Forensics 413 final
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
When is hair sent to DNA?
if hair has root or skin tag
when is hair sent to Trace
when hair is fragmented
Sexual hair
hair that grows during puberty (pubic, arm/leg, beard)
course, continuous texture
beard hair
course, double medulla, triangle cross section
asexual hair
scalp hair
Proximal
root/bulb, reaches hypodermis, nearest origin
Medial
shaft, located in the middle
Distal
tip, located farther from origin
Anagen
live hair in active growth phase (2-6 years), root is hook-shaped, has tag when forcibly removed
Categen
transition phase (1-2 weeks), root starts to shrivel up, looks “slimy”
Telogen
resting phase (2-4 months), dead hair, no skin tag or root sheath
keratinocytes
skin cells
eumelanin
black and brown hues
pheomelanin
red and yellow hues
Asian hair
coarse, dense medulla,, thick cuticle, no undulation, round cross section
African hair
moderate to fine (variation), dense pigment granules with prominent clumps, prevalent undulation, flat cross section
Caucasian hair
moderate, sparse but even pigment granules, uncommon undulation, oval cross section
straight hair texture
circular cross section
wavy/curly hair texture
ovoid cross section
Cuticle
outside layer
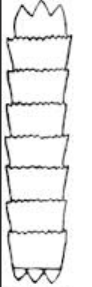
what kind of cuticle type is this?
coronal
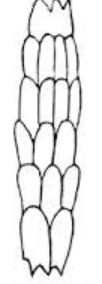
What kind of cuticle type is this?
spinous
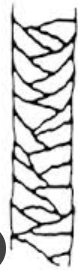
what kind of cuticle type is this?
imbricate
cortex
main body of hair shaft
cortical fusi
tiny air spaces (cavities) usually around root
medulla
dark innermost portion of hair shaft consisting of air

what animal has wineglass root shape?
deer

what animal has javelin root shape?
dog

what animal has frayed root shape?
cat

what animal has club root shape?
human
central dogma
DNA -→ RNA → proteins
transcription
The process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression
where does transcription occur?
nucleus
translation
mRNA is read and used to bind individual amino acids into polypeptide chains to create proteins in ribosomes
where does translation occur?
cytoplasm
nDNA
located in nucleus
mtDNA
located in mitochondria
usage of nDNA
blood, tissue/skin, hair (with root), fresh bones/teeth, body fluids (saliva, semen)
usage of mtDNA
skeletal remains, hair shaft, degraded low-levels of DNA
individualization
to associate evidence to a single source with a high degree of certainty
uses of forensic DNA
Matches victim to the scene
Paternity testing
Cold cases
Missing persons (using parents)
Mass disasters/ human remains
Military DNA
Convicted felons databases
VNTR and RFLP
early DNA technology that showed long sequences of non-coding DNA that required a lot of high quality DNA
Exons
coding DNA
introns
non-coding dna
gel electrophoresis
uses restriction enzymes to recognize specific VNTR nucleotide sequences and cut the DNA at these locations to form restriction fragments
PCR purpose
amplify/multiply specific DNA segment
PCR steps
denaturation, annealing, extension
PCR - denaturation step
breaks hydrogen bonds between nucleotides to get single strands
PCR - annealing step
short DNA primers bind to complementary sequences of ssDNA templates
PCR - extension step
Taq polymerase adds nucleotides to 3’ end of primers and synthesizes new complementary DNA strand
STR - short tandem repeats
Regions of repeating DNA sequences have been identified (usually in non-coding region)
allele nomenclature (D5S818)
D = DNA
5 = chromosome 5
S= single copy sequence
Represents unique DNA segment
Copy wont be found anywhere else
818 = order of discovery in which locus was identified
amount of loci/markers in CoDIS
22
first step of DNA analysis
extraction
extraction
Isolate DNA in sample from everything else
steps of extraction
Lyse the cell nucleus from:
Human biological specimen
Non-human (seeds, leaves)
Microbial specimen (anthrax)
Separation of DNA from other cellular components
Proteins
Cellular debris and internal cellular structures
carbohydrates
what extraction method is used for blood spot samples
FTA card
what extraction method is used for degraded/micro samples (automated). Can process blood, saliva, swabs, bones, and teeth.
solid-phase extraction (STR)
chelex
used for buccal swabs
what extraction method is used for challenging samples and is uses chloroform and phenol
organic
what extraction method is used for complex mixtures that separates sperm cells from non-sperm cells
differential extraction
steps of central dogma
Transcription
Translation
DNA packaging
Replicating
second step of DNA analysis
quantification
Quantification
Determine the amount of DNA present in the extract so we can add appropriate amount of extract for amplification
qPCR
real-time PCR that amplifies and quantifies DNA in real-time, allowing for precise measurement
what is third step of DNA analysis?
amplification
what is used during amplification step?
PCR
what is fourth step of DNA analysis
seperation
separation
electropherograms, loci used to create a profile of peaks, basic reading of peaks.