Bone composition
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
–relatively dense connective bone tissue
–appears white, smooth, and solid
–80% of bone mass
Compact bone (dense or cortical bone)
–located internal to compact bone
–appears porous
–20% of bone mass
Spongy bone (cancellous or trabecular bone)
External surface composed of compact bone
Interior composed of spongy bone
also called diploë in flat skull bones
Lack a medullary cavity
Short, flat, and irregular bones
What is spongey bone called in the skull?
diploë
Functions of the skeletal system
supporting framework
It interacts with all other organ systems
The skeletal system is composed of dynamic living tissues
continually rebuilds and remodels itself
Bones of the skeleton
Cartilage
Ligaments
Other connective tissues
What are the primary components of the skeletal system?
Semi-rigid connective tissue
More flexible than bone
Cartilage
What are the types of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
Fibrocartilage
cartilage within growth plates
model for formation of most bones
Hyaline cartilage
weight-bearing cartilage that withstands compression
Fibrocartilage
Anchor bone to bone
Ligaments
Anchor muscle to bone
Tendons
Greater in length than width
Have elongated, cylindrical shaft (diaphysis)
Most common bone shape
Found in upper and lower limbs
e.g., arm, forearm, fingers, thigh, leg, toes
Vary in size
Long bones
What are some examples of long bones?
Femur
Tibia
Fibula
Humerus
Ulna
Radius
Metarsals (5 long bones in foot)
Metacarpals (5 long bones in hand)
Length nearly equal to width
Short bones
What are some examples of short bones?
carpal bones (wrist bones)
sesamoid bones, bones along tendons of muscles
patella (kneecap), largest sesamoid bone
What are the bones along tendons of muscles called?
sesamoid bones
What is the largest sesamoid bone?
patella (kneecap)
Flat, thin surfaces, may be slightly curved
Provide surfaces for muscle attachment
Protect underlying soft tissues
Form:
the roof of the skull
the scapulae
the sternum
the ribs
Have elaborate shapes
E.g., vertebrae, ossa coxae (hip bones)
E.g., several bones in the skull (ethmoid, sphenoid)
Flat bones
What do flat bones form?
roof of the skull
scapulae
sternum
ribs
What are the 2 types of bone marrow?
Yellow and red
–Hemopoietic (blood cell forming)
–Contains reticular connective tissue, immature blood cells, and fat
–In children,
•located in the spongy bone and medullary cavity of long bones
-In adults,
located in portions of axial skeleton
located in proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur
e.g., skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ossa coxae
condition with reduced erythrocytes (red blood cells
Red bone marrow (myeloid tissue)
–Product of red bone marrow degeneration
–Fatty substance
–May convert back to red bone marrow
•may occur during severe anemia
•facilitates the production of additional erythrocytes
Yellow bone marrow
Yellow bone marrow can _____ back to red bone marrow
convert
When can yellow bone marrow occur?
During severe anemia
In Children where is red bone marrow located?
In the spongy bone and medullary cavity of long bones
In adults where is red bone marrow located?
In portions of axial skeleton
proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur
e.g., skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ossa coxae
condition with reduced erythrocytes (red blood cells
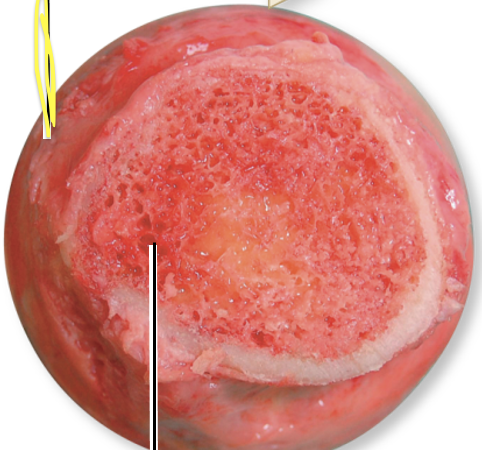
What is the yellow line pointing to?
