Briggs Bio AP Classroom Midterm Review Questions
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
some questions were literally impossible to transfer from AP classroom to here so don't ONLY study this lol, a few were skipped
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
tRNA molecules deliver amino acids to ribosomes where the amino acid next
is covalently bonded to a growing polypeptide
The CFTR protein is made up of 1480 amino acids linked together in a chain. Some humans produce a version of the CFTR protein in which phenylalanine (an amino acid) has been deleted from position 508 of the amino acid chain. Which of the following best predicts how the amino acid deletion will affect the structure of the CFTR protein?
It will affect the primary, secondary, and tertiary structures of the CFTR protein.
Which of the following describes a key difference among the 20 amino acids that are used to make proteins?
Some amino acids are hydrophobic.
Scientists examined the folded structure of a purified protein resuspended in water and found that amino acids with nonpolar R groups were primarily buried in the middle of the protein, whereas amino acids with polar R groups were primarily on the surface of the protein. Which of the following best explains the location of the amino acids in the folded protein?
Nonpolar R groups that cannot form hydrogen bonds with water are pushed into the middle of the protein.

Figure 1 shows three amino acids that are part of a polypeptide chain. Figure 2 shows the same section of the chain after a mutation has occurred.
How might this change affect the structure and function of the protein?
The R-group of the new amino acid, valine, has different chemical properties than the R-group of cysteine. This will cause the protein to misfold and not function properly in the cell.

Figure 1. A representation of a reaction involved in the formation of a biological molecule Which of the following best explains the reaction represented in Figure 1 ?
It is a dehydration synthesis reaction involved in the formation of a polypeptide.
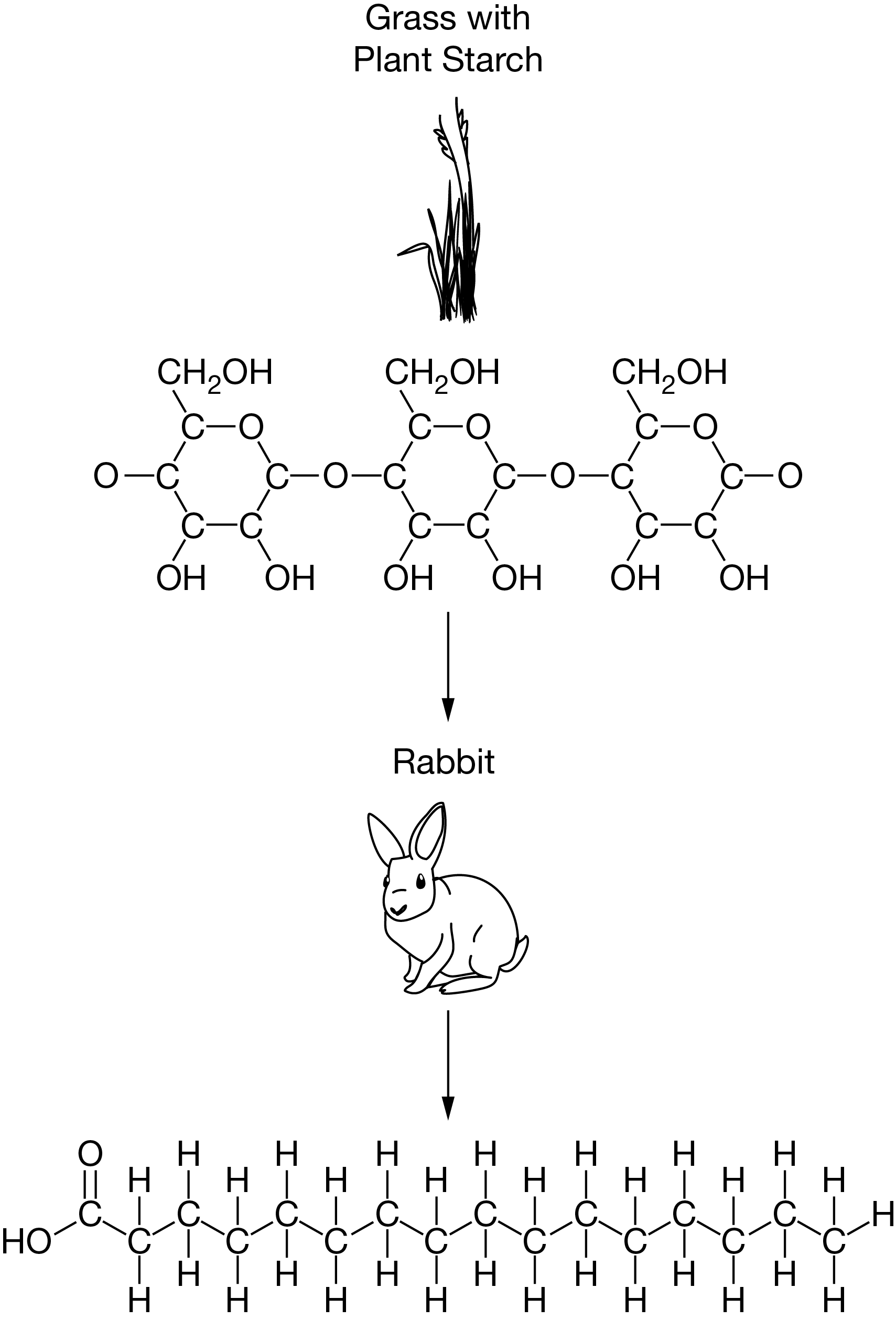
Which of the following statements best describes how organisms such as rabbits obtain the carbon necessary for building biological molecules?
Rabbits eat plants and break down plant molecules to obtain carbon and other atoms that they rearrange into new carbon-containing molecules.
Which of the following would most likely occur if cattle lost the ability to maintain a colony of microorganisms in their digestive tract?
Cattle would no longer be able to use cellulose as a primary source of glucose.
Which of the following best describes the process that adds a monosaccharide to an existing polysaccharide?
A specific enzyme removes the hydrogen (H) from the monosaccharide and the hydroxide (OH) from the polysaccharide, creating a bond between the two and creating a water (H2O) molecule.
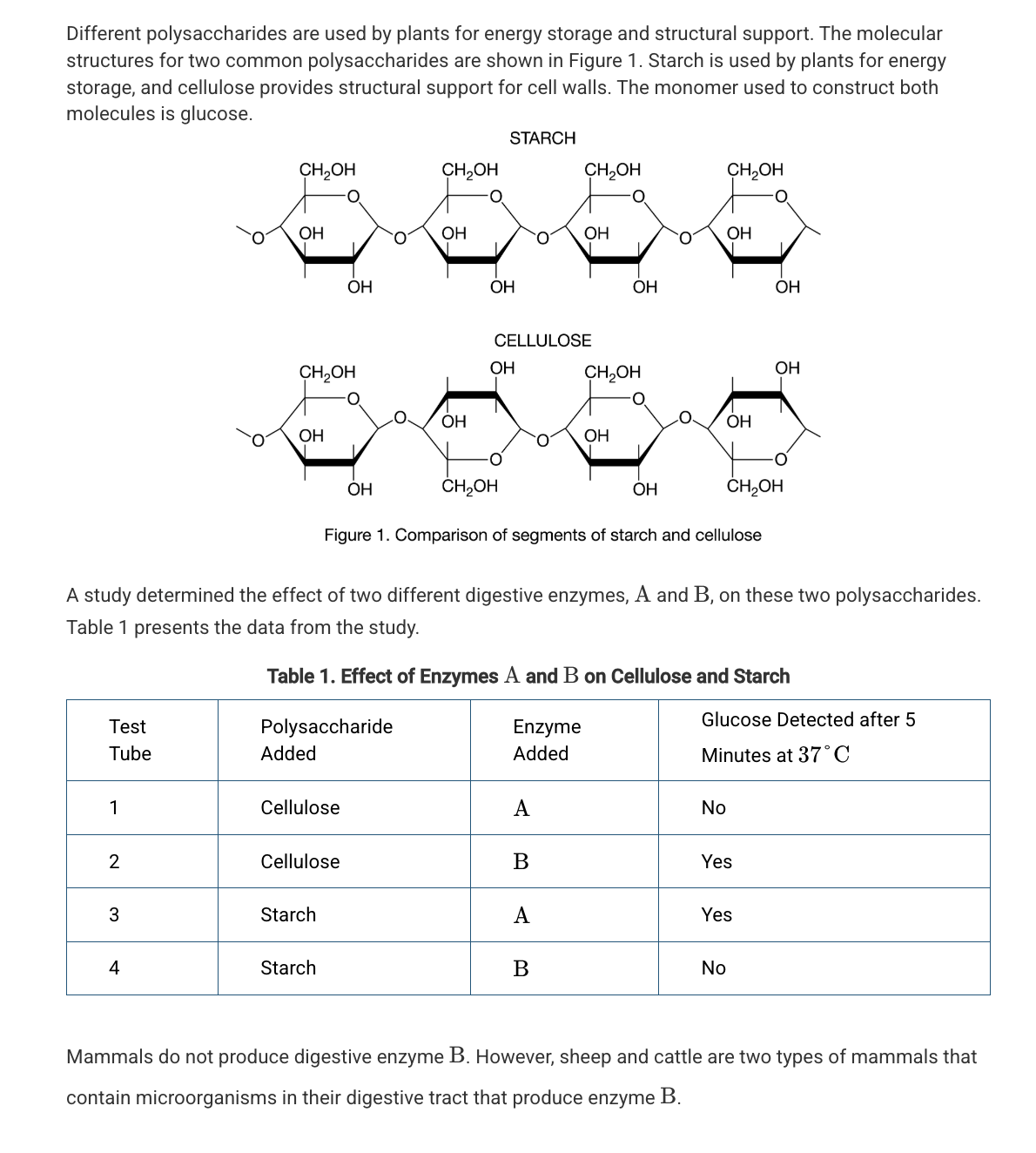
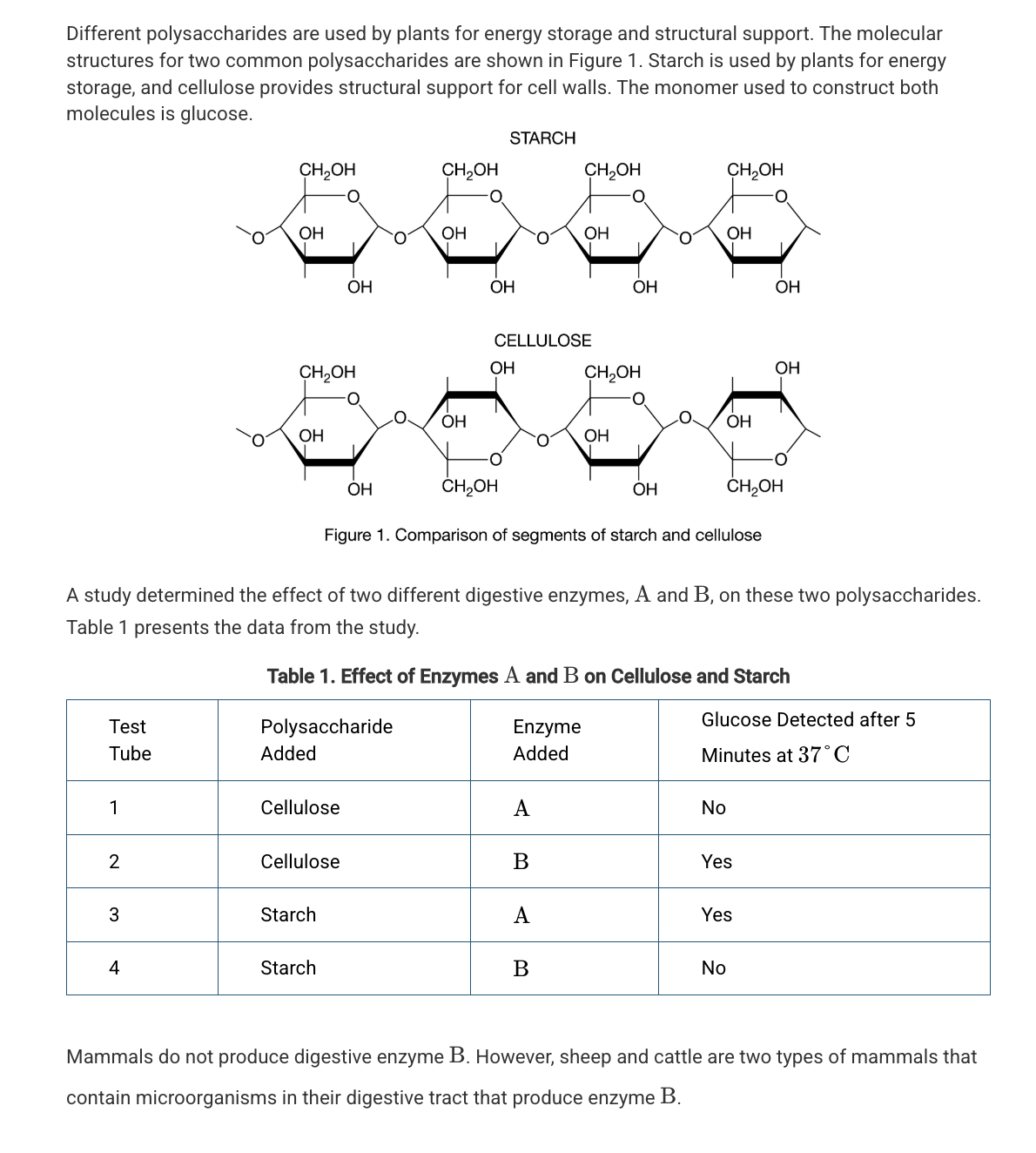
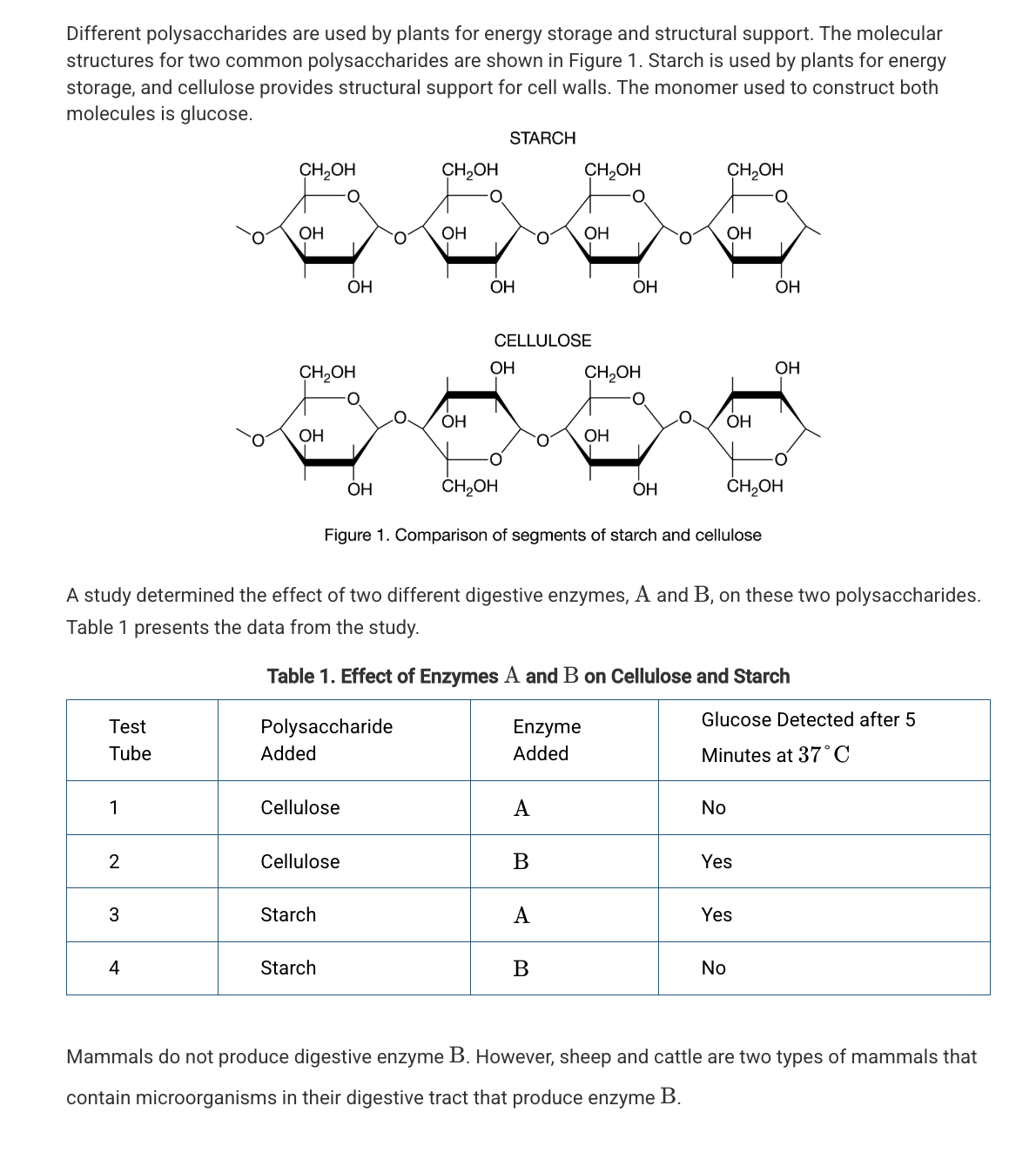
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best compares the atomic structures of starch and cellulose?
Starch and cellulose are composed of repeating glucose monomers; however, in cellulose every other glucose monomer is rotated 180 degrees.
Which of the following statements best describes the different functions of starch and cellulose in plants?
The differences in the assembly and organization of the monomers of these two polymers result in different chemical properties.
