BIO 379 exam 1
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Why do we incubate petri plates upside down?
to prevent contamination and water condensation from damaging culture
Temperature used for incubation?
37 C
Why is TSA known as general purpose medium?
it supports the growth of a wide variety of microorganisms
What is a colony? What does a colony represent?
a visible cluster of microorganisms growing on a solid medium originating from a single parent cell
Characteristics of bacterial colonies
shape, margin, elevation, size, texture, appearance, pigmentation, optical property
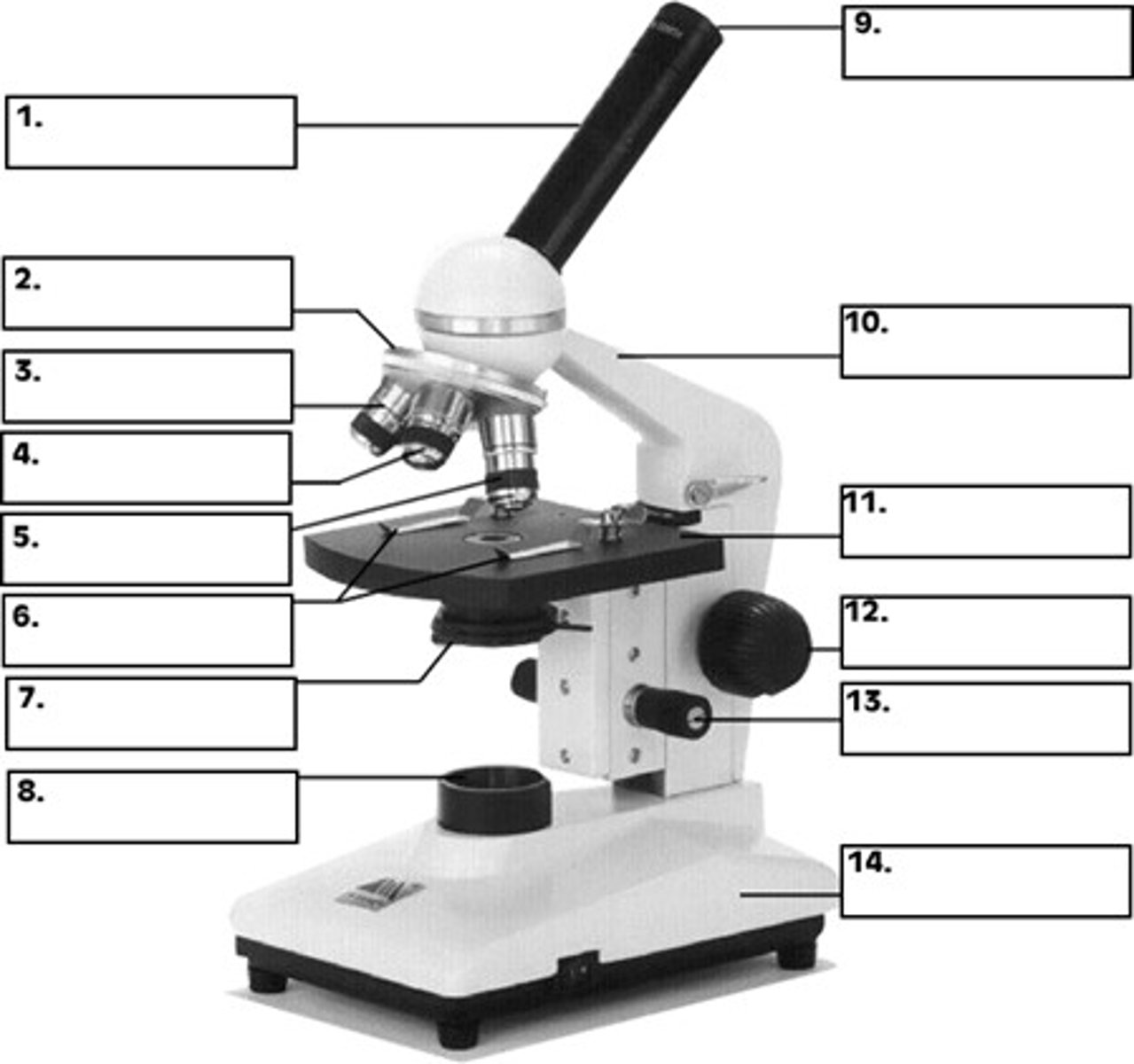
ocular lens (eyepiece)
what is 9
