Abdominal Vasculature (pre)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
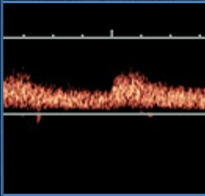
what type of resistance waveform does this show (arterial)?
low resistance
high diastolic flow
renal artery
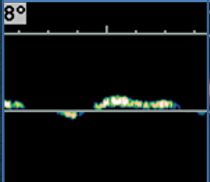
what type of resistance waveform does this show (arterial)?
high resistance
low diastolic flow
distal AO
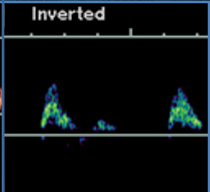
what type of resistance waveform does this show (venous)?
pulsatile
hepatic veins
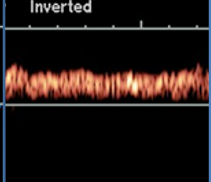
what type of resistance waveform does this show (venous)?
continuous
renal veins
how do you calculate resistive index?
RI = (peak sys - end diast) / peak systole
what is considered high RI?
1.0
what vessels are evaluated in abdominal vasculature scans?
mesenteric vasculature
aortoiliac vessels
renal arteres
renal veins
portal vein
hepatic artery
IVC
hepatic veins
what are the symptoms of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)?
abdominal pain
back pain
leg pain
pulsatile abdominal mass
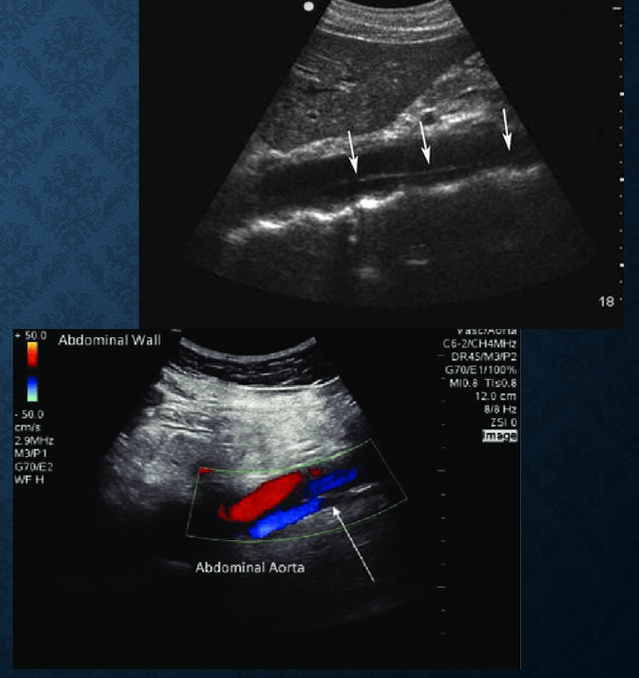
what diameter measurement of abd aorta indicates AAA? risk of rupture?
>3cms
rupture risk : >5cms
how do you measure aorta diameter?
outer to outer
which layer of the aortic wall does blood enter in an aortic dissection?
media layer
where does the SMA arise from?
anterior surface of aorta
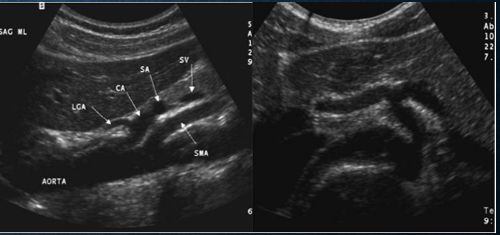
what does the SMA supply blood to?