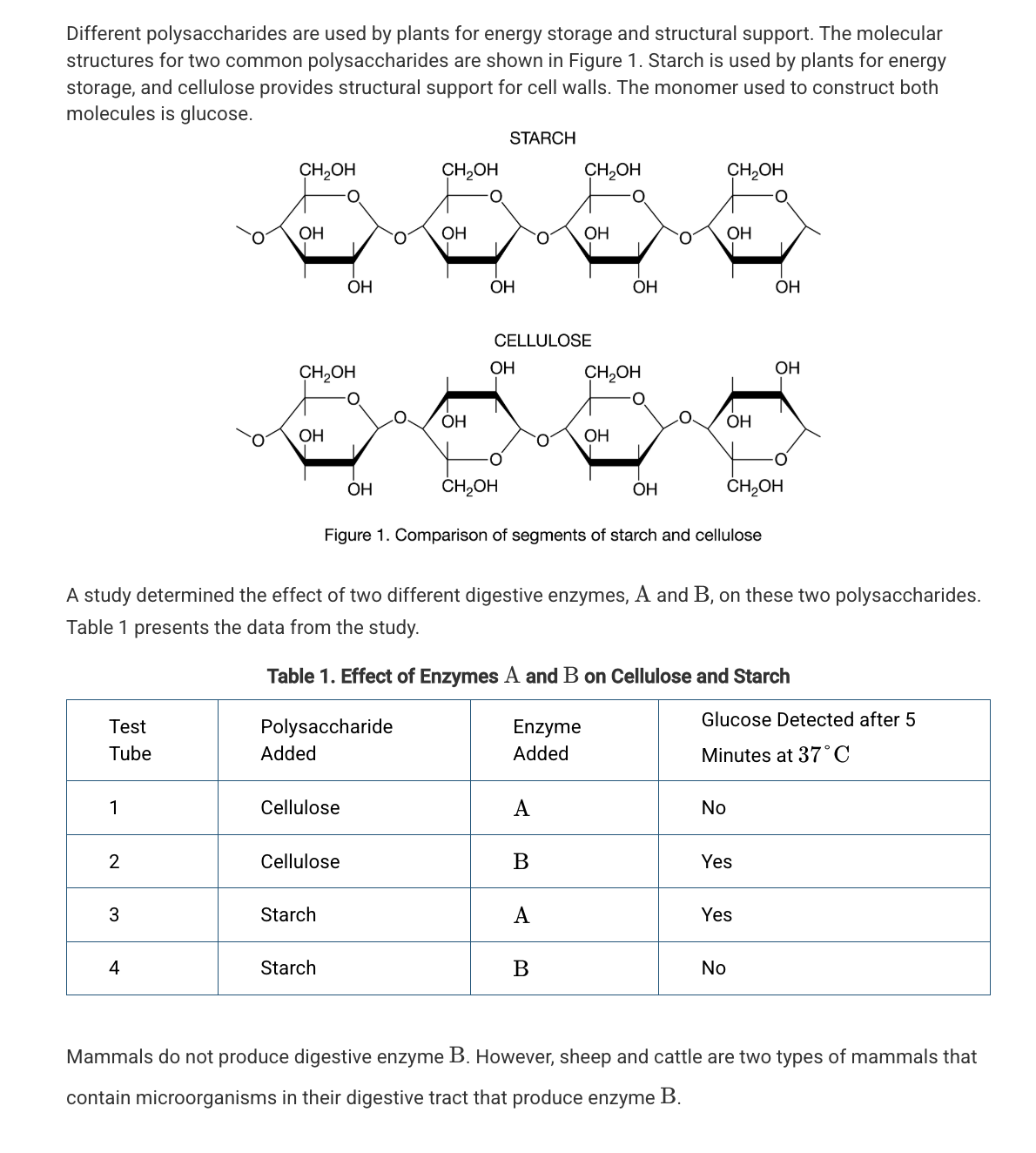
Which of the following correctly illustrates a dipeptide and an amino acid in the optimal position to form a tripeptide?
A
A chemical binds to a protein composed of a single polypeptide chain and prevents the formation of an alpha helix that is typically formed in the absence of the chemical. Which of the following best describes the effect the chemical has on the structure of the protein?
The secondary structure held together by hydrogen bonds is affected.
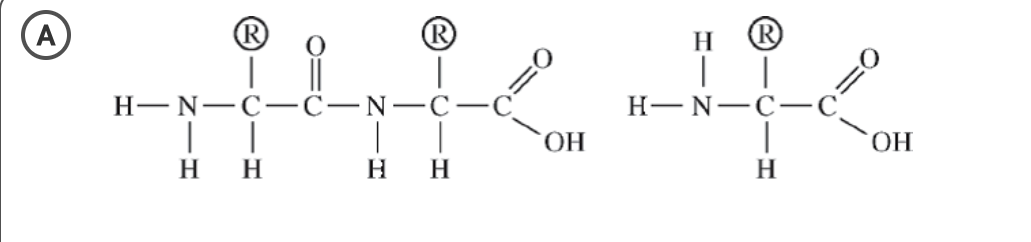
The molecular structures of linoleic acid and palmitic acid, two naturally occurring substances, are shown in the figure.
Based on the molecular structures shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature?
Palmitic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together.
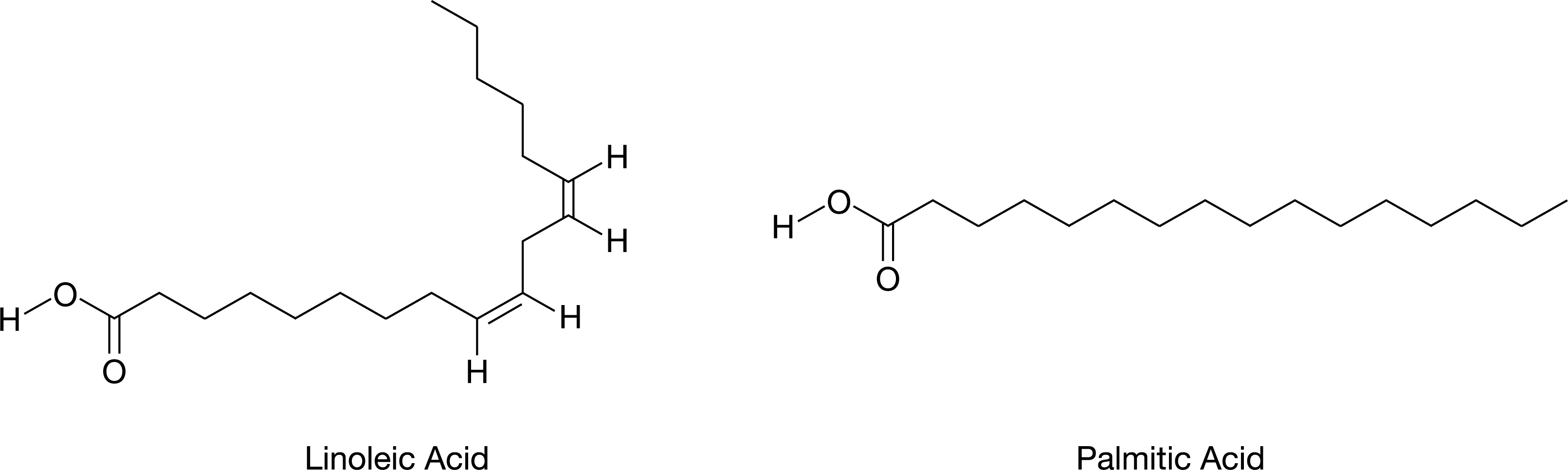
Water and ammonia interact to form hydrogen bonds, as represented in the figure.
Which statement best helps explain the formation of the hydrogen bond represented in the figure?
The nitrogen has a partial negative charge, and the hydrogen attached to the oxygen has a partial positive charge.
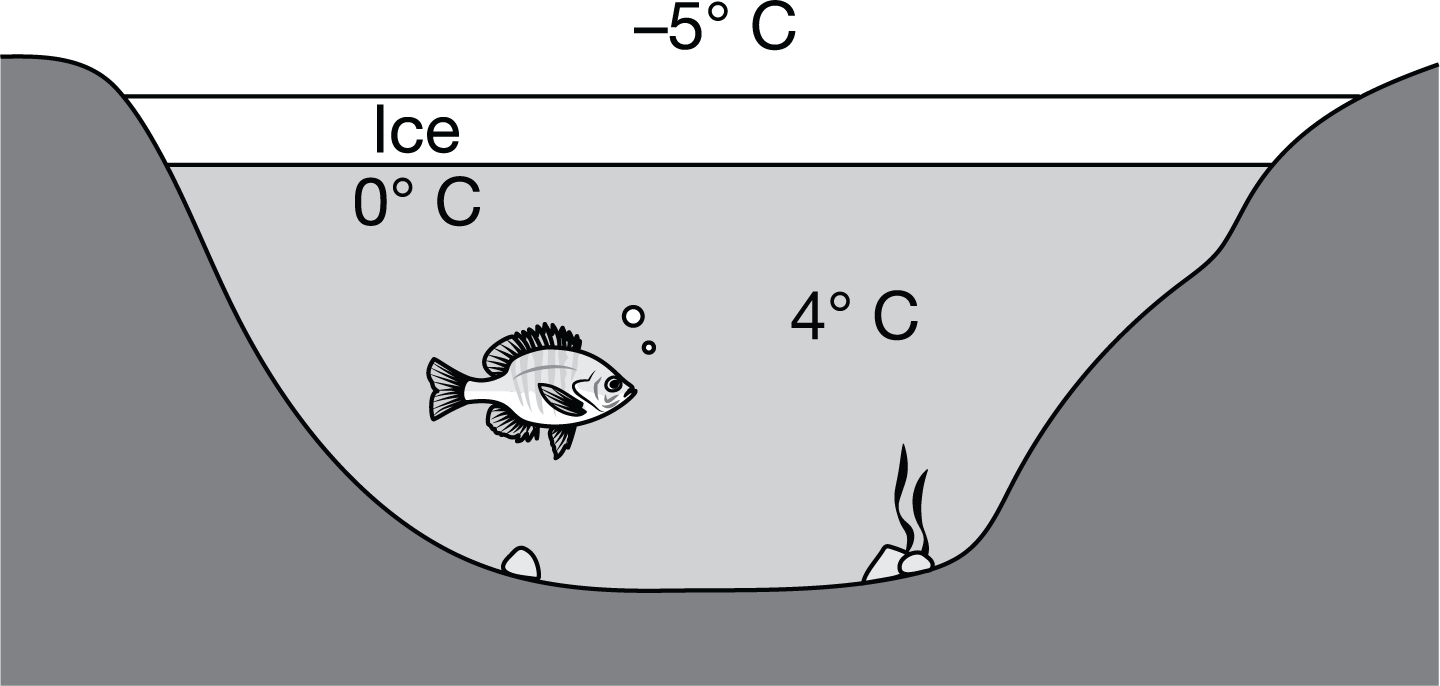
As shown in the diagram, when environmental temperatures drop below freezing, a layer of ice typically forms on the surface of bodies of freshwater such as lakes and rivers. Which of the following best describes how the structure of ice benefits the organisms that live in the water below?
The water molecules in ice are farther apart than those in liquid water, so the ice floats, maintaining the warmer, denser water at the lake bottom.
The process of hydrogenation is used in the food industry to convert lipids that are liquids at room temperature into solids at room temperature. The process involves the chemical addition of hydrogen atoms to the fatty acid tails of lipids, breaking some or all of the carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid tails. Which of the following best explains why hydrogenation converts liquid lipids to solid lipids?
Hydrogenation makes the fatty acids more saturated, enabling them to be more densely packed together.
One form of the genetic disorder lipodystrophy involves the lack of an enzyme that is required for the synthesis of triglycerides, a type of lipid. Triglycerides serve as an energy reserve in fat cells. Which of the following best describes the most likely effect of lipodystrophy on cell function?
There will be a decrease in fat storage in cells.
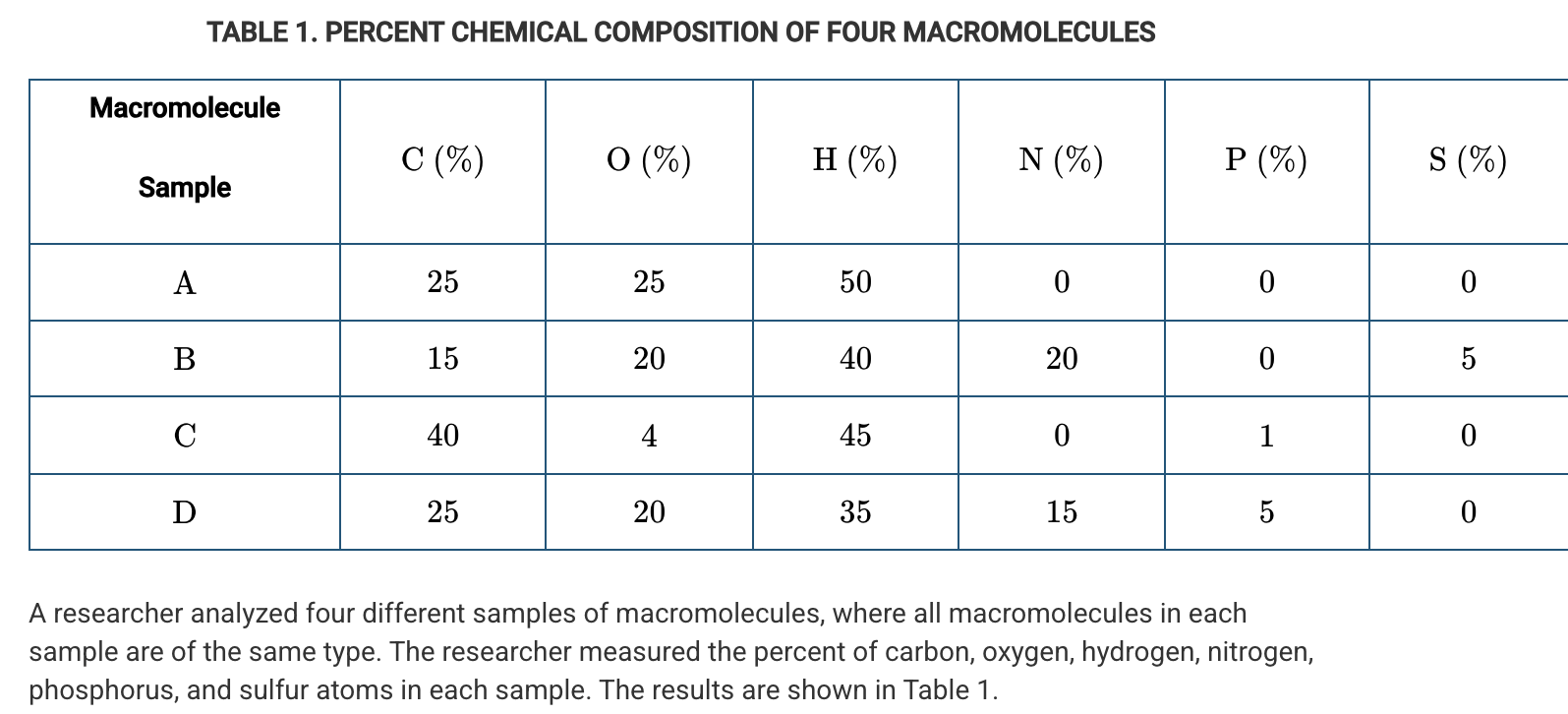
A researcher analyzed four different samples of macromolecules, where all macromolecules in each sample are of the same type. The researcher measured the percent of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur atoms in each sample. The results are shown in Table 1. Which of the following claims is best supported by the data in Table 1 ?
Sample B contains protein.
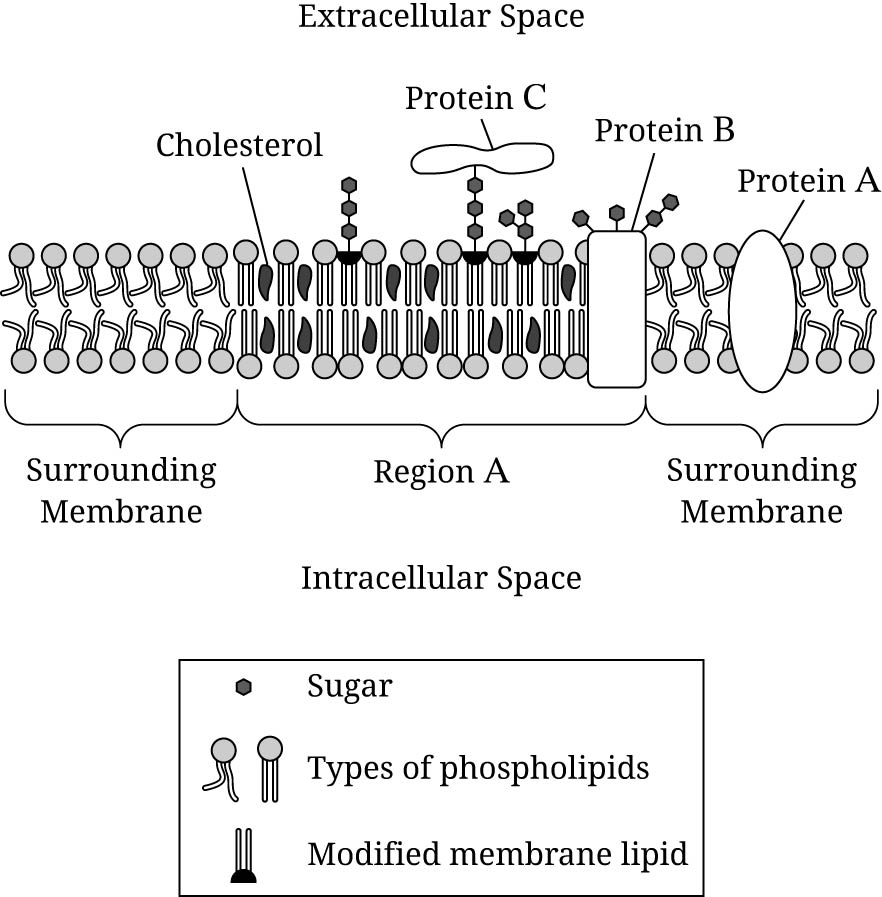
Researchers have identified regions, including region A in Figure 1, of the cell membrane that have a different density and composition than the surrounding membrane.
Which of the following best describes the chemical composition of the different types of macromolecules that make up the membrane represented in Figure 1?
All the molecules contain carbon and oxygen, but only some contain nitrogen.

Based on Figure 1, the amino acids in region A are most likely to have which of the following characteristics?
Most amino acids will be hydrophobic because they interact most favorably with the phospholipid tails.
Which of the following statements best describes the structure of complex carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides are connected by covalent bonds.
