Pediatric Medical Issues week 2
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cleft palate and lip
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is a Cleft?
abnormal opening or fissure
Typically congenital malformation, but can be acquired
can impact lips, palate, or both
What week does the velum and hard palate for in congenital development?
9th week of gestation.
Where does fusion for the primary and secondary palate form?
Incisive Foramen
Causes of Clefts
multifactorial: not one single factor
genetic
environmental factors
Environmental (exogenous) factors
teratogens: chemical agents inferring with embryonic development
environment: lead, radiation, pollution
Drugs and ingested substances: phenytoin, smoking, alcohol
Viruses: rubella, influenza
Maternal nutrition: nutritional deficiencies or obesity with diabetes
Physical interference: crowding in utero
Primary Palate
in front of incisive fossa
Nasal base, alveolar ridge, lips
Classifications of Clefts
isolated (lip/palate only) vs. in combination (both)
incomplete (doesn’t reach incisive fossa) vs. complete (reaches incisive fossa)
Unilateral vs. bilateral vs. Midline only
Cleft Primary Palate: Unilateral Incomplete
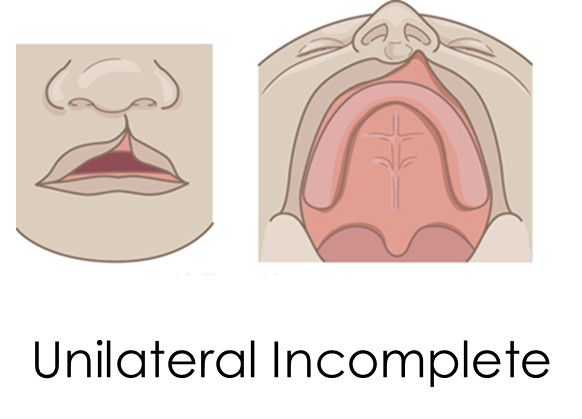
Contains primary palate, cleft-lip
Does not extend to incisive foramen