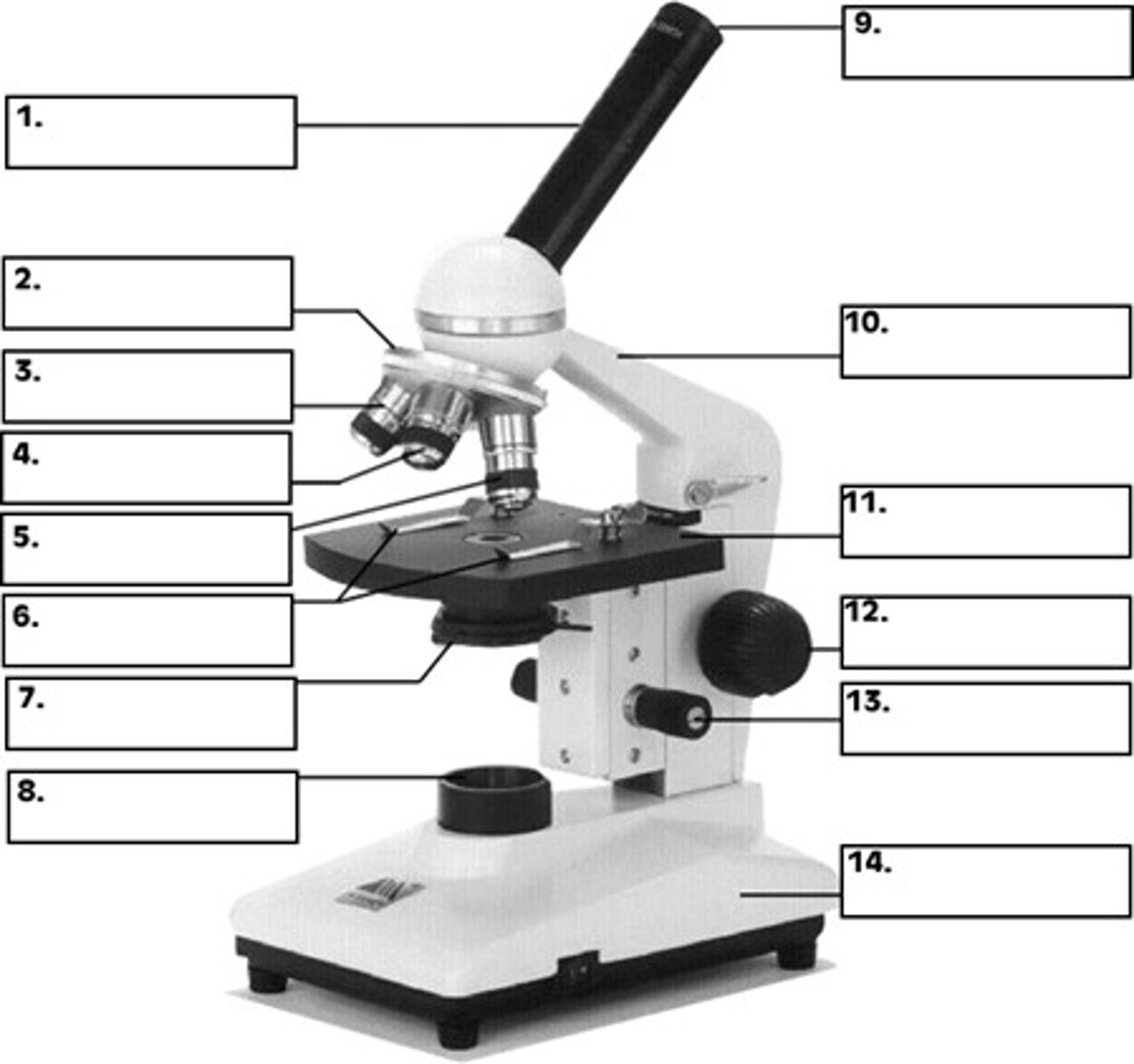
revolving nose piece
what is 2
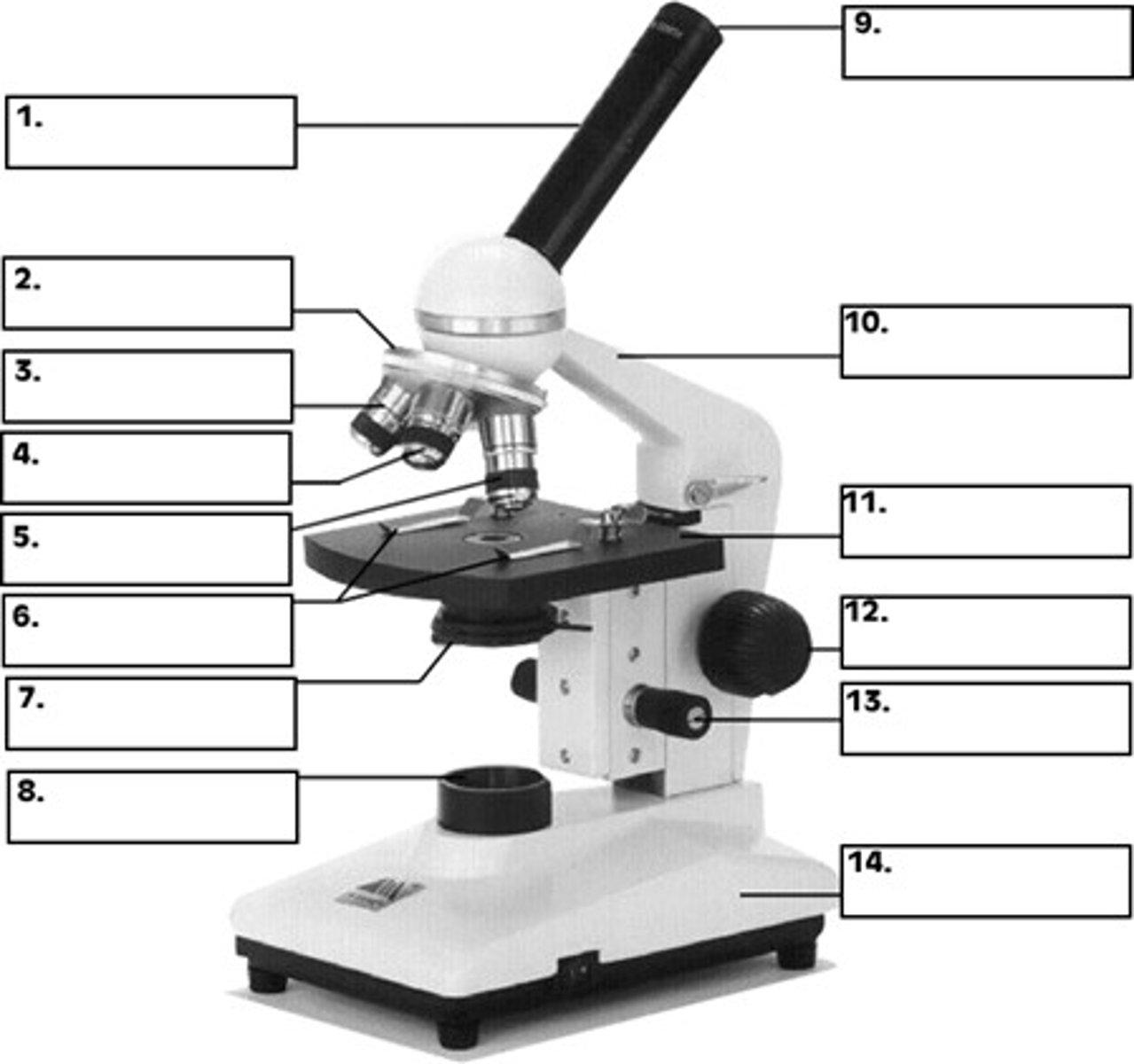
objective lens
whats 4 / 5
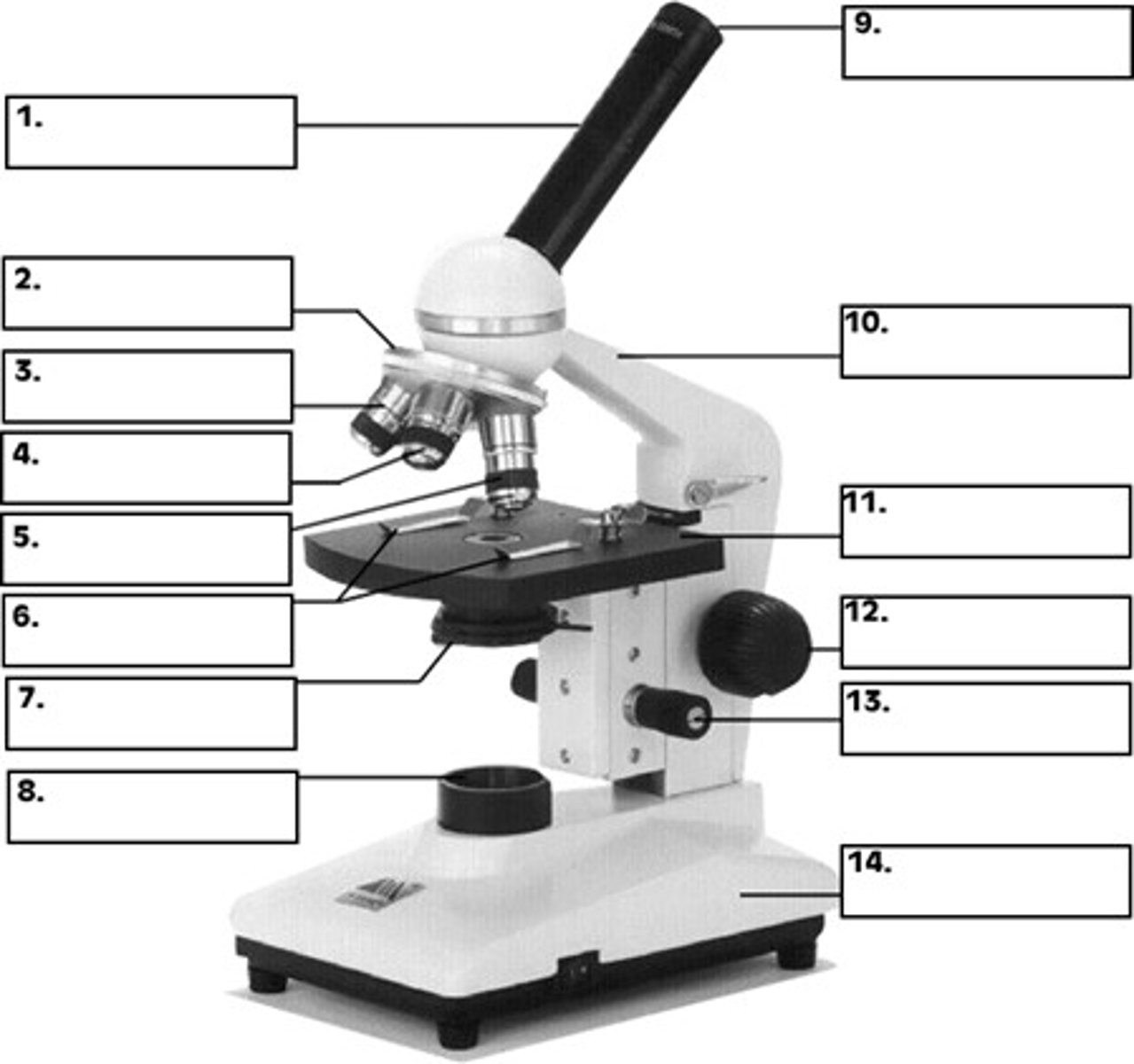
condenser
whats 7
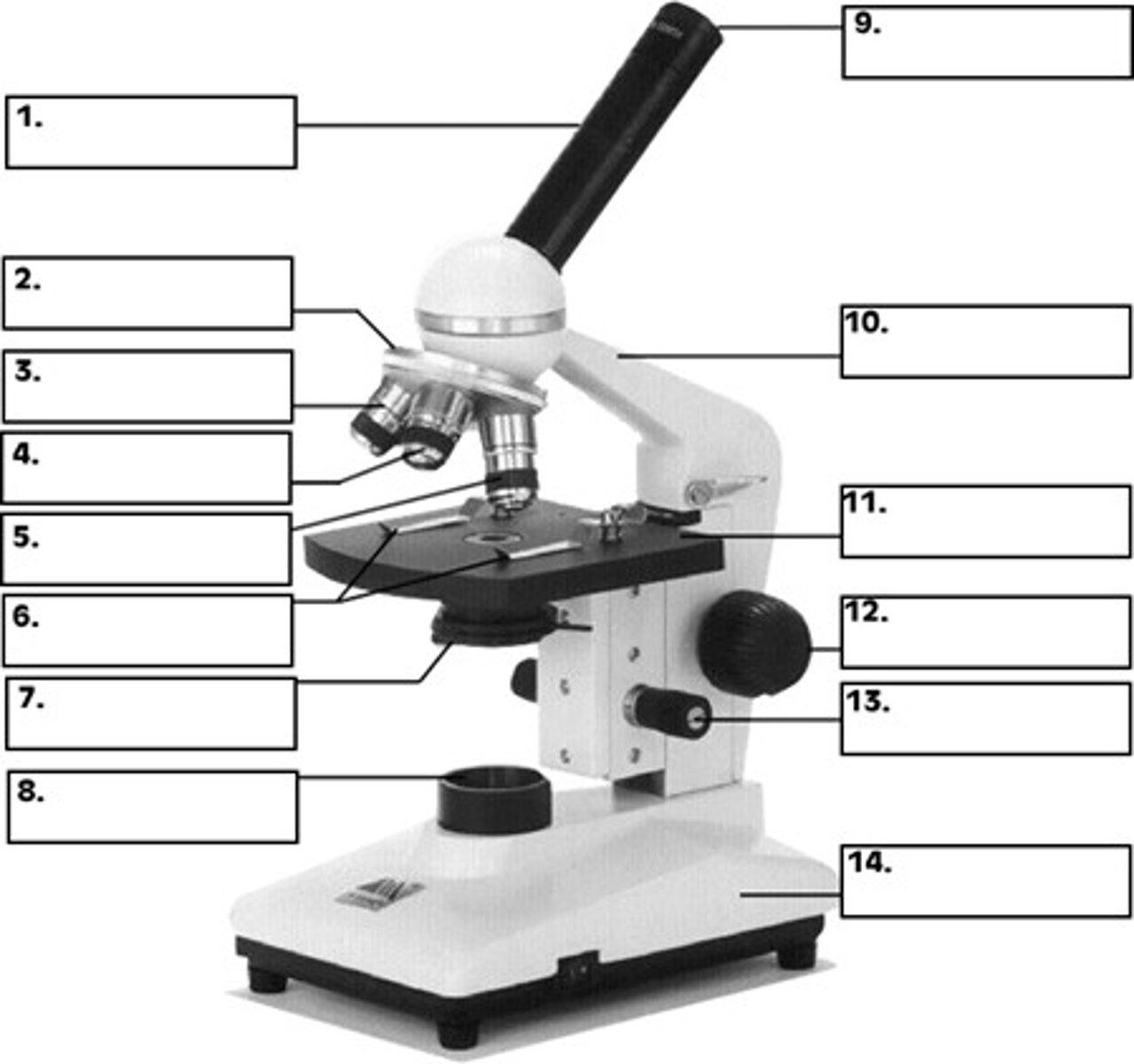
the stage
whats 11
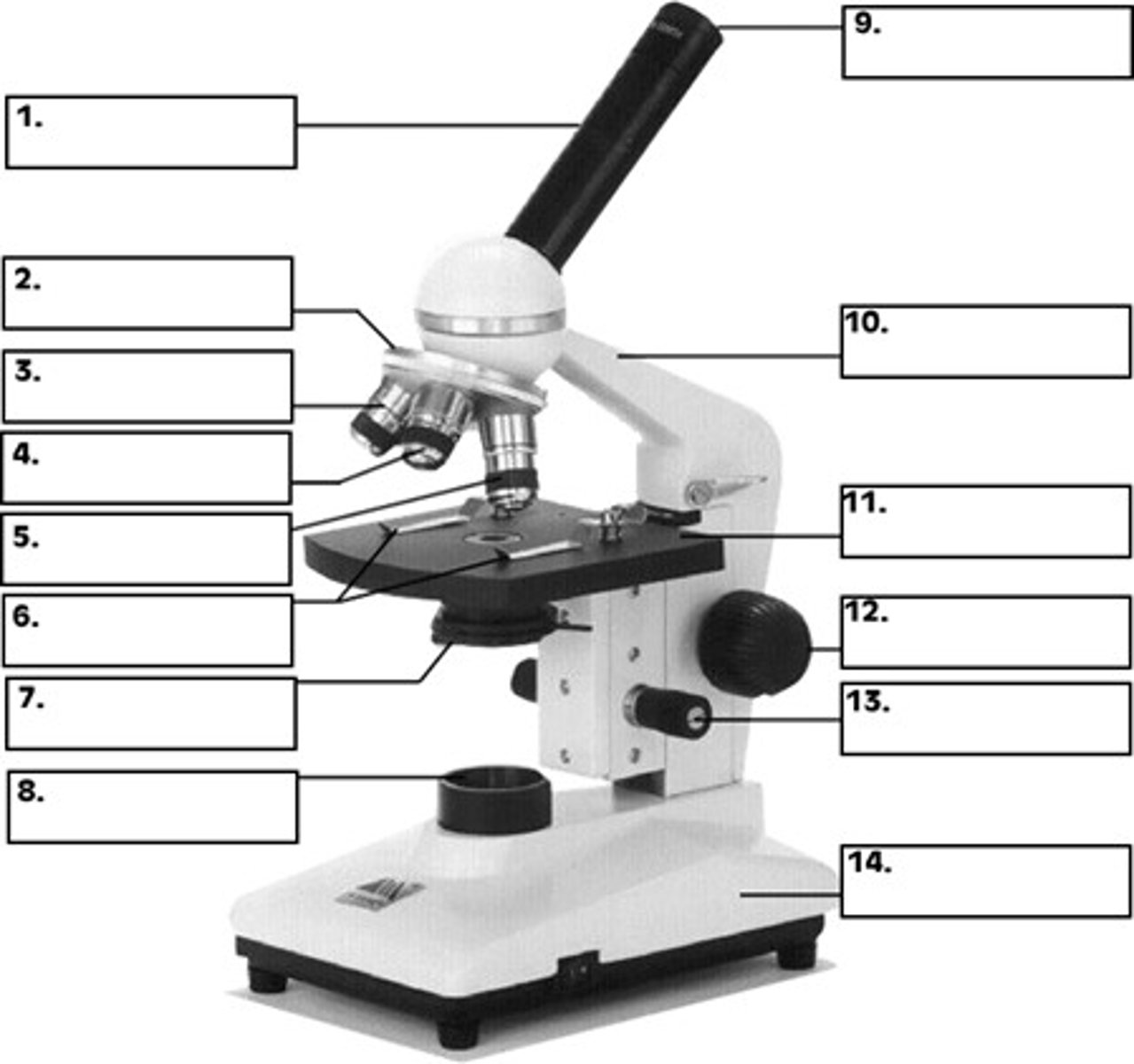
fine focus and coarse focus knob
whats 13 and 12
Purpose of immersion oil
goes between slide and lens and prevents light from bending and illuminates the image
whats total magnification
ocular lens (10x) times objective lens
ex. 10x x 40x = 100x
What characteristic of a microscope enables one to switch from one objective to another without altering the focus?