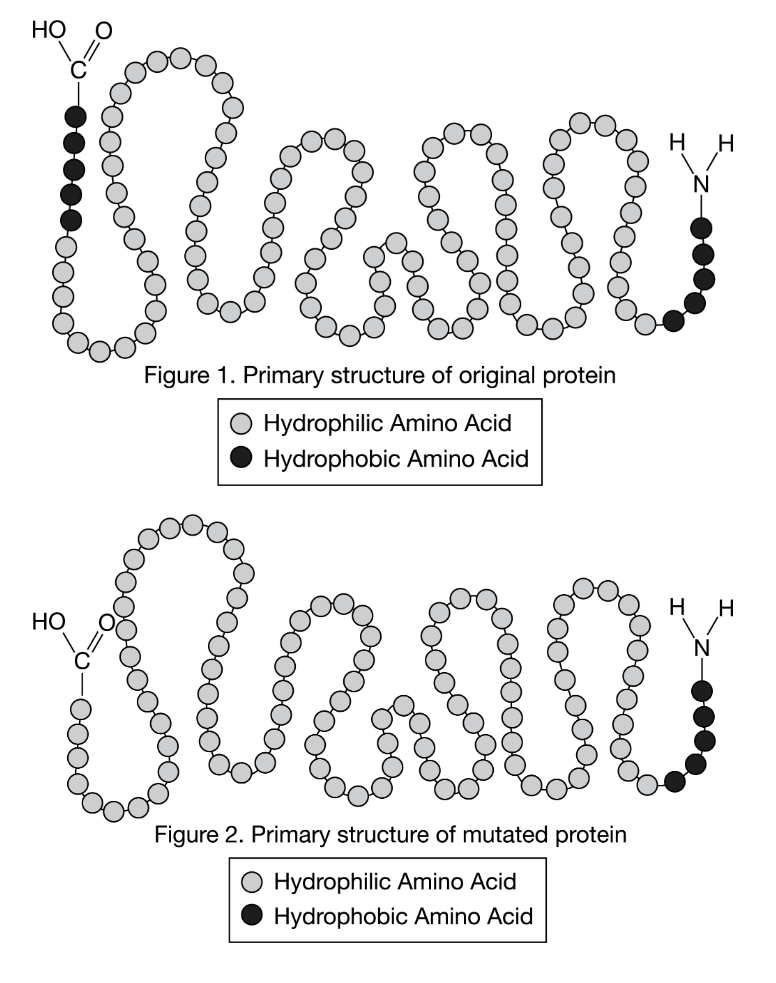
A small protein is composed of 110 amino acids linked together in a chain. As shown in Figure 1, the first and last five amino acids in the chain are hydrophobic (have nonpolar and uncharged R-groups), whereas the remaining 100 amino acids are hydrophilic (have charged or polar R-groups).
The nature of the R-group determines if the amino acid is hydrophobic or hydrophilic. A mutation results in the production of a version of the small protein that is only 105 amino acids long, as shown in Figure 2. Five of the hydrophobic amino acids are missing from one end of the chain.
Which of the following best depicts the tertiary structures of the two proteins in water? The diagrams in the options are not drawn to the same scale as those in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
A

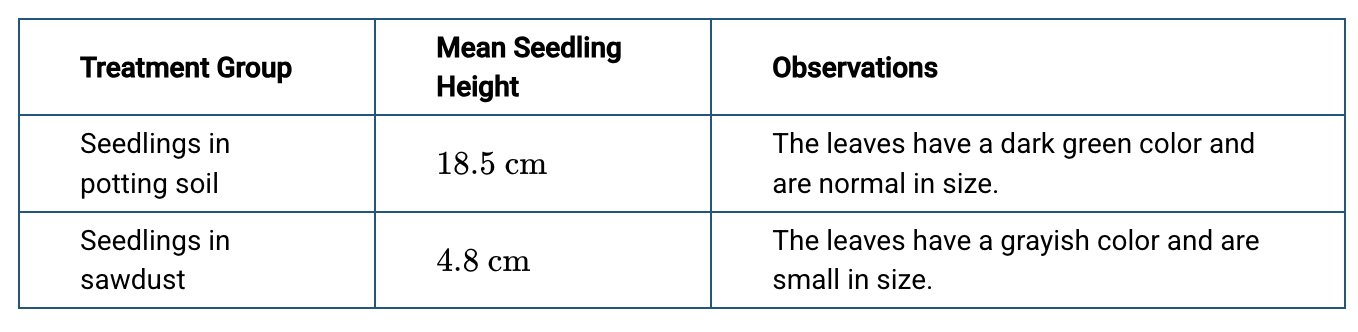
Students conducted a controlled experiment to investigate whether sawdust provides enough nutrients to support plant growth. The students separated ten nearly identical sunflower seedlings into two groups. They grew the seedlings in the first group in potting soil and the seedlings in the second group in sawdust composed mostly of cellulose. After twenty days, the students recorded observations about the seedlings in each group. The students’ observations are presented in the table.
The observed differences between the groups most likely resulted from differences in the ability of the seedlings to produce which of the following monomers?
C
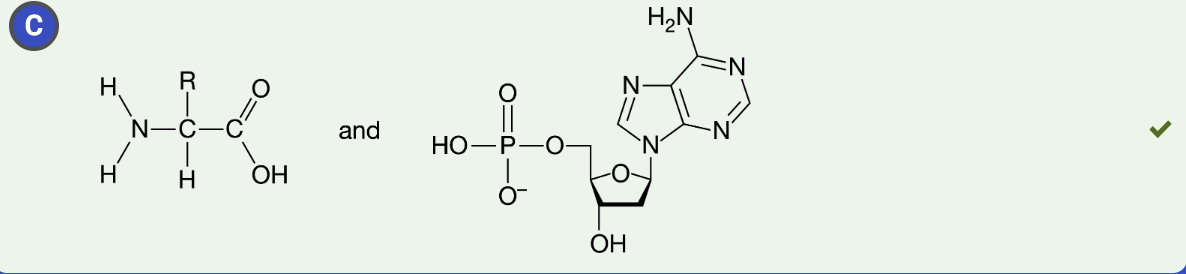
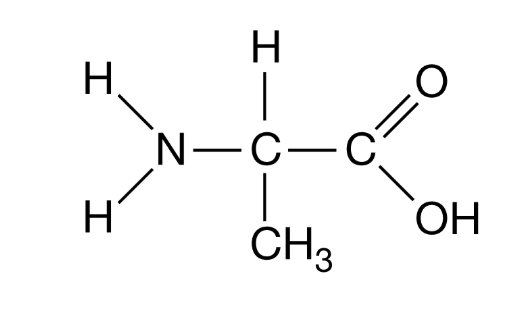
Figure 1. An amino acid
The amino acid in Figure 1 is found in a region of a polypeptide that folds away from water.
Methyl (CH3) group
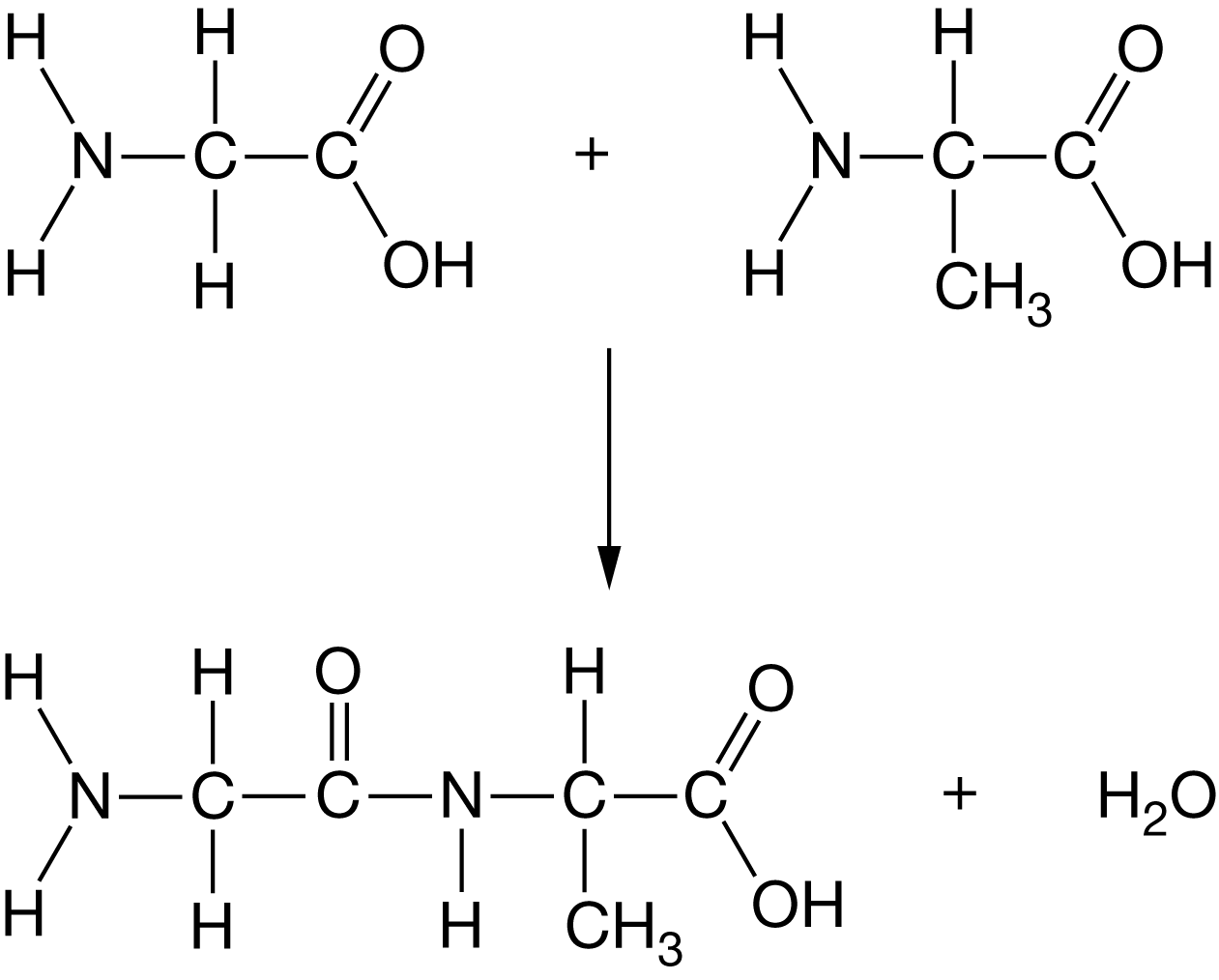
Figure 1 represents a common process that occurs in organisms.
Figure 1. Structural formula for a common biological reaction
Which of the following is an accurate description of the process shown in Figure 1 ?
The formation of a covalent peptide bond in a dehydration synthesis reaction
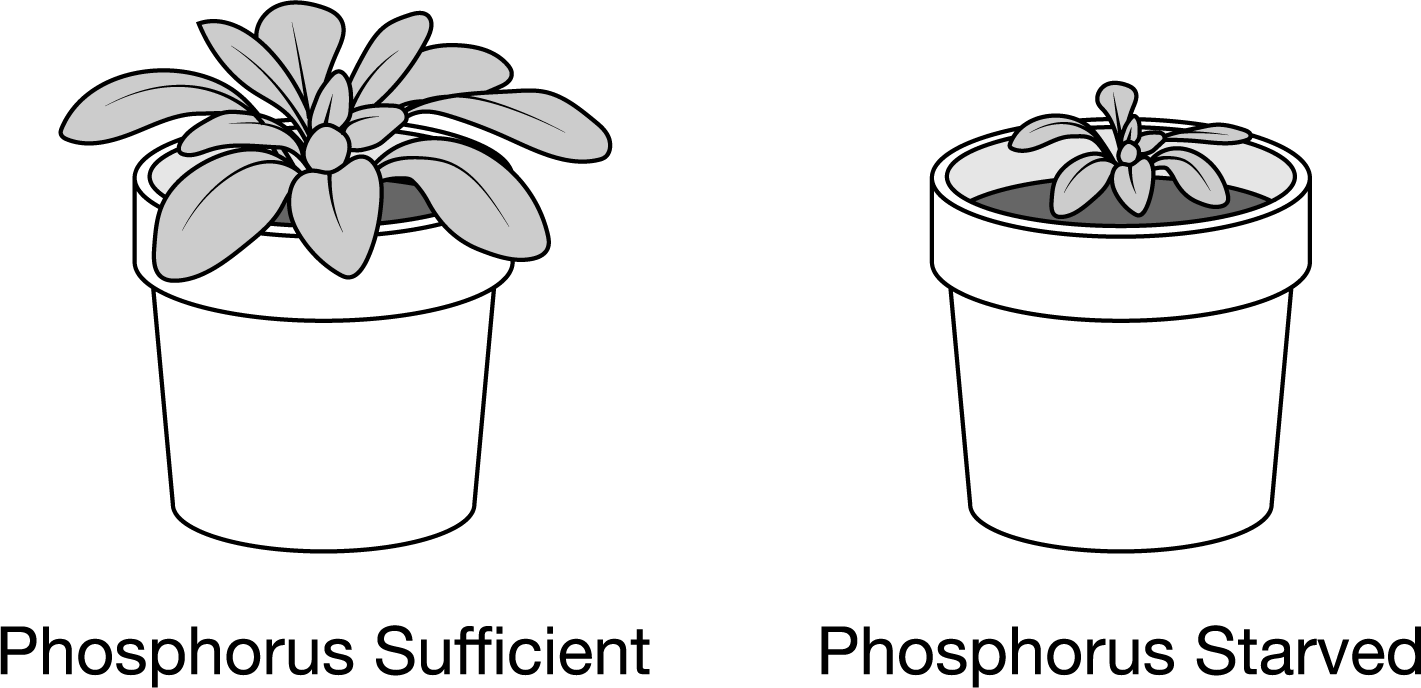

Phosphorous (P) is an important nutrient for plant growth. Figure 1 shows Arabidopsis thaliana plants grown under phosphorus‐sufficient (left) and phosphorus‐starved (right) conditions for six weeks.
Figure 1. Arabidopsis thaliana plants grown for six weeks. Which of the following is the most likely reason for the difference in leaf growth?
The phosphorus-starved plant was unable to synthesize both the required nucleic acids and lipids, limiting growth.
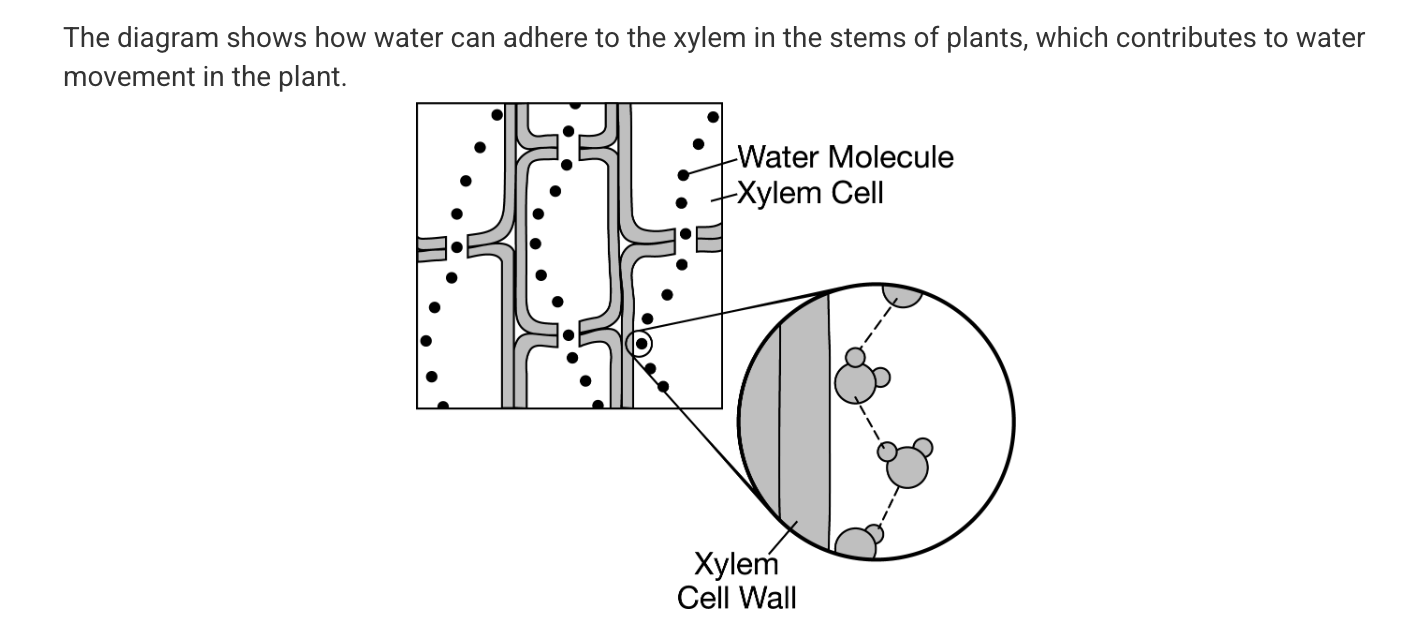
Which of the following best explains how water is able to move upward from the roots of a plant, through its xylem in the stem, and out to the leaves?
Water and the xylem are both polar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with the walls of the xylem.
Which of the following best describes the structures of carbohydrates?
They occur as monomers, chains of monomers, and branched structures.
Humans produce sweat as a cooling mechanism to maintain a stable internal temperature.
Which of the following best explains how the properties of water contribute to this physiological process?
The high heat of vaporization of water allows the body to remove excess heat through a phase change of water from liquid to gas.
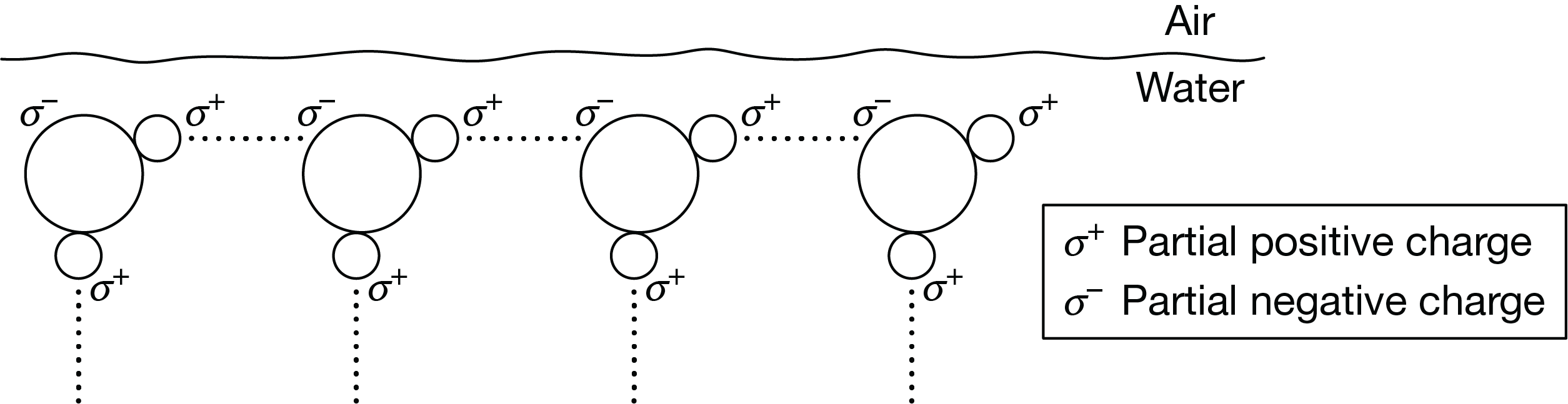
Figure 1 is a diagram of water molecules at the air-water interface at the surface of a pond.
Based on Figure 1, which of the following best describes how the properties of water at an air-water interface enable an insect to walk on the water's surface?
Hydrogen bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide surface tension, which allows the water surface to deform but not break under the insect.
Which of the following best describes how amino acids affect the tertiary structure of a protein?
The interactions of the different R-groups with other R-groups and with their environment determine the tertiary structure of the protein.
