AQA GCSE Physics - Magnetism & Electromagnetism
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Magnet
something that attracts iron and steel

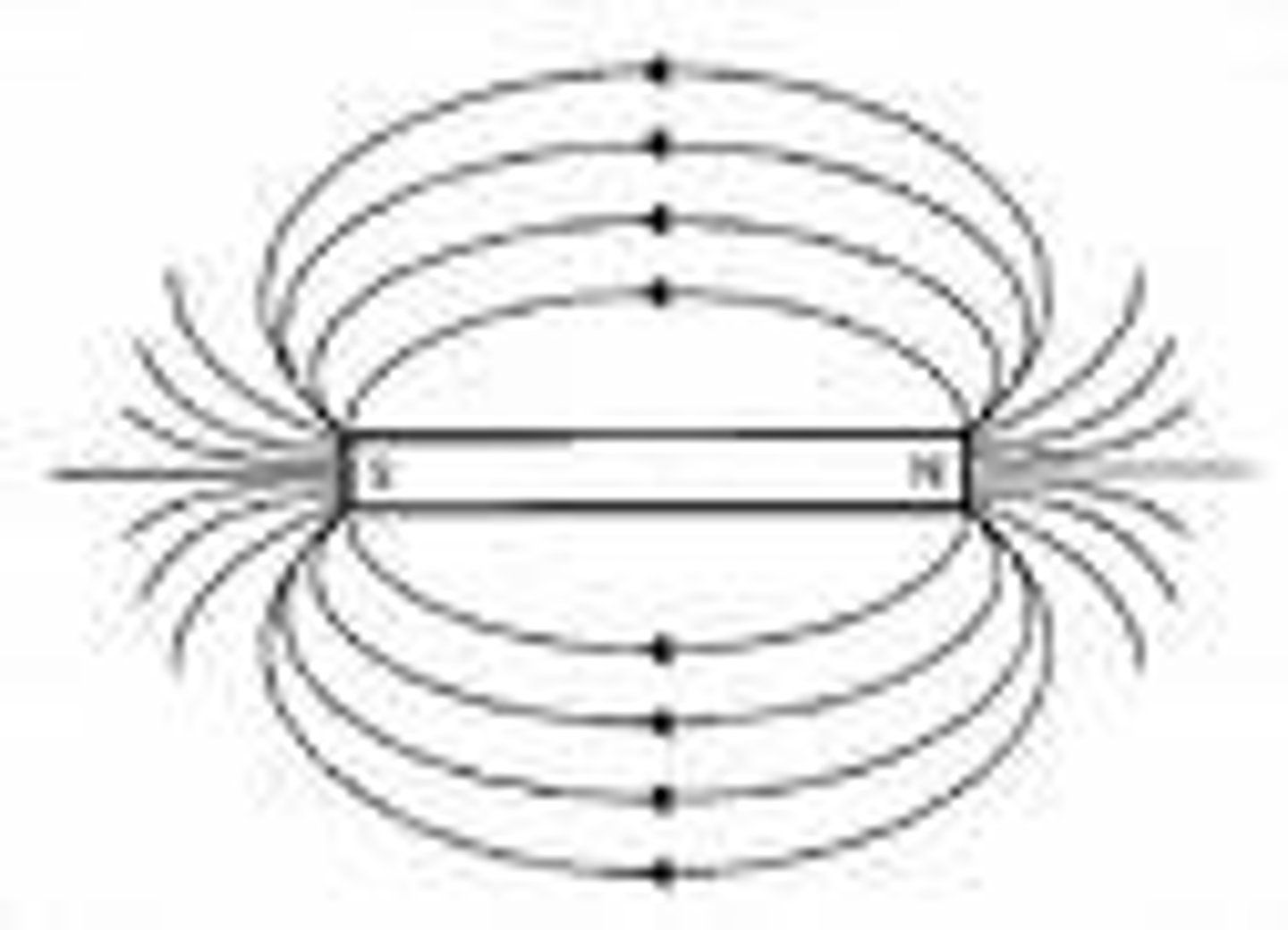
Magnetic Field
The area of magnetic force around a magnet
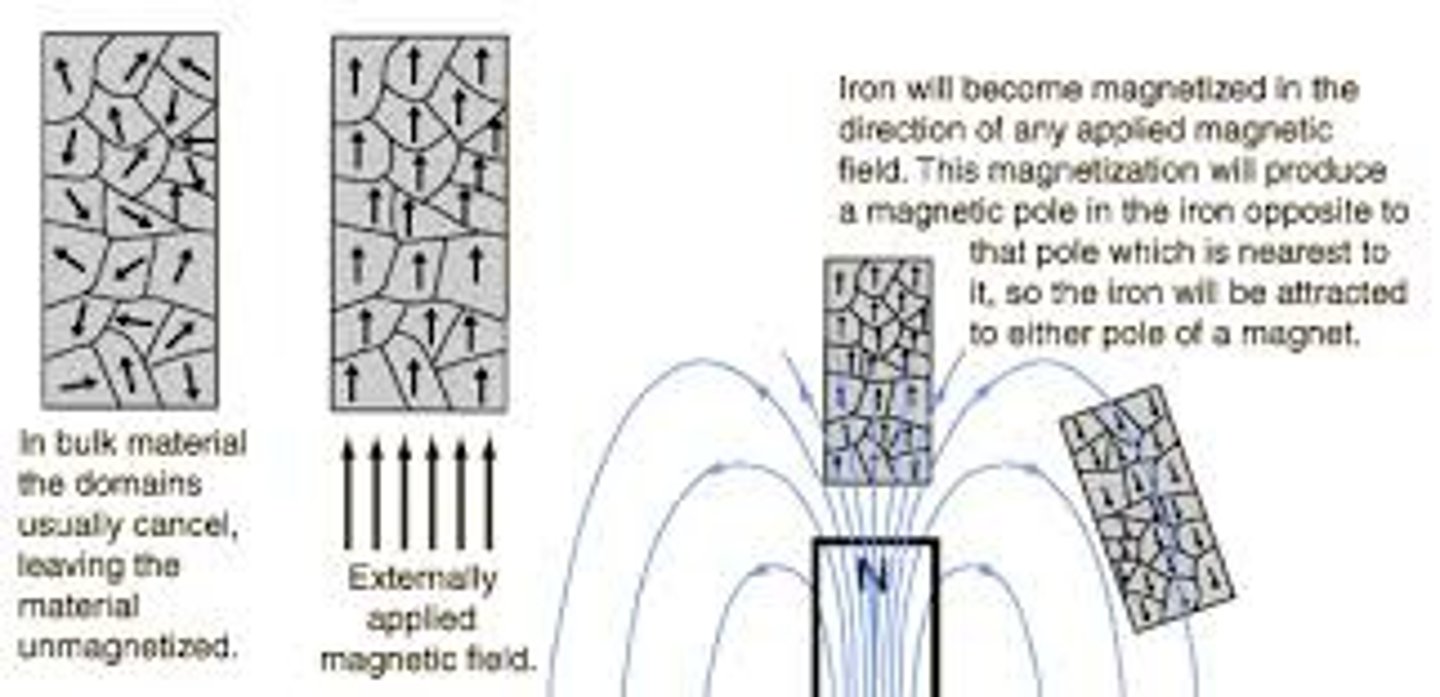
Magnetic Domains
A group of atoms whose magnetic fields are aligned
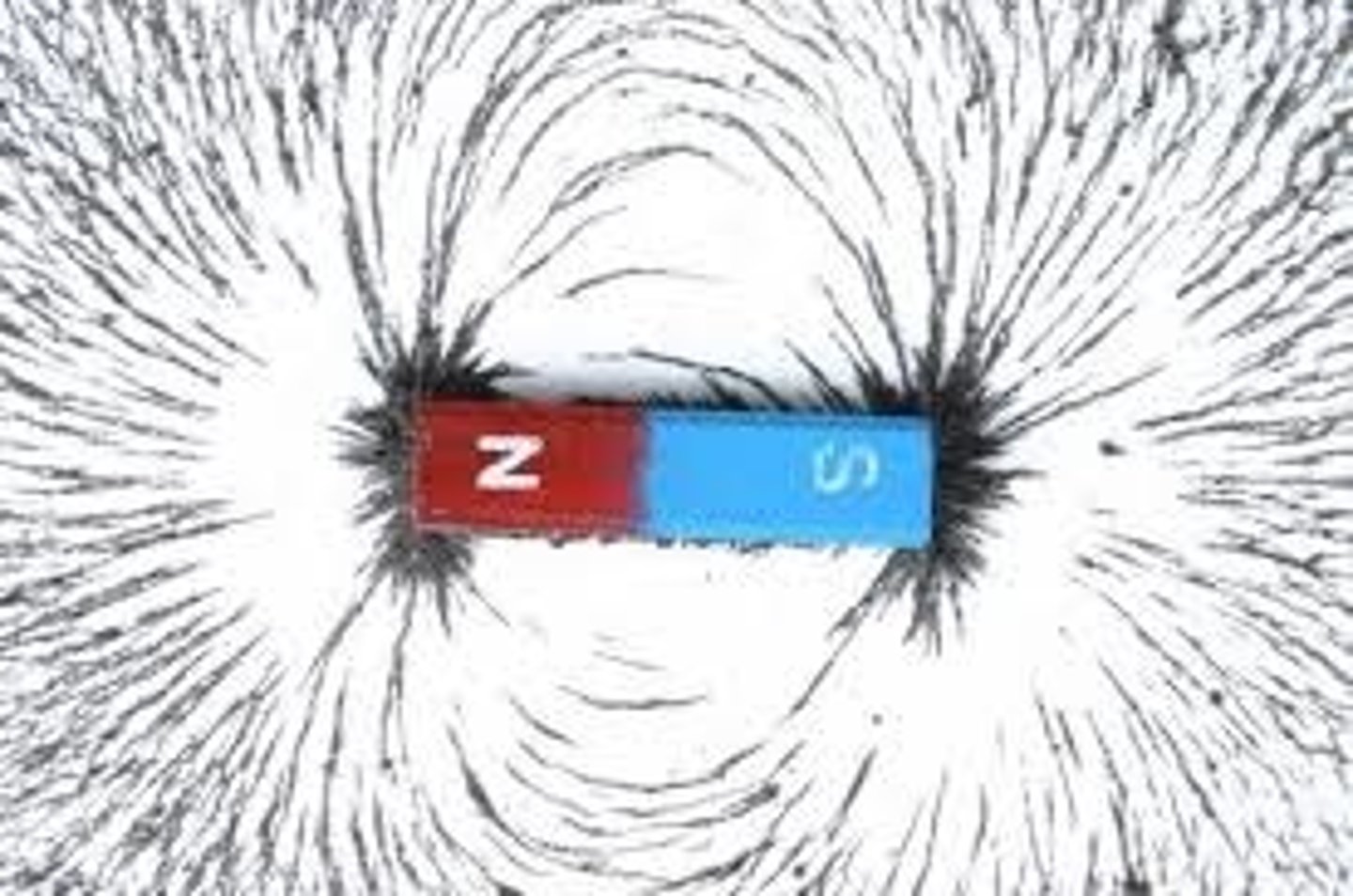
North Pole
the end of a magnet that seeks the earth's north magnetic pole.