parfocality
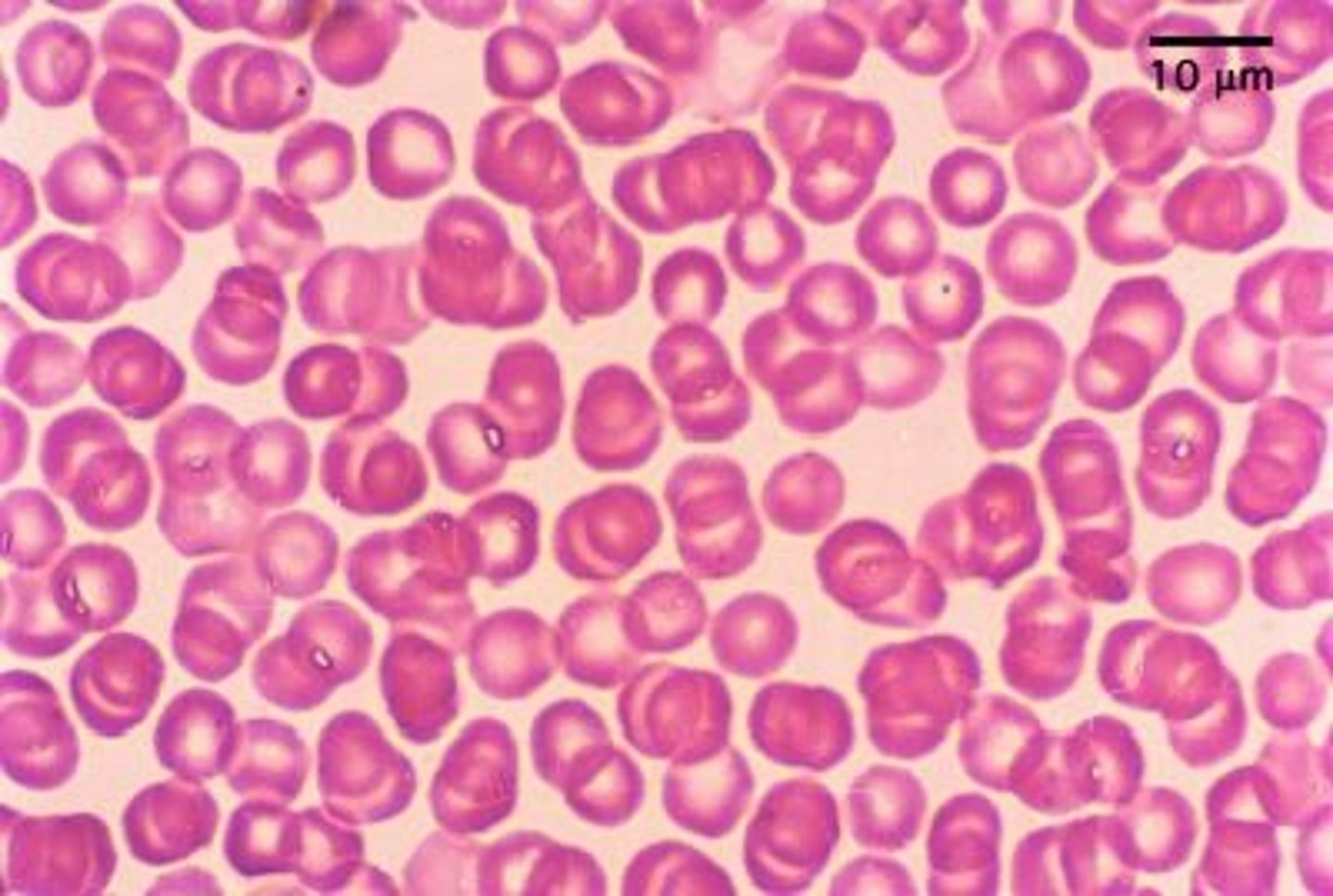
identify
identify erythrocytes
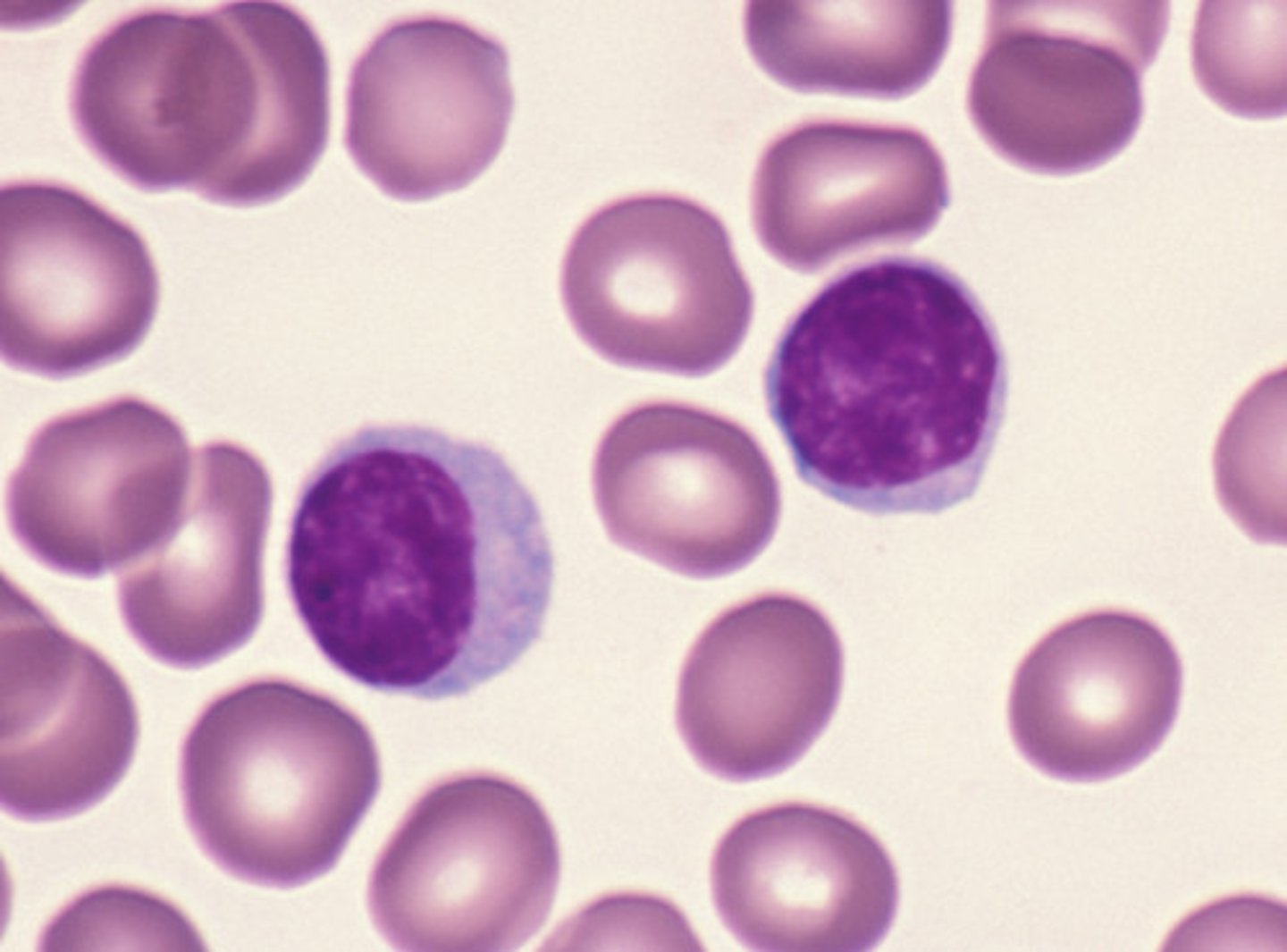
identify
identify lymphocytes
identify
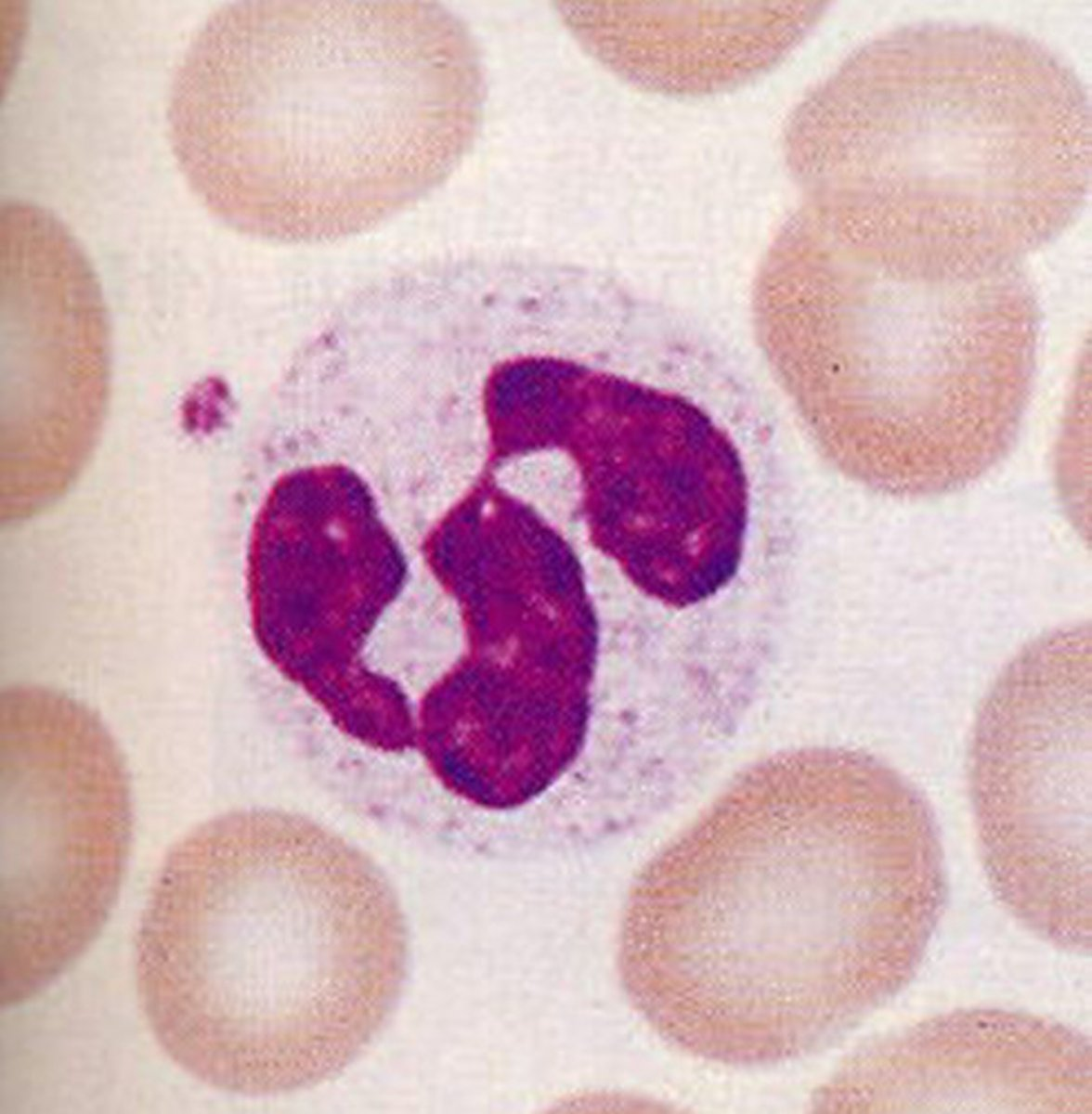
identify neutrophils
identify
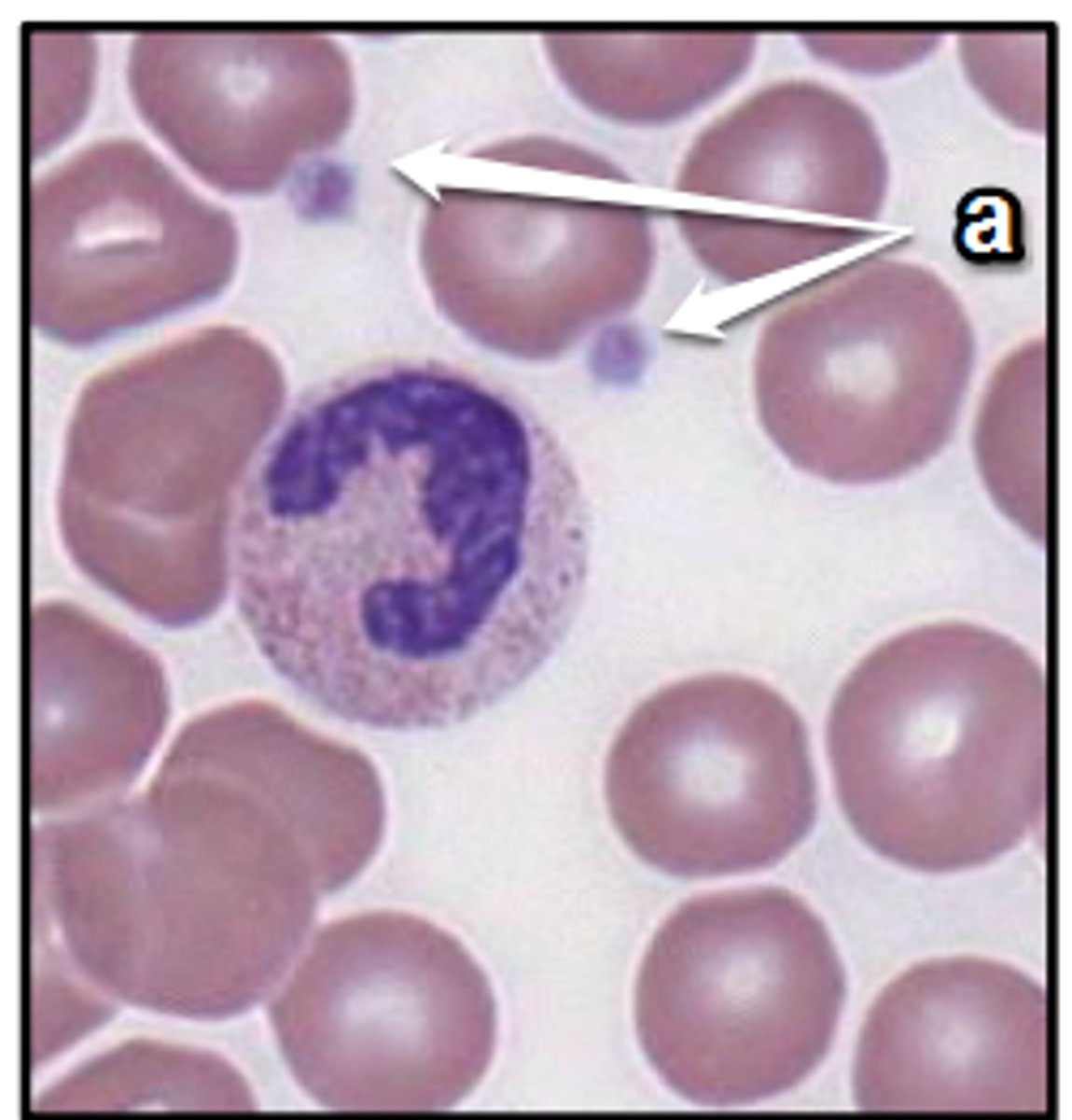
identify platelets
identify
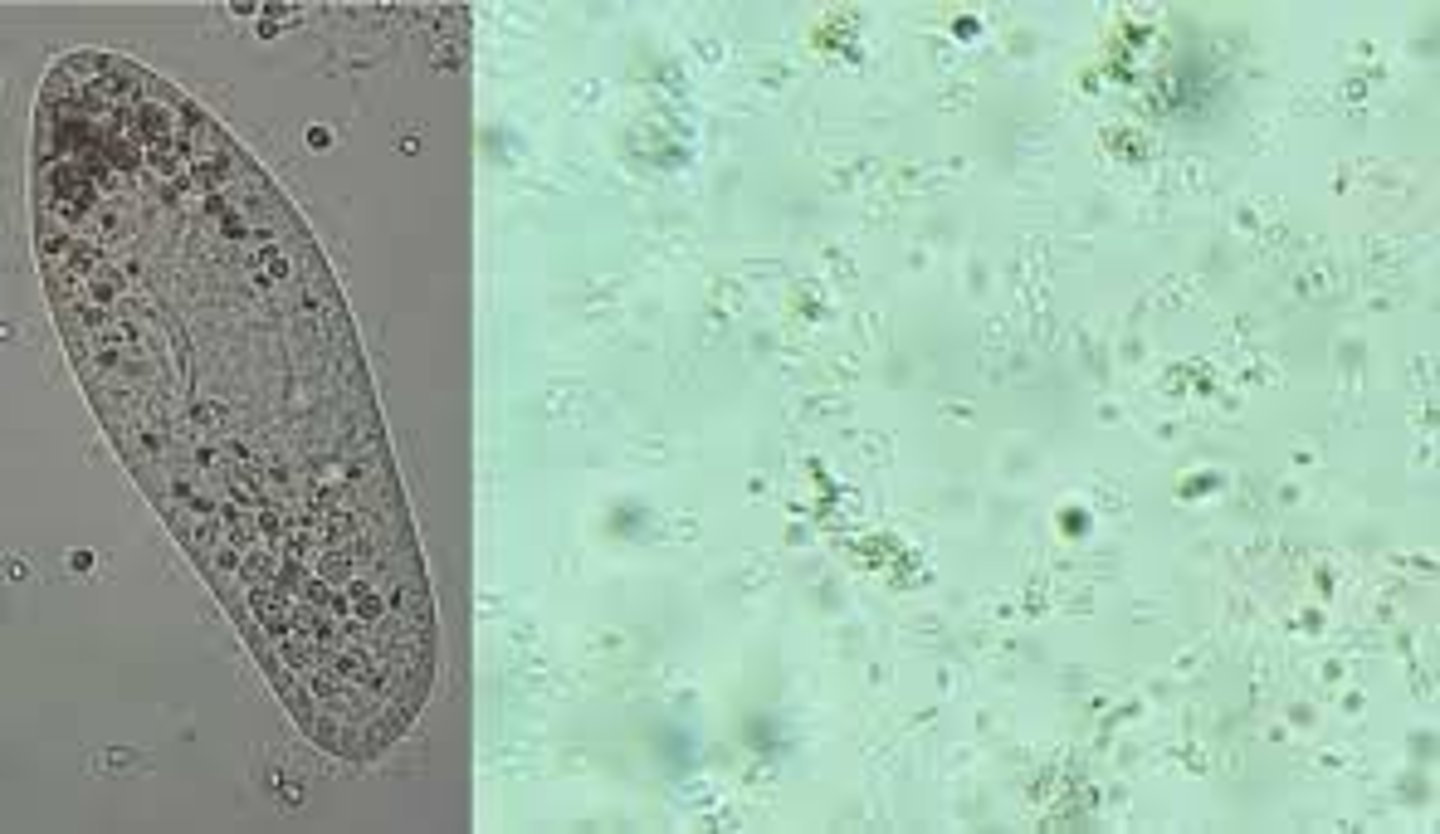
identify protozoa
identify
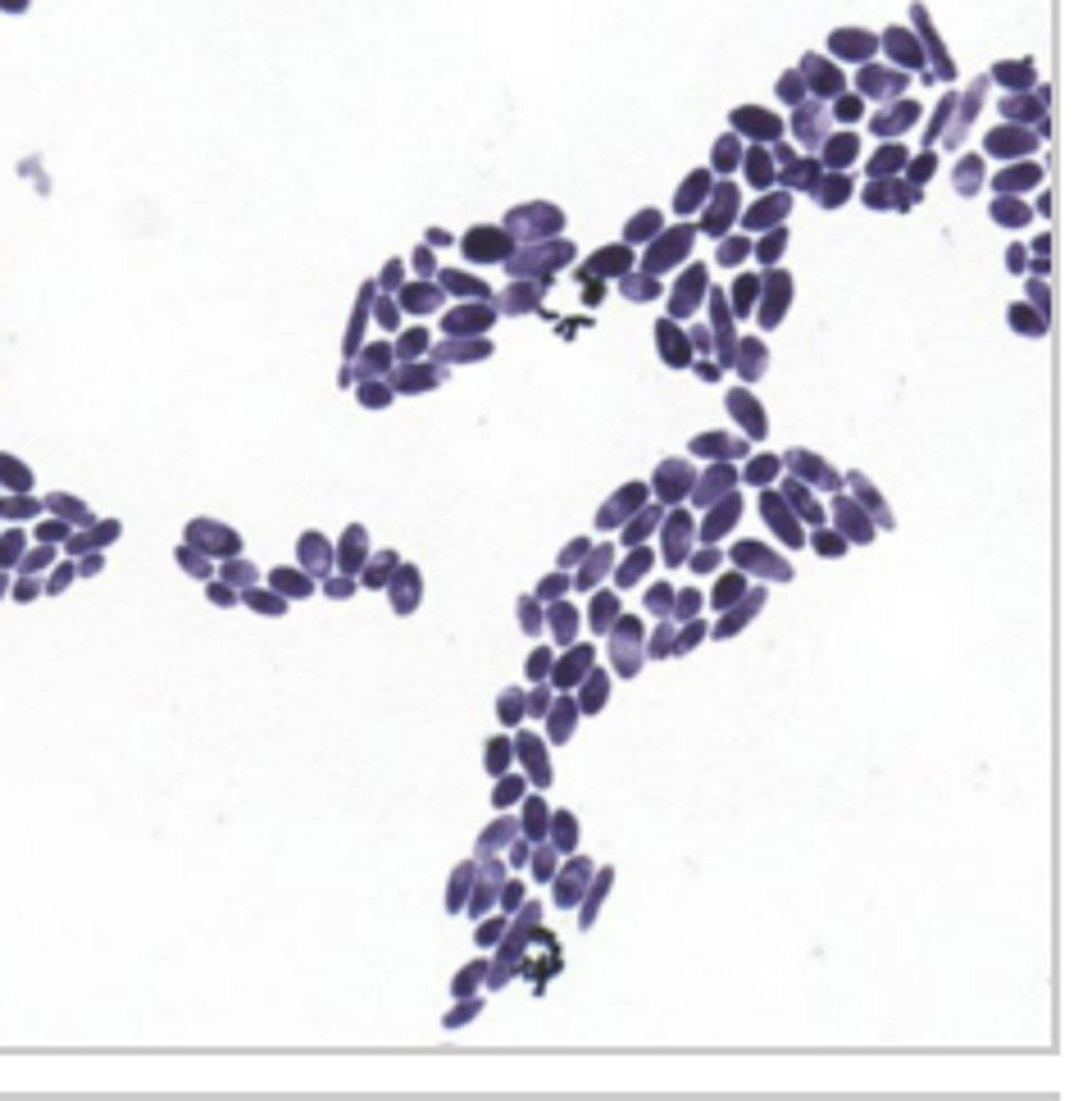
identify yeast
identify
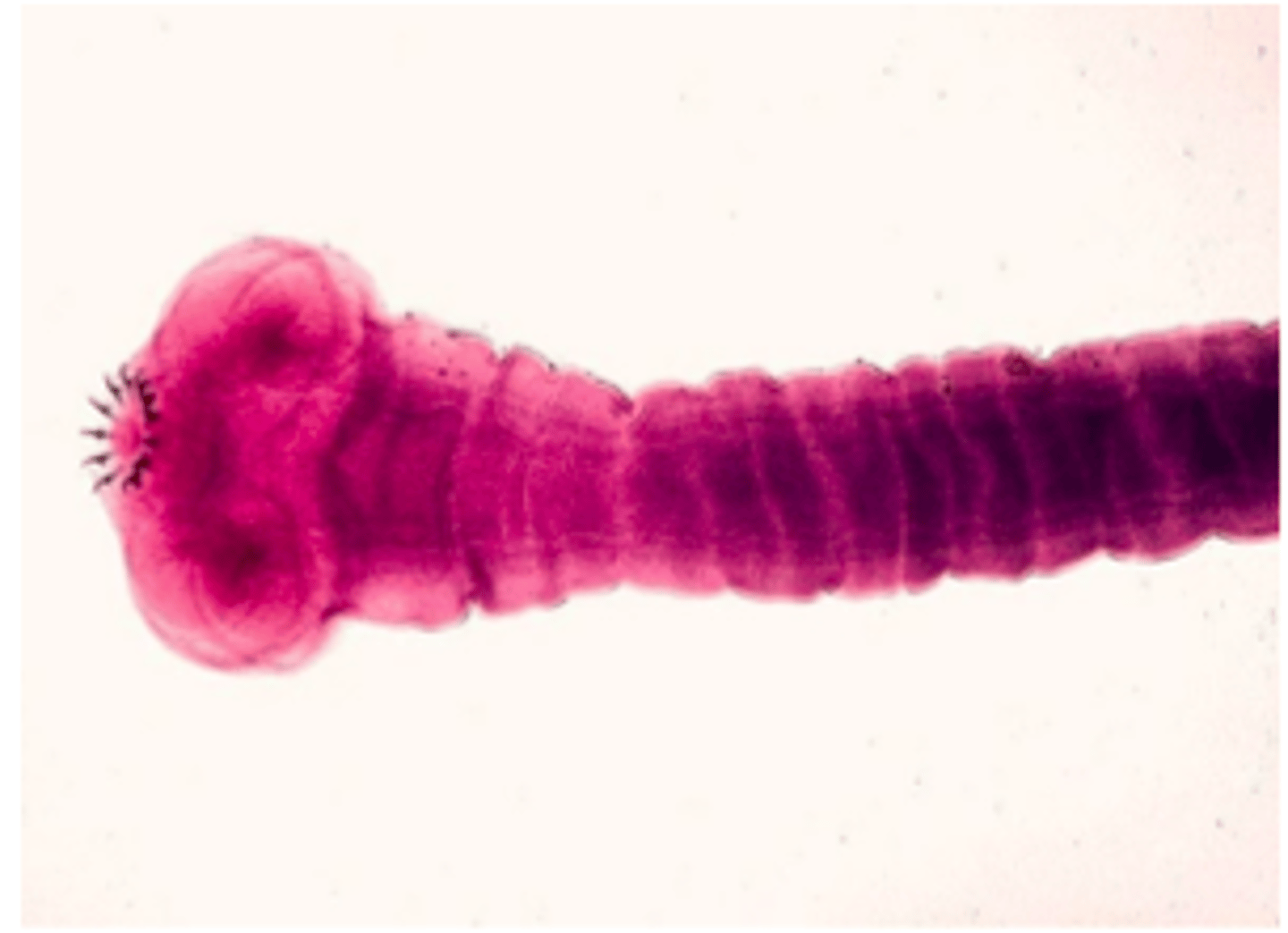