Red bone marrow
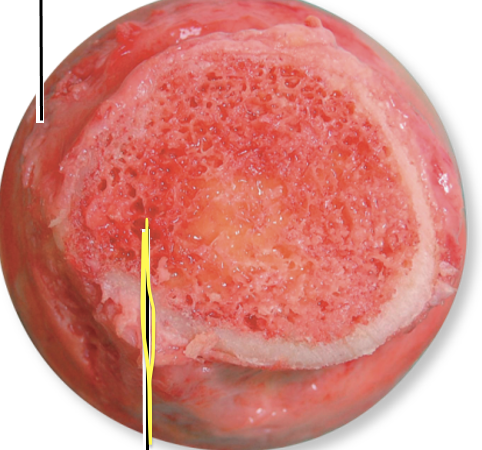
What is the yellow line pointing to?
Yellow bone marrow
Compact bone is composed of
osteons
–Small cylindrical structures
–Also known as Haversian systems
–Basic functional and structural unit of mature compact bone
–Oriented parallel to bone diaphysis
osteons
What are the Components of osteons?
Central canal
Osteocytes
Concentric lamellae
Canaliculi
Perforating canals (Volkmann canals)
cylindrical channel
lies at center of osteon and runs parallel to it
blood vessels and nerves traveling here
Central canal
What is inside the Central canal?
blood vessels and nerves
mature bone cells
found in small spaces between concentric lamellae (lacunae)
maintain bone matrix
Osteocytes
rings of bone connective tissue
surround the central canal
contain collagen fibers
oriented at an angle 90 degrees from previous and next lamellae
give bone part of its strength and resilience
Concentric lamellae
rings of bone
may run immediately internal to bone periosteum (external circumferential lamellae)
may run internal to the endosteum (internal circumferential lamellae)
run the entire circumference of bone
Circumferential lamellae
Internal to bone periosteum is called?
external circumferential lamellae
internal to the endosteum is called?
internal circumferential lamellae
may be components of compact bone between osteons
may be partially resorbed osteons
look like a “bite” taken out of them
Interstitial lamellae
tiny interconnecting channels within bone connective tissue
extend from each lacuna
travel through lamellae
connect to other lacunae and central canal
house osteocyte projections permitting intercellular contact
allow travel of nutrients, minerals, gases, and wastes between blood vessels and osteocytes
Canaliculi
Spongy Bone
open lattice of narrow rods and plates of bones
bone marrow filling spaces between
form a meshwork of crisscrossing bars
provide great resistance to stresses
Trabeculae
composed of bone matrix
osteocytes resting between lamellae
canaliculi radiating from lacunae
Parallel lamellae
What are the 2 aspects/ categories of Spongey bone?
Trabeculae and Parallel lamellae
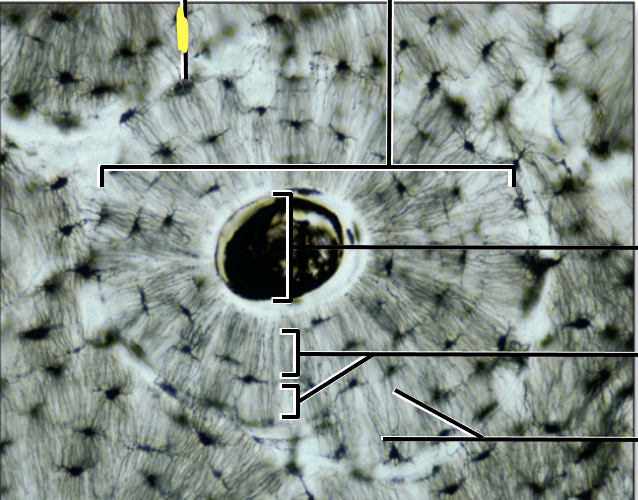
What is the yellow line pointing to?
