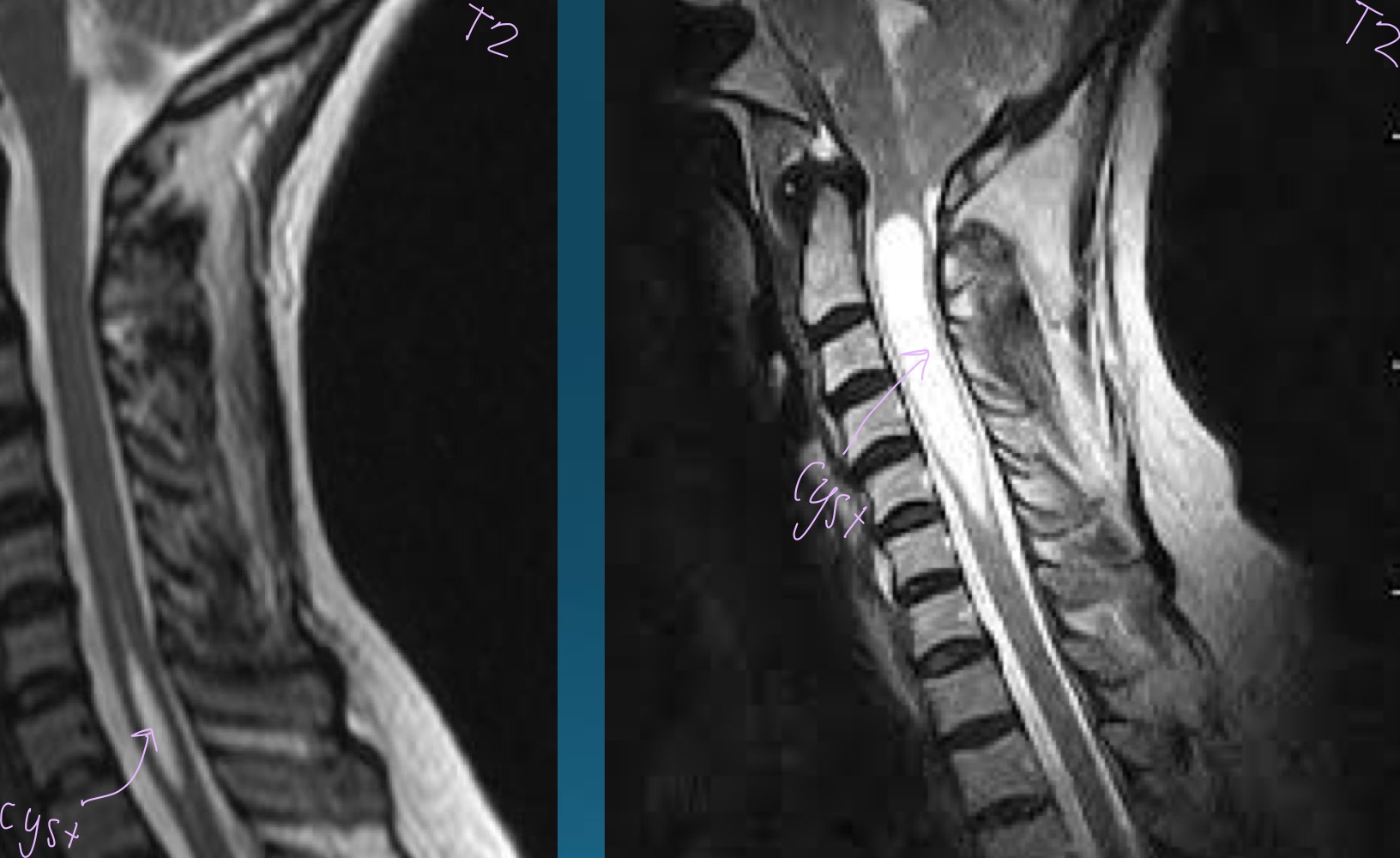
what finding is in this image?
syringomyelia
what is this clinical presentation describing?
painless swelling
deformity
weakness
instablity
crepitus
bag of bones
neuropathic arthropathy
what are the 6 Ds of hypertrophic neuropathic arthropathy
disorganization
distension
debris
destruction
dislocation
density increase
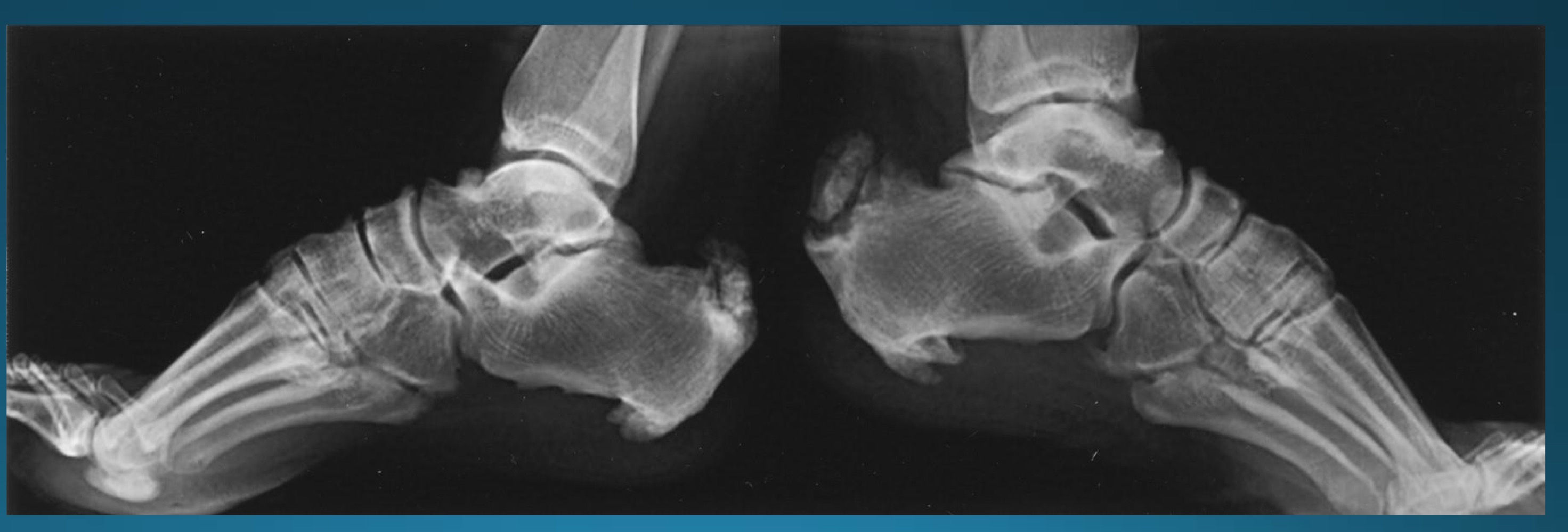
what finding is in this image
hypertrophic neuropathic arthropathy

what is the finding in this image? AKA
neuropathic arthropathy AKA charcot’s joint
what finding is in this image
atrophic neuropathic arthropathy