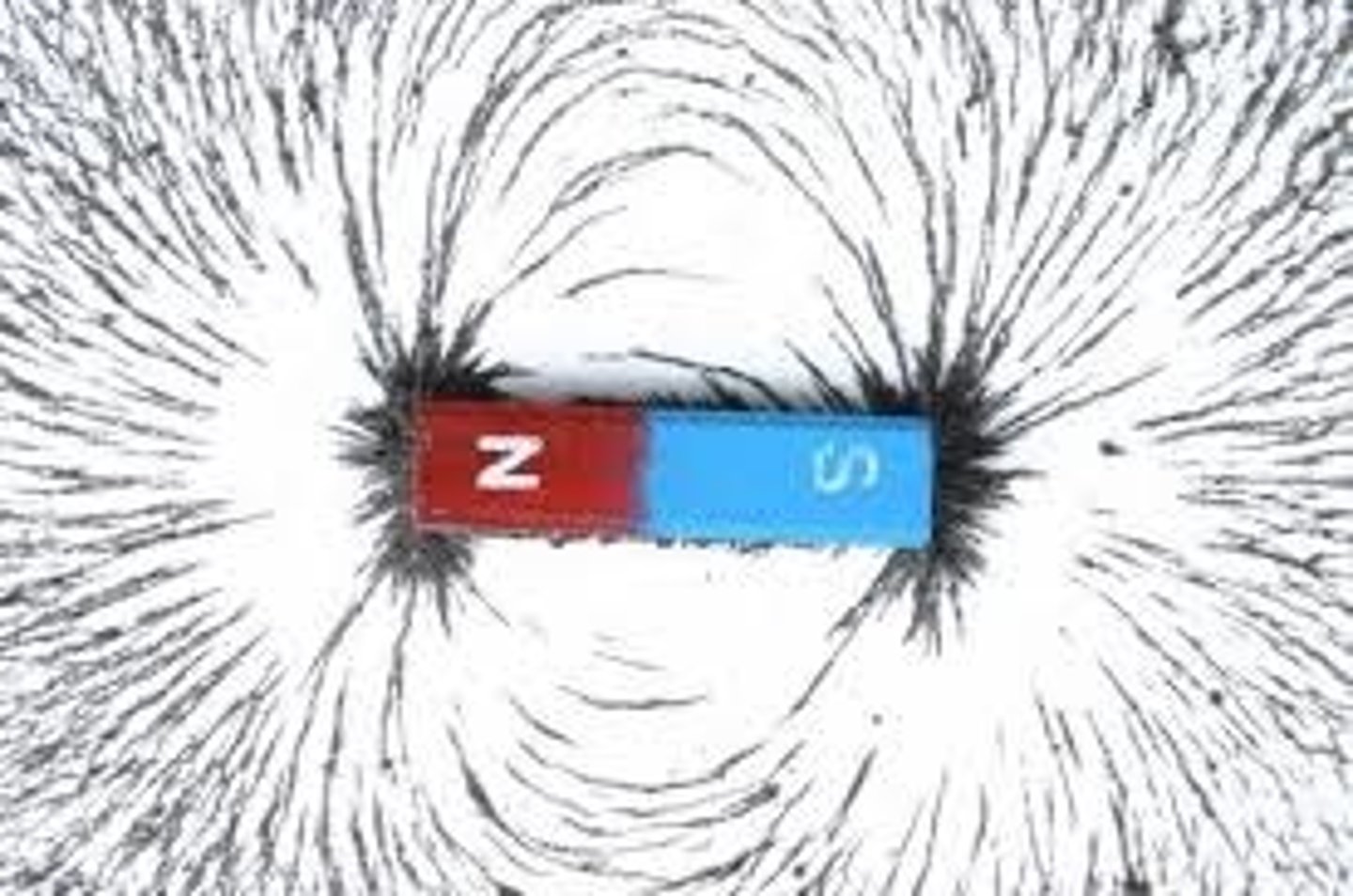
South Pole
the end of a magnet that seeks the earth's south magnetic pole.
Magnetite & Lodestone
A mineral with magnetic properties

Compass
an instrument that has a magnetized needle generally in line with the magnetic poles of the earth.

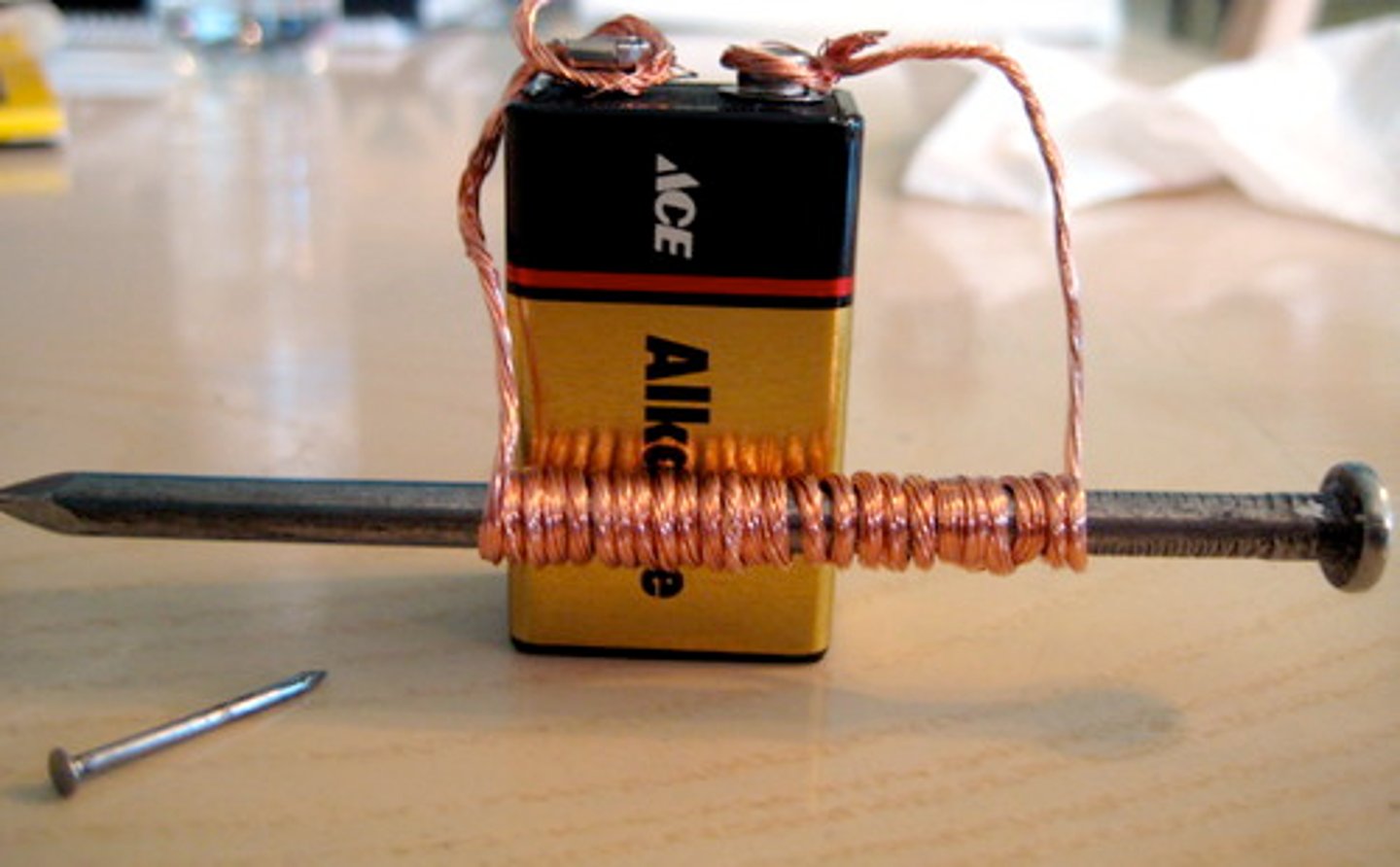
Electromagnets
A magnet created by electricity. It only works when surrounded by electric field

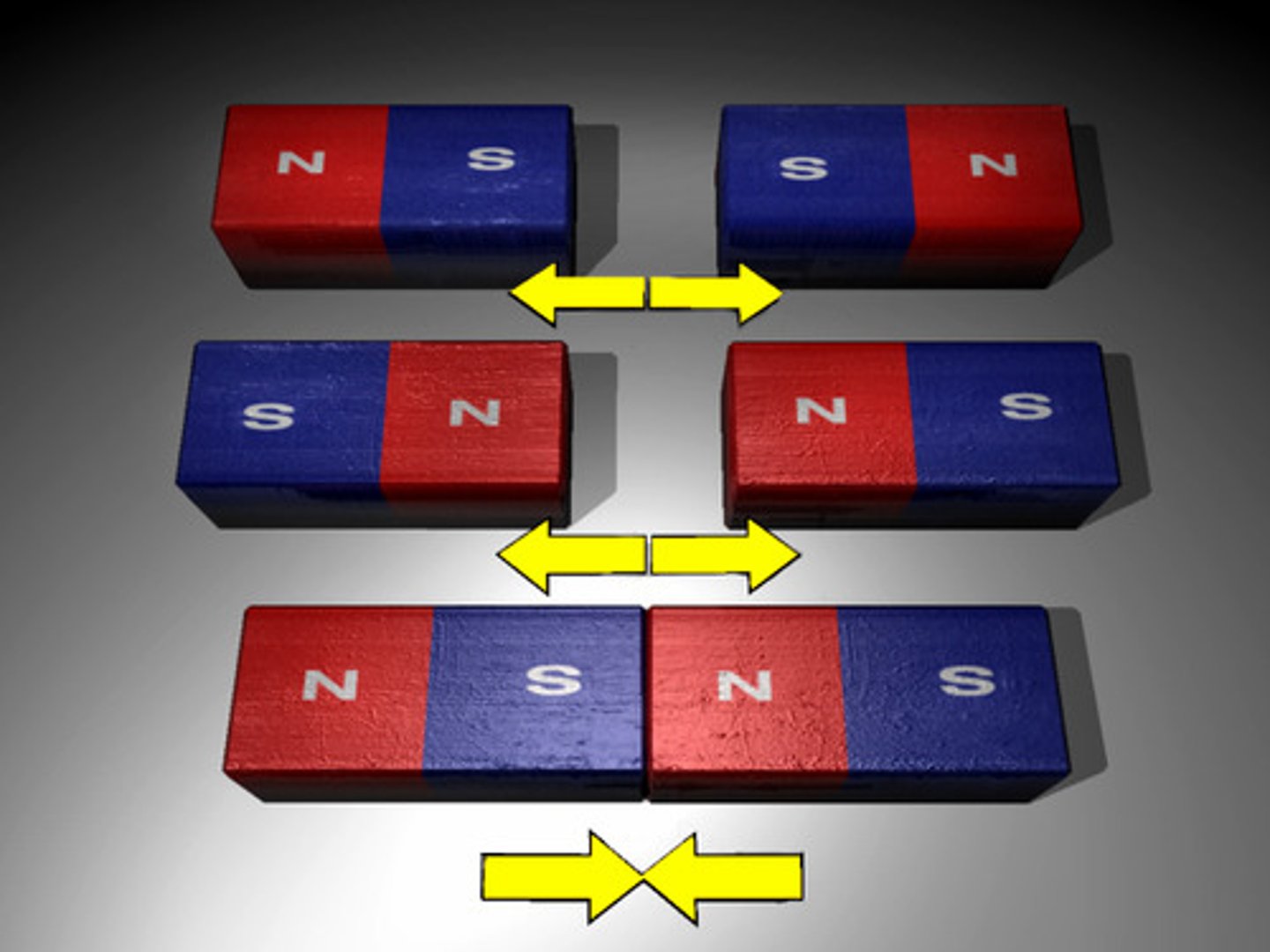
