HEMA P3 PRACTICALS
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
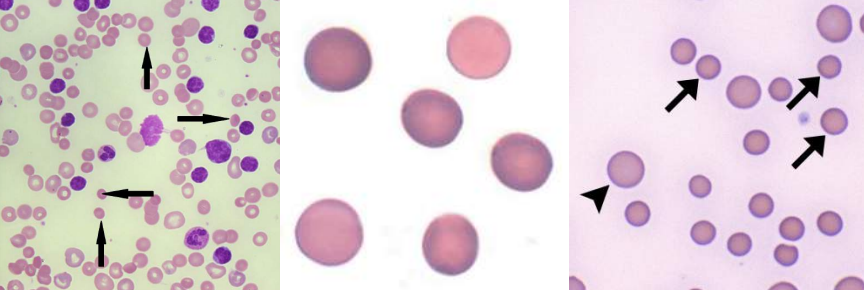
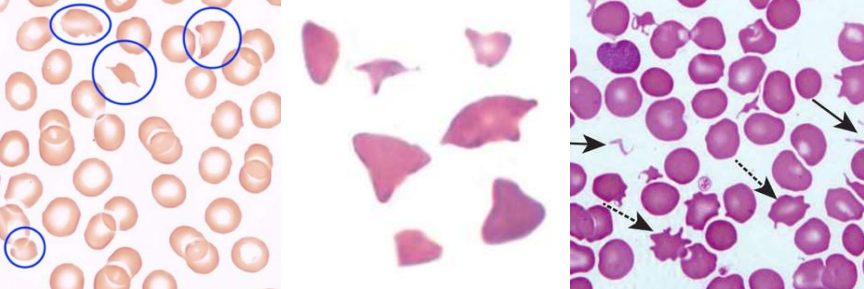
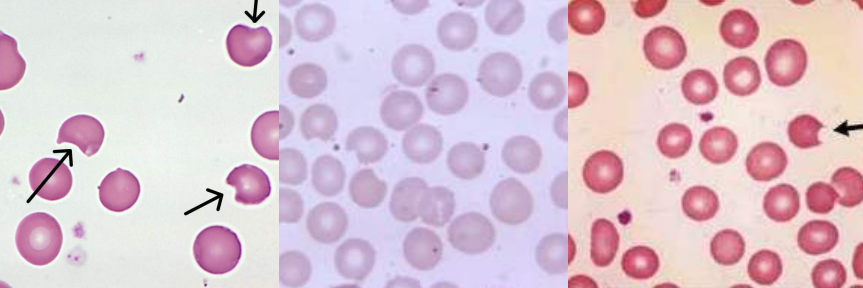
A. Spherocytes
B.
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Immune Hemolytic Anemia
Extensive Burns
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
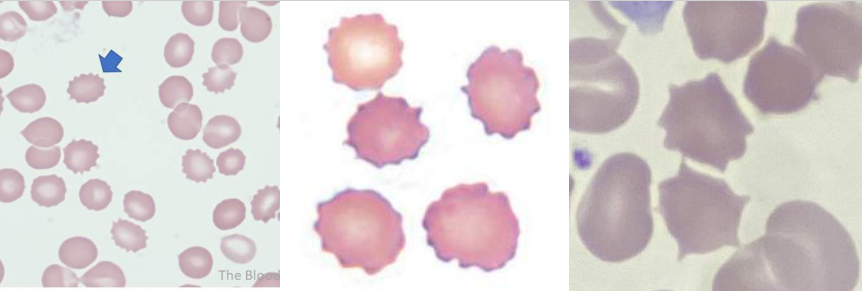
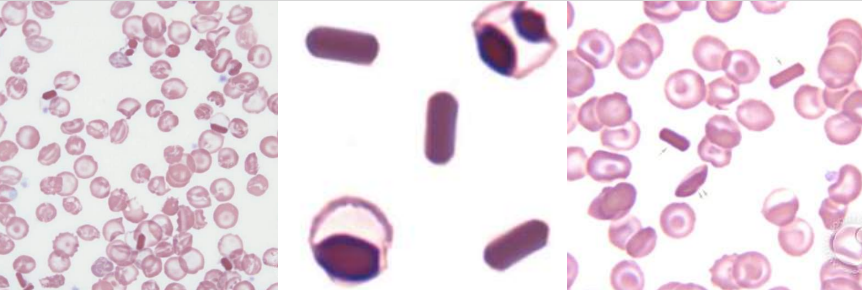
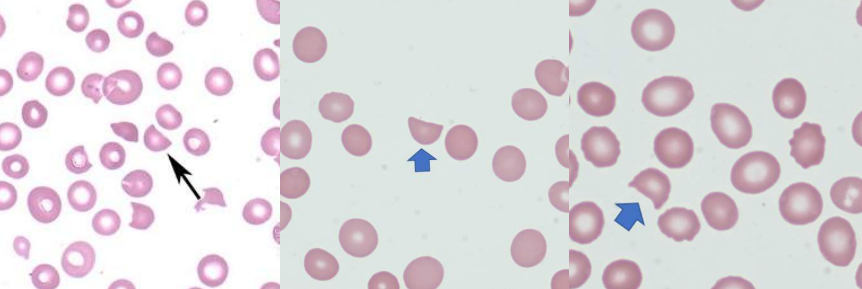
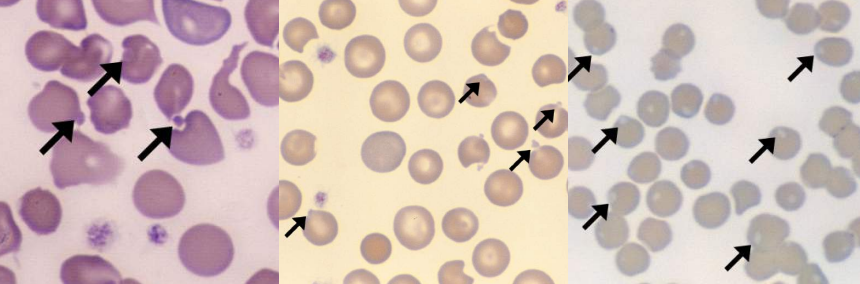
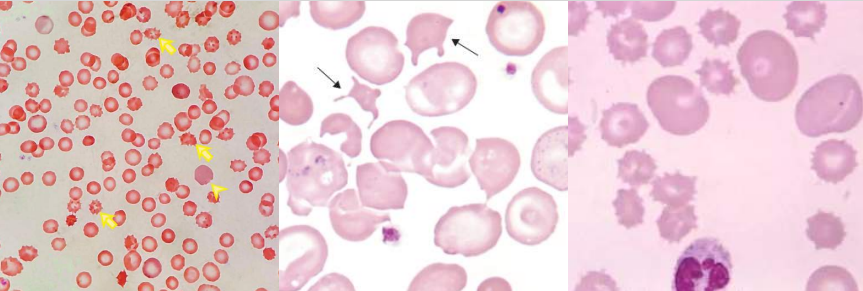
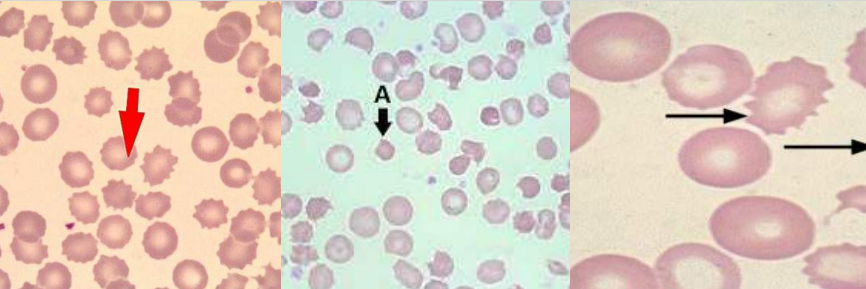
A. Burr Cell
B.
