5. SA surgery- micturition
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
what is the primary purpose of the lower urinary tract?
to store and facilitate urination at appropriate times
which nervous systems are involved in micturition?
peripheral nervous system:
1. autonomic (involuntary control with sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems)
2. somatic (voluntary control)
what nervous systems are also involved in conscious voiding?
central nervous system:
1. lumbar (L1-L4) and sacral (S1-S3) spinal cord
2. brainstem and cerebral cortex
what is the detrusor muscle?
smooth muscle surrounding the urinary bladder
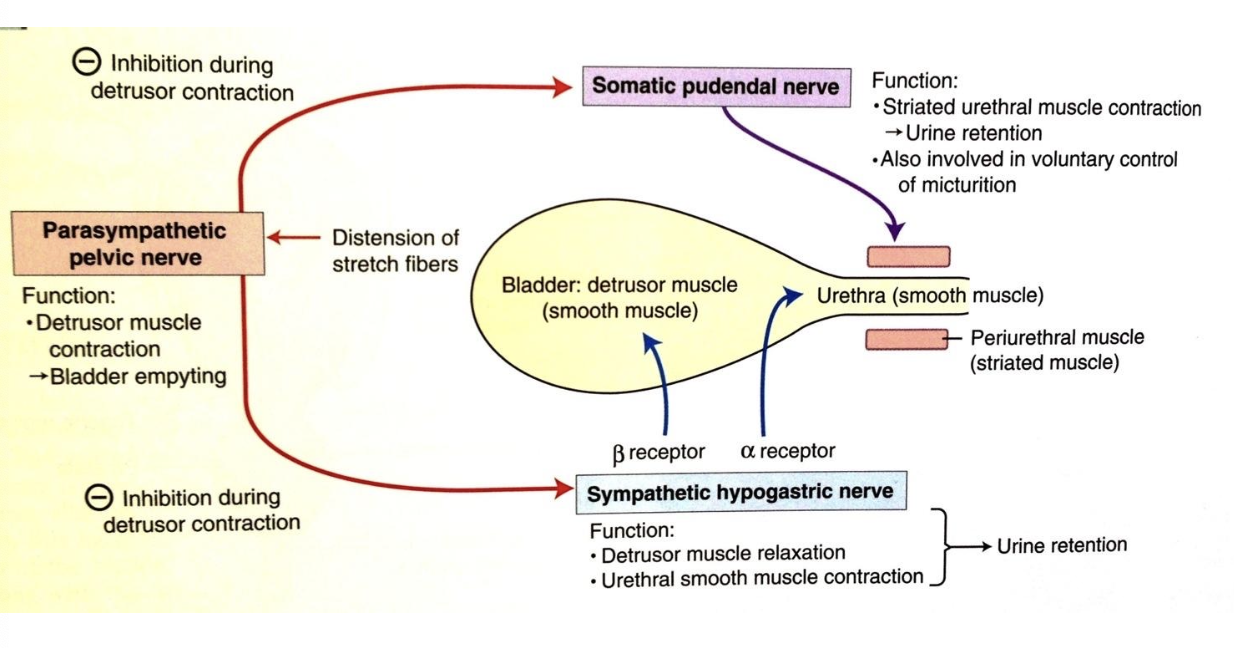
the detrusor muscle is under control of which nervous systems?