what appearance does atrophic neuropathic arthropathy typically take on ?
licked candy stick
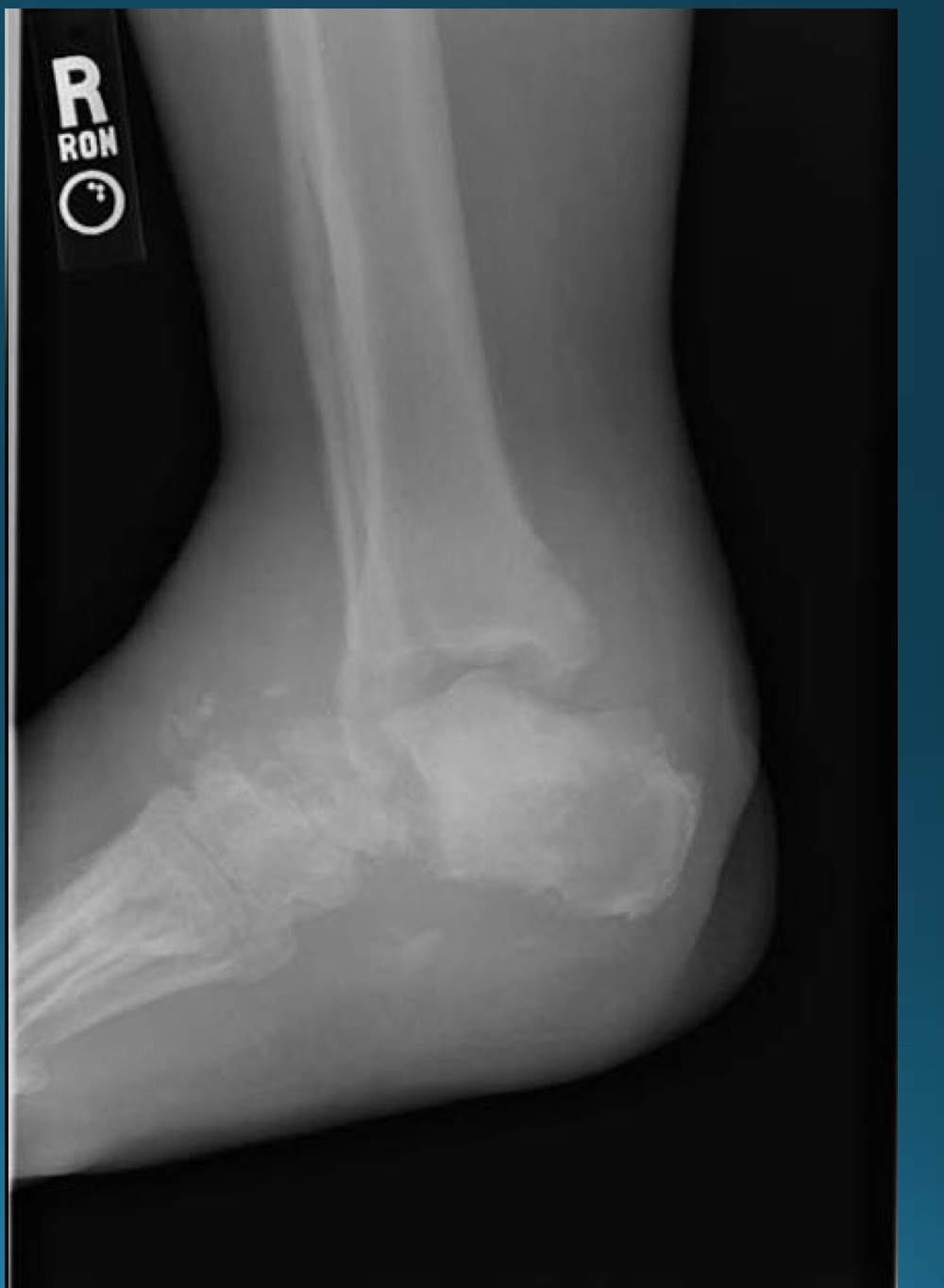
what would this charcot joint be caused by
syphilis
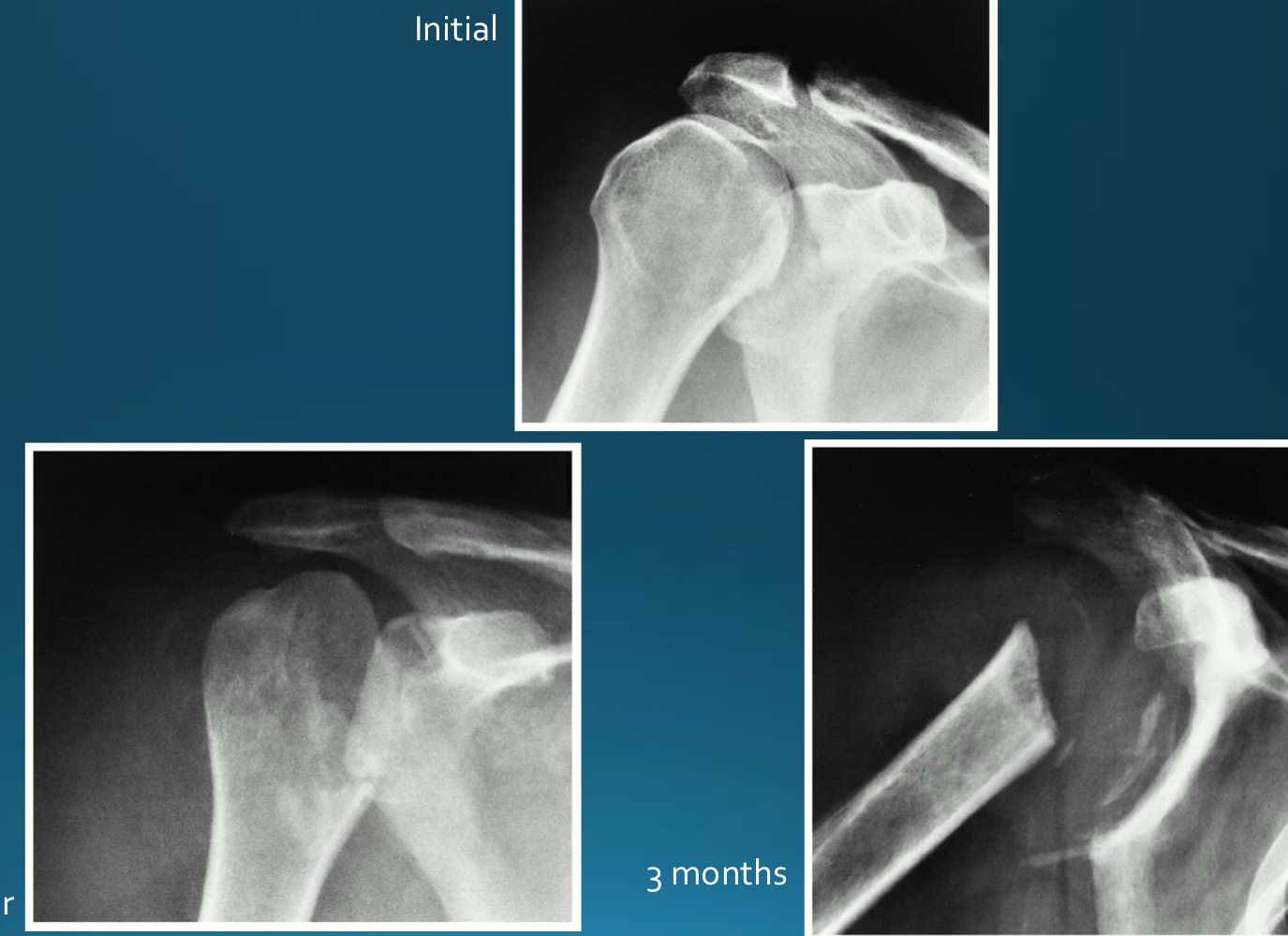
what would this charcot joint be caused by
syringomyelia
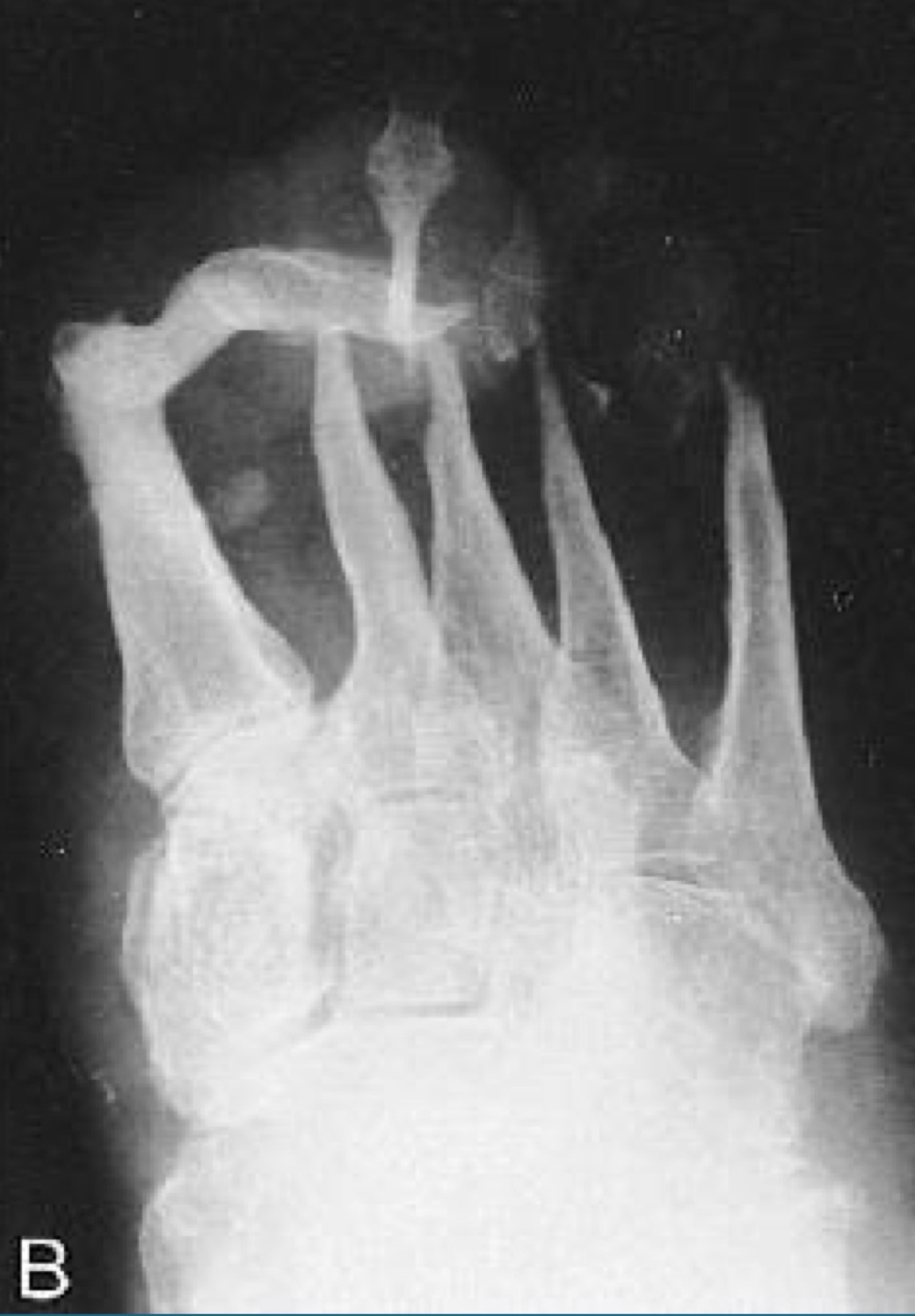
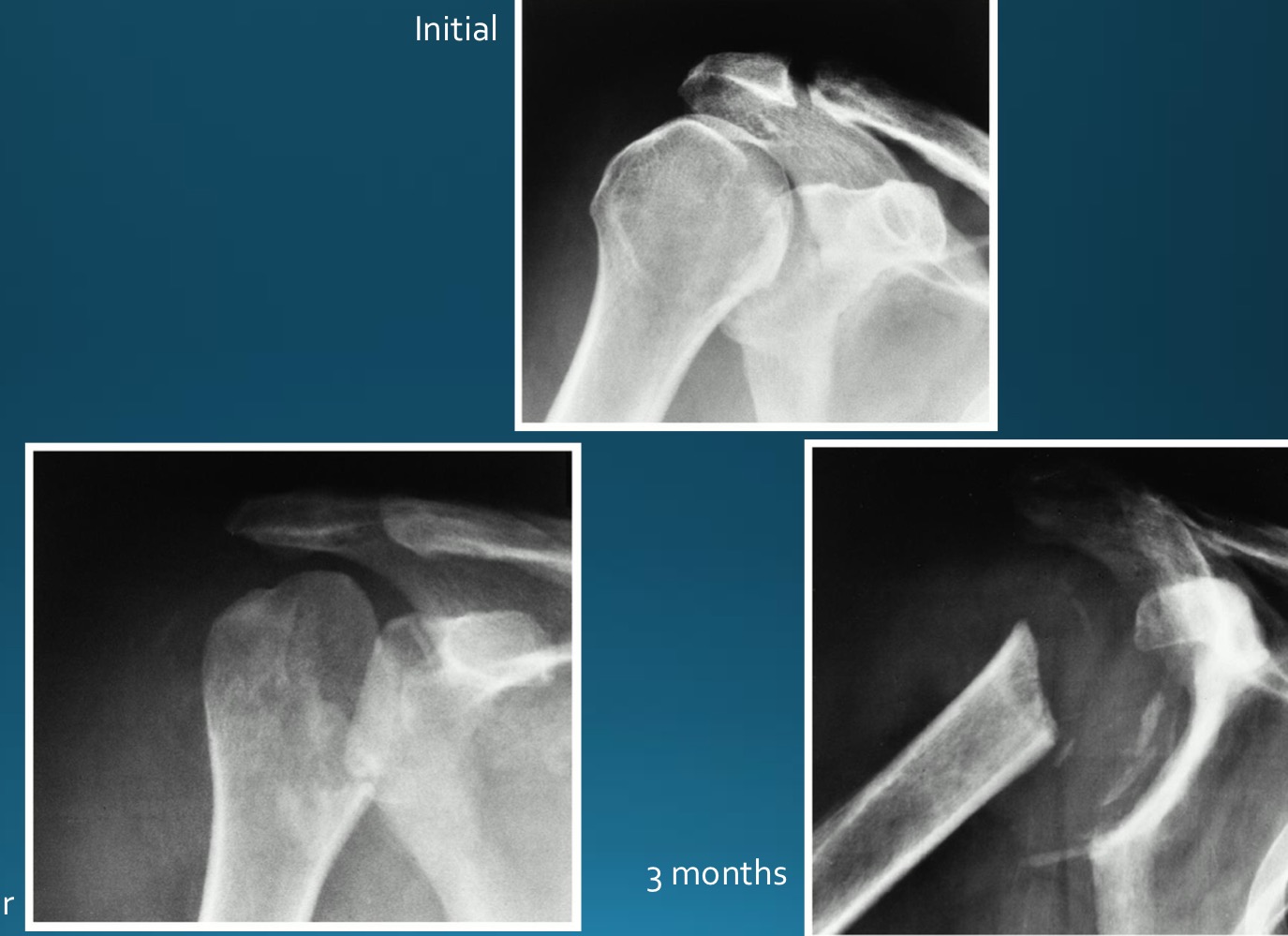
what would this charcot joint be caused by
diabetes
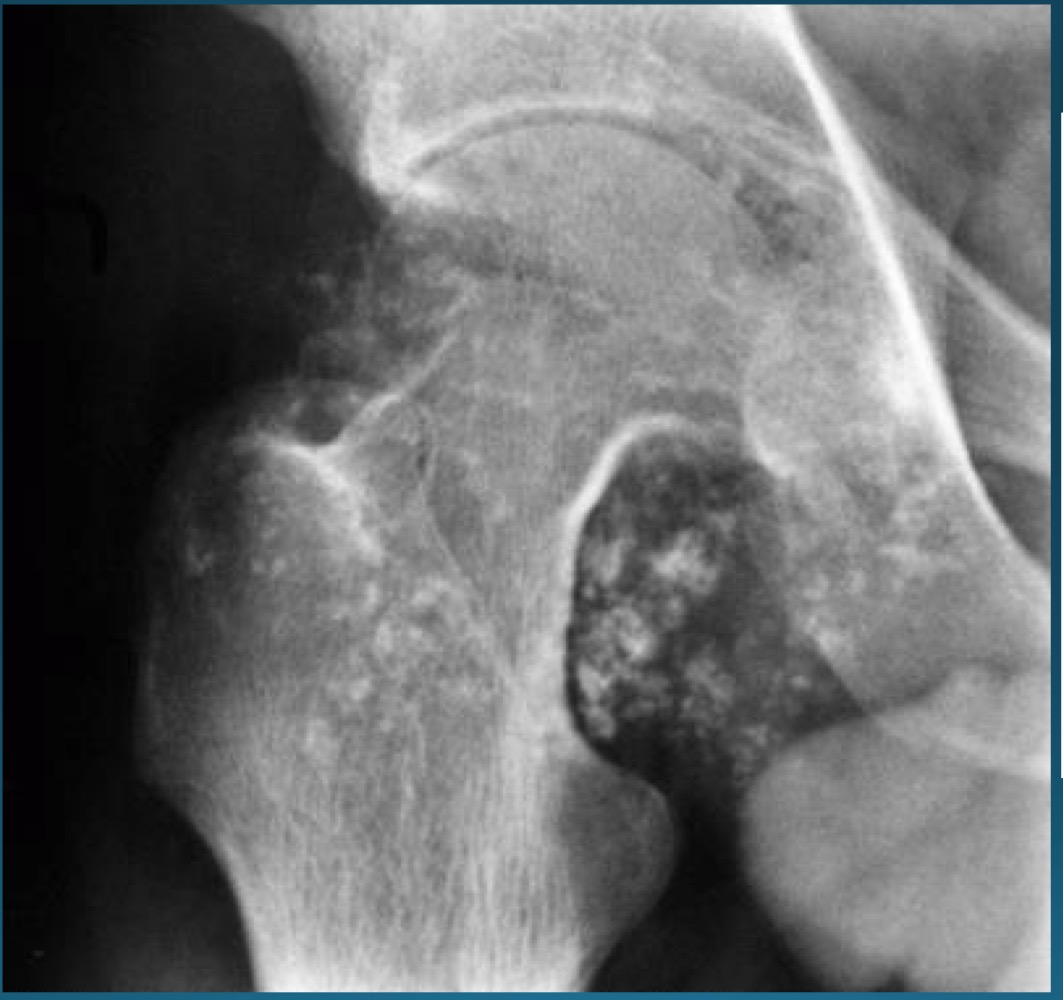
what is this finding?
synovial chondromatosis (SCM)
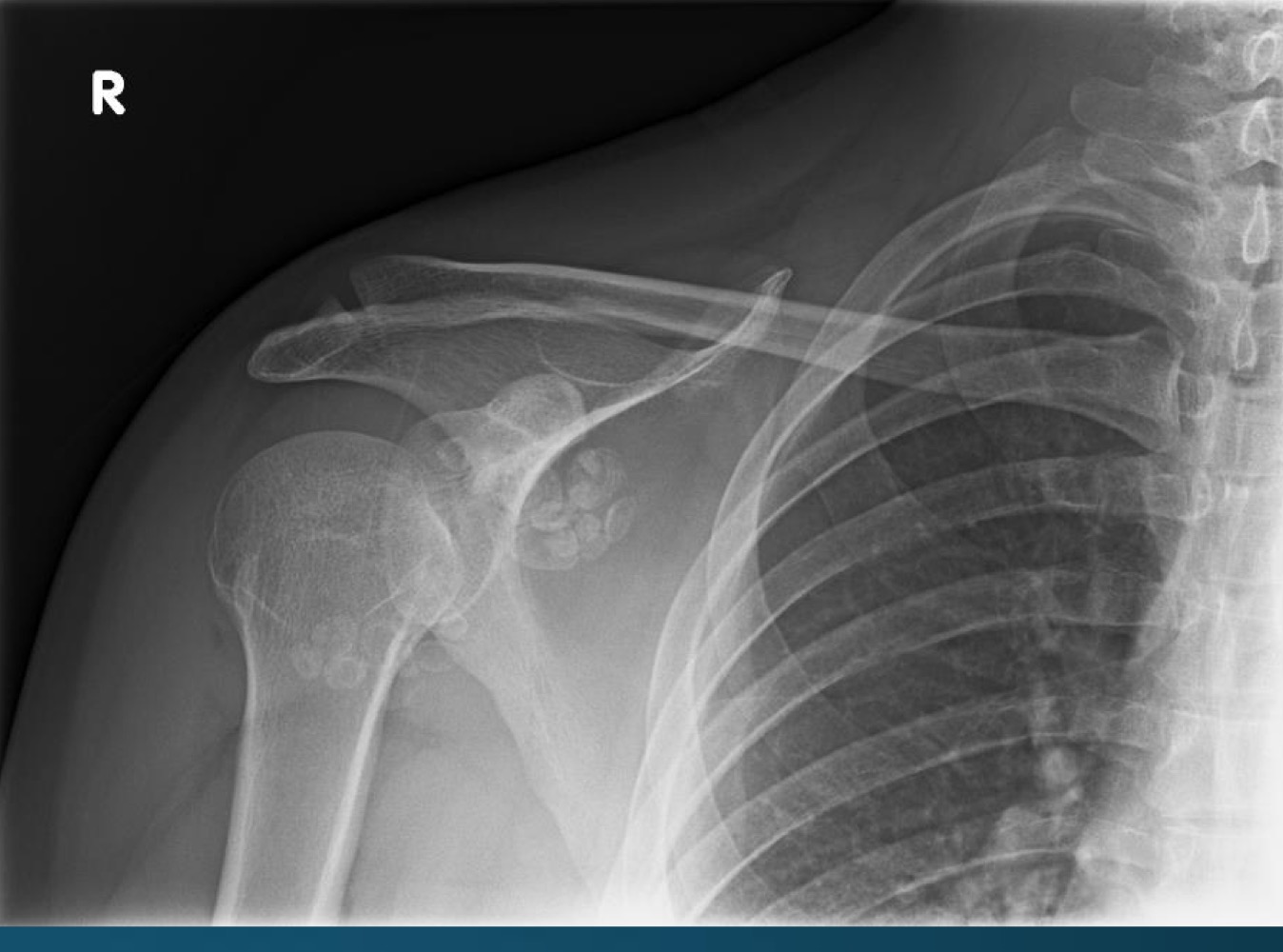
what is this finding?
synovial chondromatosis (SCM)
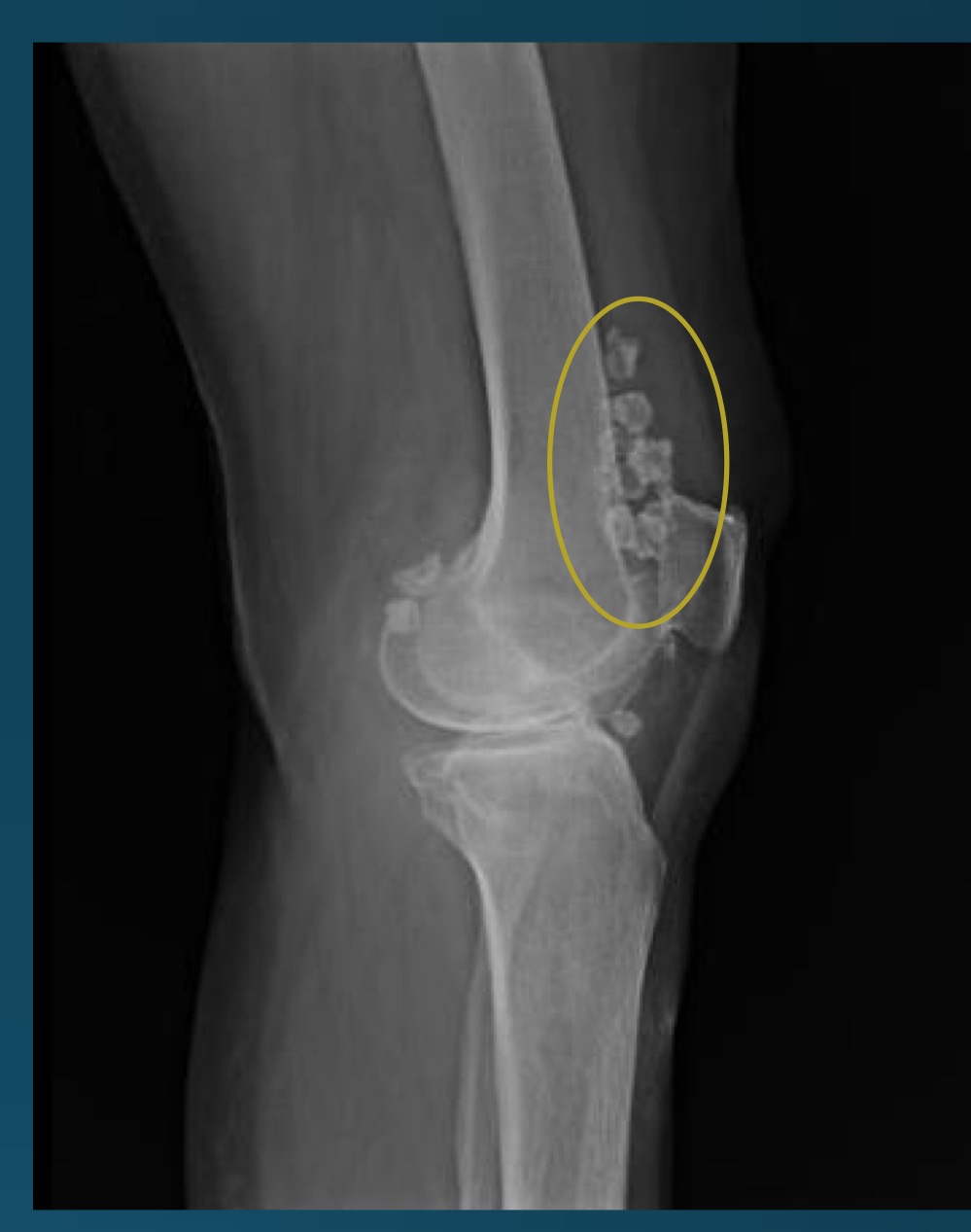
what is this finding?