identify taenia solium
identify
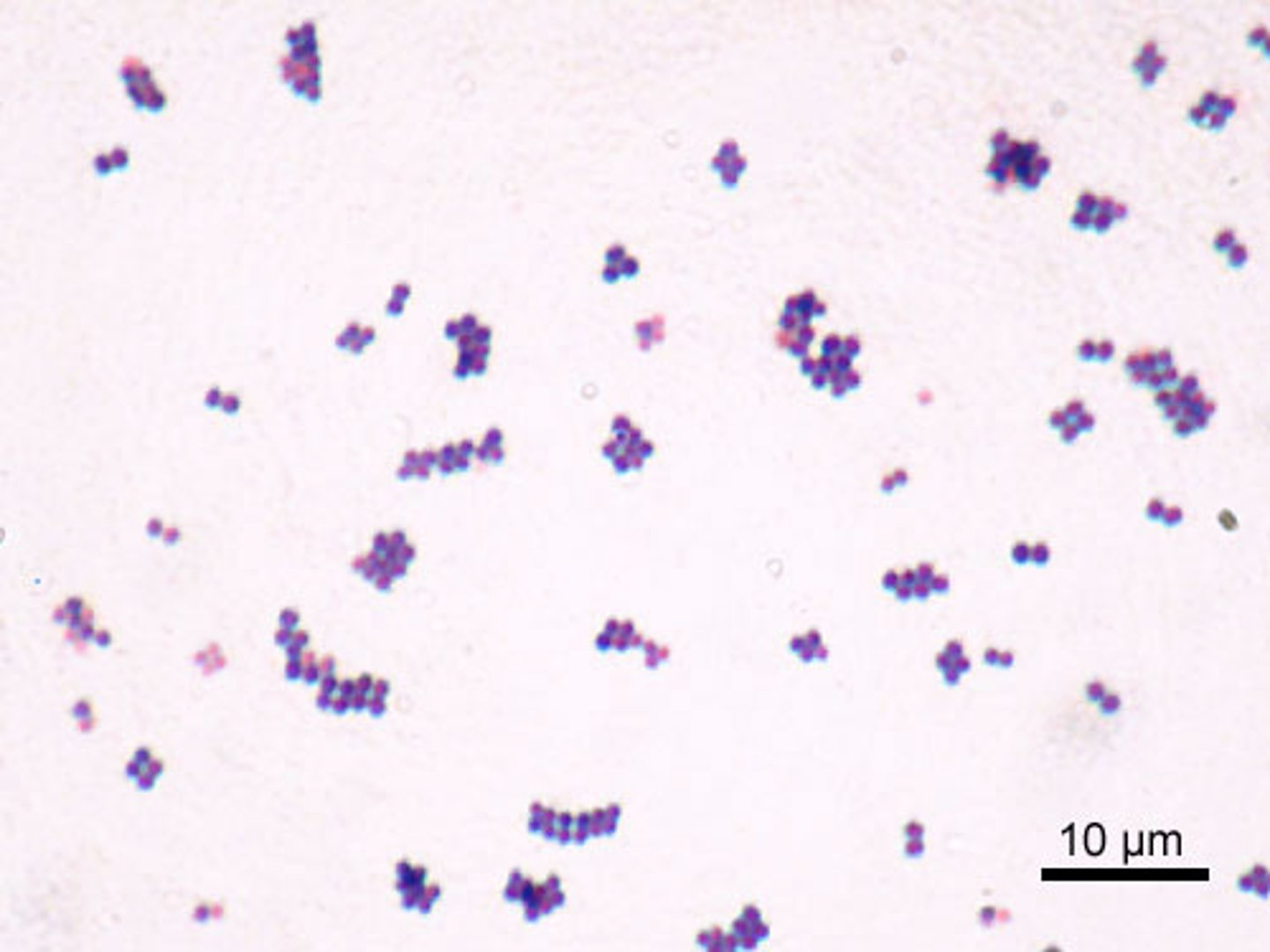
identify staphylococci
identify
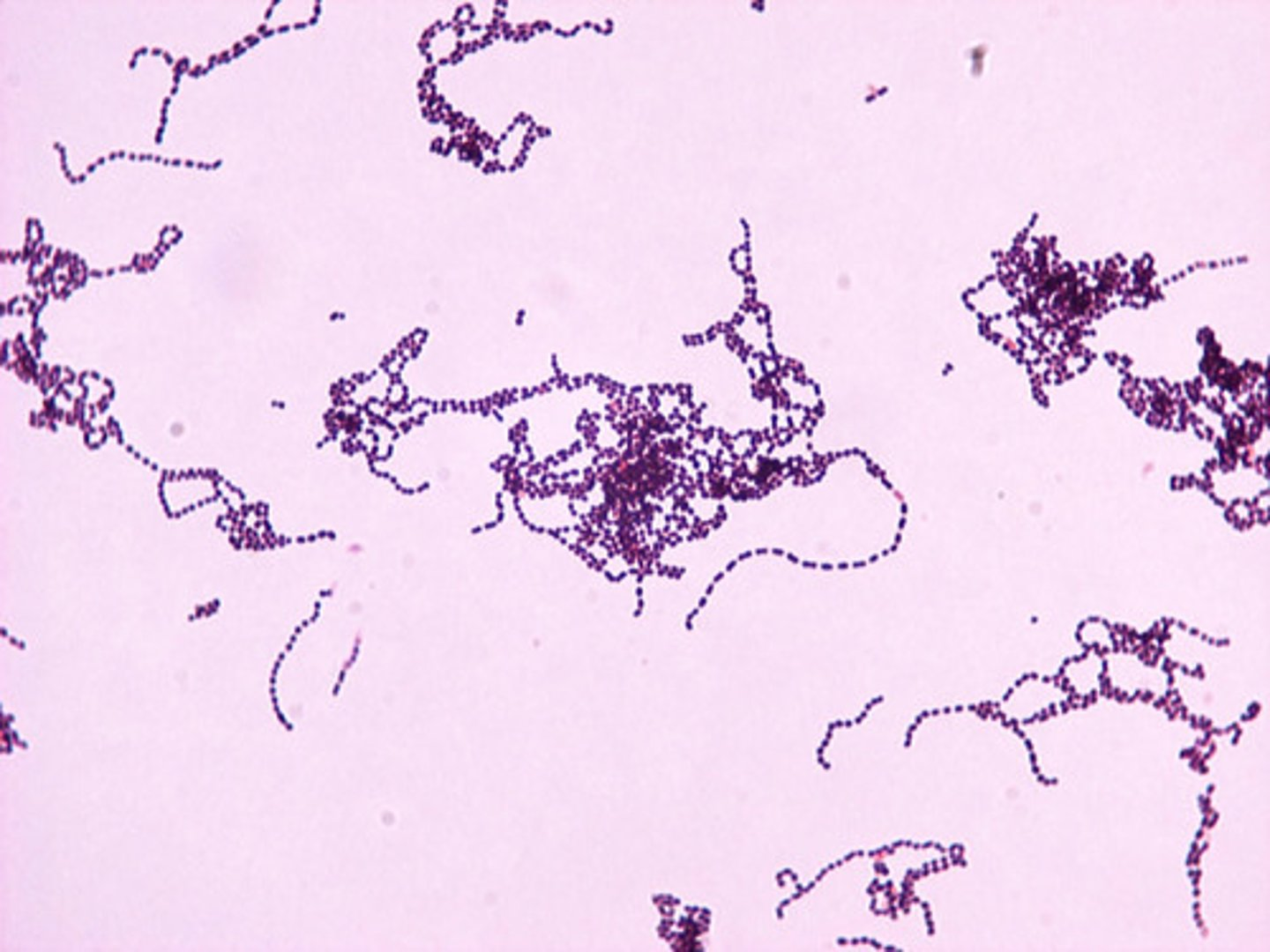
identify streptococci
identify
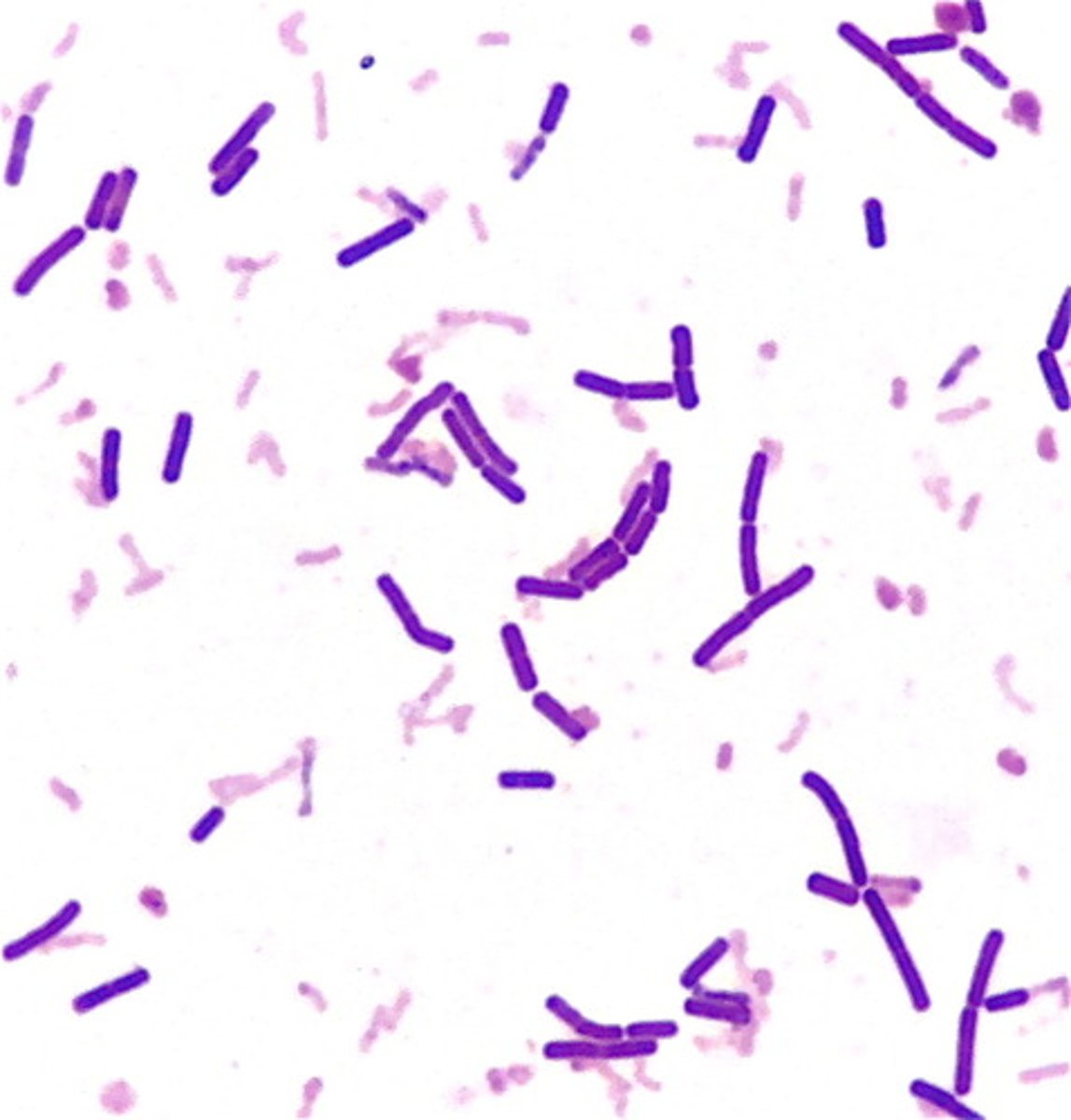
identify diplobacilli
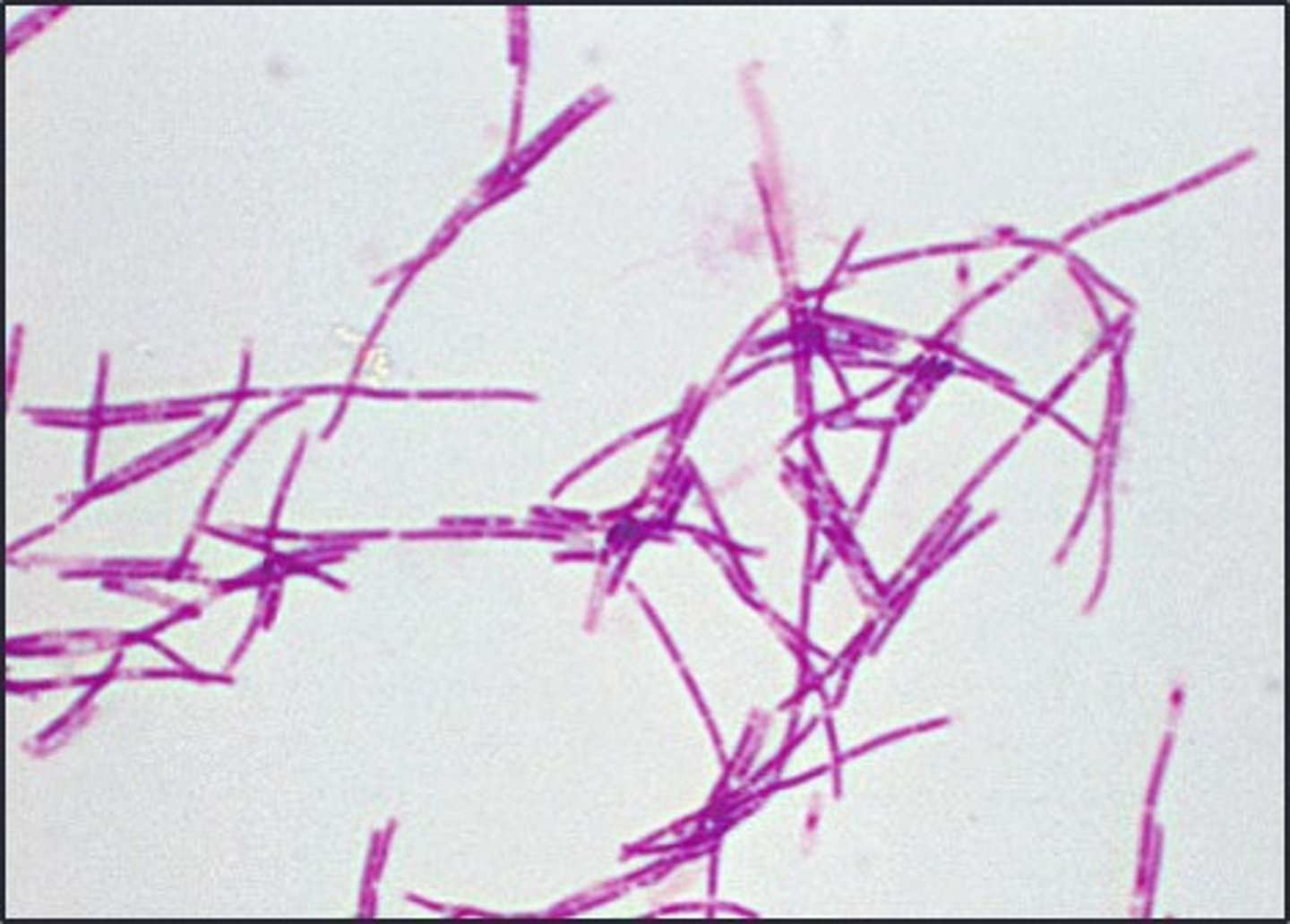
identify
identify streptobacilli
Aseptic technique and how
prevent contamination of our culture, media (sterile) and environment
-using sterile media and tools (inoculating loop)
