Biology - MedConnect Papers - Set 3
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
striated muscle tissue
skeletal muscles
striated muscle function
generate force and contract in order to support respiration, locomotion, and posture (skeletal muscle) and to pump blood throughout the body (cardiac muscle).
straited
muscles that contract and relax like giant elastic bands to allow skeletal movement
blood is a type of
connective tissue
The substantia nigra is located in the
mesencephalon
photoreceptors responsible for white and dark vision are
rods
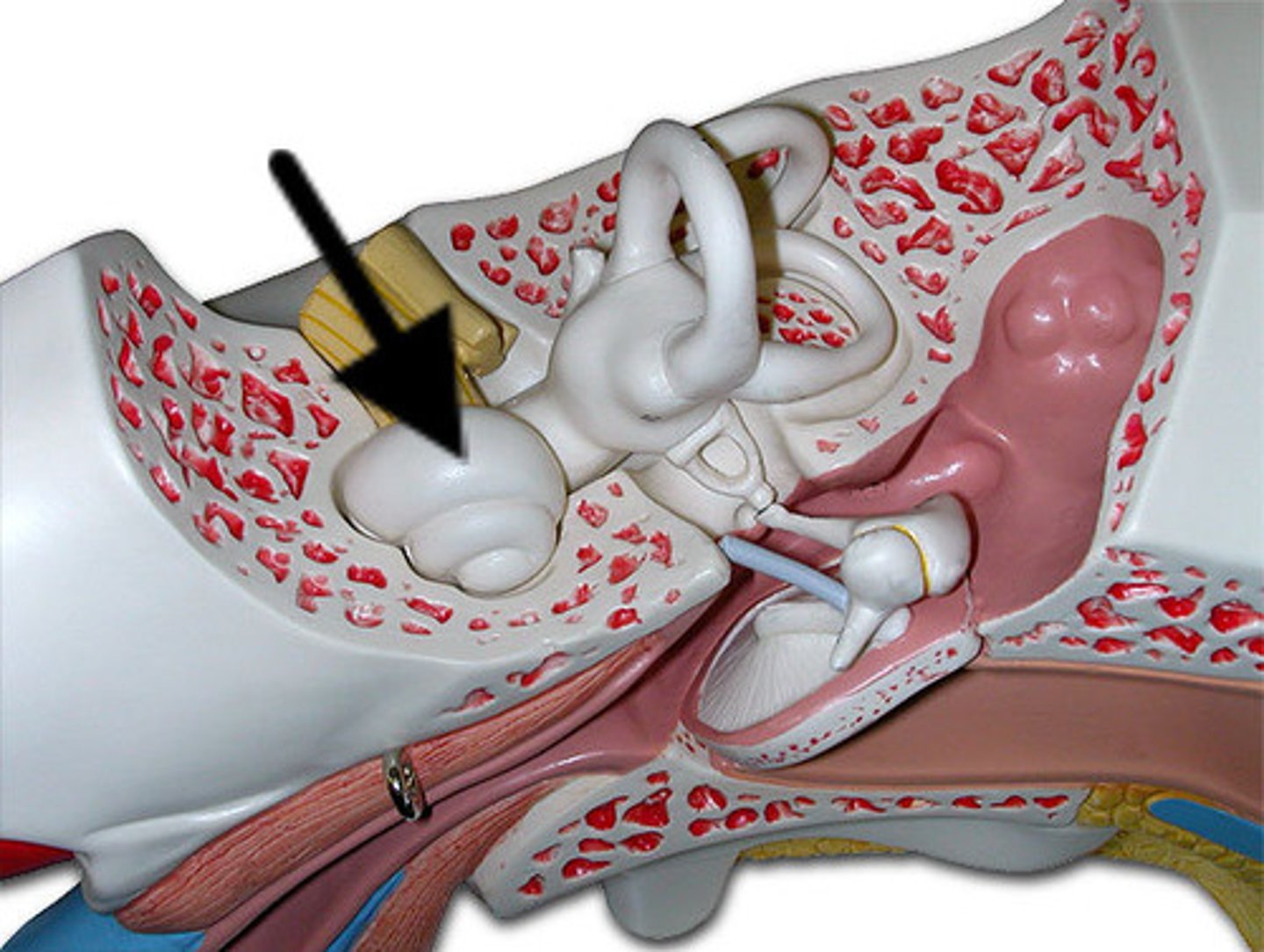
organ of corti is situated
cochlea
crossing over is performed during
prophase 1
non-membrane organelles are
ribosomes
prions are
infectious proteins
polysome is a complex of ribosomes and
mRNA
cerebellum is situated
inferior to the occipital parts of the brain not above
efferent
motor
afferent
sensory
rhD negative
do not have D antigen on blood cells
least common blood type
problem when mother incompatible with child's rhD
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of mRNA
Karyotype
Specific set of chromosomes of every species during metaphase e.g. in humans there are 46 chromosomes and 2 sex chromosomes (XX and XY).