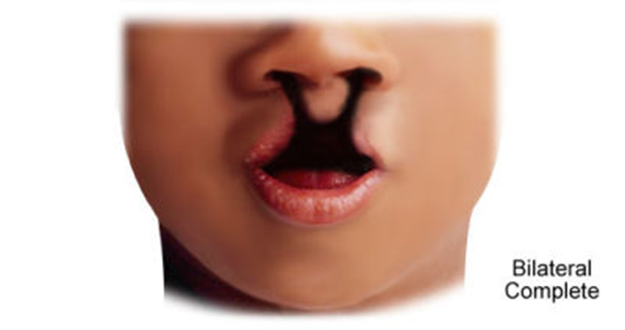
Cleft Primary Palate: Bilateral Complete
Cleft Primary Palate: unilateral Complete
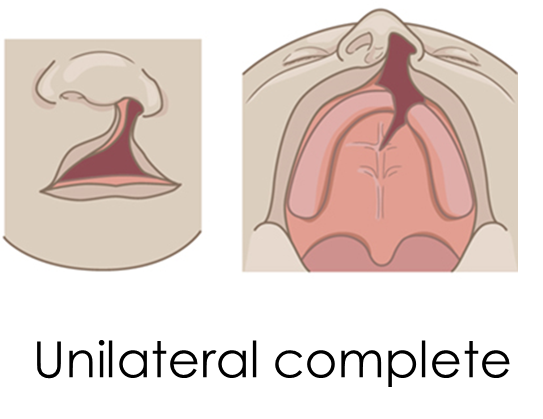
extends to incisive fossa
primary palate cleft, cleft-lip
Primary Palate Cleft:
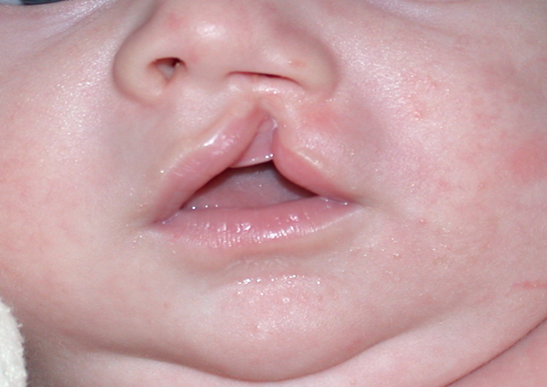
Microform cleft lip
Very mild form
looks like a scare
incomplete
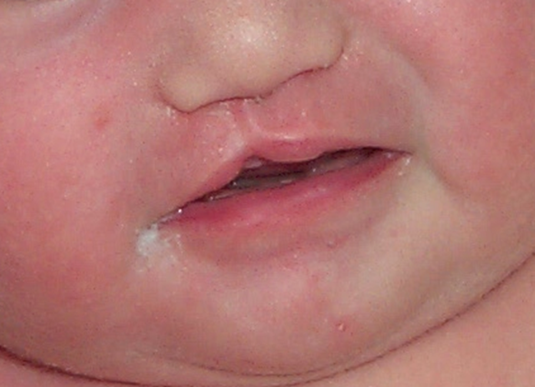
Primary Palate Cleft: Simonart’s Band
Mild affect
strand of soft tissue fills the cleft gap
incomplete
Primary Palate Cleft: Uni incomplete
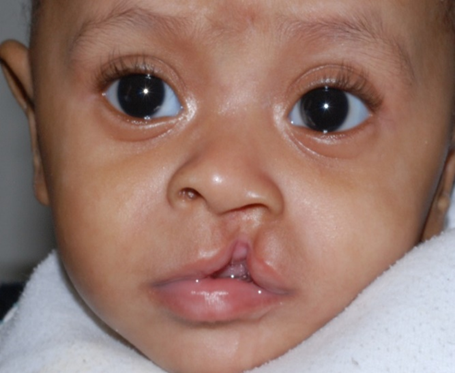
no soft tissue to fill cleft
Primary Palate Cleft: Bi incomplete
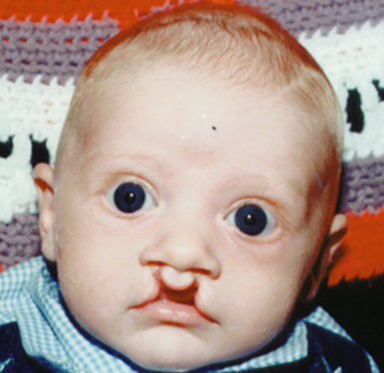
bilateral
incomplete doesn’t reach incisive fossa
Primary Palate Cleft: Unilateral complete cleft lip
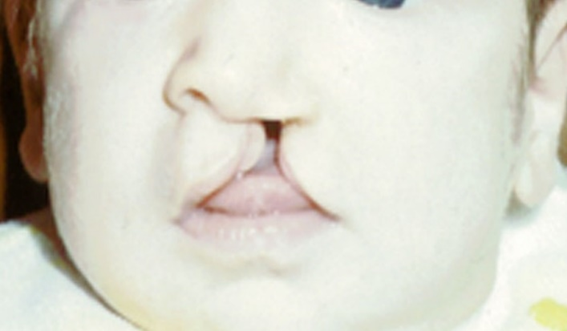
extends to the incisive fossa
Primary Palate Cleft: Bilateral Complete Cleft Lip
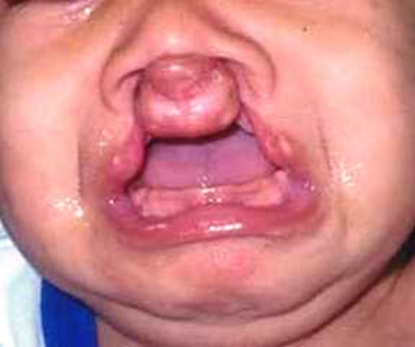
both sides (bilateral)
very wide nose typically
philtrum is called prolabial
Structure effects of cleft primary palate
´Cleft lip and orbicularis oris: muscle is affected
´Wide, flat nose with spreading nasal ala
´Short columella
´Abnormal dentition
Function effects of cleft primary palate
´Specific articulation errors (struggle with bilabial + labiodental sounds)