Researchers analyzed the composition of cell membranes of bacteria living in different environments. Thermophiles are bacteria that live at extremely high temperatures, typically at or above . Which of the following best predicts the effect of a greater proportion of saturated fatty acids, as compared with unsaturated fatty acids, on the stability of the cell membrane in thermophiles?
A greater proportion of saturated fatty acids leads to increased membrane stability at higher temperatures because saturated fatty acids pack tightly together.
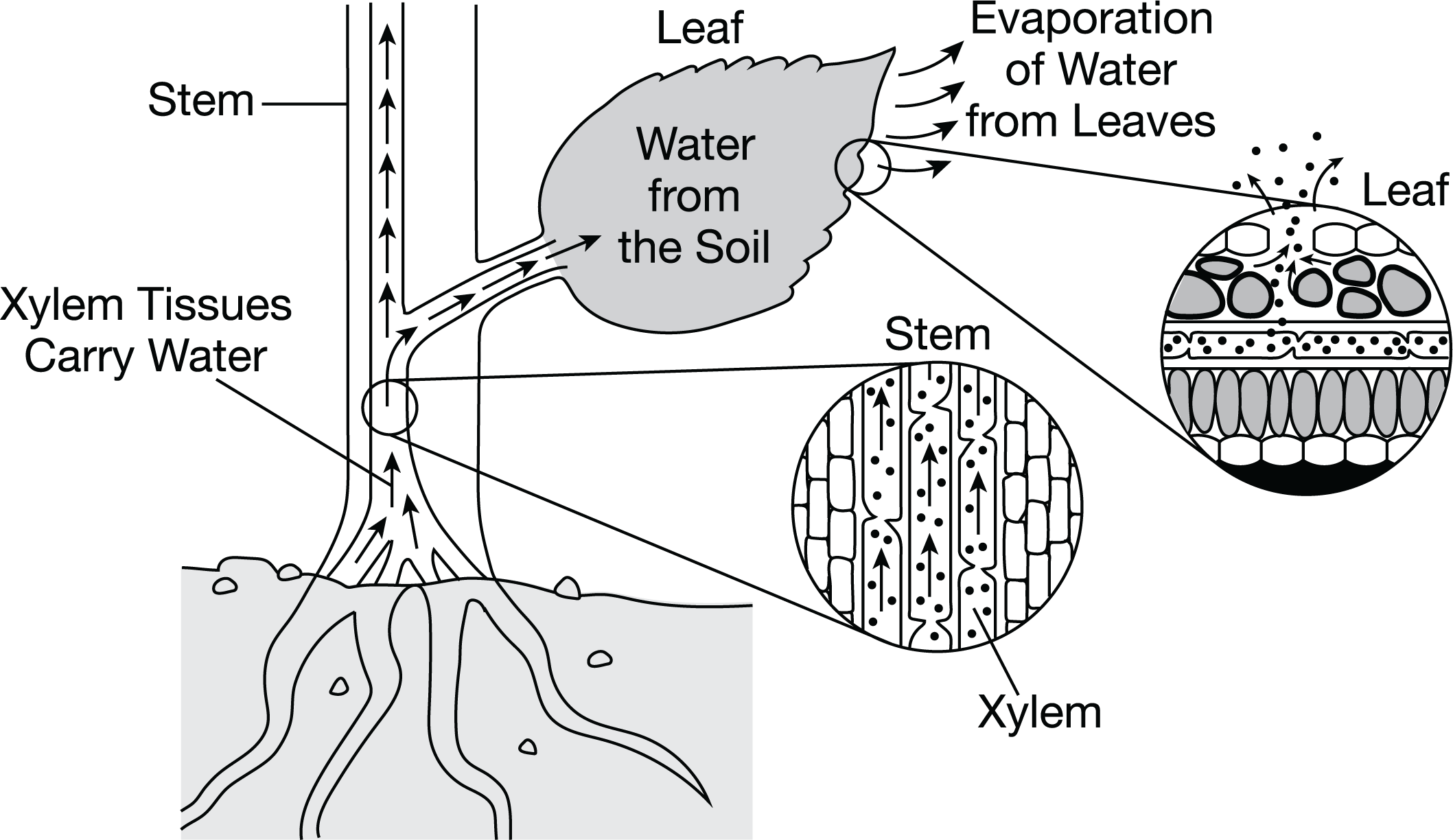
In vascular plants, water flows from root to leaf via specialized cells called xylem. Xylem cells are hollow cells stacked together like a straw. A student explains that evaporation of water from the leaf pulls water up from the roots through the xylem, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Model of water movement through the xylem, with magnified models of water movement in the stem and leaf.
Which statement describes how water is pulled up through the xylem to the leaves of the plant?
As water exits the leaf, hydrogen bonding between water molecules pulls more water up from below.
Researchers claimed that a particular organelle originated from a free-living prokaryotic cell that was engulfed by a larger cell, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. A model showing a cell engulfing a smaller cell Which of the following provides evidence to best support the researchers’ claim?
The organelle has a double membrane.
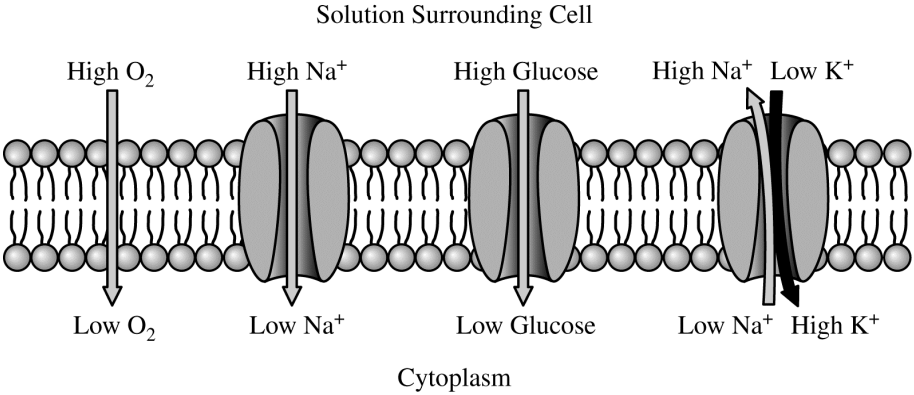
The manner in which several different ions and molecules move through a cell membrane is shown in the diagram above. For each ion or molecule, the relative concentration on each side of the membrane is indicated. Which of the following accurately describes one of the movements taking place?
Na+ transport out of the cell requires ATP hydrolysis.
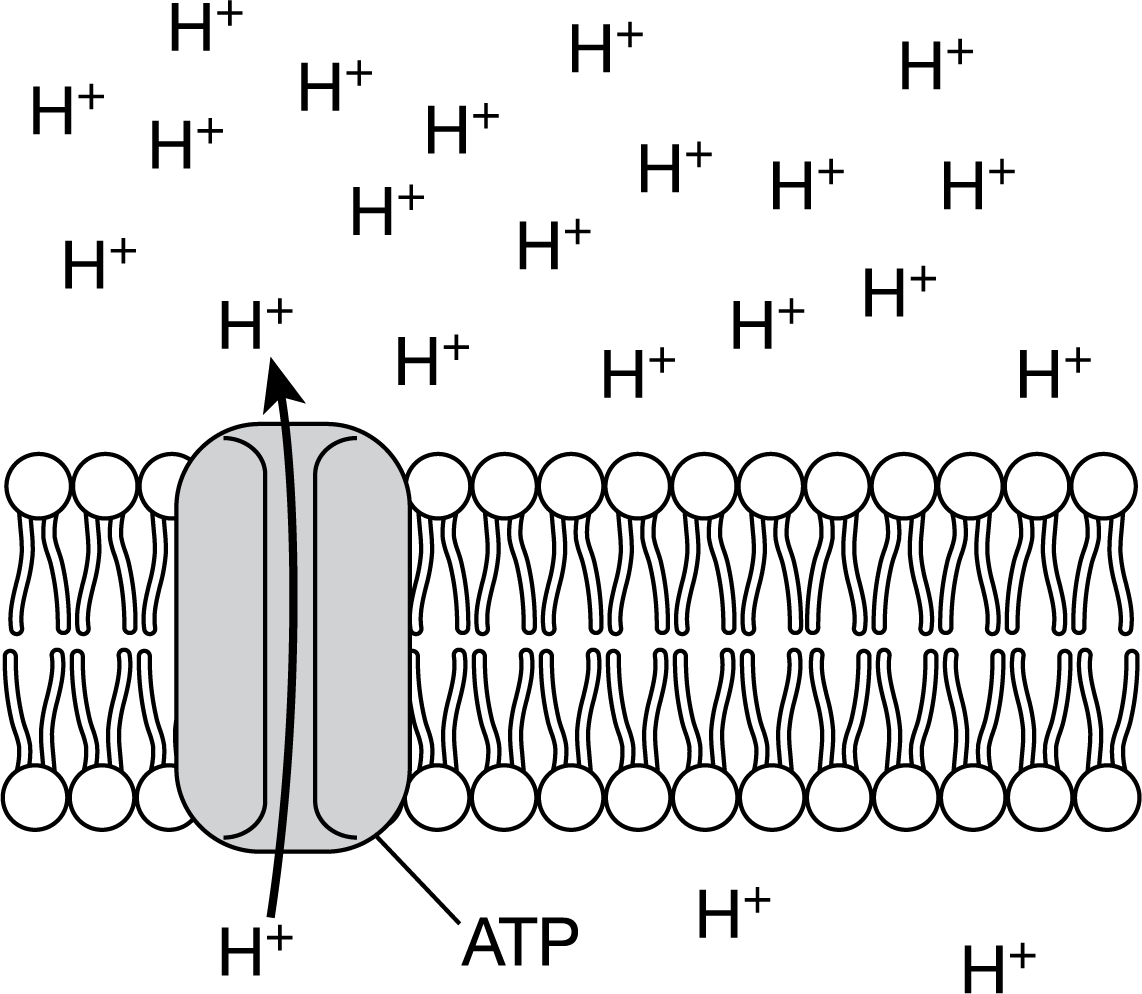
The illustration shows the active transport of hydrogen ions through a membrane protein.
Which of the following best predicts the effect of not having ATP available to supply energy to this process?
H+ ions will stop moving through the protein.
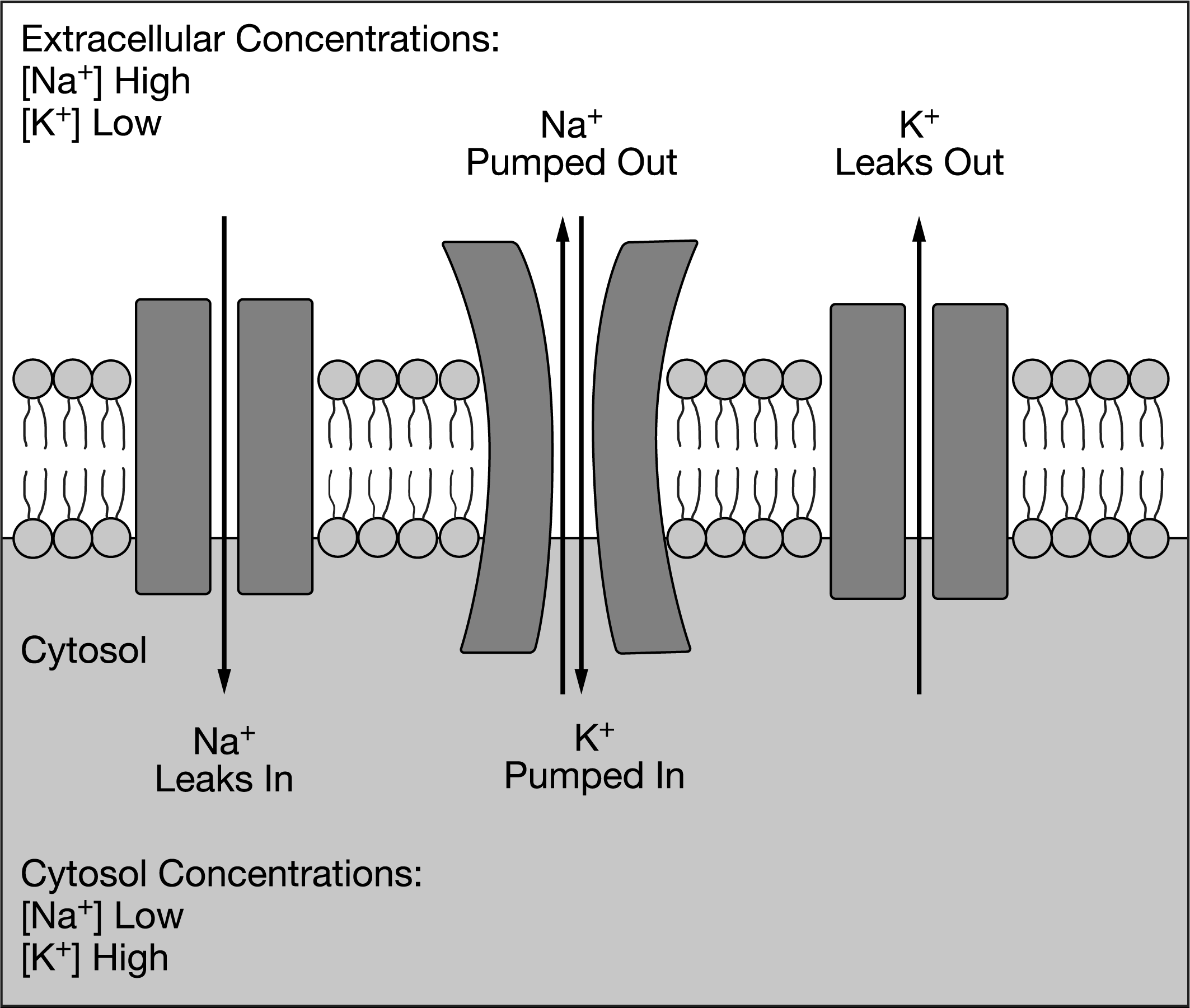
Some membrane proteins help maintain the concentrations of ions inside a cell by transporting the ions across the cell’s plasma membrane. Other membrane proteins form pores in the plasma membrane through which the ions can diffuse. A model showing the influence of membrane proteins on the movement of sodium (NA+) and potassium (K+) ions across a plasma membrane is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Section of a cell’s plasma membrane, showing ion concentrations and membrane proteins
Based on the model presented in Figure 1, which of the following changes will most likely result from a depletion of available ATP stores inside the cell?
The NA+ concentration inside the cell will increase.
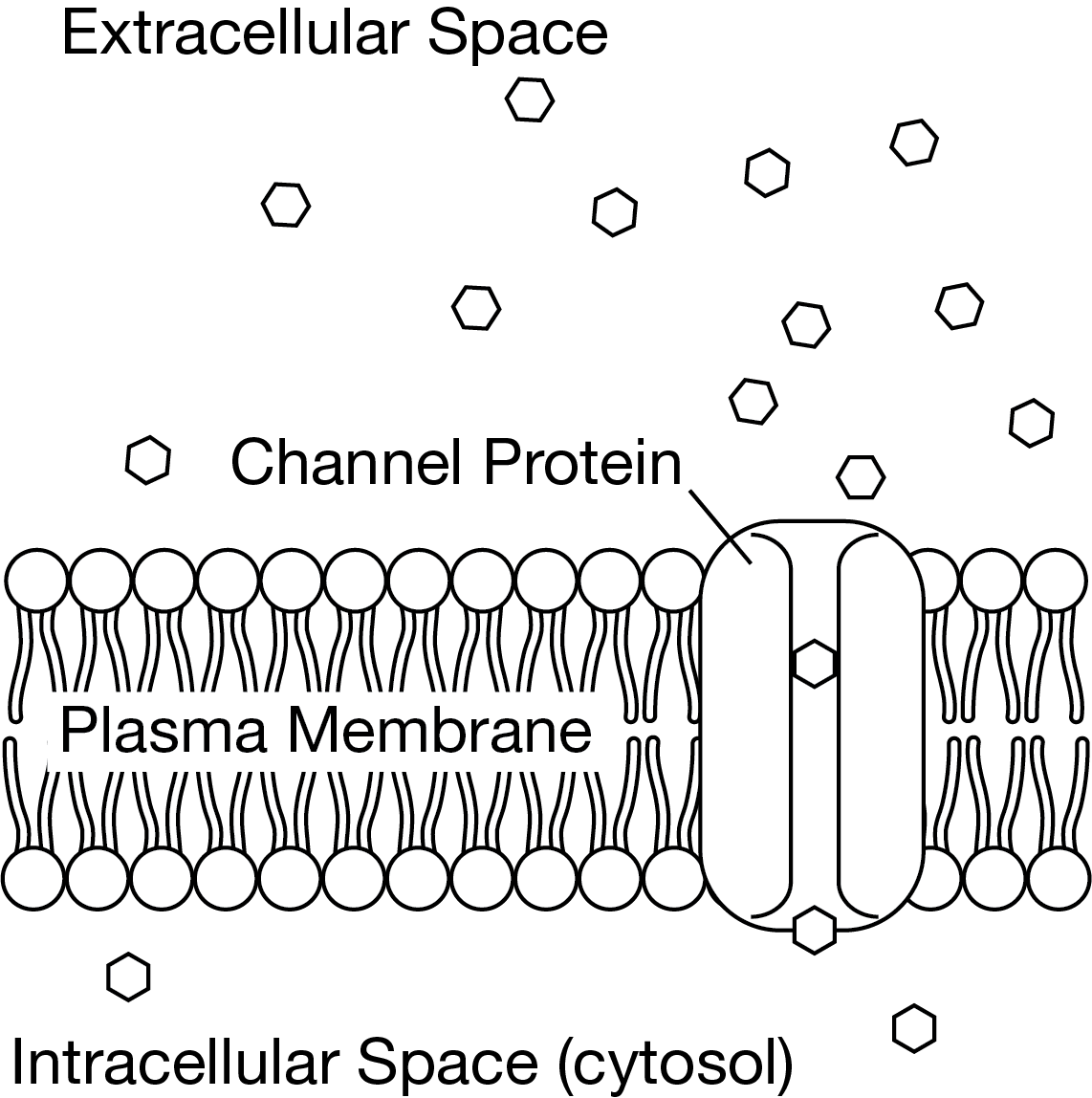
Figure 1 shows a model of how a channel protein influences the movement of a particle across a cell's plasma membrane.
An investigator wants to understand whether a newly found membrane protein is involved in membrane transport of a certain particle.
Which investigation will help determine whether the new membrane protein is a channel protein involved in membrane transport?
