Organic Chemistry PART 1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Organic Chemistry
→ A branch of chemistry that studies carbon-containing compounds
Organic Compounds
→ Compounds that contain carbon
→ Except: Carbonates, cyanides, and oxides of carbon (CO2, CO) → inorgranic compounds
Jöns Jacob Berzelius
Proposed the Vital Force Theory (Life Force Theory) → "Organic compounds are only derived from living things."
Friedrich Wöhler
Disproved the Vital Force Theory by synthesizing urea from inorganic precursors. (Ammonium Cyanate)
Common Elements in Organic Compounds
Carbon (C)
Hydrogen (H)
Oxygen (O)
Nitrogen (N)
Carbon (C)
Mass Number: 12
Atomic Number/Proton: 6
Neutron: 6
Electron: 6
Electron Configuration: 1s²2s²2p²
Valence: 4
Binding Sites: 4 - it only shares
Hydrogen (H)
Mass Number: 14
Atomic Number/Proton: 7
Neutron: 7
Electron: 7
Electron Configuration: 1s²2s²2p³
Valence: 5
Binding Sites: 3
Oxygen (O)
Mass Number: 16
Atomic Number/Proton: 8
Neutron: 8
Electron: 8
Electron Configuration: 1s²2s²2p⁴
Valence: 6
Binding Sites: 2
Nitrogen (N)
Mass Number: 1
Atomic Number/Proton: 1
Neutron: 0
Electron: 1
Electron Configuration: 1s¹
Valence: 1
Binding Sites: 1
Stability of Carbon
→ Requires 4 bonds to become stable
→ Octet Rule: Atoms prefer 8 electrons in their valence shell
Catenation
→ Ability of carbon to bond with itself to form chains and rings