synovial chondromatosis (SCM)
what is the most commong site for synovical chrondomatosis
knee
what are the types of synovical chondromatosis
primary (unknown factor)
secondary (sequala due to DJD, neuropathic joint disese, OCD, osteochondral fractures, joint dislocations)
loose bodies from synovial chondromatosis might predispose the patient to?
degenerative osteoarthritis
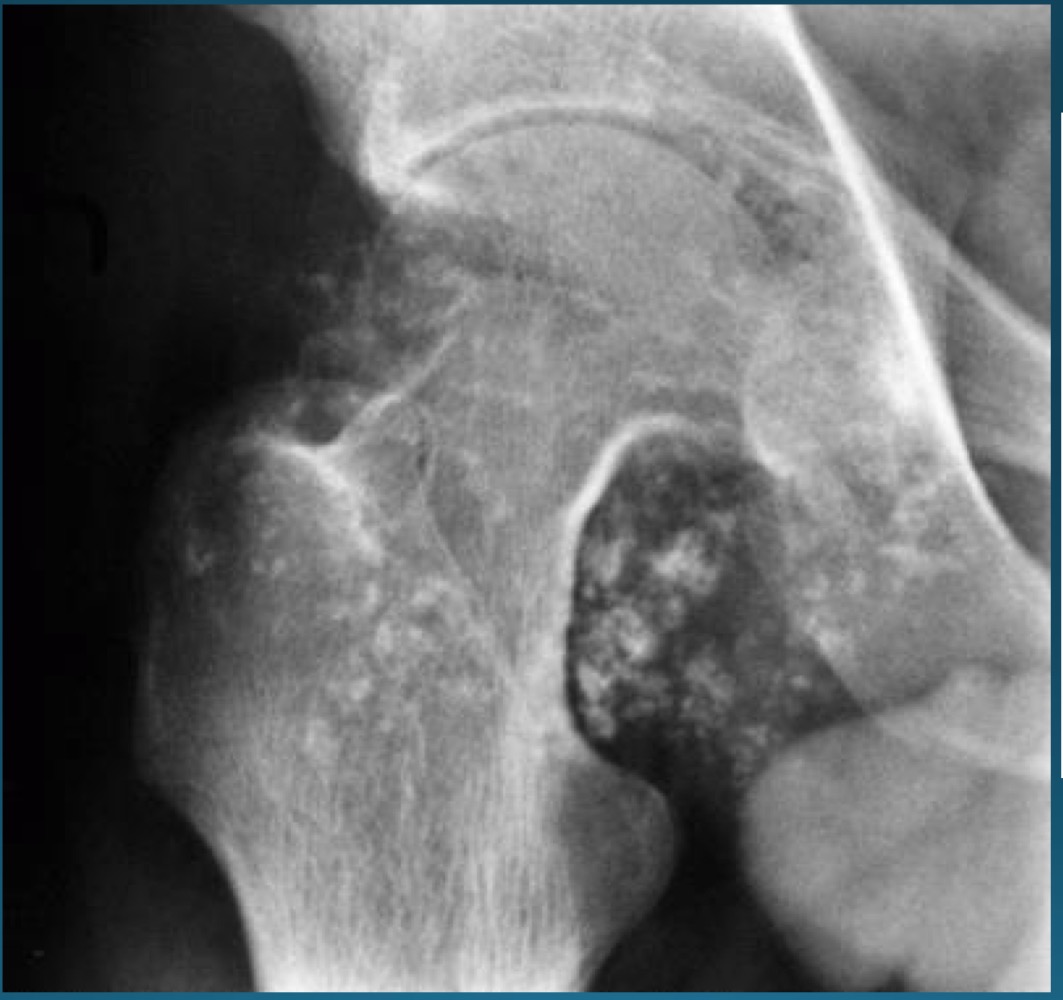
what do you call this feature? what diagnosis is this part of ?
apple core deformity, synovial chondromatosis
what does it mean to be a seropositive arthropathy
presence of RF or ACPA in serum
what is the seropositive arthropathy
RA
what is the target tissue in RA? what are the areas called that are especially at risk?
synovium
bare areas
RA causes a proliferative response in synovial joints called
pannus
using the diagnostic criteria of RA, what does one need to score to be diagnoses with definite RA
score of 6 or greater
T/F: RF is sensitive and specific to RA
false, neither
T/F: ACPA is senstive to RA, not specific
false, ACPA is specific (almonst never found in people without disease), not sensitive
onset of RA before what age denotes JRA
16
what are these clinical features describing
stiffness in morning lasting as least 1 hour
joint pain, tenderness