´Resonance affected
Clefts of secondary palate
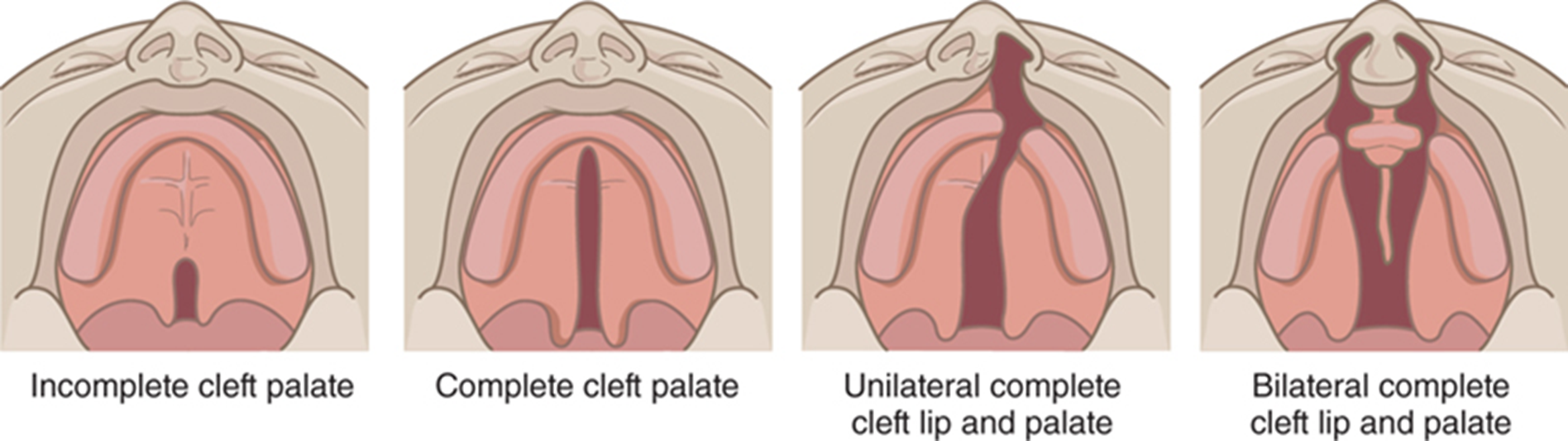
incomplete: doesn’t make it incisive fossa
complete cleft palate: extends to incisive fossa
Unilateral complete cleft lip and palate: extends from palate to the lip only on one side
Bilateral complete cleft lip and palate: extends from palate to the lip on both sides (MOST SEVERE)
Clefts of the secondary palate: Incomplete cleft palate
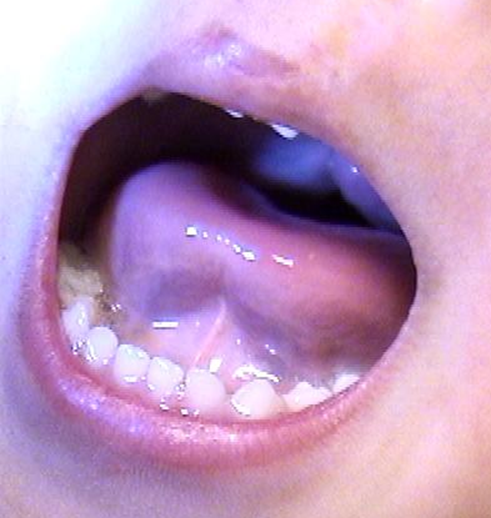
cleft palate, starts in secondary palate but DOES NOT extend to incisive fossa
Clefts of the secondary
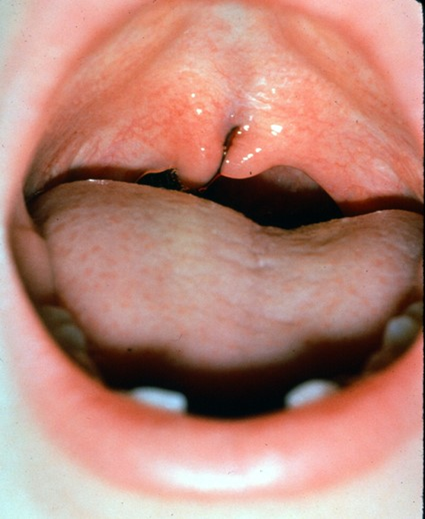
bifid uvula
incomplete cleft palate, doesn’t extend to the incisive fossa
Pierre Robin Sequence
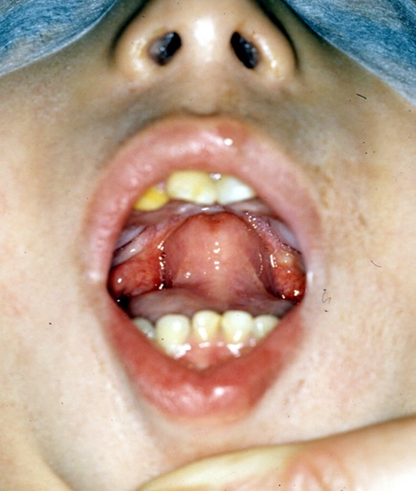
wide bell-shaped cleft palate
complete cleft palate
extends from the cleft to incisive fossa
Clefts of primary and secondary palate: Unilateral complete cleft lip and palate
cleft lip and palate
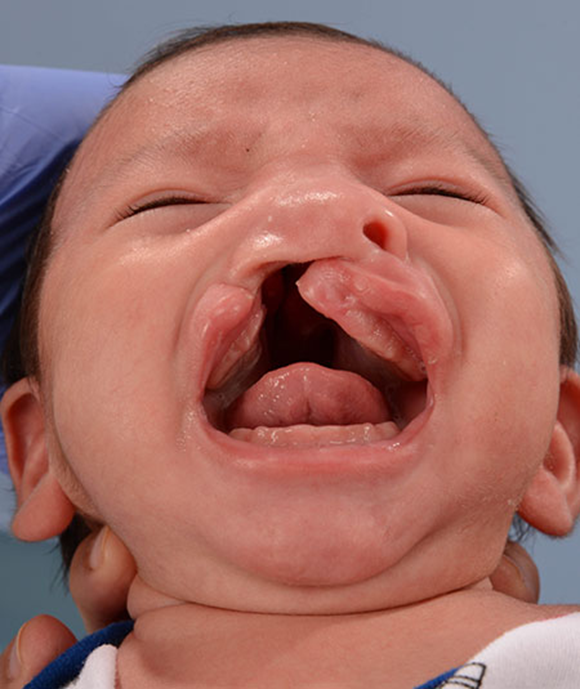
Cleft of primary and secondary palate: bilateral complete lip and palate
Most significant and severe
Clefts of the secondary palate: effect on structure
´Absent velar aponeurosis
´Altered insertion of the levator velar muscles
´Abnormalities in nasal septum
Clefts of the secondary palate effect on function
