Chem Lab Scioly, Chemistry - Science Olympiad, Science Olympiad Chemistry Lab
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Boyle's Law
-The volume of a sample of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure
-P1V1=P2V2
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
A law that if two systems are separately found to be in thermal equilibrium with a third system, the first two systems are in thermal equilibrium with each other; that is, all three systems are at the same temperature. Also known as thermodynamic equilibrium.
a=c=b b=a
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
-Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
-When energy is transformed, the quantity of energy remains the same, but its ability to do work diminishes.
Third Law of Thermodynamics
"The entropy of a perfect crystal is zero when the temperature of the crystal is equal to absolute zero (0 K)." "The crystal must be perfect, or else there will be some inherent disorder. It also must be at 0 K; otherwise there will be thermal motion within the crystal, which leads to disorder."
Gay-Lussac's Law
The pressure of a given amount of gas held at constant volume is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature.
Charles' Law
The volume of a given amount of gas held at constant pressure is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature.
Avogadro's Law
1 mol = 22.4 L - The relationship between volume and amount of gas when pressure and temperature are held constant.
Hess' Law
The heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical process is the same whether the process takes place in one or in several steps. This is also known as the law of constant heat summation.
Le Châtelier's Principle
If a change is made to a system, then the system will react in such a way so as to absorb the force causing the change.
Ideal Gas Law
A combination of all the gas laws, applicable to any gas. Relates temperature, volume, and pressure to each other. Further explanation in van der Waals' equation.
van der Waals' Equation
As there are attractive forces between molecules, the pressure is lower than the ideal value. To account for this the pressure term is augmented by an attractive force term a/V2. Likewise real molecules have a volume. The volume of the molecules is represented by the term b. The term b is a function of a spherical diameter d known as the van der Waals diameter. The van der Waals' equation accounts for these inaccuracies.
Kinetic Theory of Heat (1)
The gas consists of very small particles, so the average distance between the gas particles is comparatively large.
Kinetic Theory of Heat (2)
Gas particles have the same mass.
Kinetic Theory of Heat (3)
The number of molecules is so large that statistical treatment can be applied.
Kinetic Theory of Heat (4)
Gas molecules are in constant, random, and rapid motion.
Kinetic Theory of Heat (5)
The rapidly moving particles constantly collide among themselves and with the walls of the container. All these collisions are perfectly elastic. This means, the molecules are considered to be perfectly spherical in shape, and elastic in nature.
Kinetic Theory of Heat (6)
Except during collisions, the interactions among molecules are negligible. (That is, they exert no forces on one another.) This implies the dynamics of the molecules can be treated classically. The equations of motion of the molecules are time-reversible.
"The average kinetic energy of the gas particles is proportional to the temperature of the system and depends only on it."
Kinetic Theory of Heat (7)
The time during collision of molecule with the container's wall is negligible as compared to the time between successive collisions.
Open System
Matter, heat, and work can cross the boundary to enter or exit the system.
Closed System
Heat and work can cross the boundary, but matter can't cross the boundary.
Isolated System
Neither matter, heat, or work can cross the boundary.
Diatheric System
Heat can cross the boundary, but nothing else.
Adiabatic System
Heat may not cross the boundary, but everything else can.
Isentropic process
No transfer of heat or matter, and the process is reversible.
ionic compound
In solid state, it has a high melting point
Volume of a cube formula
L•W•H
Density
D=m/v ; Intensive
specific heat formula
Q= mcP(change in Temperatures)
Sublimation
Process that convert a solid straight to a gas
List of thing that can be study w/o change identity of the substance
Texture, odor, melting point
Condensation occur where?
The line between gas and liquid
Forward reaction is best described as...
Endothermic reaction in which energy is absorbed
Mass
extensive
Boiling point
intensive
odor
Extensive
Melting point
Intensive
Length
Extensive
Density
Intensive ; 2.8 g/cm^3
Volume
Extensive ; 15dm^3
Luster
(n.) the quality of giving off light, brightness, glitter, brilliance. ; intensive
Temperature
Extensive
Ductility
The ability to be pulled into thin wires ; intensive
Area
Extensive
Conductivity
Intensive
Hardness
Intensive
Color
Intensive
Malleability
the ability of a solid to be hammered without shattering ; intensive
Shape
Extensive
Weight
Extensive
Mixture
Can be identify with (aq)
Which element presents in all organic compounds?