large and small bowel
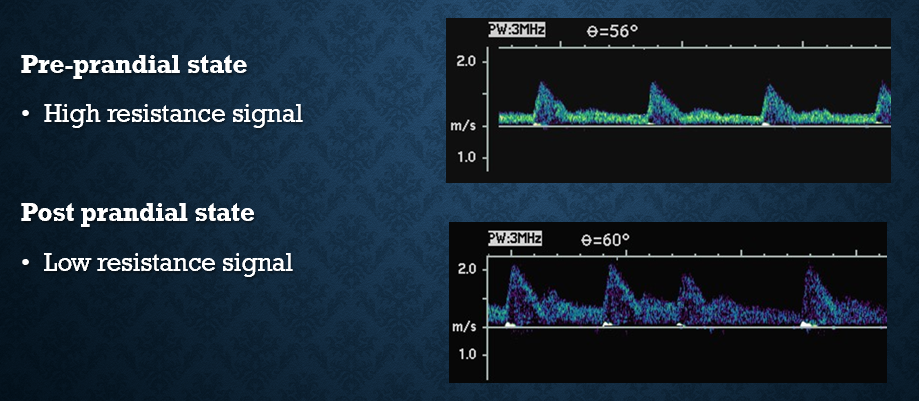
how do SMA doppler signals vary pre vs post prandial (before vs post meal)
pre : high resistance
post : low resistance
sends more blood to bowel
EDV should double
what are symptoms of small bowel/mesenteric ischemia?
post prandial pain
SMA evaluated
weight loss
change in eating habits
which vessels should be evaluated in the presence of atherosclerotic disease?
origins of celiac axis
SMA
IMA
they will be evaluated for stenosis (disease significant if 2/3 vessels are diseased)
SMA/aorta ratio of - is suggestive of >70% stenosis
3.5
what is the criteria for atherosclerotic disease of SMA? Celiac?
syst velocity
EDV
SMA
syst : >275cm/s
edv : >45cm/s
celiac
syst : >200 cm/s
edv : >45 cm/s
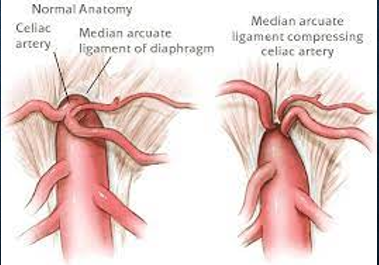
what is median arcuate ligament syndrome (MAL) and which vessel does it affect?
MAL is a fibrous band that extends from the diaphragmatic crura and passes superior to the celiac artery
can cause celiac artery compression during expiration which could mimic stenosis