-using Bunsen burner
-PPE
-washing hands
-disinfecting work area
pure culture vs mixed culture
- only one species of microbe growing on plate/ broth
- 2 or more species growing together on plate/ broth
The most common method to obtain a pure culture of a bacterium
streak plate (using the T Streak method)
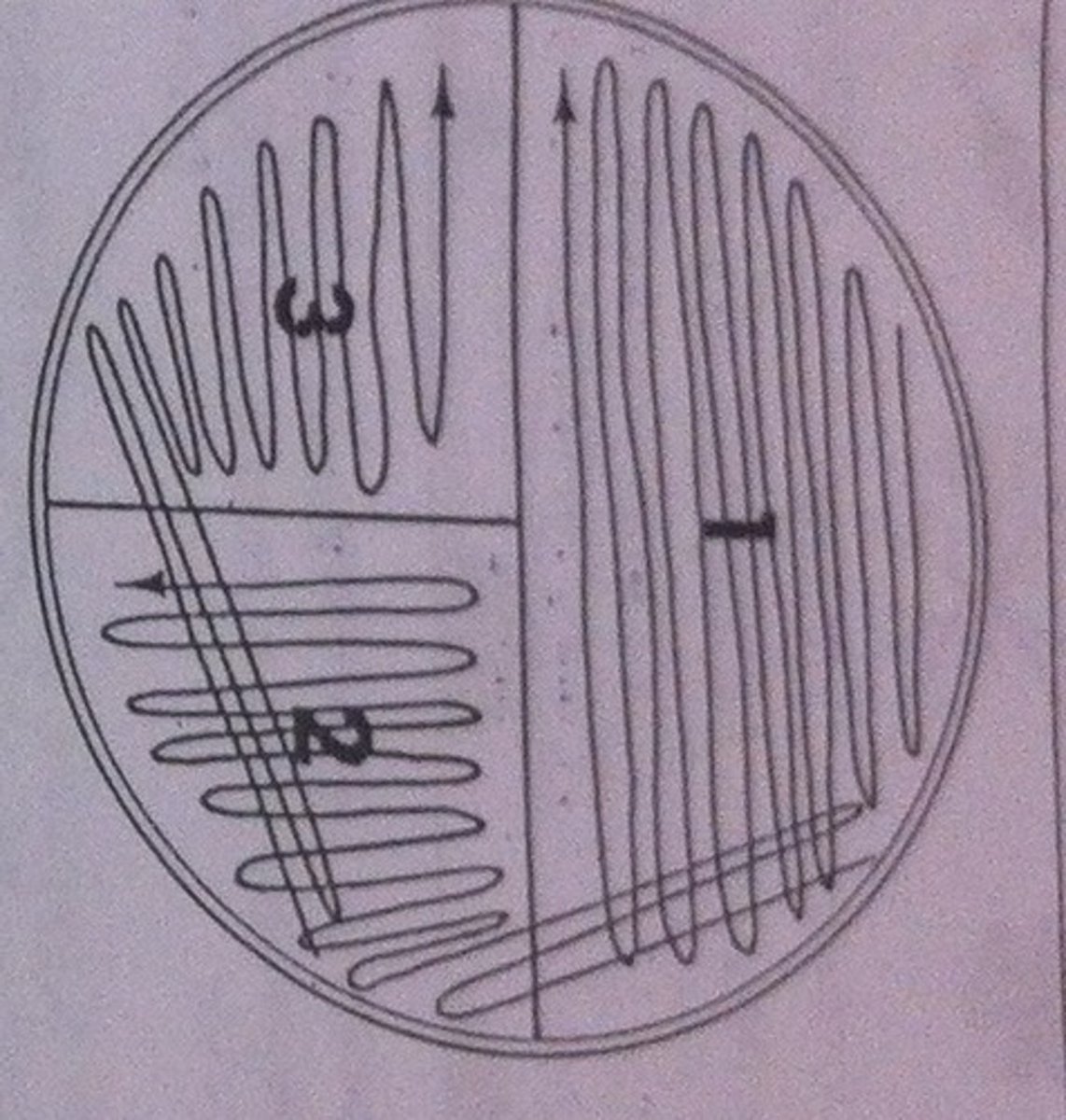
Why is it important to only work with isolated colonies when performing experiments in microbiology?
