Prisms
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
what is a prism, anatomy of a prism, deviation of light by a prism, opthalmic prism.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
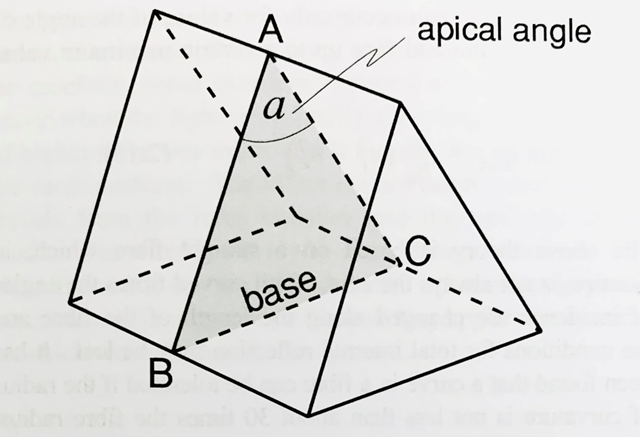
what is a prism
A solid piece of glass or plastics bounded by plane polished faces
how are prisms usually represented in optics
as a triangular section
what are prisms used for in optometry
to relieve symptom arising from muscular defects in binocular vision such as heterophoria
base of a prism
one face of the prism that is left unpolished (at the bottom)
principle section of the prism
(ABC) - used in constructing ray diagrams
refracting faces
the two faces of the prism (AB and AC)
as light rays hit this surface/enter they are refracted and then get refracted again
what does the letter “a” represent
apical angle of the prism
refraction by a prism (brief)
When a light ray enters a prism, it gets refracted by the first refracting surface and is further refracted by the second surface
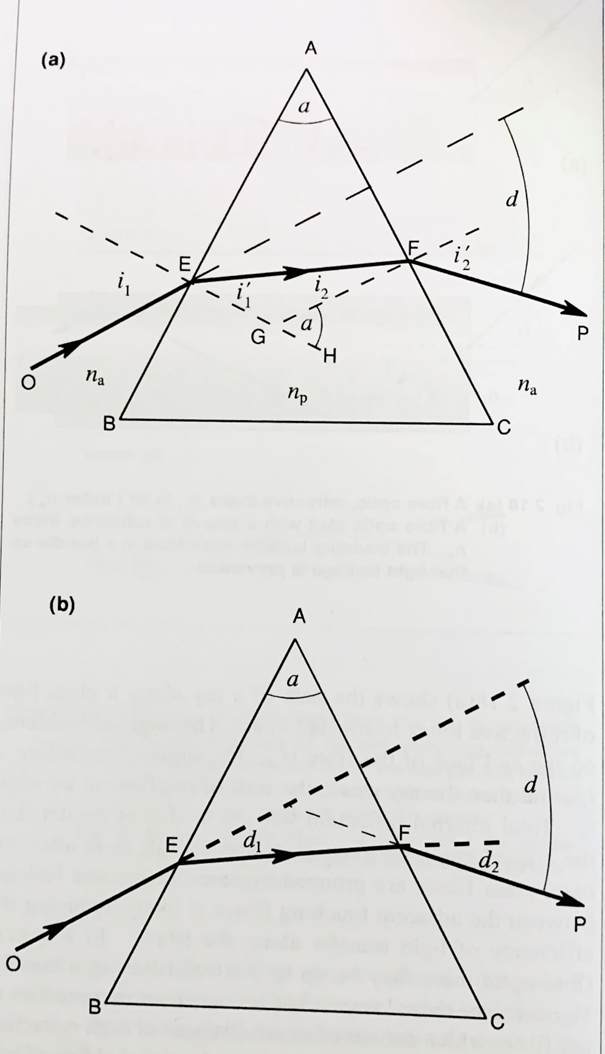
np
refractive index of prism (ABC)
na
refractive index of air (1)