´Velopharyngeal insufficiency
´Feeding problems and nasal regurgitation
´Eustachian tube malfunction : middle ear infections
Submucous Cleft: embryology
etiology: results in the nasal surface
classic triad of characteristics
types: Overt vs. Occult
Submucous Cleft: types
can only officially be seen on nasal surface through nasopharyngoscopy
Submucous cleft: effect on structure
´Depends on the extent: can go unnoticed
´May include a minor abnormality of the uvula or a defect of the nasal surface of the velum and hard palate
´May include an altered insertion of the levator velar muscles
Submucous cleft: Effect on function
´Velopharyngeal insufficiency
´Feeding problems and nasal regurgitation
´Eustachian tube malfunction
earlier it’s addressed less it’s dramatic
Facial Clefts: types and severity
Can be midline or oblique
beyond the palate facial cleft
can be cause by: generic defects or amniotic bands
Facials Clefts: midline clefts
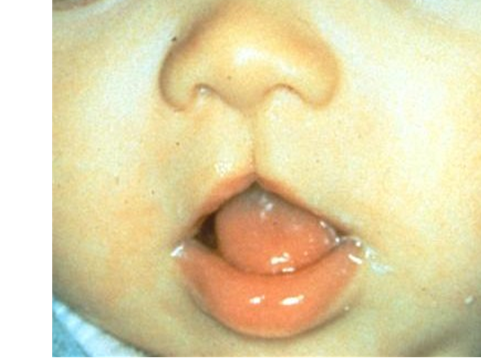
Facial clefts: oblique clefts
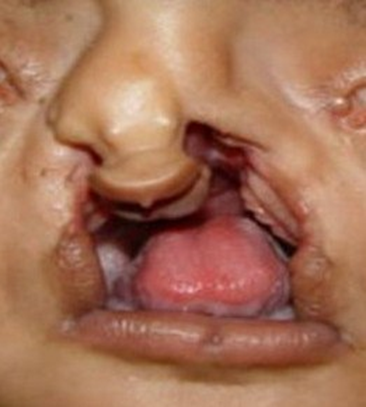
Facial clefts structure effects:
´Many structures of the face and skull can be affected
Facial Clefts: effects on function
´Cognition
´Language
´Speech
´Resonance
´Hearing
´Feeding/swallowing
Incidence of Clefts
2nd most common birth defect in the united states