Uremia
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
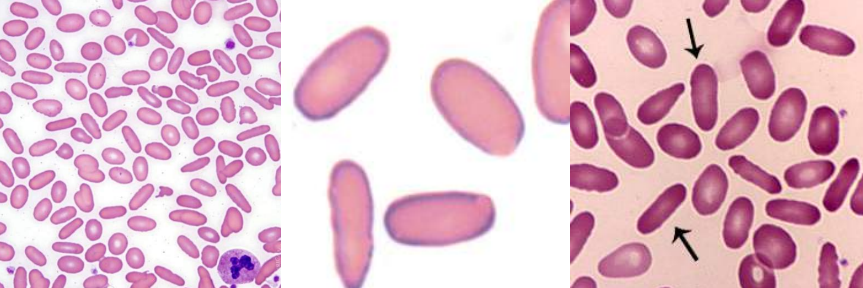
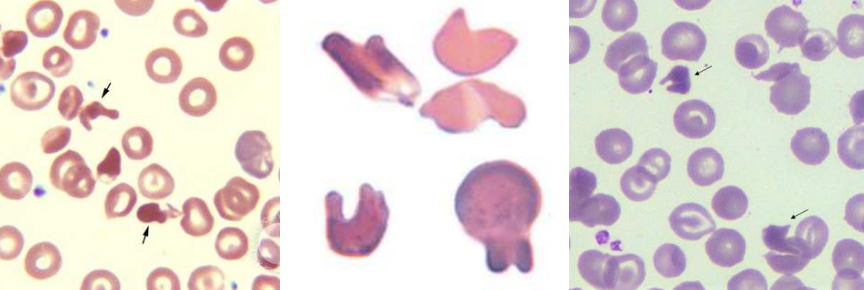
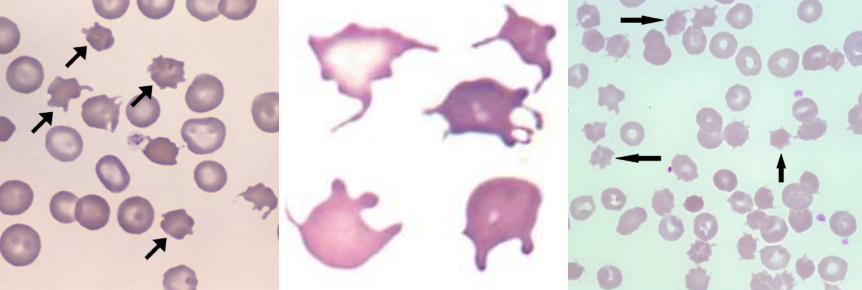
A. Elliptocytes / Ovalocytes
B.
Hereditary Elliptocytosis / Ovalocytosis
Iron deficiency anemia
Thalassemia Major
Myelophthisic anemias
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
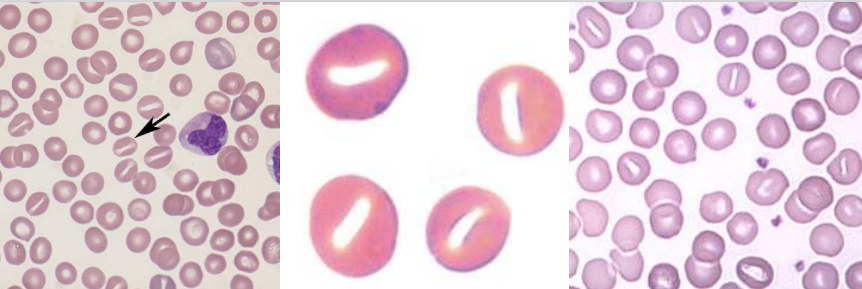
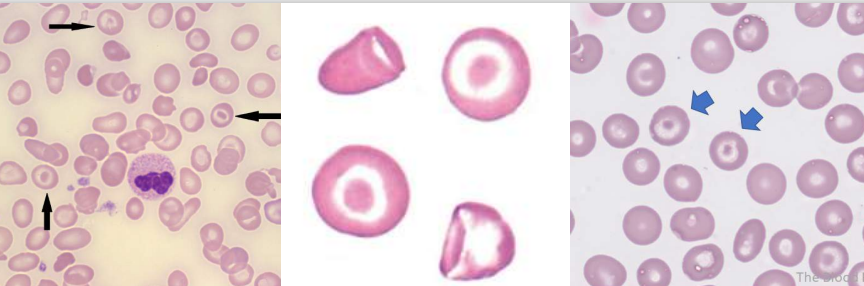
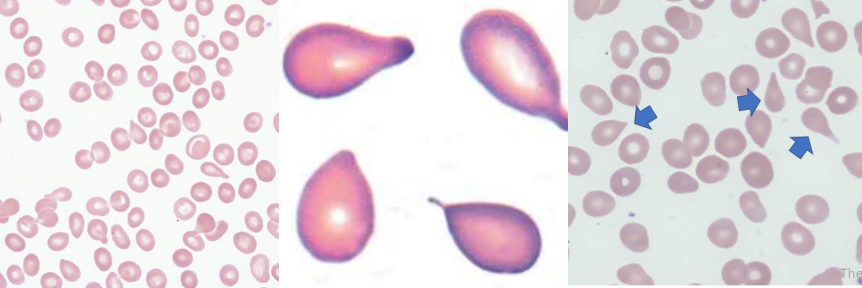
A. Stomatocytes
B.
Hereditary Stomatocytosis
Rh Deficiency Syndrome
Acquired Stomatocytosis (liver disease, alcoholism)
Artifacts
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A. Sickle Cells
B.
Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell-b-thalassemia
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
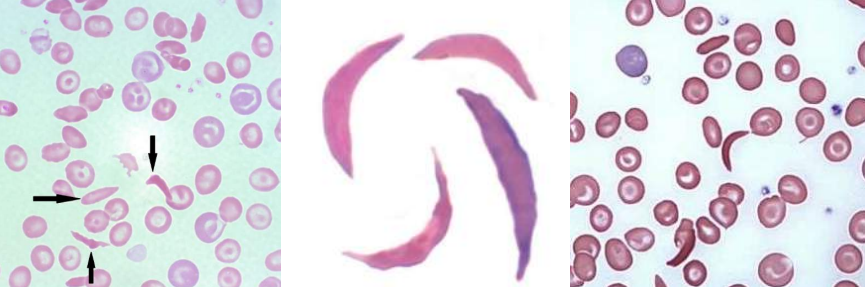
A. Hb C Crystals
B. Hb C disease
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A. Hb SC crystals
B. Hb SC disease
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A. Target Cells (Codocytes)
B.
Liver disease
Hemoglobinopathies
Thalassemia
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A. Schistocytes (Schizocytes)
B.
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Extensive burns
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A. Helmet cells (Keratocytes)
B. Same as schistocyte
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Extensive burns
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A, Acanthocytes (Spur cells)
B.
Severe liver disease (Spur cell anemia)
Neuroacanthocytosis (Abetalipoproteinemia, McLeod syndrome)
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A. Teardrop Cells (Dacryocytes)
B.
Primary Myelofibrosis
Myelophthisic Anemia
Thalassemia
Megaloblastic Anemia
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
A. Diffuse basophilia
B.
Hemolytic Anemia
After treatment for iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency
C. RNA
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Composition of Inclusion
A. Basophilic stipplings
B.
Lead Poisoning
Thalassemias
Hemoglobinopathies
Megaloblastic anemia
Myelodysplastic syndromes
C. Precipitated RNA
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Composition of Inclusion
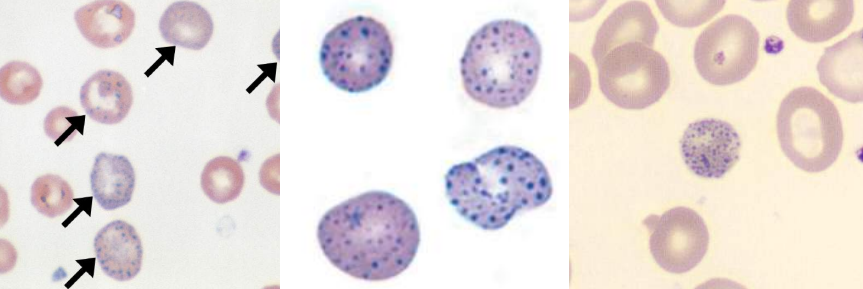
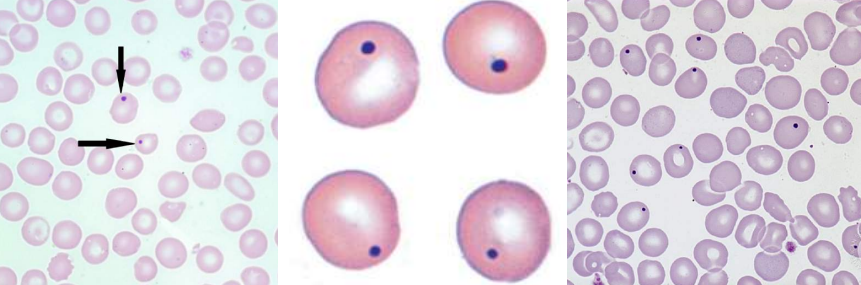
A. Howell-Jolly Bodies
B.
Hyposplenism
Postsplenectomy
Megaloblastic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Thalassemia
Myelodysplastic syndromes
C. DNA (Nuclear fragments)
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Composition of Inclusion
A. Heinz Bodies
B.
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Unstable hemoglobins
Oxidant drugs / chemicals
C. Denatured hemoglobin
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Composition of Inclusion
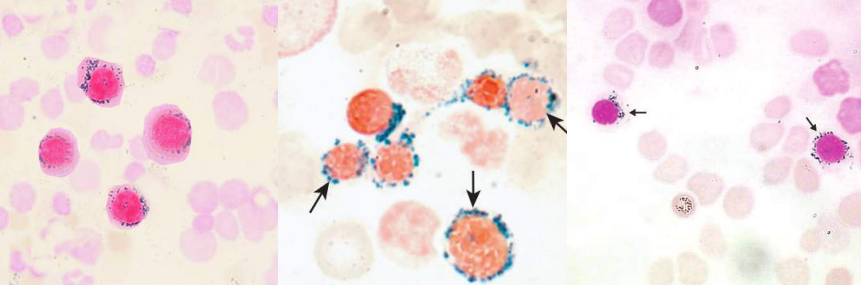
A. Pappenheimer bodies
B.
Sideroblastic anemia
Hemoglobinopathies
Thalassemias
Megaloblastic anemia
Myelodysplastic syndromes
Hyposplenism
Postsplenectomy
C. Iron
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Composition of Inclusion
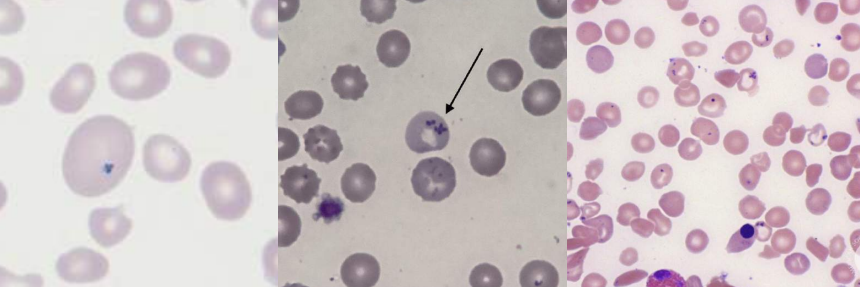
A. Cabot rings
B.