Add more of the proteins to the plasma membrane and measure the rate of the particle movement
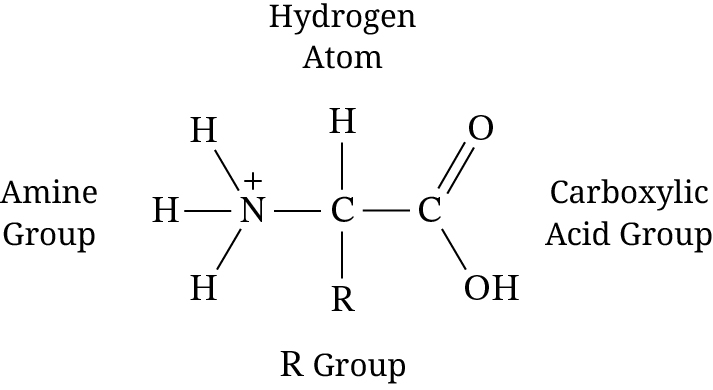
Which of the following amino acid components shown in Figure 1 best determines the interaction between an embedded protein and the hydrophobic regions of the cell membrane?
The R group bonded to the central carbon
Aquaporins are channel proteins that facilitate the transport of water across the cell membrane. One group of researchers hypothesizes that without functional aquaporins, no water will be able to enter the cell. A different group proposes an alternative hypothesis, stating that even with nonfunctional aquaporins, a small amount of water will still cross the cell membrane. An experiment is set up in which plant cells with mutated (nonfunctional) aquaporins and plant cells with normally functioning aquaporins are both placed in distilled water. Which of the following data would support the alternative hypothesis?
Cells with mutated aquaporins exhibit moderate turgor pressure and are hypertonic.
A scientist designed an experiment to test an artificial membrane that mimics the phospholipid bilayer of a cell. The scientist built a tube that was divided by an artificial membrane and filled with distilled water. The scientist put a known amount of a protein into the water on one side of the membrane. After some time, the scientist measured the concentration of the protein on either side of the membrane but found that there had been no change.
Which of the following experimental changes would allow the scientist to observe transport of a solute across the artificial membrane?
Use a small, nonpolar solute instead of a protein
If ATP breakdown (hydrolysis) is inhibited, which of the following types of movement across cell membranes is also inhibited?
Passage of a solute against its concentration gradient
ATPase requires the use of ATP to move ions from one side of a cell membrane to another. The amino acid cysteine is important to the function of ATPase. A change in the cysteine prevents the ATPase from functioning. Which of the following best describes what will happen to the movement of ions if there is a change in the cysteine of ATPase?
The electrochemical gradient will change.
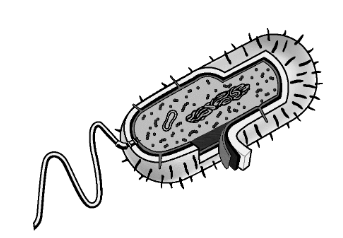
The diagram above represents a typical rod-shaped bacterium. Which of the following best describes a feature shown in the diagram that is unique to archaea and bacteria?
The organism does not have a nuclear membrane surrounding its genetic material.
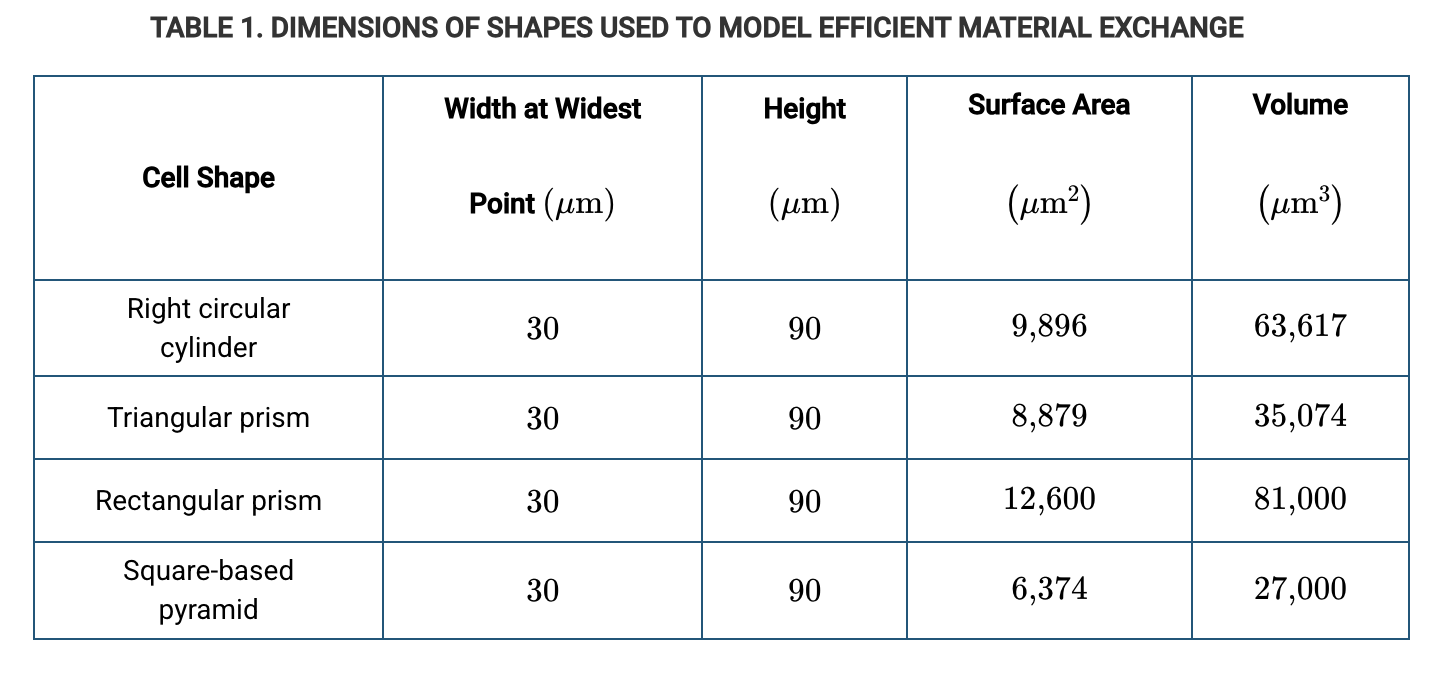
In an experiment, the efficiency of oxygen exchange across the plasma membrane is being assessed in four artificial red blood cells. The table above lists some properties of those artificial cells. Other conditions being equal, which artificial cell is predicted to be the most efficient in exchanging oxygen with the environment by diffusion?
Triangular prism
Plant cell walls are composed of cellulose, while fungal cell walls are composed of chitin. A group of scientists hypothesize that this difference means the cell wall has largely different functions in plant cells and fungal cells. Alternatively, another group of scientists hypothesize that despite their biochemical differences, plant and fungal cell walls serve similar functions. Which of the following observations would best support the alternative hypothesis described above?
In both plant cells and fungal cells, the cell wall surrounds the outside of the cell membrane.
Cholesterol is an important component of animal cell membranes. Cholesterol molecules are often delivered to body cells by the blood, which transports the molecules in the form of cholesterol-protein complexes. The complexes must be moved into the body cells before the cholesterol molecules can be incorporated into the phospholipid bilayers of cell membranes. Based on the information presented, which of the following is the most likely explanation for a buildup of cholesterol molecules in the blood of an animal?
The animal’s body cells are defective in endocytosis.
Which of the following best describes the primary mechanism of transport whereby carbon dioxide moves from inside a cell to outside the cell?
Carbon dioxide passively diffuses between the membrane lipids.
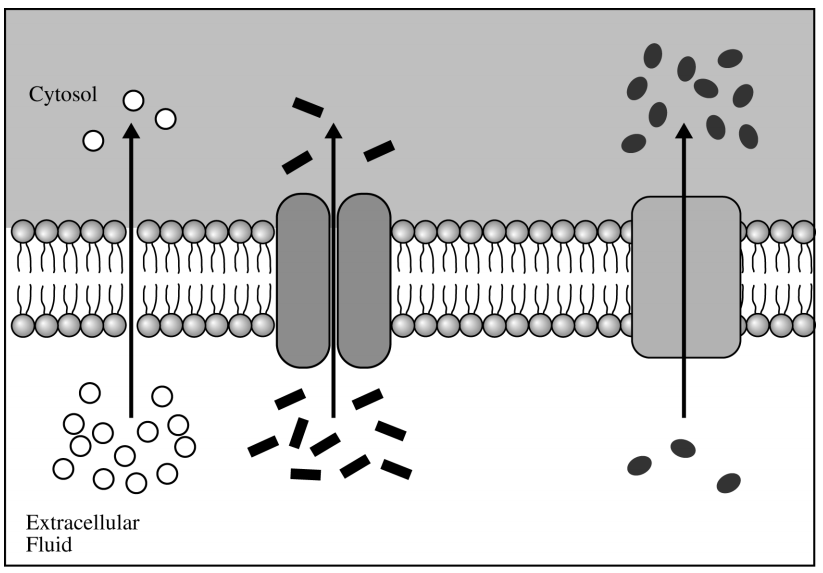
Which of the following scientific questions is most relevant to the model represented in the figure above?
Which molecular substance is actively transported across the plasma membrane?
Which of the cell types represented in Table 1 is most efficient at acquiring nutrients by diffusion?
Cell type 2
Which of the following best describes a cell that is likely to have an extensive Golgi complex?
A stomach cell that produces and releases digestive enzymes
A student used a microscope to observe a wet-mount slide of red onion epidermal cells that were suspended in a 1% NaCl solution. The student then added a 15% NaCL solution to the slide and observed the changes that occurred.
Original Wet-Mount Slide: normal cells
After Adding 15% NaCl: cells shriveled
Which of the following most directly explains the changes in the cells?
The movement of water from the central vacuoles of the cells into the solution

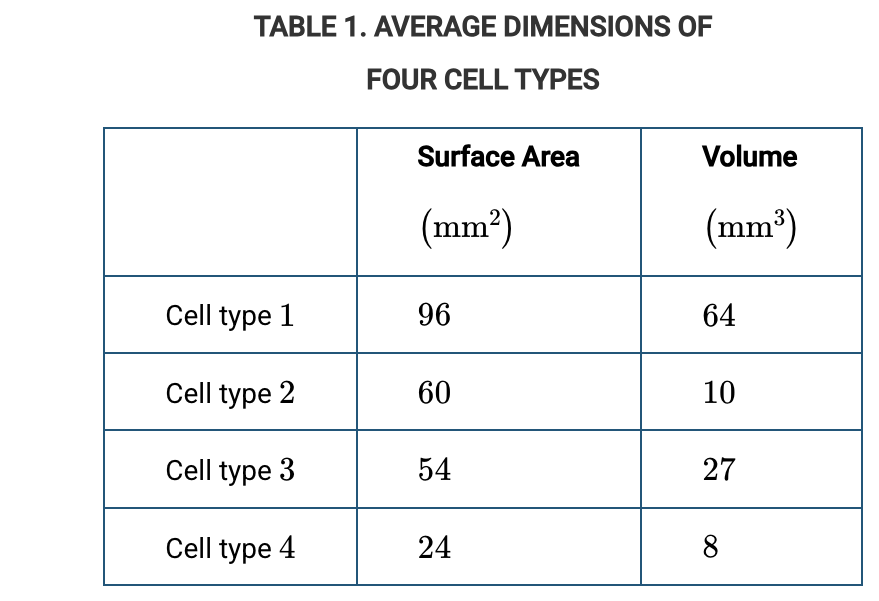
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF. I
Which of the following describes why a glucose transporter is needed to move glucose into the cell?
Glucose is large and polar and cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer.
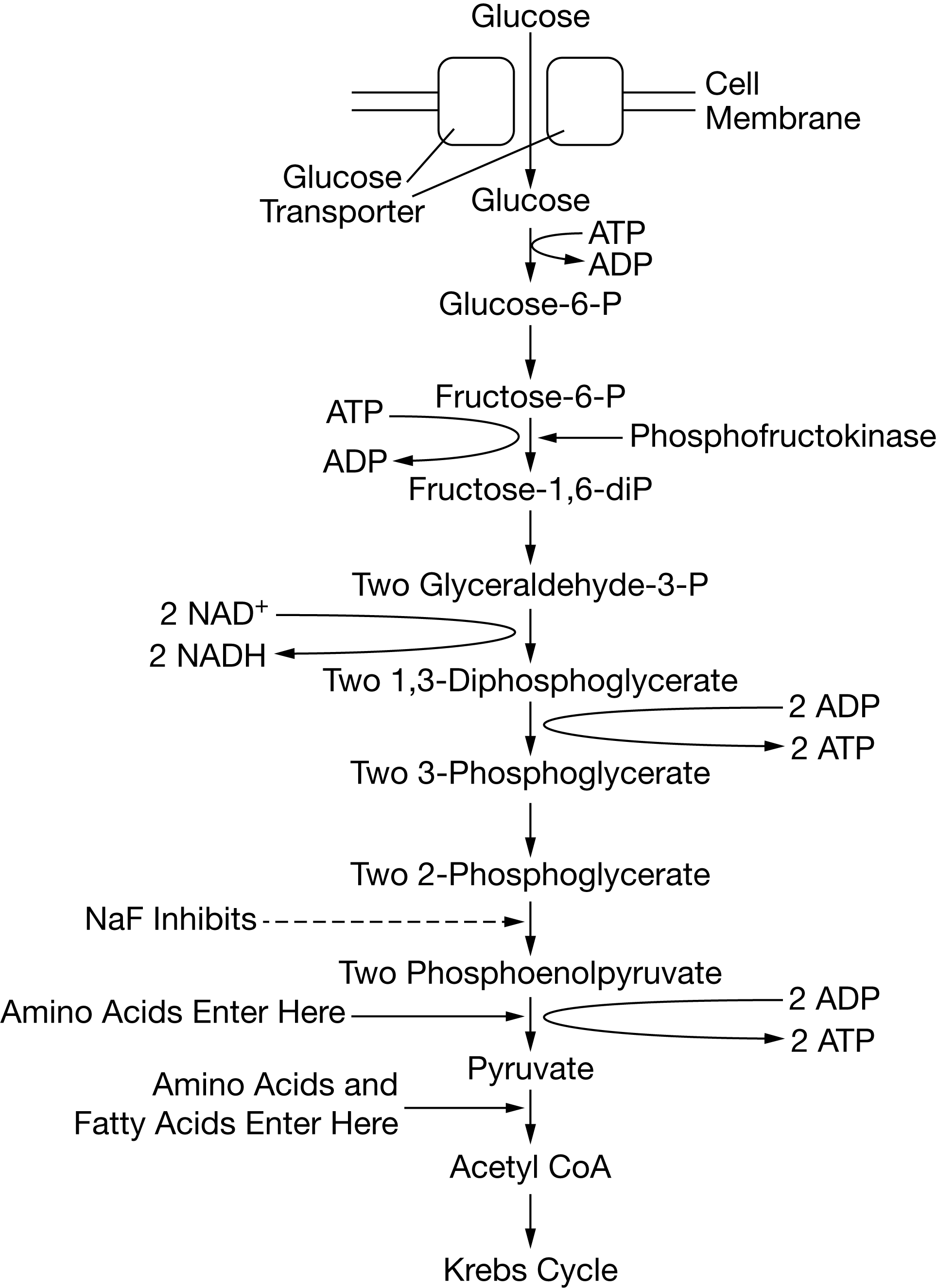
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF
If NaF is added to cells undergoing cellular respiration, which of the following will most likely accumulate in the cells?
2-phosphoglycerate
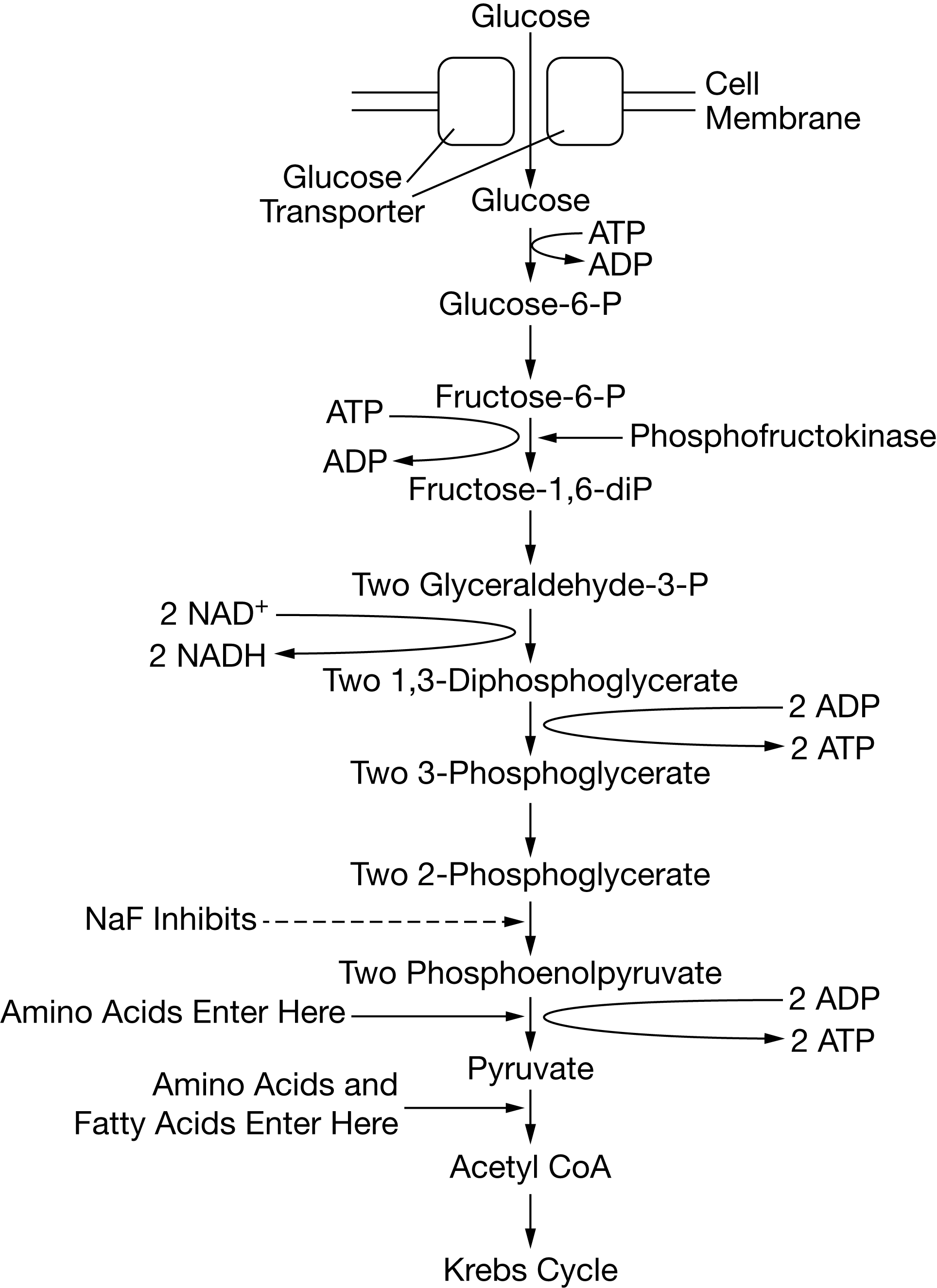
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF
Based on Figure 1, the net number of ATP molecules produced during glycolysis from the metabolism of a single glucose molecule is closest to which of the following?