what are the normal ranges of velocties for SMA? Celiac? IMA?
celiac : 98-105 cm/s
SMA : 97-142cm/s
IMA : 93-189 cm/s
patients with renal artery stenosis usually present with
uncontrollable hypertension
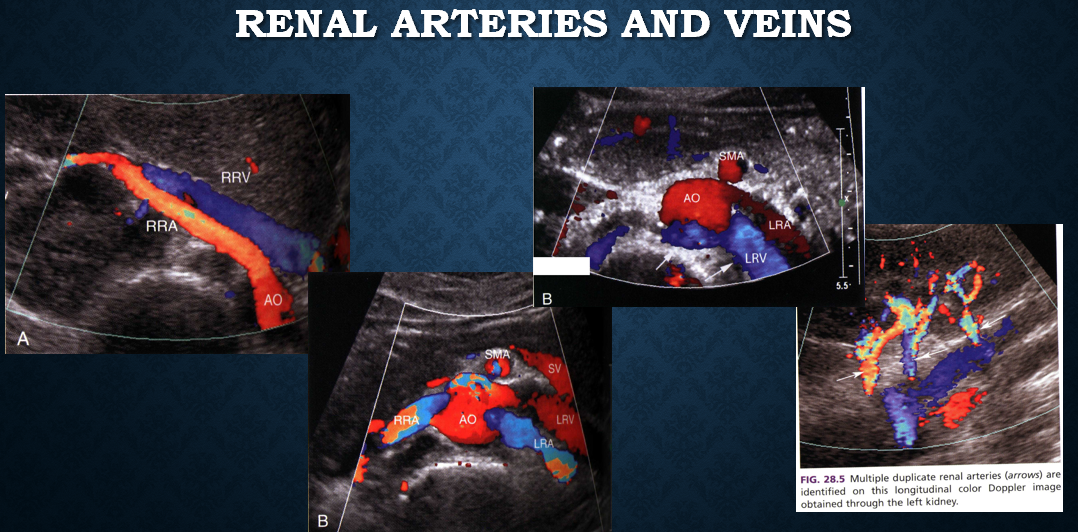
renal artery protocol
prox ao (PSV)
renal arteries from origin of ao to hilum of kidney in trv (2D, color)
MRA prox, mid and distal (PSV &EDV)
sag kidney (PSV & EDV)
segmental arteries in UP and LP of each kidney
accessory renal arteries
calculate RAR ratio (renal to aortic ratio)
RAR = renal artery PSV
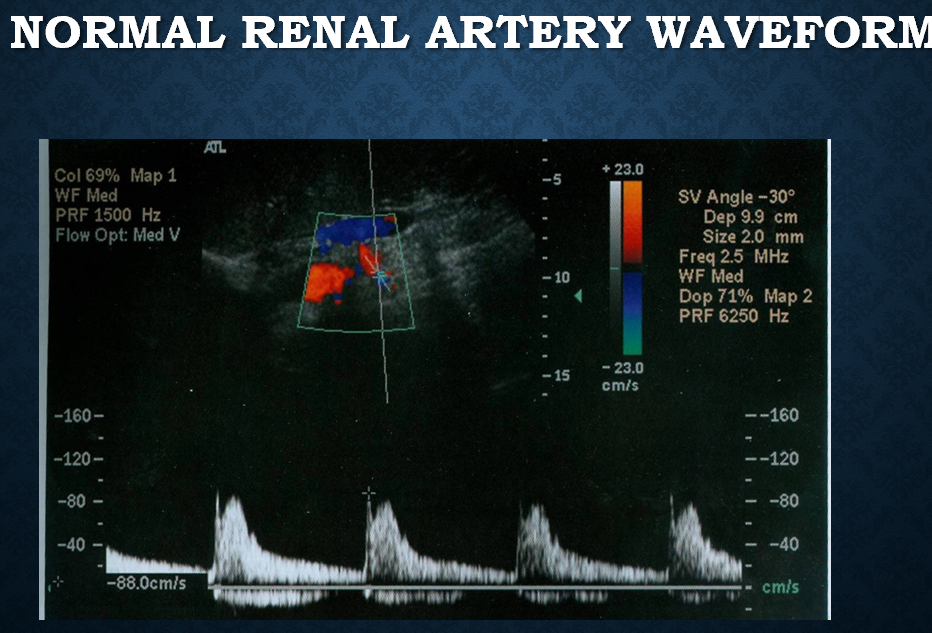
what is a normal arterial waveform for the kidney?
low resistance
what is a normal arterial waveform for the aorta?
high resistance
what is a normal & abnormal aortic PSV value?
normal : <3.5
abnormal : >3.5
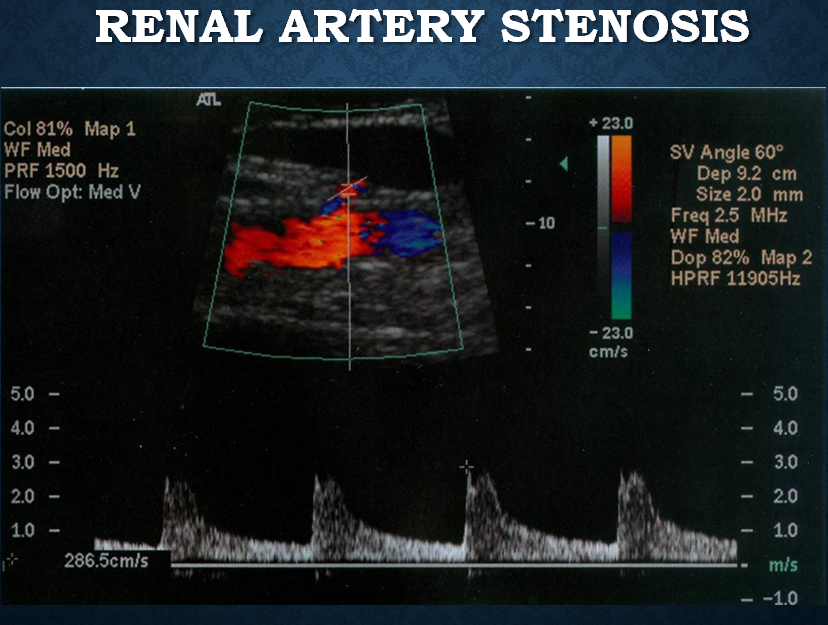
RAS if PSV of main renal artery is
180-200cm/s
what are looking for when evaluating renal veins?
renal vein thrombosis (partial or complete)
where does the IVC lie in relation to the aorta?
