Health Assessment Exam #2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:52 PM on 10/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
1
New cards
What subjective data is collected during a respiratory assessment?
cough, SOB, chest pain when breathing, history of respiratory infection, smoking history, environmental exposure, and self care behaviors
2
New cards
What should be inspected during a respiratory assessment?
- thoracic cage: shape and configuration
- skin integrity: color and condition
- position in which patient takes to breathe
- quality of respirations
- skin integrity: color and condition
- position in which patient takes to breathe
- quality of respirations
3
New cards
What should be palpated during a respiratory assessment?
- confirm symmetric chest expansion with breathing, respiratory excursion
- check for fremitus: palpable vibration over the lungs with vocalization, looking for symmetry of vibration
- chest wall for tenderness, temperature, moisture, lumps or masses
- check for fremitus: palpable vibration over the lungs with vocalization, looking for symmetry of vibration
- chest wall for tenderness, temperature, moisture, lumps or masses
4
New cards
What should be percussed during a respiratory assessment and what are the expected sounds over the lung fields?
over lung fields
- resonance: low-pitched, clear, hollow sound, healthy
- hyper-resonance: lower-pitched booming sounds, too much air is present, common in COPD patients
- dull: soft, muffled, abnormal density, possible indication of a mass
diaphragmatic excursion: how far the diaphragm extends during inhalation
- resonance: low-pitched, clear, hollow sound, healthy
- hyper-resonance: lower-pitched booming sounds, too much air is present, common in COPD patients
- dull: soft, muffled, abnormal density, possible indication of a mass
diaphragmatic excursion: how far the diaphragm extends during inhalation
5
New cards
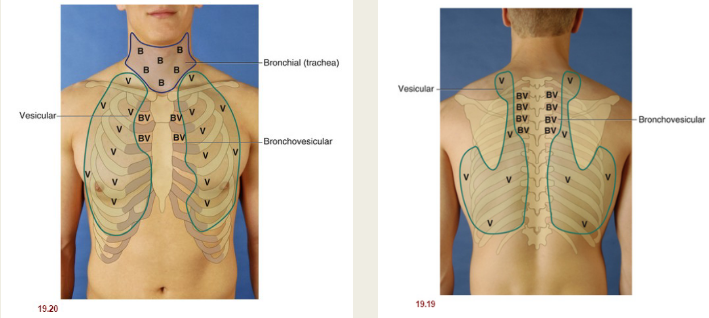
What areas are auscultated during a respiratory assessment?
bronchial, bronchovesicular, and vesicular
6
New cards
What are characteristics of bronchial lung sounds?
pitch: high
amplitude: loud
duration: inspiration will be slightly shorter than expiration
quality: harsh, hollow, tubular
amplitude: loud
duration: inspiration will be slightly shorter than expiration
quality: harsh, hollow, tubular
7
New cards
What are characteristics of bronchovesicular lung sounds?
pitch: moderate
amplitude: moderate
duration: inspiration and expiration are equal
quality: mixed
amplitude: moderate
duration: inspiration and expiration are equal
quality: mixed
8
New cards
What are characteristics of vesicular lung sounds?
pitch: low
amplitude: soft
duration: inspiration will be slightly longer than expiration
quality: rustling, like the sounds of the wind in the trees
amplitude: soft
duration: inspiration will be slightly longer than expiration
quality: rustling, like the sounds of the wind in the trees
9
New cards
What are characteristics of fine crackles?
- discontinuous
- fine, high pitched crackling
- end of inspiration
- not cleared by cough
- fine, high pitched crackling
- end of inspiration
- not cleared by cough
10
New cards
What causes fine crackles?
fluid and mucous in the lungs. seen in pneumonia, HF, COPD, asthma, and chronic bronchitis
11
New cards
What are the characteristics of coarse crackles?
- discontinuous
- low pitched, bubbling or gurgling
- start early in inspiration, extend into expiration
- low pitched, bubbling or gurgling
- start early in inspiration, extend into expiration
12
New cards
What causes coarse crackles?
fluid and mucous in the lungs but usually seen in more advanced disease. seen in pneumonia, HF, COPD, asthma, chronic bronchitis, pulmonary edema, and pulmonary fibrosis
13
New cards
What are characteristics of wheezes?
- continuous
- high-pitched, musical sound similar to squeak
- more common in expiration
- occurs in small airways
- high-pitched, musical sound similar to squeak
- more common in expiration
- occurs in small airways
14
New cards
What causes wheezes?
air flowing through constricted airways. seen in asthma, COPD, and HF
15
New cards
What are characteristics of rhonchi?