Megaloblastic anemia
Myelodysplastic syndromes
C. Remnant of mitotic spindle
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Composition of Inclusion
A. Hb H
B. Hb H disease
C. Precipitated β-globin chains of hemoglobin
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Composition of Inclusion
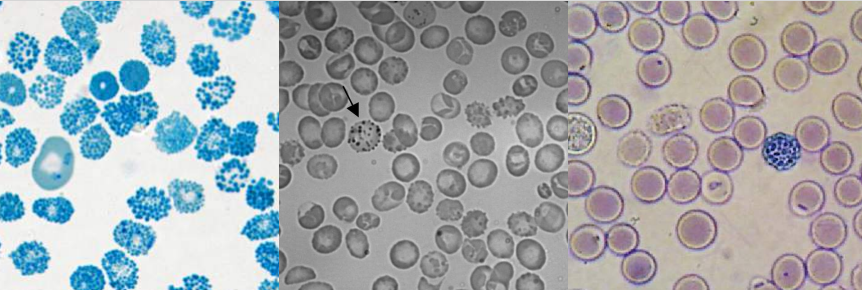
A. Ringed Sideroblasts
B. Sideroblastic anemia
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
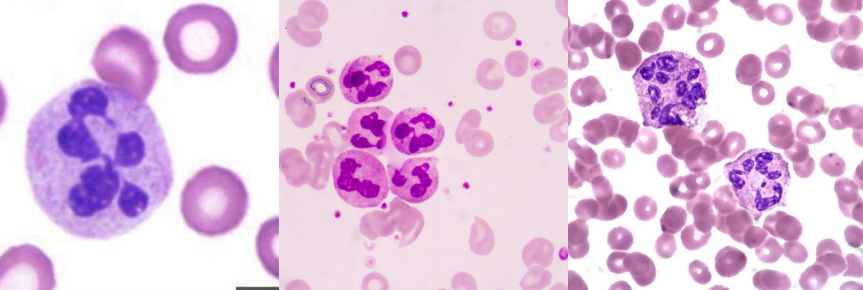
A. Hypersegmented neutrophils and oval macrocytes
B. Megaloblastic anemia
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
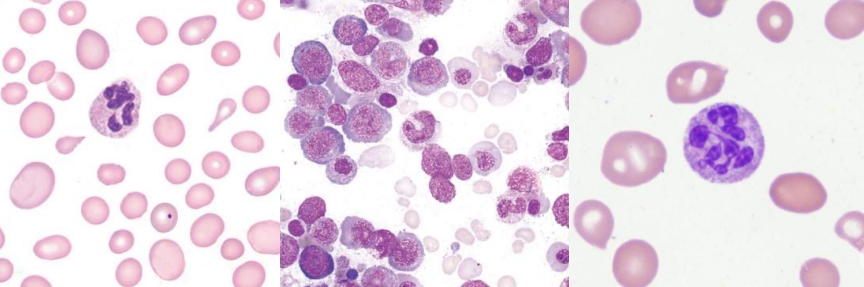
A. Aplastic anemia
B.
Idiopathic acquired aplastic anemia
Secondary acquired aplastic anemia
A. Identify the disease / Condition
B. What are the two major categories of this condition?
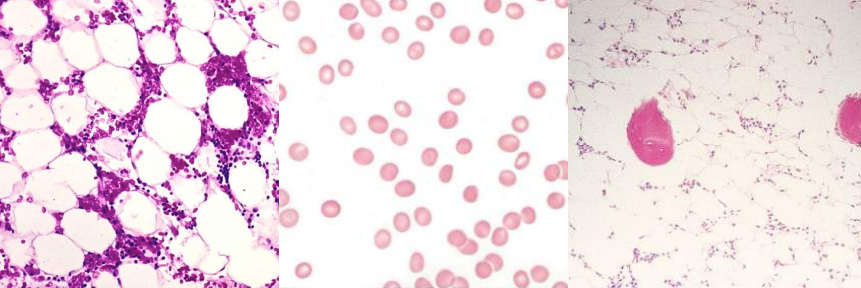
A. Pure Red Cell Aplasia
A. Identify the disease / condition
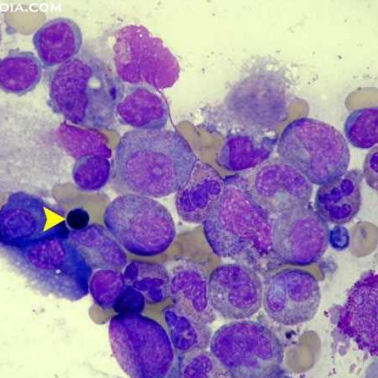
A. Myelophthisic anemia (presence of tear drop cells)
A. Identify the disease / condition
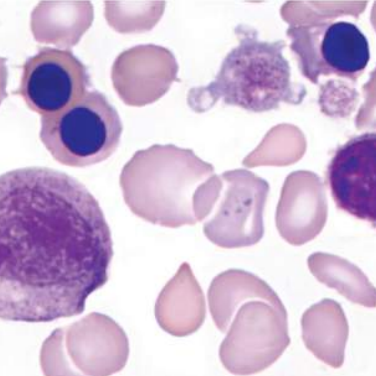
A. Congenital Dyserythropoetic Anemia
A. Identify the disease / condition
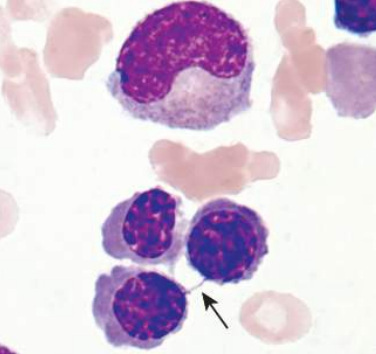
A. Hereditary spherocytosis
B. Ankyrin and Spectrin
A. Identify the disease / Condition
B. The most common mutated proteins are those that code for ______ and ______
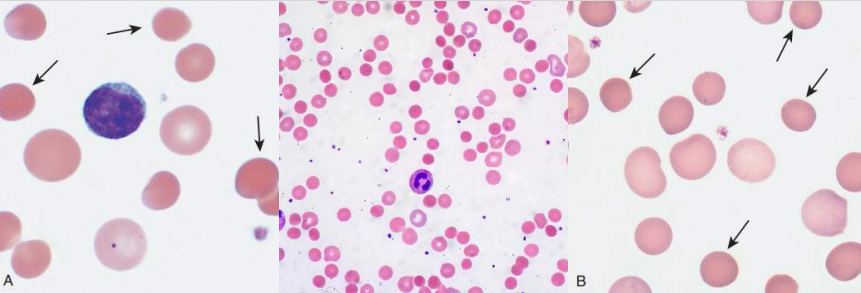
A. Hereditary Elliptocytosis
B.