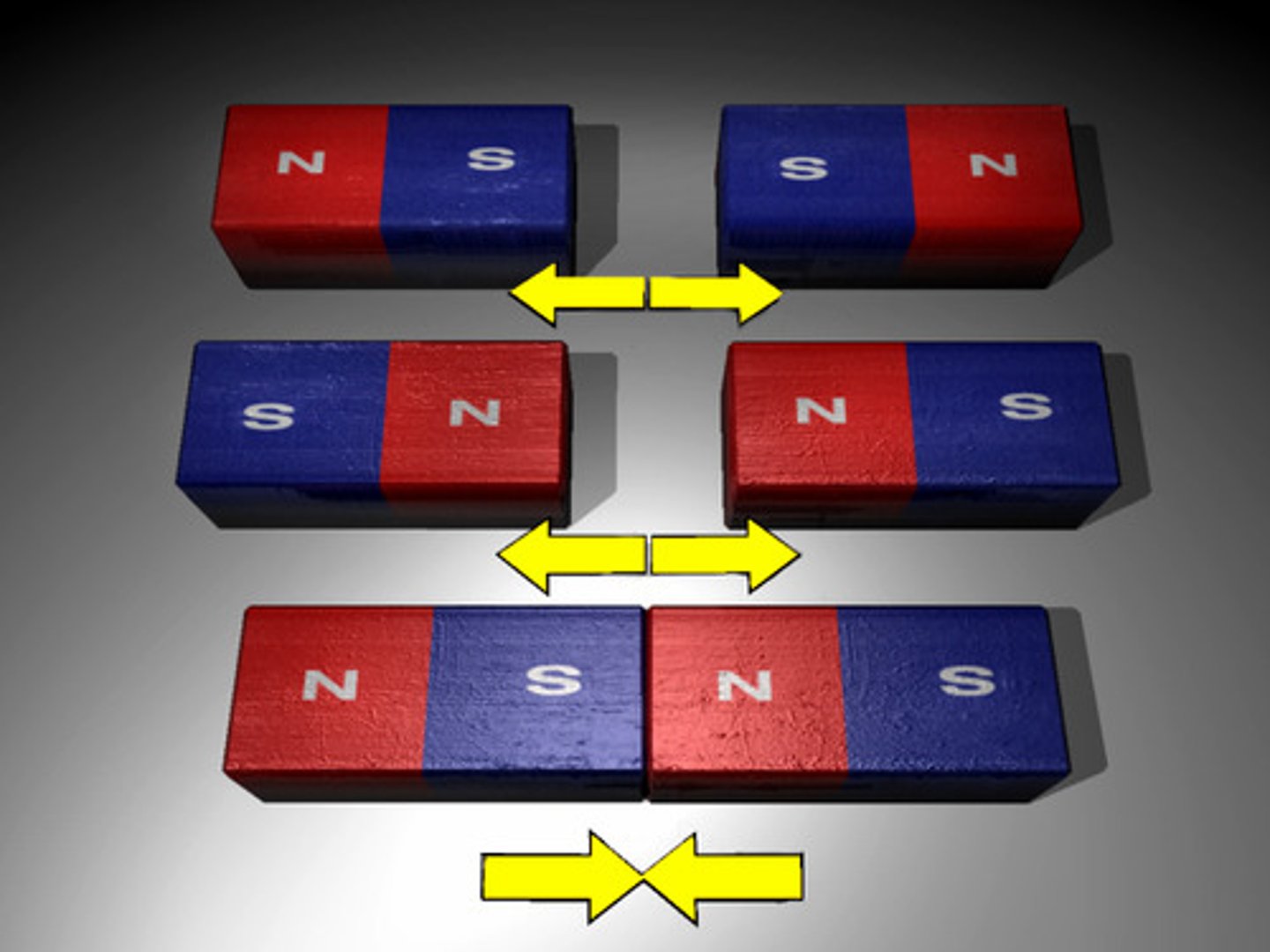
Attraction
When two magnets or magnetic objects are close to each other, there is a force that pulls the two poles together
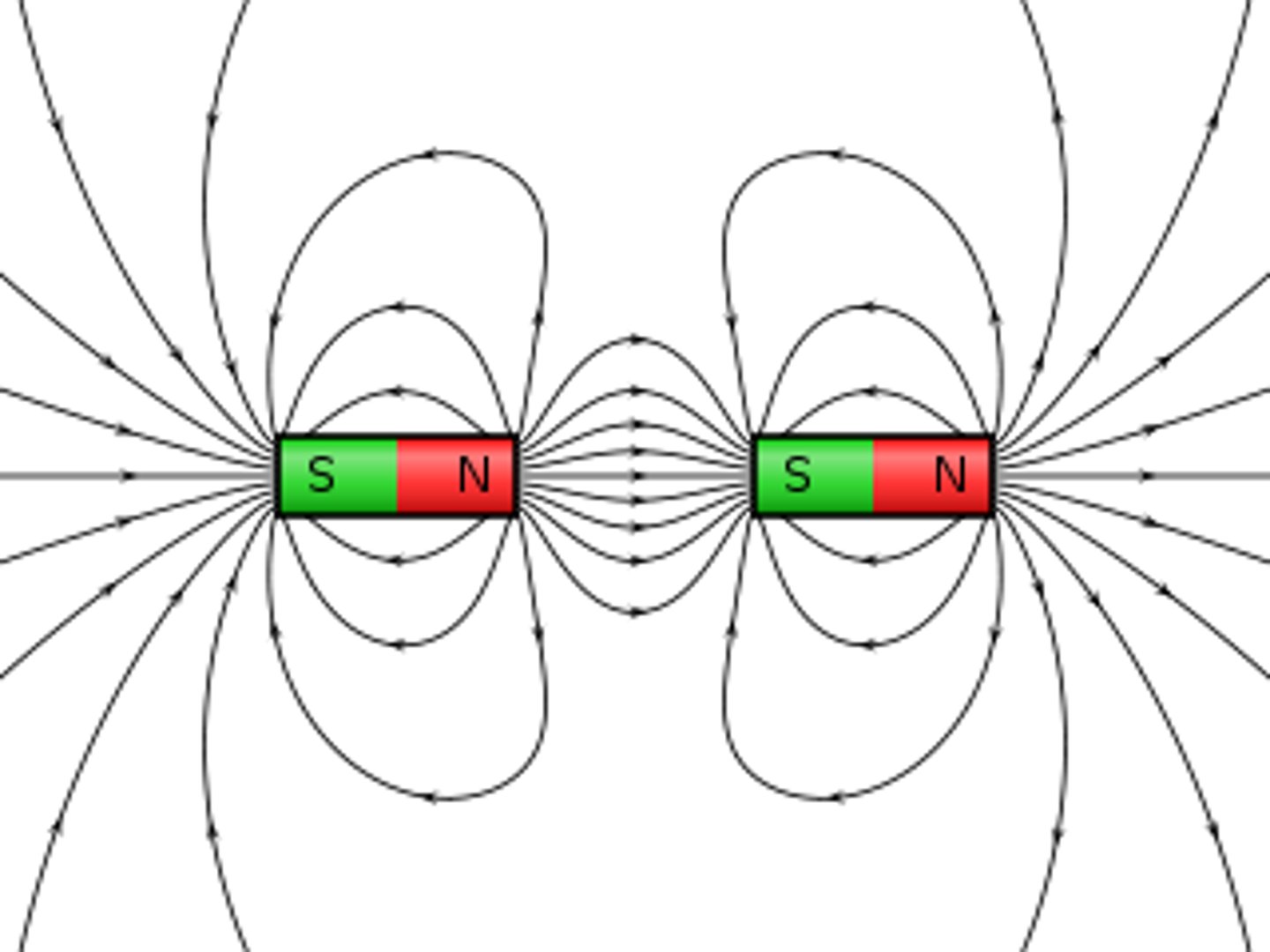
Repulsion
When two magnetic objects have like poles facing each other, the magnetic force pushes them apart.
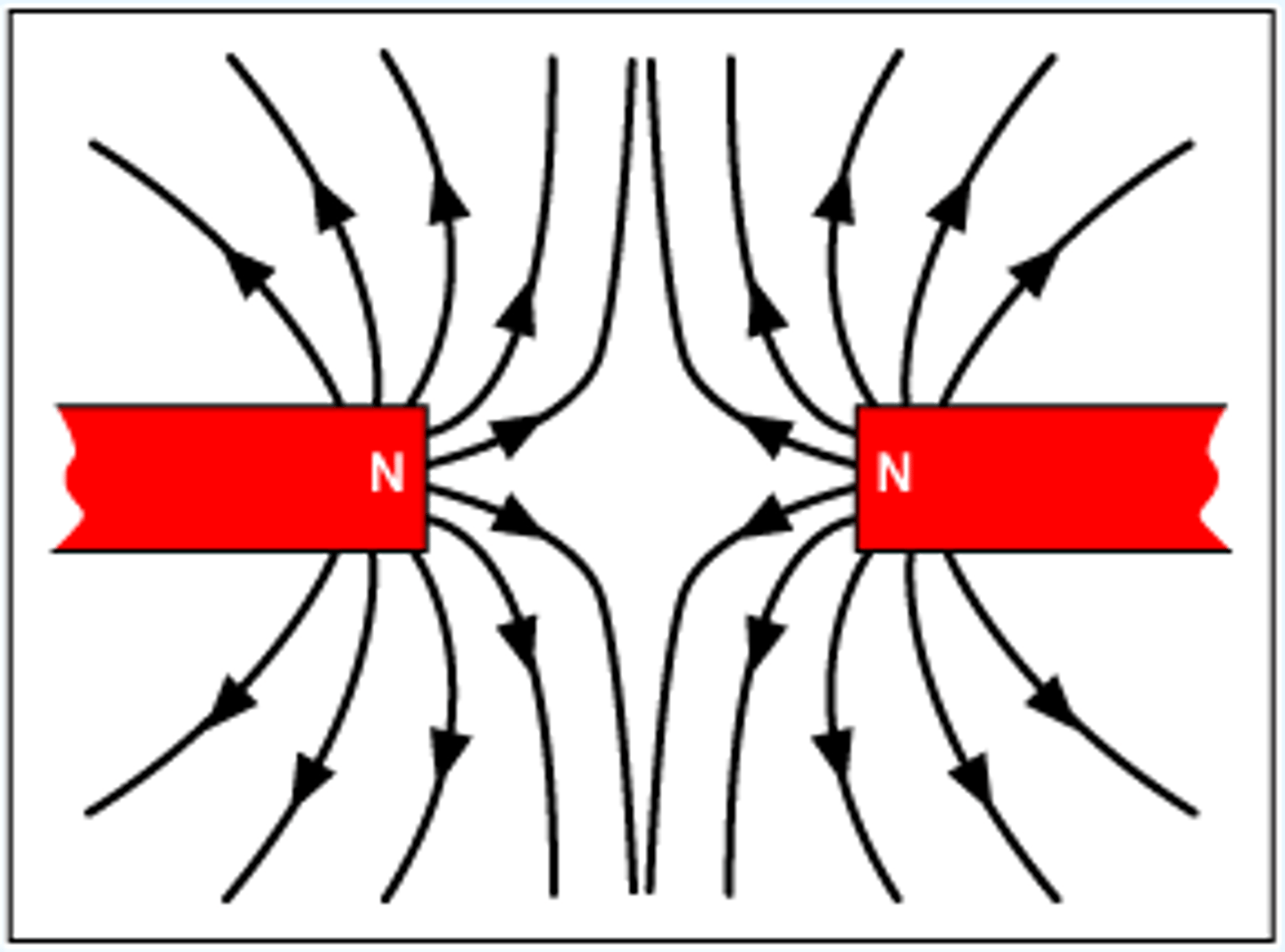
Magnetic poles
The two areas of a magnet with the strongest magnetic force.