- continuous
- low-pitched, coarse, loud, low snoring or moaning tone
- more common in expiration
- coughing may clear
- low-pitched, coarse, loud, low snoring or moaning tone
- more common in expiration
- coughing may clear
16
New cards
What causes rhonchi?
secretions or obstructions in the larger airways. seen in obstructed trachea, bronchitis, and pneumonia
17
New cards
What are characteristics of pleural friction rub?
- superficial, low-pitched, coarse rubbing or grating sound
- sounds like two surfaces rubbing together
- heard throughout inspiration and expiration
- loudest over the lower anterolateral surface
- not cleared by cough
- sounds like two surfaces rubbing together
- heard throughout inspiration and expiration
- loudest over the lower anterolateral surface
- not cleared by cough
18
New cards
What causes pleural friction rub?
when inflammation roughens the surfaces of the visceral and parietal pleura. seen in pleurisy, pericarditis, and pericardial effusion
19
New cards
What are characteristics of stridor?
- high pitched whistling or gasping sound with harsh sound quality
- heard during inspiration
- heard during inspiration
20
New cards
What causes stridor?
obstruction or narrowing in upper airway. seen in children with croup or epiglottitis
21
New cards
What is the suprasternal notch?
little notch that is above the sternum and between the clavicles
22
New cards
What is the manubrio-sternal angle?
"angle of Louis", where the manubrium meets the sternum, in line with 2nd rib, landmark for assessment locations
23
New cards
How many lobes does each lung have?
right: 3 lobes (but shorter than left lung)
left: 2 lobes
left: 2 lobes
24
New cards
What are expected findings in a respiratory assessment?
- spinous process in straight line, symmetric features
- AP diameter 1:2
- skin warm, dry and intact, no tenderness
- tactile fremitus symmetric
- resonance on percussion
- normal breath sounds
- AP diameter 1:2
- skin warm, dry and intact, no tenderness
- tactile fremitus symmetric
- resonance on percussion
- normal breath sounds
25
New cards
What are unexpected findings in a respiratory assessment?
- curved spine: scoliosis or kyphosis, asymmetrical features
- barrel chest, pectus excavatum, pectus carinatum
- skin not intact, hot or cold, diaphoretic
- tactile fremitus asymmetrical
- hyperresonance or dull sounds
- adventitious lung sounds: crackles, wheezes, stridor, pleural rub
- barrel chest, pectus excavatum, pectus carinatum
- skin not intact, hot or cold, diaphoretic
- tactile fremitus asymmetrical
- hyperresonance or dull sounds
- adventitious lung sounds: crackles, wheezes, stridor, pleural rub
26
New cards
What subjective data is collected during a breast, axilla and lymphatics assessment?
breasts: pain, lumps, discharge, rash, swelling, trauma, history of breast disease, surgery, self care behaviors
axilla/lymphatics: tenderness, lump, swelling, rash
axilla/lymphatics: tenderness, lump, swelling, rash
27
New cards
What should be inspected during a breast, axilla, and lymphatics assessment?
breast: symmetry and shape, skin integrity, and nipple symmetry, skin integrity, and drainage
axilla/lymphatics: bulging, discoloration, edema
axilla/lymphatics: bulging, discoloration, edema
28
New cards
What should be palpated during a breast, axilla and lymphatics assessment?
breasts: lumps, masses and tenderness
axilla/lymphatics: enlarged nodes and tenderness
axilla/lymphatics: enlarged nodes and tenderness
29
New cards
What are expected findings in a breast, axilla, and lymphatics assessment?
- symmetry of breasts and nipples
- skin warm, dry and intact
- regional lymphatics without bulging or tenderness
- no tenderness or masses in breasts
- breasts should lift symmetrically with arms lifted over head
- skin warm, dry and intact
- regional lymphatics without bulging or tenderness
- no tenderness or masses in breasts
- breasts should lift symmetrically with arms lifted over head
30
New cards
What are unexpected findings in a breast, axilla, and lymphatics assessment?
