Plant Taxonomy Lab Exam 3
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
1
New cards
what phylum did we study in laboratory 5
Magnoliophyta
2
New cards
what are the three organs in angiosperms which we examined
root
stem
leaf
stem
leaf
3
New cards

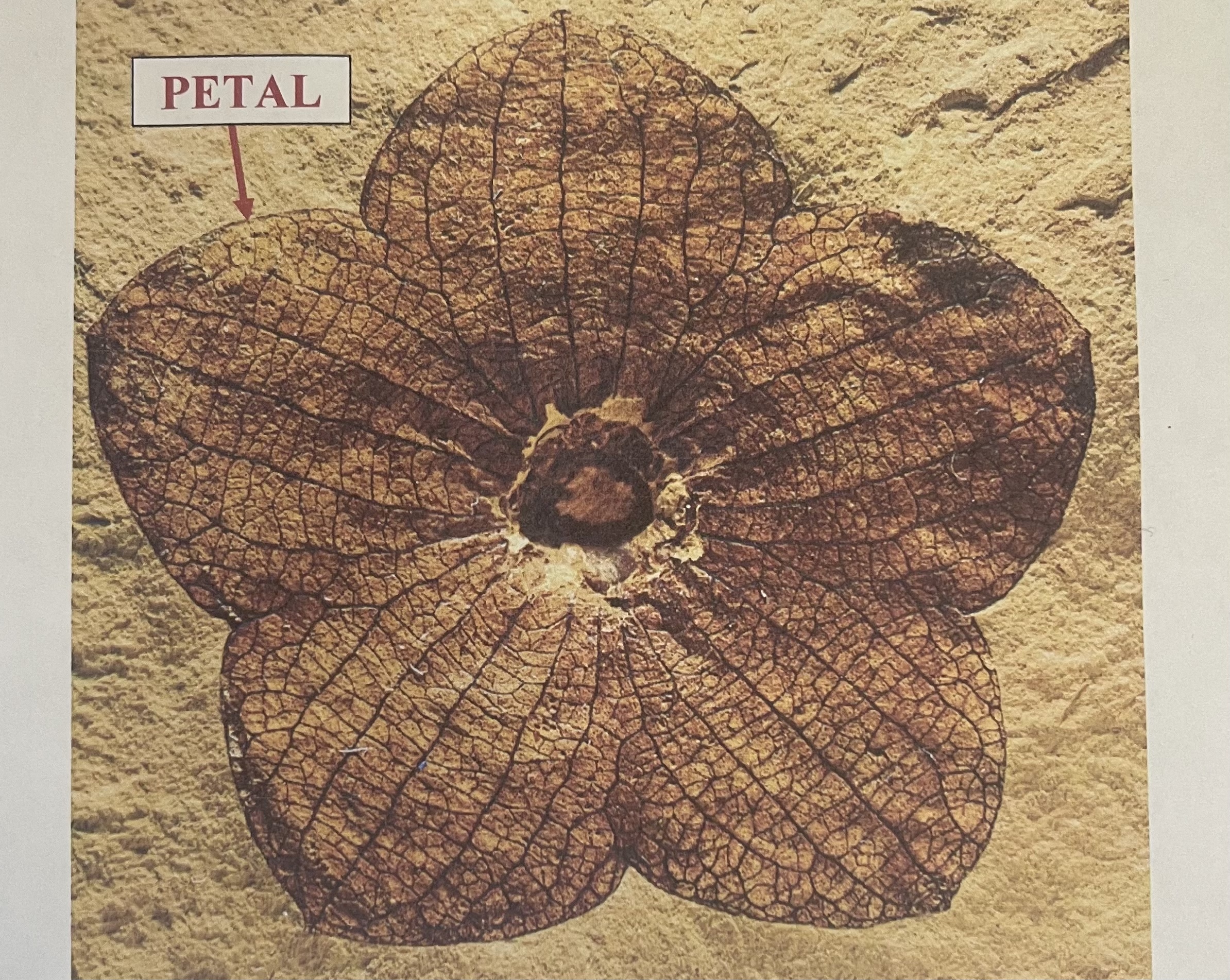
