NPB101: Neurophysiology Part 3
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
PNS is made up of ____
neurons
T/F: PNS neurons live inside
False, they dont formally live inside the brain and spinal cord
PNS is made up of ____ neurons & ____ neurons.
afferent neurons & efferent neurons
Afferent neurons
carry sensory information
Afferent neurons carry ___ information from ____ tissues
sensory, peripheral
Afferent bring info from
Gi tract
surface of skin
visceral organ
Info processed by brain or spinal cord
Efferent neurons
carry information to control (motor)
Efferent neurons carry ____ to control ____ tissues
information, peripheral
Efferent neurons ___ transmit signals that ____ the activity of muscles and glands
axons, control
Being consciously perceived means
coming to the surface of the skin or they’re going to a very specialized organ that’s designed for detecting stimuli
Three subdivisions of Peripheral Afferents that carry info towards the CNS
General Somatic Sensory Afferents
Special Sensory Afferent
Visceral Sensory Afferent
Innervating
supply (the body/skin) with nerves
General Somatic Sensory Afferent
Touch sensitive neurons that are innervating the skin
somatic (body)
General Somatic Sensory Afferent are ___ sensitive neurons & also ___ sensitive
pain, temperature
The General Somatic Sensory Afferent is pain and temperature sensitive because
Both pain & temperature are innervating the skin because the skin is a multi use organ
Special Sensory Afferent
Neurons that are innervating specific organs that detect stimuli
ex: eye detect light waves
skin: protection
ear: soundwaves
tongue: special sensory afferent
These are all specialized organs
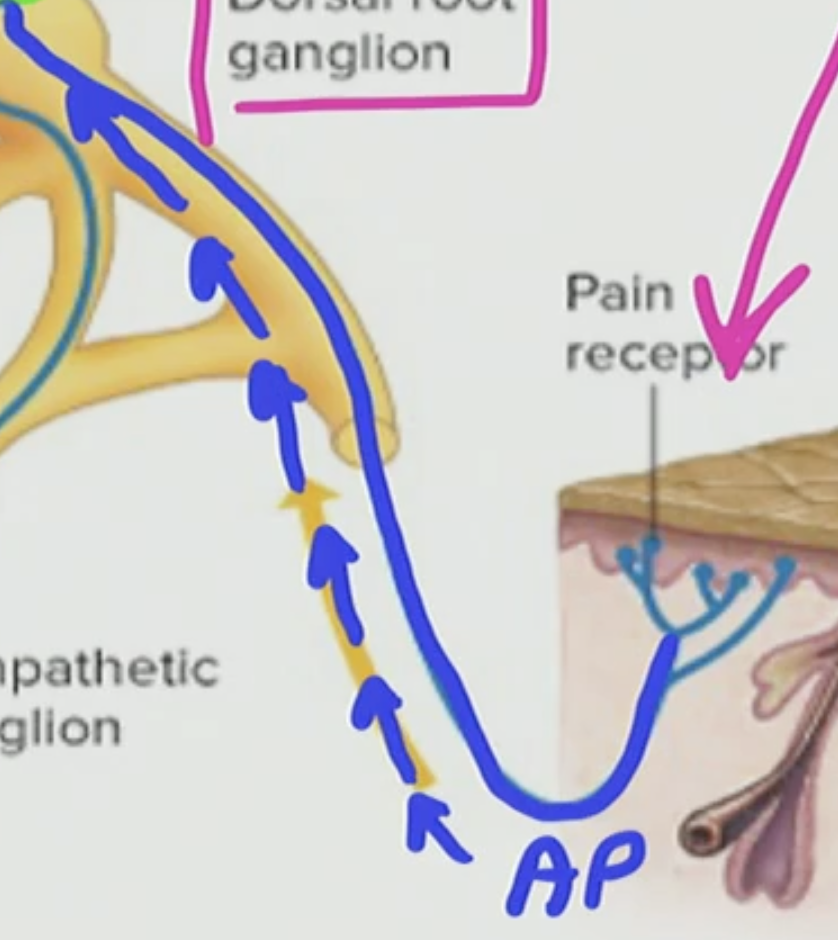
General Somatic Sensory Afferent touch receptor
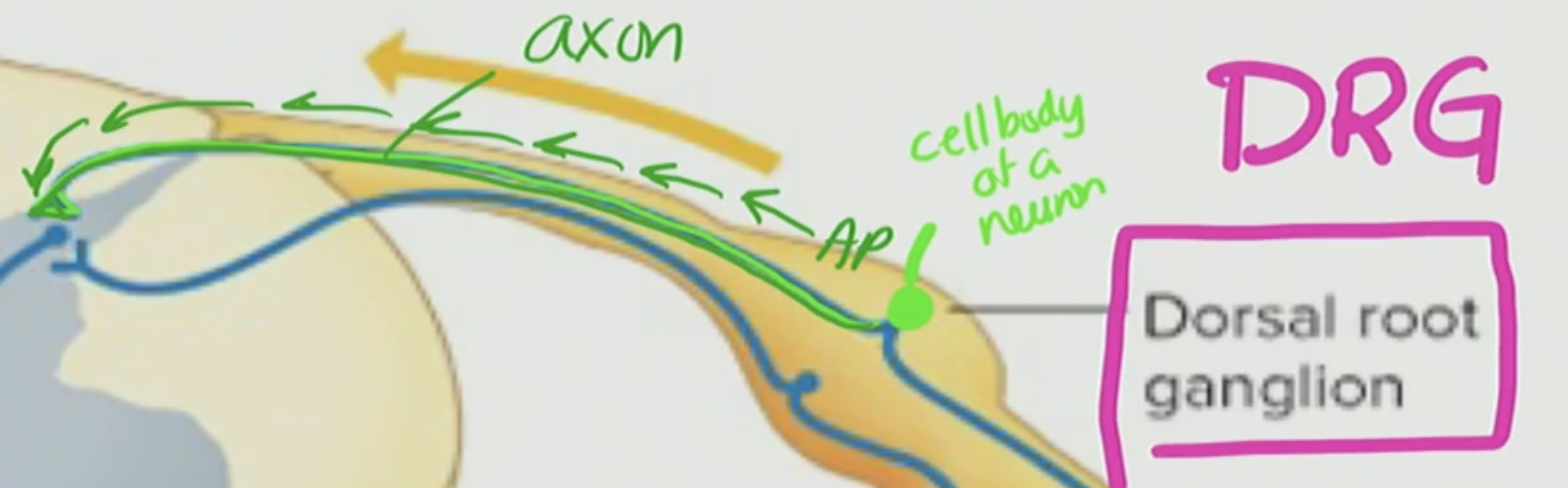
Dorsal Root Ganglia
has a cell body of a neuron with an axon that has a terminus that has AP propagating
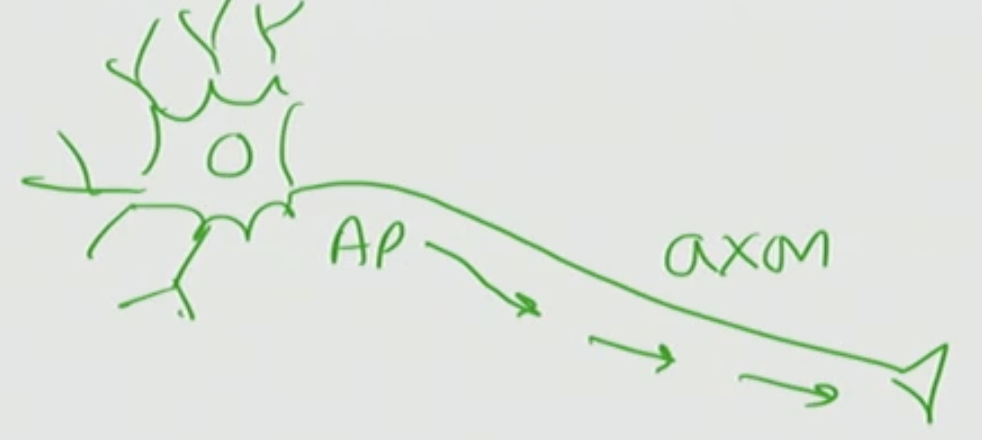