- asymmetry of breasts and/or nipples
- supernumerary nipple
- pain or discharge from nipple
- skin not warm, dry and intact, redness or lesions
- regional lymphatics with bulging or tenderness
- tenderness or masses in breasts
- retraction of breasts from fibrosis (breasts don't lift symmetrically when arms lifted above head)
- supernumerary nipple
- pain or discharge from nipple
- skin not warm, dry and intact, redness or lesions
- regional lymphatics with bulging or tenderness
- tenderness or masses in breasts
- retraction of breasts from fibrosis (breasts don't lift symmetrically when arms lifted above head)
31
New cards
What is hypoxemia?
below normal level of oxygen in blood
32
New cards
What is bronchophony?
the abnormal transmission of sounds from the lungs or bronchi
33
New cards
What is tanner staging?
sexual maturity rating, objective classification system that is used to document a patient's puberty progression
34
New cards
What is gynecomastia?
enlarged breasts in men
35
New cards
What are the valves of the heart?
atrioventricular valves: tricuspid and mitral valve
semilunar valves: aortic and pulmonary valve
semilunar valves: aortic and pulmonary valve
36
New cards
How does blood flow through the body?
superior and inferior vena cava (return deoxygenated blood to the heart) --> right atrium --> tricuspid valve --> right ventricle --> pulmonary valve --> pulmonary artery --> lungs --> pulmonary veins (oxygenated blood) --> left atrium --> mitral valve --> left ventricle --> aortic valve --> aorta --> body
37
New cards
What are the heart sounds and what causes them?
S1: closing of the tricuspid and mitral valves, beginning of systole (contraction)
S2: closing of the pulmonary and aortic valves, end of systole and starts diastole (relaxation)
S3: not usually heart and is the ventricles filling abnormally, immediately after S2
S4: not usually heard and occurs when the ventricles are resistant to filling due to stiffening or thickened tissue, just before S1
murmurs: turbulent blood flow, a gentle blowing or swooshing sound
S2: closing of the pulmonary and aortic valves, end of systole and starts diastole (relaxation)
S3: not usually heart and is the ventricles filling abnormally, immediately after S2
S4: not usually heard and occurs when the ventricles are resistant to filling due to stiffening or thickened tissue, just before S1
murmurs: turbulent blood flow, a gentle blowing or swooshing sound
38
New cards
How does an electrical impulse travel through the heart?
the SA node initiates the impulse --> the impulse goes across the atria to the AV node --> impulse travels to the right and left branches of the Bundle of His, stimulating the heart to contract
39
New cards
What occurs if the SA node is not working?
the AV node will take over and maintain a pulse of 40-60 bpm. if the SA and AV node aren't working the right and left branches of the Bundle of His will take over and maintain a pulse of 20-40 bpm
40
New cards
What subjective data is collected during a cardiac assessment?
chest pain, dyspnea, orthopnea, cough, fatigue, cyanosis or pallor, edema, nocturia, past cardiac hx, family hx, diet, smoking, alcohol, exercise, and drug use
41
New cards
What should be inspected during a cardiac assessment?
- overall chest and back
- look for jugular vein distortion, indicates heart failure or fluid volume overload
- look for jugular vein distortion, indicates heart failure or fluid volume overload
42
New cards
What should be palpated during a cardiac assessment?
- overall chest and back
- carotid artery
- apical pulse (4th or 5th interspace midclavicular)
- heaves or lifts or thrills
- carotid artery
- apical pulse (4th or 5th interspace midclavicular)
- heaves or lifts or thrills
43
New cards
What should be auscultated during a cardiac assessment?
- carotid artery with the bell of the stethoscope in the angle of the jaw, midcervical, and base of neck
- have pt hold their breath
- you are listening for bruits
- valves: aortic, pulmonary, Erb's point, tricuspid, and mitral
- listen for S1, S2, S3, S4
- listen with diaphragm
- note rate, rhythm and identify S1 and S2
- have pt hold their breath
- you are listening for bruits
- valves: aortic, pulmonary, Erb's point, tricuspid, and mitral
- listen for S1, S2, S3, S4
- listen with diaphragm
- note rate, rhythm and identify S1 and S2
44
New cards
What are bruits?
murmurs in a vessel from turbulent blood flow
45
New cards
When is S1 and S2 the loudest?
S1 is louder than S2 at the apex of the heart and S2 is louder than S1 at the base of the heart
46
New cards
What are the expected findings in a cardiac assessment?
- no JVD
- no heave or lift
- no thrill
- carotids 2+, equal bilateral and no bruit
- no cardiac enlargement with percussion
- S1 and S2 sounds
- regular rhythm
- HR 50-100
- no heave or lift
- no thrill
- carotids 2+, equal bilateral and no bruit
- no cardiac enlargement with percussion
- S1 and S2 sounds
- regular rhythm
- HR 50-100
47
New cards
What are unexpected findings in a cardiac assessment?