High carbon-carbon C-C bond energy
Tetravalency - large # of bonds
Small atomic size
Hybridization
Atomic orbitals fuse to form new hybrid orbitals
Atomic orbitals - these are region in space in which electrons are most likely to be found.
Sublevel s
Meaning: Sharp
Shape: Sphere
# of Orbitals : 1
# of Electrons: 2
Sublevel p
Meaning: Principal
Shape: Dumbbell
# of Orbitals : 3
# of Electrons: 6
Sublevel d
Meaning: Diffuse
Shape: Four-leaf clover
# of Orbitals : 5
# of Electrons: 10
Sublevel f
Meaning: Fundamental
Shape: Complex
# of Orbitals: 7
# of Electrons: 14
Hybrid Orbitals
orbitals of equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the same atom
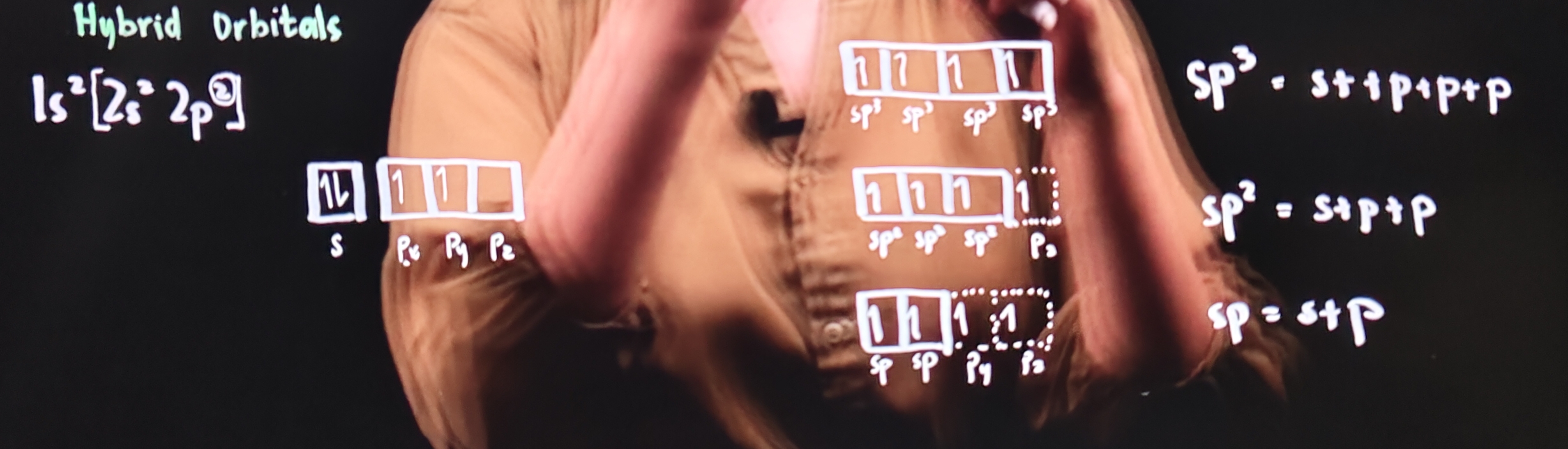
Sigma bond (σ)
First bond, hybridized orbital
Pi bond (π)
Second/third bond, unhybridized orbital
sp³
Sigma bond (σ): 4
Pi bond (π): 0
sp²
Sigma bond (σ): 3
Pi bond (π): 1
sp¹
Sigma bond (σ): 2
Pi bond (π): 2
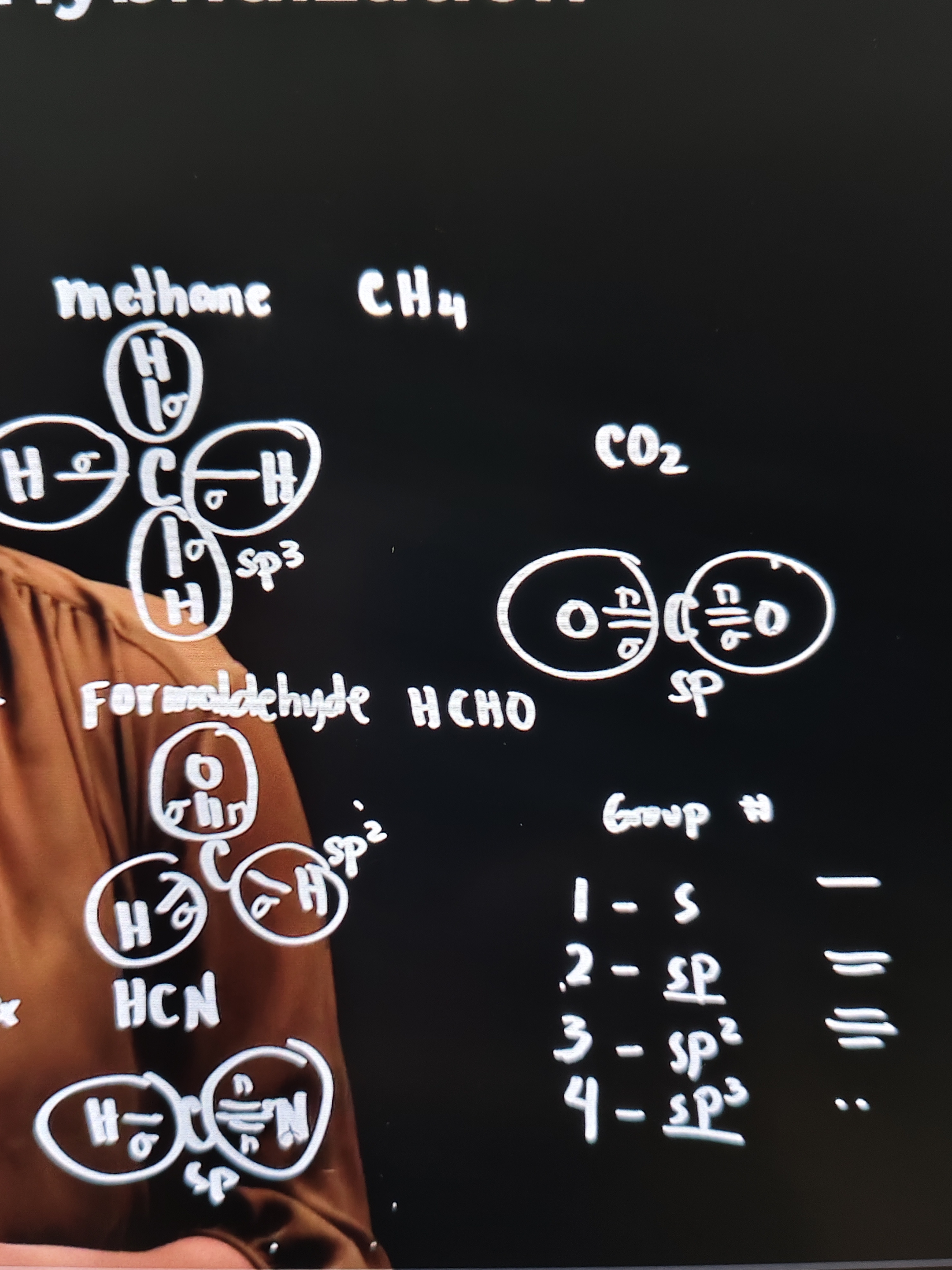
Methane CH4
Carbon bonded to 4 hydrogen atoms
Bond between H and C is called SIGMA BOND
Meaning 4 sigma bonds have formed - so the hybridization is sp³
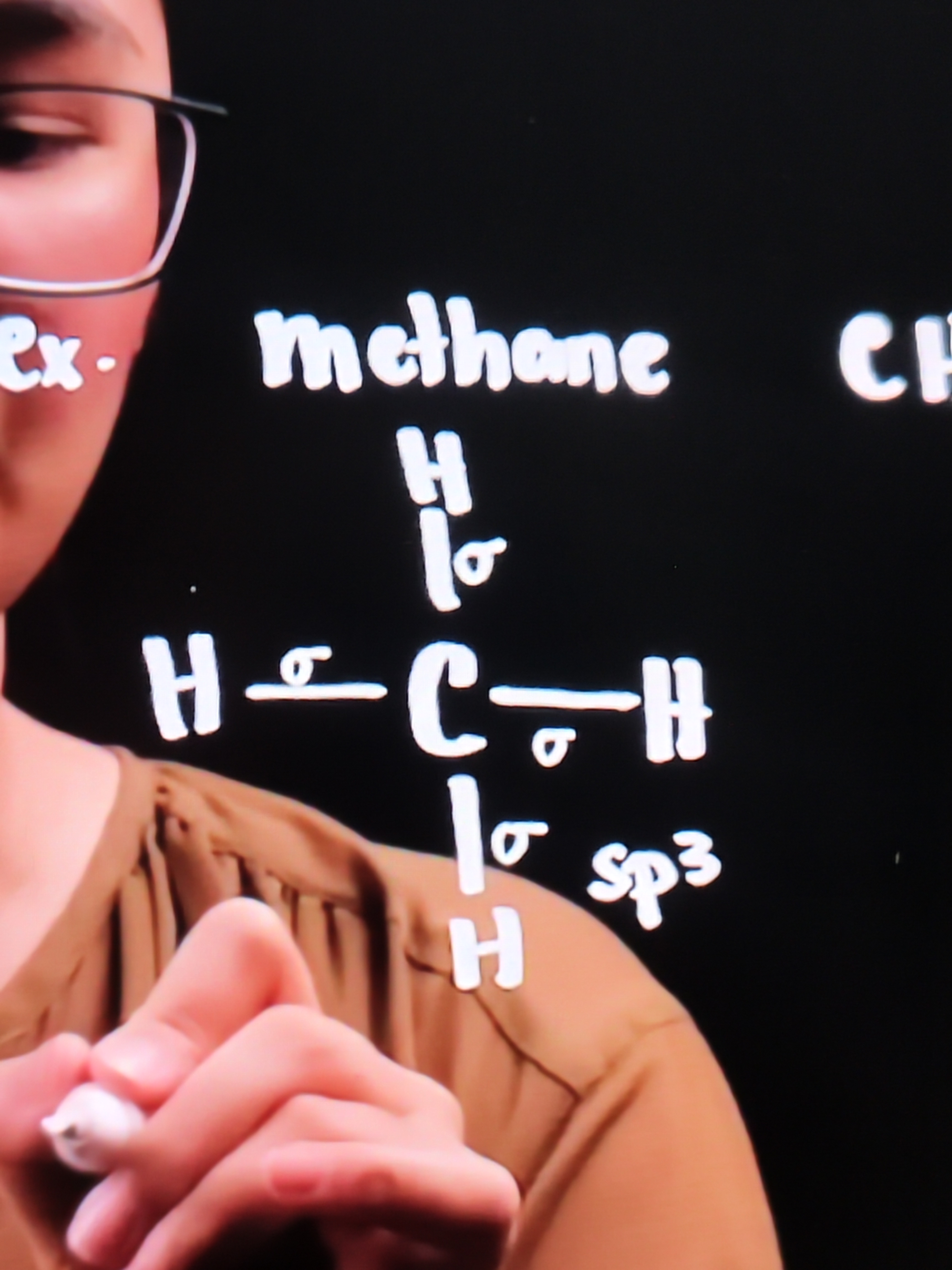
Formaldehyde
2 single bonds and 1 double bond
3 sigma bond and 1 pi bond
So the hybridization is sp²
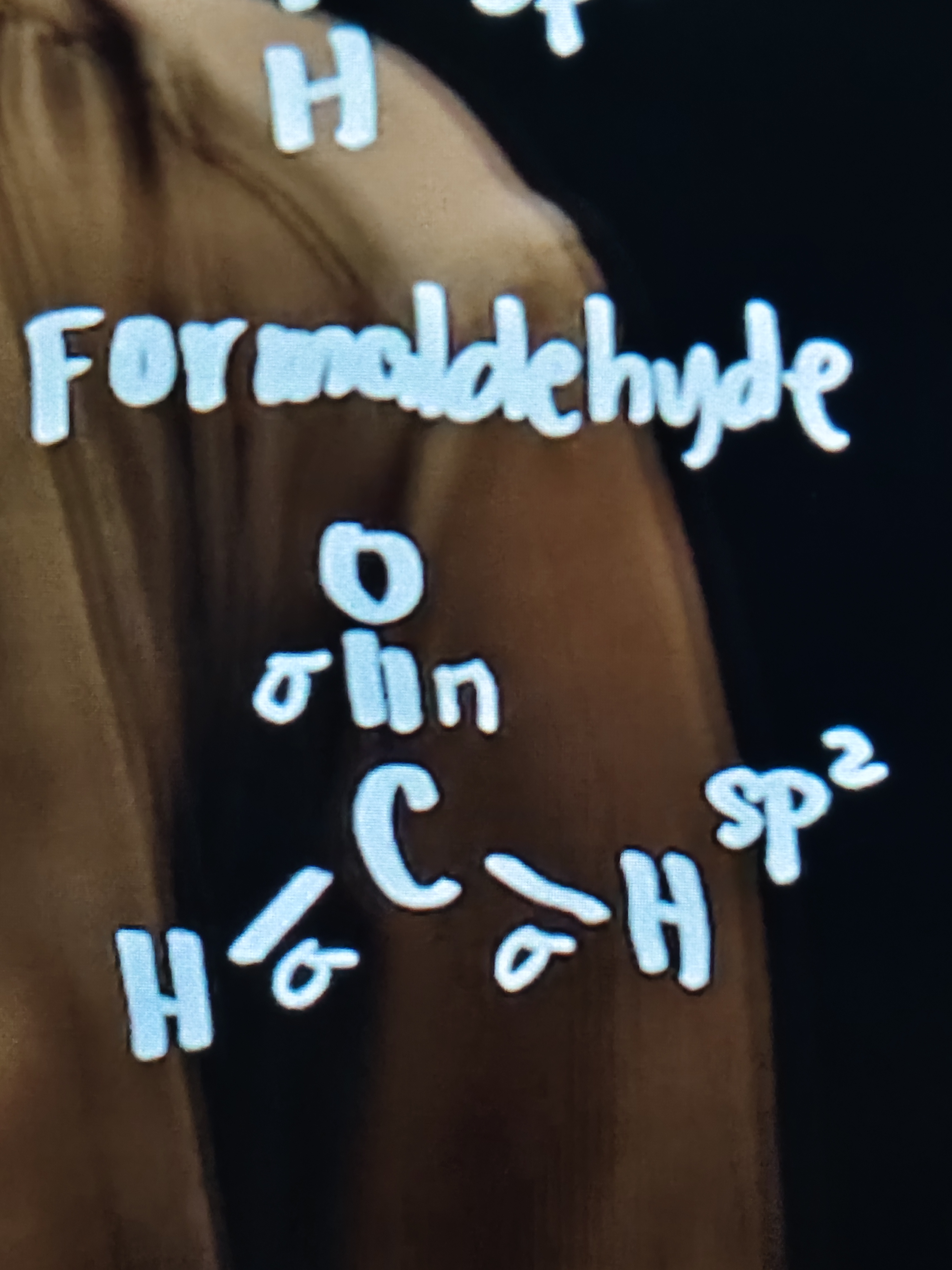
HCN
There is 1 single bond and 1 triple bond