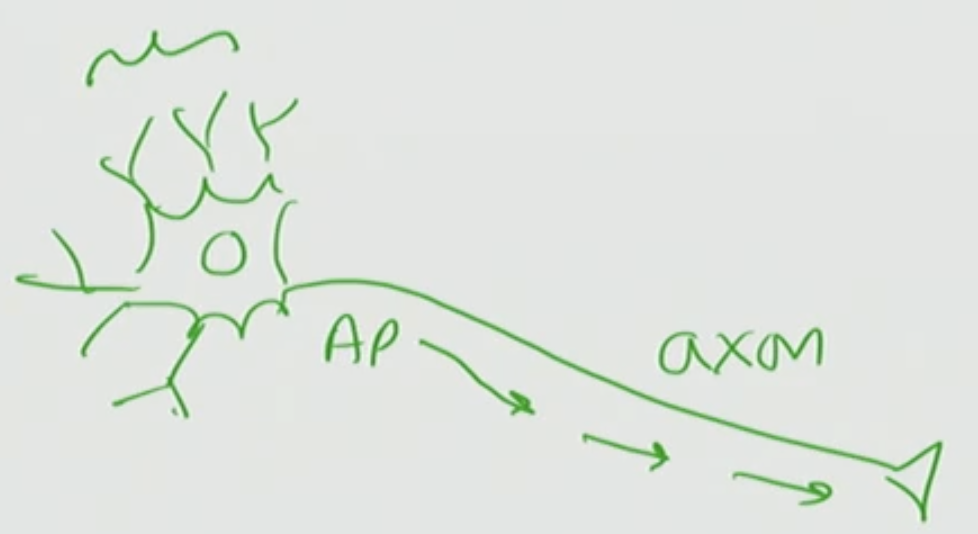
What are these structures called on the neuron
Dendrites
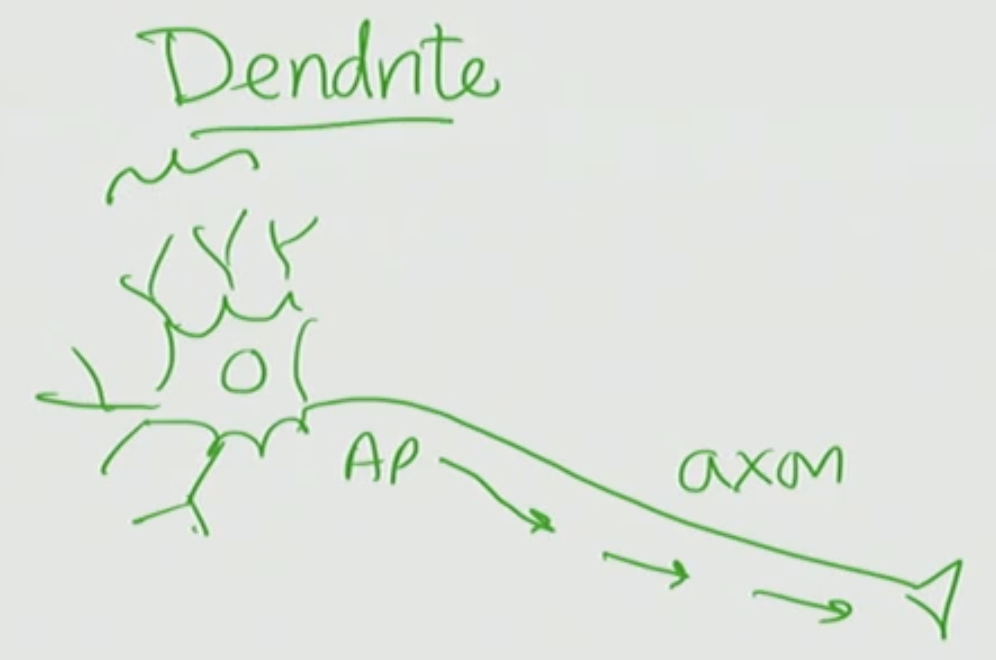
Dendrites
receives information coming into the neuron
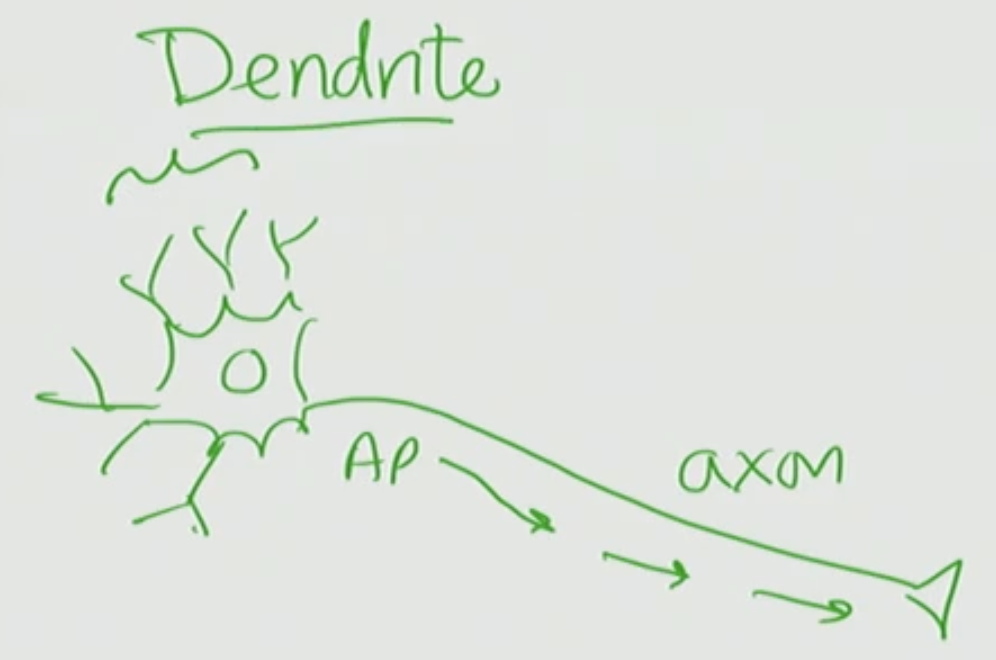
What can form on a dendrite?
The synaptic connection between two neurons where a neuron comes in and forms a synapse with a target neuron is that can form on a dendrite
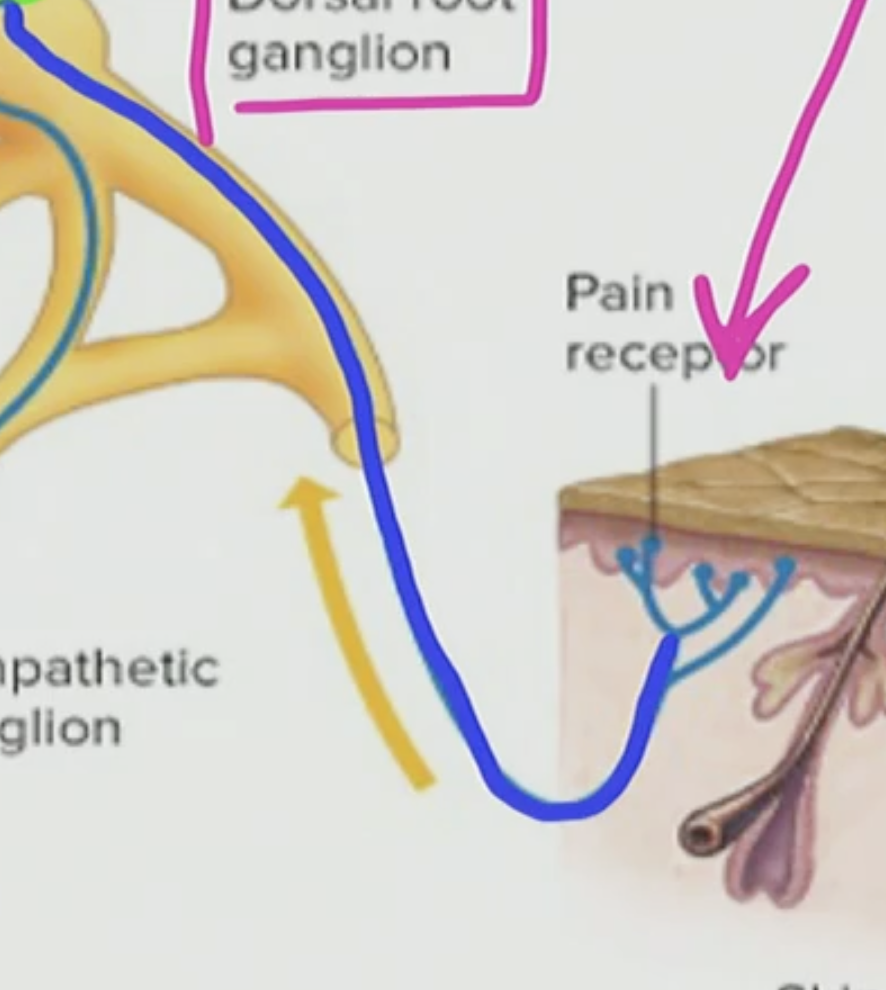
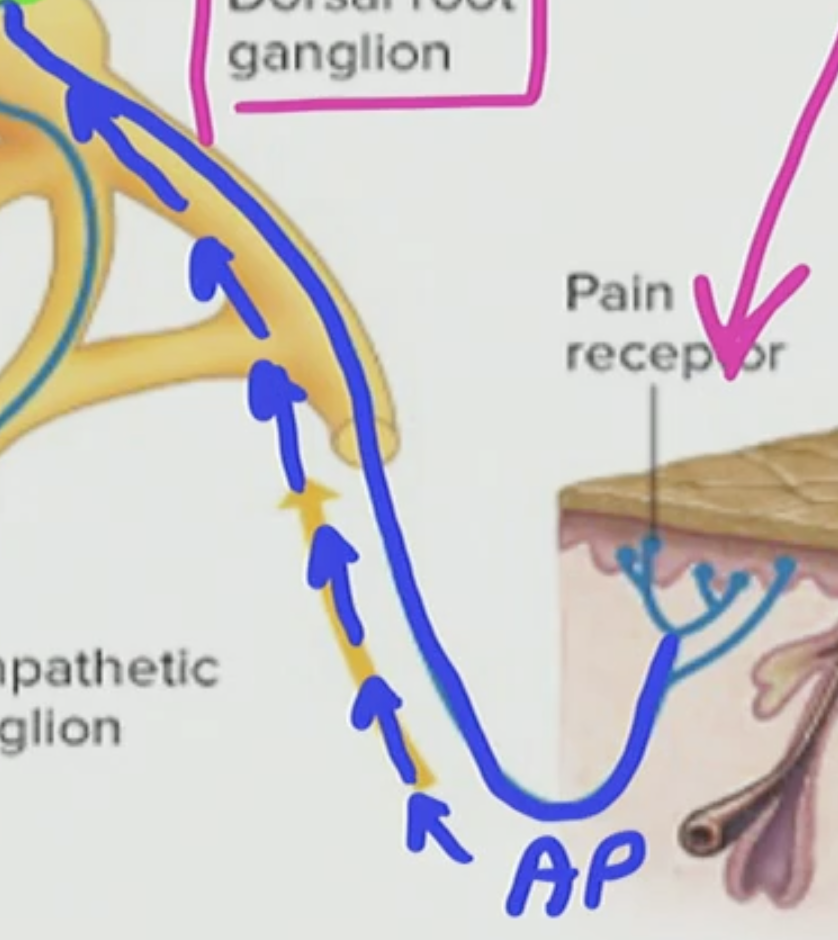
What is this blue thing in the touch receptor?
This is a modified dendrite
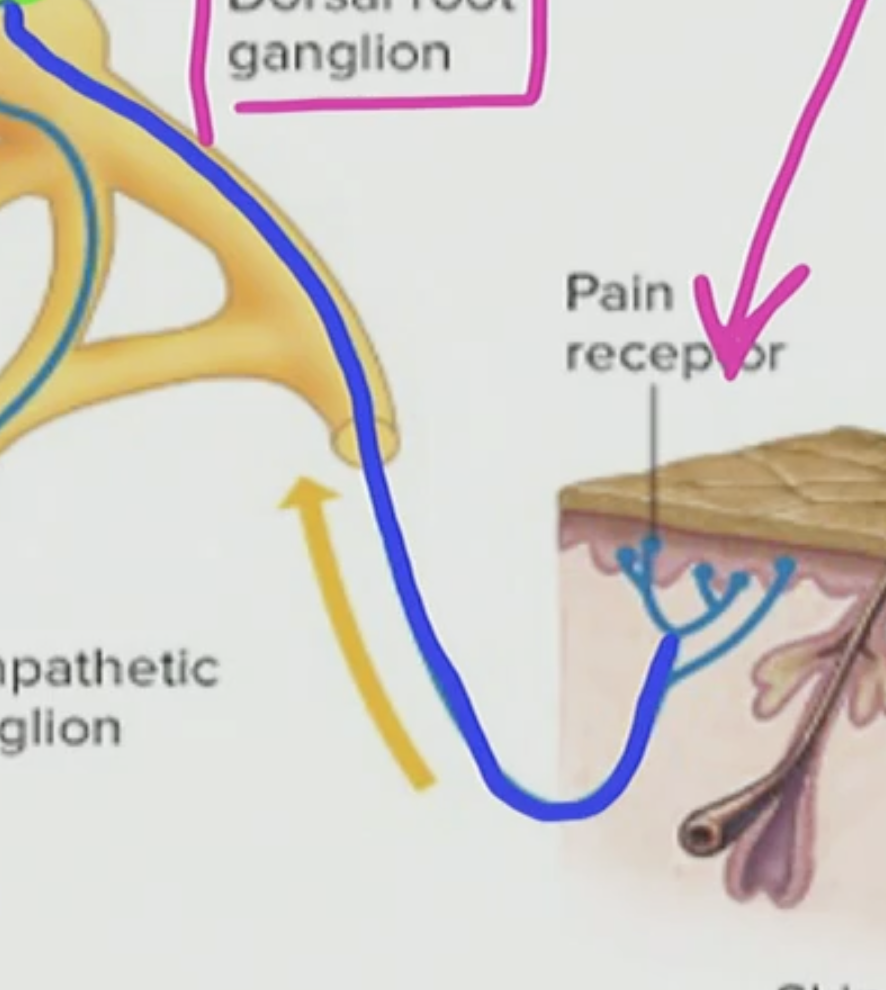
What can travel through this modified dendrite?
