Mock
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/119
Last updated 5:27 PM on 1/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
Plasma membrane function
* control movement of substances into and out of the cell
* Has receptor molecules to allow it to respond to chemicals like hormones
* Has receptor molecules to allow it to respond to chemicals like hormones
2
New cards
Cell wall
* made of cellulose
* Supports plant cells
* Supports plant cells
3
New cards
What are plant cell walls made of?
Cellulose
4
New cards
Lysosome function
* contains digestive enzymes to digest invading cells or to brea down worn out cell components
* Kept separate in a membrane so that enzymes don’t digest the cell
* Kept separate in a membrane so that enzymes don’t digest the cell
5
New cards
Ribosome function
Site of protein translation
6
New cards
RER function
* folds and processes proteins that have been made at the ribosomes
7
New cards
RER description
A system of membranes enclosing a fluid-filled space, the surface is covered with ribosomes.
8
New cards
SER function
Synthesises and processes lipids
9
New cards
SER description
Like RER but without ribosomes
10
New cards
Mitochondrion shape
Oval shaped with a double membrane
11
New cards
Golgi body function
Processes an packages new lipids and proteins as well as making lysosomes
12
New cards
Vesicle function
Transports substances in and out of cell via the plasma embrace and between organelles.
13
New cards
Centriole function
Involved with the separation of chromosomes during cell division.
14
New cards
Centriole description
* Small, hollow cylinders made of microtubules.
* Found in animals cells but only some plant cells
* Found in animals cells but only some plant cells
15
New cards
What are cilia and flagella made from
Microtubules
16
New cards
Protein pathway
mRNA is transcribes → out of nuclear pore → ribosome on R.E.R → Golgi body
17
New cards
4 functions of the cytoskeleton
* support organelles and their positioning
* Help to strength the cell and maintain its shape
* Transport organelles and material within the cell
* Cell cause the cell to move
* Help to strength the cell and maintain its shape
* Transport organelles and material within the cell
* Cell cause the cell to move
18
New cards
Arrangement of microtubules in cilia
9 pairs around and 1 pair in the middle
19
New cards
Size of eukaryotic ribosomes
80S
20
New cards
Size of prokaryotic ribosomes
70S
21
New cards
Cell walls of fungi are made of
Chitin
22
New cards
Cell walls of plants are made of
Cellulose
23
New cards
Are prokaryote organelles membrane bound?
Prokaryotic organelles are not membrane bound
24
New cards
Magnification =
Image size / object size
25
New cards
What unit must lengths be in when calculating magnification?
Doesn’t matter but all must be in the same unit
26
New cards
Mm to µm
X 1000
27
New cards
µm to nm
X 1000
28
New cards
Resolution is
How detailed the image is - or how well the microscope distinguishes between two pints that are close together.
29
New cards
Will increasing the magnification increase the resolution?
No
30
New cards
Light microscope maximum resolution
0\.2µm
31
New cards
T.E.M maximum resolution
0\.00002 µm
32
New cards
S.E.M maximum resolution
0\.002 µm
33
New cards
Light microscope maximum magnification
X 1500
34
New cards
T.E.M maximum magnification
> x 1,000,000
35
New cards
S.E.M maximum magnification
< x 500,000
36
New cards
Which electron microscope can produce 3D images?
SEM
37
New cards
Which electron microscope passes electrons through the sample?
TEM
38
New cards
Laser scanning confocal microscopes
Used to scan a specimen tagged it’s fluorescent dyes.
39
New cards
Why can laser scan in confocal microscopes do?
Look at objects at different depths in thick specimens.
40
New cards
Which two polysaccharides is starch made of?
Amylose and amylopectin
41
New cards
Which form of glucose is amylopectin made from?
α-glucose
42
New cards
Which form of glucose is amylose made from?
α-glucose
43
New cards
Amylose is a long ___ chain of alpha glucose
Unbranched
44
New cards
Amylopectin is a long ___ chain of alpha glucose
Branched
45
New cards
Starch is insoluble, making it a good ___ molecule.
Storage
46
New cards
Why is amylose being unbranched ideal?
It can be compact and fit more in a smaller place.
47
New cards
Why is amylopectin being branched ideal?
It can be easily broken down into α-glucose by enzymes.
48
New cards
What is the main storage molecule in animals?
Glycogen
49
New cards
Where is glycogen stored?
The liver
50
New cards
Which form of glucose is glycogen made from?
α-glucose
51
New cards
Why is glycogen being branched important?
Enzymes can attack and release glucose easily
52
New cards
Why is glycogen being compact important?
This makes it good for storage (you can fit more in a smaller space)
53
New cards
Amylose is made in what structure?
Alpha-helix
54
New cards
Cellulose is made in what structure?