allows a specific microorganism to be studied
differential stain purpose
reveals differences in cell structure or composition
What color would a Gram negative cell be after the decolorization step?
colorless
What color would a Gram positive cell be after the decolorization step?
purple
Why do you need to blot the slide dry before decolorizing?
prevents dilution and allows to tell difference between Gram +/-
What do you think would happen if you forgot to heat fix the cells during gram staining
bacteria would wash off the slide during staining
What color would a Gram positive cell be if you stained fist with safranin and counterstained with crystal violet?
still purple
simple stain vs differential stain
simple only uses one dye and differential is used to tell difference between microbe types (gram +/-)
Gram Staining procedure
step 1. flood heat fixed slide with Crystal Violet
step 2. flood slide with Iodine to bind to the Crystal Violet
step 3. apply decolorizer (Ethanol/ Acetone) to differentiate between types
step 4. Counter stain pink with Safranin (stains gram- pink and gram+ remains purple)
how would the gram +/- look if you forgot to heat fix
there would be no visible cells
how would the gram +/- look if you forgot crystal violet?
gram + : pink
gram - : pink
how would the gram +/- look if you forgot Iodine?
gram + : pink
gram - : pink
how would the gram +/- look if you forgot decolorizer?
gram + : purple
gram - : purple
how would the gram +/- look if you forgot safranin?
gram + : purple
gram - : no color
method used in lab to look for bacteria motility?
hanging drop
what is selective media
'selects' certain microbes to grow while inhibiting others (MacConkeys Agar and Mannitol Salt Agar)
what is differential media
uses indicators to tell the difference between certain species of bacteria
differential media vs differential stain
the media differentiates bacteria based on the growth on the plate, while the stain differentiates bacteria based on their appearance under a microscope
what makes MAC selective & differential
- Crystal violet and bile salts
- Lactose and a pH indicator Neutral Red
what makes MSA selective & differential
selective: high (7.5%) NaCl concentration
differential: mannitol and a pH indicator Phenol Red
What would growth on a MAC plate indicate (with genus and species name)
gram -
Escherichia coli
What would growth on a MAC plate that is pink indicate (with genus and species name)
- Gram-
-lactose fermenter
-Escherichia Coli
What would growth on a MAC plate that is colorless indicate (with genus and species name)
- gram-
-Non Lactose fermenter
-Salmonella Enterica
what would no growth on a MAC plate indicate (with genus and species name)
- Gram +
-Staphylococcus Aureus
What would growth on a MSA plate indicate (with genus and species name)
- Gram+
- Staphylococcus Aureus
- halotolerant
What would growth on a MSA plate that is yellow indicate (with genus and species name)
-Gram +
-Mannitol Fermenter
-Staphylococcus Auerus
-halotolerant
What would growth on a MSA plate that is colorless indicate (with genus and species name)
-Gram +
-Non Mannitol fermenter
-Streptococcus Epidermis
-halotolerant
What would no growth on a MSA plate indicate (with genus and species name)
-Gram -
-Escherichia Coli
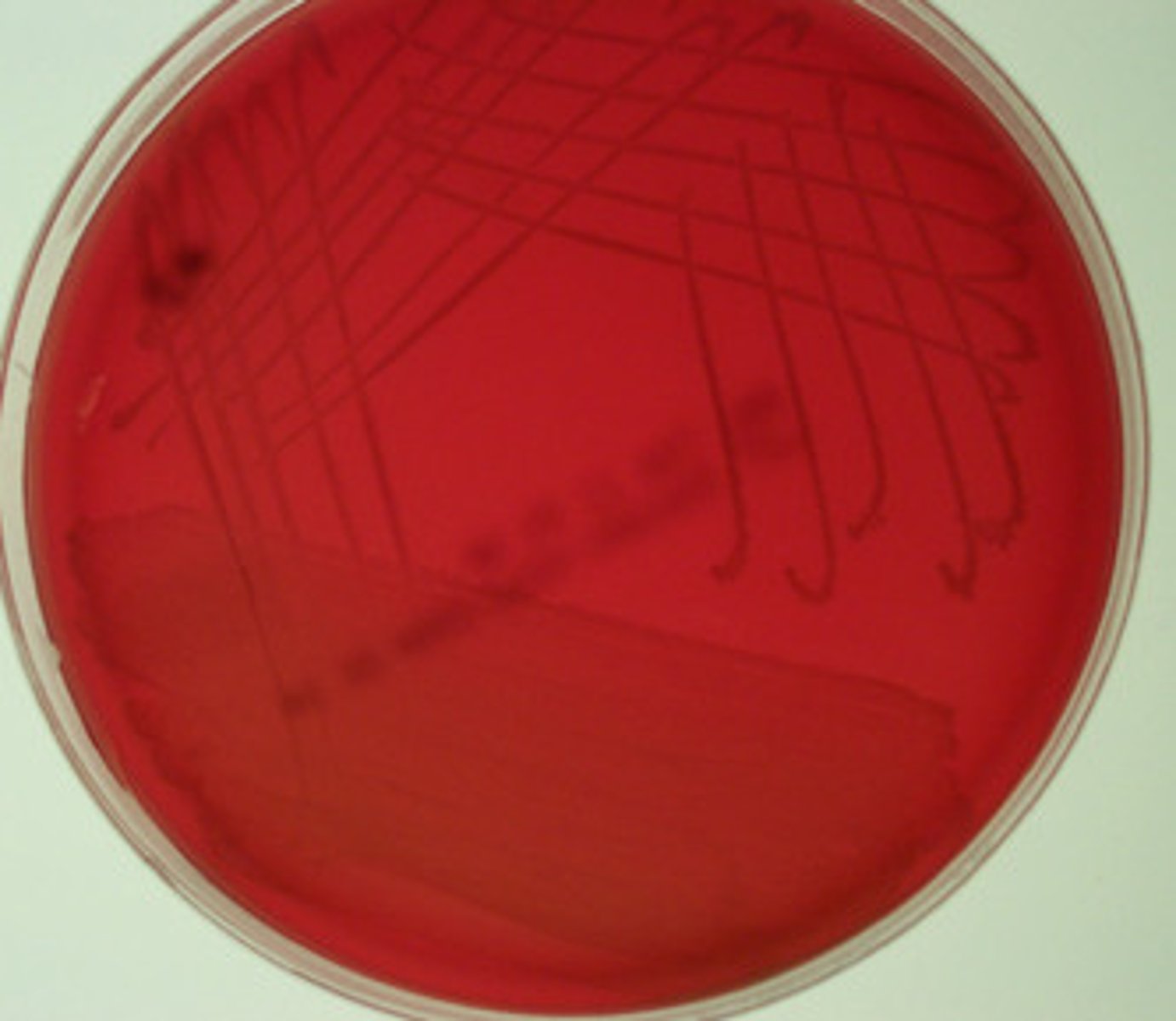
What makes blood agar plate differential
detects microorganisms different abilities to produce hemolysins that lyse RBC
-uses 5% sheep's blood
Beta hemolysis
-appears clear zone around a colony
-complete lyses of RBC
-Staphylococcus Aureus & Streptococcus Pyogenes
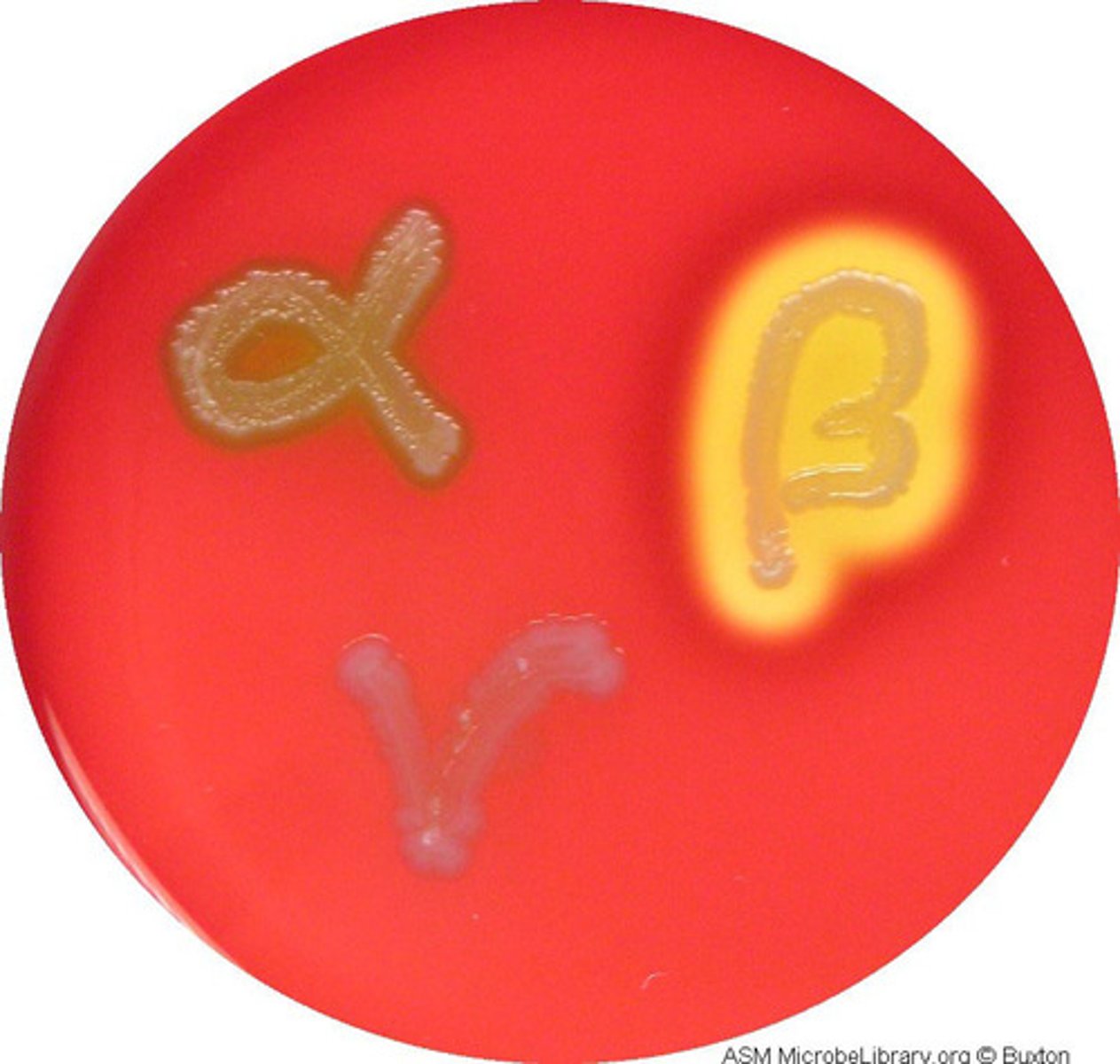

Alpha hemolysis
-appears greenish zone around colony
-partial lyses of RBC
-streptococcus pneumoniae
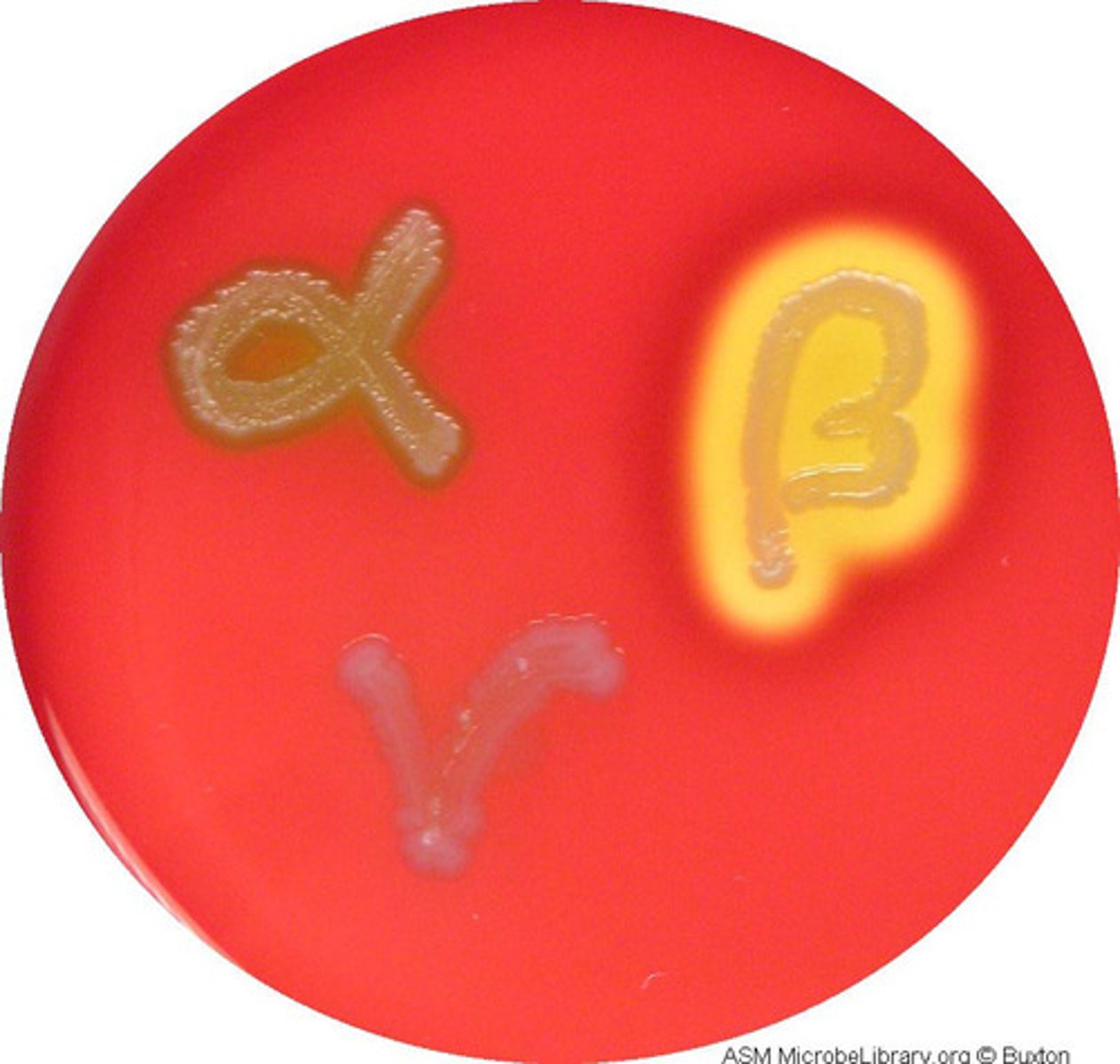

gamma hemolysis
-no visible change in agar around the colony
-no breakdown of RBC
-staphylococci / streptococci
What is being tested in the phenol red broths
ferments a carbohydrate and produces acid, a differential test
What 4 sugars do the phenol red broths test for?
