cytology morphology of cells lect pt.1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what is the cell?
main structural, functional and metabolic unit of the organism
A biosystem – open
self regulating, self reproducing
outline the cell theory (5)
cell elementary unit of the living body
all organisms made of cells
all cells have similar organisation
reproduce by division
linked together and influence eachother
glycocalyx
gel-like dense meshwork surrounding cells
hyaloplasm
clear fluid portion of cytoplasm
cytoplasm
semi-fluid portion of cytoplasm
size of cell
6-60 mcm
oocyte size
200 um
shapes of cells
flatten
Cuboidal
cylindrical
Polygonal
Stellate (like stars)
Pear
Pyramidal
Spindle
morphology
morphology describes the shape, structure, form, and size of cells
plasmalemma
less common term meaning plasma membrane
glycocalyx
a network of polysaccharides that project from cellular surfaces of bacteria
cytoplasm
material living inside cell excluding nucleus so includes cytosol and other materials
cytosol/hyaloplasm
gel-like substance within the cell that surround the cells organelles
obliged cell examples by membrane
endoplasmic reticulum
mitochondria
peroxisomes
lysosomes
coated vesicles
non membrane
ribosomes
cytocentre
microfilaments (myofibril, neurofibril, flagella)
cell inclusions
glycogen
lipid drops
protein granules
pigments
crystals
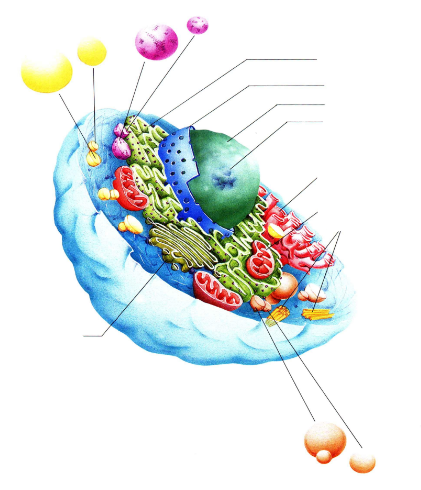
label
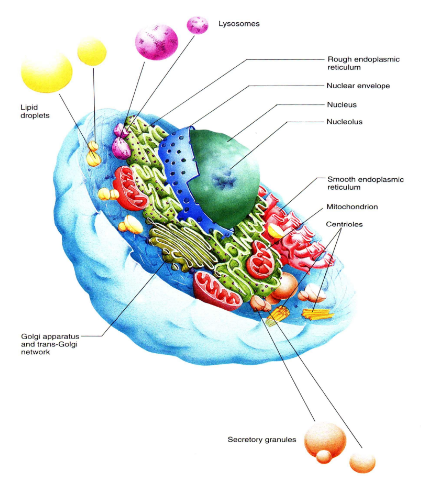
what are cells made of?
water - 90%
organic substances :
monomer : amino acids, glycerol, monosaccharides, nucleotides
polymer : proteins, lipids, DNA, RNA
how thick plasma membrane?
8-10 nm thick
sandwich model
Davson & Danielli
2 protein layers
1 lipid bilayer between
outer is hydrophilic
inner hydrophobic
fluid model
Singer & Nickleson
2 lipid layers with globular proteins attached
integral protein - attached to both lipid layers
semi-integral protein - attached to one of the lipid layers
peripheral proteins - attached to the head of the lipid molecules
65% lipid
35% proetin
1% carb
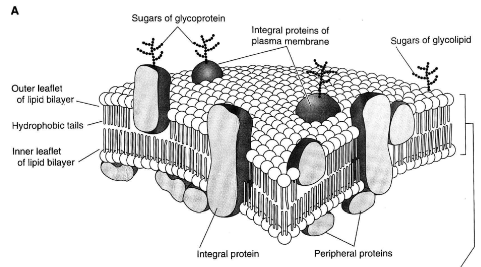
describe integral, semi-integral and peripheral proteins
integral protein - attached to both lipid layers
semi-integral protein - attached to one of the lipid layers
peripheral proteins - attached to the head of the lipid molecules
COOH and PO4 ends
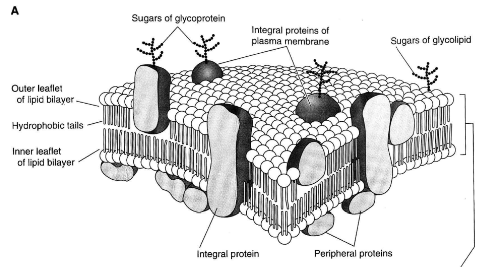
phospholipids
most amount of lipids in the elementary membrane
make the lipid bilayer
hydrophilic head
hydrophobic tail
cholesterol
inside the lipid bilayer
C H O
glycolipids
lipids with sugar
outer layer of the membrane
fo interaction between cells and cell-matrix
make the outer surface of the membrane negatively charged
glycoproteins
protein with sugar
outer layer of membrane
cell receptors
located outer part of membrane
attached to specific molecules (ligands)
recognise the proper molecule
transport proteins
for transport of amino acids, monosaccharides, ions
connecsones - transport of ions and low molecule substances
attaching proteins
for attaching cellsone to another
Ca ++ dependent
Ca ++ independent
tranductor proteins
between cell receptors and adynilate cyclase (secondary tranductor)