Beta-pleated sheet
55
New cards
Cellulose is the major component of ___ in plants.
Cell walls
56
New cards
Cellulose is made from which form of glucose?
β-glucose
57
New cards
By which bonds are cellulose chains linked together?
Hydrogen bonds
58
New cards
Cellulose chains linked together by hydrogen bonds form what?
Microfibrils
59
New cards
bonds form between monosaccharides to produce
Glycosidic, polysaccharides
60
New cards
Monomers of proteins
Amino acids
61
New cards
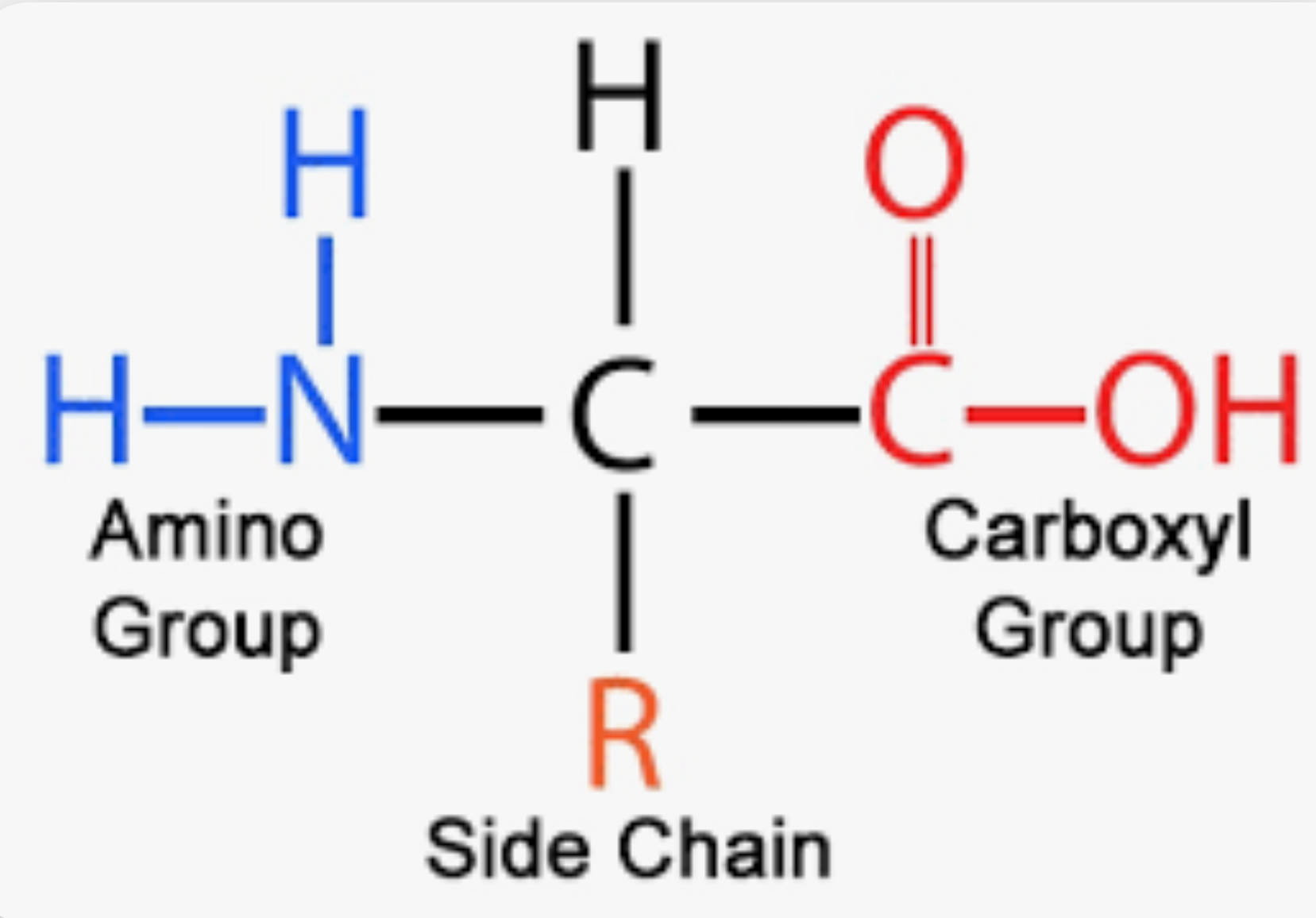
\
General structure of an amino acid
62
New cards
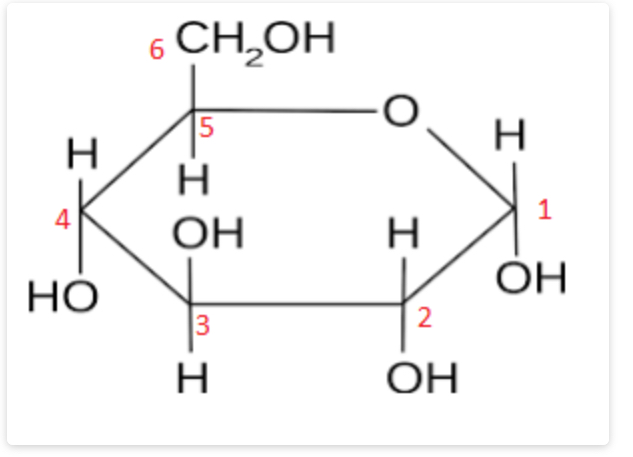
α-glucose isomer
63
New cards
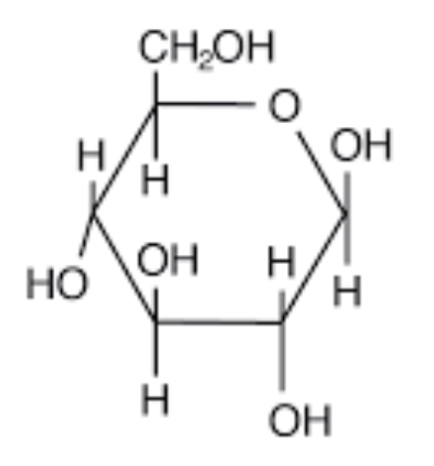
β-glucose isomer
64
New cards
Bond between amino acids
Peptide bond
65
New cards
Five main elements in proteins
C, H, O, S, N
66
New cards
What sort of reaction links amino acids?
Condensation
67
New cards
What sort of reaction breaks amino acids apart?
Hydrolysis
68
New cards
Which bonds are in primary structure of proteins?
Peptide bonds
69
New cards
Which bonds are in the secondary structure of proteins?
Hydrogen bonds
70
New cards
Which bonds are in the tertiary structure of proteins?
Disulphide bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions
71
New cards
What is a conjugated protein?
A protein with a prosthetic group attached
72
New cards
How many polypeptide chains is the quaternary structure of haemoglobin made up of?
4
73
New cards
What is the prosthetic group of haemoglobin?
Haem
74
New cards
Name three globular proteins?
Haemoglobin, insulin, amylase
75
New cards
Name three fibrous proteins?
Collagen, Elastin, Keratin
76
New cards
What is the function of collagen?
To make up animal connective tissues, such as bone, skin and muscle (minerals can bind to protein to increase rigidity)
77
New cards
Which test would you use for proteins?
Biuret test
78
New cards
What and why must you add before carrying out the biuret test?
NaOH solution as the solution must be alkaline
79
New cards
What is a positive result for the biuret test?
Colour change from blue to purple
80
New cards