IVC lies to the right of the aorta
what kind of doppler signal is seen in the IVC?
continous with respiratory variation
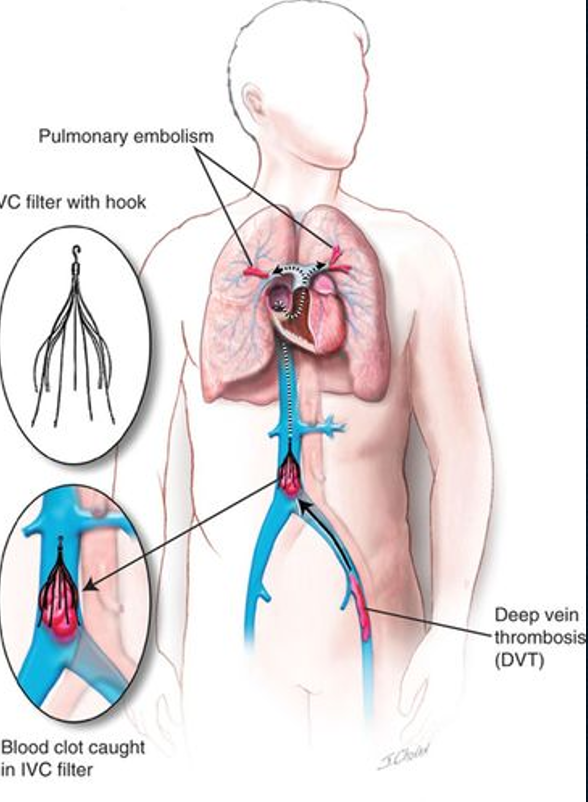
why do we evaluate the IVC?
pts with history of DVT
history of cancer (esp wilm’s tumor or renal cell CA)
pts with IVC filter
post op liver transplant
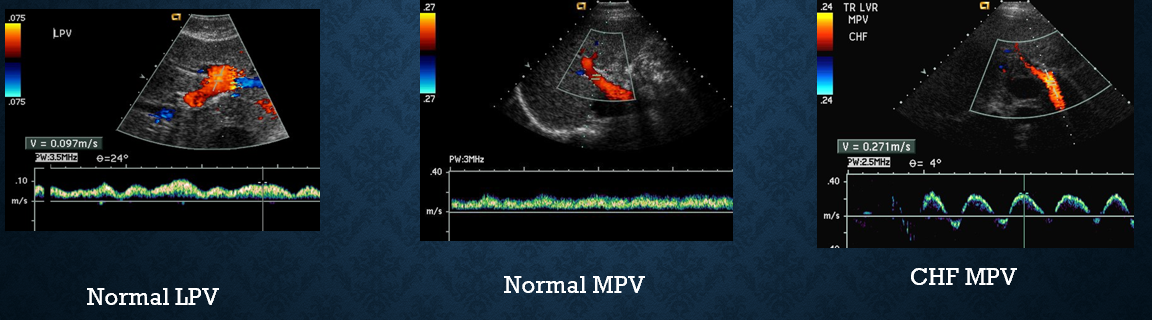
how does CHF affect the IVC?
increases IVC diameter
IVC exhibits pulsatile doppler waveform
what are the causes of IVC thrombosis?
extension of thrombus from tributary vein (renal/iliac)
compression from external mass
abd/pelvic mass
enalrged lymph nodes
tumor invasion
renal cell carcinoma
what is the purpose of an IVC filter?
catch cloths from lower leg(s) to prevent pulmonary embolism
placed in infrarenal location
what is the purpose of the portal venous system?
transport blood from bowel and spleen into the liver
where is the MPV formed?
at junction of splenic vein and SMV
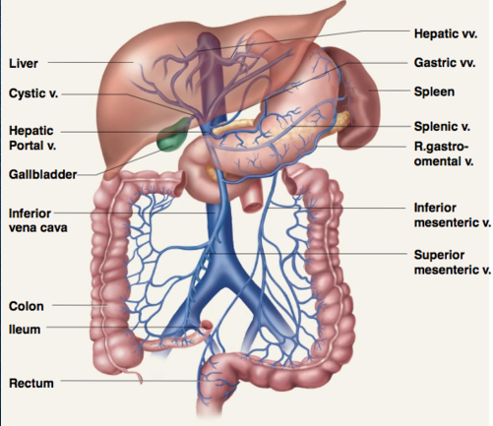
what percentage of blood in the liver is received by the portal vein?