incidence based on - racial background, gender, laterality, type
Racial Incidence of cleft lip/palate
American Indians
Asians
Caucasians
African Americans
Cheilorraphy
cleft lip surgery
Palatoplasty
cleft palate surgery
All of the following structures are part of the velopharyngeal valve EXCEPT
velum (soft palate)
Base of the tongue
lateral pharyngeal walls
posterior pharyngeal wall
base of the tongue
Which population has the highest prevalence of clefts
native Americans
What is the correct term for a cleft of the secondary palate that does not extend to the incisive foramen?
incomplete cleft palate
All the following are characteristics of an overt submucous cleft palate EXCEPT:
A protrusive Premaxilla
Where are Adenoids located at?
Nasopharynx
In normal embryological development, where does fusion of the secondary palate begin?
Incisive Foramen
Craniofacial Syndromes
usually more severe genetic
Morphology
the shape/form of a living organism
Dysmorphology
malformation: genetic condition causing abnormality
deformation: relates to abnormal physical force relating to an embryo or fetus
Syndromic Cleft Lip
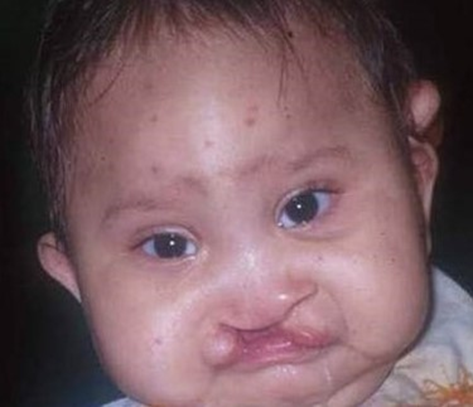
genetic- malformation
Amniotic band syndrome
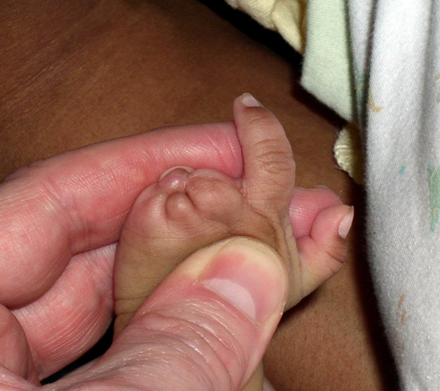
deformation- genetic
Syndrome