SPTA1
SPTB
EPB41
A. Identify the disease / Condition
B. What are the defective genes? (3)
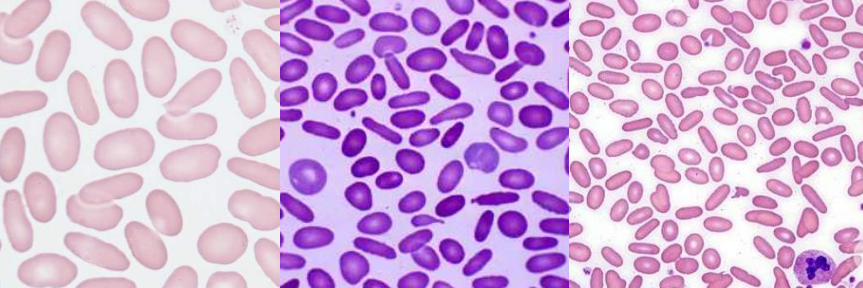
A. Hereditary Pyropoikilocytosis
B. TRUE
A. Identify the disease / Condition
B. TRUE OR FALSE.
This is now considered as a severe form of HE
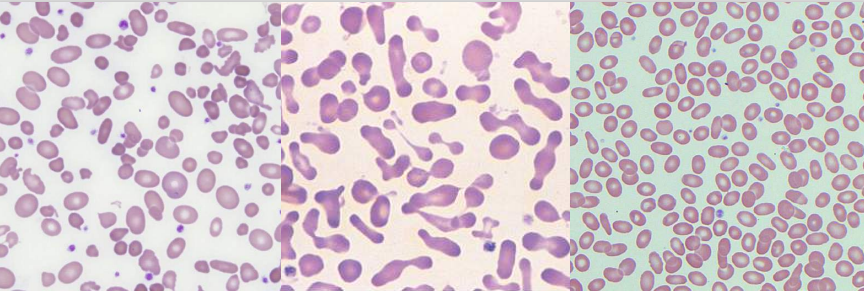
A. Overhydrated Hereditary Stomatocytosis
and Dehydrated Hereditary Stomatocytosis
B. RHAG Gene (Overhydrated); 16q23-24 (dehydrated)
A. Identify the disease / Condition
B. This has been linked with mutations in the __________
A. Spur Cell Anemia
A. Identify the disease / condition
A. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
A. Identify the disease / condition
A. Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
A. Identify the disease / condition
A. Thrombocytopenic Purpura (presence of schistocytes)
A. Identify the disease / condition
A.
Idiopathic TTP
Secondary TTP
Inherited TTP (aka Upshaw-Schulman syndrome)
B. Von willebrand factor cleaving protease known as ADAMTS-13
A. What are three 3 classifications?
B. This is a deficiency in?
A. Traumatic Cardiac Hemolytic Anemia
A. Identify the disease / condition
A. Malaria
A. Identify the disease / condition
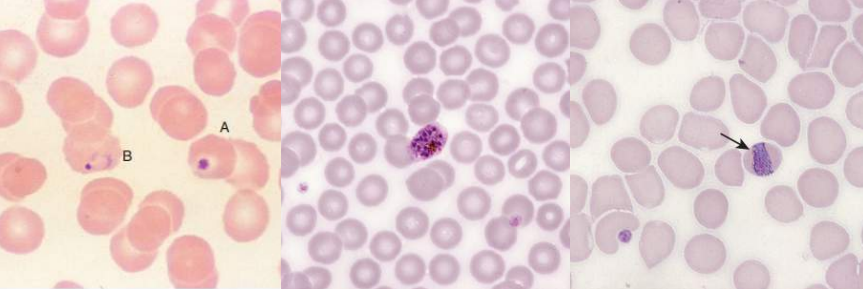
A. BABESIOSIS
A. Identify the disease / condition
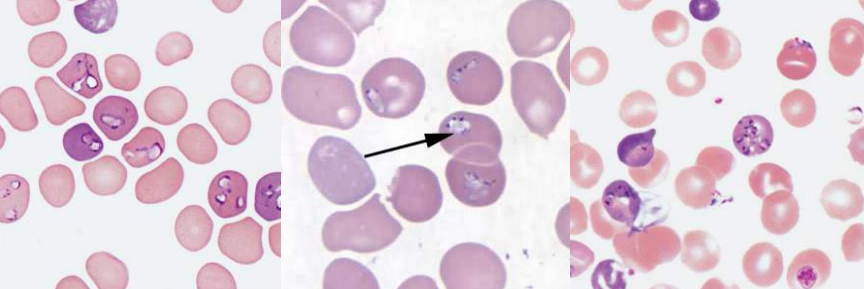
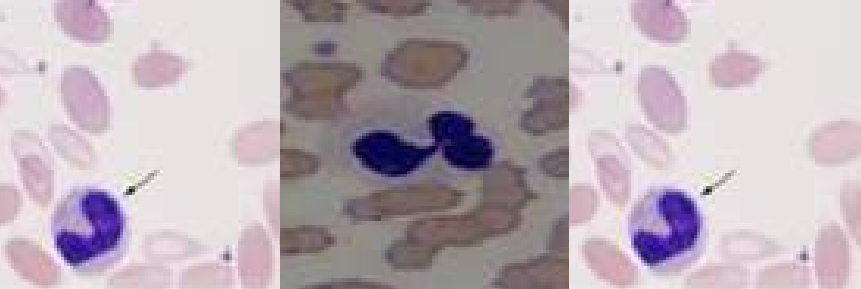
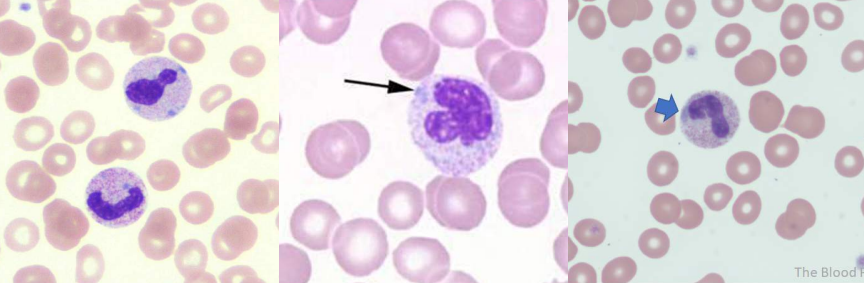
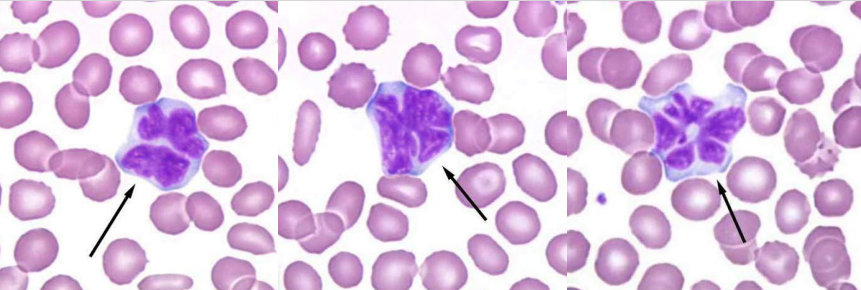
A. Hyposegmented Neutrophils
B. Pelger-Huet Anomaly
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
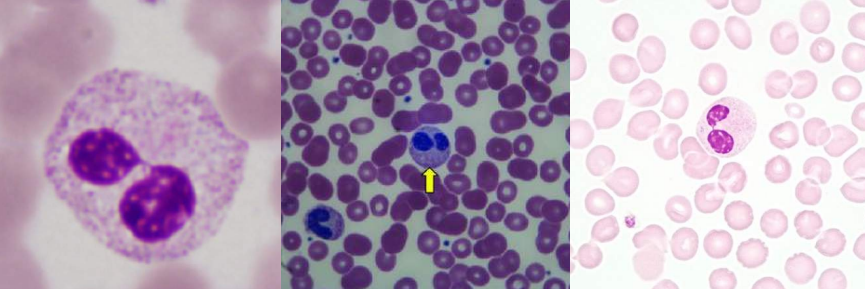
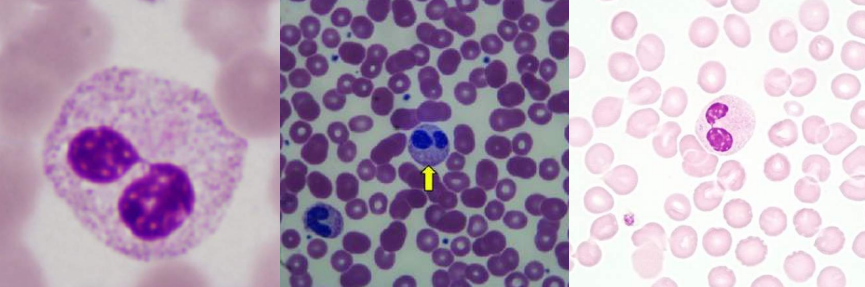
A. Hypersegmented Neutrophils
B. Megaloblastic Anemia
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
A. Auer Rods
B. Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
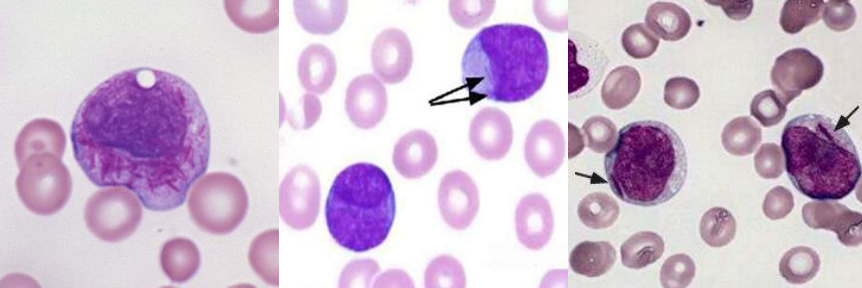
A. Dohle Bodies
B.