75% (50% oxygenated)
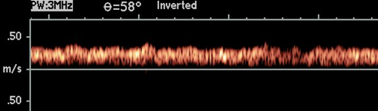
what does doppler look like in the portal vein?
continous hepatopetal flow with slight respiratory variation
flow is pulsatile/biphasic with cardiac issues
what are the causes of portal vein thrombosis?
cirrhosis
alcohol (most common)
biliary
tumor invasion
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
pancreas
metastatic
hypercoagulable states
intraperitoneal inflammation
pancreatitis
appendicitis
what does acute portal vein thrombosis look like on US?
enlarged vein with echoes
lack of flow by CDV/CDE
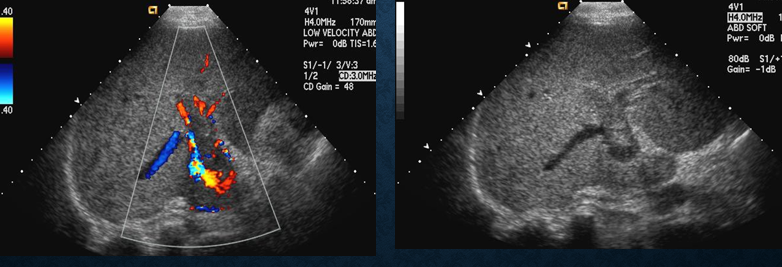
what does chronic portal vein thrombosis look like on US?
small echogenic vein (difficult to detect)
enlarged hepatic artery
what is cavernous transformation of the portal vein?
multiple small, tortuous collaterals around MPV in porta hepatis
what causes cavernous transformation of the portal vein?
complete portal vein thrombosis
extrahepatic portal vein thrombosis
what is portal hypertension?
increased pressure in portal venous system resulting in impdence of blood flow through the liver
what casues portal hypertension?
alcoholic cirrhosis
pancreatitis
hepatitis
sickle cell anemia
coagulative disorders
hepative vein thrombosis
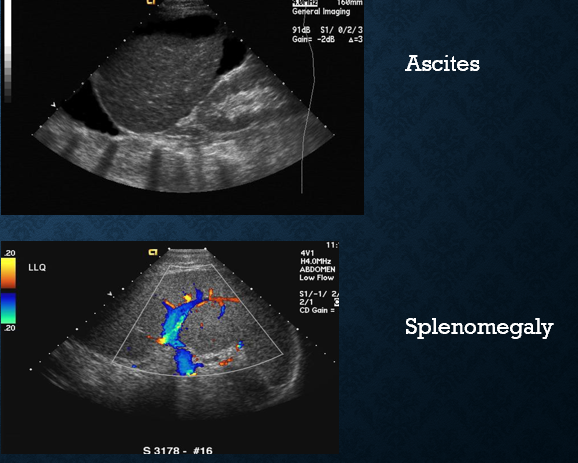
what are clinical signs of portal hypertension?
ascites
splenomegaly
GI bleeding
hepatic encephalopathy
underlying liver disease
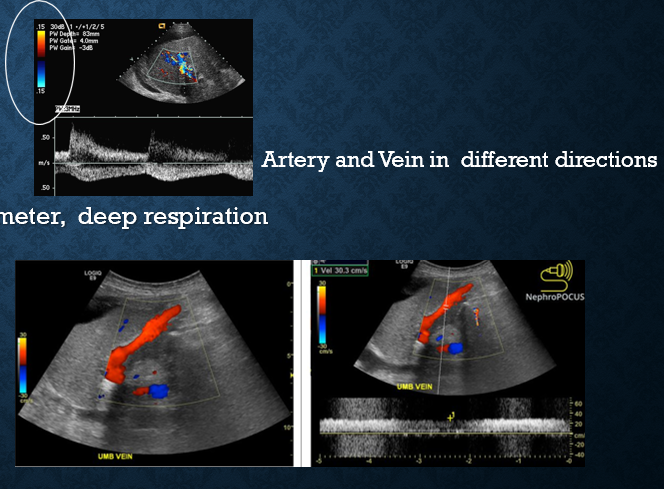
what ultrasound criteria indicates portal hypertension?