2
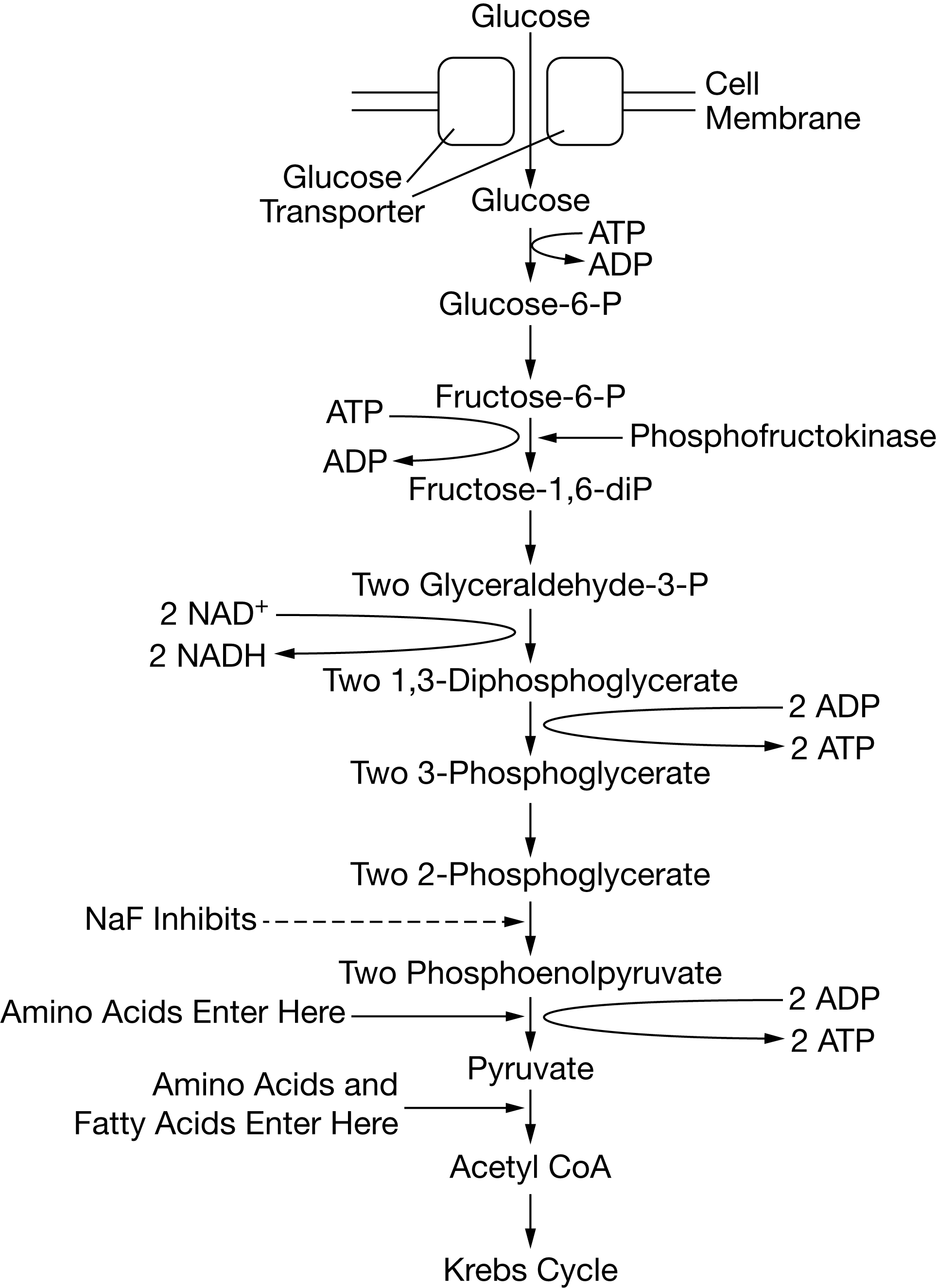
Certain chemicals, including sodium fluoride (NaF), are capable of inhibiting specific steps of glycolysis. Figure 1 shows the steps of the glycolysis pathway, indicating where various macromolecules enter the pathway as well as the specific reaction inhibited by NaF
An increase in the concentration of protons in the cytosol will most likely have which of the following effects on glycolysis?
glycolytic enzymes will denature as a result of the increased H+ raised to the positive power concentration
Which of the following statements best supports the claim that certain organelles within eukaryotic cells evolved from free-living prokaryotic cells?
Some organelles contain their own DNA that is more similar to prokaryotic DNA in structure and function than to the eukaryotic DNA found in the cell's nucleus..
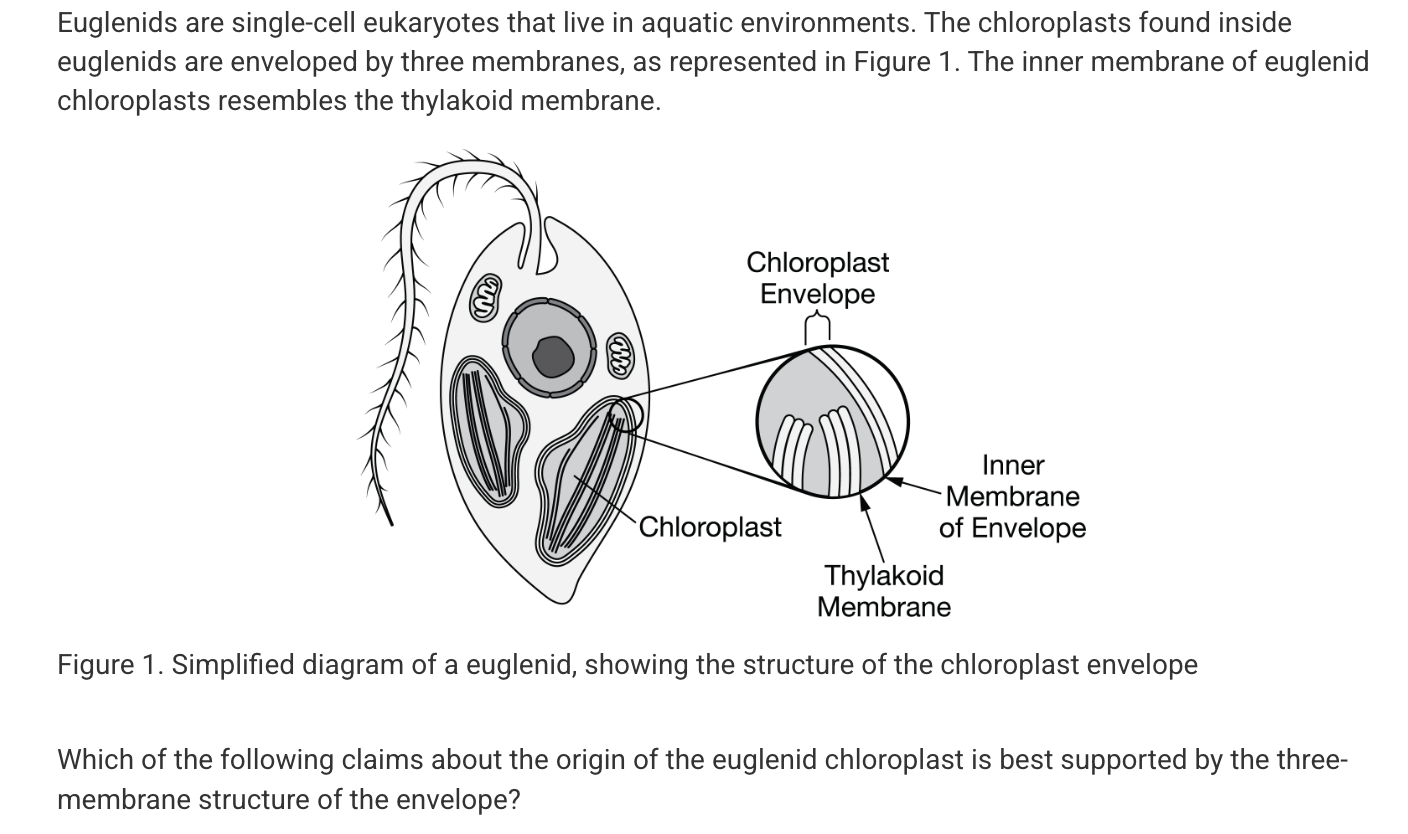
It originated from the incorporation of a photosynthetic prokaryote into a eukaryotic cell by two endosymbiotic events.
Organelles such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum have membranes that compartmentalize reactions and other metabolic processes. To function properly, the organelles must move substances across their membranes. Which of the following statements describes a feature shared by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum that increases the efficiency of their basic functions?
They have highly folded membranes.
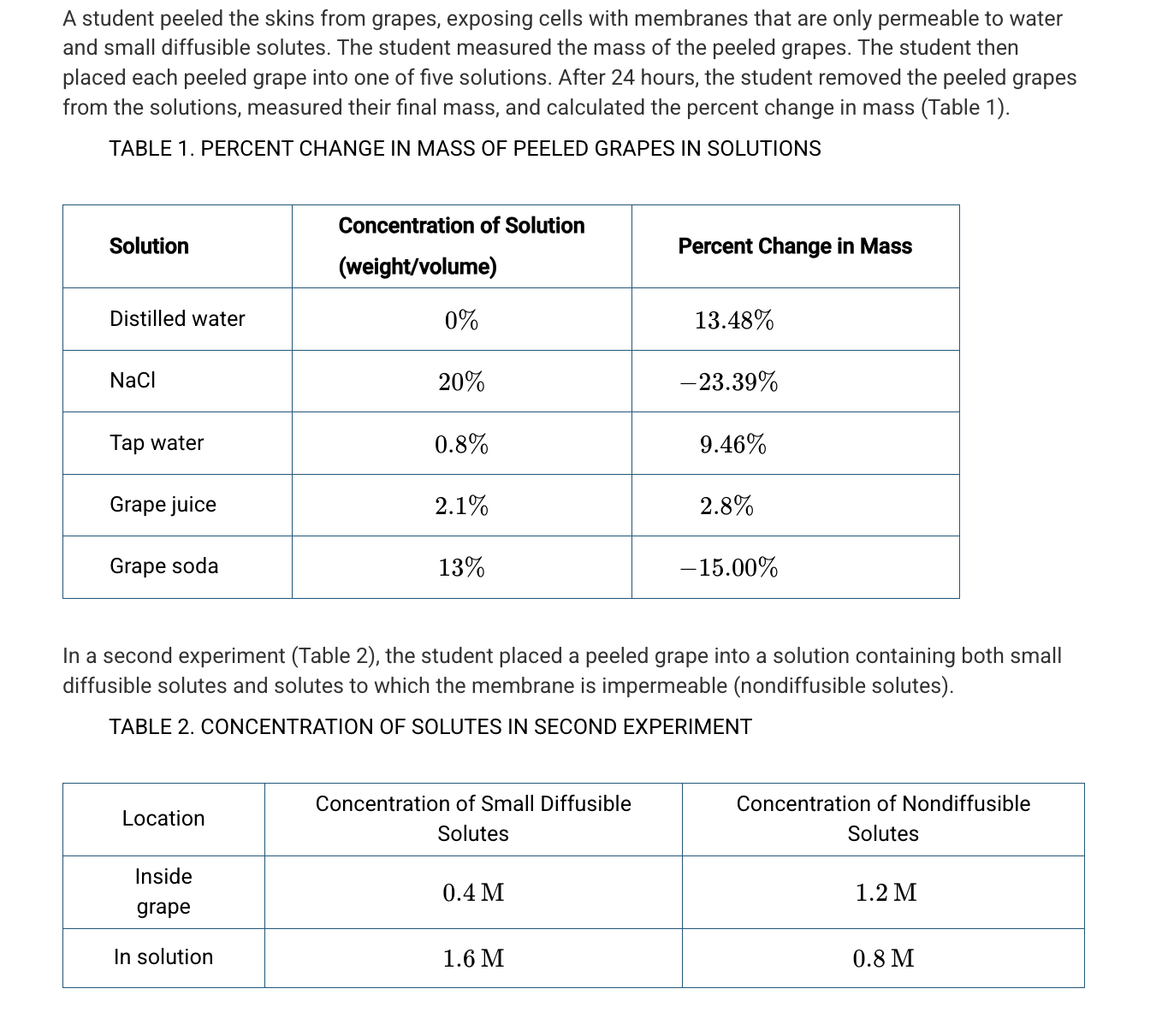
Based on Table 1, which of the following best explains the difference in water potential between certain solutions and the grapes?
Grape soda and NaCl have a lower water potential because these two solutions caused the grape to lose water.
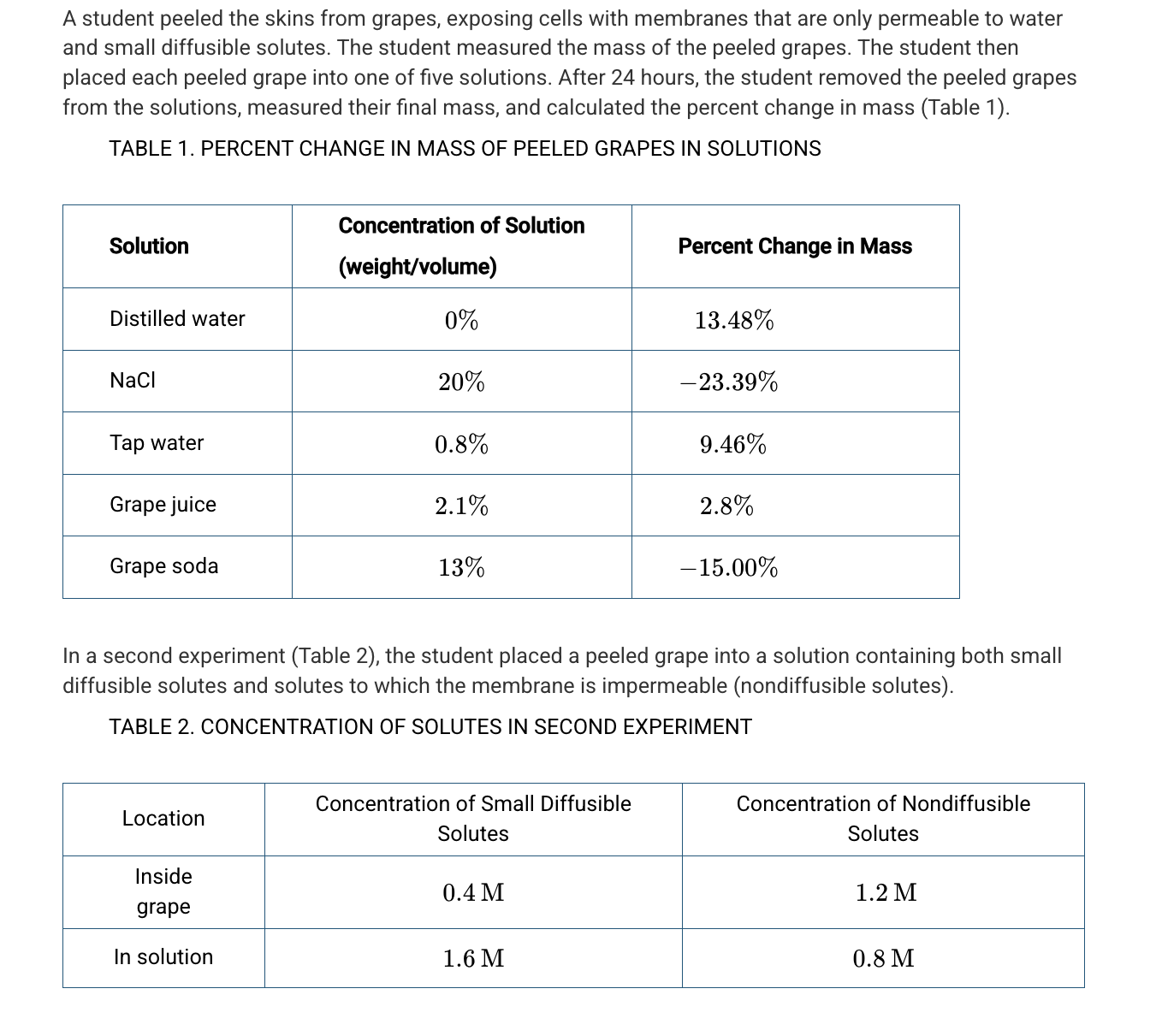
Based on Table 1, which of the following percentages is closest to the solute concentration of the grape?
5.5%
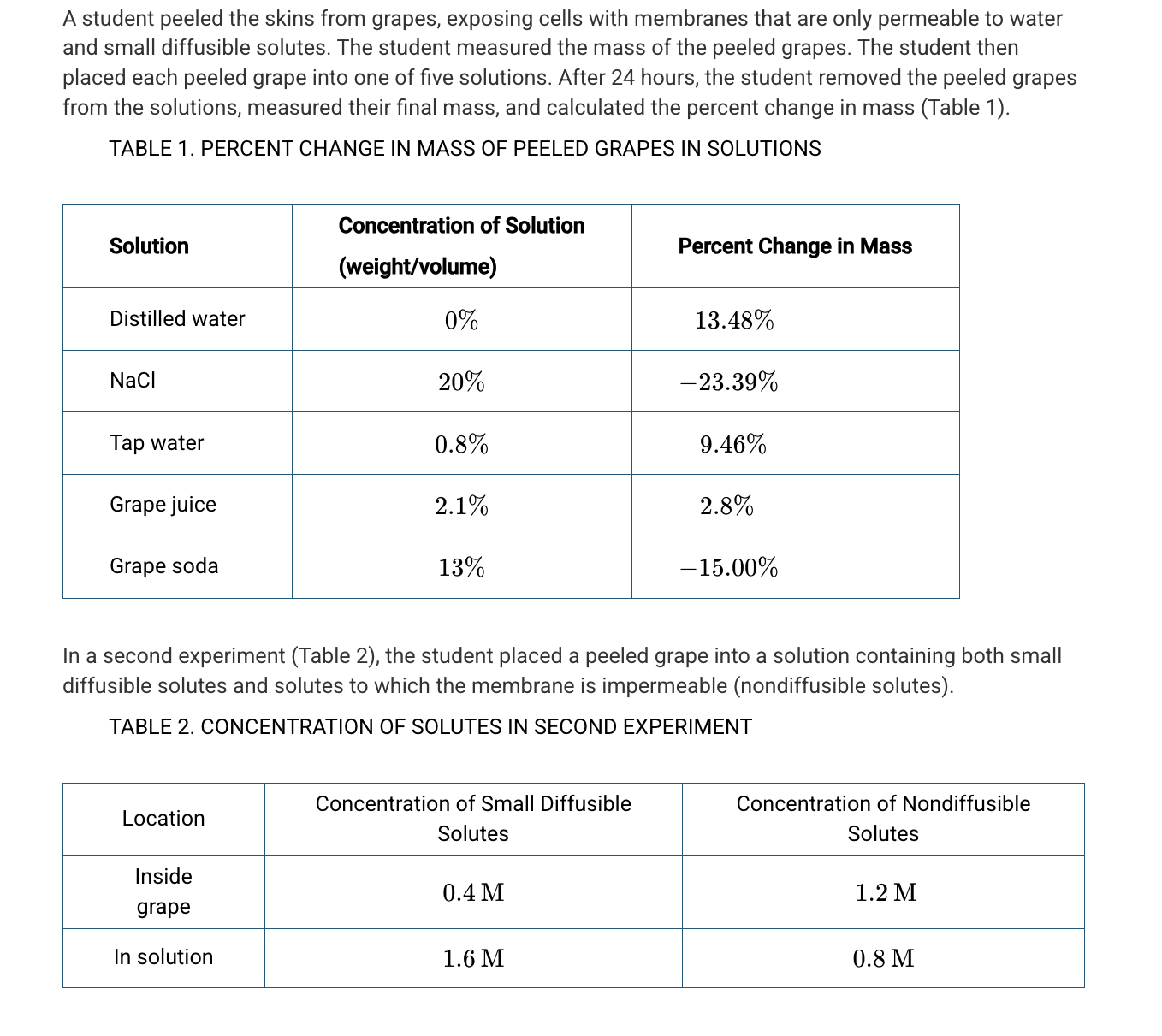
A student hypothesizes that the solute concentration of grape juice is higher than the solute concentration of the actual grape because the grape juice has added sugar. Based on the data in Table 1, which of the following best evaluates the student’s hypothesis?