Carbon
Physical changes
The product stay almost the same to the reactants
Four properties of acids
Less than 7.0 on pH scale; contains H+ ions; turn blue litmus red; it is liquid
Three properties of a base
More than 7.0 on pH scale; slippery; turn litmus paper blue; taste bitter
covalent bond
Covalent chemical bonds involve the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atom
Polar Covalent/ dipole-dipole interactions
in which the sharing of the electron pair is unequal, with the electrons spending more time around the more nonmetallic atom
Hydrogen bonding
H-F, H-O, H-N
Non-polar/ London dispersion forces
Ionic bond
In chemical bonds, atoms can either transfer or share their valence electrons. In the extreme case where one or more atoms lose electrons and other atoms gain them in order to produce a noble gas electron configuration, the bond is called an ionic bond.
When ask about who have the higher boiling point
The one that have more carbon
Measuring Concentration (units)
~Molarity
~Molality
~Ppm
~Ppb
Molarity
moles of solute/liters of solution
Molality
moles of solute/kg of solution
ppm (parts per million)
(mass of solute/mass of solution)*10^6
ppb (parts per billion)
(mass of solute/mass of solution)*10^9
acid
~a substance that produces (donates) hydrogen ions in solution
~accepts electrons
base
~substance that takes (accepts) hydrogen ions in water
~donates electrons
pH
equal to the negative logarithm of the concentration of Hydrogen Ions in the solution
pOH
the negative of the common logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration
pH+pOH=....
14 (always)
strong acids
~HCI (hydrochloric)
~HClO4 (perchloric)
~HClO3 (chloric)
~H2SO4 (sulfuric)
~HNO3 (nitric)
~HBr (hydrobromic)
~HI (hydroiodic)
strong bases
(usually salts)