AP can travel through the modified dendrite
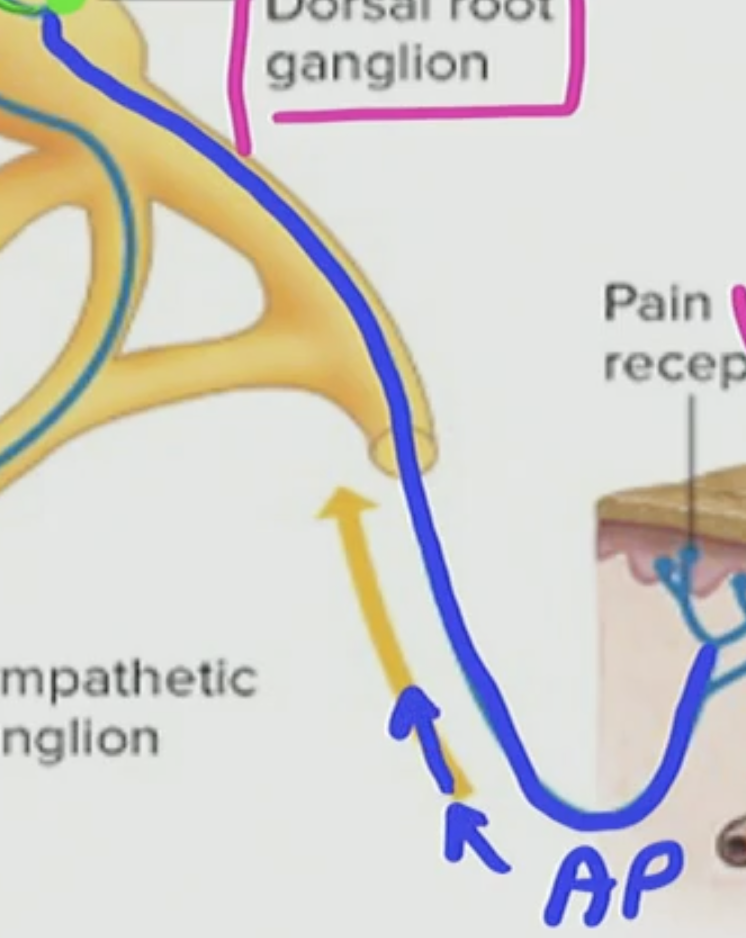
T/F: AP cannot travel through dendrites
True BUT with the exception of a modified dendrite
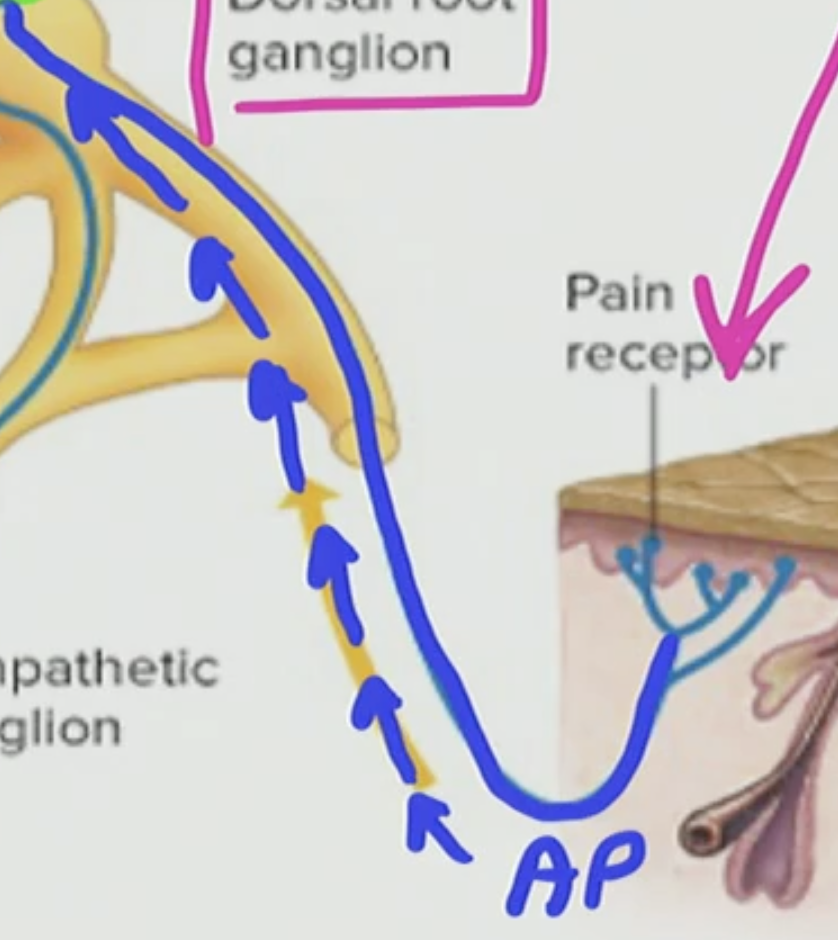