Food poisoining
Infections
Following chemotherapy
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
A. Atypical Lymphocytes
B.
Cytomegalovirus
Drugs
Epstein-Barr virus (infectious mononucleosis)
Syphilis
Toxoplasmosis
Viral hepatitis
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
A. Chediak-Higashi granules
B. Chediak-Higashi syndrome
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
A. Alder-Reilly granules
B.
Alder-Reilly anomaly
Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hurler’s)
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
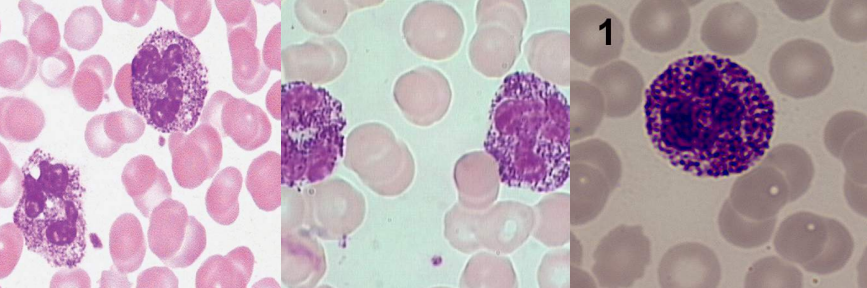
A. Toxic Granules / Vacuoles
B.
Infections
Burns
Malignancy
Chemical poisoning
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
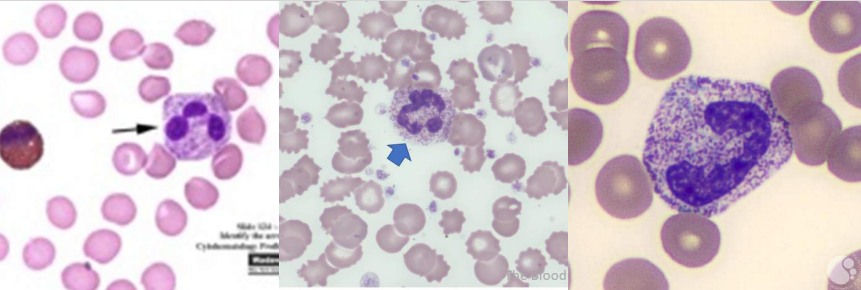
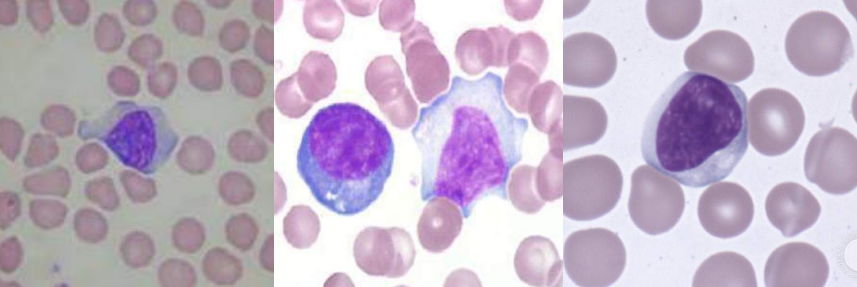
A. Smudge cells / Basket cells
B. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
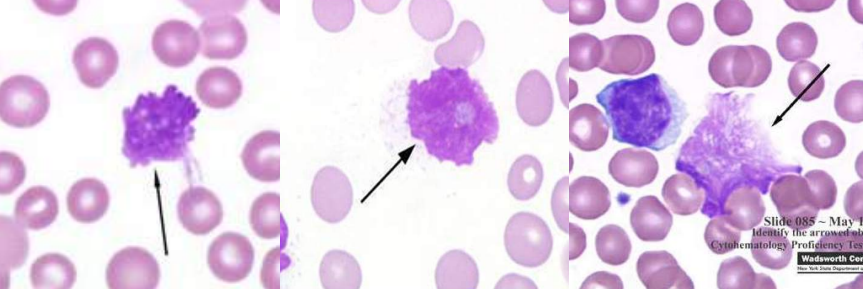
A. LE Cells
B. Lupus Erythematosus
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
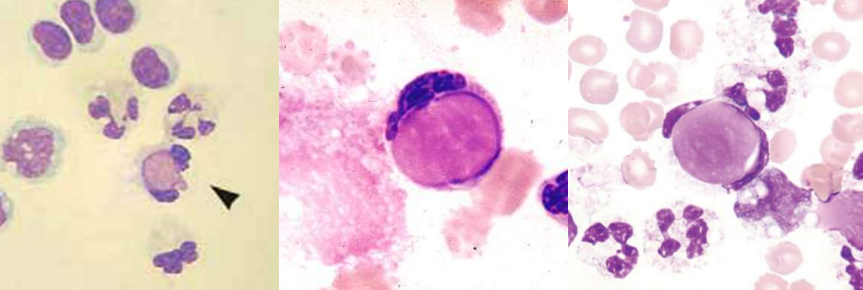
A. Hairy Cells
B. Hairy Cell Leukemia
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
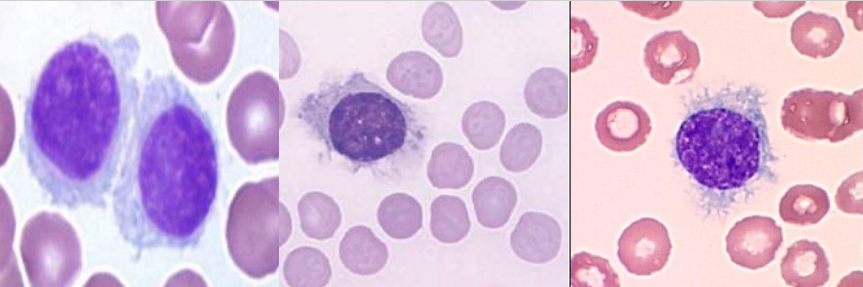
A. Sezary Cells
B.