what is this fossil in the image
hint: oldest known angiosperm fossil
\~130 mya, cretaceous
hint: oldest known angiosperm fossil
\~130 mya, cretaceous
__Archaefructus__

4
New cards

what is this fossil in the image
hint: angiosperm fossil
\~50 mya, tertiary
hint: angiosperm fossil
\~50 mya, tertiary
__Florissantia__
5
New cards
what two classes within the Magnoliophyta phylum did we observe
Magnoliopsida
Liliopsida
Liliopsida
6
New cards
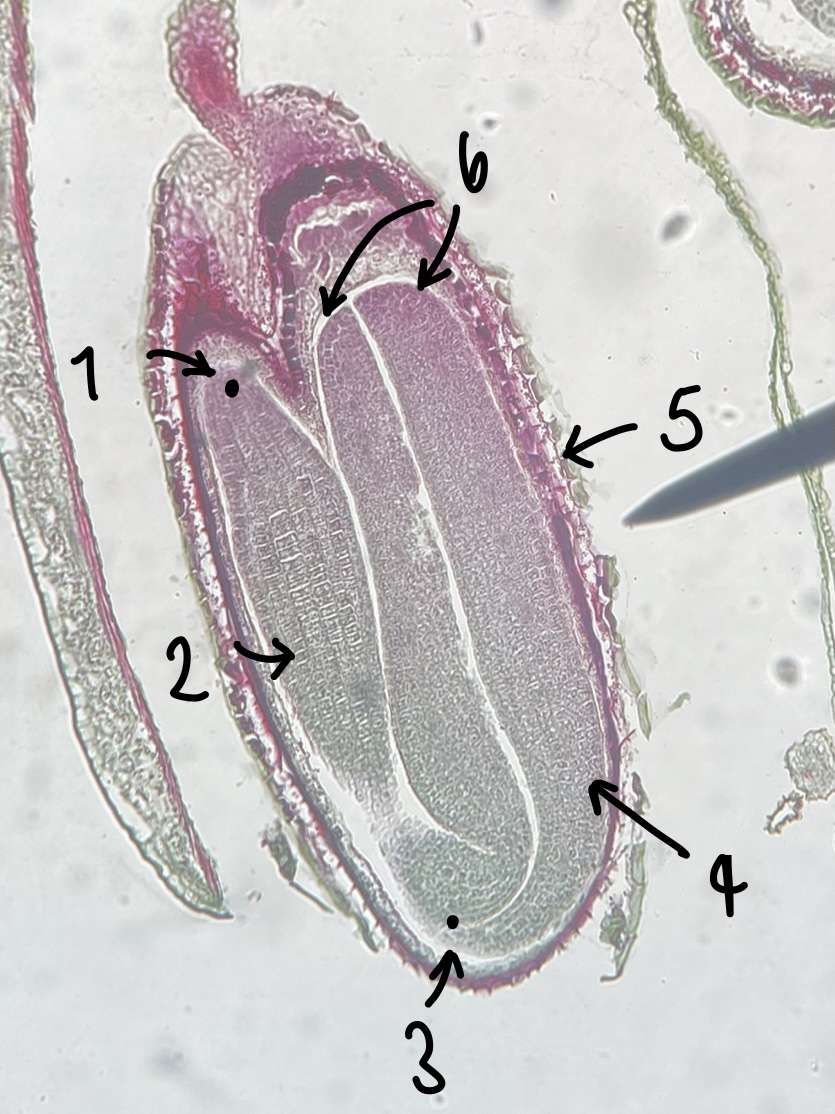
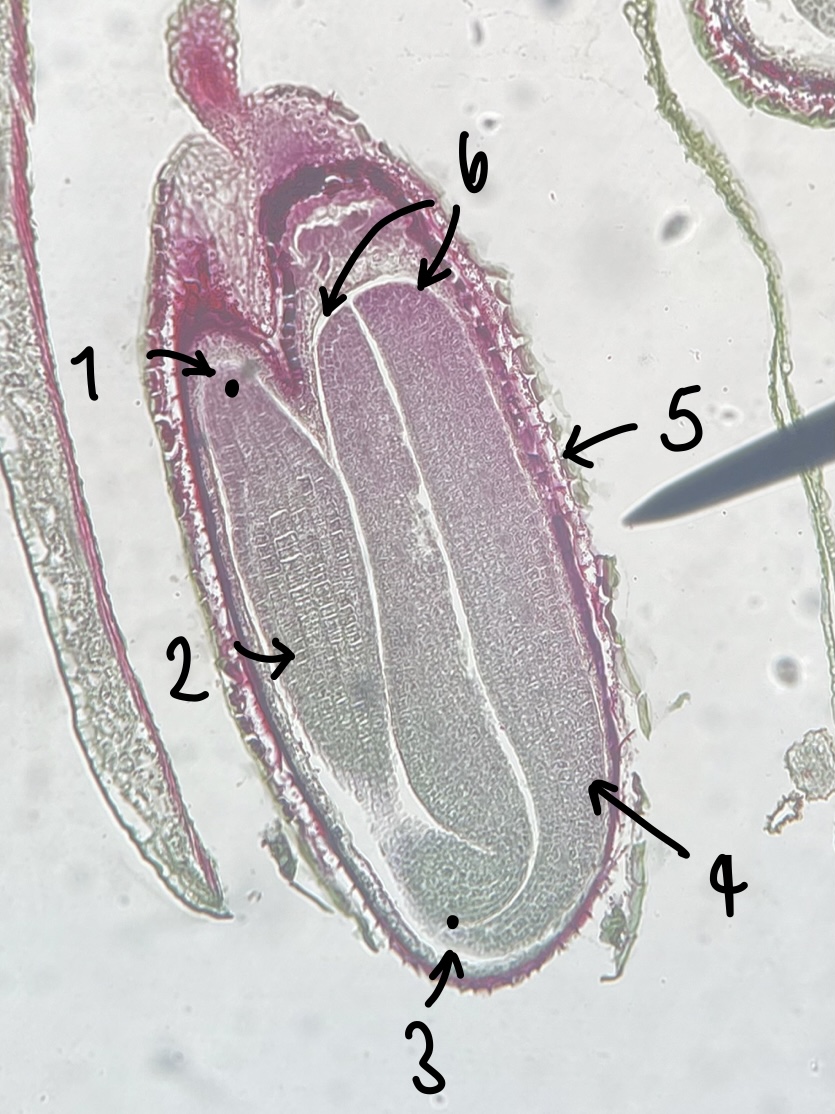
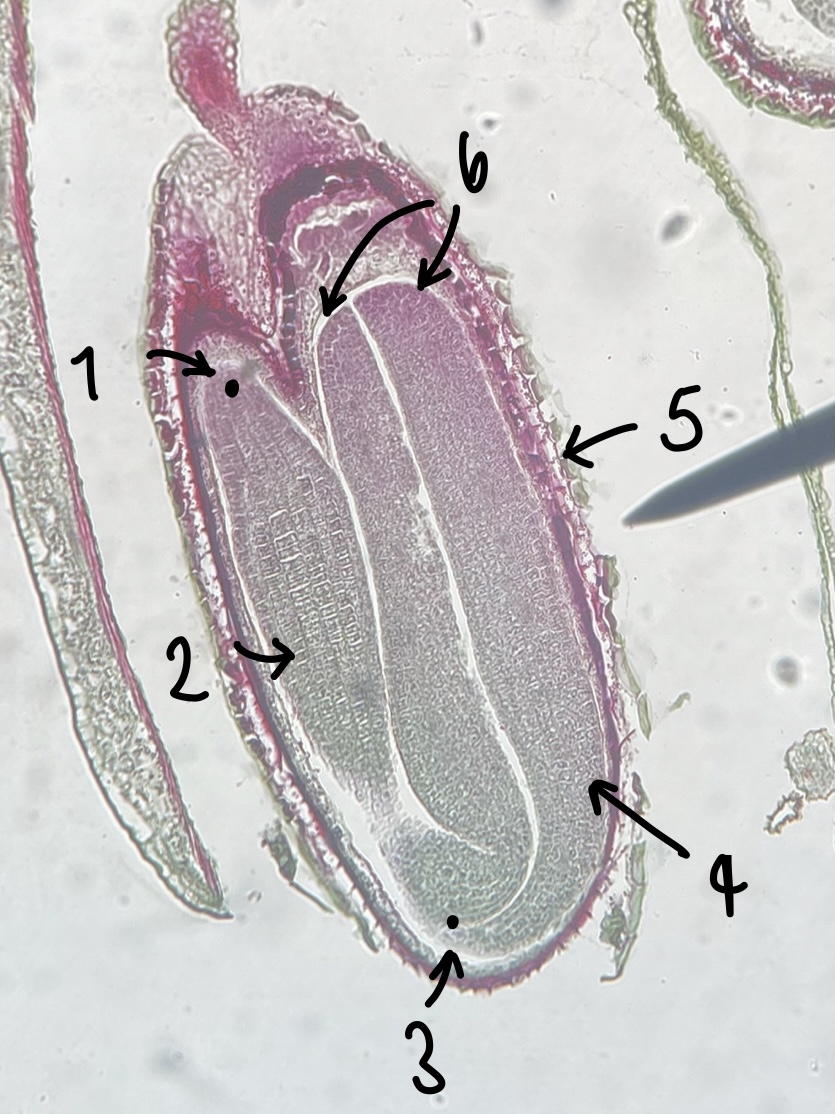
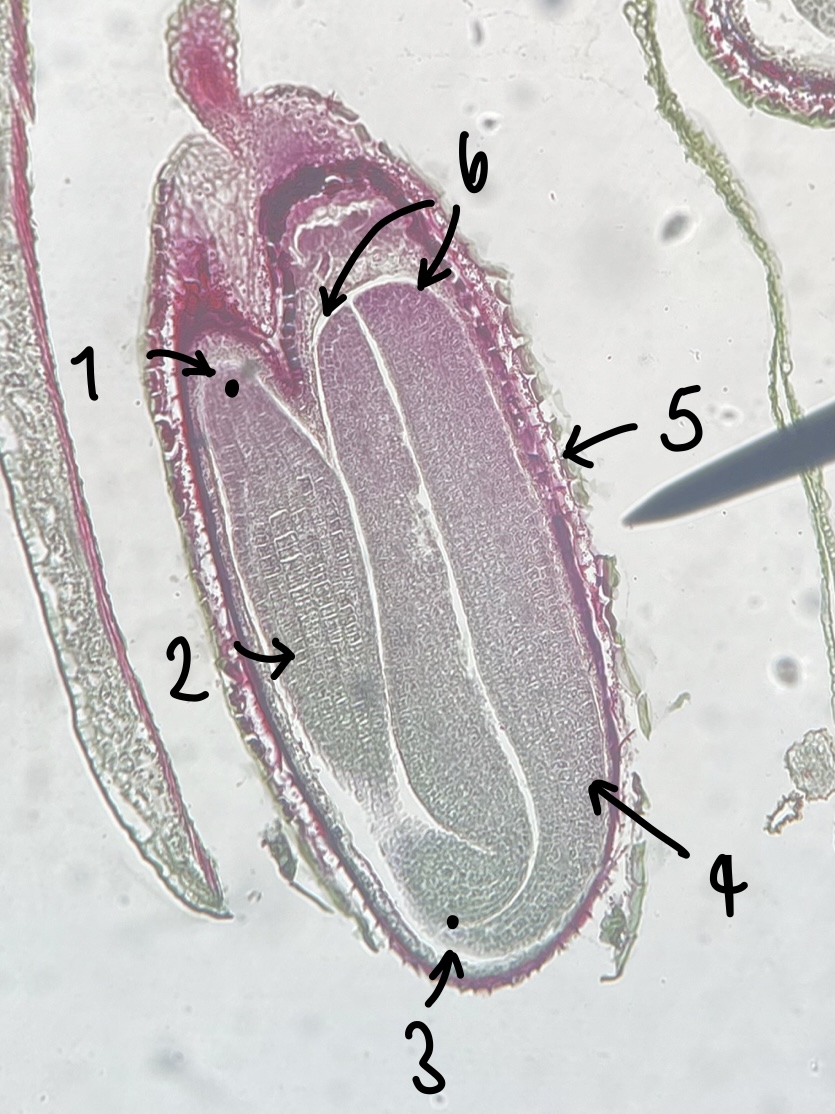