Homeostasis:
maintaining a stable, relatively constant internal environment
Grey matter
this is the darker colour in the brain or spinal cord. Grey matter in the brain consists of neuronal cell bodies
Oestrogen is produced by
ovaries fat cells adrenal glands
oxytocin is produced by
pituitary gland
mesencephalon
is the precursor to the midbrain
pons
part of the brain stem that connects the cortex with the cerebellum
[brain stem ]
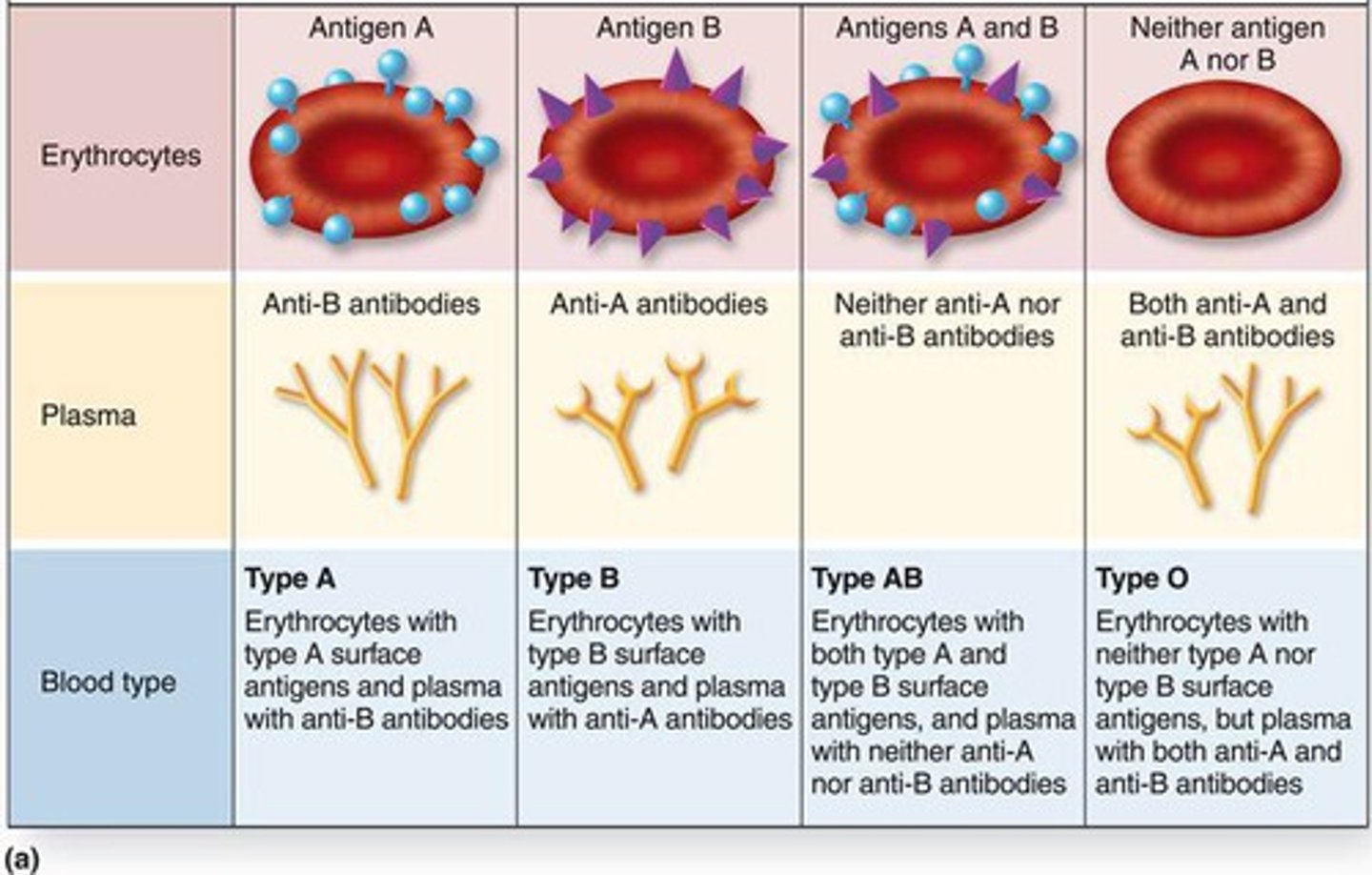
antigens on RBC
type A- A
type B -B
type AB- B and A
type O- none
[toxic can only live with its type of toxin, O is unquie ]
antibodies in plasma
type A- beta B
type B -alpha A
type AB- none
type O- alpha and beta
(anti-B antibodies in type A blood would attack red blood cells with B antigens)
antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
antibody
A protein that acts against a specific antigen
Phage
is a virus which infects a bacterium
number of amino acids
20 amino acids
degenerate code
multiple codons encode a single amino acid
only 20 types of amino acids that can be coded for
enzyme trypsin breaks down
protein
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
46 chromosomes
Malpighian tubules
tubules that excrete metabolic wastes into the hindgut in arthropods
[pig-wastes]
location of Malpighian
nephron
sensory organ is made up of
various receptor neurones
white matter in the spinal cord and brain consists
mainly of myelinated axons
grey matter consists
of neuronal cell bodies
HIV is an
RNA Virus
pancreatic juice is produced in the pancreas and contains
s pancreatic enzymes and is released via the entry of acidic chyme into the duodenum which stimulates the S cells to release secretin.