lacuna (with osteocyte)
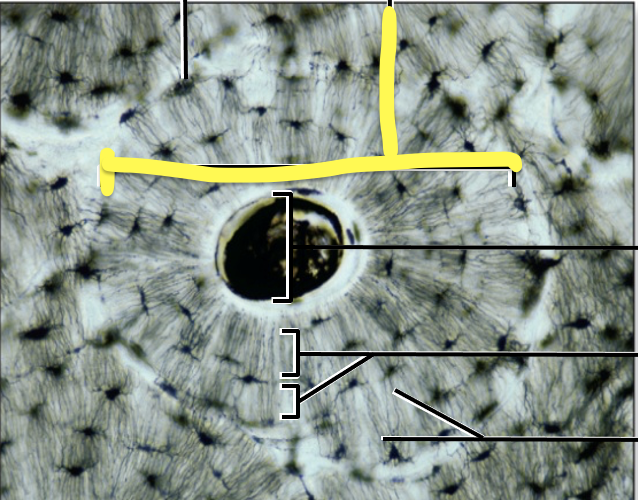
What is the yellow line pointing to?
Osteon
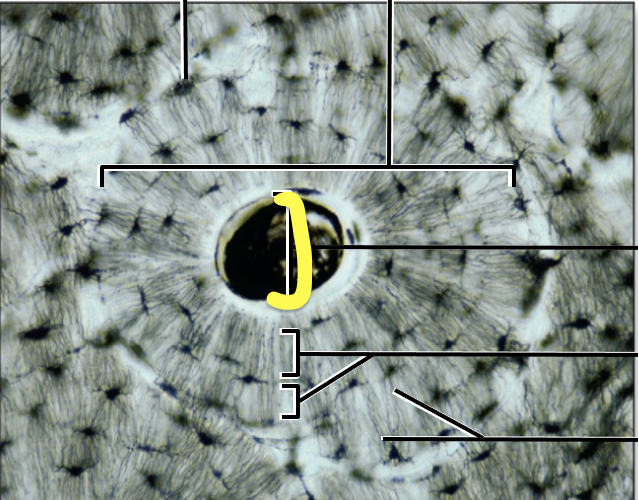
What is the yellow line pointing to?
Central Canal
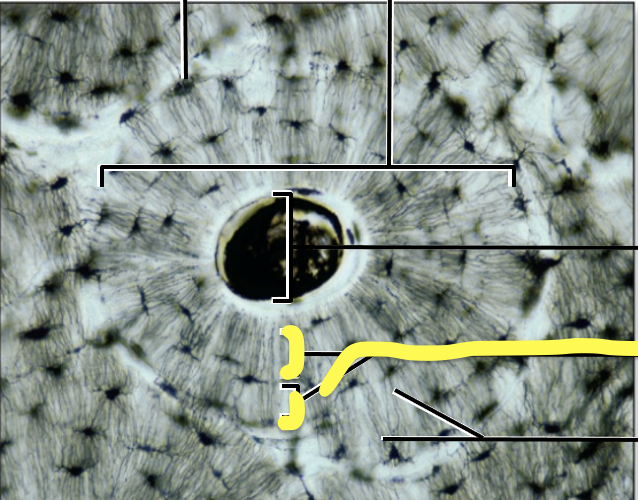
What is the yellow line pointing to?