parasympathetic and sympathetic (autonomic)
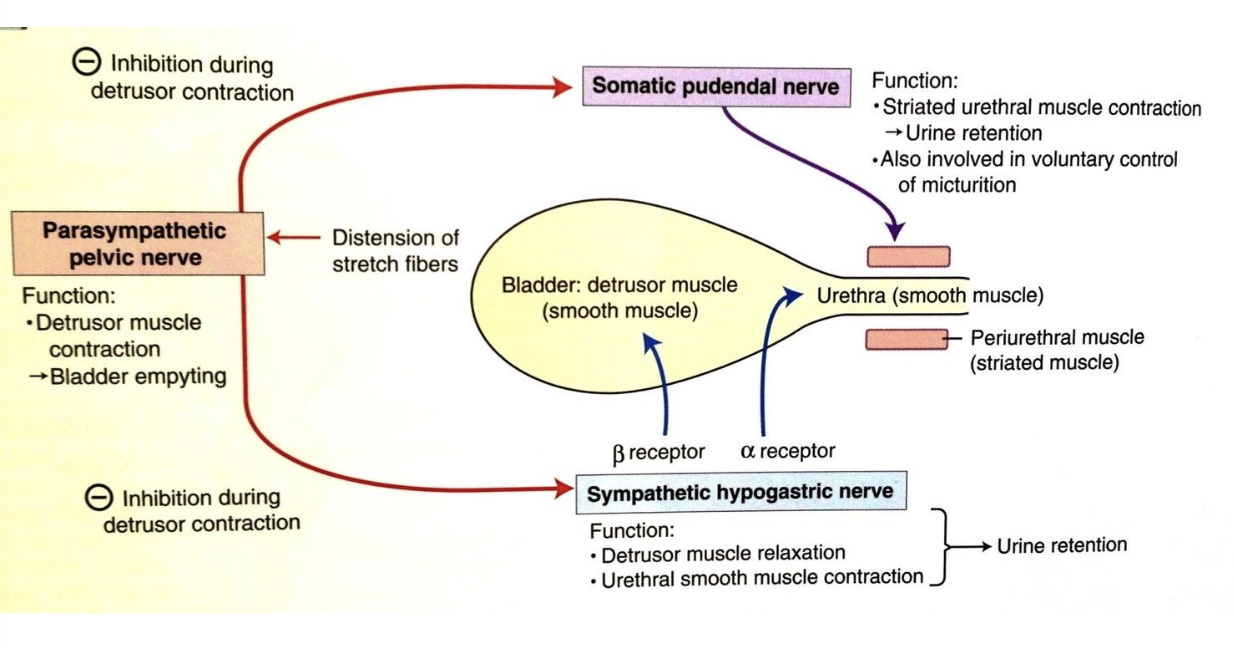
how does parasympathetic information reach the detrusor muscle/bladder wall? what type of receptors?
via the pelvic nerve (S1-S2)
acetylcholine to muscarinic receptors
what is the action of parasympathetic input on the detrusor muscle?
contraction for the voiding phase
how does sympathetic information reach the detrusor muscle/bladder wall? what type of receptors?
via the hypogastric nerve (L1-L4)
beta-adrenergic receptors (beta for relaxing detrusor)
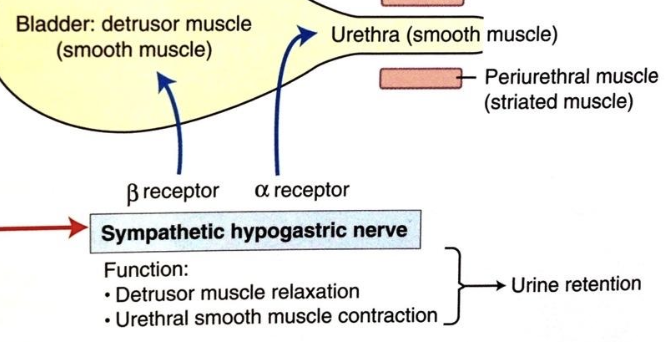
what is the action of sympathetic input on the detrusor muscle?
relaxation for the storage phase (allows bladder to fill)
what type of muscle is the external urethral sphincter made of?
striated muscle
the external urethral sphincter is under control of which nervous system?
somatic nervous system
acetylcholine to nicotinic receptors
which nerve innervates the external urethral sphincter?
pudendal nerve (S1-S3)
what are the actions of the external urethral sphincter under somatic control?
-inhibition for voiding (CNS inhibits pudendal n.)