Atoms
The smallest particle of an element, has all the properties of an element
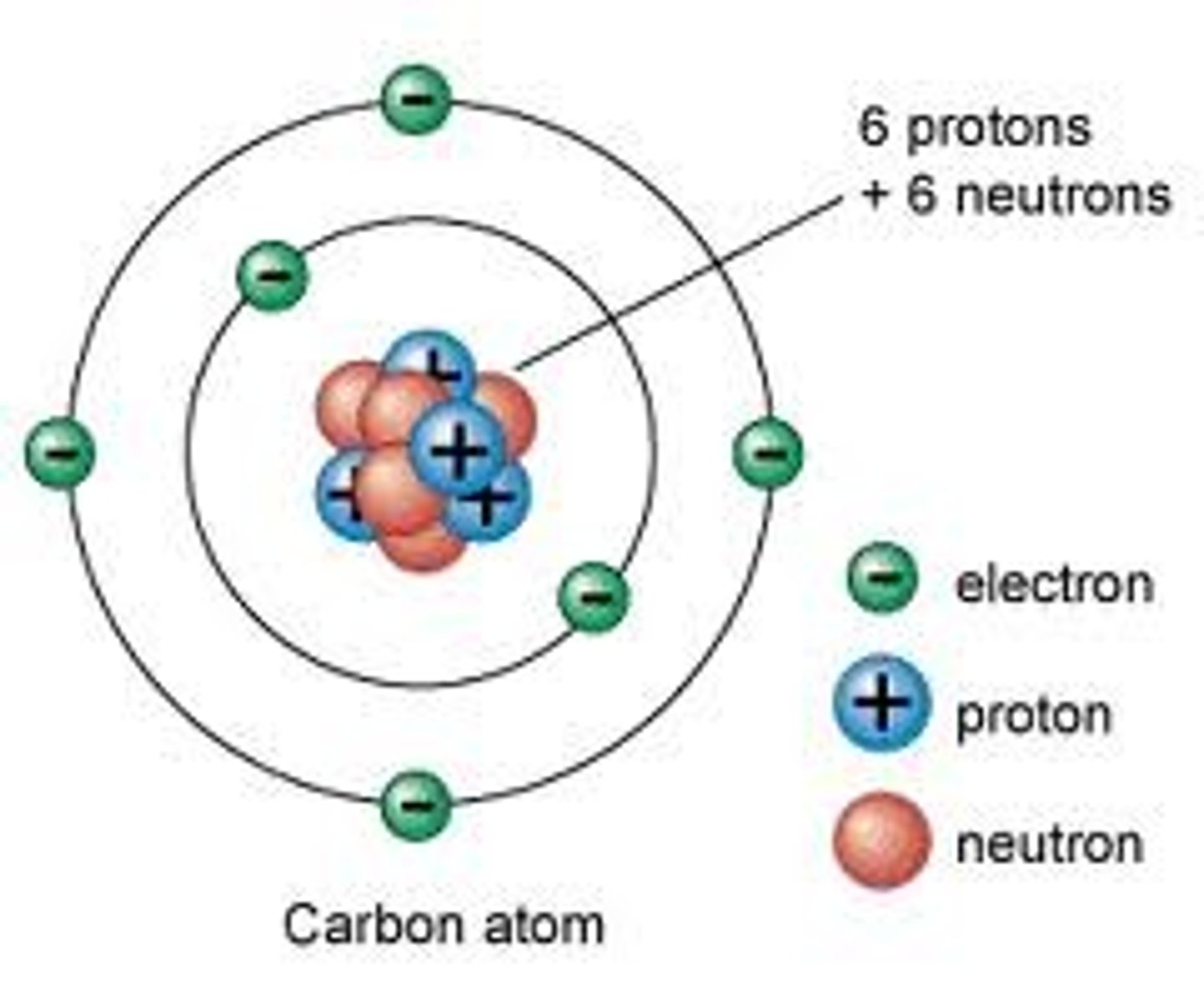
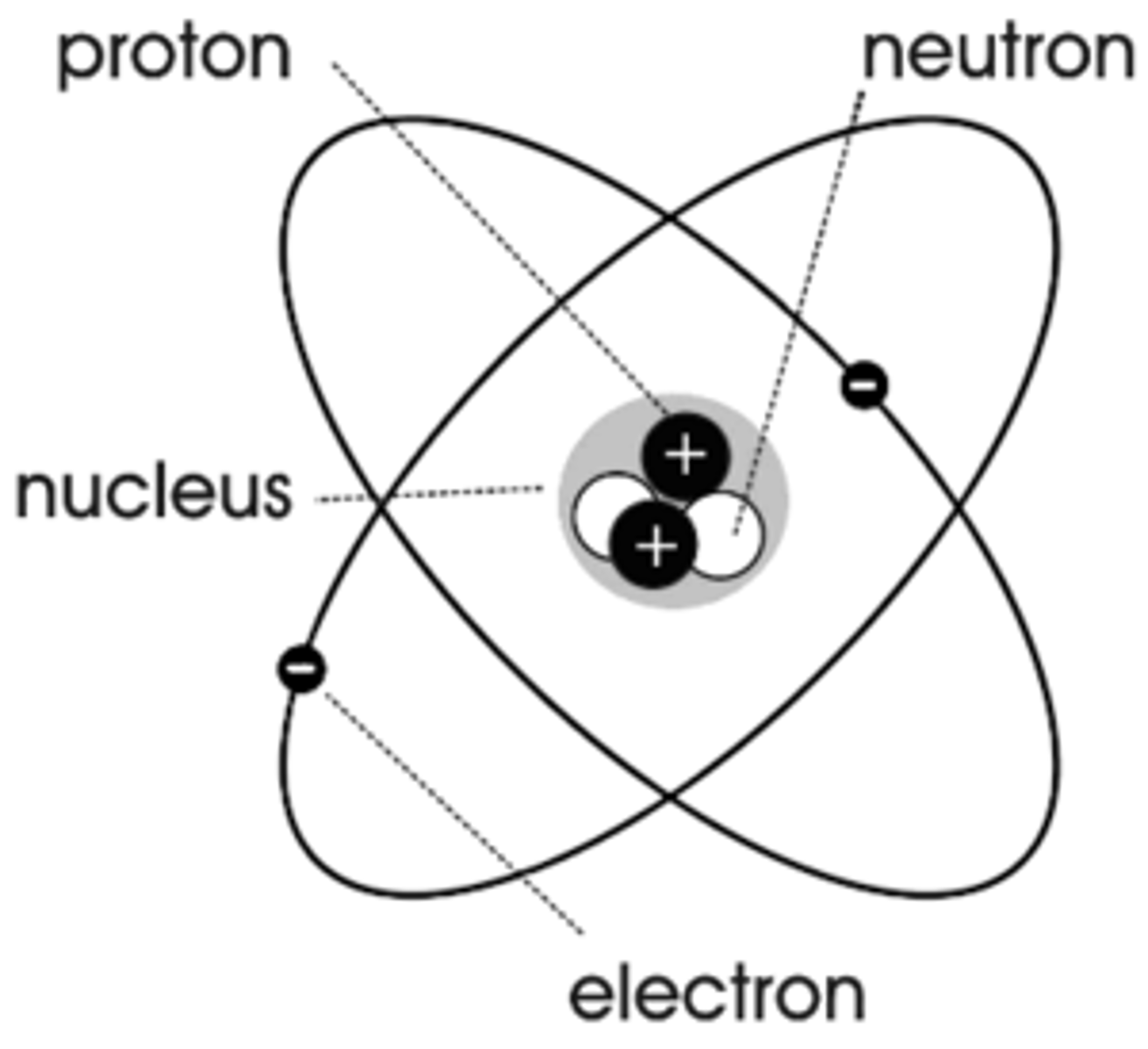
Proton
A positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom
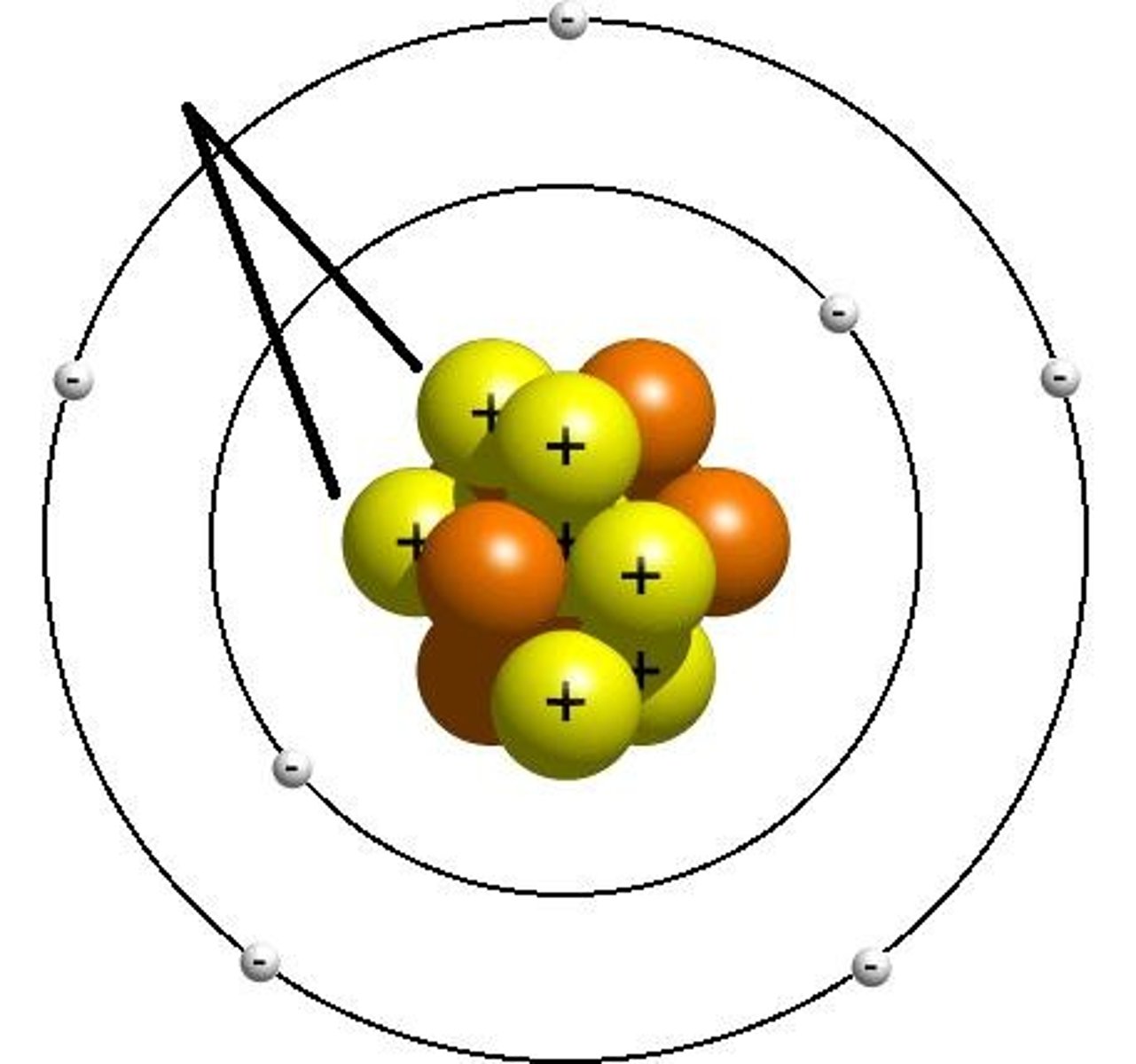
Neutrons
Neutron a particle that does not carry an electrical charge (neutral)

Nucleus
The core at the center of every atom
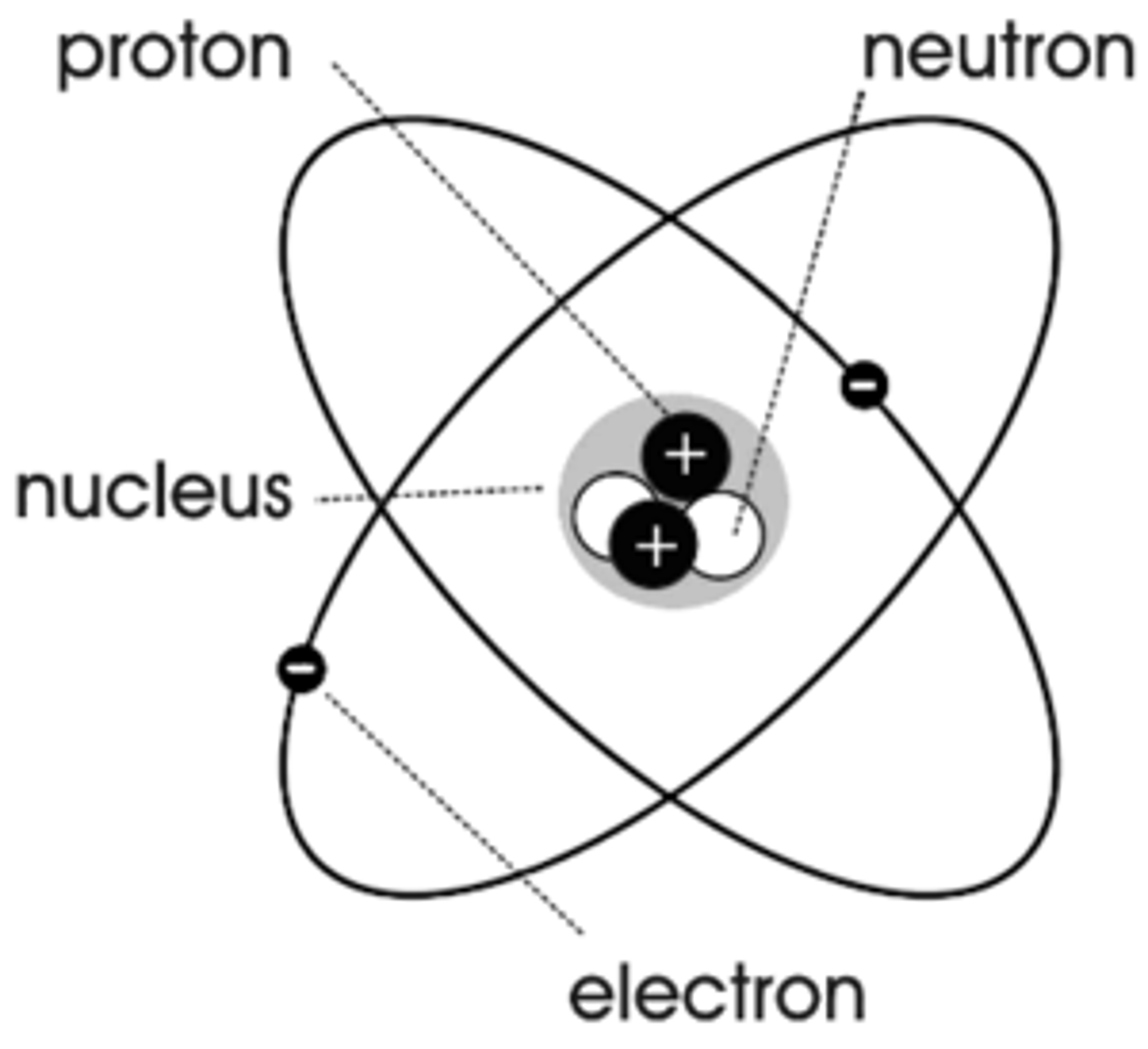
Electron