~NaOH
~KOH
~Ca(OH)2
~Mg(OH)2
Weak acids and bases
acids
~Acetic acid (vinegar)
~Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
bases
~ammonia
dynamic equilibrium
state of weak acids and bases
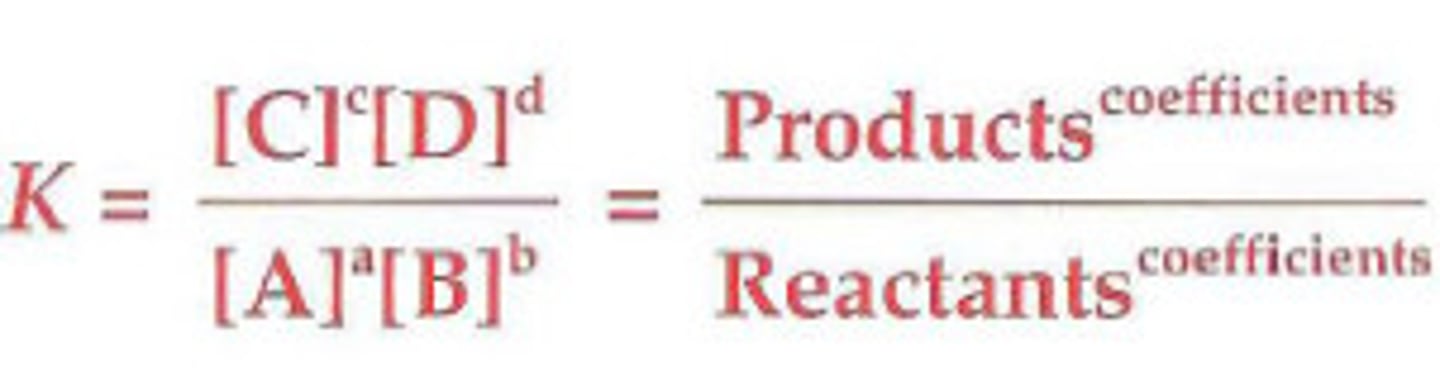
Equilibrium constant (K)
The value obtained when equilibrium concentrations are substituted into the reaction quotient
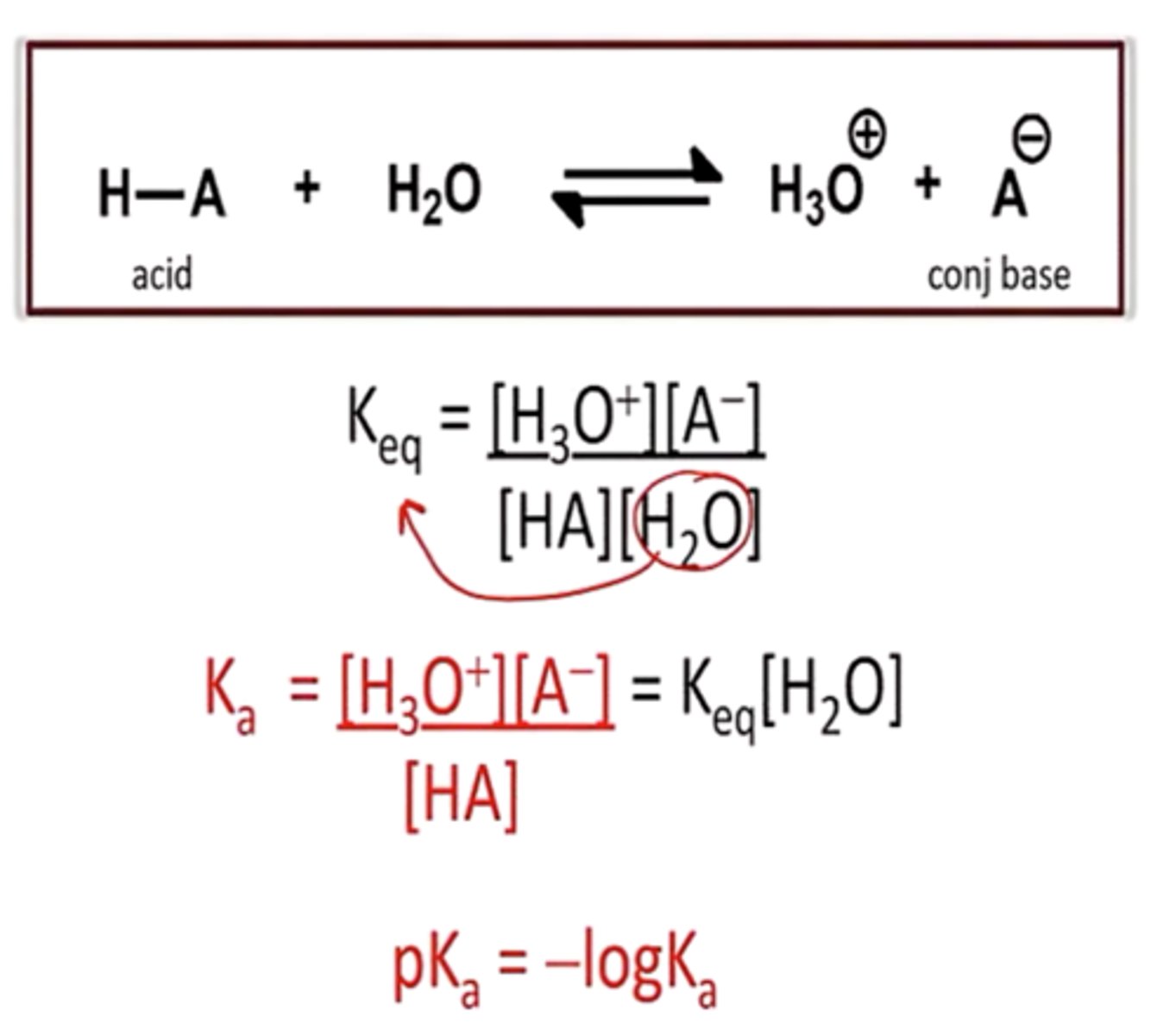
Ka
acid dissociation constant
Kb
-base dissociation constant
Kb=([B+][OH-])/([BOH])
-the smaller the Kb, the weaker the base
![<p>-base dissociation constant</p><p>Kb=([B+][OH-])/([BOH])</p><p>-the smaller the Kb, the weaker the base</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b344ef4e-ebae-4954-b7fd-966a743fefd0.jpg)
Ions
Alkali and Alkaline Metals (Groups 1 and 2)
Strong Acids
Carbonates - CO32-
Bicarbonates - HCO3-
Sulfites - SO32-
Bisulfites - HSO3-
Oxides - O2-
Acetate - CH3COO-
Ascorbate - C6H7O6-
Neutralization
~Acids react with bases in neutralization reactions
~Forms water and a salt (for all of the acids and bases we need to know for this)
~Net Ionic Equations
physical properties
Any property that can be observed without changing the composition of the object
examples of physical properties
Density
Color
Conductivity
Boiling and Melting Points
Resistance
Elasticity
Heat Capacity
Specific Heat
Solubility
Magnetism
Extensive and Intensive properties
extensive properties
depend on the amount of matter that is present
intensive properties
do not depend on the amount of matter present
examples of extensive properties
mass
length
volume
solubility
examples of intensive properties
Conductivity
Density
Color
Temperature
Resistance
Magnetism
Boyle's Law
-The volume of a sample of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure
-P1V1=P2V2