What is this modified dendrite process called
This is called the afferent process as you know afferent does sensory
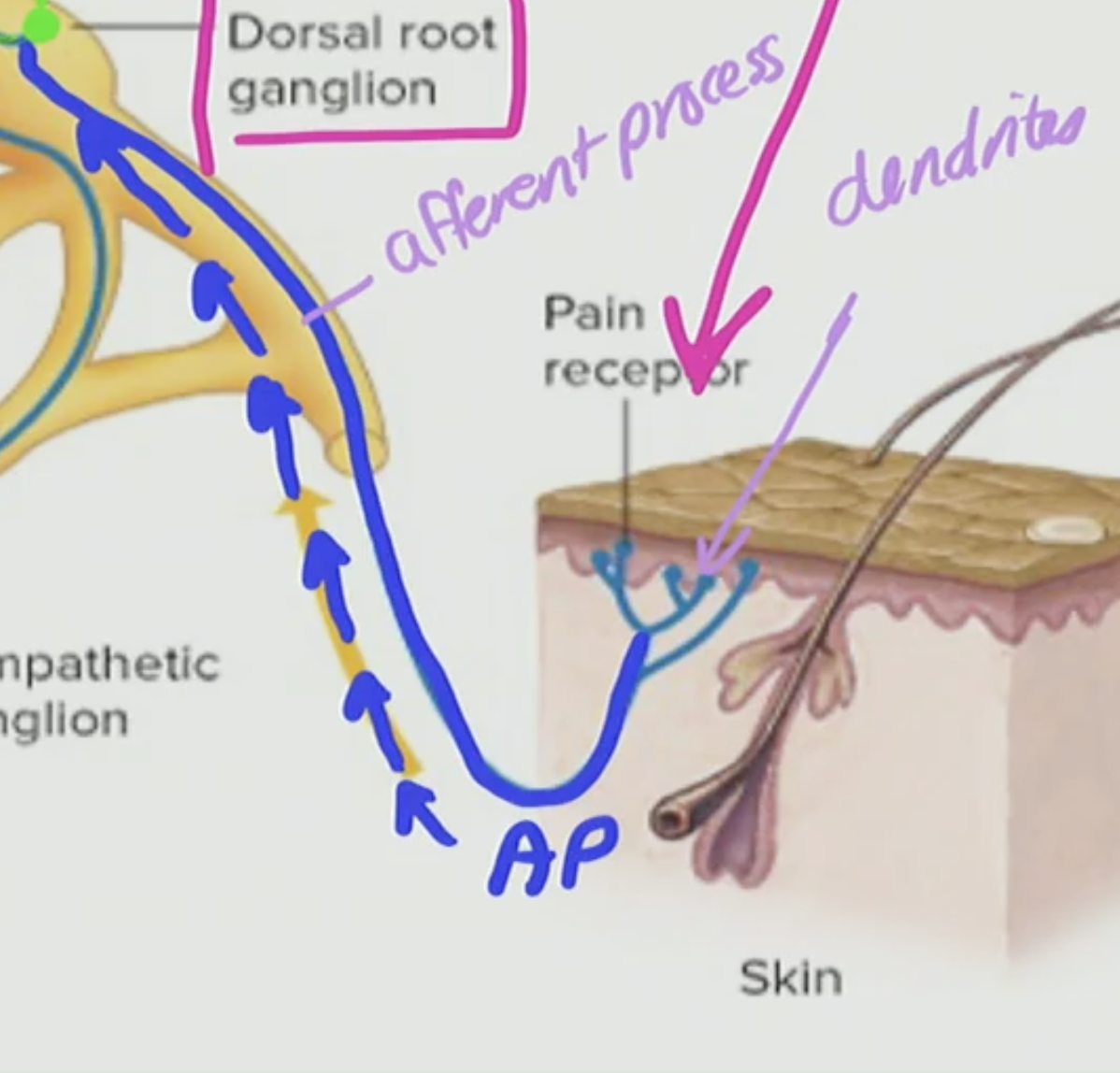
Where are the actual dendrites?