Sezary syndrome
Mycosis Fungoides
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
A. Grape cells / Mott cells
B.
Multiple myeloma
Reactive states of lymphocytes
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
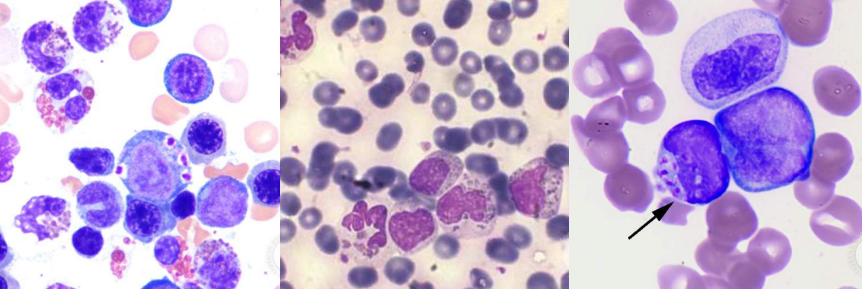
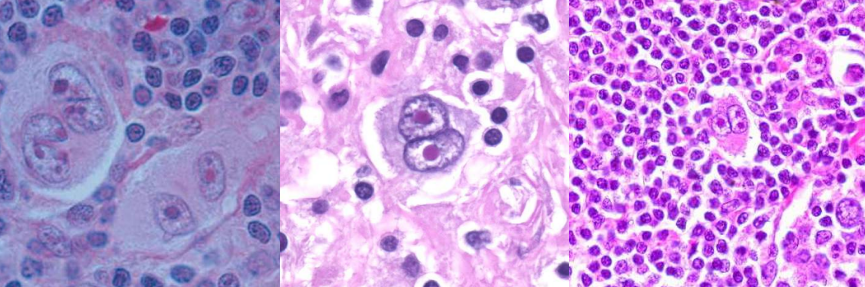
A. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
B. Reed-Sternberg cell
C. Owl’s Eye Appearance
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
C. What is the appearance?
A. Flame Cells
B. Multiple Myeloma
A. Identify the abnormality / cell
B. This is seen in what condition / disease
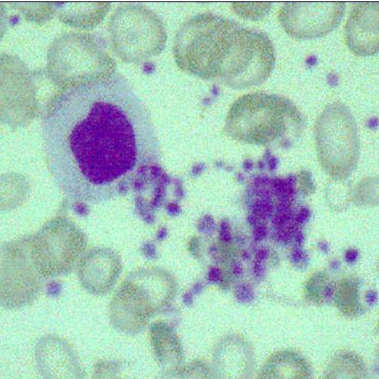
Essential Thrombocytopenia
A. Identify the disease / Condition
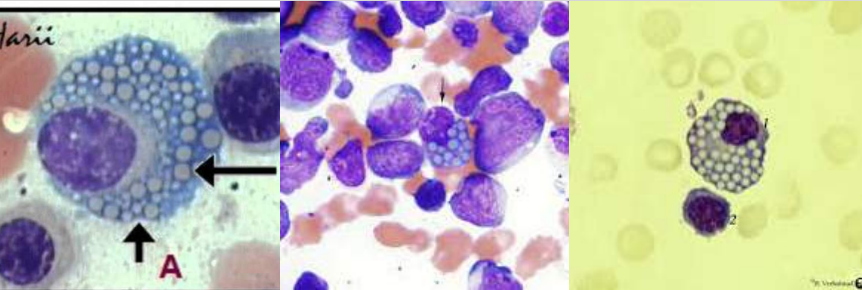
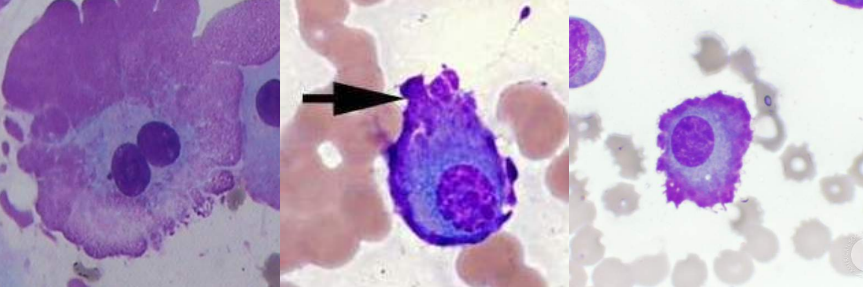
A. Gaucher Cells
B. Gaucher Disease
C. β-glucocerebrosidase
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Enzyme deficient
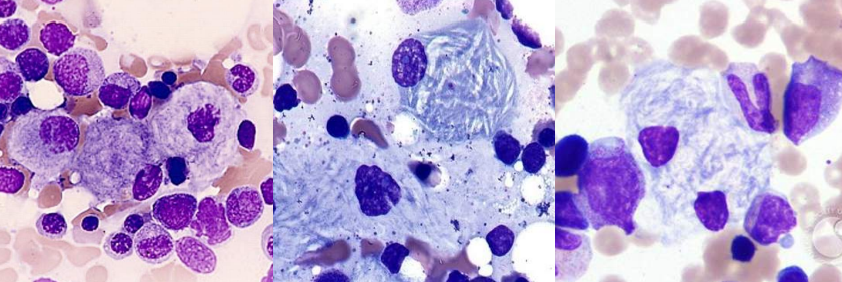
A. Niemann-Pick cells
B. Niemann-Pick disease
C. Sphingomyelinase
A. Identify the cell
B. Identify the disease / condition
C. Enzyme deficient
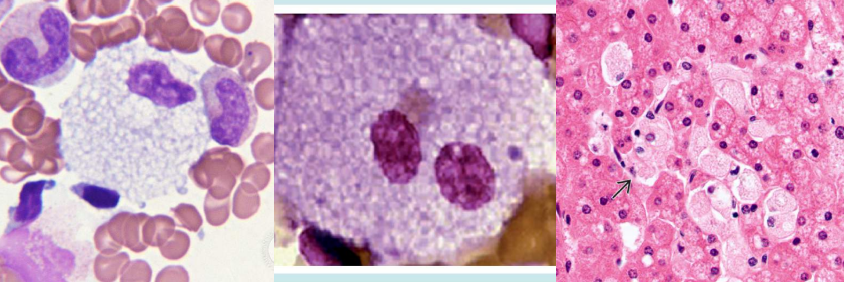
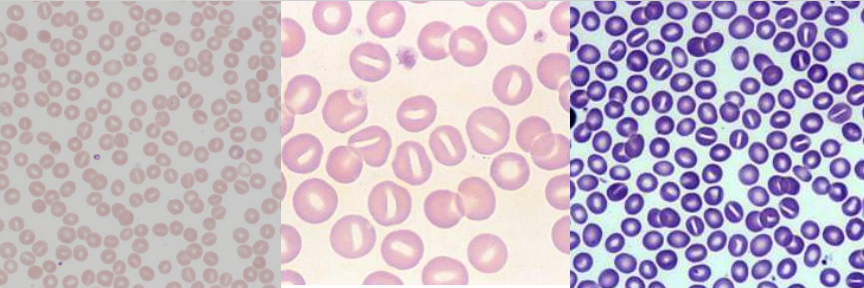
Anisocytosis
- Hemolytic Anemia
- Megaloblastic Anemia
- Iron deficiency Anemia
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Abnormal variation in RBC volume or diameter Parameter: RDW (Normal: 11.6-14.6); 20% increased
Macrocyte
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Chronic liver disease
- Bone marrow failure
- Reticulocytosis
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Large RBC (>8 mm in diameter) MCV: >100 fL
Oval Macrocyte
Megaloblastic Anemia
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Large oval RBC
Microcyte
- Anemia of chronic inflammation
- Sideroblastic anemia
- Thalassemia / Hb E disease and trait
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Small RBC (< 6 um in diameter)
MCV: < 80 fL
Poikilocytosis
- Severe anemia; certain shapes helpful diagnostically
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Abnormal variation in RBC shape
Spherocytes
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Immune hemolytic anemia
- Extensive burns (along with schistocytes)
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Small, round, dense RBC with no central pallor
Elliptocyte / Ovalocyte
- Hereditary elliptocytosis or ovalocytosis
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Thalassemia major
- Myelophthisic anemias
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Elliptical (cigar-shaped), oval (egg-shaped) RBC
Stomatocytes
- Hereditary stomatocytosis
- Rh deficiency syndrome
- Acquired stomatocytosis (liver disease, alcoholism) - Artifact
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
RBC with slit-like area of central pallor
Sickle cells
- Sickle cell anemia
- Sickle cell-β-thalassemia
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Thin, dense, elongated RBC pointed at each end; may be curved
Hb C crystals
Hb C disease
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Hexagonal crystal of dense hemoglobin formed within the RBC membrane
Hb SC crystals
Hb C disease
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Finger-like or quartz-like crystal of dense hemoglobin protruding from the RBC membrane
Target cells (Codocytes)
- Liver disease
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Thalassemia
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
RBC with hemoglobin concentrated in the center and around the periphery resembling a target
