Crime and Deviance
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms

Edward Sutherland (1949)
People from “chaotic social backgrounds” are more likely to be involved in crime as both perpetrators and victims.

Social Exclusion Report (2002)
32% of prisoners have been homeless, and are more likely to have grown up in care.

Williams et al (2012)
It’s more common for the prison population to have: run away from home, truant from school and have no qualifications.

Cavadino and Dignan (2001)
The difference between working and middle class crime is not as high as PRCF suggest, due to bias in the CJS towards the higher classes.

The British Crime Survey (2010-2011)
Young households, lone parents and unemployed people are 2x as likely to be burgled, and unemployed people are 2x as likely to be victims of violence.

Young (1988)
“The myth of the equal victim” - working class people are impacted more by crime than upper classes.

Merseyside Crime Survey (1984)
The poor suffer more heavily from the impact of crime, and are more likely to experience multiple victimisation.
Ministry of Justice
Men commit approximately 80% of crime each year.
In December 2019, men made up 79,000/82,000 prisoners in the UK.
Chivalry Thesis
Women are treated more leniently by the CJS
Young (1988)
“The meaning of a punch” - all crimes are not created equal
Hammer and Saunders (1984)
20% of women on a street in Leeds had been sexually assaulted and not reported it.
Stanko (2002)
Over a 24 hour period, an incident of sexual assault was reported every second in the UK.
Walklate (2006)
Many women were unable to leave abusive relationships, especially if they had children with the abuser or were financially dependent on them.

Cuckooing
When elderly people have their homes taken over by gangs to store drugs.

10-17 year olds are only 10% of the population…
…but are responsible for 23% of police recorded crime.

McVie (2004)
Grouping crime data into age groups can mask specific findings.

Young (1988)
Age should be considered alongside other social factors when looking at crime statistics.

Islington Crime Survey
Young white females are 29x more likely to be assaulted than those over 45.

CSEW (2009)
Began including children ages 10-15 and found higher levels of victimisation among children than PRCF suggest.

Gov.UK (2023)
27.2 stop and searches occur per 1000 black people, whereas only 5.6 occur per 1000 white people.

Bowling and Phillips (2006)
The crown prosecutor on service are more likely to drop cases involving black suspects due to a lack of evidence.

Eastern European Immigration Moral Panic
Politicians and the media falsely link higher crime rates with immigration despite crime levels not being impacted by immigration.

Ministry of Justice (2007)
The Muslim prison population has doubled in the last 10 years to 12,000 people.

CSEW (2012-2013)
Mixed race, Black and Asian ethnic groups are more likely to be victims of personal crime than white people.

Home Office (2005)
Black people are 5x more likely to be murdered than their white counterparts.
In 1/3 gun murders, both victim and suspect are black.

Gov.UK (2017-2020)
Men from mixed ethnic backgrounds are the more likely to be victims of crime than men from any other group.

Despite being only 3.1% of the population in 2013…
…Black people composed 14.2% of all stop and searches.
Franko Aas (2007) - global organised crime
The cross border activities of organised crime groups, exploiting to their advantage, increasing global interconnectedness
Gov.UK (2019-2020)
There has been a 50% rise in modern slavery crimes recorded by the police
The Guardian (2019)
Over 1100 children were trafficked into the UK for the drug trade
ONS (2020)
Roughly 3.2 million people are impacted by fraud every month
Gastrow (2013)
• Popular perceptions of organised crime groups are outdated and romanticised
• National borders are irrelevant to organised crime groups but essential for governments trying to tackle them
Castells (2000)
Organised crime groups function like business and even link with other crime groups.
Robertson (1995)
‘Glocalisation’ - the impact of global organised crime is dependant on local conditions and vice versa

Franko Aas (2007) - Green Crime
Any crime that impacts the environment or wildlife

Carrabine et al (2004)
• primary green crime - directly inflicts harm on the environment e.g littering
• secondary green crime - crimes committed to try and assist green crime e.g modern slavery