glucose, sucrose, lactose, mannitol
what does red broth with growth, no gas bubble indicate
neutral reaction (-) and pH at 7
what does yellow broth with no gas bubble indicate
acid produced (+) and lower pH
what does yellow broth and gas bubble in Durham's tube indicate
acid and gas produced (+/g)
Clinically, what does the catalase test determine?
if the microorganism produces the enzyme catalase
What is the substrate/reagent used for the catalase test?
hydrogen peroxide
what does it mean to be catalase positive
-produces the enzyme catalase
-aerobe / facultative anaerobe
-staphylococcus epidermis
-foams bubbles of O2
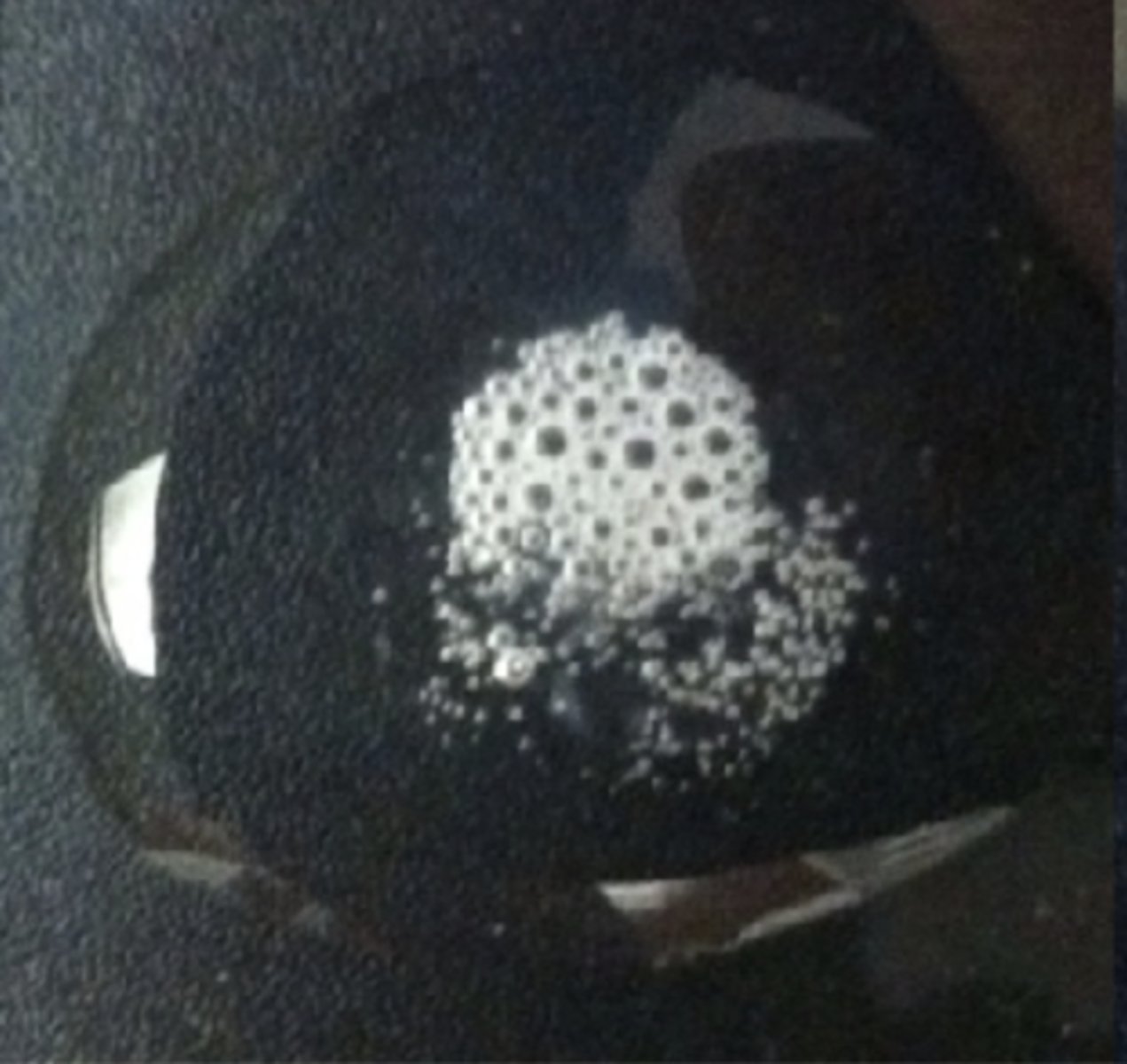

what does it mean to be catalase negative
-anaerobic / facultative anaerobe
-*streptococcus pyogenes*
-doesn't foam

what does the oxidase test determine
if a microorganism produces cytochrome c oxidase that is in the electron transport system
The _______ test is used to determine the presence/absence of the respiratory enzyme _________ in bacterial species.
the OXIDASE test is used to determine the presence/ absence of the respiratory enzyme cytochrome oxidase in Gram - bacteria
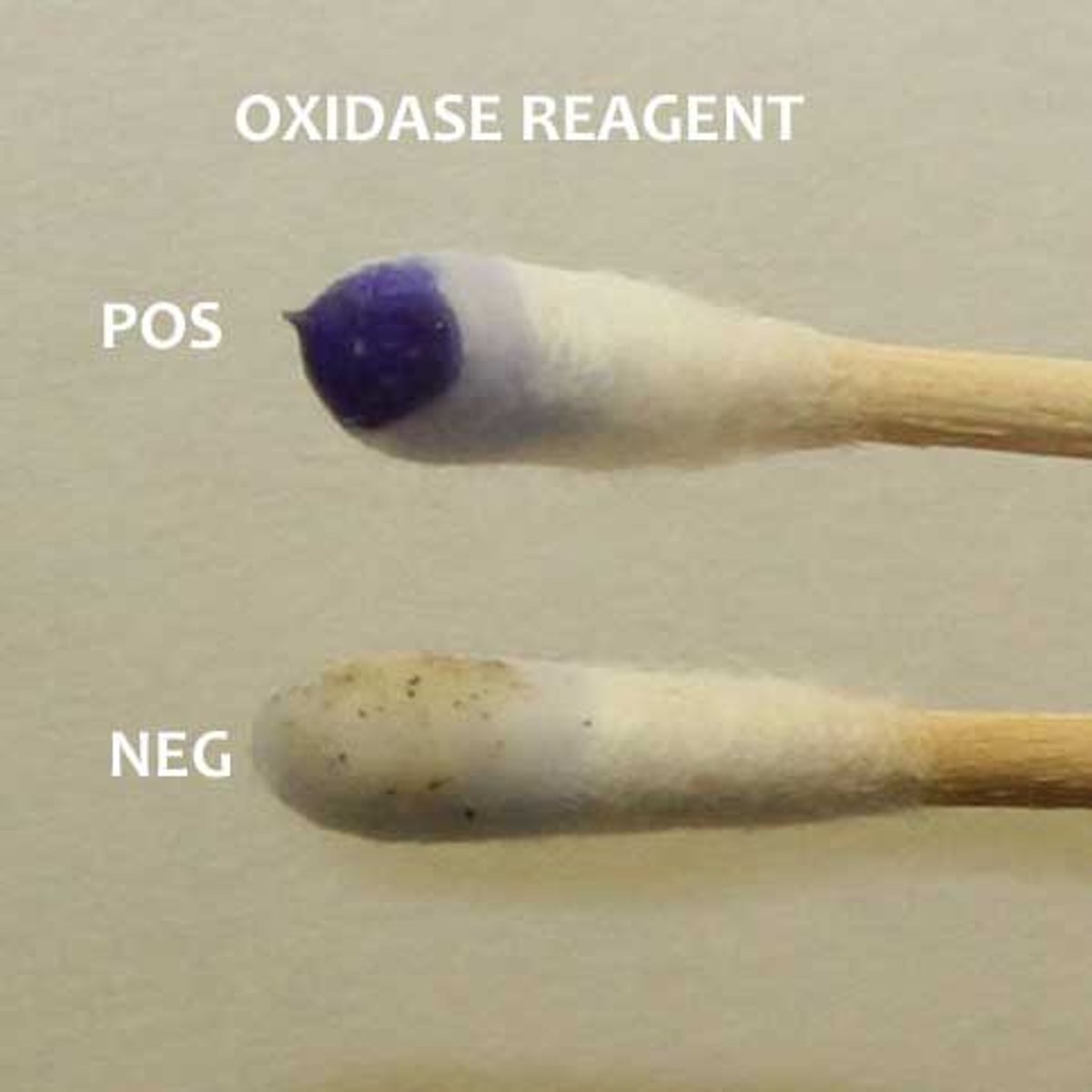
What does a positive oxidase reaction look like?
should become dark purple within 30 seconds**
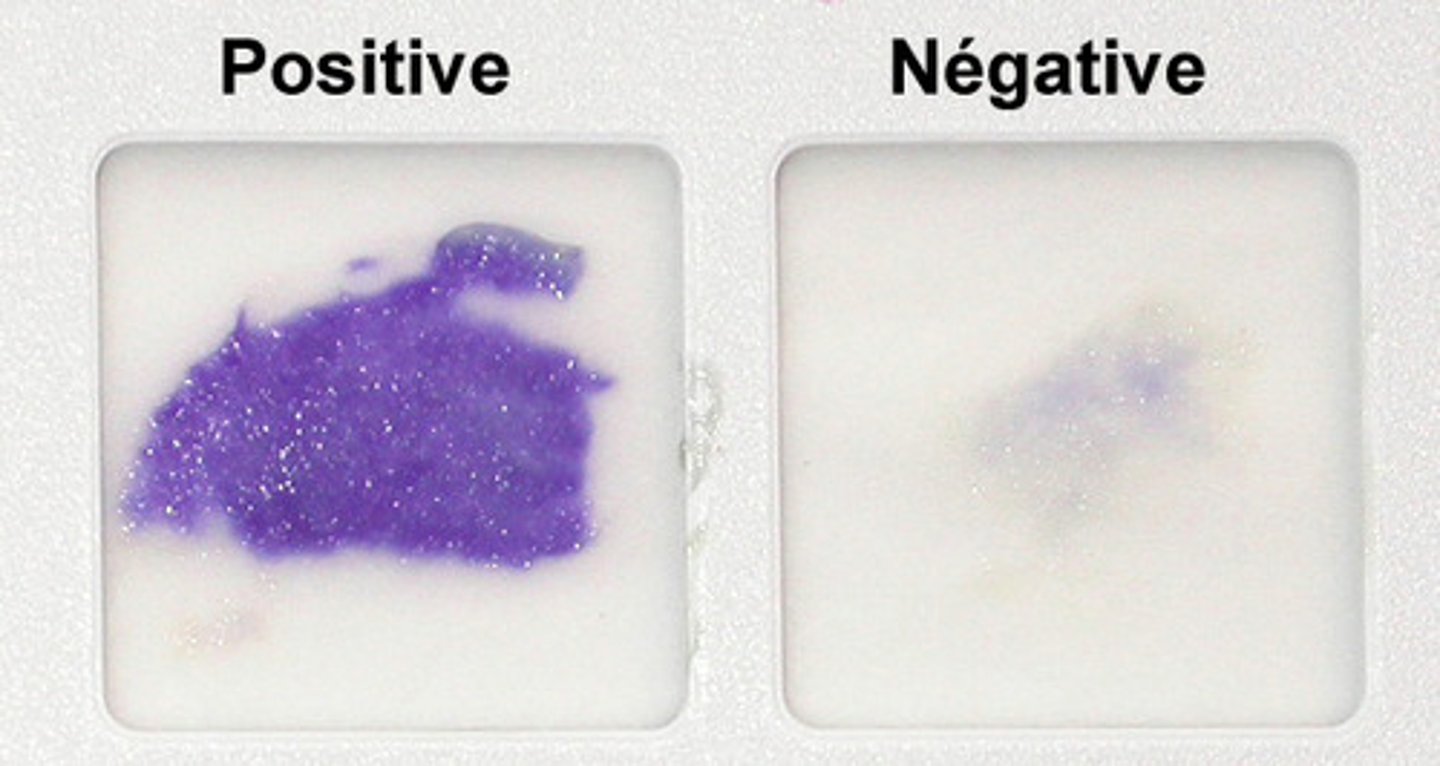
What does a negative oxidase reaction look like?