pattern of multiple malformations that are genetically related
e.g. down syndrome
Sequence
series of multiple abnormalities that result from a single initiating malformation
Association
pattern of multiple malformations in people w/ no known genetic cause
Pierre Robin Sequence (PRS)
small mandible
tongue obstructs palatal fusion
u-shaped palate
struggles w/feeding and sleep apnea is commong
CHARGE Syndrome
Prevelence 1 in 9000-15,000 live birth
C.olobama eyes: defect in iris, appears as black notch
H.eart defect
A.tretic chonae- need airway support, synopsis in the nose
R.etarded Growth
G.enitourinary anomalies- hypoplastic/hypodevelopment
ea.r malformations- inner and outer ear possible, hearing loss common
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
not genetic- caused by use of alcohol by pregnant women
Pierre Robin Sequence Palate (both common)
facial features: short palpebral fissures, indistinct philtrum, thin upper lip, flat midfacel micrognathia, ear anomalies
FAS: phenotypic features
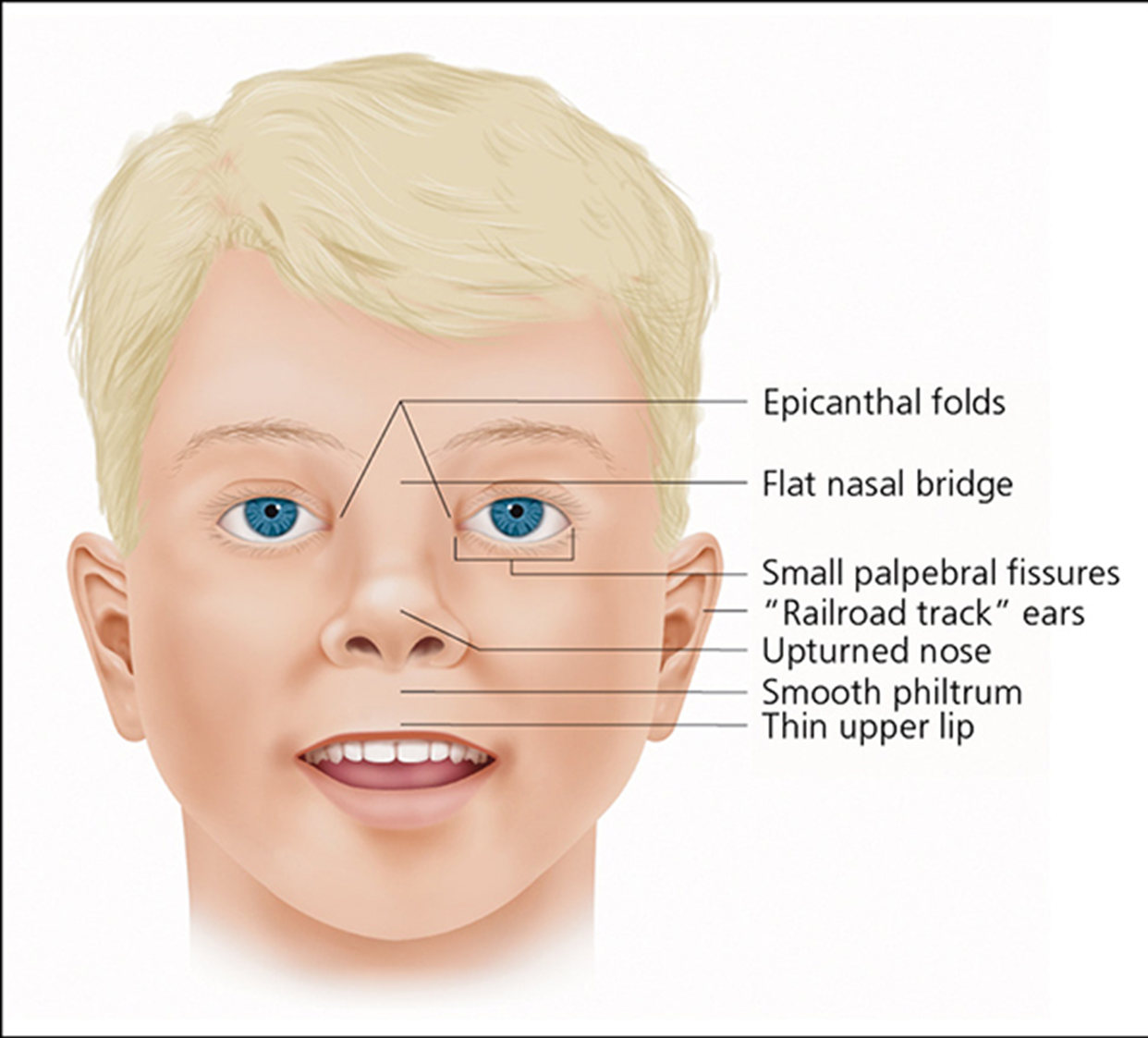
Stickler Syndrome
pierre robin sequence plus:
wide, flat face,
myopia, and eye abnormalities (near sightedness)
sensorineural hearing loss
skeletal abnormalities- scoliosis common
Juvenile arthritis and joint disorders
Autosomal dominant condition
Van Der Woude Syndrome