-contraction for storage (CNS stimulates pudendal n.)
what type of muscle is the internal urethral sphincter?
smooth muscle
which nerve innervates the internal urethral sphincter?
hypogastric nerve (L1-L4)
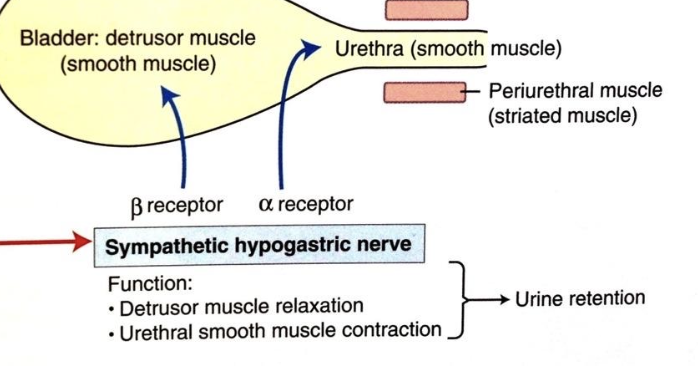
what type of receptors does the internal urethral sphincter have?
alpha adrenergic
(alphas are aggro, contracts)
what are the actions of the internal urethral sphincter?
-contraction for storage phase
-inhibition for voiding phase
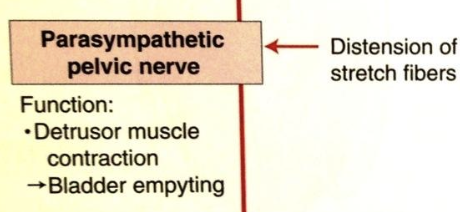
what is the normal physiology of micturition?
1. stretch receptors in bladder wall carry afferent info about bladder distention to spinal cord
2. this info is carried along spinothalamic and fasciculus gracilis to CNS