Concentric lamellae
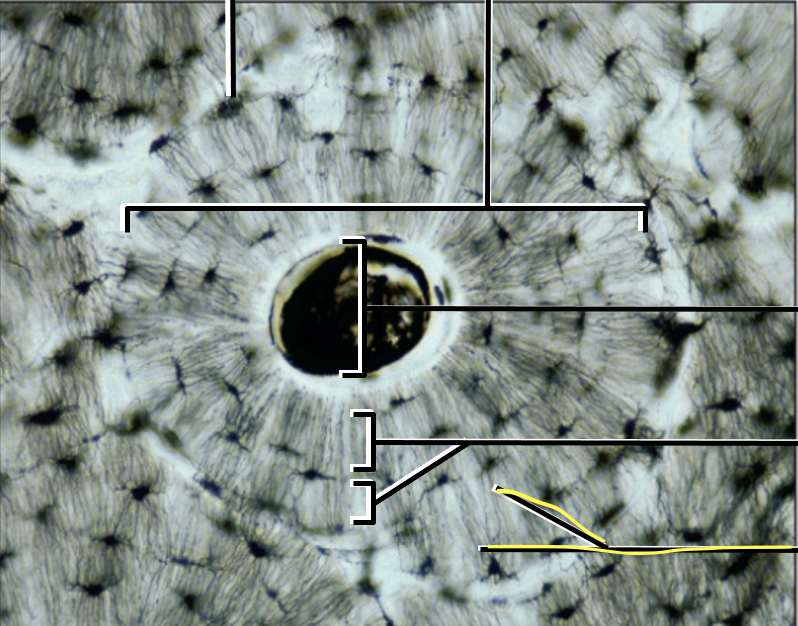
What is the yellow line pointing to?
Cuniculi
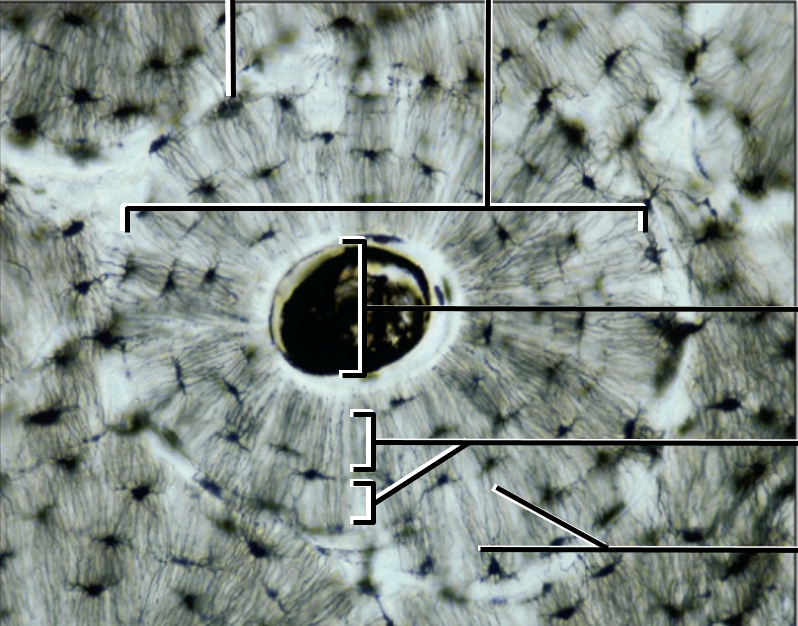
what is this?
Compact Bone
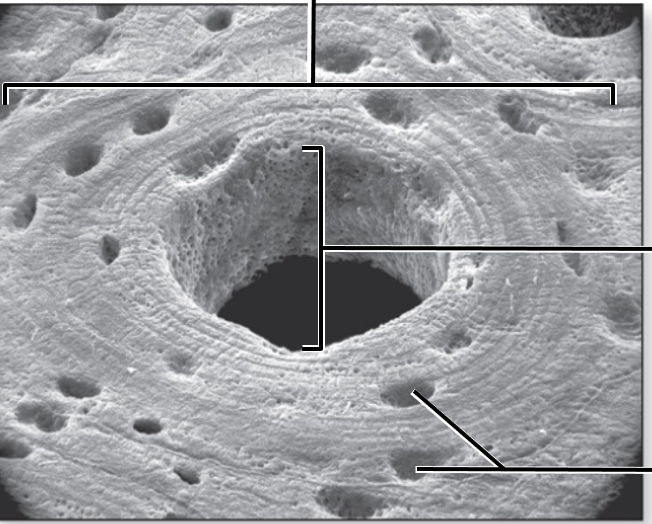
what is this?
Compact Bone