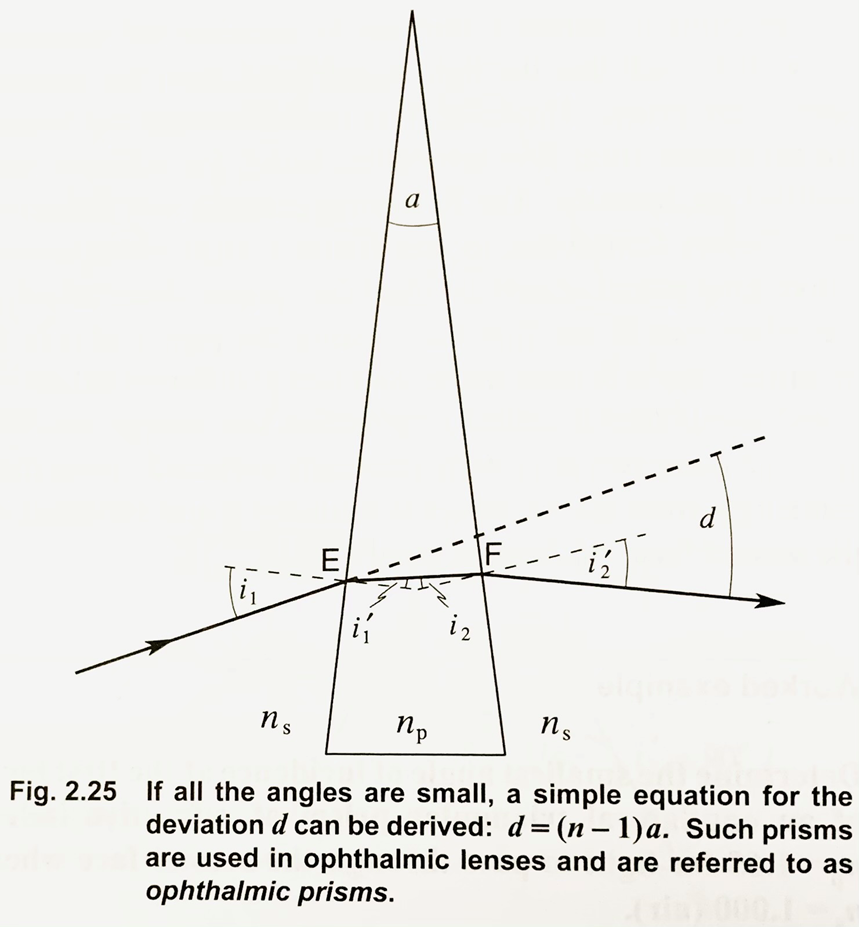
what is OE
the incident ray at the first surface
explain the deviation of light in a large prism (where the apical angle is more than 10 degrees)
the incident ray at the first surface is OE
after refraction the light travels in the direction EF to undergo further refraction at the second surface emerging in the direction FP
ideally the light should travel in the same direction as OE however as the prism has a different refractive index (to air) refraction occurs and the the ray is deviated and then undergoes further refraction at FP
what is i1 and i1’
angle of incidence and angle of refraction at the first surface
what is i2 and i2’
angle of incidence and angle of refraction at the second surface
what is d1 and d2
d1 = angle of deviation at the first surface
d2 = angle of deviation at the second surface
d (total deviation) = d1 + d2
how can we use the angle of incidence and refraction to work out d1 and d2
i1 = i1’ + d1
rearranged : d1 = i1 - i1’
i2 = i2’ - d2
rearranged : d2 = i2’ - i2
as vertically opposite angles are equal
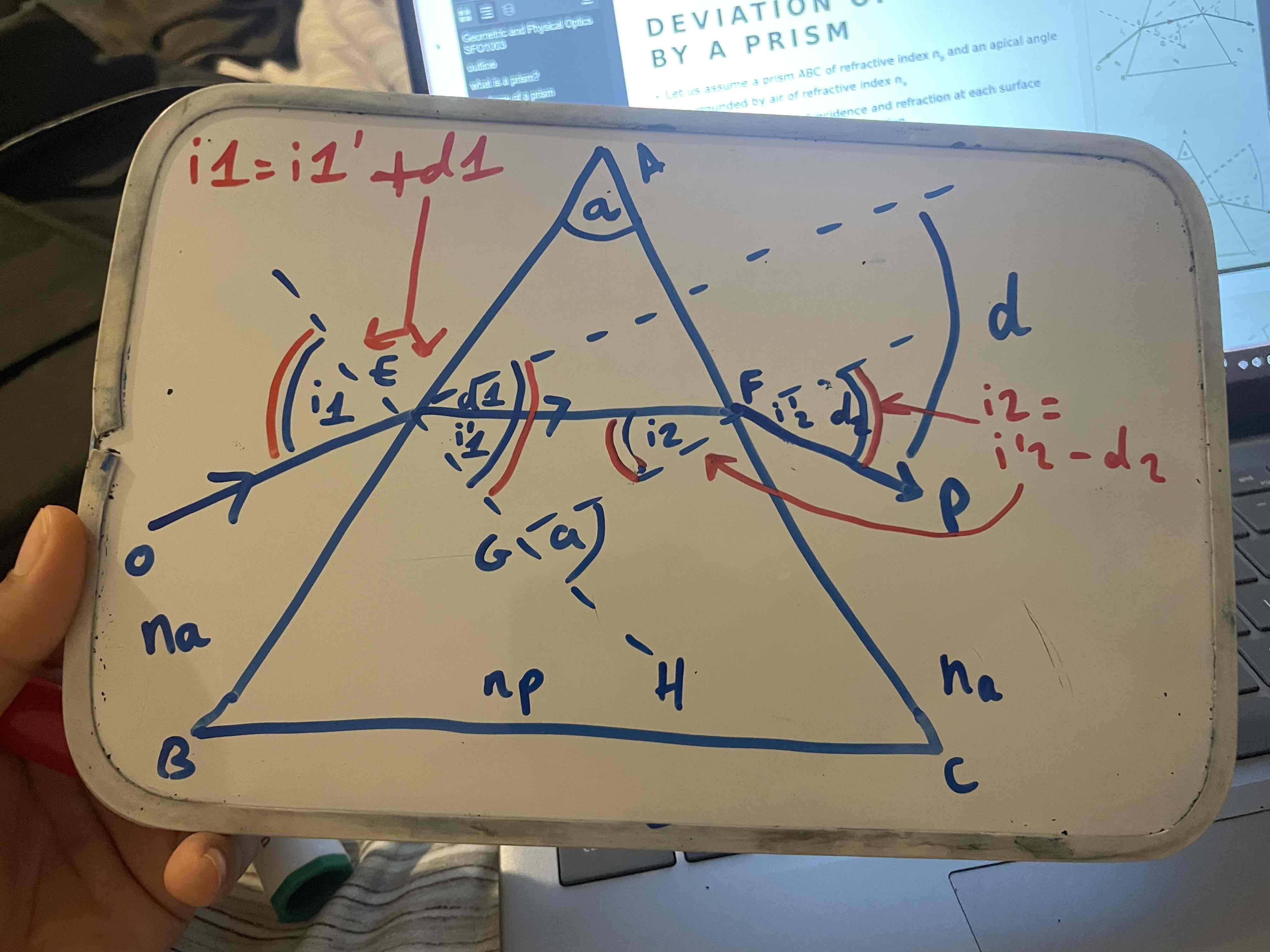
explain relationship between the an external angle and the opposite interior angle in a polygon (AEFG)
in this type of quadrilateral an external angle equals the opposite interior angle
<EAF = <FGH = a
both of the apical angles are equal
explain the relationship between an external angle and the interior angles in a triangle
an external angle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles
<FGH = <GEF + <EFG
a = i1’ + i2
how can we use the above information to work out the total deviation in a prism
d1 = i1 - i1’
d2 = i2’ - i2
d = (i1 - i1’) + (i2’ - i2)
remove the brackets:
d = i1 - i1’ + i2’ - i2
group the positive values and negative values together:
d = (i1 + i2) - (i1’ + i2)
looking at triangles we know that a = i1’ + i2 so we can simplify the above:
d = (i1 + i2’) - a
Final formula^^^
what does the deviation of light by a prism depend on
the apical angle and the angles of incidence and emergence
defining feature of an opthalmic prism
the apical angle is small, usually less than 10 degrees

formula to work out the deviation of light in an opthalmic prism
d = (n-1)a
n = refractive index of a prism (np)
a = apical angle of the prism