doesn't change color or takes longer than 30 seconds to become dark purple
examples of oxidase positive bacteria
gram- pseudomonas and vibrios ((Pseudomonas fluorescens)
what does the urea test test for
for presence of urease, uses a pH indicator
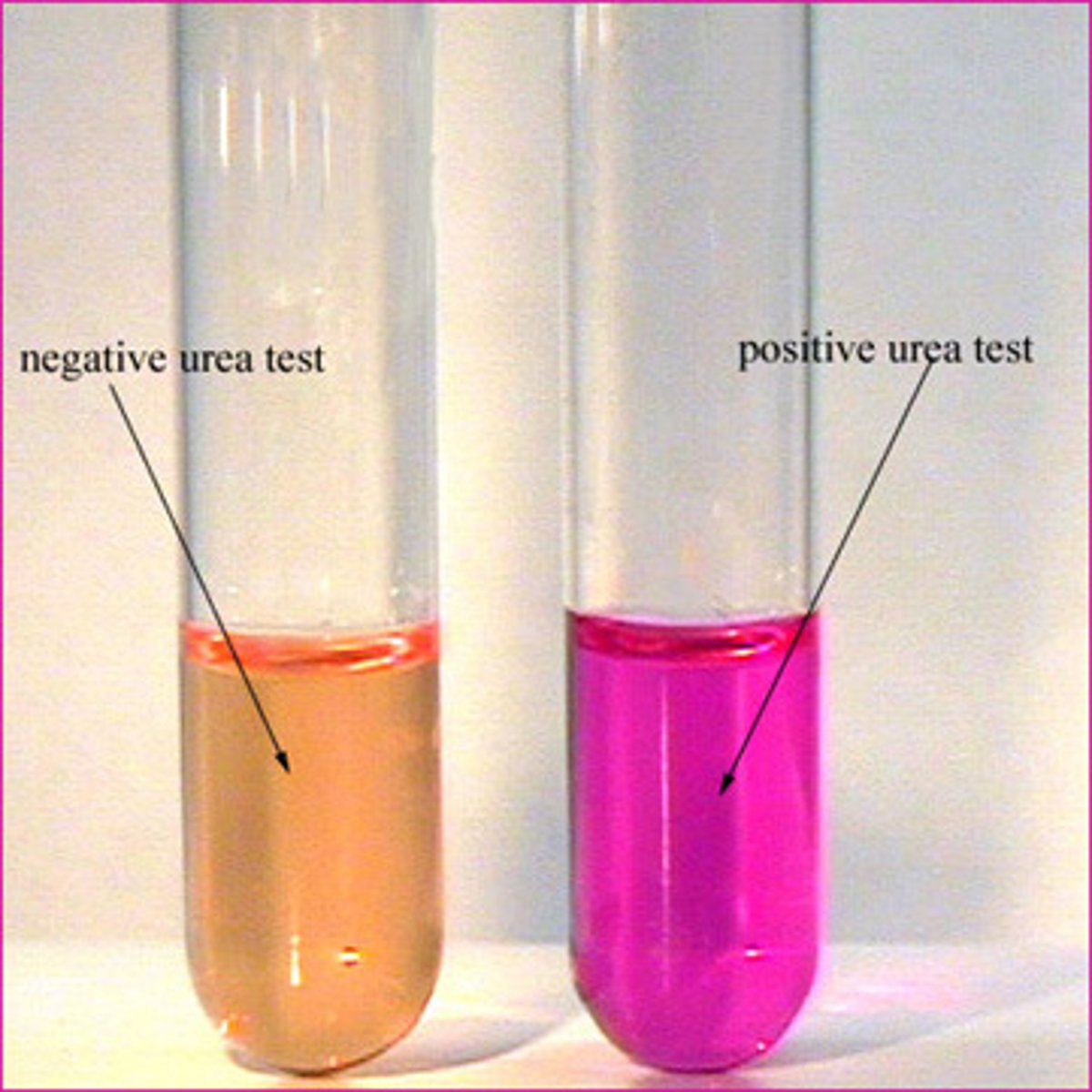

How is the presence of the enzyme urease detected in the medium?
when the bacterium hydrolyzes urea, ammonia is released and increases pH, causing indicator to change to a magenta color indicating a pos test
What is the substrate and product for the enzyme urease?
substrate: urea
products: carbon dioxide and ammonia
Name a bacterial Genus/organism that would test positive for urease?
Staph. saprophyticus
gelatin hydrolysis test purpose
used to determine the ability of an organism to produce extracellular proteolytic enzymes (gelatinases) that can liquefy gelatin in the vertebrate connective tissue.
What is a positive test for gelatinase and how do we interpret it?
a gelatinase positive organism will secrete gelatinase when in gelatin, and it will liquefy the medium (takes 7-14 days of incubation)
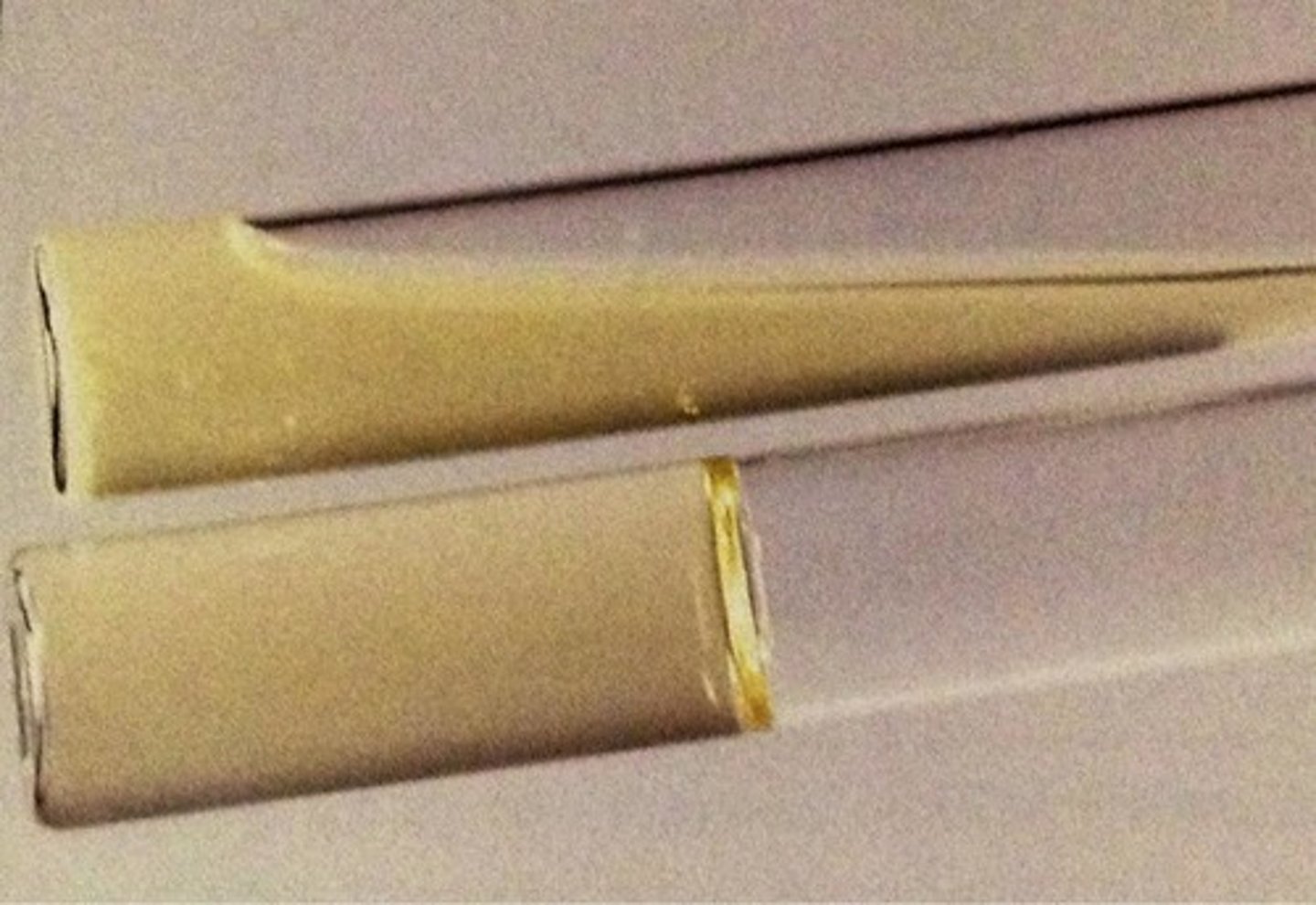

What is a negative test for gelatinase and how do we interpret it?
the organism will not liquefy the medium
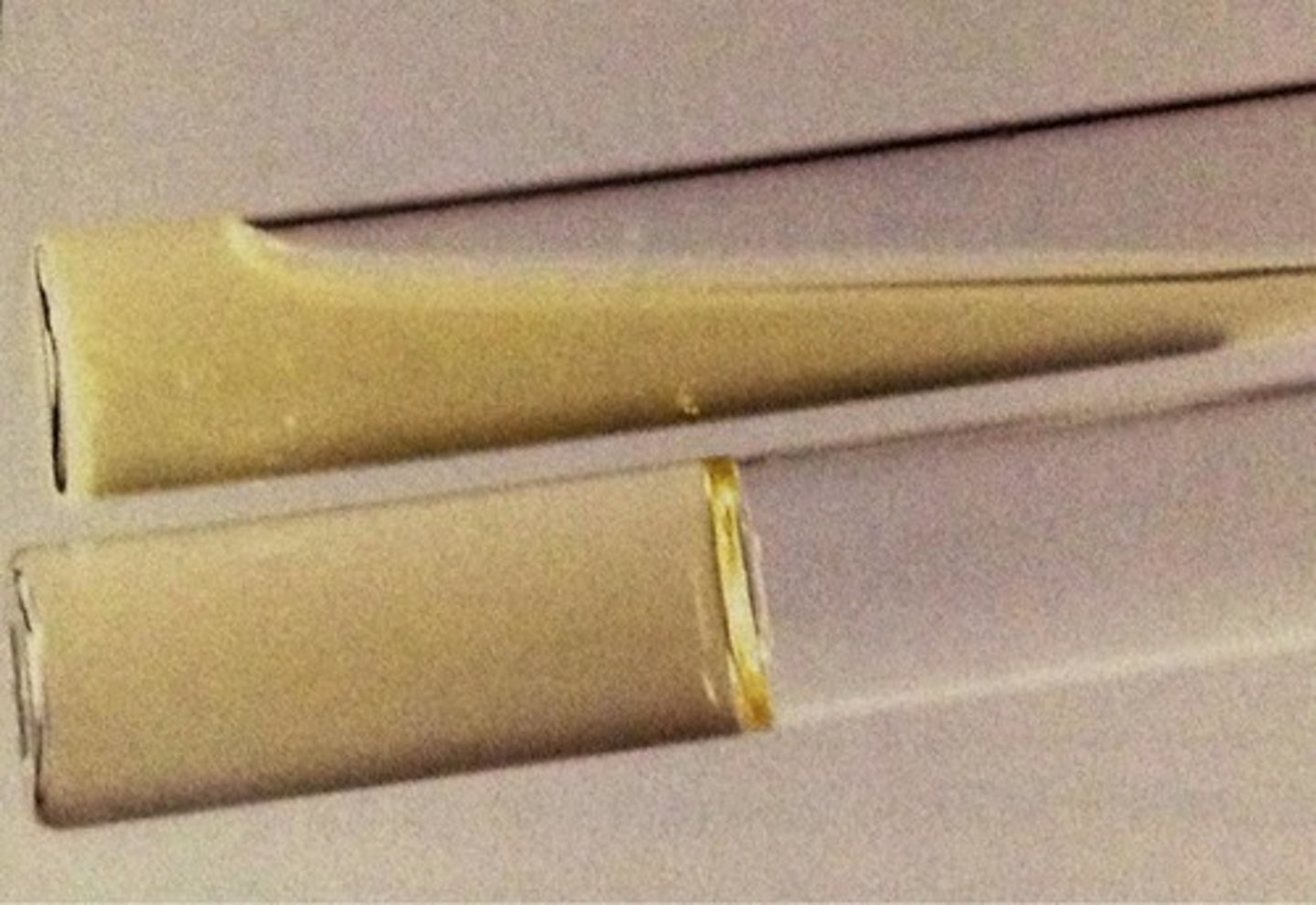

Name a bacterial Genus/organism that would test positive for the gelatin hydrolysis test
Pseudomonas fluorescens
What information can be gathered from looking at a gram stained bacterial smear?
Gram reaction, Cell Size, Cell shape, Cell grouping