enzymes
more than 30
ATP-asa, AP-asa, RNC-asa, cAMP-asa
ways of transmembrane transport
Passive- without energy supply and conductor (transport proteins)
Diffusion
Filtration
Оsmosis
Аctive transport – K+-Na+ pump spdium potassiom ion pump 2K in 3Na out
energy supply - АТP
conductor (transport proteins)
against the gradient
Transport with the help of transport proteins (permiases) which are electrically charged
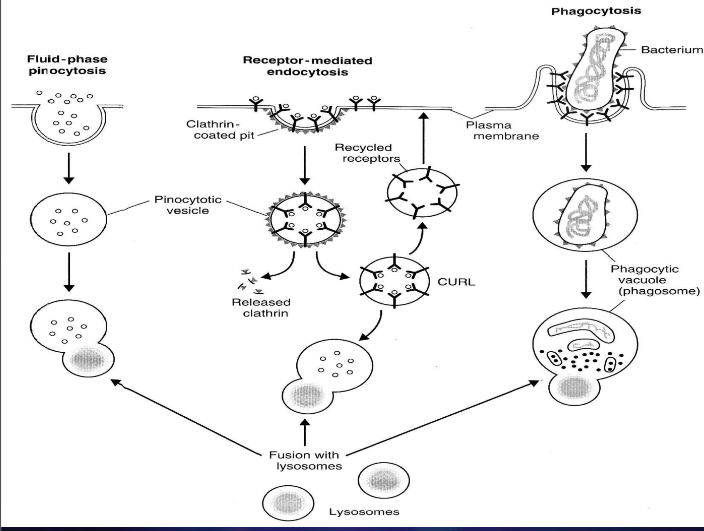
cytosis
transport of large molecules
connexones
transport ions and low molecule substances
endocytosis types
phagocytosis - solid particles
pinocytosis - fluids
fluid-phase pinocytosis - without coated vesicles
receptor-mediated endocytosis - with coated vesicles
protein clathrin - clathrin coated pit
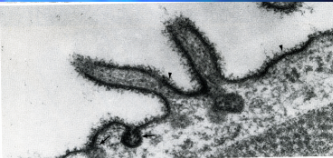
glycokyte rough structure
cytosol
cytoplasm without the organelles
made of water, ions, proteins, glucose, ATP
compartmentalization
different parts in the cell surrounded by biomembranes possess different chemicals, metabolism
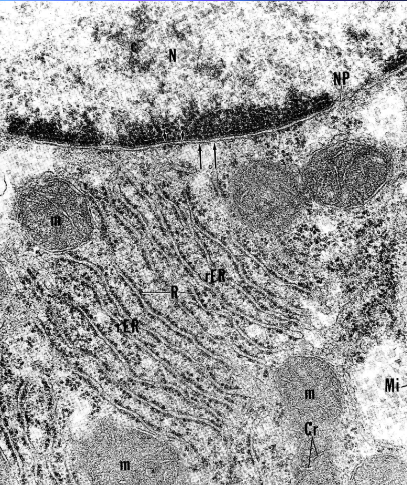
endoplasmic reticulum (microscope, type, component, origin)
seen with ELECTRON microscope only
membrane bound organelle made of parallel cysternae
50% of membrane in the cell, elementary membrane
made of 60% protein 40% lipid
originate from plasmalema (cell membrane), nuclear membrane
smooth and rough type
smooth ER (size, functions)
morphology
system of cysternae (7nm)
tubules packed by smooth membrane
function
synthesis of lipid, steroid, glycogen, glucoaminoglycanes
transport of substances in the cell
depot of Ca ions (muscle contraction)
production of Cl- ions for HCL in the parietal cells of the stomach
detoxification
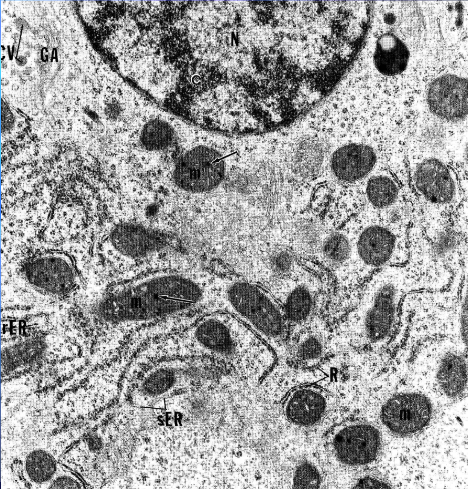
rough ER (size, localisation)
morphology
membrane bound cysternae 10 nm wide
ribosomes on outer
linked to nuclear membrane
stained with basic dye basophilia becaus eof ribosomes/RNA
localisation
in basic part, as nissl granulation in the neurons
golgi apparatus (microscope, morphology, location)
can be seen with light microscope AgNO3 impregnation
network of cysternae, vacuoles and vesicles
near the nucleus, 50-200nm wide
vacuoles - concentration and transport of the proteins
vesicles - transport of proteins
proximal - cis zone of production
distal - trans zone of maturation
mitochondria (function, morphology, microscope)
has enzymes for Kreb’s cycle for ATP production, give energy to cell
light microscope - rods and dots using iron-hematoxylin
electron microscope - membrane bound organelles outer and inner
outer is smooth inner is folded cristae
enzymes for Krebs cycle
intermembranous space, inner mitochondreal space
matrix - Ca2+, PO42+, DNA - self division
difference between apocrine, melocrin and holocrine
Definition:These are three types of glandular secretion methods.
apocrine - releases its product by budding off a portion of the cell membrane, allowing the cell to remain intact
melocrine - secretes products directly through the cell membrane without losing any cellular materia
holocrine - involves the entire cell disintegrating to release its contents, resulting in cell death