bilateral and symmetrical invovlement
fusiform soft tissue swelling
weight loss
fatique
myalgia
RA
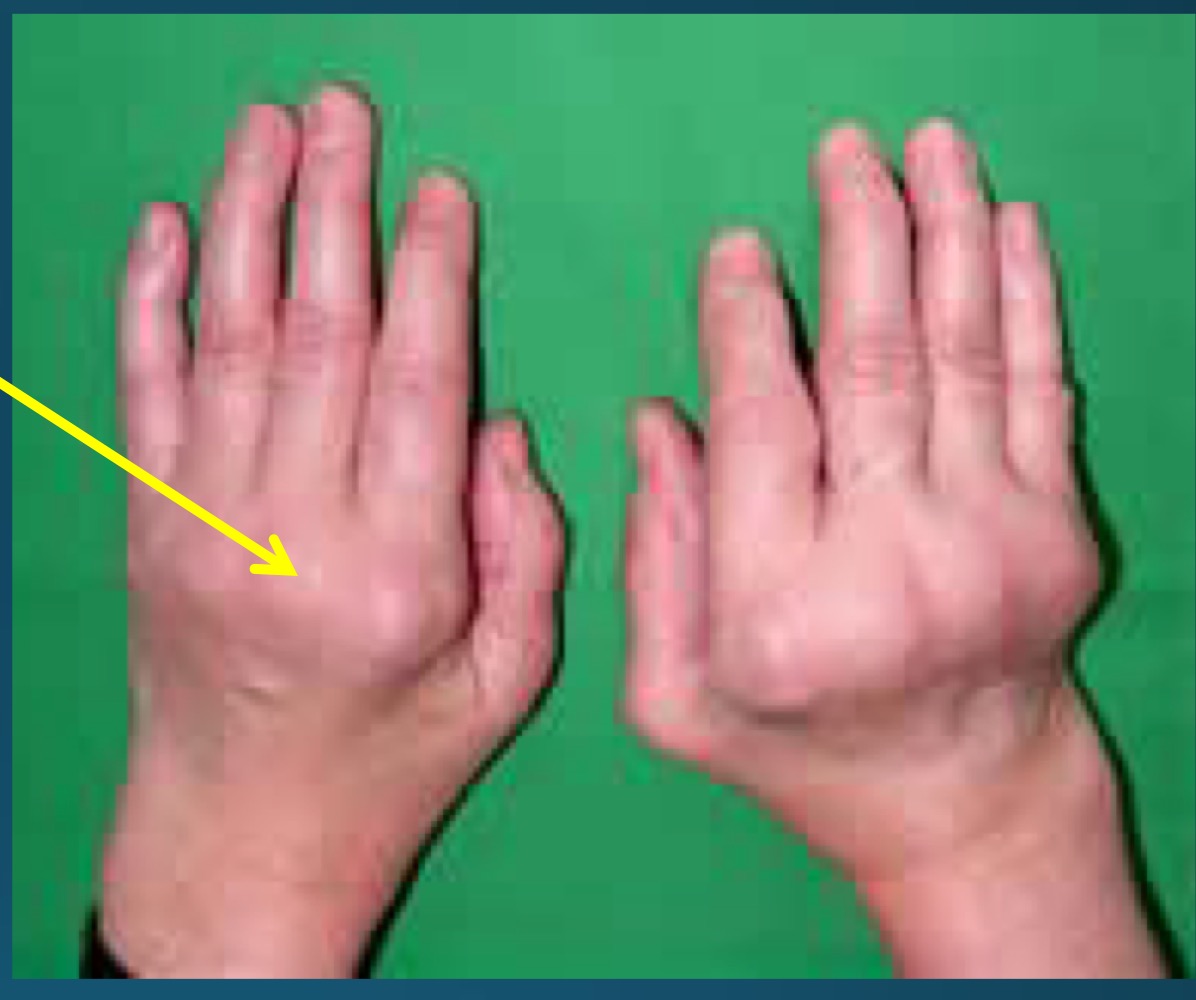
What are these called and what is it a common clinical feature of ?
Haygarth’s nodes
RA
what syndrome has a common co-existence with RA? what are the symptoms
sjogren’s syndrome
xerostomia (dry mouth)
xeropthalmia (dry eyes)
xeroderma (dry skin)
what are these called?
rheumatoid nodules
T/F: RA typically presents with sclerosis and osteophytosis on radiographs
false
what are hallmark radiographic signs of RA
bilateral symmetic involvment
periarticular soft tissue swelling
marginal erosions
uniform loss of joint space
juxta articular osteoporosis
ADI instability
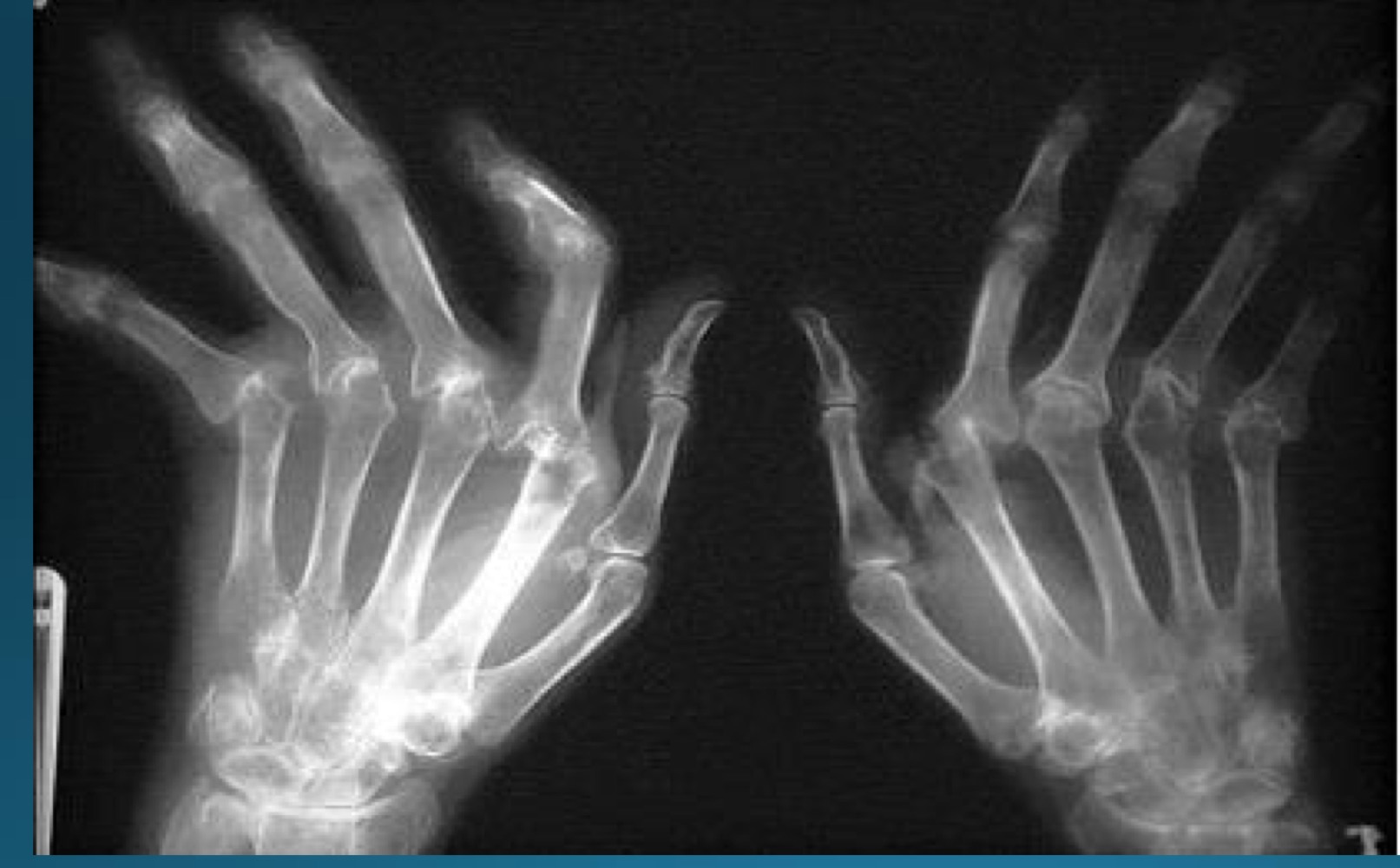
what is the diagnosis
RA
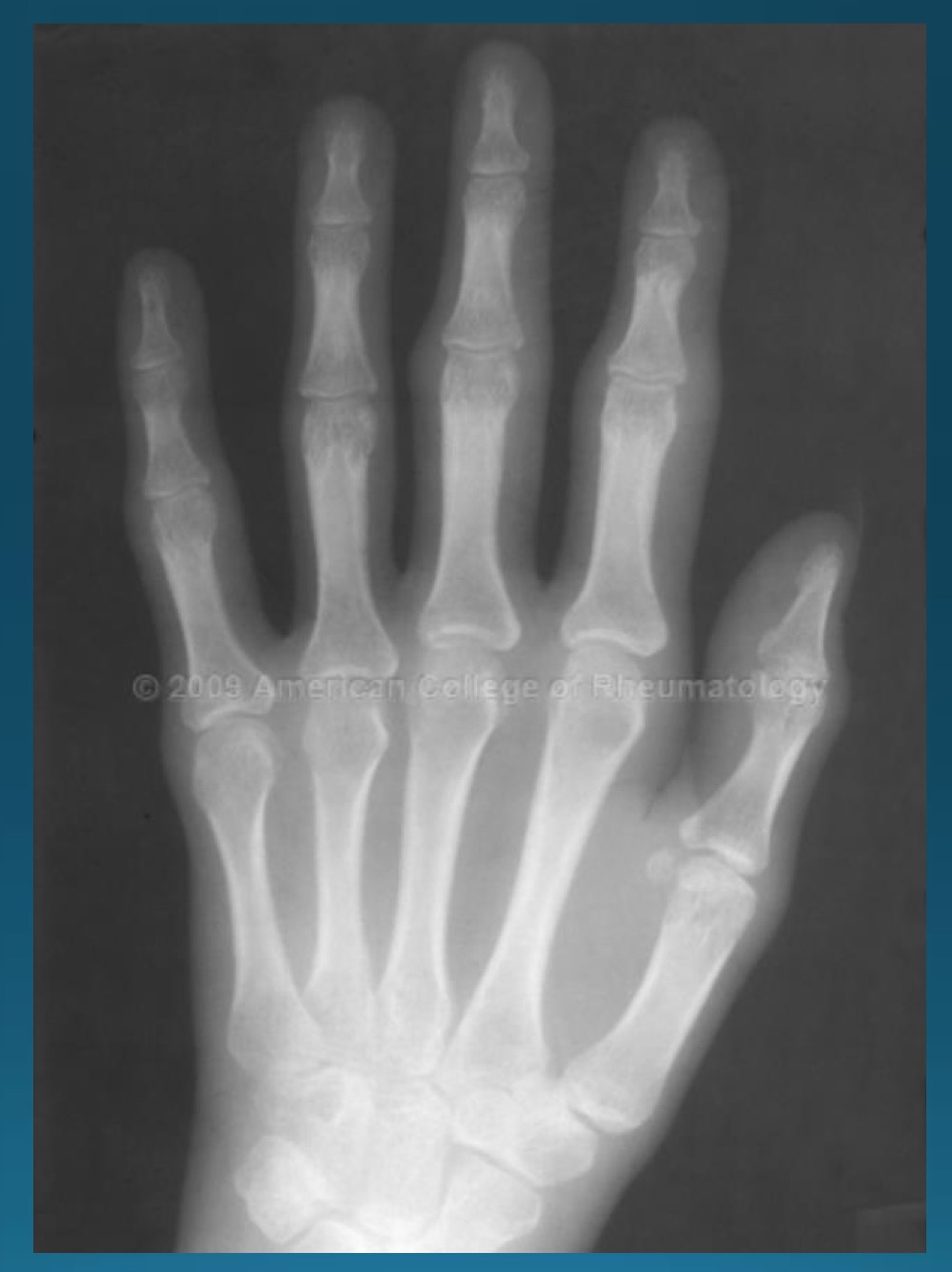
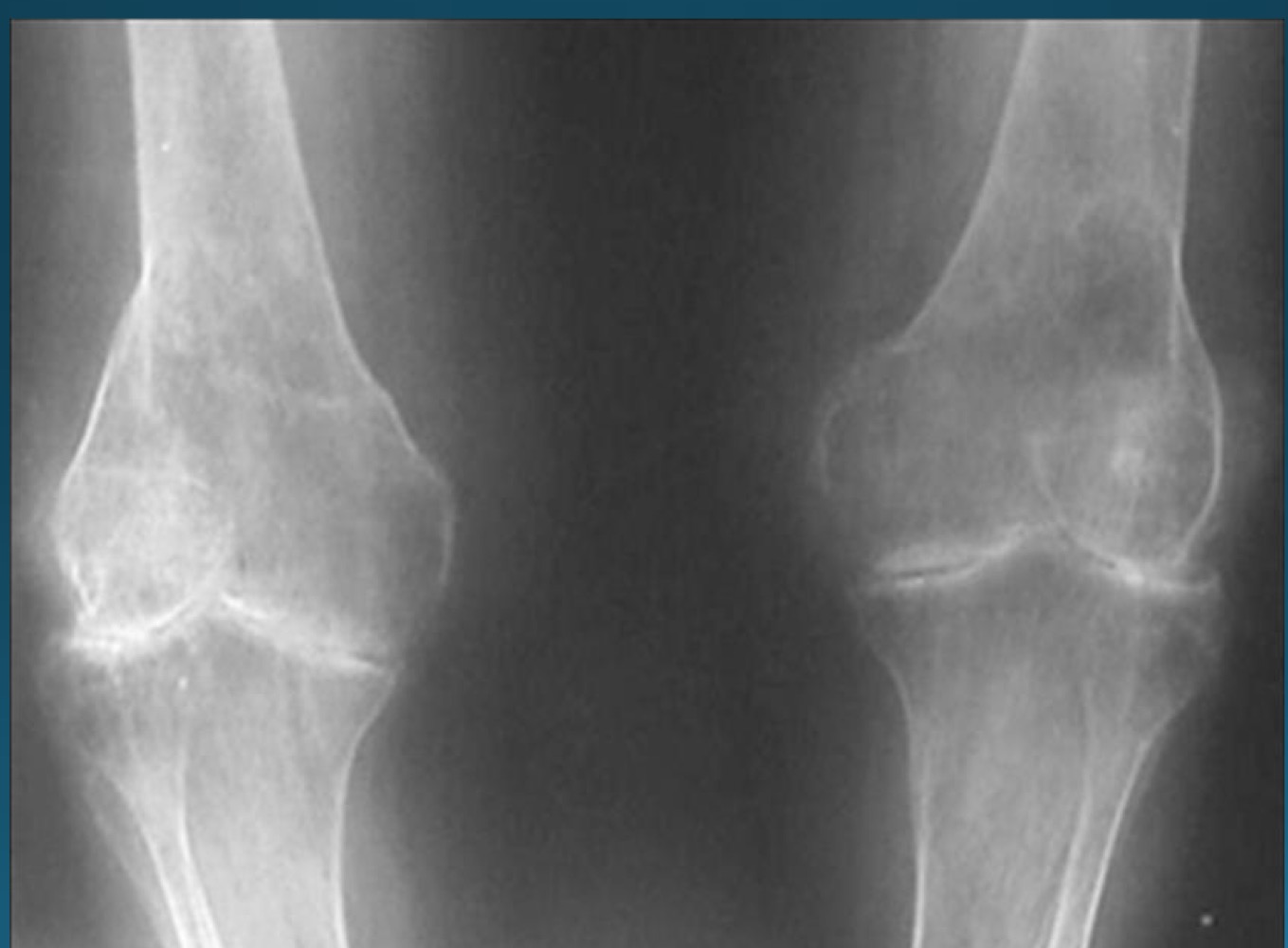
what is the diagnosis and major finding?
periarticular swelling
RA
what is the diagnosis
RA
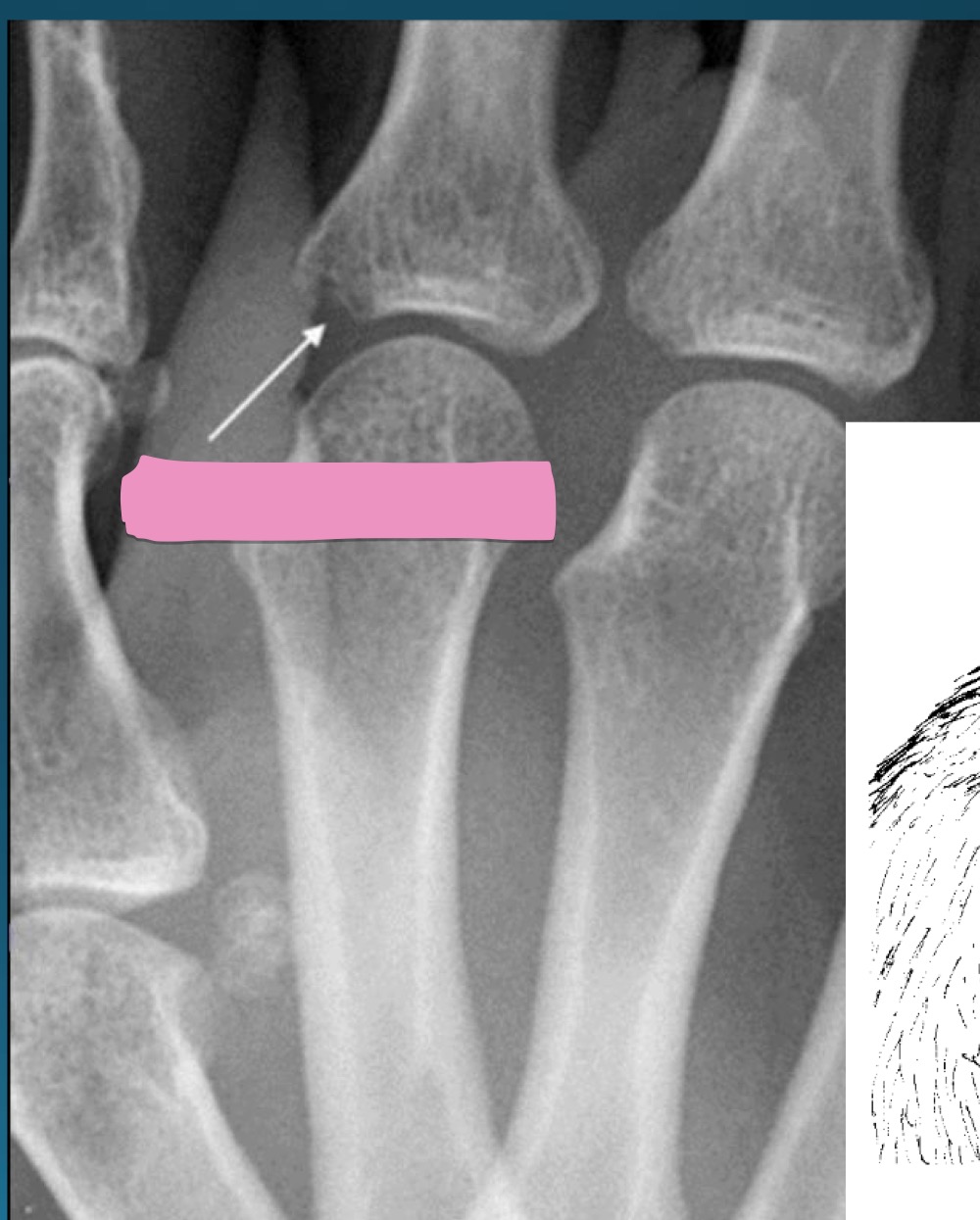
what do they call this feature?
part of what diagnosis>?
rat bite erosion
RA

diagnosis?
RA
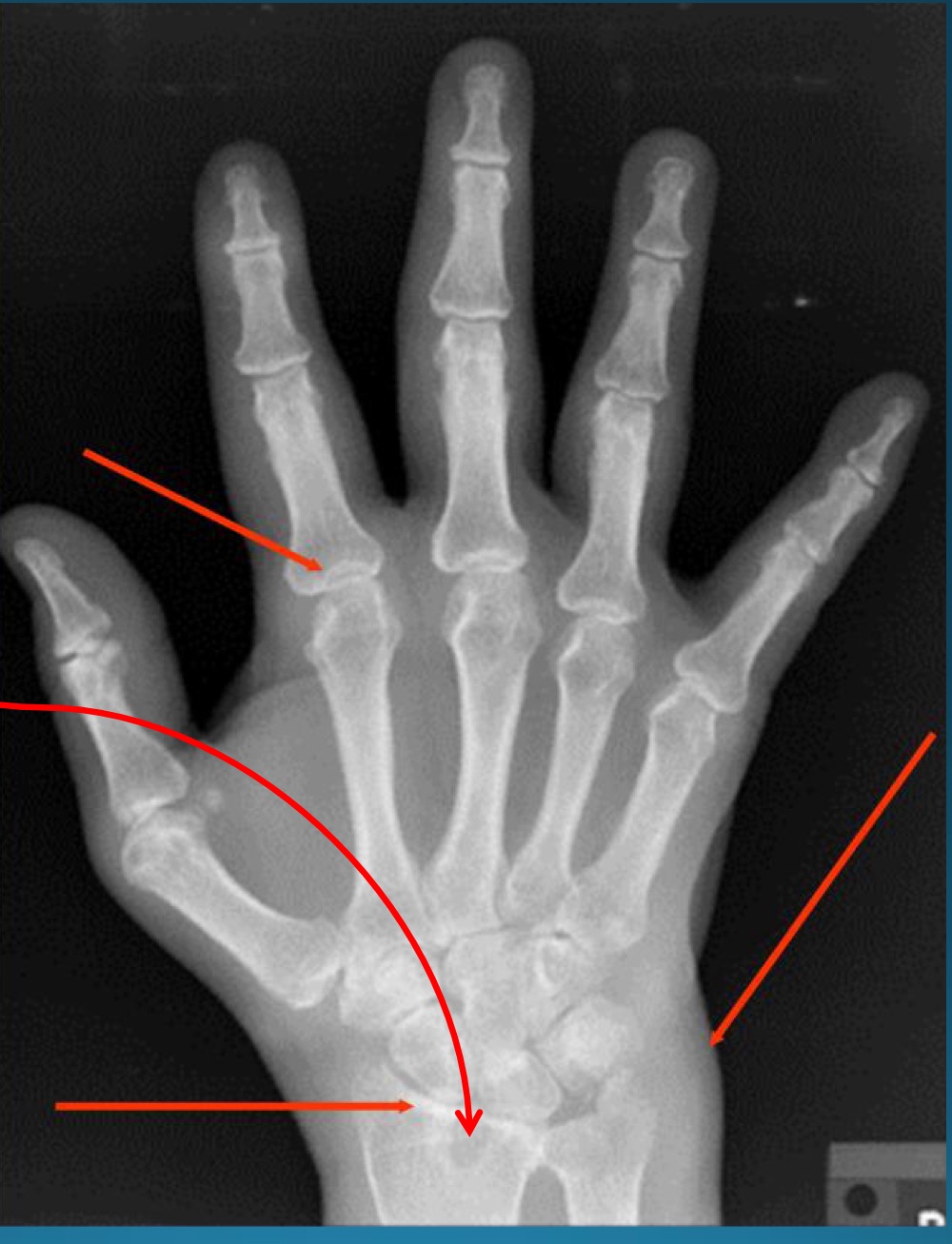
red arrows are pointing to what feature?
part of what diagnosis?
pseudocysts
RA
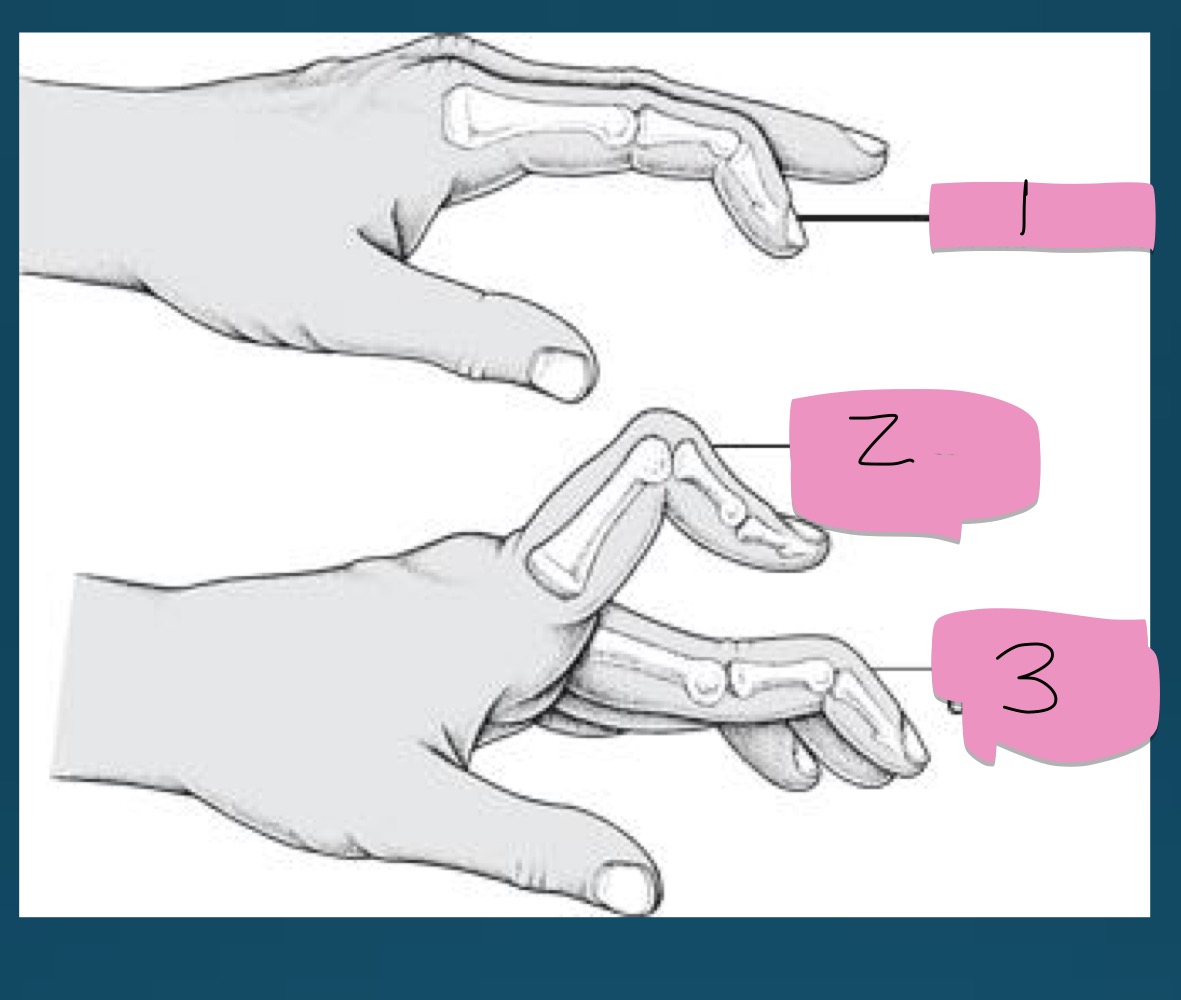
what is the number 1 presentation called?