So there is 2 sigma bonds and 2 pi bonds
The hybridization is sp

CO2
There is 2 double bonds O=C=O
2 sigma bonds, and 2 pi bonds
The hybridization is sp

true
Group #
1 - s
2 - sp
3 - sp²
4 - sp³
check how many groups are attached to carbon to easily determine the hybridization
Ethane
Attached to the first carbon is: 4 sigma bonds - so it's sp³
Attached also to the second carbon is: 4 sigma bonds - so it's also sp³

Ethene
Attached to the 1st carbon is: 3 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond
Attched to the 2nd carbon is: 3 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond also
The hybridization is sp²

Ethyne
Attched to the 1st carbon is: 2 sigma bonds and 1 pi bond
Attched to the 2nd carbon is: 2 sigma bonds and 2 pi bonds
The hybridization is sp
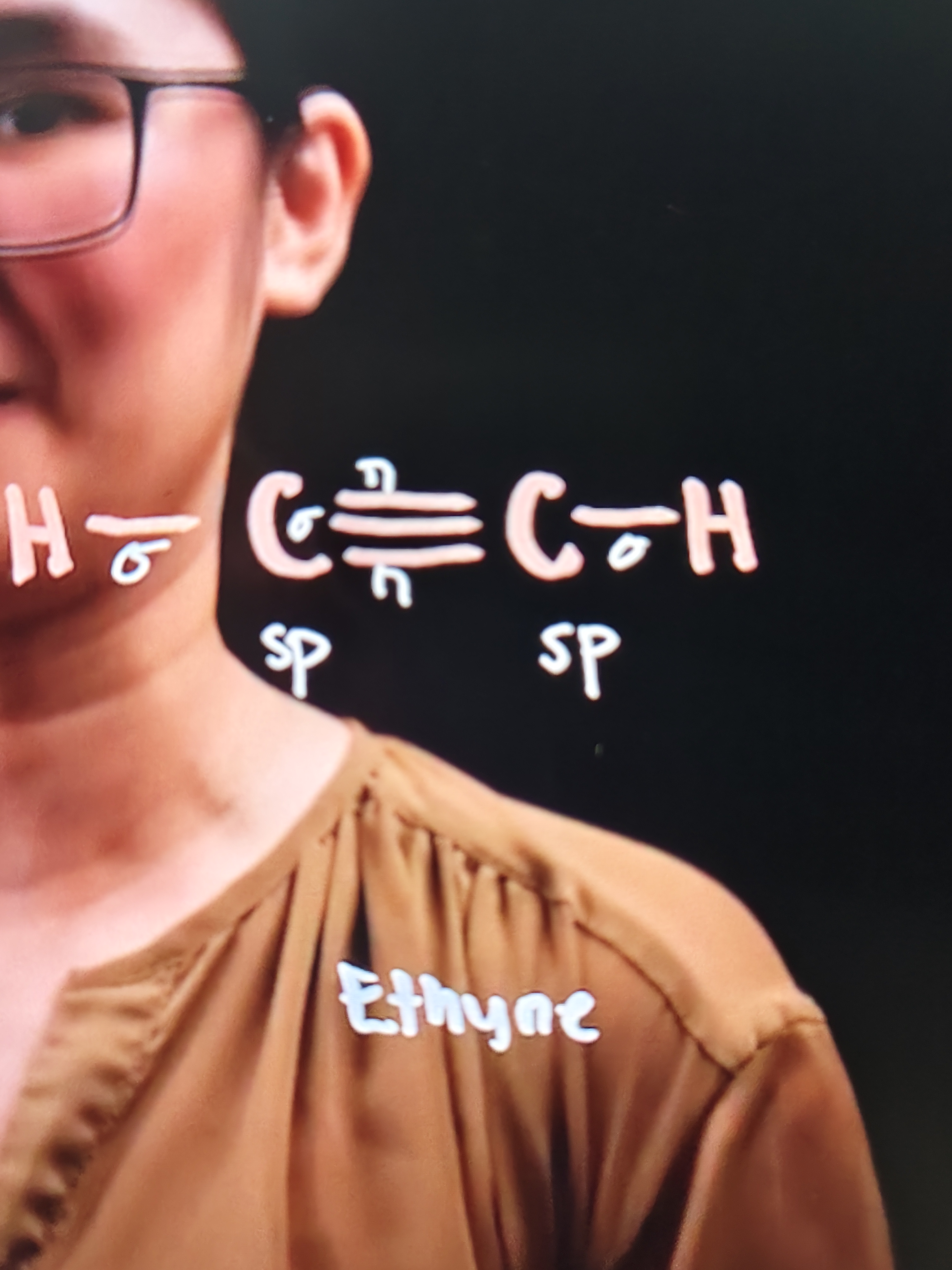
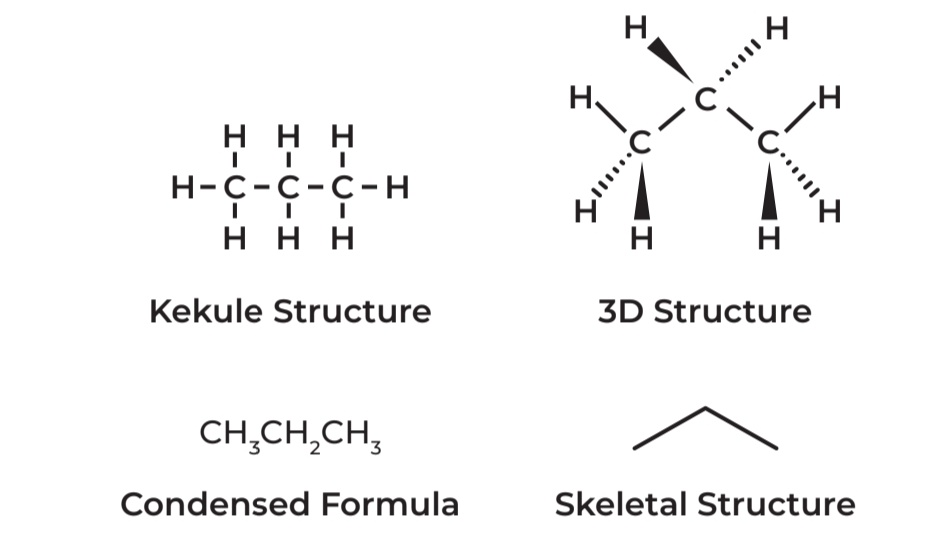
true
Different structural formula of a molecule with the molecular formula, C3H8 - PROPANE
true
Draw the Kekule Structure of the following
1. CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃
2. CH₃CHCH₂
3. CH₃CH₂COOH
4. CH₃CH₂COCH₂COOH

C. sp³ - sp³
What are the hybridizations of the orbitals between carbons 3 and 4 in the molecule CH₂=CHCH₂CH₂CH₃?
A. sp² - sp³
B. sp² - sp²
C. sp³ - sp³
D. sp - sp²
B. sp² - sp²
What are the hybridizations of the orbitals between carbons 1 and 2 in the molecule CH₂=CHCH₂CH₂CH₃?