hepatofugal flow
portal vein diameter >13mm
decreased splenic vein flow
recanalized umbilical vein (originates from left portal vein)
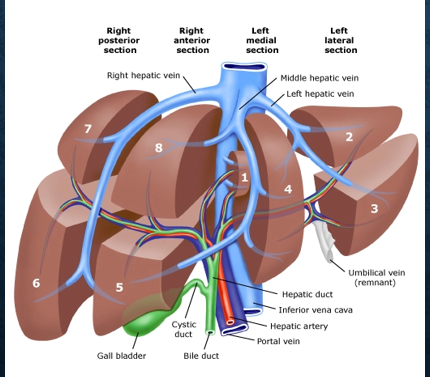
what is the purpose of hepatic veins?
return blood back into systemic circulation
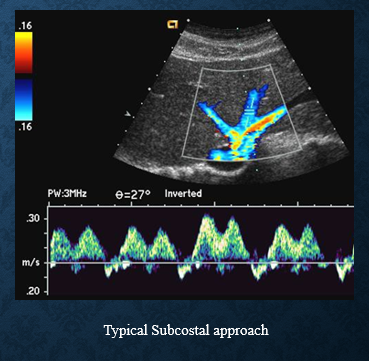
normal hepatic vein waveform
how does CHF affect hepatic veins?
causes hepatic veins to dilate
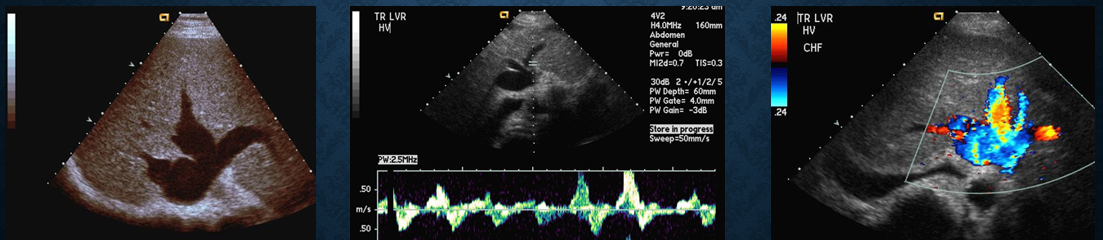
what is budd chiari syndrome?
narrowing or blockage of HV → hepatic vein thrombosis
what causes budd chiari?
hypercoagulable states
compression by tumors or masses
what are the sonographic signs of budd chiari syndrome?
non visualization of one or more hepatic veins
continous/flattened doppler signal
IVC obstructed
enlarged caudate lobe (volume overload)
PV flow sluggish or reversed (due to outflow obstruction)
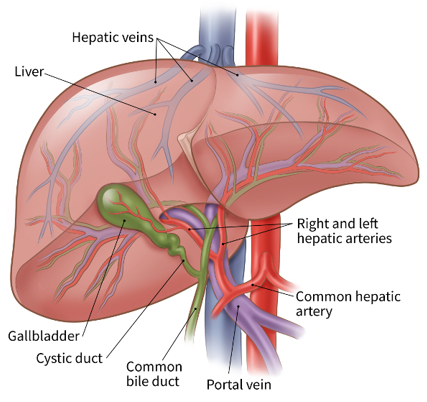
where is the hepatic artery located? where does it go?