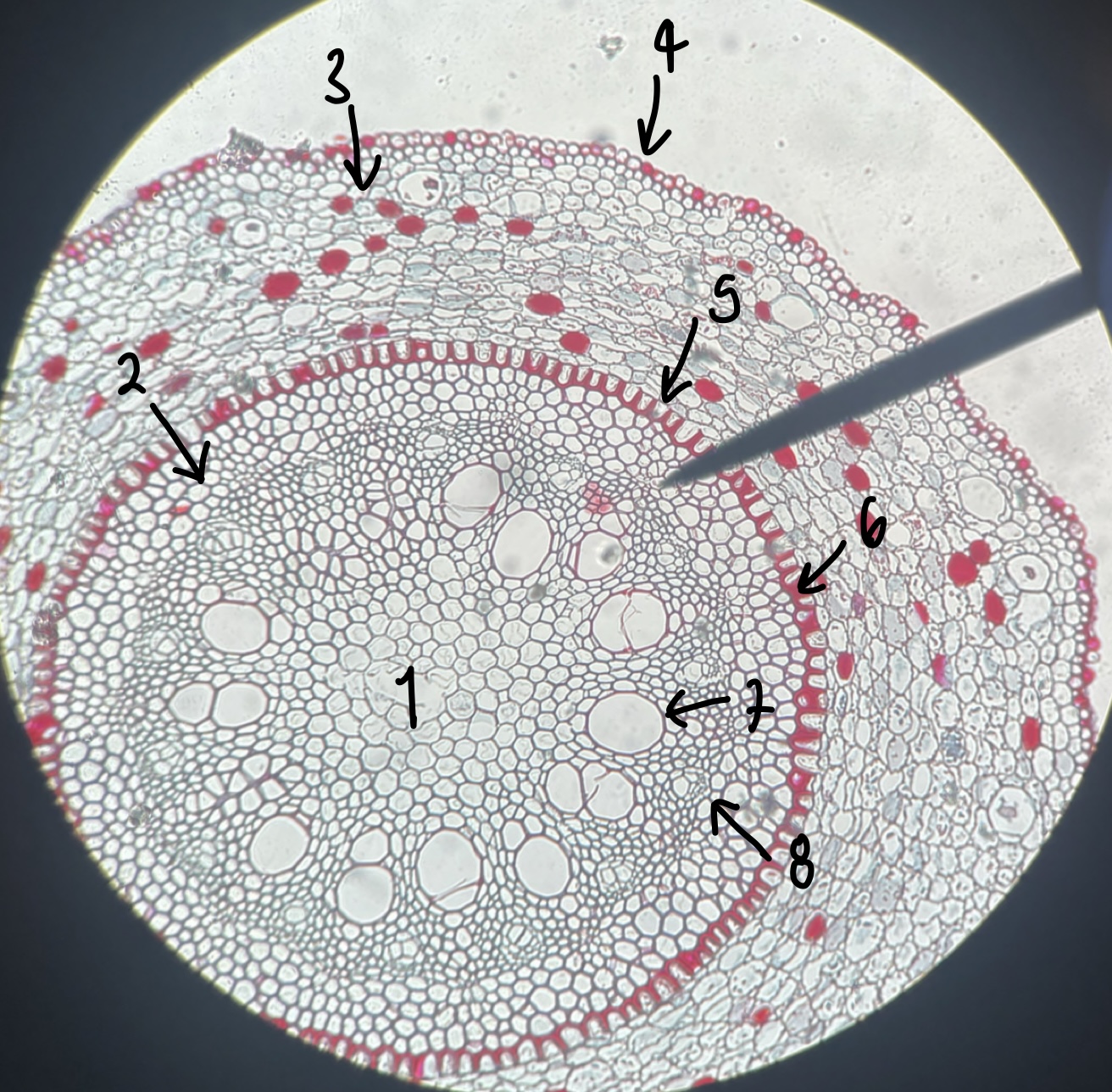
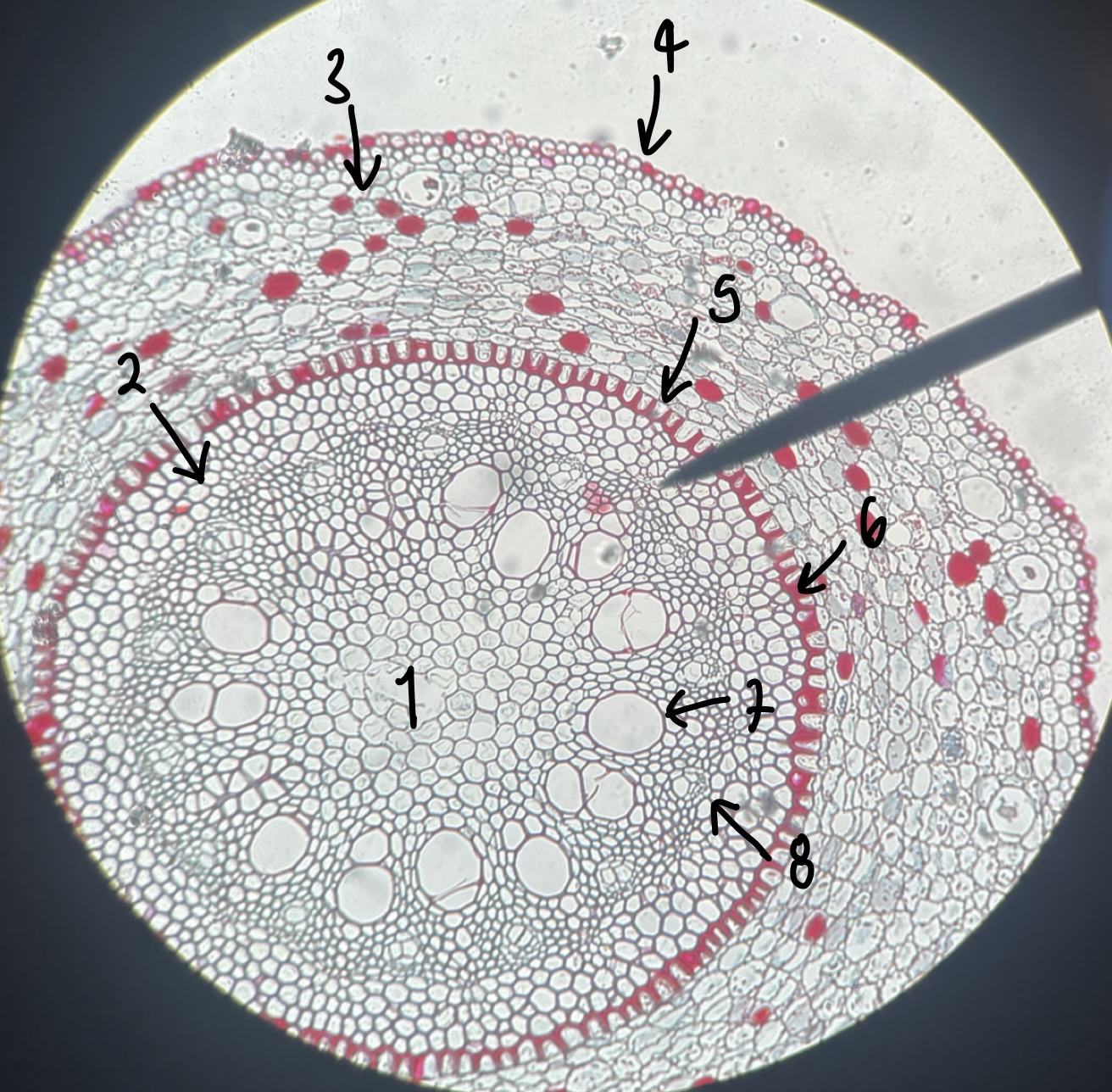
what genus of Magnoliopsida seed did we observe