A. sp² - sp³
B. sp² - sp²
C. sp³ - sp³
D. sp - sp²
VSEPR Theory
• Model used in chemistry to predict the Geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms
• Electron pairs located in bonds REPEL to affect the geometry of the bonds in a molecule
Steric #
lone pair + sigma bond
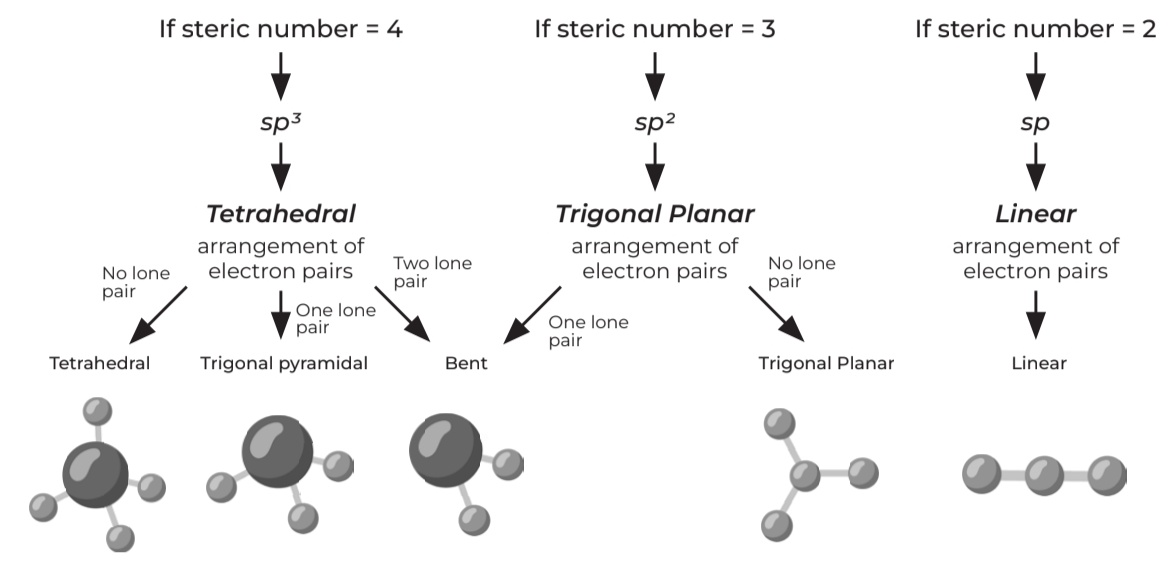
If steric number = 4
• sp³
Tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs
• One lone pair → Trigonal pyramidal
• Two lone pair → Bent
• No lone pair → Tetrahedral
If steric number = 3
• sp²
Trigonal Planar arrangement of electron pairs
• No lone pair → Trigonal Planar
• One lone pair → Trigonal Planar
If steric number = 2
• sp
Linear arrangement of electron pairs
• Linear
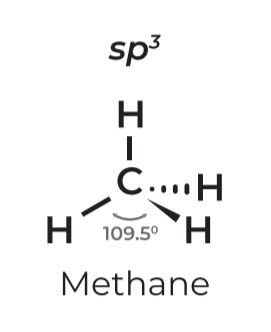
• sp³
• Steric # 4
• Lone pairs: 0
• Geometry: TETRAHEDRAL
• Angle: 109.5º
• Example: METHANE
• sp³
• Steric # 4
• Lone pairs: 1
• Geometry: Trigonal pyramidal
• Angle: 107º
• Example: Ammonia
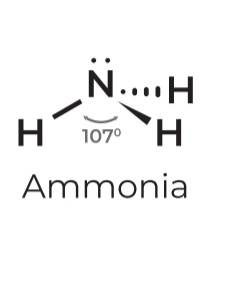
• sp³
• Steric # 4
• Lone pairs: 2
• Geometry: Bent
• Angle: 104.5º
• Example: Water
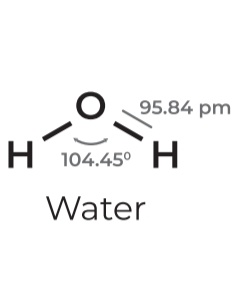
• sp²
• Steric # 3
• Lone pairs: 0
• Geometry: Trigonal Planar
• Angle: 120º
• Example: Formaldehyde
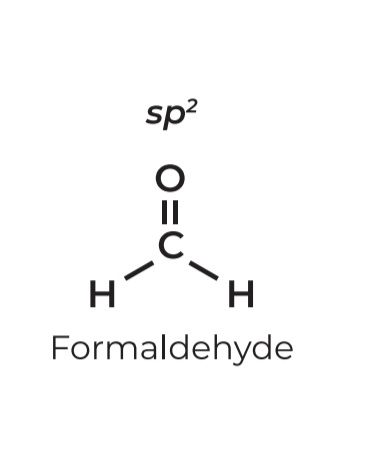
• sp²
• Steric # 3
• Lone pairs: 1
• Geometry: Bent
• Angle: 118º
• Example: Ozone
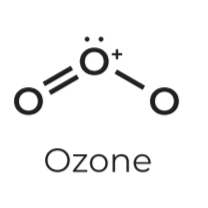
• sp
• Steric # 2
• Lone pairs: 0
• Geometry: Linear
• Angle: 180°
• Example: Hydrogen Cyanide
note: this is most likely to happen in triple bonds

TRIGONAL PLANAR
Predict the shape:
Check for bonds (lone pair, sigma bonds)
Priority is central atom
The molecule below is Boron Trifluoride
Remember: Steric # = lone pair + sigma bonds
As you can see, there are 3 sigma bonds