Tiny, negatively charged particle that usually exists in outer region of an atom
Magnetic Poles
Where magnetic field lines are strongest, ends of a bar magnet
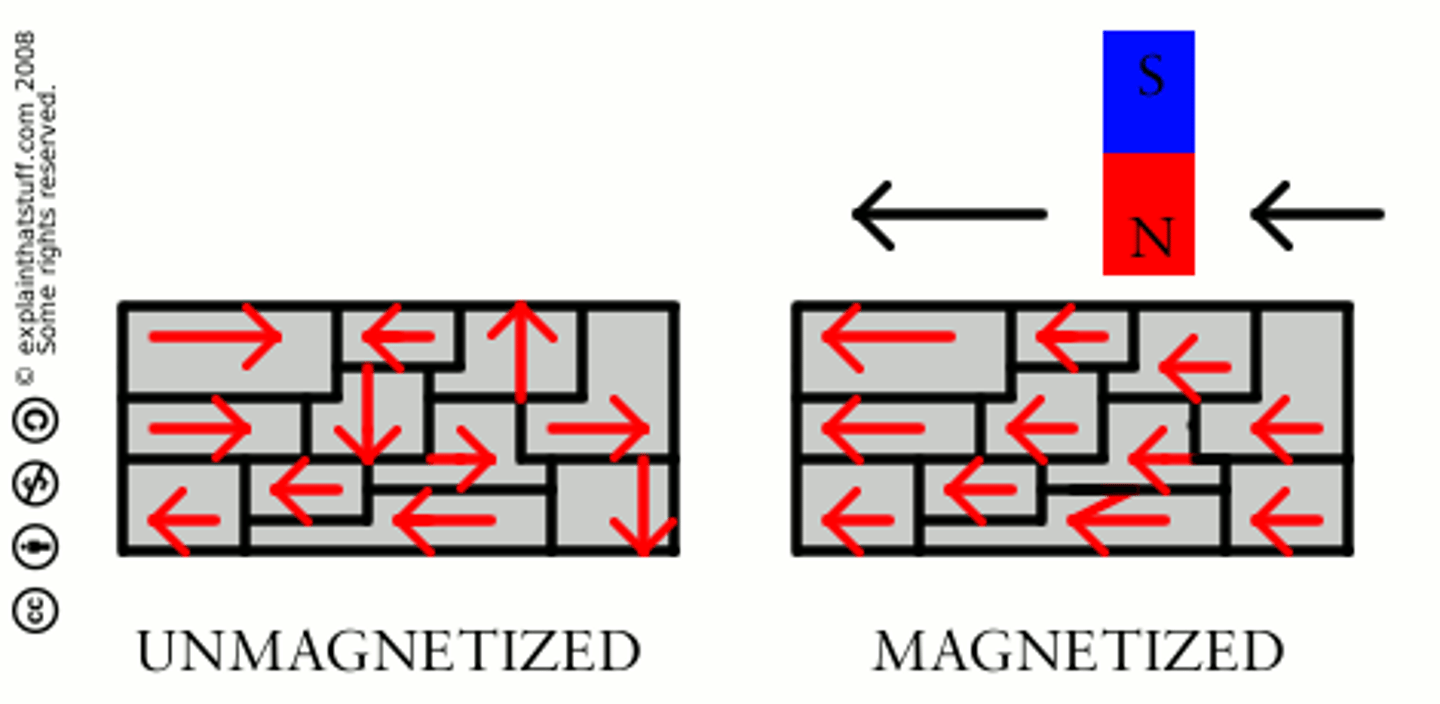
Ferromagnetic Material
A material that can be magnetized because it contains magnetic domains
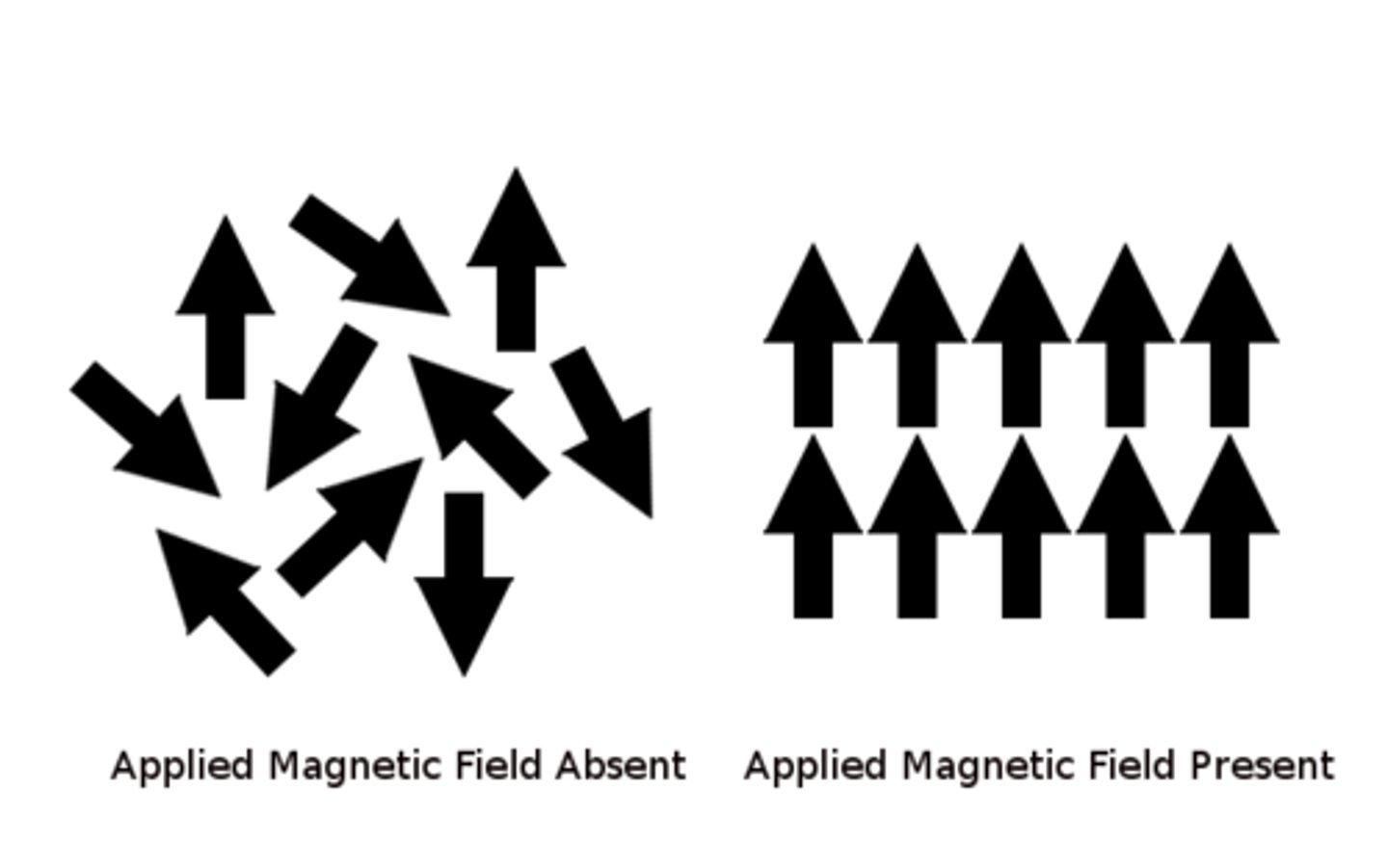
Magnetic Domain
Region where electrons are aligned into magnetic fields---spinning electrons are unpaired.