it is the right branch off the celiac axis
follows portal vein into liver via porta hepatis → divides into right and left branch
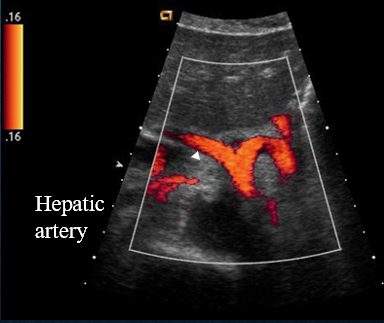
where is the hepatic artery in relation to the main PV?
hepatic artery is superior to the main PV
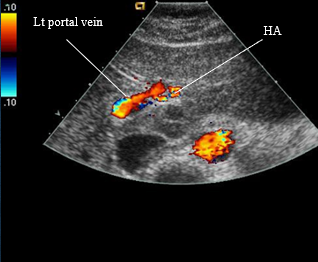
normal hepatic artery views
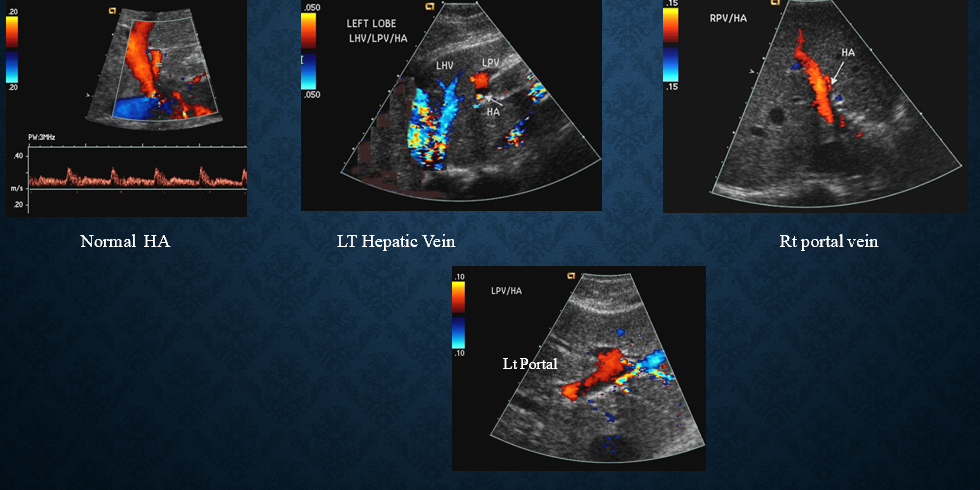
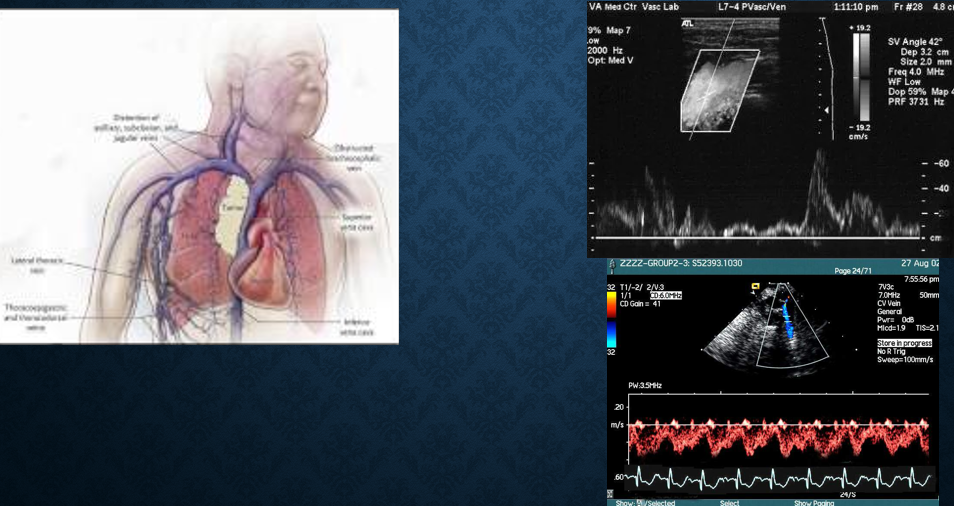
what is SVC syndrome?
collection of clinical signs resulting from partial/complete obstruction of blood flow through SVC
obstruction most commonly from thrombus formation or tumor infiltration