Schistocytes (Schizocytes)
- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia* (along with microspherocytes)
- Macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia
- Extensive burns (along with microspherocytes)
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Fragmented RBC caused by rupture in the peripheral circulation
Helmet cells (Keratocytes)
- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia* (along with microspherocytes)
- Macroangiopathic hemolytic anemia
- Extensive burns (along with microspherocytes)
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
RBC fragment in shape of a helmet
Folded cell
- Hb C disease
- Hb SC disease
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
RBC with membrane folded over
Acanthocytes (Spur cells)
- Severe liver disease (spur cell anemia)
- Neuroacanthocytosis (abetalipoproteinemia, McLeod syndrome)
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
Small, dense RBC with few irregularly spaced projections of varying length
Burr cells (Echinocytes)
- Uremia
- Pyruvate kinase deficiency
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
RBC with blunt or pointed, short projections that are usually evenly spaced over the surface of cell; present in all fields of blood film but in variable numbers per field
Teardrop cells (Dacryocytes)
- Primary myelofibrosis
- Myelophthisic anemia
- Thalassemia
- Megaloblastic anemia
RBC Abnormality: ?
Commonly Associated Disease: ?
Cell Description:
RBC with a single pointed extension resembling a teardrop or pear
Diffuse Basophilia
RNA
Hemolytic anemia after treatment for iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiency
Inclusion: ?
Composition: ?
Associated Diseases: ?
Appearance in Supravital Stain:
Dark blue granules and filaments in cytoplasm (seen in reticulocytes)
Appearance in Wright Stain:
Bluish tinge throughout cytoplasm; also called polychromasia (seen in polychromatic erythrocytes)
Basophilic Stippling
Precipitated RNA
- Lead poisoning
- Thalassemias
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
Inclusion: ?
Composition: ?
Associated Diseases: ?
Appearance in Supravital and Wright Stain:
Dark blue-purple, fine or coarse punctate granules distributed throughout cytoplasm
Howell-Jolly Bodies
DNA (Nuclear Fragments)
- Hyposplenism
- Postsplenectomy
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Hemolytic anemia
- Thalassemia
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
Inclusion: ?
Composition: ?
Associated Diseases: ?
Appearance in Supravital and Wright Stain:
Dark blue-purple dense, round granule; usually one per cell; occasionally multiple
Heinz Bodies
Denatured Hemoglobin
- G6PD Deficiency
- Unstable hemoglobins
- Oxidant drugs/chemicals
Inclusion: ?
Composition: ?
Associated Diseases: ?
Appearance in Supravital Stain:
Round, dark blue-purple granule attached to inner RBC membrane
Appearance in Wright Stain:
Not visible
Pappenheimer Bodies
Iron
- Sideroblastic anemia
- Hemoglobinopathies
- Thalassemias
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Hyposplenism
- Postsplenectomy
Inclusion: ?
Composition: ?
Associated Diseases: ?
Appearance in Supravital and Wright Stain:
Irregular clusters of small, light to dark blue granules, often near periphery of cell
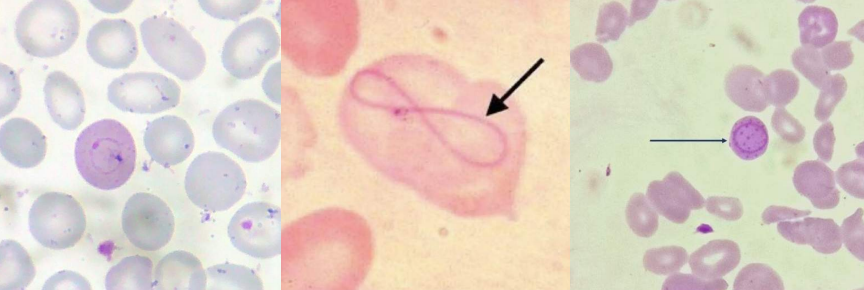
Cabot Rings
Precipitated β-globin chains of hemoglobin
Hb H disease
Inclusion: ?
Composition: ?
Associated Diseases: ?
Appearance in Supravital Stain:
Rings or figure-eights
Appearance in Wright Stain:
Blue rings or figure-eights