part of what diagnosis?
mallet finger (flexion of DIP)
RA
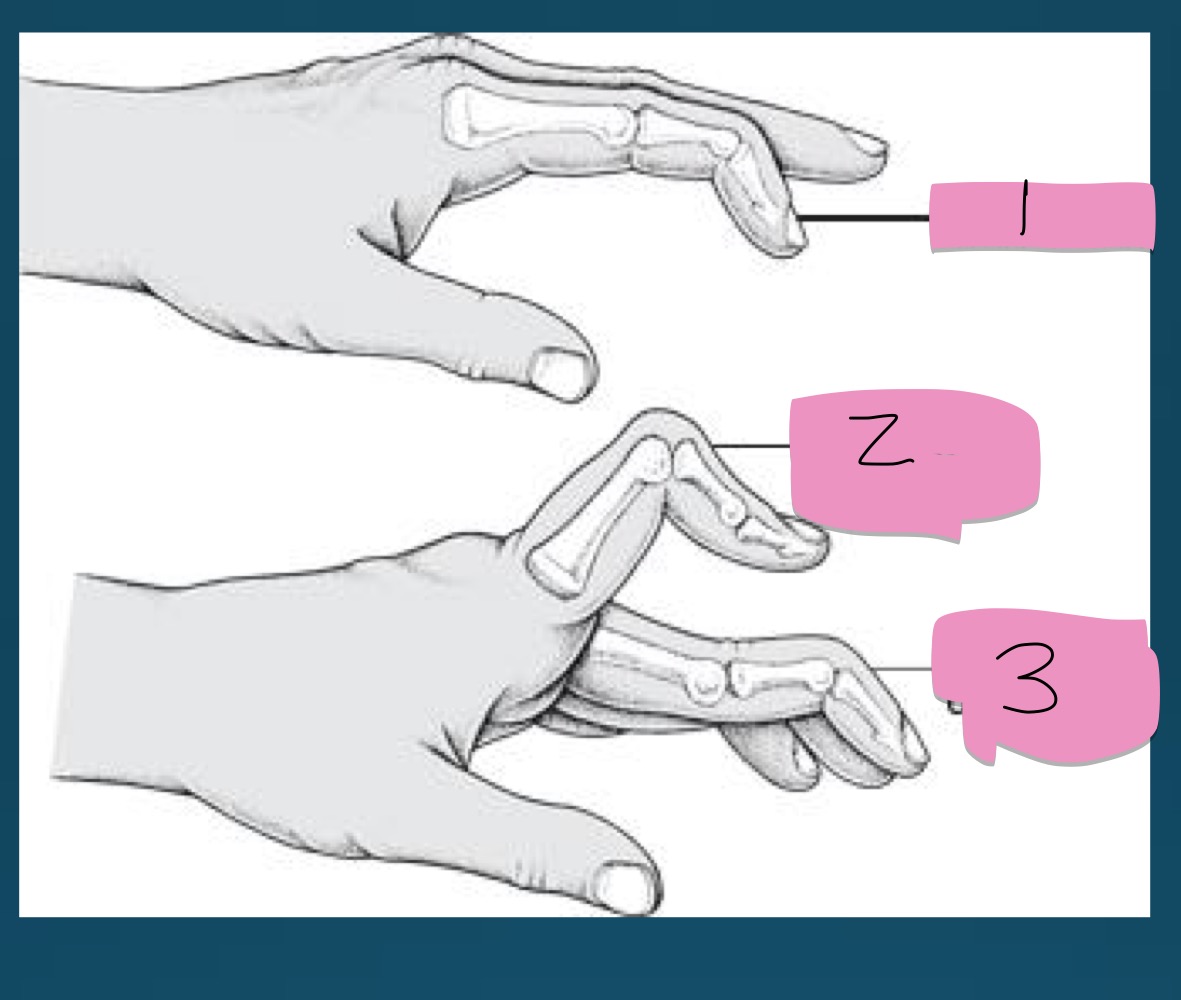
what is the number 2 presentation called?
part of what diagnosis?
boutinniere deformity (flexion of PIP)
RA
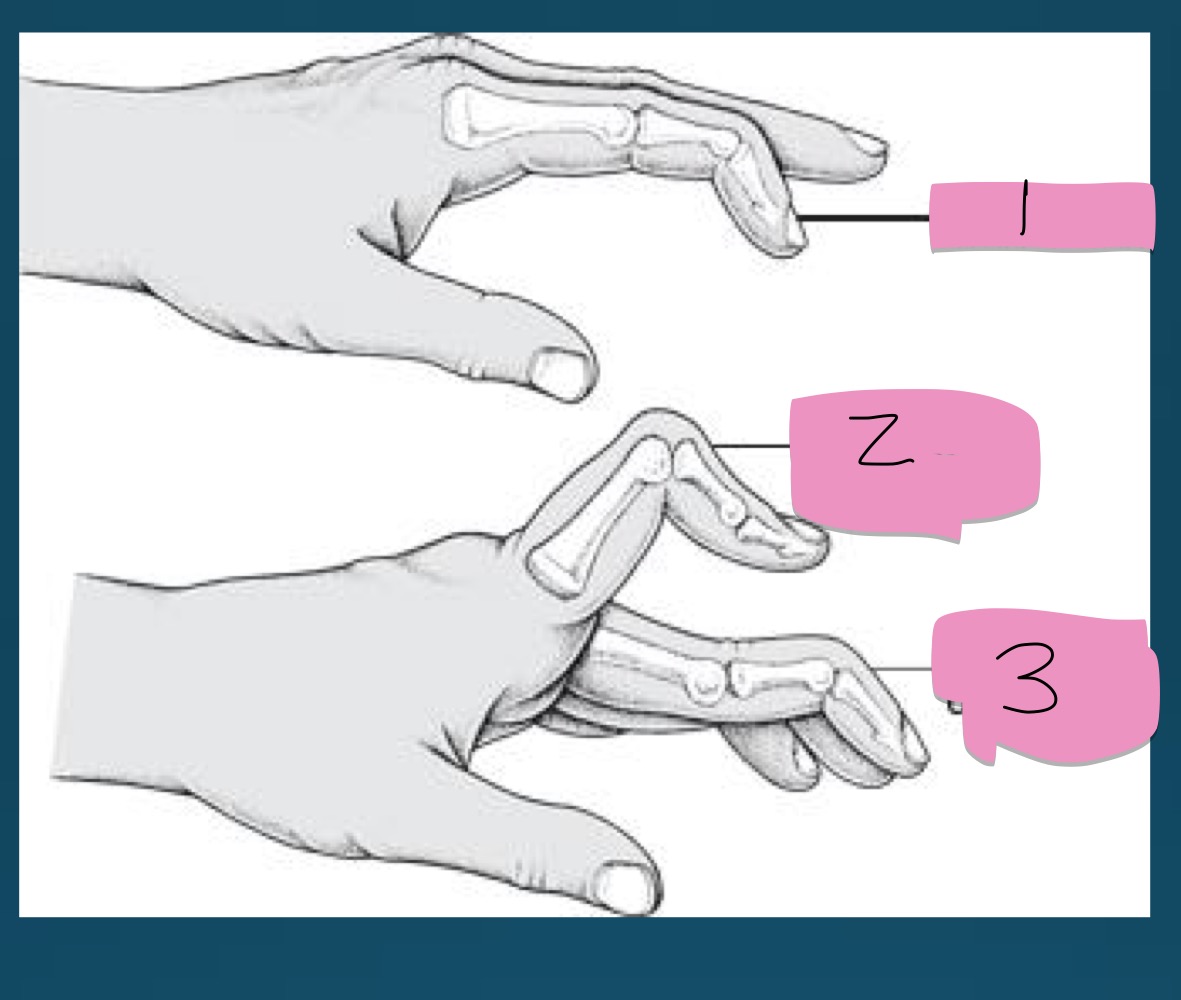
what is the number 3 presentation called?
part of what diagnosis?
swan neck deformity (flexion of DIP with extension of PIP)
what are the target sites of RA
MCP and PIP
ulnar styloid
mid carpals
radiocarpal
2-3 metacarpal heads
marginal erosion due to RA are often located on what side of metacarpals
radial side
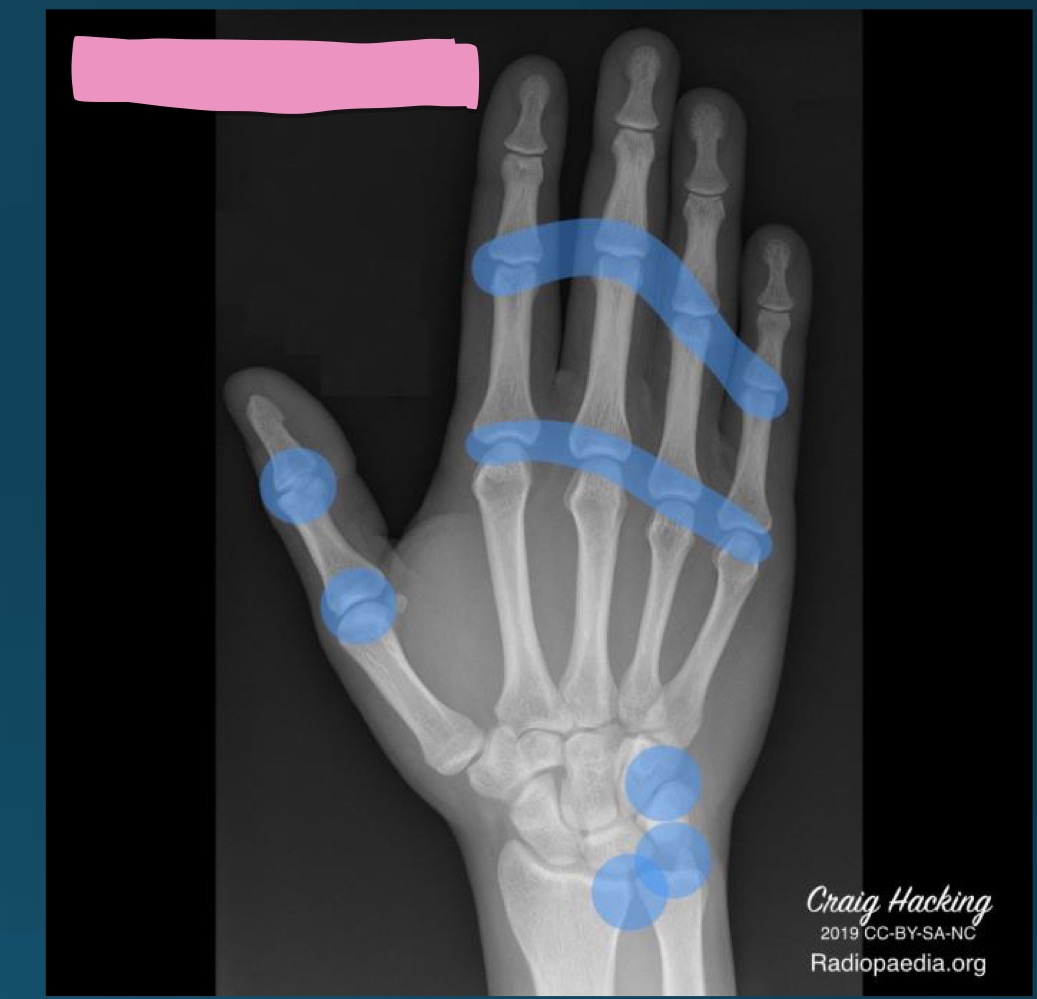
what diagnosis is this distribution describing
RA
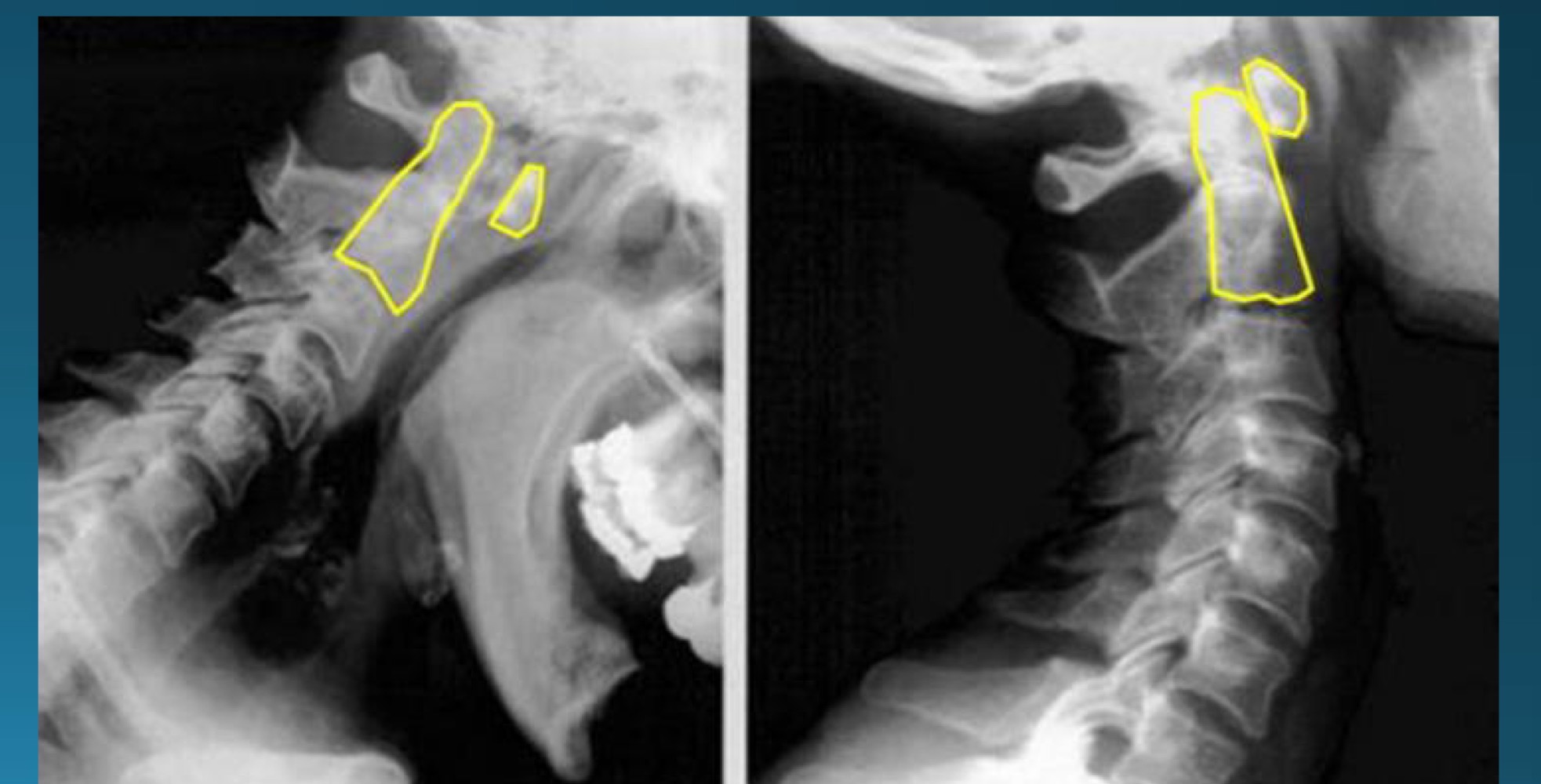
what’s happening in this image?
may be part of what arthritic diagnosis?
ADI instability (increase in distance)
RA
what is a normal ADI distance?