What test would you use for starch?
Iodine solution
81
New cards
How should iodine solution be prepared for the starch test?
Iodine dissolved in potassium iodide solution
82
New cards
What indicates the presence of starch in an iodine test?
Brown or orange to a blue-black colour
83
New cards
What test would you use for lipids?
Emulsion test
84
New cards
2 step process for emulsion test
Dissolve test substance in ethanol, pour into water
85
New cards
What is a positive result in the emulsions test?
A milky layer on top of the water
86
New cards
What test would you use to test for sugars?
Benedict’s test
87
New cards
What two steps must you do for the biuret test?
Add NaOH, add copper (II) sulphate solution
88
New cards
Reducing sugars are all monosaccharides except for…
Maltose and lactose
89
New cards
To test for a reducing sugar add ___ to a sample and heat in a boiling water bath
Benedict’s solution
90
New cards
Positive Benedict’s result
Colour change from blue up to brick-red precipitate.
91
New cards
How to test for non-reducing sugars
Heat in boiling water bath with Benedict’s
92
New cards
In paper and thin layer chromatography, the mobile phase is the ___
Liquid solvent
93
New cards
In paper chromatography, the stationary phase is the ___
Chromatography paper
94
New cards
In thin-layer chromatography, the stationary phase is a ___
Thin layer of solid like slice gel (on a glass or plastic plate)
95
New cards
Rf value =
Distance travelled by spot/distance travelled by solvent
96
New cards
What do you call the distance the solvent has reached in chromatography?
Solvent front
97
New cards
What should you draw the line for chromatography in?
Pencil
98
New cards
Cloning definition
The process of producing genetically identical cells or organisms from the cells of an existin organism
99
New cards
Vegetative propagation definition
The production of plant clones from non-reproductive tissues.
100
New cards
Rhizome definition
Stem structures that grown horizontally underground away from the parent plant. They have nodes that new shoots and roots can develop from