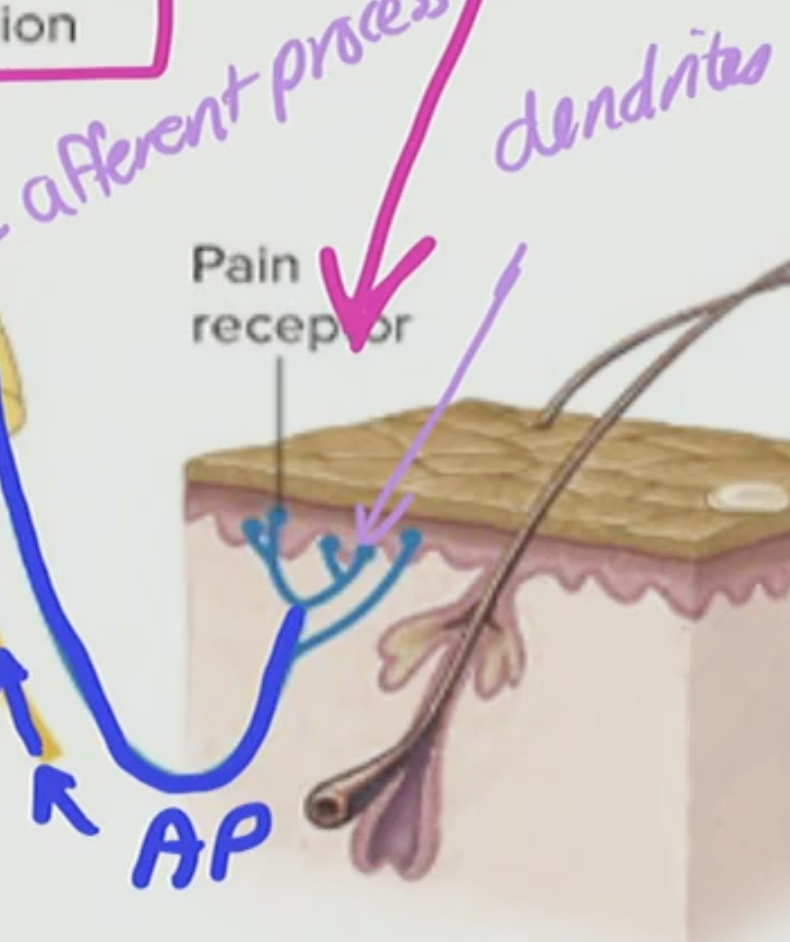
So in the General Somatic Neuron they are all built with the ___ process
afferent
The afferent process can be __list__ sensitive
touch, pain, temperature
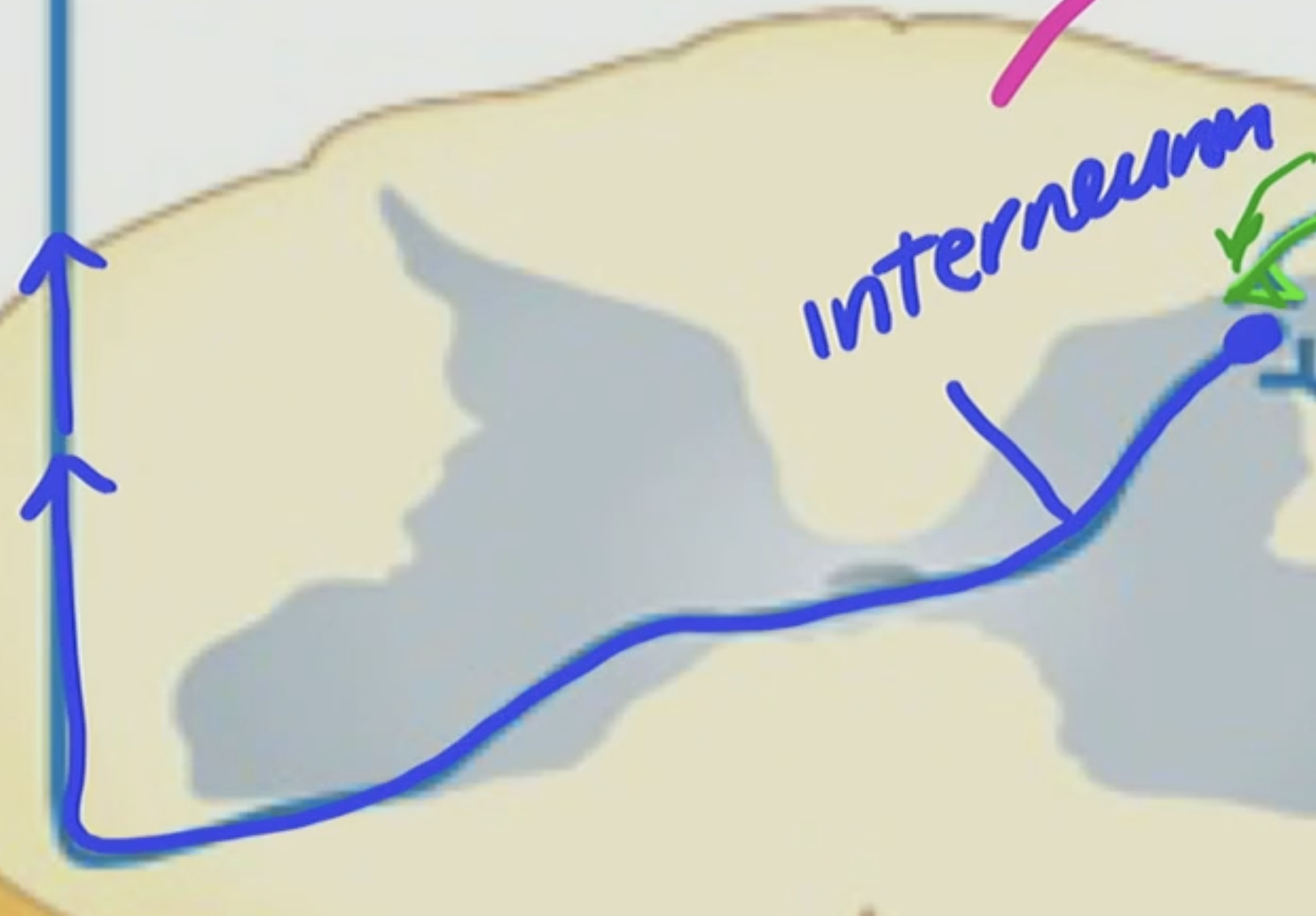
Interneuron
sends info to the brain
This is set in the Gray Matter of our spinal cord
Special Senses are found in the ____ structures that are only designed to pick up a ____
specific, stimulus
Olfactory and taste buds are parts of what afferent?