Potter (2010)
Studied food riots around the world and found that the poorest always suffer the most from environmental damage
Erikson (1966) - functionalism
• argues that public degrading ceremonies deter criminals from offending
• looked to previous crime to show how society is progressing e.g pride parades
Davis (1961) - functionalism
• Crime and deviance can act as a ‘safety valve’ to allow groups to let off stream
• e.g saw prostitution as a safe outlet for men to prevent rape from occurring, and so the crime of prostitution prevents the worse crime of rape
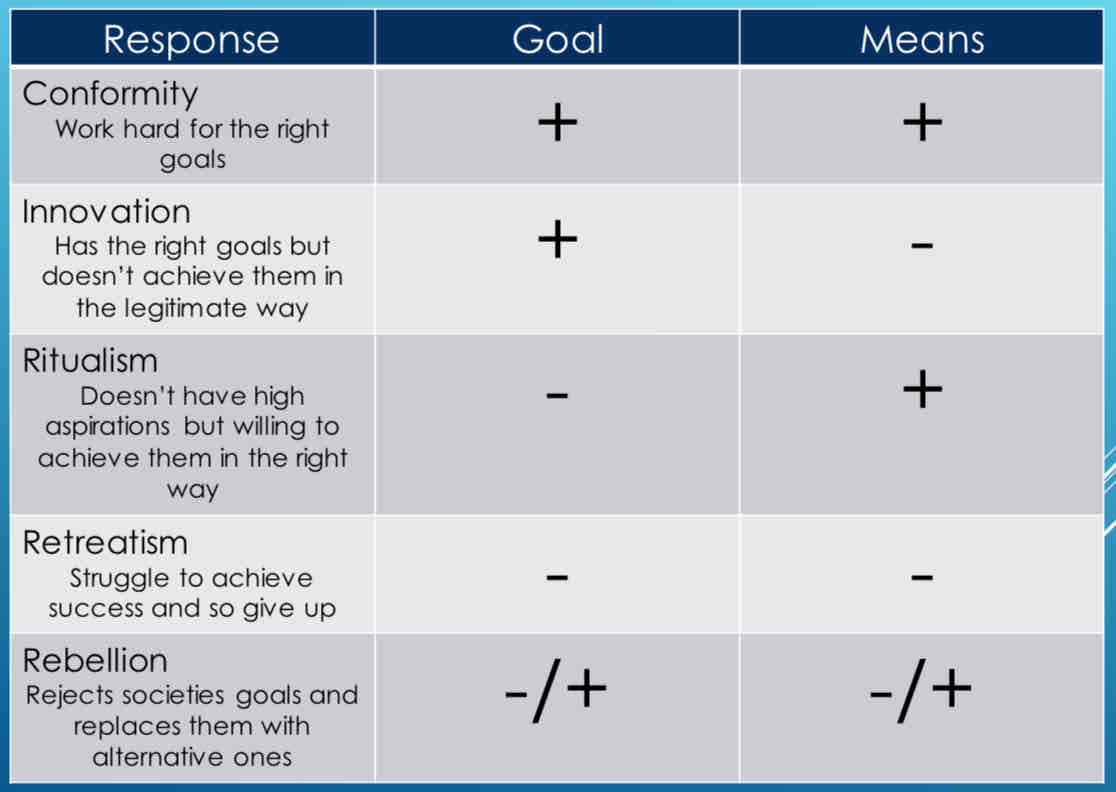
Merton (1938) - functionalism
Strain theory
Albert Cohen (1955) - subcultural theory
Status frustration
Cloward and Ohlin (1961) - subcultural theory
Criminal, conflict and retreatist subcultures.
Miller - subcultural theory
Focal concerns
Trouble
Excitement
Autonomy
Fate
Smartness
Toughness
Winlow (2001) - subcultural theory
Young boys are often pushed towards violence through the media. Masculine identities stem from fighting.
Ferrell (1999) - cultural criminology
explains that cultural criminology stresses the “energy of everyday life”
Katz (1988) - cultural criminology
Lure and attractions of crime
Lyng (2005)
“Edgework” - pushing the boundaries of the law to escape societal constraints
Young (2003) - cultural criminology
Bulimic society - intensity of exclusion
Presdee (2002) - cultural criminology
The carnival of crime
Becker (1963) - interactionism
Outsiders - deviance is socially constructed and so identity factors don’t matter when examining crime
Cohen (1972) - interactionism
Moral panic and folk devils
Malinowski (1966) - interactionism
Publicly labelling deviance is what makes it severe
Lemert (1951) - interactionism
Primary and secondary deviance
Matza (1964) - interactionism
Young people drift in and out of deviancy, but feel a moral obligation to the law.
Young (1971) - interactionism
Deviancy amplification
Althusser (1970) - Marxism
Repressive state apparatus and Ideological state apparatus help to maintain a capitalist structure
Box (1983) - Marxism
Power and Crime - “avoidable killings” vs murder
Sutherland (1949)
White collar crime is “a crime committed by someone of respectability and high social status in the course of their occupation”
Tombs (1999) - Marxism
The amount of unlawful workplace deaths vastly outweighs the number of homicides
Goldstraw - White (2010) - Marxism
Those convicted of white collar crimes don’t view themselves as real criminals
Chambliss (1973) - Neo Marxism
The saints and the roughnecks
Stuart Hall (1978) - Neo Marxism
Policing the crisis - mugging
Taylor, Walton and Young (1972) - Neo Marxism
3 reasons for crime
Circumstances surrounding the choice to offend
The outcome of the act
Effects of the societal reaction
The CCCS - Neo Marxism
Youth deviance is a reaction to young people’s identity feeling under threat
Hirsche (1969) - right realism
A lack of at least ¼ social bonds causes crime:
Attachment
Commitment
Involvement
Belief
Charles Murray (1984) - right realism
Sterilise the underclass to stop crime
Wilson and Kelling (1982) - right realism
Broken window theory
Clarke (1980) - right realism
Crime will occur when the benefits of criminality outweigh the costs
Wilson (1975) - right realism
Crime can only be addressed by enforcing the law e.g. three strikes and you’re out policy
Matthew’s and Young (1992) - left realism
Square of crime
Braithwaite (1989) - left realism
Disintegrative - shaming the individual
Reintergrative - blame society
Lea and Young - left realism
Relative depravation and marginalisation
Heidensohn - feminism
Women are more controlled in society so commit less crimes
Pat Corlen (1987) - feminism
Women who reject the class and gender deal are more likely to engage in criminality
Smart (1976)
Girls are limited to the private domestic sphere
Adler (1975) - feminism
Women’s liberation increases their participation in crime
Messerschmidt (1993) - feminism
Hegemonic masculinity causes criminality