- chest pain, fatigue
- cyanosis
- JVD
- heave or lift
- thrill
- carotids absent, weak or bounding, unequal bilaterally
- carotid bruit
- cardiac enlargement with percussion
- S1 or S2 split sounds, S3, S4, murmur, or clicks
- irregular rhythm
- HR less than 50 or more than 100
- cyanosis
- JVD
- heave or lift
- thrill
- carotids absent, weak or bounding, unequal bilaterally
- carotid bruit
- cardiac enlargement with percussion
- S1 or S2 split sounds, S3, S4, murmur, or clicks
- irregular rhythm
- HR less than 50 or more than 100
48
New cards
What are the different pulse sites?
temporal, brachial, radial, ulnar, femoral, popliteal, anterior tibial, dorsalis pedis, and posterior tibial
49
New cards
What is arteriosclerosis?
thickening and hardening of the artery walls
50
New cards
What is atherosclerosis?
buildup of fats in and on artery walls
51
New cards
What is interstitial space?
surrounds tissue cells, filled with interstitial fluid, allows for movement of ions, proteins, and nutrients across the cell barrier
52
New cards
What is the function of the spleen?
destroys old RBC, produce antibodies, store RBCs, and filter microorganisms
53
New cards
What is the function of the tonsils?
respond to local inflammation
54
New cards
What is the function of the thymus?
important in developing T lymphocytes, the B lymphocytes originate in the bone marrow and mature in the lymphoid tissue
55
New cards
What is the function of the appendix?
responds to gut flora
56
New cards
What subjective data is collected during a peripheral vascular and lymphatics assessment?
- leg pain or cramps
- skin changes on arms or legs
- swelling in arms or legs
- lymph node enlargement
- skin changes on arms or legs
- swelling in arms or legs
- lymph node enlargement
57
New cards
What are lymph nodes?
small, oval clumps of lymphatic tissue located along the lymph vessels that filter fluid before it is returned to the bloodstream
58
New cards
What objective data is collected during a peripheral vascular and lymphatics assessment in the arms?
inspect: lesions, color, symmetry
palpate: tenderness, temp, check capillary refill, radial pulses, brachial pulse, and epitrochlear nodes
palpate: tenderness, temp, check capillary refill, radial pulses, brachial pulse, and epitrochlear nodes
59
New cards
How do you rate pulse?
- 0: absent
- 1+: weak
- 2+: normal
- 3+: increased, full, bounding
- 1+: weak
- 2+: normal
- 3+: increased, full, bounding
60
New cards
What objective data is collected during a peripheral vascular assessment in the legs?
- inspect: color, presence of lesions, swelling, varicose veins
- palpate: temp, moisture, pulses (femoral, popliteal, dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial), swelling/edema
- palpate: temp, moisture, pulses (femoral, popliteal, dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial), swelling/edema
61
New cards
How do you rate edema?
- 1+: mild, slight indentation
- 2+: moderate pitting, indentation subsides quickly
- 3+: deep pitting, indentation remains for a short time, legs look swollen
- 4+: very deep pitting, indentation lasts a long time
- 2+: moderate pitting, indentation subsides quickly
- 3+: deep pitting, indentation remains for a short time, legs look swollen
- 4+: very deep pitting, indentation lasts a long time
62
New cards
What are expected findings in a peripheral vascular assessment?
- arteries: 2+, regular pulses bilaterally, warm, intact skin over extremities, expected hair growth patterns, no bruit
- veins: no varicosities
- no edema
- veins: no varicosities
- no edema
63
New cards
What are unexpected findings in a peripheral vascular assessment?
- arteries: absent, weak or bounding pulses, irregular pulses, cool skin over extremities, unexpected hair growth patterns, bruit
- veins: varicosities
- edema
- wounds that won't heal or heal slowly
- veins: varicosities
- edema
- wounds that won't heal or heal slowly
64
New cards
What are expected findings in a lymphatics assessment?
- no edema
- no painful lymph nodes
- no swollen lymph nodes
- no painful lymph nodes
- no swollen lymph nodes
65
New cards
What are unexpected findings in a lymphatics assessment?
- edema
- painful lymph nodes
- swollen lymph nodes
- painful lymph nodes
- swollen lymph nodes