Cobalt, Nickel, Iron
Materials with strong magnetic properties (Fields)

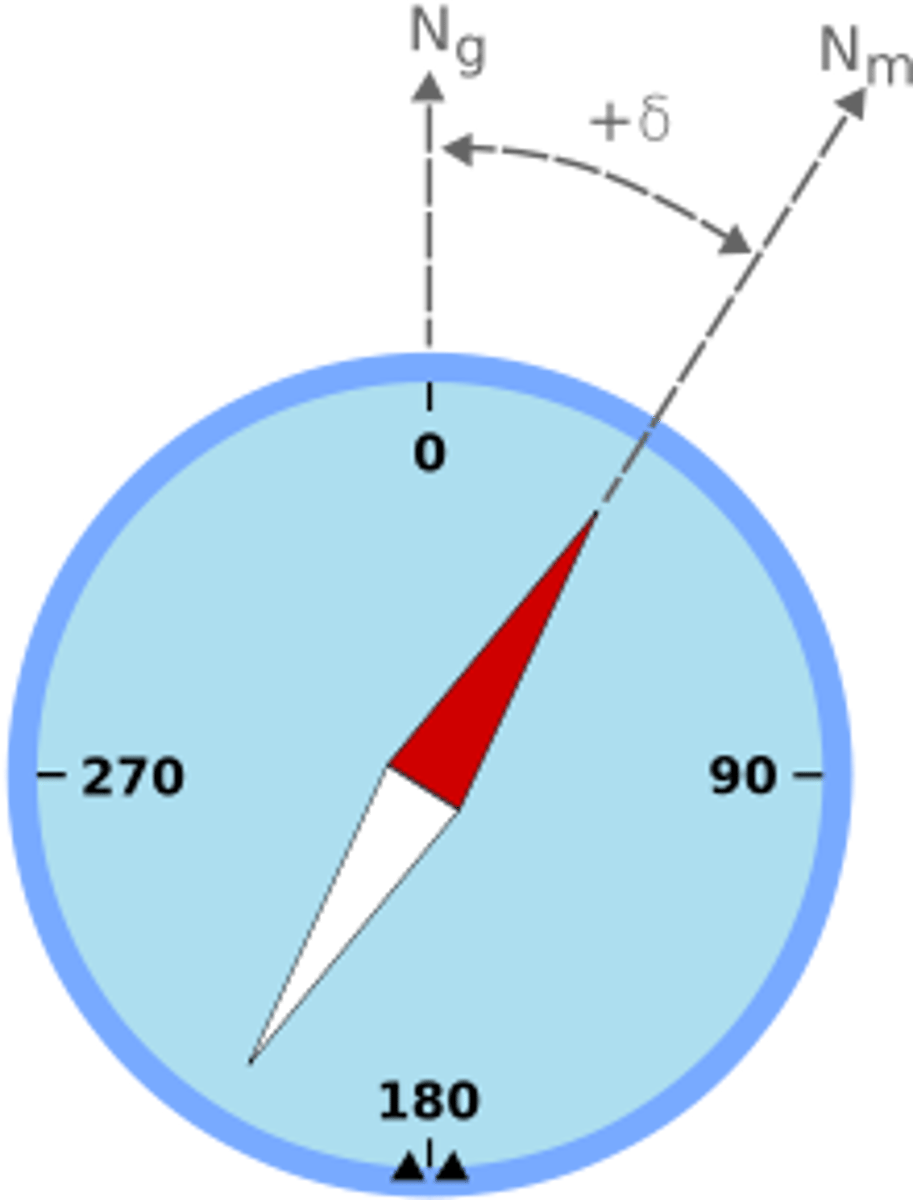
Magnetic Declination
the angle between the geographic north pole and the magnetic north pole.
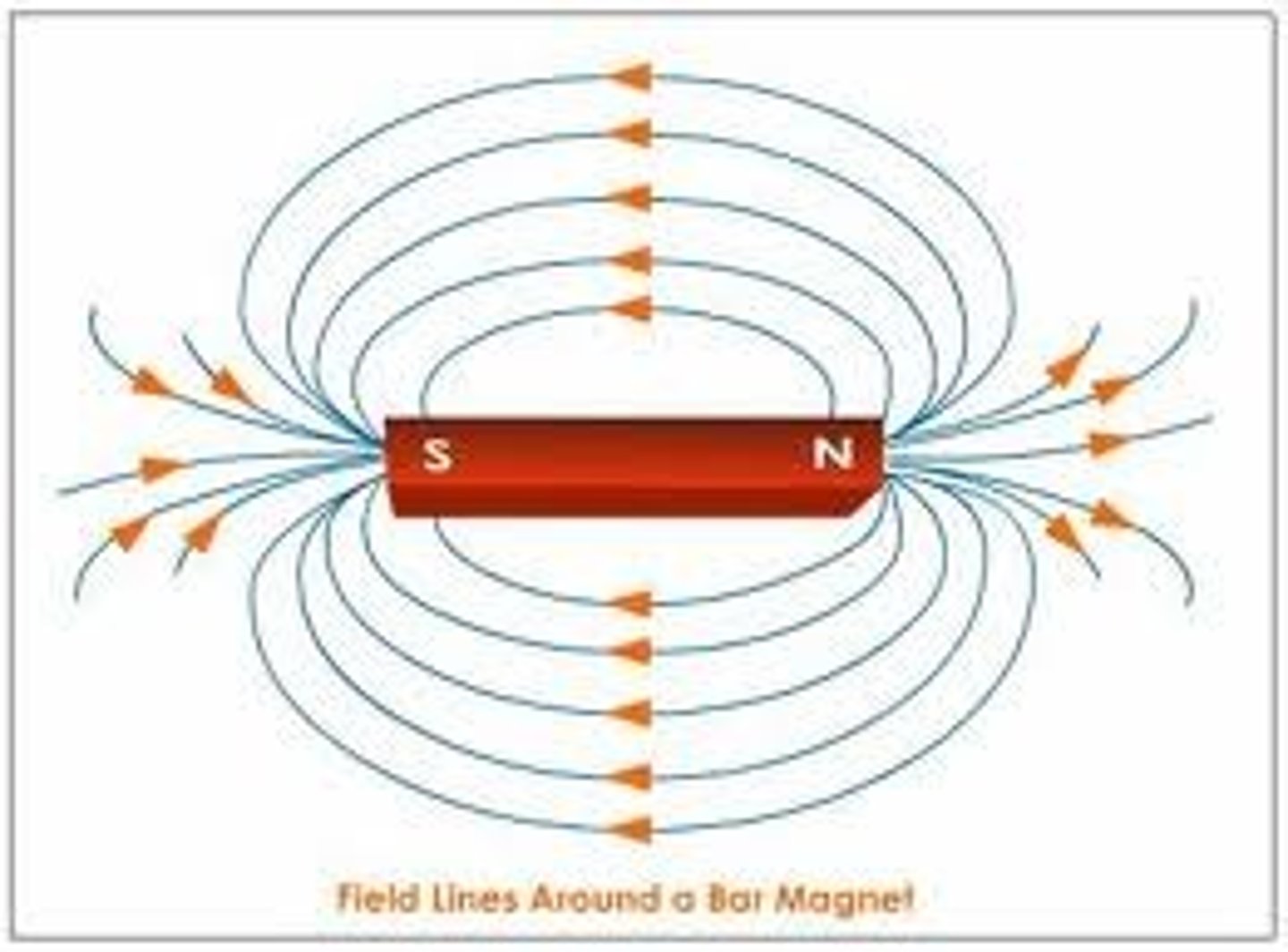
Magnetic Field Lines
Lines that map out the magnetic field of an object. They are closer at the poles of the magnet where the field is stronger. The lines are parallel and never cross.