1-3 mm in adults
1-5 in children
chamberlain’s line measures from ____ to ____
what landmark should not go above it?
ospithion to hard palate
odontoid
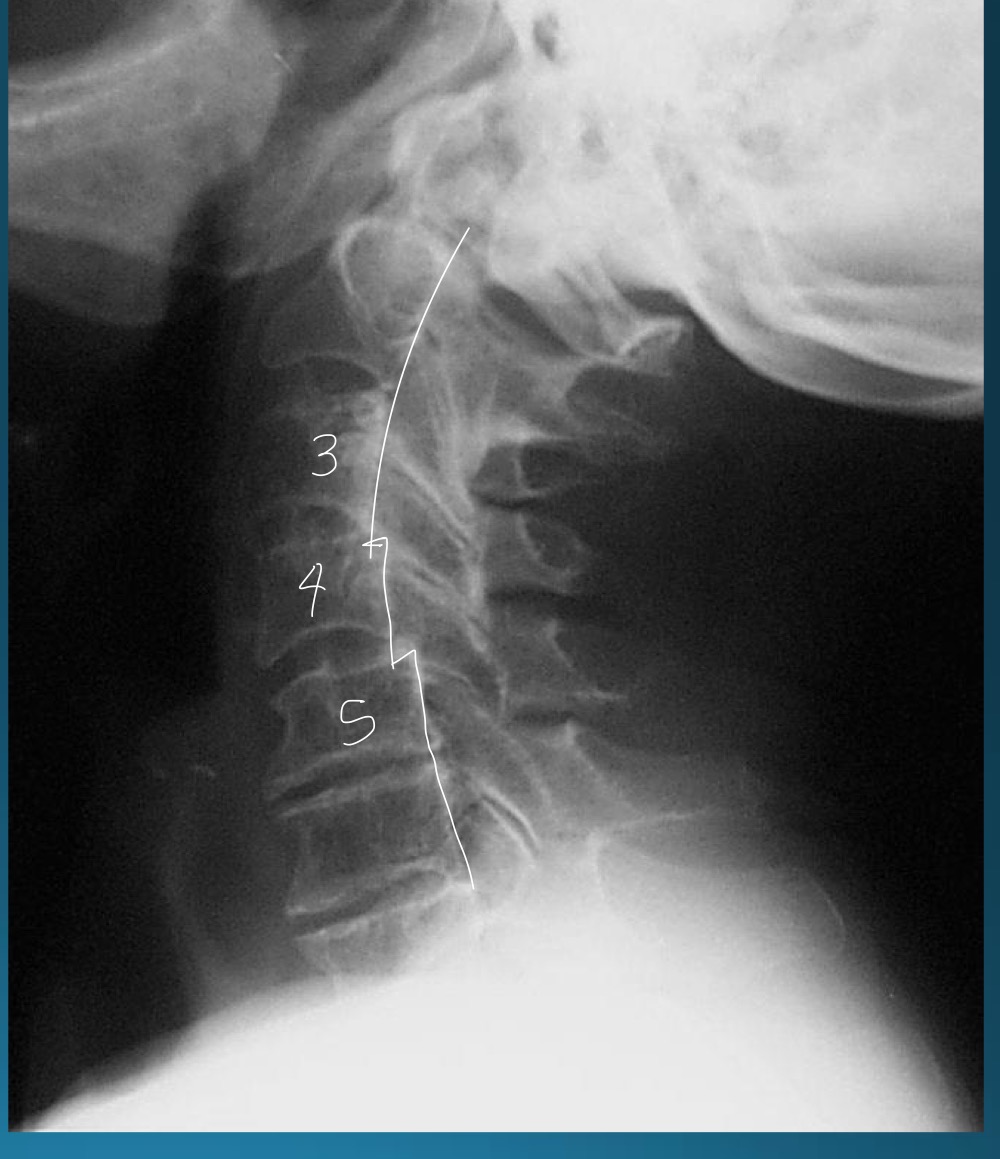
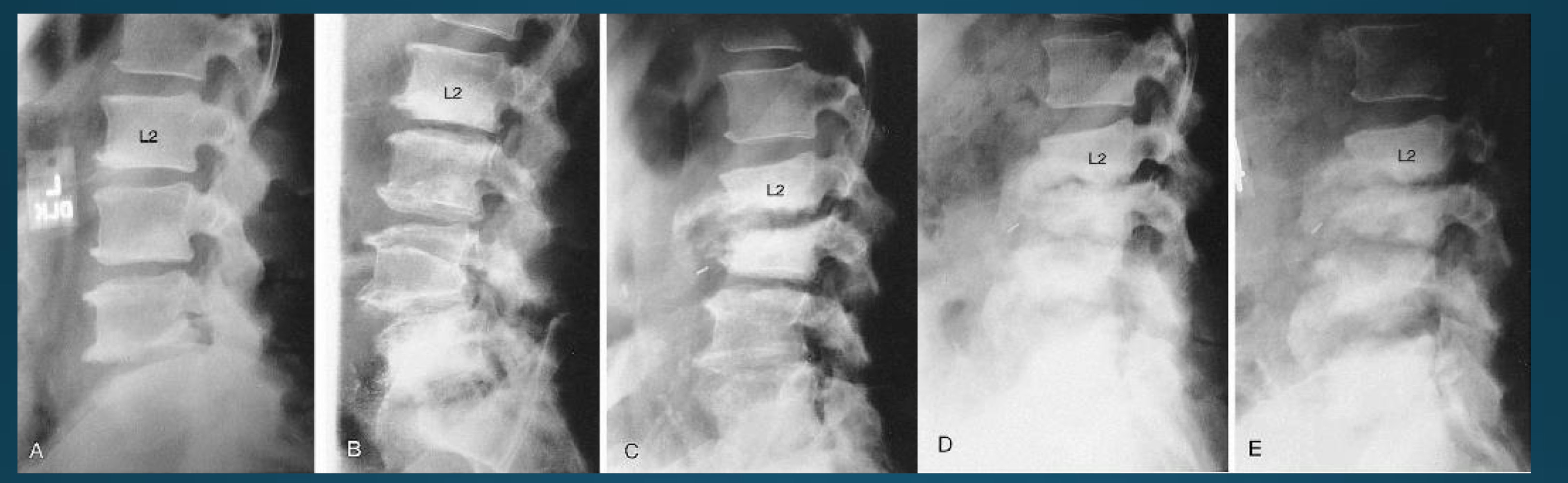
what is this appearance called?
often associated with what diagnosis?
stepladder appearance (subaxial subluxation)
RA
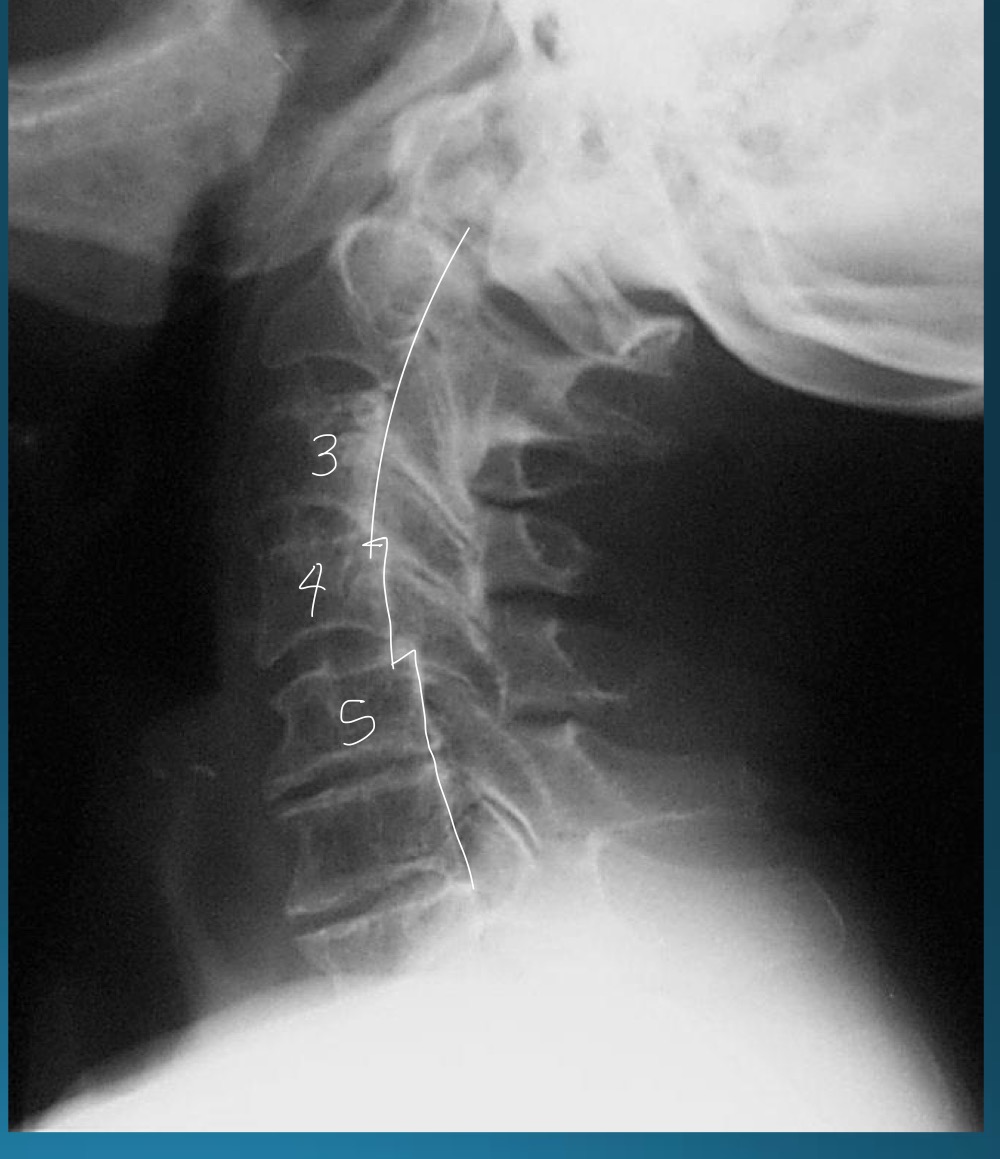
RA impact on cervical arthrosis has what characteristics?
loss of disc height
endplate erosions (esp in posterior 2/3)
multisegmental involvement
absence of osteophytes and sclerosis
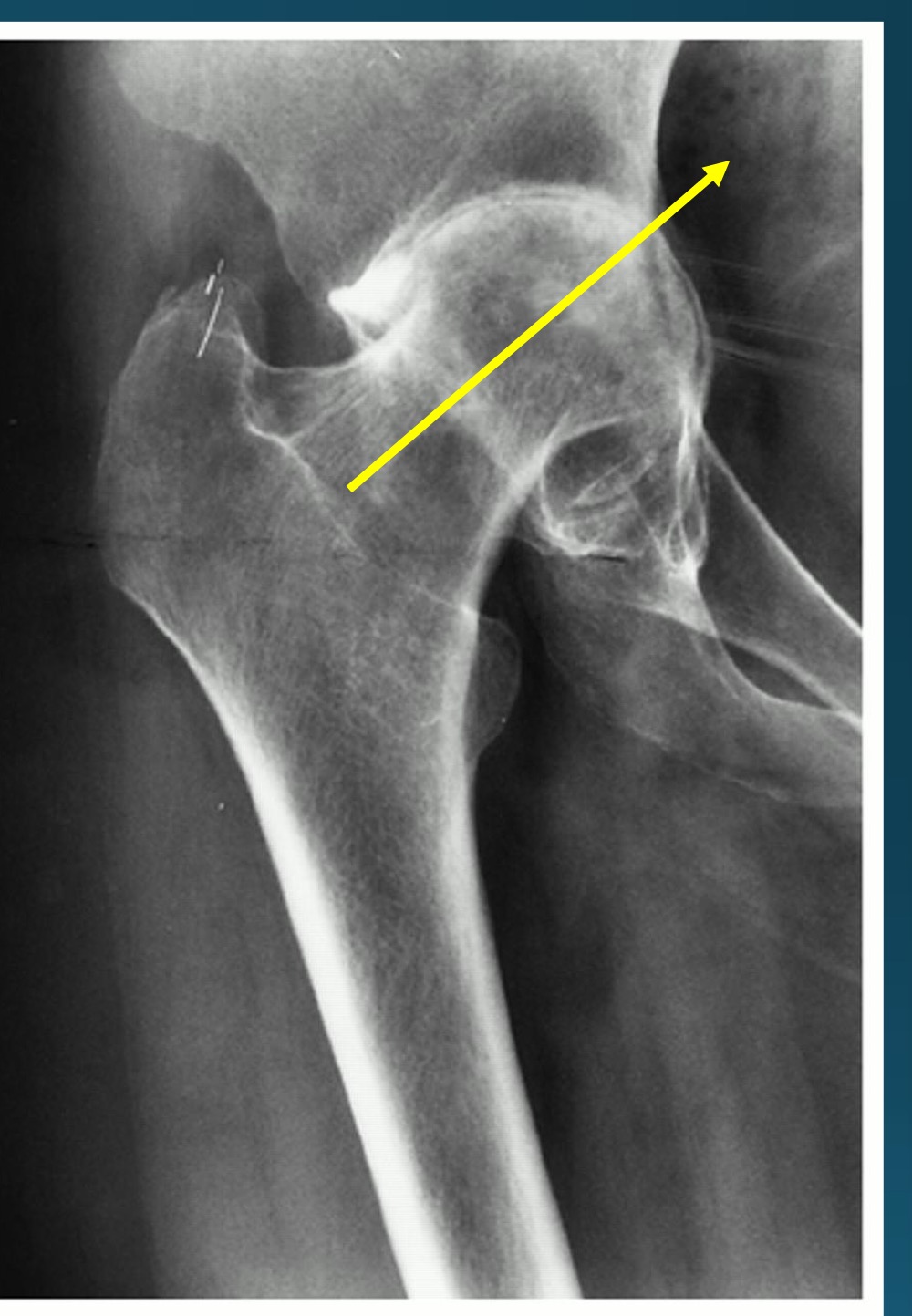
RA impact on hip can cause what
protrusio acetabuli
what is found in the posterior medial knee in knee arthritis due to RA?
baker’s cyst
baker’s cyst is found between what two muscles?
semimembranosus
medial head of gastrocnemius
RA + pneumoconiosis =
caplan’s syndrome
RA + leukopenia + splenomegaly =
Felty’s syndrome
is RA a contraindication to adjusting? if so, what kind?
yes, absolute at involved joints
what are these clinical features part of
age 2-16
fever
rash
lymphadenopathy
iridocyclitis
receded, hypoplastic mandible causing bird like face
juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JRA)
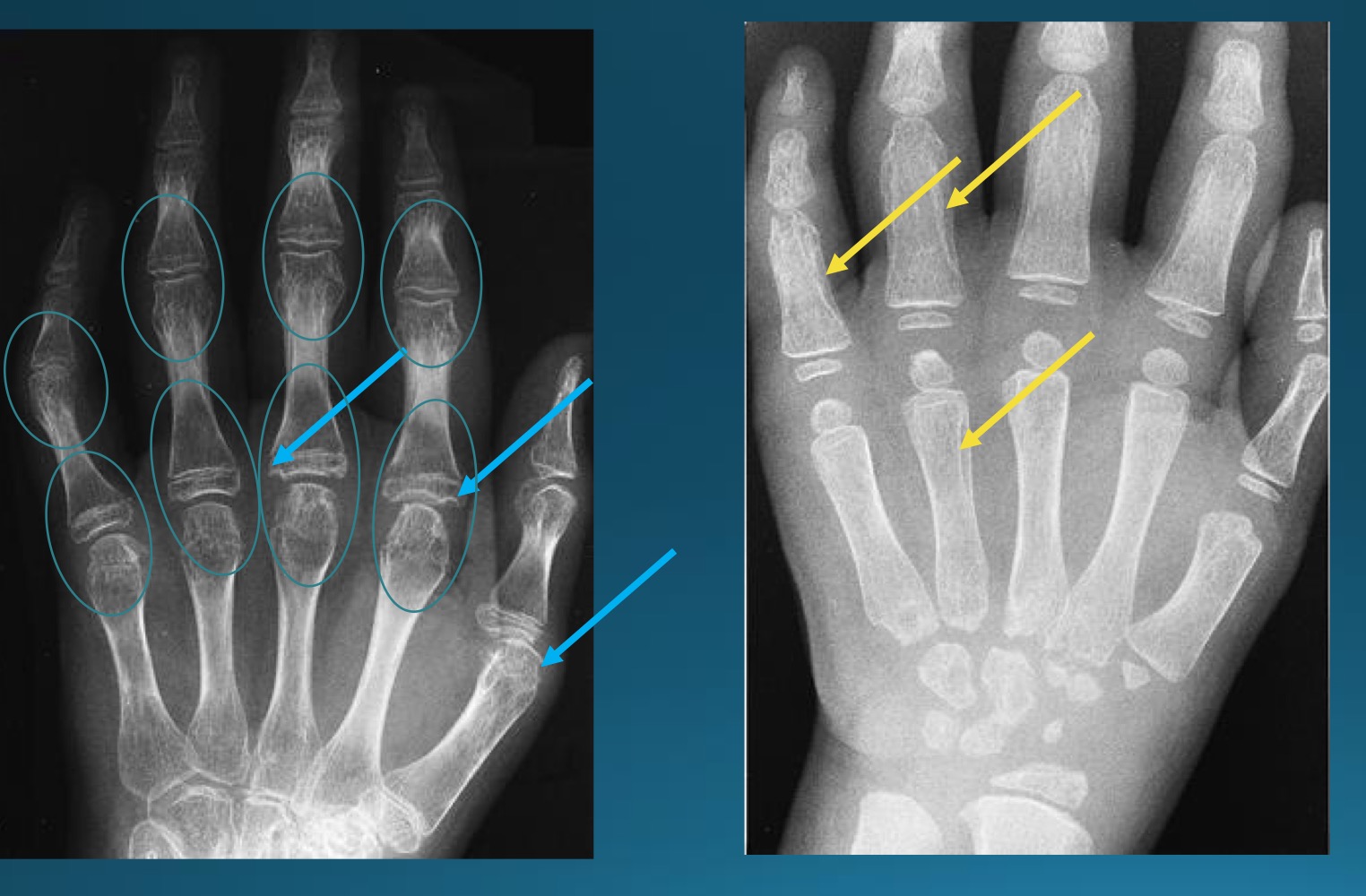
what is the diagnosis?