nucleoid is found
in prokaryotic cells only encloses the genetic material
prostate is
gland
DNA biological properties
main hereditary molecule
biological properties of proteins
structural, regulatory, transport, protective, catalytic
polysome
A complex formed when multiple ribosomes are translating the same mRNA into proteins.
also polyribosome
heart wall layers number
3
inner layer of the heart
endocardium
longitudinal wall division in heart into right and left parts in each part there is
an atrium and a ventricle
outermost layer of the heart
epicardium
cones
are photoreceptor cells in the eye that are trichromatic so give colour vision
prion
abnormal protein in the brain which can cause abnormality in other proteins via misfolding
blood group B erythrocytes contain
antigens B
which one is a limb muscle
biceps
limb muscles
skeletal muscles of upper and lower extremities
which bone is not a part of the skeleton of the free upper limb?
humerus ulna radius shoulder blade
shoulder blade
ear ossicles are located in the
middle ear
the iris is situated behind
cornea
pupil is located
center of iris
retina is located
back of the eye
it is the innermost layer of the eye
sclera is
white of the eye, outer layer of the eye
the primary protein structure is not determined by amino acid residues ?
number, folding type arrangement
folding
prokaryotes are
eubacteria and cyanobacteria
golgi complex consists of
cisternae and vesicles
the tertiary structure of proteins is the
folding of the chain in space
oxytocin stimulates
"milk let down" during pregnancy and uterine contractions during childbirth
milk ejection
Carbohydrates are the basic
source of energy for the cells
epidermal cells are restored
trough division of living cells in the deeper layers
proteolysis
decomposition of proteins into amino acids
done by trypsin
centromere
is a special region of a chromosome, near the middle. It is where 2 identical sister chromatids stay in contact as the chromosome attaches to the spindle in mitosis
neuron
a specialised cell of the nervous system that is electrically excitable. Transmits impulses and communicates with other neurons through synapses
polysome
a group of ribosomes bound to an mRNA molecule like 'beads' on a 'thread'.It consists of a complex of an mRNA molecule and 2/+ ribsomes that act to translate mRNA instructions into polypeptides
roads
a type of specialised light-sensitive cell (photoreceptor) in the retina in the eye ( back of the eye) that provides side vison and the ability to see objects in dim light
secondary constriction
-an be found even if a primary constriction( at centromere) is present
- site at which chromosome can bend at
-these are useful when required to identify chromosomes from a set
sister chromatids
refers to identical copies (chromatids) formed by the DNA replication of a chromosomes , with both copies joined by a common centromere
satellite chromosomes
chromosomes that contain secondary constructs that serve as identifying markers
substrates of replication
deoxyribonucleotides
substrates of transcription
ribonucleotides
blood group A erythrocytes prosses
antigens A
pepsin breaks down
proteins
contractile
actin and myosin
become shorter
actin and myosin are in
two of the contractile proteins that reside inside the muscle cell.