Ways to destroy a magnet (rearrange the domains)
Drop it
heat it
put it in an alternating current's field
Ways to magnetize an object
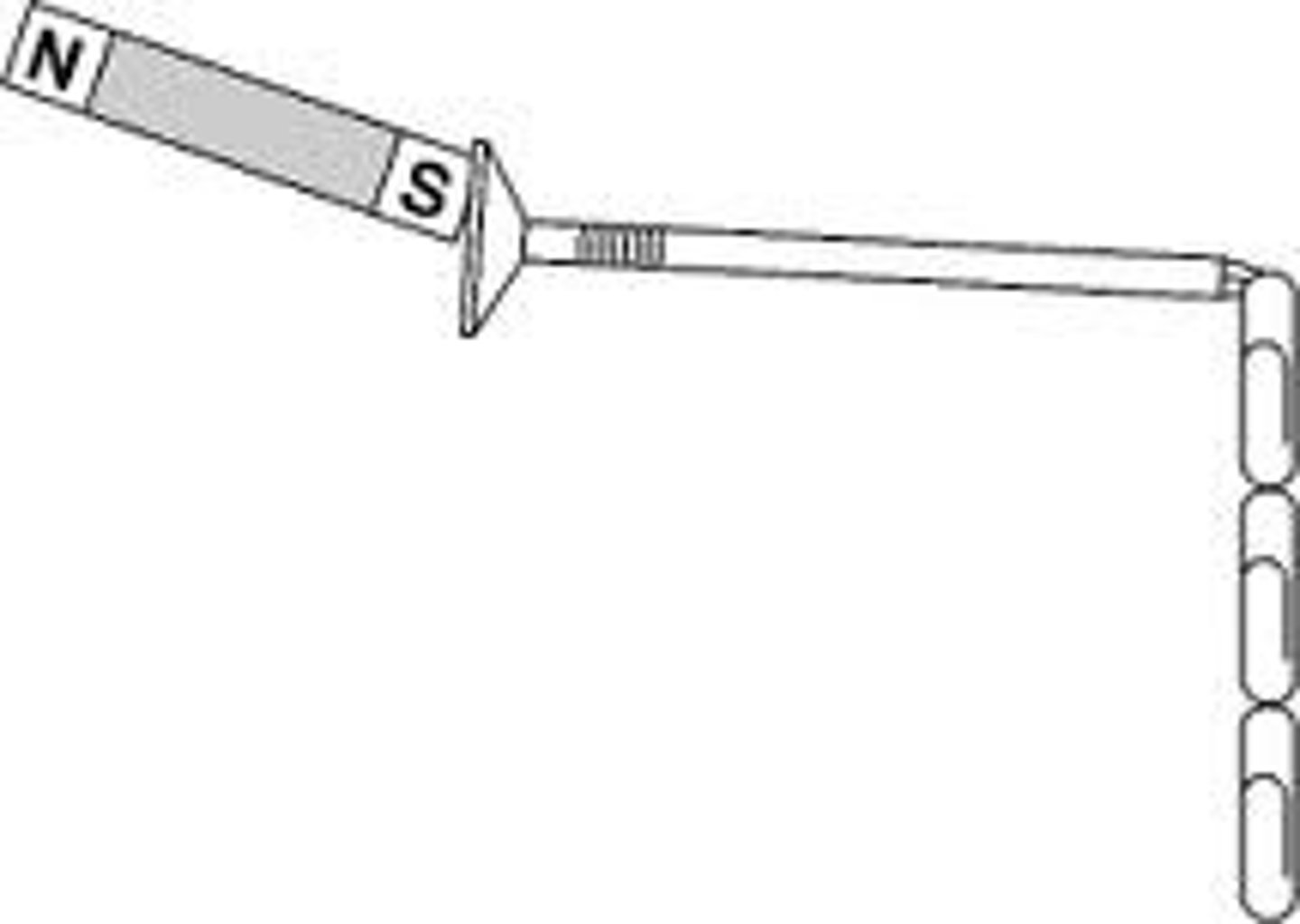
Magnetic Induction
Rubbing an object to align domains
Run electric current through it
Magnetic Induction
Magnetizing an object by putting it in a strong magnetic field.
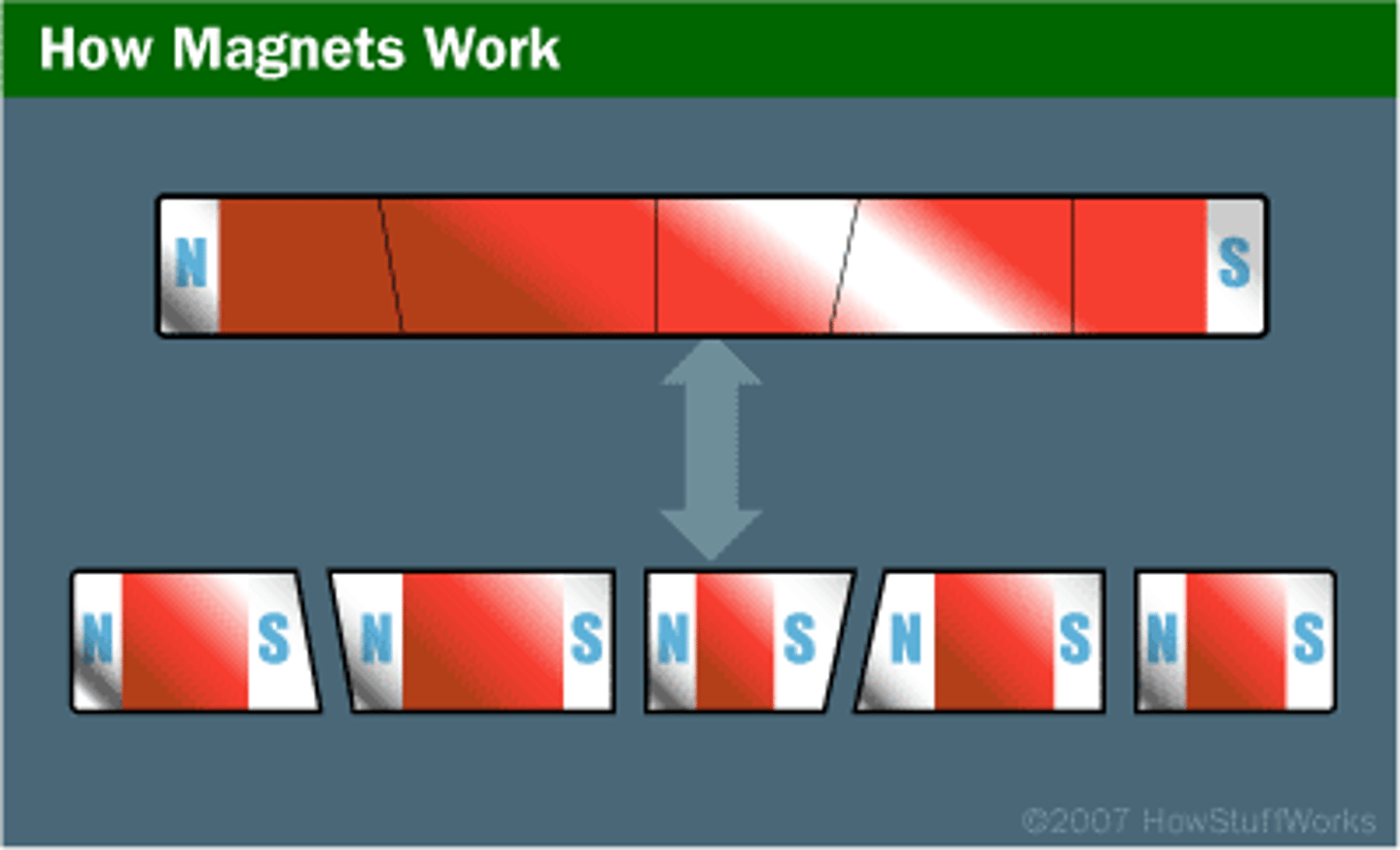
Breaking a magnet
Will create 2 magnets, each with a north and south pole
Temporary Magnets
Materials that become magnetized easily, but lose magnetism easily as well.
Permanent magnets
Materials that maintain their magnetism

Electric Current
Moving electric charges
Solenoid
Coil of wire with electric current---wrap around a solid ferromagnetic core to produce an electromagnet.

Strength of electromagnet depends on
