Development and learning
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
developmental psychology
physical, cognitive, emotional, and social change throughout a lifespan
zygote
fertilized egg
embryo
An organism in the earliest stage of development
fetus
9 weeks after conception, organism starts to look human
teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
fetal alcohol syndrome
physical and cognitive function deficits in children caused by their birth mother's heavy drinking during pregnancy. In severe cases, symptoms include a small. out-of-proportion head and distinct facial features
rooting reflex (root)
when something touches a baby's cheek, they turn toward the touch and root in that direction
grasping reflex
Stroking the palm of a baby's hand causes the baby to close his or her fingers in a grasp.
habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.
maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
potentially traumatic events that occur during childhood, such as abuse, neglect, and violence
synaptic pruning
the process in which the brain removes neurons and synapses that it does not need
critical period
an optimal period early in the life of an organism when exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces normal development
gross motor skills
coordination involving large muscles and whole body movements
fine motor skills
coordination involving the small muscles of the body
stability and change
Do personalities and behaviors stay consistent throughout our lives (stability) or do they evolve over time (change)?
nature vs. nurture: question
are our traits and behaviors primarily shaped by genetics (nature) or by our environment and upbringing (nurture)?
nature and nurture big idea
both nature and nurture matter to human development. developmental psychologists are interested in how they interact and contribute to development
continuous and discontinuous stages of development
is human development a gradual process (continuous) or does it occur in distinct, defined stages (discontinuous)?
longitudinal studies
research that follows and retests the same people over time
cross-sectional studies
research that compares people of different ages at the same point in time
gender
in psychology, the attitudes, feelings, and behaviors that a given culture associates with a person's biological sex
sex
in psychology, the biologically influenced characteristics by which people define male, female, and intersex
intersex
possessing male and female biological sexual characteristics at birth
aggression
any physical or verbal behavior intended to harm someone physically or emotionally
relational aggression
an act of aggression (physical or verbal) intended to harm a person's relationship or social standing
male answer syndrome
men are more likely than women to hazard answers than to admit they don't know
X chromosome
the sex chromosome found in females and males. females typically have 2 X chromosomes; males typically have 1. an X chromosome from each parent produces a female child
y chromosome
the sex chromosome typically found only in males. when paired with an X chromosome from the mother, it produces a male child.
testosterone
the most important male sex hormone. Males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs during the fetal period and the development of male sex characteristics during puberty
estrogens
sex hormones, such as estradiol, the contribute to female sex characteristics and are secreted in greater amounts by females than males
primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
secondary sex characteristics
nonreproductive sexual traits, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality and body hair
spermarche
the first ejaculation
menarche
the first menstrual period
role
a set of expectations (norms) about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave
gender roles
a set of expected behaviors, attitudes, and traits for men and for women
sexual aggression
any physical or verbal behavior of a sexual nature that is unwanted or intended to harm someone physically or emotionally. Can be expressed as either sexual harrassment or sexual assault
gender identity
our personal sense of being male, female, neither, or some combination of male and female, regardless of whether this identity matches our sex assigned at birth, and the social affiliation that may result from this identity
social learning theory
the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
gender typing
the acquisition of a traditional masculine or femenine role
androgyny
displaying traditionally masculine and traditionally feminine psychological characteristics
transgender
gender identity differs from what is typical for that person's birth-assigned sex
sexual orientation
the direction of one's sexual attraction
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Jean Piaget
developmental psychologist who formulated a 4 stage theory of development for children
schemas
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
accomodation
adapting our schemas to incorporate new information
sensorimotor stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to nearly 2 years of age) at which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities
parallel play
activity in which children play side by side without interacting
object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived
preoperational stage
In Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 7 years of age) at which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
conservation
the principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects
reversibility
the cognitive ability to understand that certain actions of processes can be reversed
egocentric
in Piaget's theory, the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view
pretend play
using imagination to create scenarios and act out roles
concrete operational stage
In Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 7 to 11 years of age) at which children can perform the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete (actual, physical) events
formal operational
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning at about age 12) at which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts
Lev Vygotsky
Russian developmental psychologist who emphasized how the child's mind grows through interaction with the social-cultural environment
scaffold
In Vygotsky's theory, a framework that offers children temporary support as they develop higher levels of thinking
zone of proximal development
the zone between what a child can and can't do - what a child can do with help
theory of mind
people's ideas about their own and other's mental states - about their feelings, perceptions and thoughts, and the behaviors these might predict
imaginary audience
imagining what others think about us
personal fable
teens believing that they are unique and special and what happens to "most people" would never happen to them
moral intuitions
quick gut feelings
dementia
a cognitive disorder that impairs memory, cognition, and decision making
terminal decline
in the last 3 or 4 years of life, and especially as death approaches, cognitive decline typically accelerates
language
our agreed-upon systems of spoken, written, or signed words and the ways we combine them to communicate meaning
phonemes
in language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
morphemes
in a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning; may be a word or part of a word (such as a prefix)
grammar
in a language, a system of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand others. Semantics is the language's set of rules for deriving meaning from sounds, and syntax is its set of rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences
universal grammar (UG)
humans' innate predisposition to understand the principles and rules that govern grammar in all languages.
babbling stage
the stage in speech development, beginning around 4 months, during which an infant spontaneously utters various sounds that are not all related to the household language
cooing
early vowel-like sounds that babies produce
one-word stage
the stage in speech development, from about age 1 to 2, during which a child speaks mostly in single words
two-word stage
beginning about age 2, the stage in speech development during which a child speaks mostly two-word statements
telegraphic speech
early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram—"go car"—using mostly nouns and verbs.
critical period - language
Childhood seems to represent a critical period for mastering certain aspects of language before the language learning window closes.
aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke's area (impairing understanding).