JRA
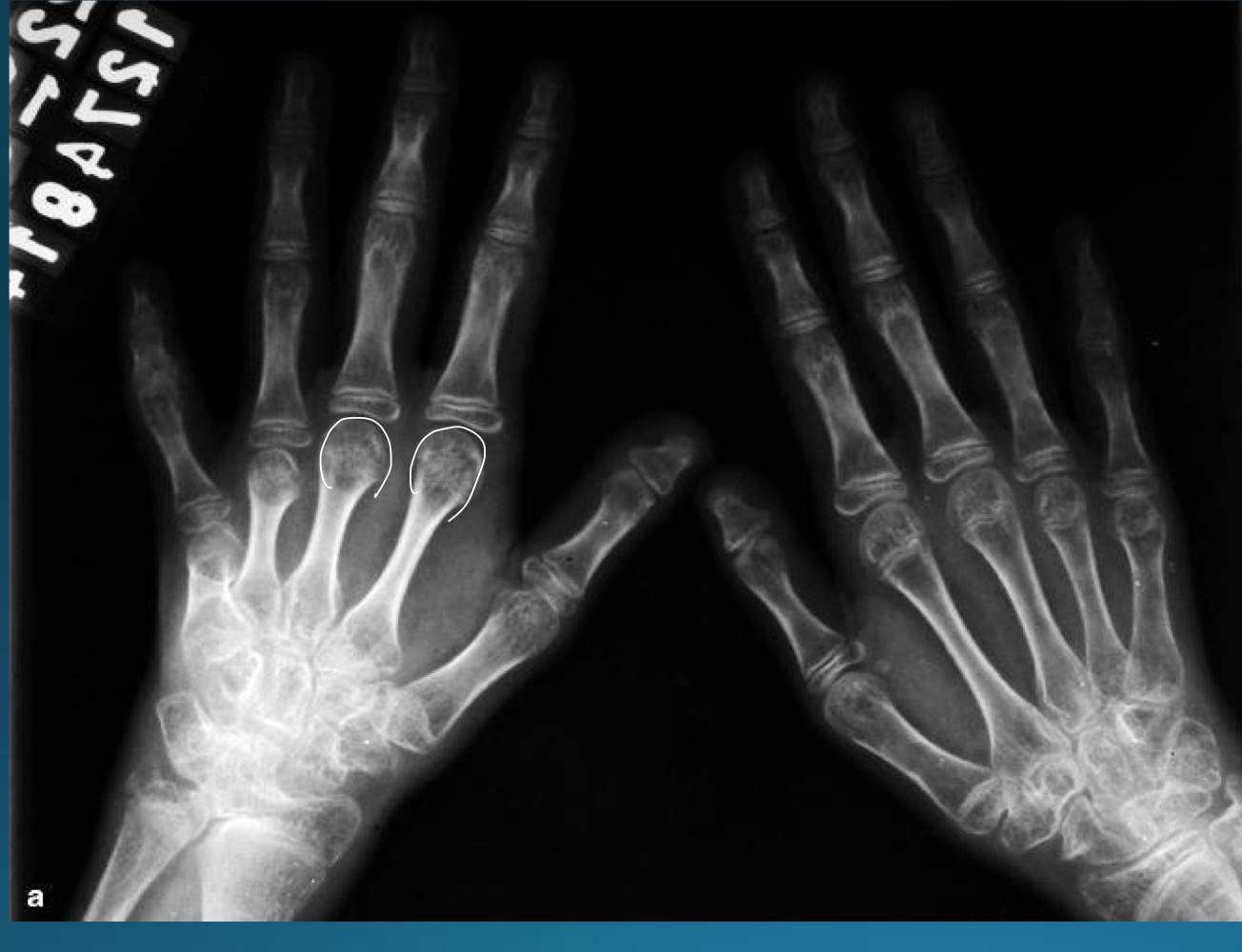
what is the diagnosis?
JRA
what are the common radiographic features of Juvenile idiopathic/rheumatoid arthritis?
soft tissue swelling
osteoporosis
transverse growth arrest lines
periostitis
ballooned epiphyses
what are the most common seronegative arthropathies?
psoriatic arthritis
enteropathic
ankylosing spondylitis
reactive
what lab tests might be positive in ankylosing spondylitis
HLA B27
elevated ESR and CRP
what are the targer sites of AS
bone-ligament junctions
fibrous joints (SI)
synovial joint (spine and root joints)
fibrocartilaginous joints (IVD, symphysis pubis, sternomanubrial)
what is an extraskeletal feature of AS
iritis

what is the diagnosis?
AS
sacroilitis
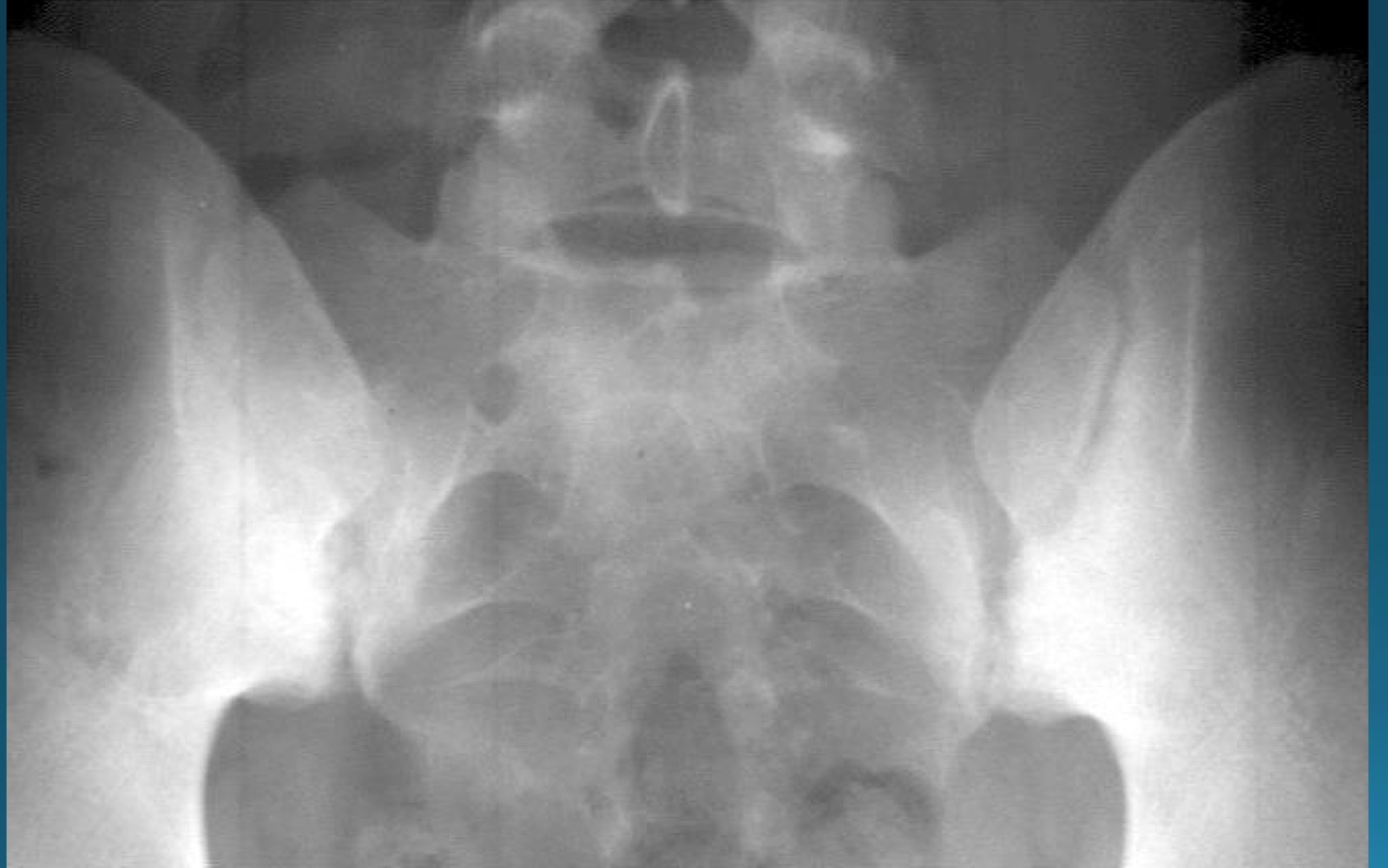
what are the signs seen in this image? what diagnosis would you make
rosary bead appearance (wavy appearance in SI joint area)
star sign (at superior angle of SI joint)
AS
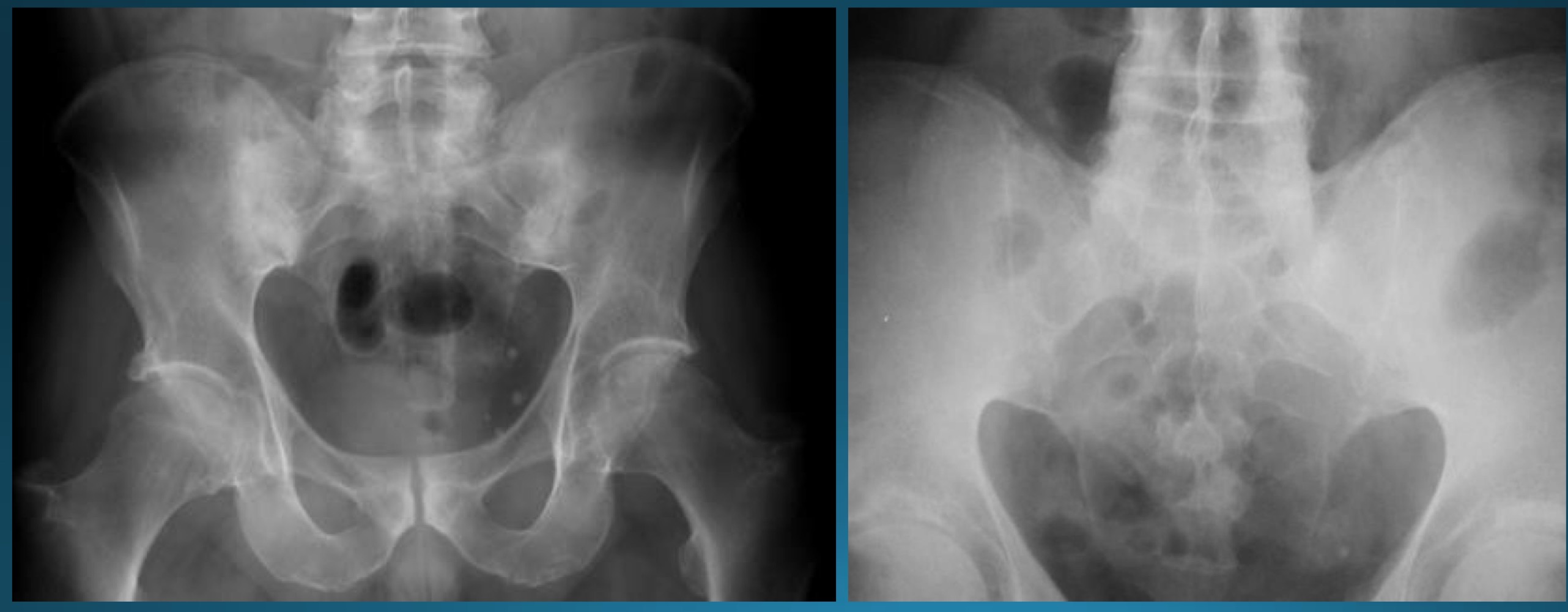
what are the signs seen in this image? what diagnosis would you make?
ghost joint (line in SI joint area but no space)
star sign (at superior angle of SI joint)
AS
what causes erosion at anterior corner of vertebral bodies in AS?
osteitis
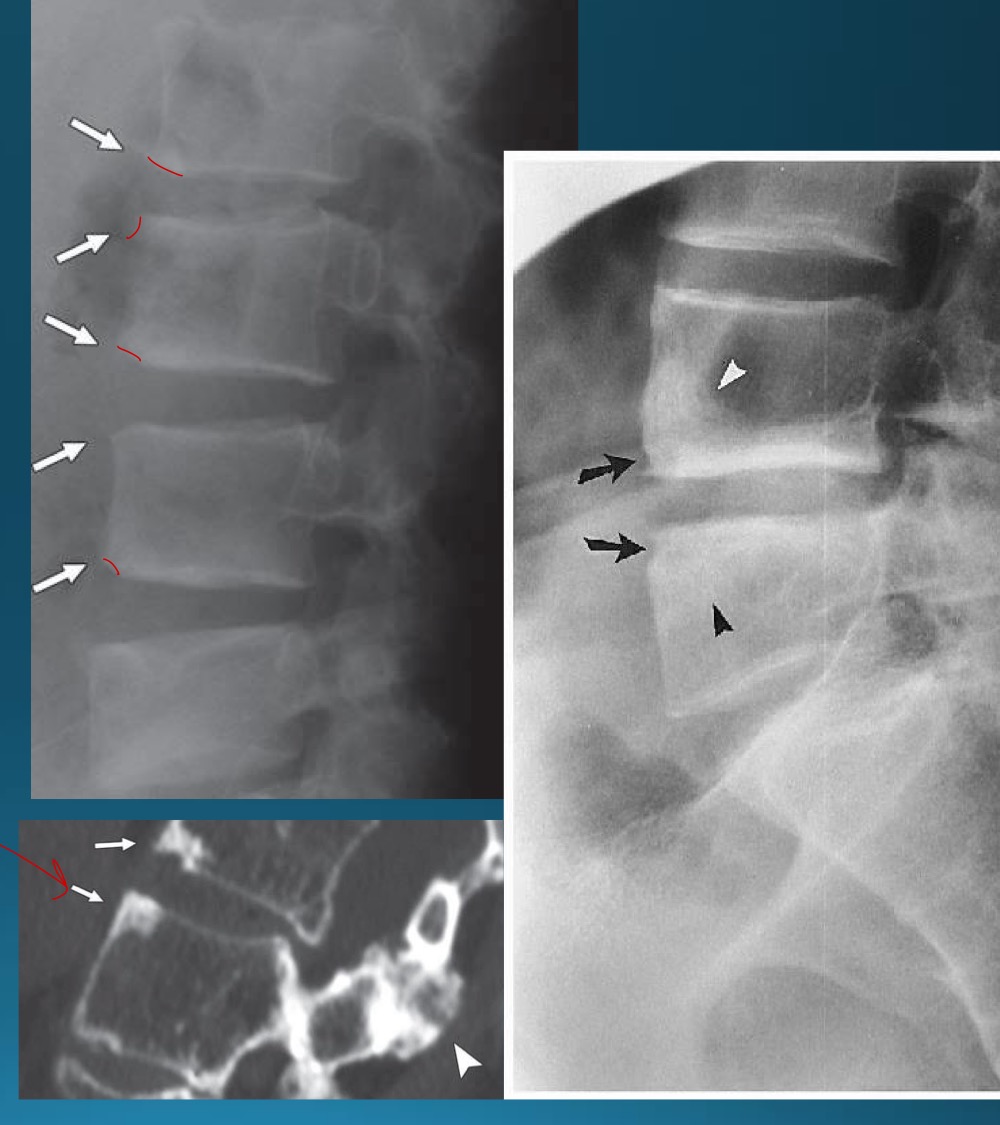
what are the signs seen in this image? what diagnosis would you make?