olfactory and tastebuds are part of the special sensory afferents
Visceral Sensory Afferents
innervate our internal organs
Visceral Sensory Afferents go along the same pathway as our ____ ____ afferents
general somatic
Visceral input ___ to the ____ and turn ___ an involuntary autonomic response
talks, brainstem, on
Visceral Sensory Afferent carry ____ stimuli applied to ____ organs
sensory, internal
Do we consciously perceive these stimuli (sensory stimuli applied to internal organs)?
No, we dont feel blood vessels stretching and our stomach acids working, so no
Peripheral Motor Efferent Neurons
These neurons carry “demand” info from spinal cord to target organs
Peripheral Motor Efferent Neurons has two subdivisions
Somatic Efferent Neurons
Autonomic Efferent Neurons
Somatic Efferent Neurons do (voluntary/involuntary) ____ control of your ___ muscle
voluntary, skeletal
Autonomic Efferent Neurons do (voluntary/involuntary) ____ control to your ___
involuntary, organs (lungs, heart)
Lower Motor Neuron
controlled by upper motor neurons (brain)
Example of Lower Motor Neuron (Somatic Efferents)
wiggling fingers, so plan to wiggle our finger in our brain —> talks to lower motor neuron and send signals to muscle
T/F: Somatic motor neurons are controlled by both voluntary & involuntary inputs
True, Somatic Motor Neurons are controlled by voluntary input and also controlled by involuntary input
T/F: The Autonomic NS controls the visceral organs
True the Autonomic NS does control the Visceral Organs
Autonomic NS in term of the efferent pathway (motor) is broken up into how many distinctive parts
a. 2
b. 5
c. 6
d. 3
2
What are the two distinctive parts of the Autonomic Efferent?
Parasympathetic (PNS)
Sympathetic (SNS)
T/F: The heart received input from only PNS
False, the heart receives input from both PNS & SNS
When you receive input from both branches what is this called?
Dual input
T/F: The effects of the PNS are opposite (ANTAGONISTIC) of the SNS
True, example: in SNS heart beats faster and beats stronger & in PNS the heart beats slower
Why are branches antagonistic?
PNS & SNS are antagonistic (opposite of eachother) because it gives FINE CONTROL & allows super quick control of organs
Speed up heart rate by ___ the rate ____ activity while simultaneously ____ the rate of ______
increasing, sympathetic, decreasing, parasympathetic
Dual input example
Speed up heart rate by increasing the rate of SNS activity while simultaneously decreasing the rate of PNS. This creates fine control
T/F: Dual input does not have exceptions
False dual input does have exceptions
Dual input exceptions
Salivary Glands: both inputs are stimulatory
Blood vessels: primarily SNS
Sweat Glands: primarily SNS
T/F: SNS quiets things/shuts things down
False, SNS actually activates things while PNS shuts things down
T/F: SNS does “Rest & Digest”
False, PNS actually does Rest & Digest while SNS does Fight or Flight
Rest & Digest
when your body is relaxed after eating a meal & your body is trying to incorporate those calories to build of glycogen & fat stores —>PNS
Fight or Flight
in these really stressful situations your PNS ⬇ while your SNS ⬆, SNS talks to organs saying beat faster to do fight or flight
T/F: when you are in Rest & Digest you need your heart beating faster and pushing out blood
False, when you are in Rest & Digest you need that blood flow to go to digestion as you are in a relaxed state
Neurons talking to a target process
we use neurotransmitters: norepinephrine & acetylcholine
T/F: Acetylcholine is associated with PNS
True, acetylcholine is associated with PNS while norepinephrine is associated with SNS
Acetylcholine has two parts
{Nicotinic & Muscarinic } Ach-R a.k.a Cholinergic receptors
Muscarinic
in Visceral organs that bind to acetylcholine and generate internal intracellular signal (second messengers) primary receptor
Norepinephrine bind to receptors
{a1, a2, B1, B2} adrenergic receptors which have different subtypes
T/F: Adrenergic receptors do second messengers
True
Adrenergic stimulation
cAMP
T/F: If the target does not have any receptors it cannot get a particular response
True, no target no response
T/F: Cholinergic receptors bind to acetylcholine
True Cholinergic receptors bind to acetylcholine (Ach) as it mediates our PNS responses
T/F: Adrenergic receptors bind to norepinephrine
True, Adrenergic binds to norepinephrine or epinephrine which is the neurotransmitter mediating the sympathetic response
Adrenaline
that is epinephrine