Broca's area
a frontal lobe brain area, usually in the left hemisphere, that helps control language expression by directing the muscle movements involved in speech
wernicke's area
a brain area, usually in the left temporal lobe, involved in language comprehension and expression
linguistic determinism
Whorf's hypothesis that language determines the way we think
linguistic relativism
the idea that language influences the way we think
overgeneralization
errors in the application of grammar rules (don't know the exceptions)
ecological systems theory
a theory of the social environments influence on human development, using five nested systems (microsystem; mesosystem; exosystem; macrosystem; chronosystem) ranging from direct to indirect influences
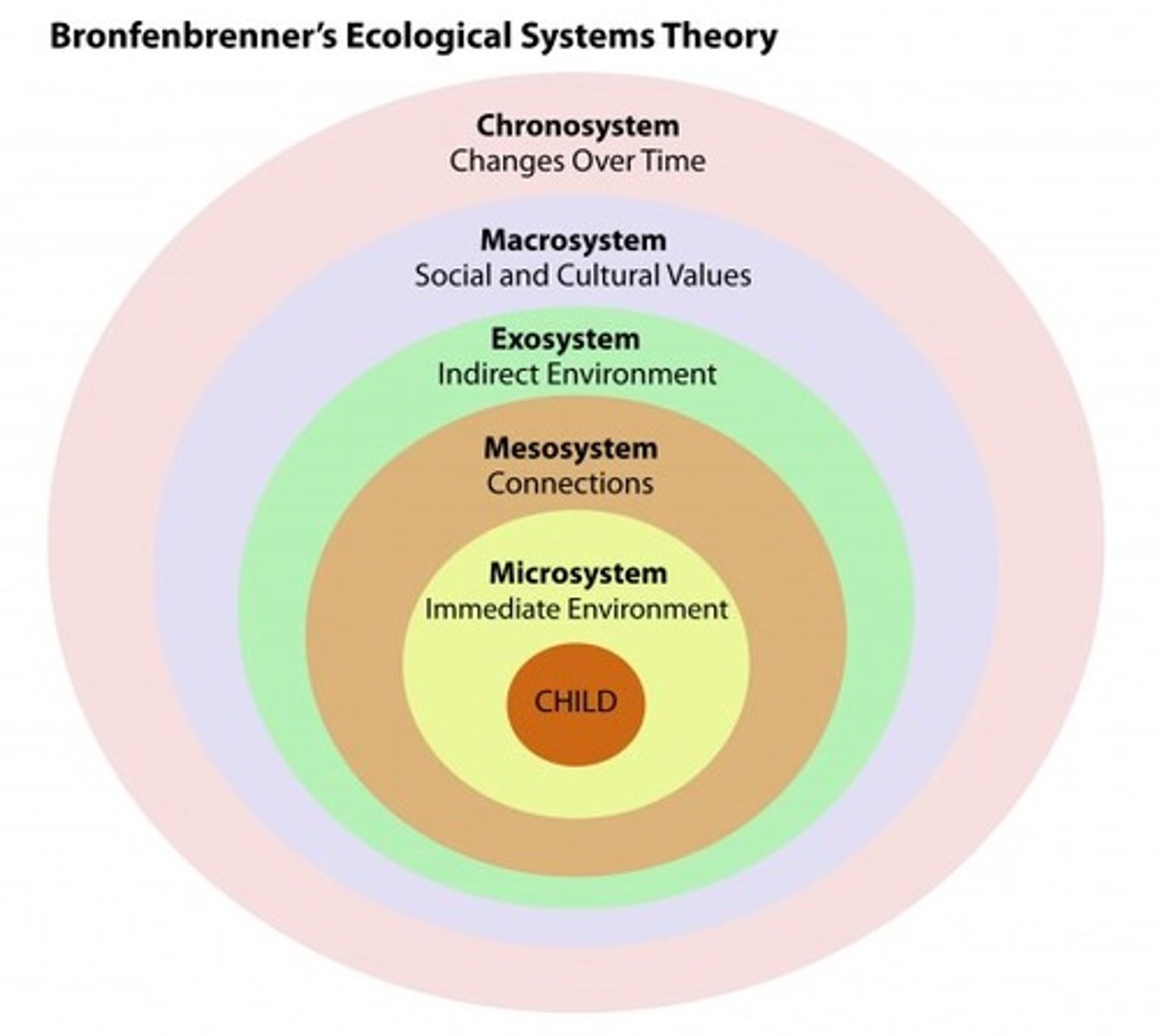
seperation anxiety
the distress displayed by infants when away from caregivers
stranger anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
attachment
an emotional tie with others; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to caregivers and showing distress on separation
imprinting
the process by which certain animals form strong attachments during early life
strange situation
a procedure for studying child-caregiver attachment; a child is placed in an unfamiliar environment while their caregiver leaves and then returns, and the child's reactions are observed
secure attachment
demonstrated by infants who comfortably explore environments in the presence of their caregiver, show only temporary distress when the caregiver leaves, and find comfort in the caregiver's return
insecure attachment
demonstrated by infants who display either a clinging, anxious attachment or an avoidant attachment that resists closeness
disorganized attachment
infants who show no consistent behavior during these separations and reunions
temperament
a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
basic trust
according to Erik Erikson, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; said to be formed during infancy by appropriate experiences with responsive caregivers
avoidant attachment
people experience discomfort when getting close to others and use avoidant strategies to maintain distance from others
self-concept
all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves, in answer to the question, "Who am I?"
authoritarian
parents are coercive. They impose rules and expect obedience
permissive
parents are unrestraining. They make few demands, set few limits, and use little punishment.