3. CNS decides if appropriate time or not for urination send info via tectospinal and reticulospinal tract
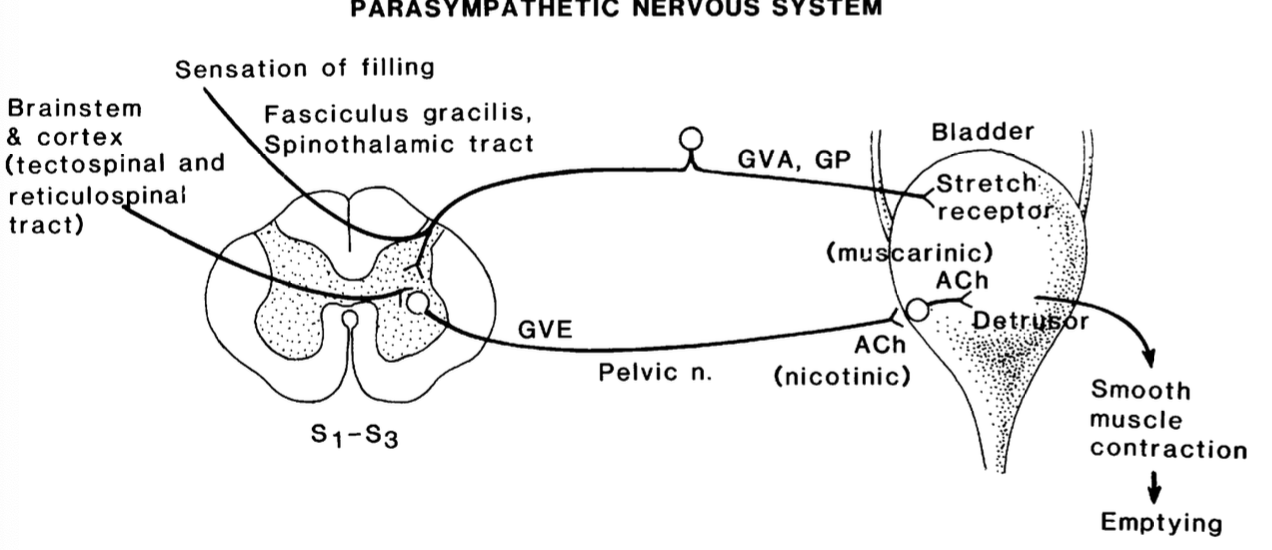
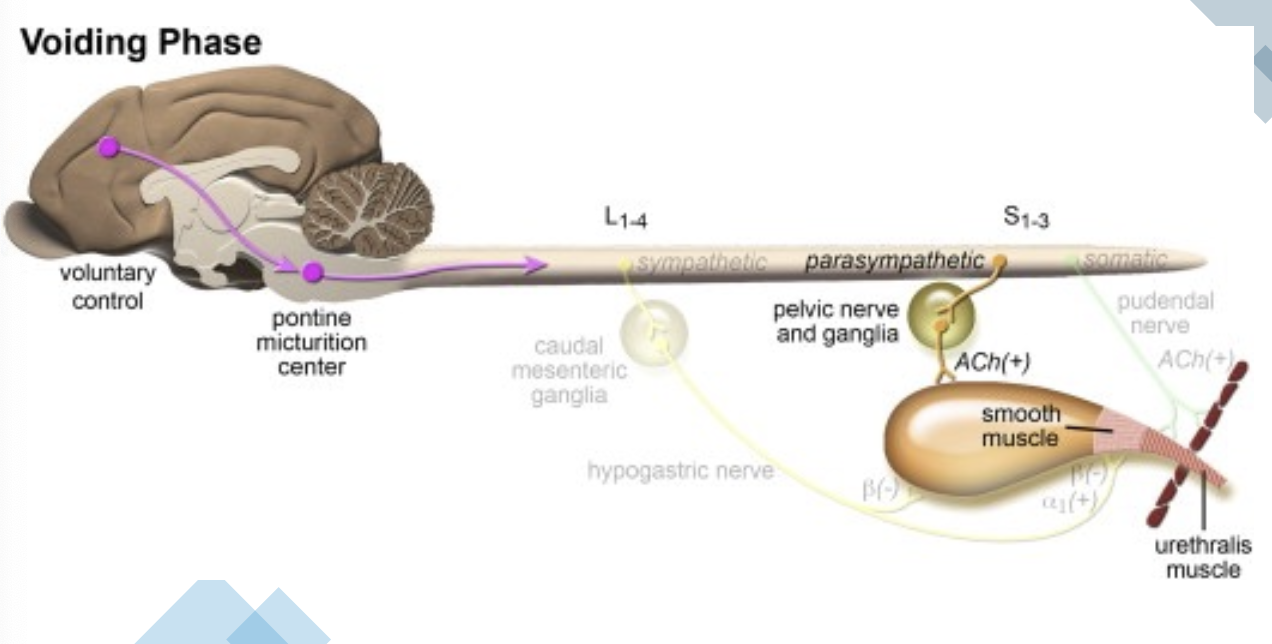
which nervous system dominates the voiding phase?
parasympathetic (rest and relax)
how is the voiding phase initiated (once brain decides OK)?
1. motor info travels down tectospinal and reticulospinal tracts to motor in S1-S2
2. reaches bladder via pelvic nerve
3. detrusor muscle contracts for bladder emptying (via acetylcholine neurotransmitter and muscarinic receptor)
what other function needs to occur during the voiding phase?
inhibition of the external urethral sphincter (and internal urethral sphincter)
how is inhibition achieved during the voiding phase?