Boron has no lone pairs: only the Trifluoride
0 + 3 = 3
Steric number is 3; sp² Hybridization
If 0 lone pair, the shape is ____
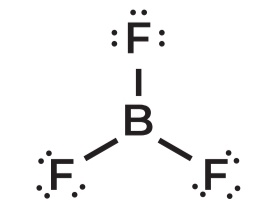
LINEAR
Predict the shape:
Check for bonds (lone pair, sigma bonds)
Priority is central atom
Remember: Steric # = lone pair + sigma bonds
As you can see, there are 2 sigma bonds
Carbon has no lone pairs: only the 2 oxygen
0 + 2 = 2
Steric number is 2; sp Hybridization
There is only 1 sp so the shape is ____
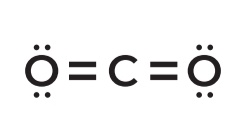
IUPAC Prefixes 1-10
• 1 - METH
• 2 - ETH
• 3 - PROP
• 4 - BUT
• 5 - PENT
• 6 - HEX
• 7 - HECT
• 8 - OCT
• 9 - NON
• 10 - DEC
IUPAC Prefixes 11-20
• 11 - UNDEC
• 12 - DODEC
• 13 - TRIDEC
• 14 - TETRADEC
• 15 - PENTADEC
• 16 - HEXADEC
• 17 - HEPTADEC
• 18 - OCTADEC
• 19 - NONADEC
• 20 - EICOS
2-Hydroxypropanoic acid
What is the IUPAC name of lactic acid?
Description: Milk acid; produced by bacteria in decomposing plants and milk products
There is 3 carbons: so the prefix is PROP
Since it is a carboxylic acid - this is propanoic acid
In carbon #2 there is an OH - hydroxy group
2-Hydroxypropanoic acid
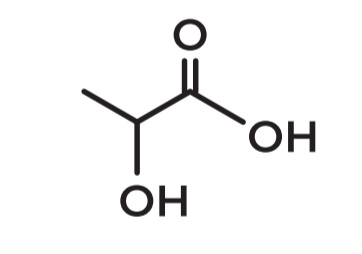
B. Lactic acid
Hydroxy acid
A. Pyruvic acid
B. Lactic acid
C. Acetic Acid
D. Sulfuric Acid
D. 2-hydroxyl propionic acid
What could be another name for lactic acid?
A. Bichloroacetic acid
B. Dihydroxy succinic acid
C. Ethanedioic acid
D. 2-hydroxyl propionic acid
B. Lactic Acid
Select the carbohydrate used as acidulant, especially in infant feeding formula:
A. Mannitol
B. Lactic Acid
C. Citric Acid
D. Tartaric Acid
Common Prefixes
No. of Carbon → Prefix
• 1 - FORM
• 2 - ACET
• 3 - PROPION
• 4 - BUTYR
• 5 - VALER
• 6 - CAPRO
• 7 - ENANTH
• 8 - CAPRYL
• 9 - PELARGON
• 10 - CAPR