The hypothesis is not supported because the mass of the grape increased in the grape juice.
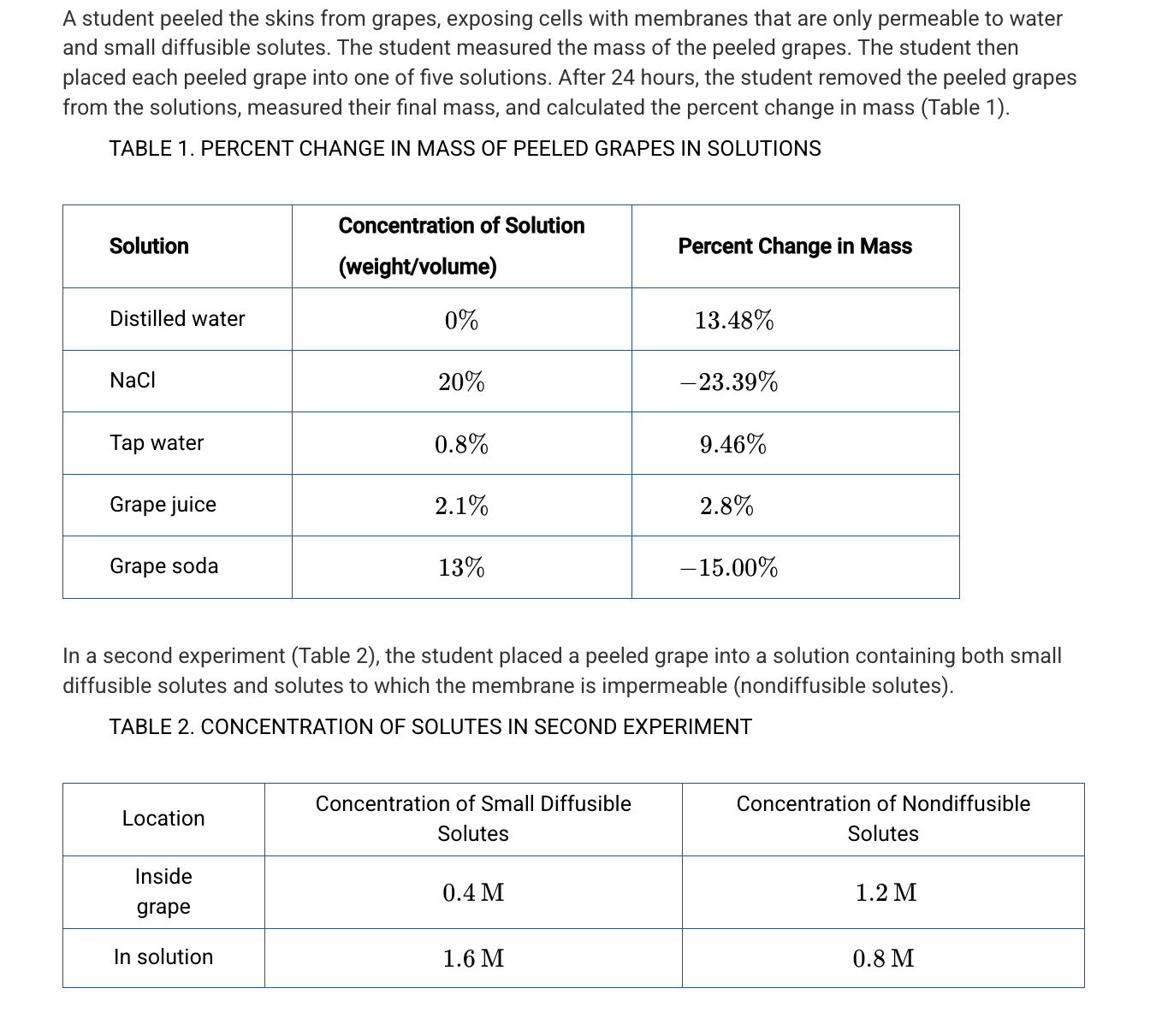
Assuming a negligible pressure potential, which of the following best predicts the net movement of the small diffusible solutes and water in the second experiment (Table 2) ?
Small diffusible solutes will diffuse into the grape cells, followed by water.
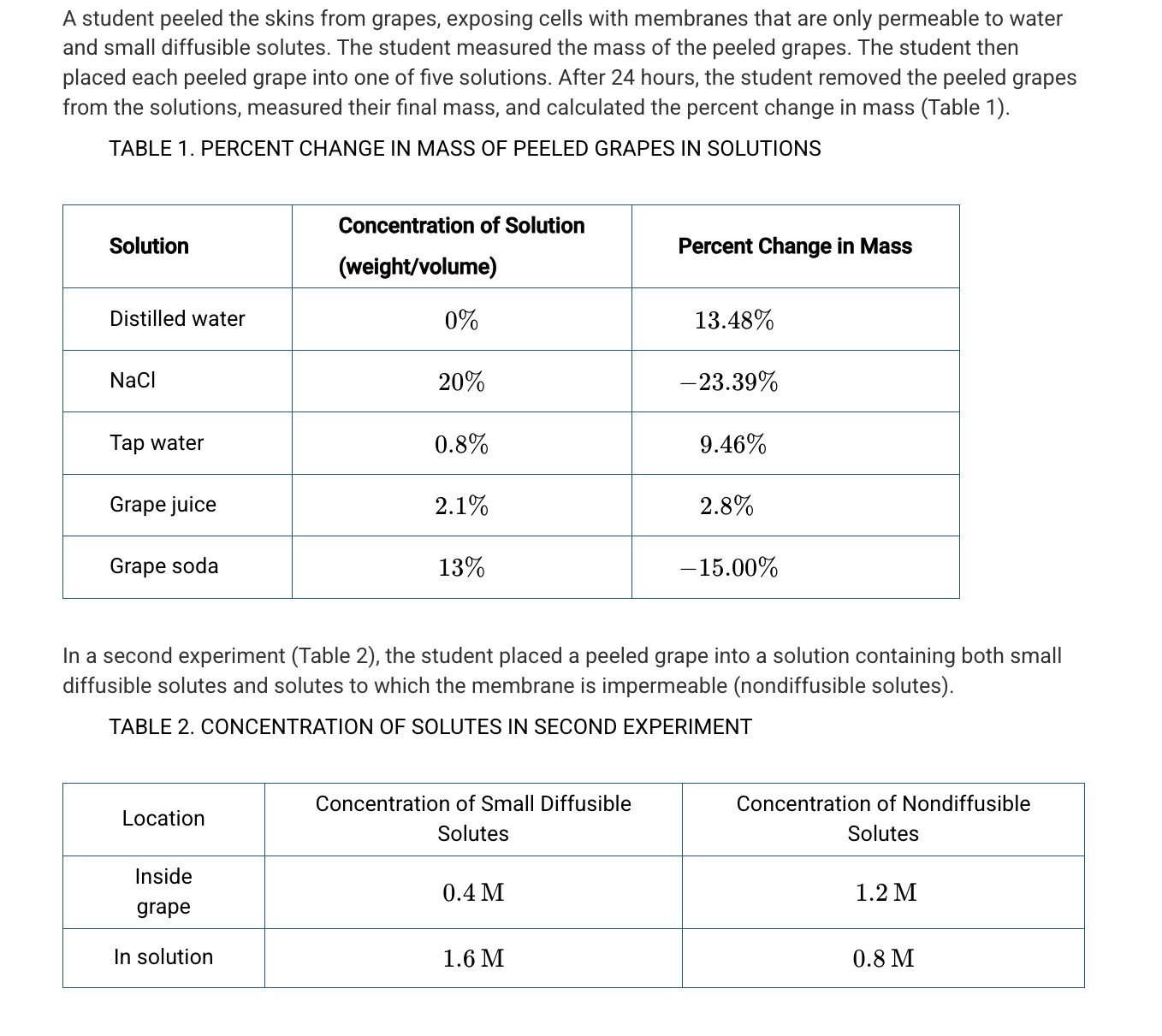
Mercurial sulfhydryl is an inhibitor of aquaporins. Which of the following is the most likely effect of adding mercurial sulfhydryl to the distilled water solution?
The grape cells will gain water more slowly because of a lack of facilitated diffusion.
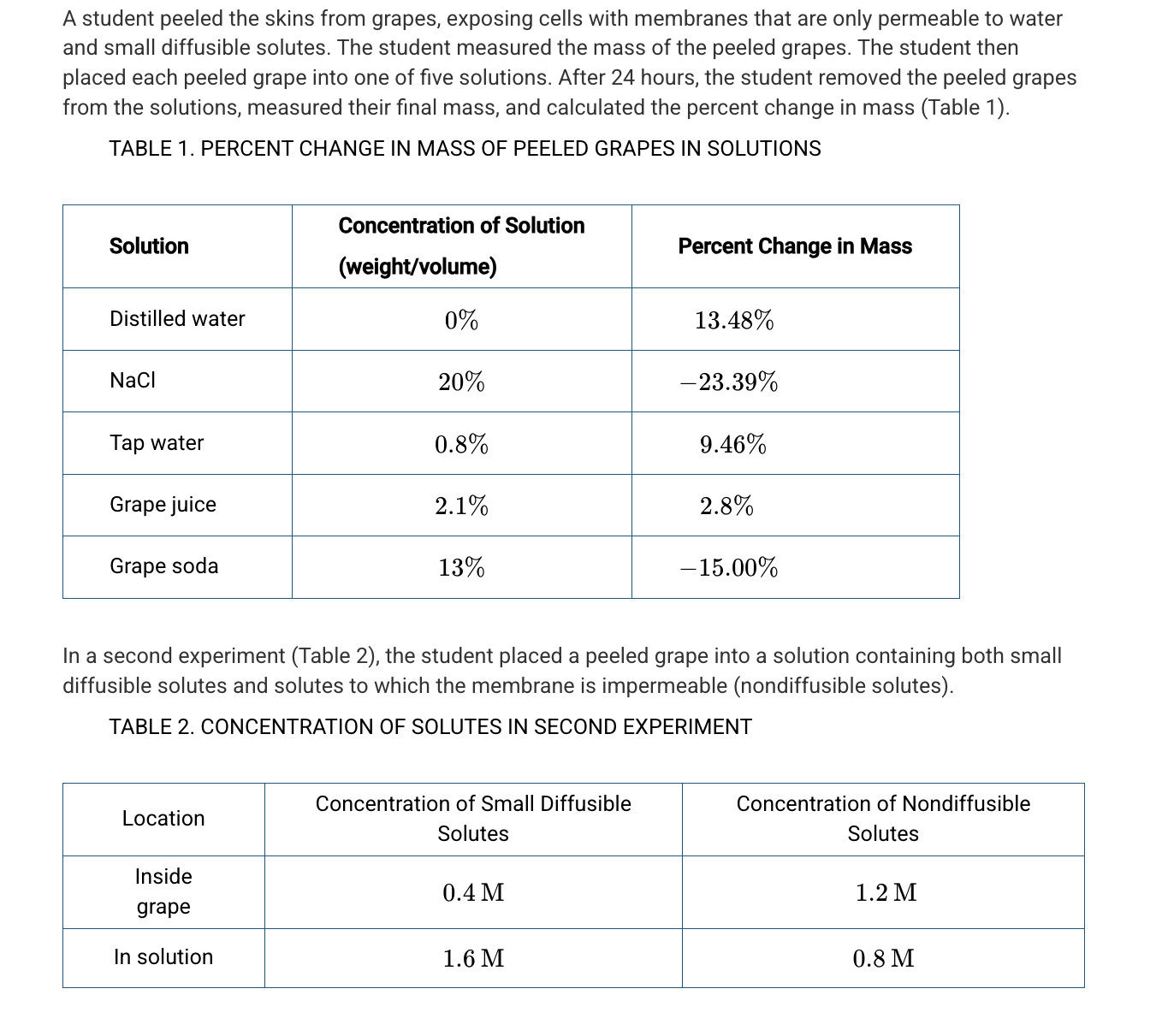
Which of the following best explains why larger grapes have a different rate of water absorption per gram of mass than smaller grapes do?
The rate is slower because smaller grapes have a larger surface-area-to-volume ratio than the larger grapes do.
A human kidney filters about 200 liters of blood each day. Approximately two liters of liquid and nutrient waste are excreted as urine. The remaining fluid and dissolved substances are reabsorbed and continue to circulate throughout the body. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is secreted in response to reduced plasma volume. ADH targets the collecting ducts in the kidney, stimulating the insertion of aquaporins into their plasma membranes and an increased reabsorption of water. If ADH secretion is inhibited, which of the following would initially result?
The person would produce greater amounts of dilute urine.
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a disorder of red blood cells that causes the cells to be smaller and spherical instead of having the usual flattened, biconcave shape. The average diameter of normal red blood cells is 7.2μm, and the average diameter of red blood cells in a person with HS was found to be 6.7μm. The normal red blood cell has an average surface area of 136μm2 and an average volume of 91μm3.
Which of the following provides an accurate calculation of the surface area to volume ratio of an HS red blood cell, as well as a prediction of its effect on the efficient transferring of oxygen compared to a normal red blood cell?
The ratio is 0.89 and the cells are less efficient at transferring oxygen.
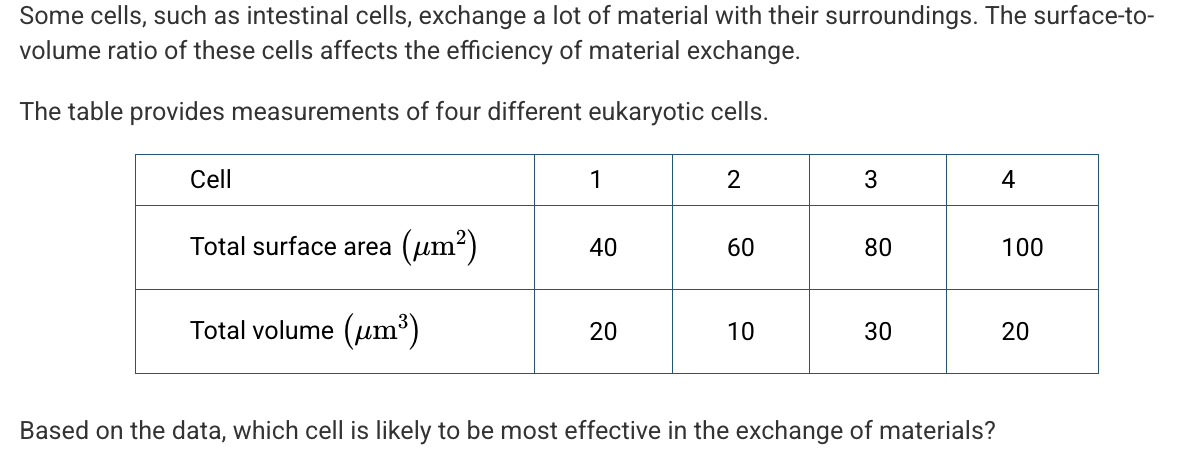
Cell 2
Which of the following best explains why hydrolytic enzymes are typically transported to the lysosome after they are synthesized by ribosomes?
These enzymes are essential for breaking down organic molecules.
Changing the shape or morphology of the mitochondrial inner membrane can change the efficiency of mitochondrial function. Which of the following outcomes will most likely result from a change in the shape of the mitochondrial inner membrane from a highly folded surface to a smooth, flat surface?
Mitochondria will become less efficient because the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membranes will decrease.
Membrane-bound organelles have been an important component in the evolution of complex, multicellular organisms. Which of the following best summarizes an advantage of eukaryotic cells having internal membranes?
Organelles isolate specific reactions, increasing metabolic efficiency.
The endosymbiont theory proposes a model for the evolution of mitochondria. According to the model, an ancestral eukaryote engulfed a small, free-living prokaryotic organism. The engulfed prokaryote then formed an endosymbiotic relationship with the eukaryotic host. Which of the following observations best supports the model?
Mitochondria and some prokaryotes share similar metabolic reactions that produce ATP
Which of the following accurately describes a model of active transport?
A membrane protein binds a specific molecule outside of the cell and moves the molecule into the cell where there is already a high concentration of the molecule compared with the outside.
Which of the following statements is true regarding the movement of substances across cell membranes?
Ions are unable to move through the phospholipid bilayer because the nonpolar tail regions of the phospholipids are hydrophobic.
Researchers studying osmoregulation in a specific crab species measured the change in water content within the crabs’ muscles when the crabs were exposed to water with different salt concentrations (Figure 1).
Which of the following claims about the crab’s muscle water content is most likely supported by the data shown in Figure 1?
Which of the following claims about the crab’s muscle water content is most likely supported by the data shown in Figure 1?