Strength of power source
Coils on solenoid
Core size of solenoid
Galvanometer
Uses a solenoid to measure an electric current
ex. gas gauge in a car
Electric Motor
Uses an electromagnet to turn an axel or coil of wire
Transforms electrical energy to mechanical
Ex. appliances
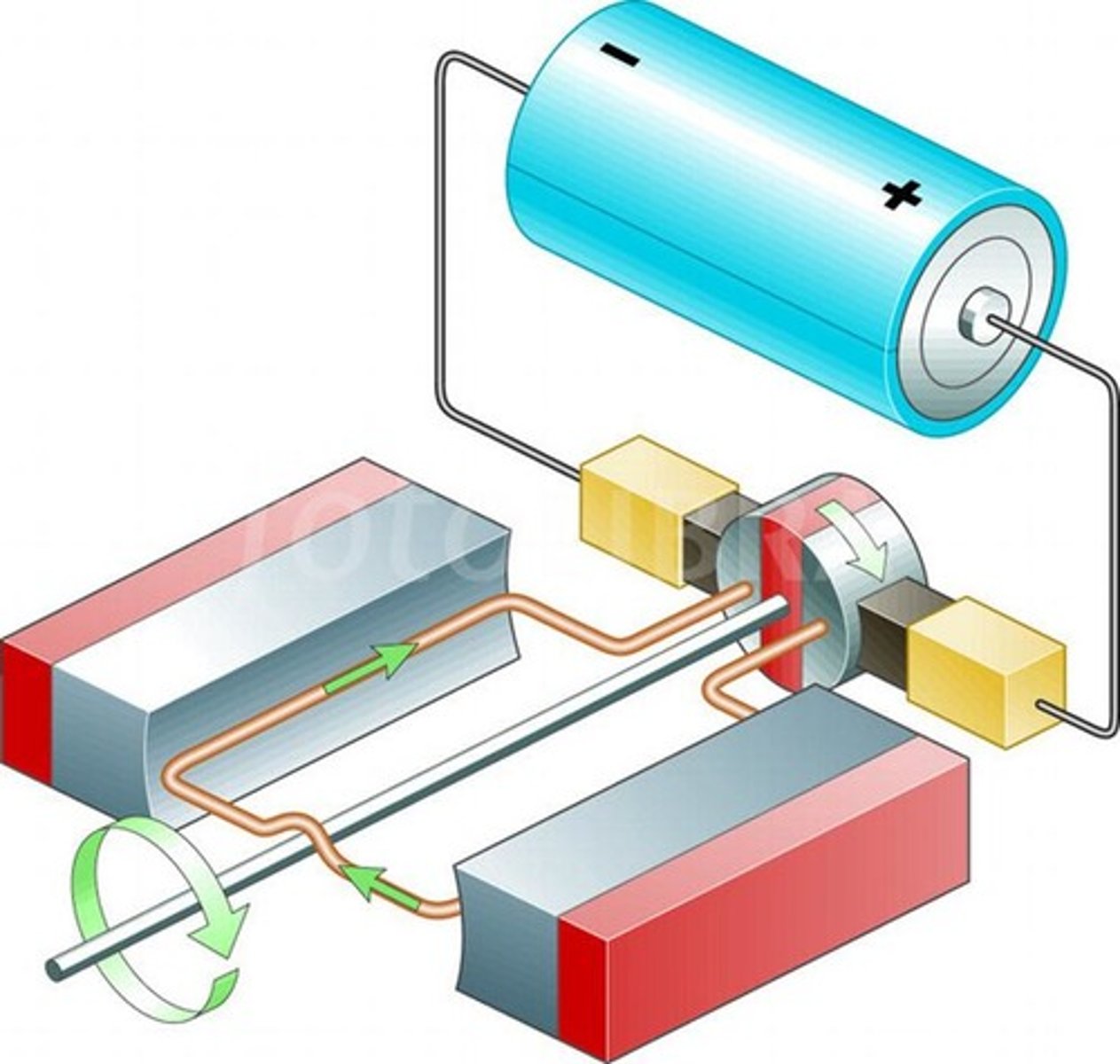
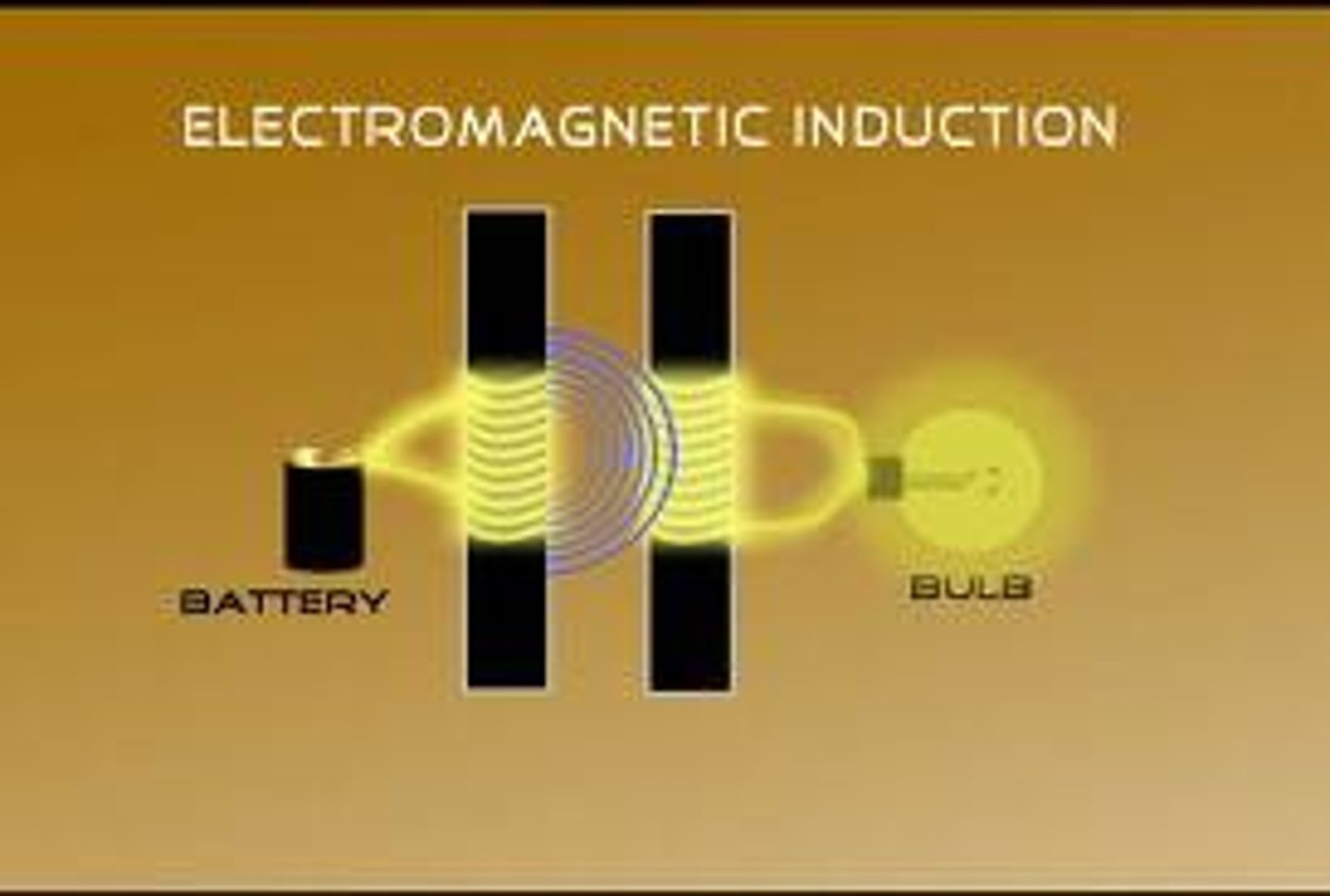
Electromagnetic Induction
Creating a current using an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
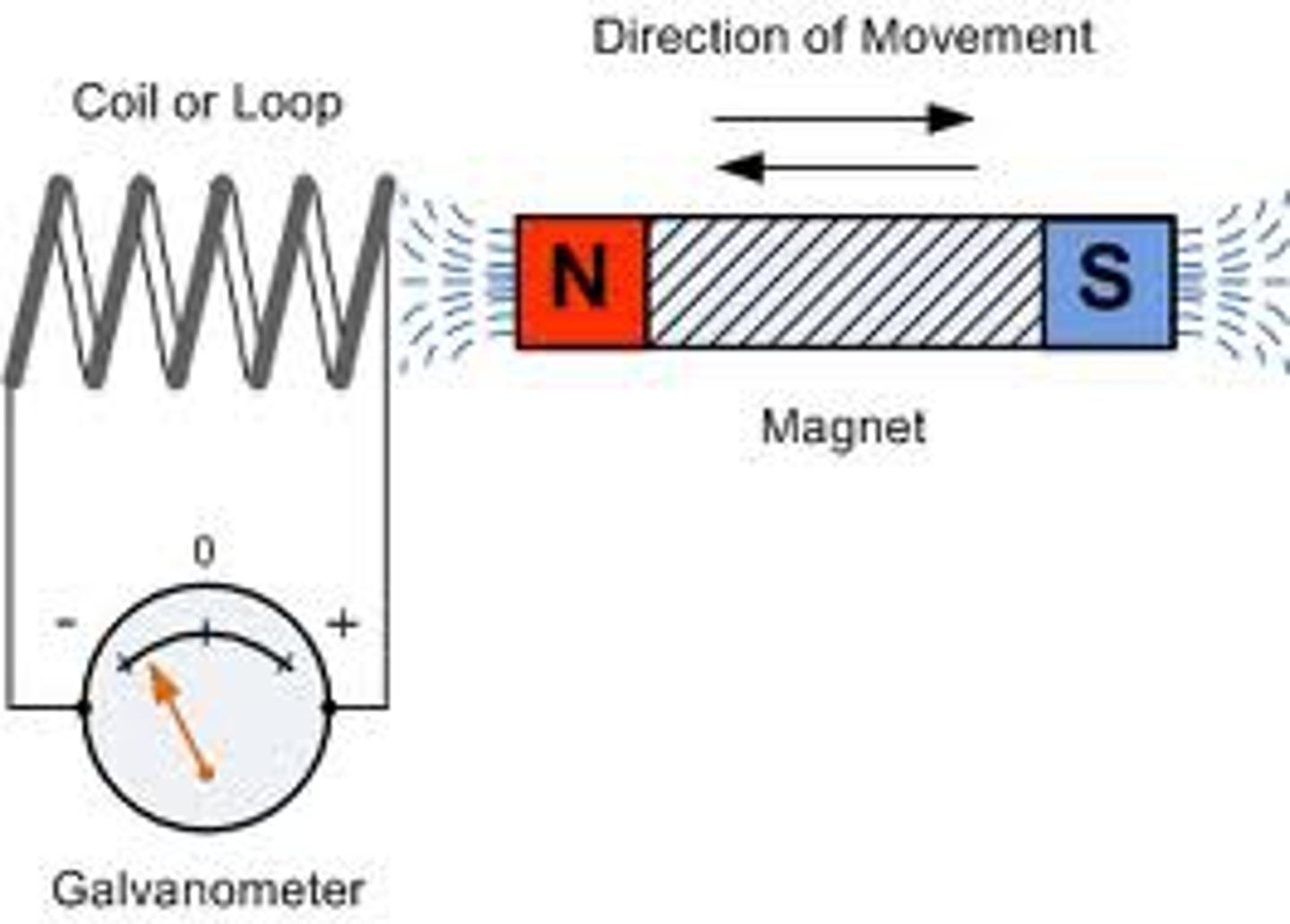
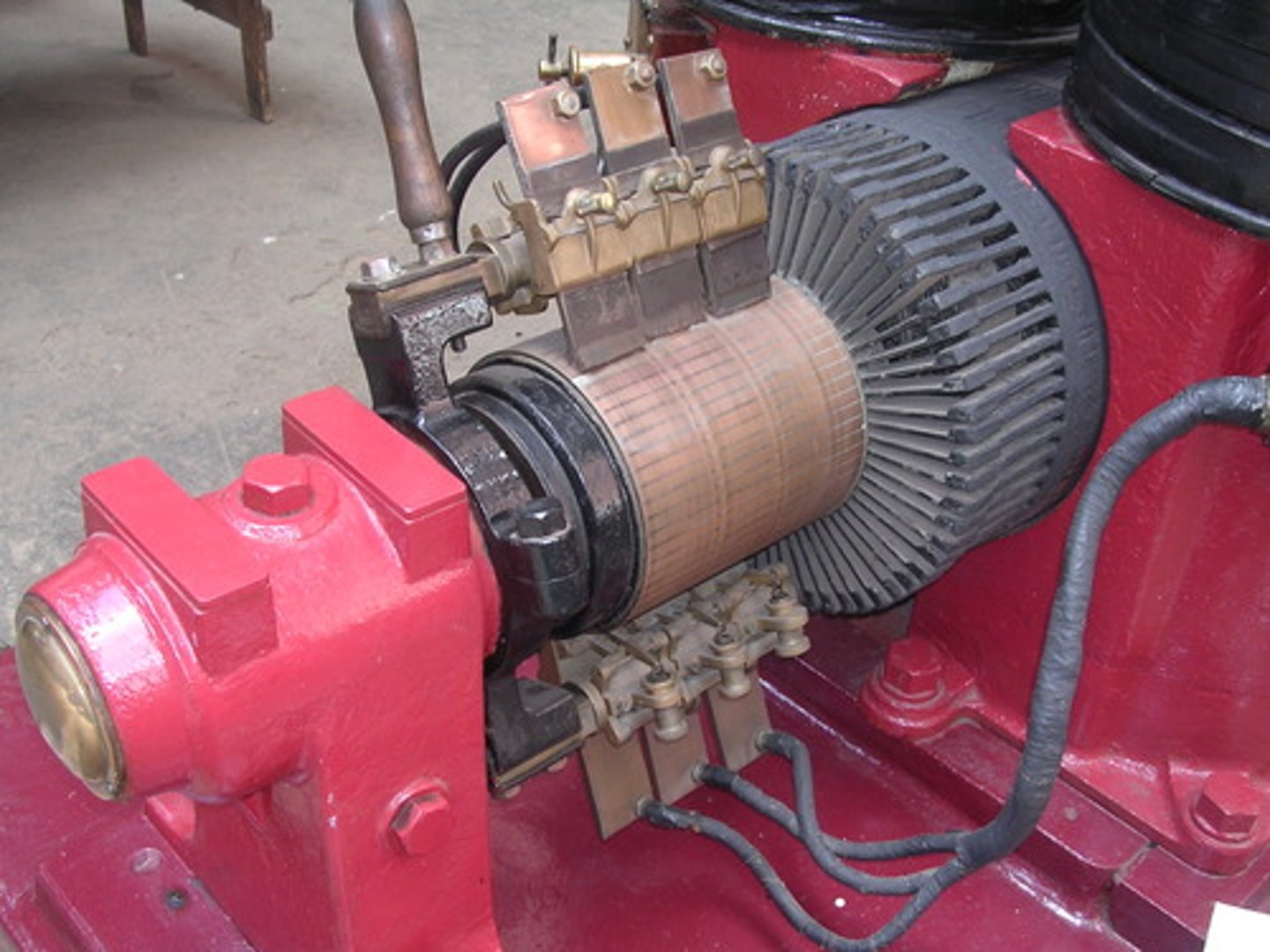
Generator
A device that uses a coil of wire (turbine) rotating in a magnetic field to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy

Transformers
Increase (Step up) or decrease (Step Down) the voltage of a current as it goes to and from a power plant to your home.