bilateral complete cleft lip and palate
have bilateral lip pits on lower lip
Autosomal dominant: 50% risk of recurrence
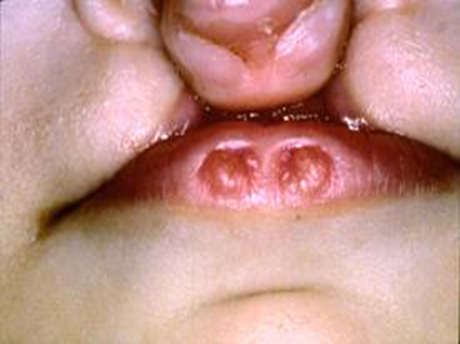
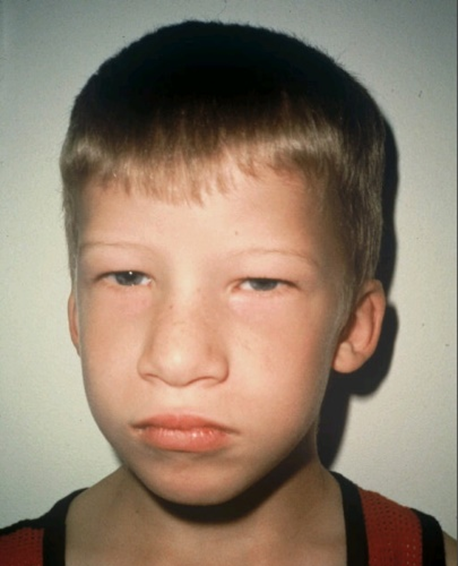
Velocardiofacial/22q 11.2 deletion syndrome
deletion of gene on chromosome 22
velo: velopharyngeal dysfunction
cardio: minor cardiac, vascular anomalies
facial: dysmorphic facial features
Other: Learning disabilities, oral motor dysfunction, psychological concerns, other medical problems
most common characteristic is hypernasal speech
apraxia of speech is common
Importance of genetic evaluation
anticipation: helps to anticipate problems through knowledge of the natural history of the syndrome
treatment: allow parents and providers to plan for appropriate treatment and have realistic goals
family planning: provides information about the reoccurrence risk for family planning
What is the correct terms for a cleft of the secondary palate that does not extend to the incisive foramen
incomplete cleft palate
all of the following are characteristics of an overt submucous cleft palate except
a bifid uvula
zona pellucia
a hypoplastic uvula
a protrusive premaxilla
a protrusive premaxilla
A pattern of VP closure that is accomplished primarily by the velar and PPW movement.
coronal pattern