-CNS send inhibitory signals to the sympathetic nervous system
-also inhibition of neurons in sacral spinal cord (S1-S3; pudendal nerve) to relax external urethral sphincter
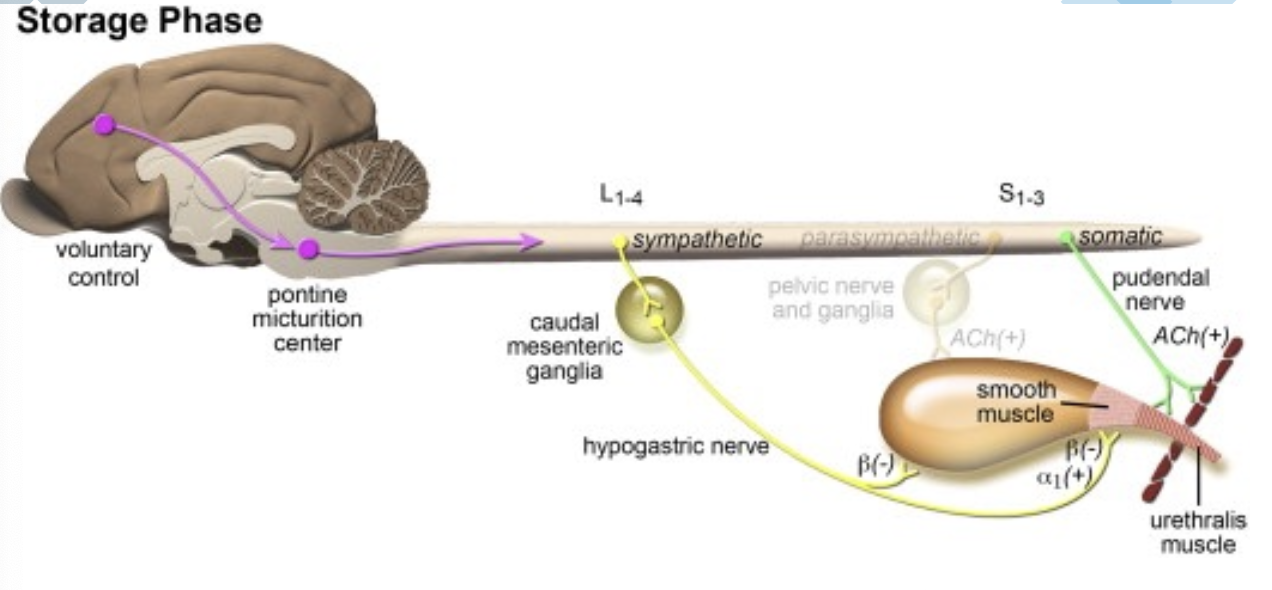
which nervous system dominates the storage phase?
sympathetic nervous system (flee, dont pee)
how is the storage phase initiated?
1. inhibition of the parasympathetic NS in the S1-S2 pelvic nerve to detrusor muscle
2. sympathetic stimulation in L2-L5 and pre-ganglionic fibers synapse at the caudal mesenteric ganglion (cholinergic)
3. post-ganglionic fibers reach bladder body and neck/urethra via hypogastric nerve
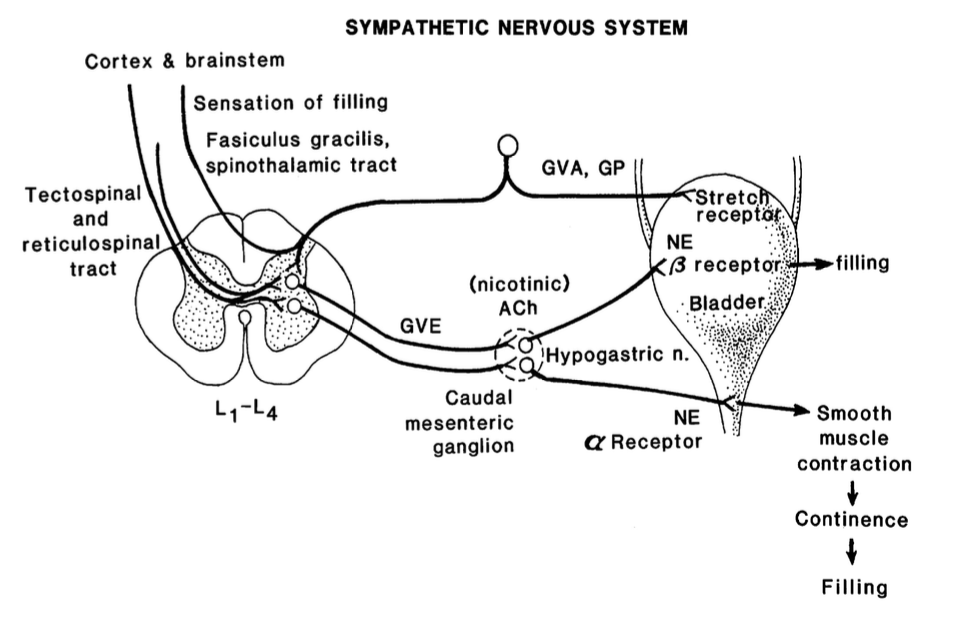
which receptors do post-ganglionic fibers from the hypogastric nerve terminate for the body of the bladder?