romanus lesion (erosion at corner of vertebral body )
shiny corner sign (sclerosis at angles of vertebral body romanus lesion)
AS
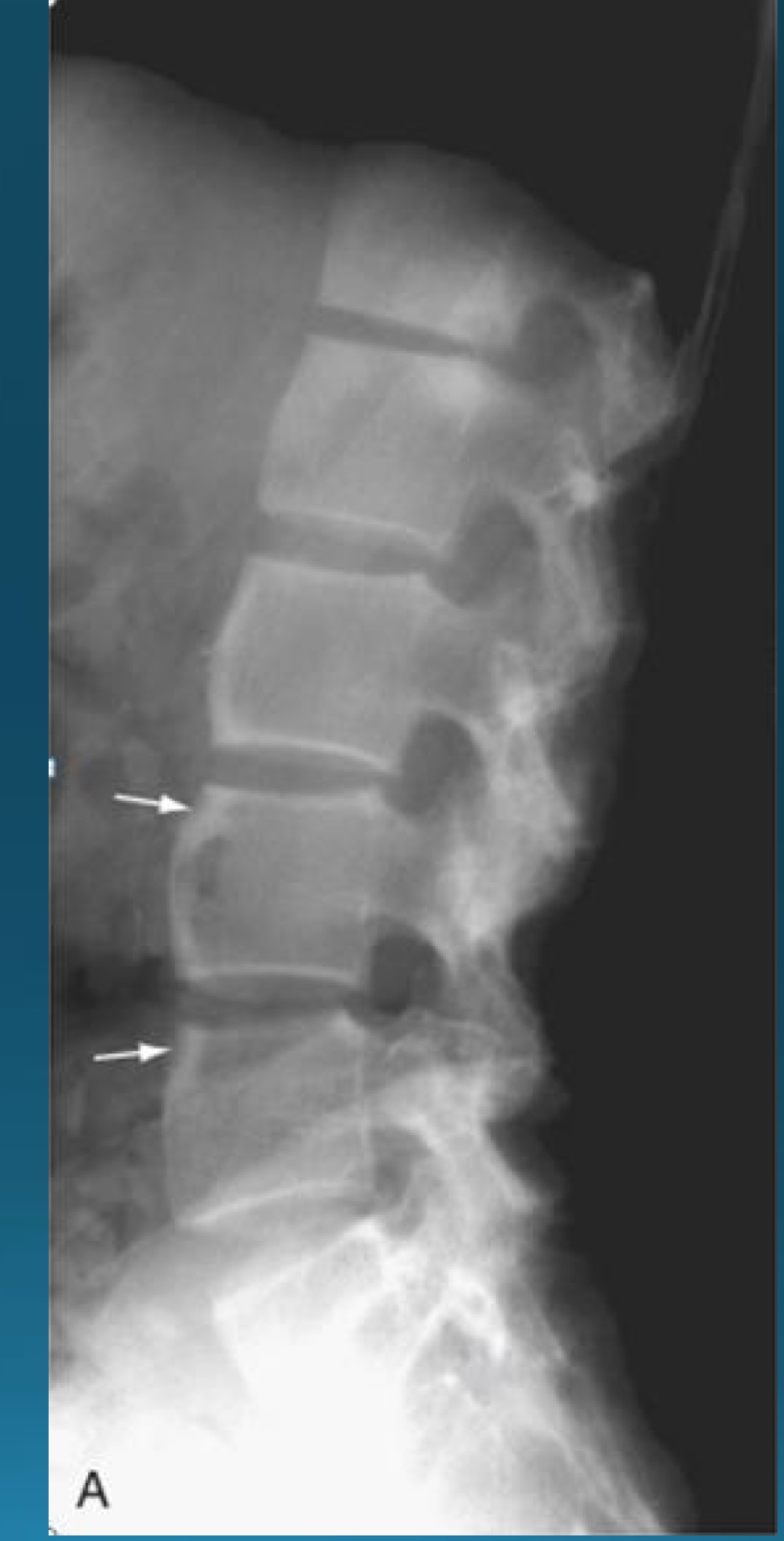
what are the signs seen in this image? what diagnosis would you make?
barrel shaped vertebra
AS
what type of seronegative arthritis is marked by marginal syndesmophytes?
AS
what is the difference between AS and DISH ossification between vertebra
facet joints are ankylosed in AS
appearance of spine in AS AKA
bamboo spine
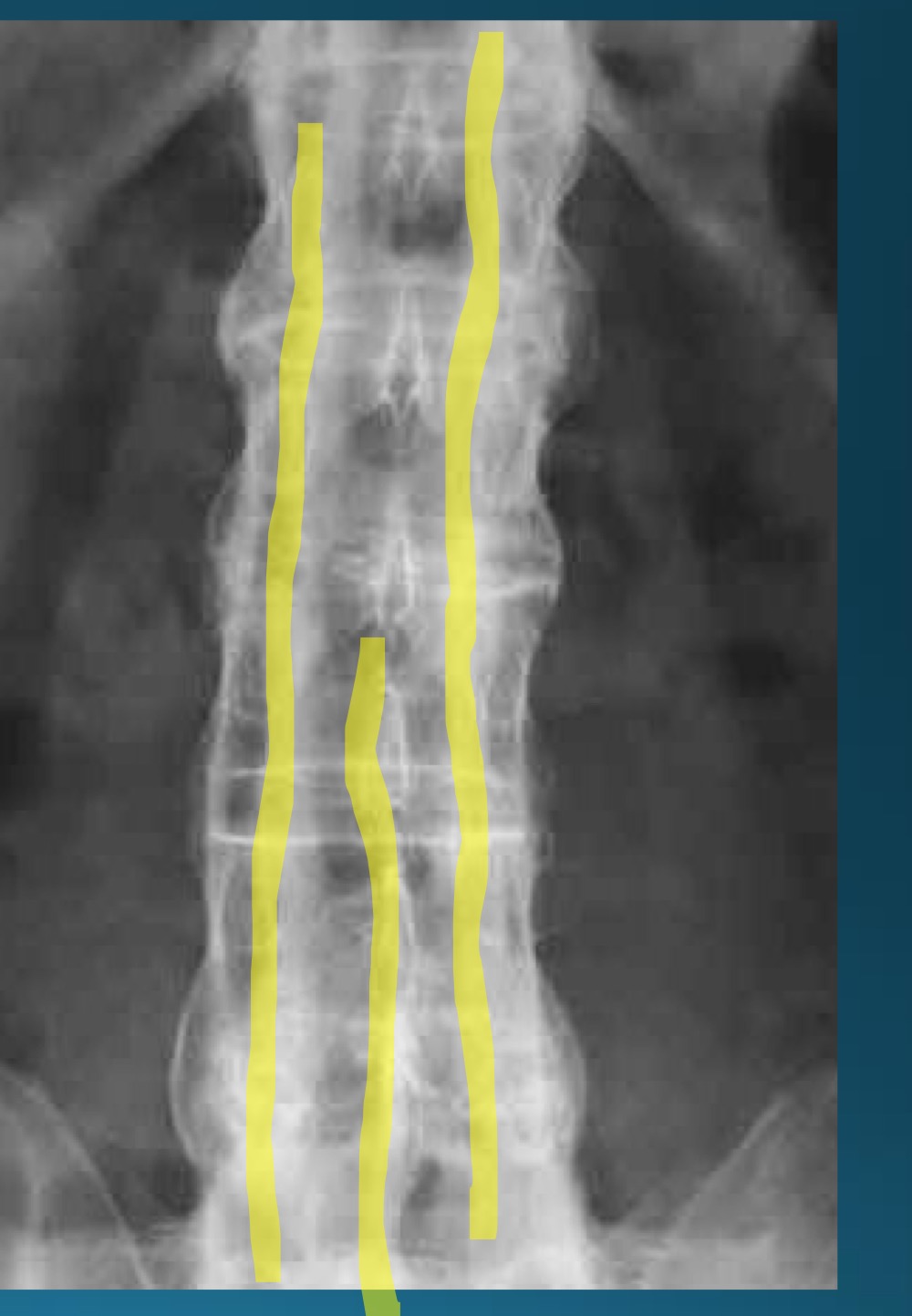
what do you call this sign? what diangosis is this apart of?
trolley track sign
AS
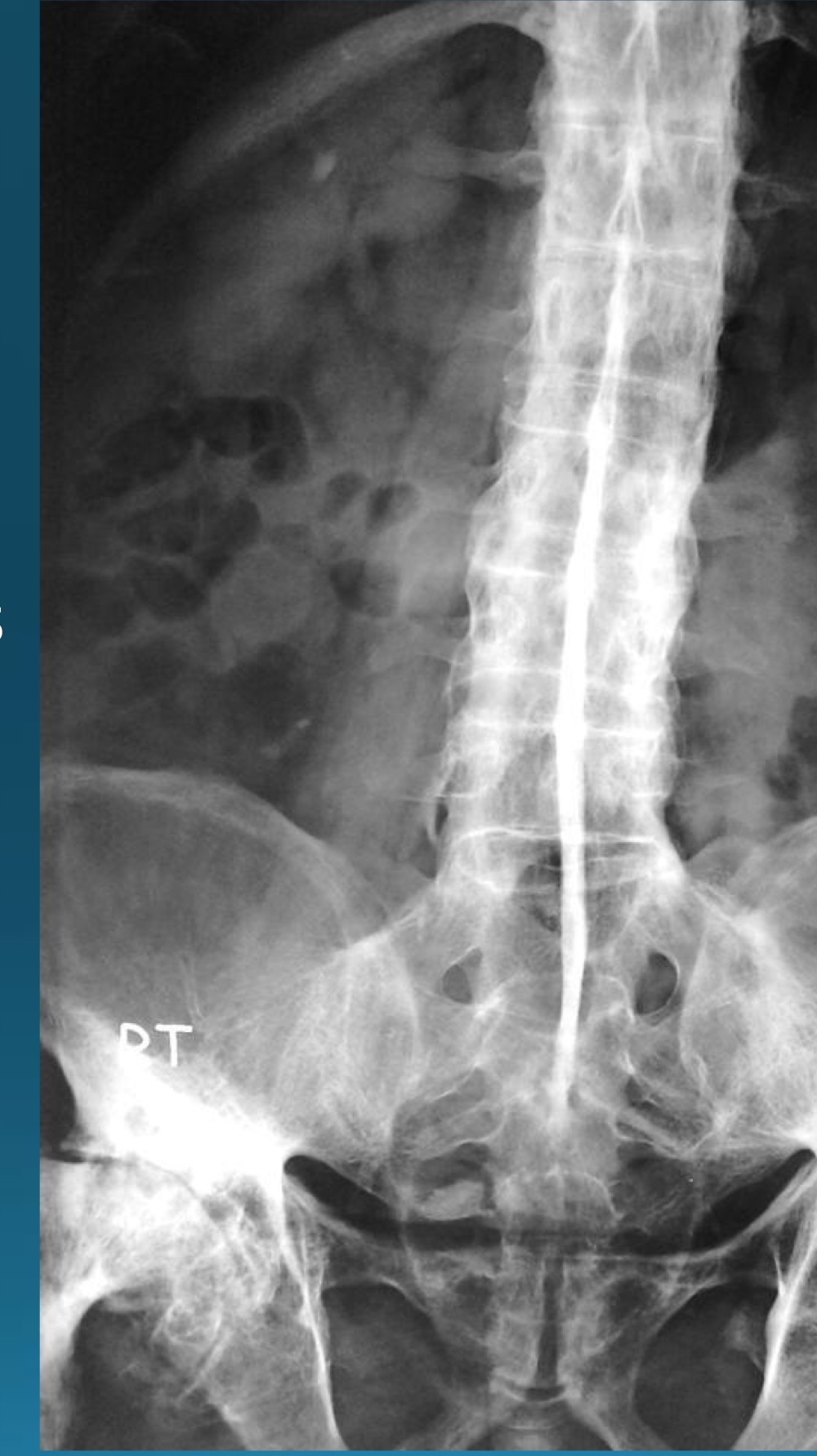
what do you call this sign? what diangosis is this apart of?
dagger sign
AS
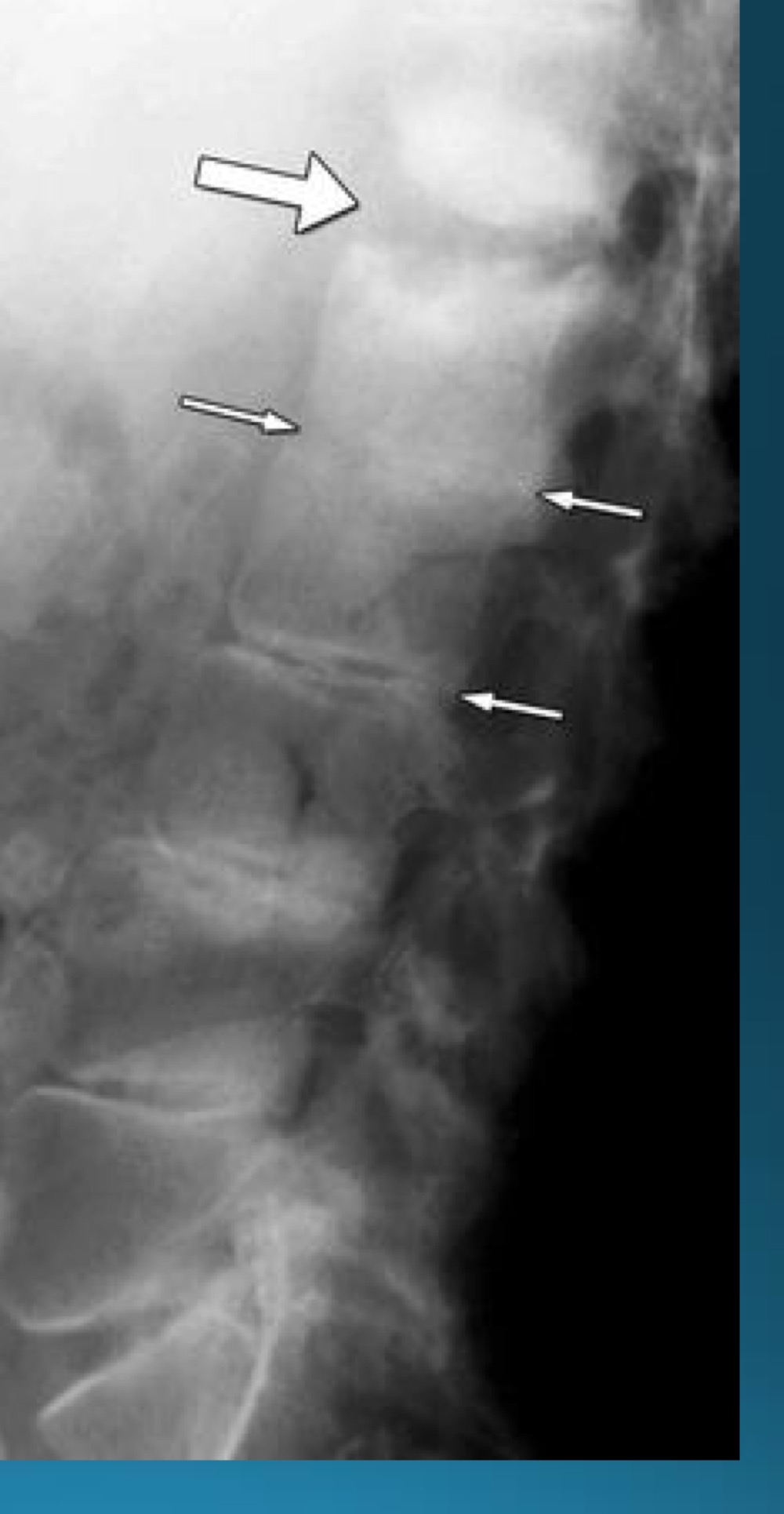
what do you call this sign? what diangosis is this apart of?
andersson lesion
AS