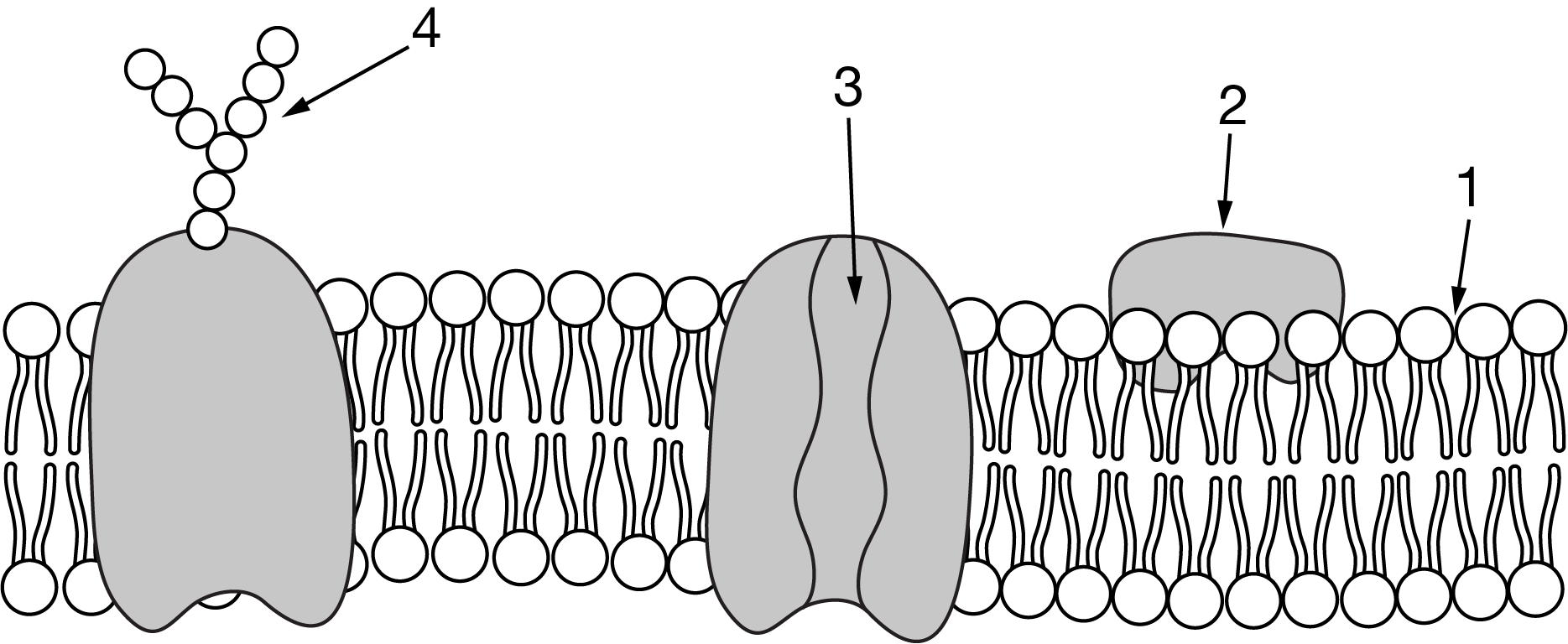
Figure 1. Testosterone movement across the cellular membrane
Testosterone is a small steroid hormone that is important in cell signaling. Which of the following describes where testosterone enters a cell and why it is able to cross at that point?
1, testosterone is nonpolar and can diffuse through the membrane.
The model below shows the structure of a portion of a plasma membrane in an animal cell.
Which statement best explains the orientation of the phospholipid molecules in this model?
The hydrophilic phosphate groups of the phospholipid molecules are attracted to the aqueous internal and external environments.
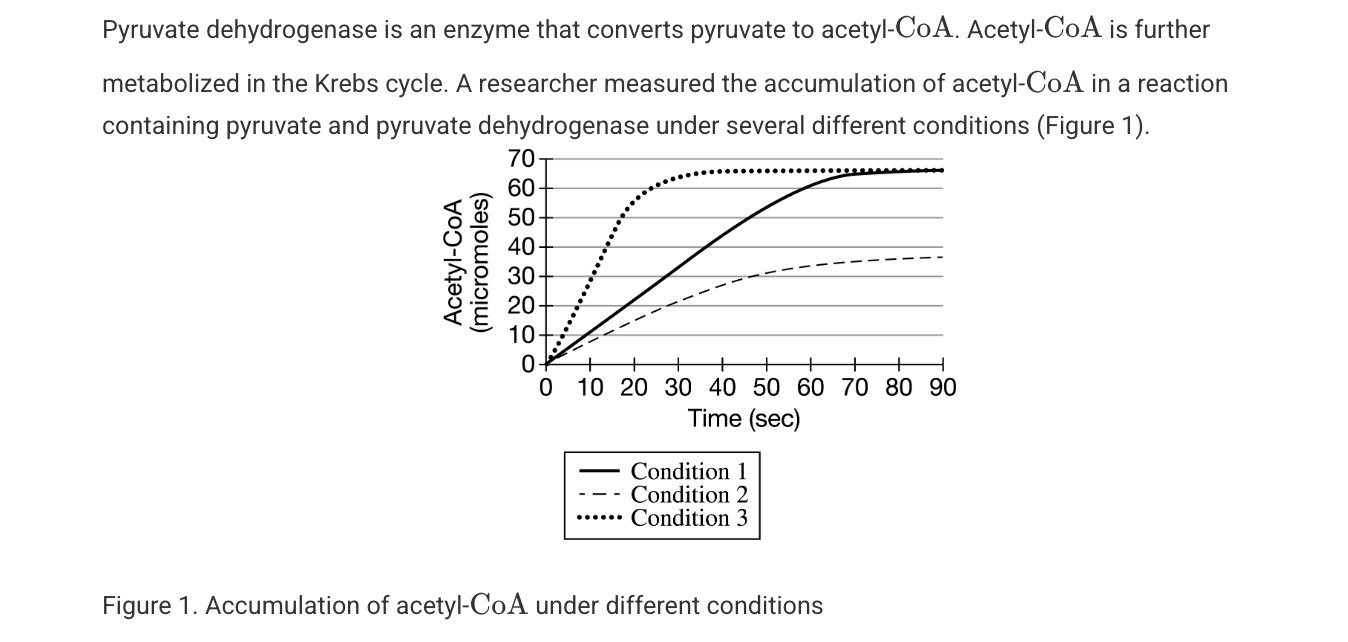
Which of the following best describes the cellular location where pyruvate dehydrogenase is most likely active?
The mitochondrial matrix
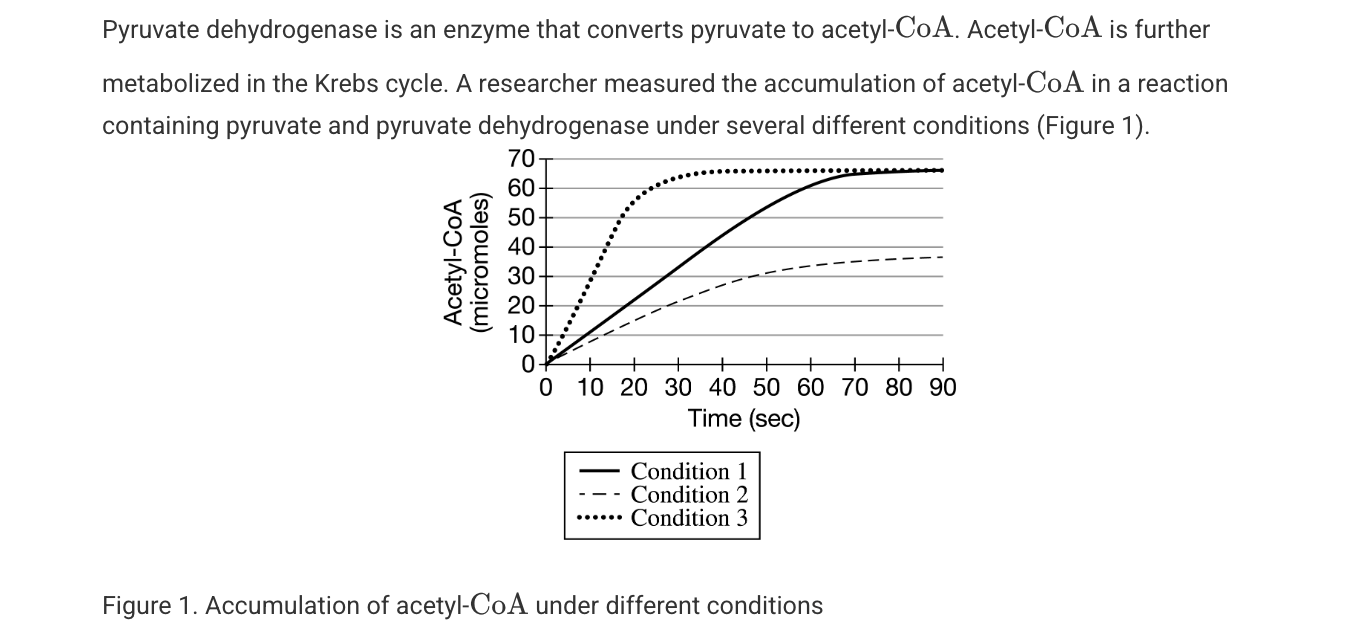
The maximum production rate of acetyl-COA under condition is closest to which of the following?
1 micro-molecule per/sec
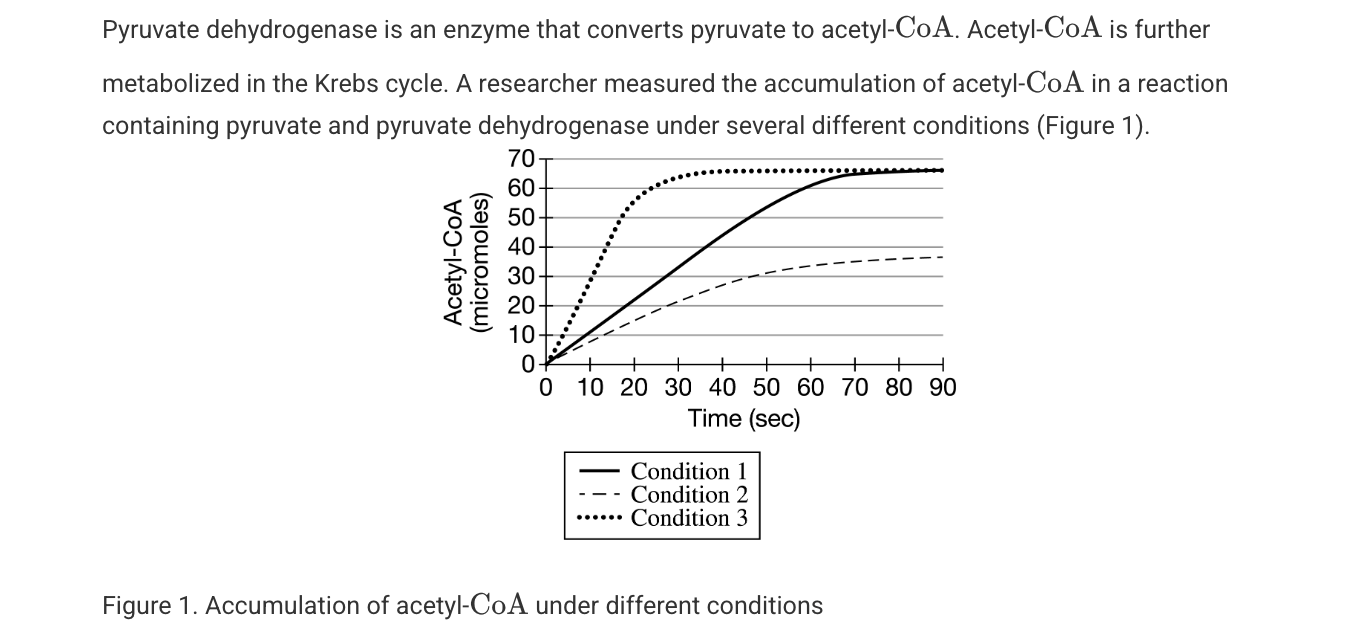
Which of the following observations provides the best evidence that acetyl-CoA negatively regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase activity?
The rate of the pyruvate dehydrogenase–catalyzed reaction is slower in the presence of a higher concentration of acetyl-.CoA
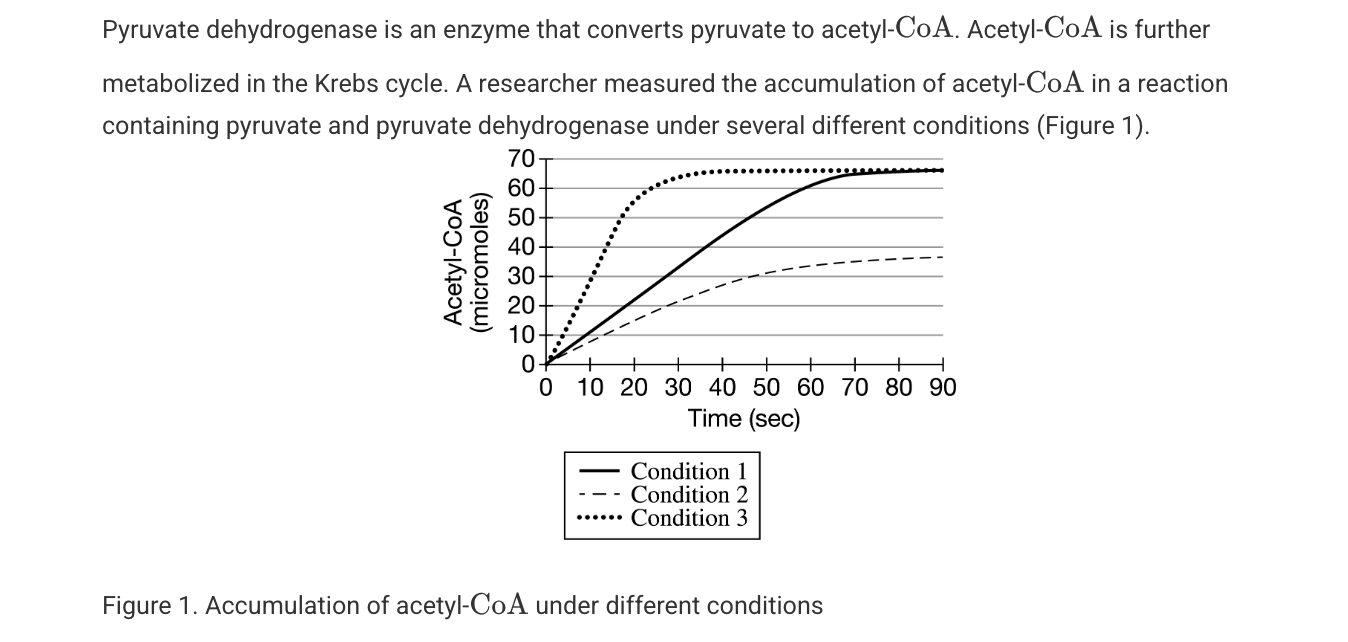
Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency is a genetic disease most commonly linked to a mutation in the -subunit of the mitochondrial enzyme that causes the enzyme to cease functioning. As a result of the mutation, affected individuals build up dangerous amounts of lactic acid. Which of the following best explains the buildup of lactic acid in individuals with the mutation?
Cells undergo fermentation because pyruvate cannot be metabolized to proceed into the Krebs cycle.
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is a protein that catalyzes the conversion of acetylcholine to acetate and choline. When the concentration of AChE in an aqueous solution is held constant, the rate of the reaction catalyzed by AChE increases with increasing concentrations of substrate. At low concentrations of acetylcholine, a small increase in the substrate concentration results in a large increase in the reaction rate. At high concentrations of acetylcholine, however, a large increase in the substrate concentration results in only a small increase in the reaction rate. Which of the following statements correctly explains the observed effect of the acetylcholine concentration on the rate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
The active site of AChE is specific for acetylcholine, and only one substrate molecule can occupy the active site at a time.
Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) is an enzyme that aids in the decomposition of ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH) into nontoxic substances. Methyl alcohol acts as a competitive inhibitor of ethyl alcohol by competing for the same active site on ADH. When attached to ADH, methyl alcohol is converted to formaldehyde, which is toxic in the body.
Which of the following statements best predicts the effect of increasing the concentration of substrate (ethyl alcohol), while keeping the concentration of the inhibitor (methyl alcohol) constant?
Competitive inhibition will decrease because the proportion of the active sites occupied by substrate will increase
Directions: This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all. This group of questions refers to molecules of the following substances. (A) Cytochrome (B) FADH2 (C) NAD+ (D) NADP+ (E) Oxygen (O2)
Coenzyme that transfers electrons from the Krebs cycle to the mitochondrial electron-transport chain at a lower energy level than that of electrons entering at the beginning of the chain
FADH2
Directions: This group of questions consists of five lettered headings followed by a list of phrases or sentences. For each phrase or sentence, select the one heading to which it is most closely related. Each heading may be used once, more than once, or not at all. This group of questions refers to molecules of the following substances. (A) Cytochrome (B) FADH2 (C) NAD+ (D) NADP+ (E) Oxygen (O2)
An intermediate electron acceptor for oxidations that occur in both glycolysis and in Krebs cycle reactions
NAD+
Catalase is an enzyme found in yeast cells that facilitates the chemical breakdown of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. An experiment was conducted to determine the effect of pH on catalase function. Five buffer solutions of varying pH (2, 4, 6, 8, and 10) were prepared and added to separate test tubes. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was added to each test tube. Yeast was added, and the reactions were timed. After 1 minute the amount of oxygen gas released was determined by measuring the foam layer produced in each test tube. Figure 1 illustrates the experimental setup.
Figure 1. Illustration of experimental procedure
A set of five additional test tubes were prepared and used as controls. Which of the following best describes the contents expected to be contained in one of the five control test tubes?
pH 4 buffer solution and hydrogen peroxide only

Researchers investigated the dynamics of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The researchers prepared a series of reactions, each with the same concentration of enzyme but with different concentrations of substrate. The researchers measured the amount of product in each reaction mixture after minutes. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following best describes how an increase in the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture affected the frequency of enzyme‑substrate interactions?
The frequency of enzyme-substrate interactions increased until all of the active sites were interacting with substrate.

Researchers investigated the dynamics of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The researchers prepared a series of reactions, each with the same concentration of enzyme but with different concentrations of substrate. The researchers measured the amount of product in each reaction mixture after minutes. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following experimental designs would best allow researchers to investigate the effect of a variable on the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
Measure reaction rates at different pH levels when the enzyme concentration remains the same and the substrate concentration is 100 μm.

Researchers investigated the dynamics of a reaction catalyzed by an enzyme. The researchers prepared a series of reactions, each with the same concentration of enzyme but with different concentrations of substrate. The researchers measured the amount of product in each reaction mixture after minutes. The results are shown in Figure 1.
Which of the following questions best addresses whether a particular inhibitor is competitive or noncompetitive?
Does the inhibitor bind to an allosteric site or the active site of the enzyme?
The electron transport chain (ETC) is made up of several carrier molecules that transport electrons. These carrier molecules are found within membranes. Which of the following statements best explains why these carrier molecules are typically found within membranes?
The energy derived from the ETC creates a difference in the concentration of protons on either side of the membrane.
Experimental evidence shows that the process of glycolysis is present and virtually identical in organisms from all three domains, Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Which of the following hypotheses could be best supported by this evidence?
Glycolysis is a universal energy-releasing process and therefore suggests a common ancestor for all forms of life.