beta-adrenergic receptors
which receptors do post-ganglionic fibers from the hypogastric nerve terminate for the urethra/neck of the bladder?
alpha-adrenergic receptors
what does stimulation of the beta-adrenergic receptors of the body of the bladder result in?
relaxation of detrusor smooth muscle (therefore bladder distends to store urine)
what does stimulation of the alpha-adrenergic receptors of the bladder neck/urethra result in?
contraction of the smooth muscle (internal urethral sphincter) allowing urine to stay in the bladder
what nervous system controls the voluntary portion of the storage phase?
somatic nervous system
where is somatic input sent to control the voluntary portion of the storage phase?
neurons travel to the pudendal nerve to innervate the striated muscle of the urethra (external urethral sphincter)
transmission via acetylcholine to nicotinic receptors
what are 2 categories of disorders of micturition?
1. neurogenic
2. non-neurogenic
what are causes of non-neurogenic micturition disorders?
-anatomic (e.g. ectopic ureters)
-primary sphincter mechanism incompetence (+/- hormone related)
what are 3 neurogenic causes of disorders of micturition?
1. upper motor neuron
2. lower motor neuron
3. reflex dyssynergia
if an animal has an UMN bladder, where is the lesion located?
lesion is cranial to S1-S3
what are signs of an UMN bladder?
-difficult to express bladder
-loss of inhibition
-increased tone
-loss of voluntary control (high residual vomume)
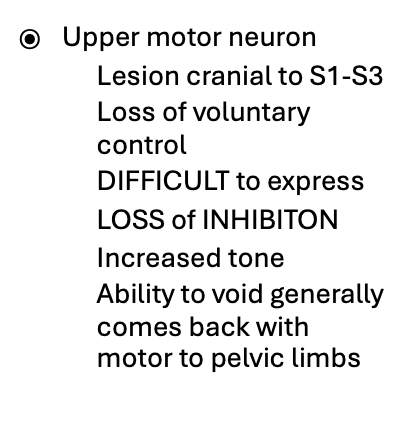
can UMN bladders regain ability to void?
yes, ability to void generally comes back with motor to pelvic limbs
if an animal has an LMN bladder, where is the lesion located?
lesion is in S1-S3
what are signs of a LMN bladder?
-loss of voluntary control
-easy to express bladder
-decreased tone
-residual volume is higher than UMN bladder

what is reflex dyssynergia?
loss of coordination between detrusor contraction and urethral relaxation (no synergy)
which general drug categories are used for disorders of micturition?
1. adrenergic antagonists (phenoxybenzamine, prazosin, acepromazine)
2. smooth muscle stimulants (bethanacol)
3. skeletal muscle stimulants
4. skeletal muscle relaxants (diazepam, dantrolene)
What drug(s) can be used as adrenergic agonists for disorders of micturition?
Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) Proin
what is the MOA of adrenergic agonists for disorders of micturition?
acts at smooth muscle of the bladder neck/internal urethra to increase tone to help with storage phase
what is phenylpropanolamine (PPA/proin)?
alpha adrenergic agonist
what is phenylpropanolamine (PPA/proin) used for?
used for primary sphincter mechanism incompetence
has no significant effects on blood pressure
What drug(s) can be used as adrenergic antagonists for disorders of micturition?
phenoxybenzamine,
prazosin,
acepromazine
(the other PPA)
what is the MOA of adrenergic antagonists for disorders of micturition?
acts on smooth muscle of the bladder neck/urethra to decrease tone to help with urine voiding
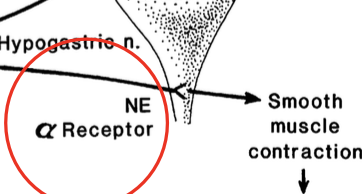

what is phenoxybenzamine?
non-specific alpha adrenergic antagonist

what is prazosin?
specific alpha-1 adrenergic antagonist
what are the side effects of phenoxybenzamine and prazosin?
hypotension (alpha-adrenergic antagonist)
what are phenoxybenzamine and prazosin used for?
used for function outlet obstruction:
-UMN bladder
-cats w/ urethral spasm
-reflex dyssynergia

what is acepromazine?
phenothiazine with alpha adrenergic antagonist effects

what are the side effects of acepromazine?
hypotension and sedation
What drug(s) can be used as smooth muscle stimulants for disorders of micturition?
Bethanocol
What is the MOA of smooth muscle stimulants for disorders of micturition?
acts to increase smooth muscle tone of detrusor muscle to help with urine voiding
What is bethanocol?
Parasympathomimetic agent with muscarinic effects (trying to act like pelvic n.)
What is bethanacol used for?
increases contraction of the detrusor muscle,
used for reflex dyssnergia or detrusor atony
If you use bethanacol you must also use ___
phenoxybenzamine (alpha adrenergic antagonist) to relax the internal urethral sphincter
What are side effects of bethanacol?
anorexia,
salivation,
lacrimation,
abdominal cramping,
vomiting, diarrhea
what is the MOA of skeletal muscle relaxants for disorders of micturition?
acts to relax striated muscle (external urethral sphincter) to aid in voiding
What drug(s) can be used as skeletal muscle relaxants for disorders of micturition?
diazepam, dantrolene

what is diazepam used for in disorders of micturition?
skeletal muscle relaxant, used for urethral striated muscle spasms
cats can get idiosyncratic hepatotoxicosis w/ diazepam!

what is dantrolene?
direct acting skeletal muscle relaxant

what are side effects of dantrolene?
hepatotoxicity

Case: 6 yo MN Dachshund with IVDD at T12-T13. Paraplegic with deep pain present. Is the bladder going to be: UMN, LMN, or not effected?
UMN
Case: 6 yo MN Dachshund with IVDD at T12-T13. Paraplegic with deep pain present.
For an UMN bladder, is the bladder going to be easy or harder to express?
difficult to express because increased tone
Case: 6 yo MN Dachshund with IVDD at T12-T13. Paraplegic with deep pain present.
For an UMN bladder, what class of medications would you start her on?
Alpha adrenergic antagonist (goal is to RELAX smooth muscle internal urinary sphincter by inhibiting alpha receptors)
e.g. phenoxybenzamine (non-specific alpha adrenergic antagonist)
Case: 6 yo MN Dachshund with IVDD at T12-T13. Paraplegic with deep pain present.
If you choose phenoxybenzamine, what is a side effect of this drug?
Hypotension
Case: 2 yo FS Lab dx with primary sphincter mechanism incompetence.
What her clinical signs?
incontinence
Case: 2 yo FS Lab dx with primary sphincter mechanism incompetence.
What drug would you start her on?
Phenylpropanolamine (PPA Proin, alpha adrenergic agonist as goal is to INCREASE tone of internal urethral sphincter)
Case: 2 yo FS Lab dx with primary sphincter mechanism incompetence.
What class of drug is PPA?
alpha adrenergic agonist