Bisceps
flexes the elbow
lumbar vertebrae are
largest in size
Mineralcorticoids (aldosterone)
-Target: kidneys
-Effect: stimulates reabsorption of sodium in the kidneys; increases blood pressure and blood volume
Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
- increase blood sugar levels (esp. during stress)
-regulate metabolism of organic compounds
-reducing inflammation
spinal cord is made up of
white and grey ,atter
white matter
myelinated axons
grey matter
unmyelinated neuron cell bodies and short, unmyelinated axons
[depressed and cold didn't get insulation]
viroids
ngle stranded RNA molecules that have no surrounding capsids
phages
A virus that infects bacteria; also called a bacteriophage.
Prions
infectious protein particles that do not have a genome
eubacteria
Kingdom of unicellular prokaryotes whose cell walls are made up of peptidoglycan
cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic, oxygen-producing bacteria (formerly known as blue-green algae).
during anaphase the chromosomes
consist of normal quantity of DNA
Endoplasmic Reticulum consists of
flat-tube like tanks and vesicles
most important event in interphase is
DNA replication
what forms skeletal muscles
- each fibre is a single cylindrical muscle cell
-hundred of muscle fibres bundle together
-bundle is wrapped in connective tissue
-wrapping connective tissue sheath is called epimysium
number of lumbar vertebrae
in adult humans
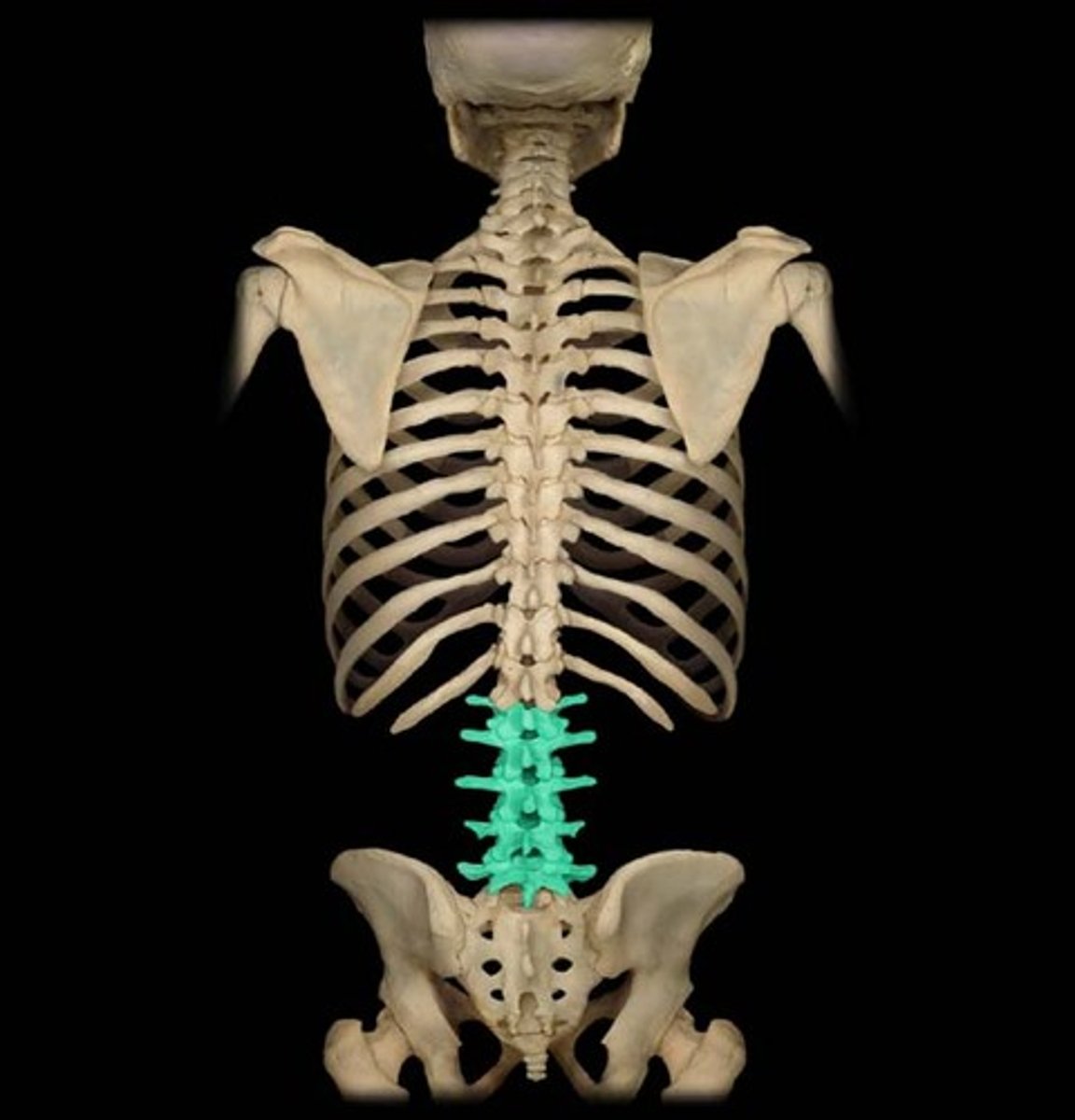
location of 5 lumbar vertebrae
beneath thoraic vertebrae
thoraic vertebrae
12
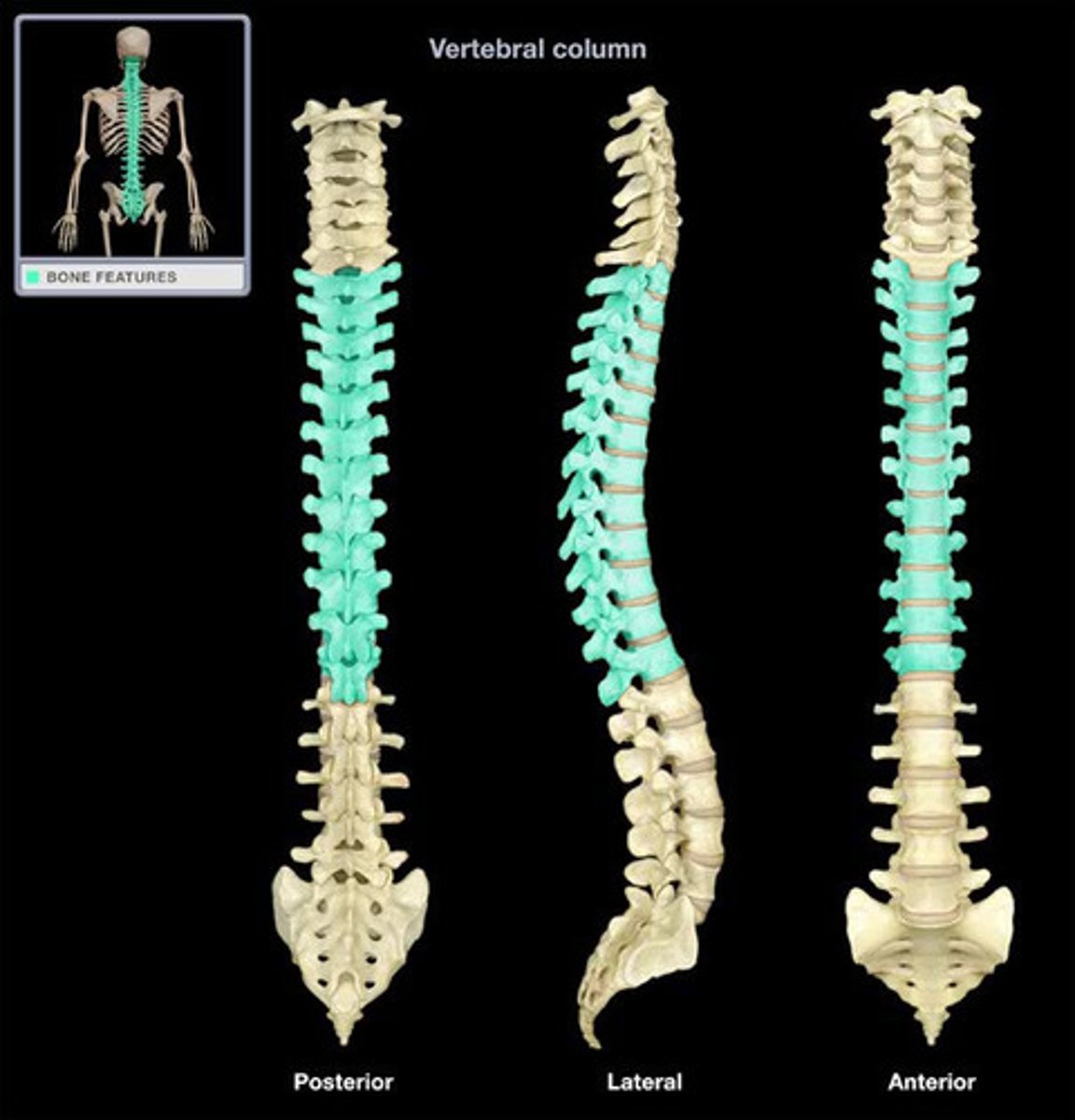
why are the lumbar vertebrae the largest vertebrae
to be able to support the weight of the body when standing due to the effects of gravity