__Capsella__
7
New cards
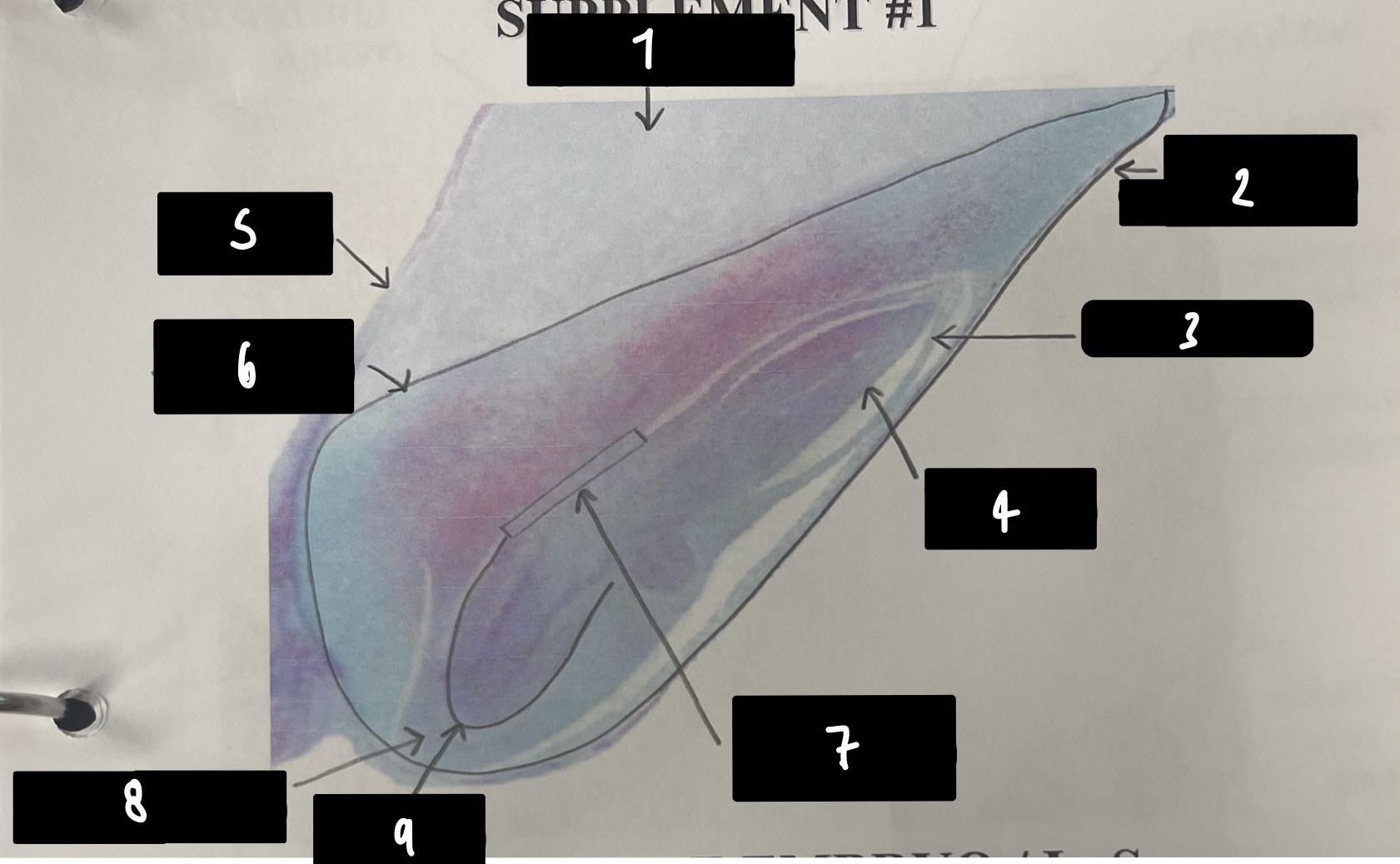
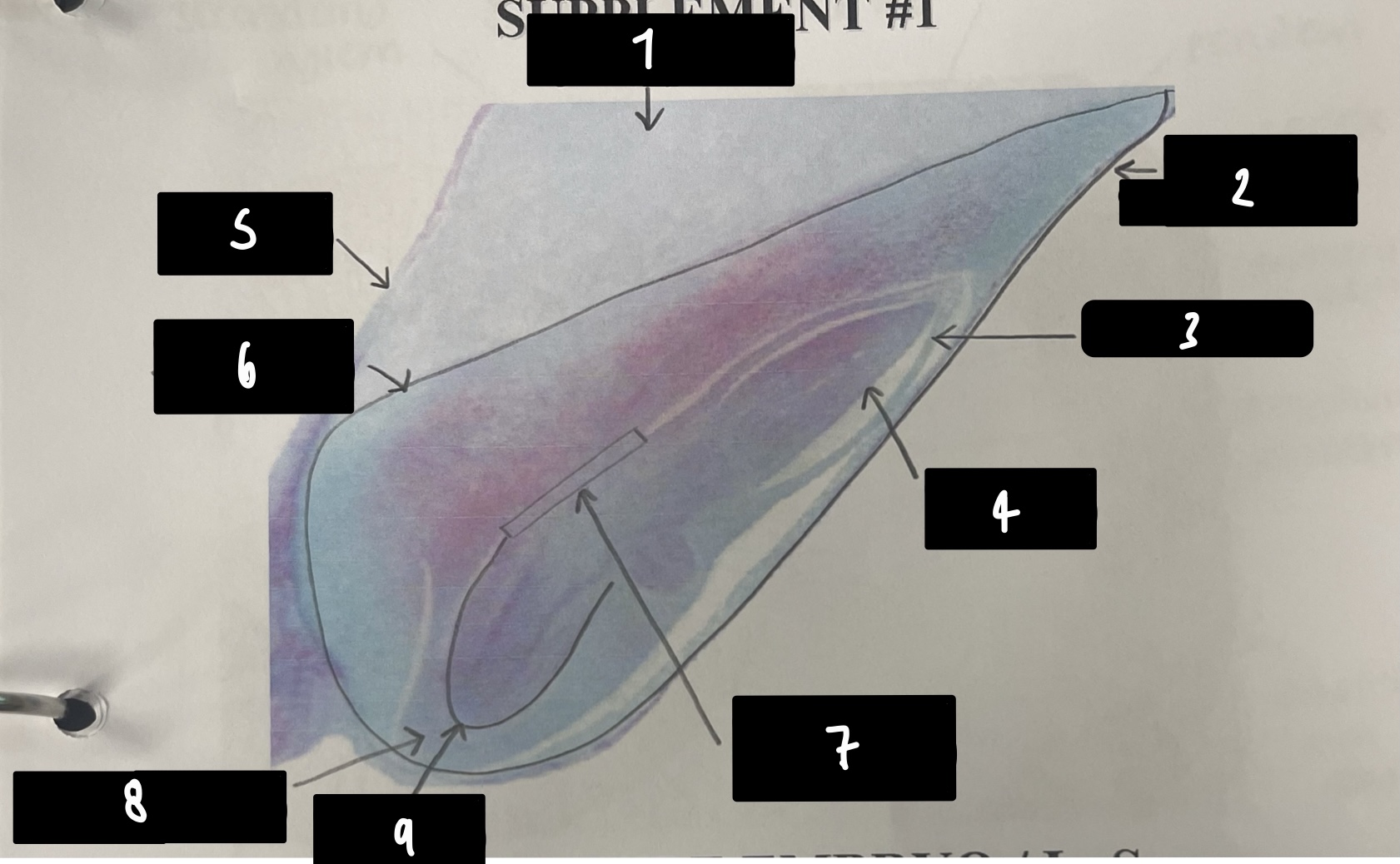
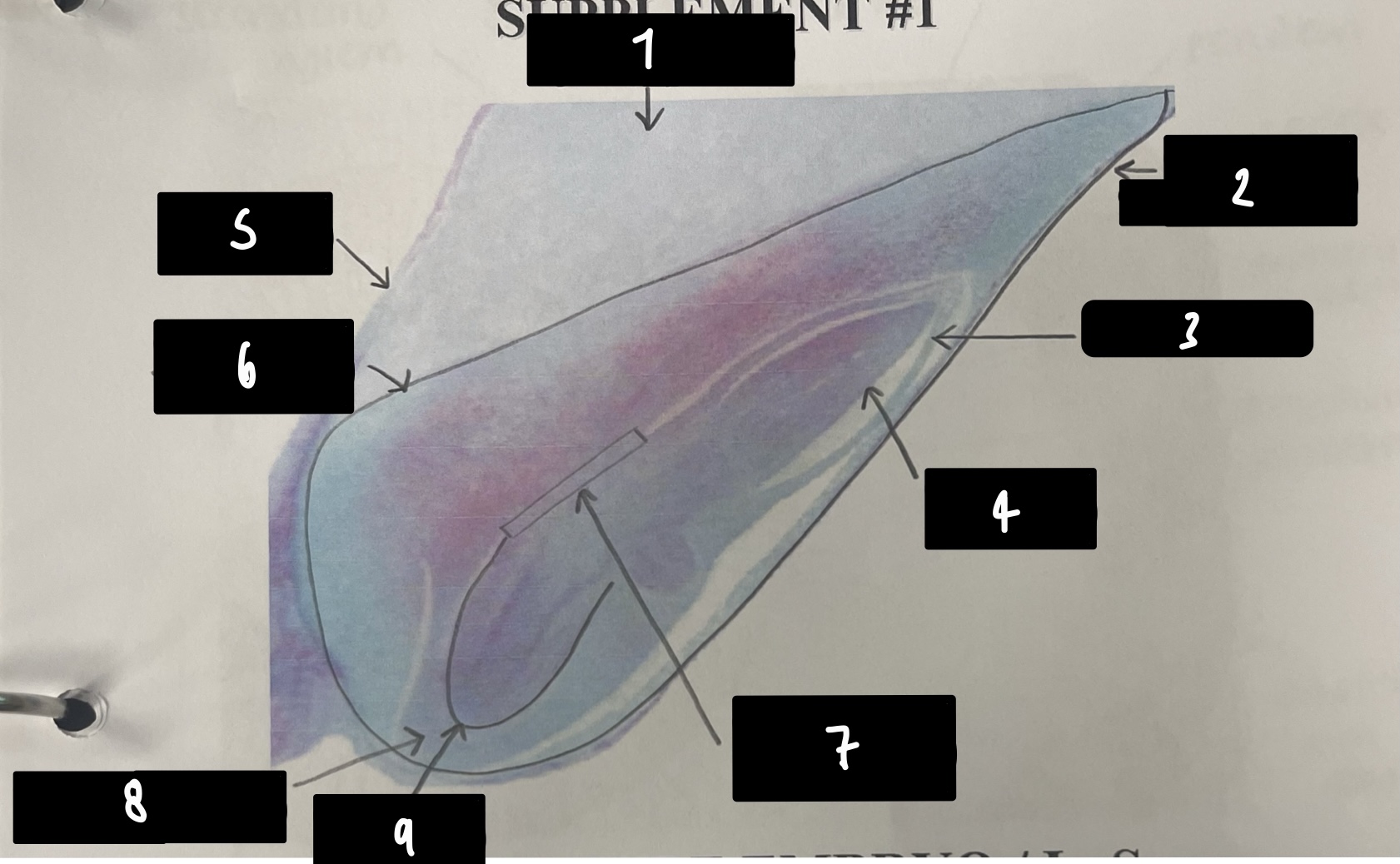
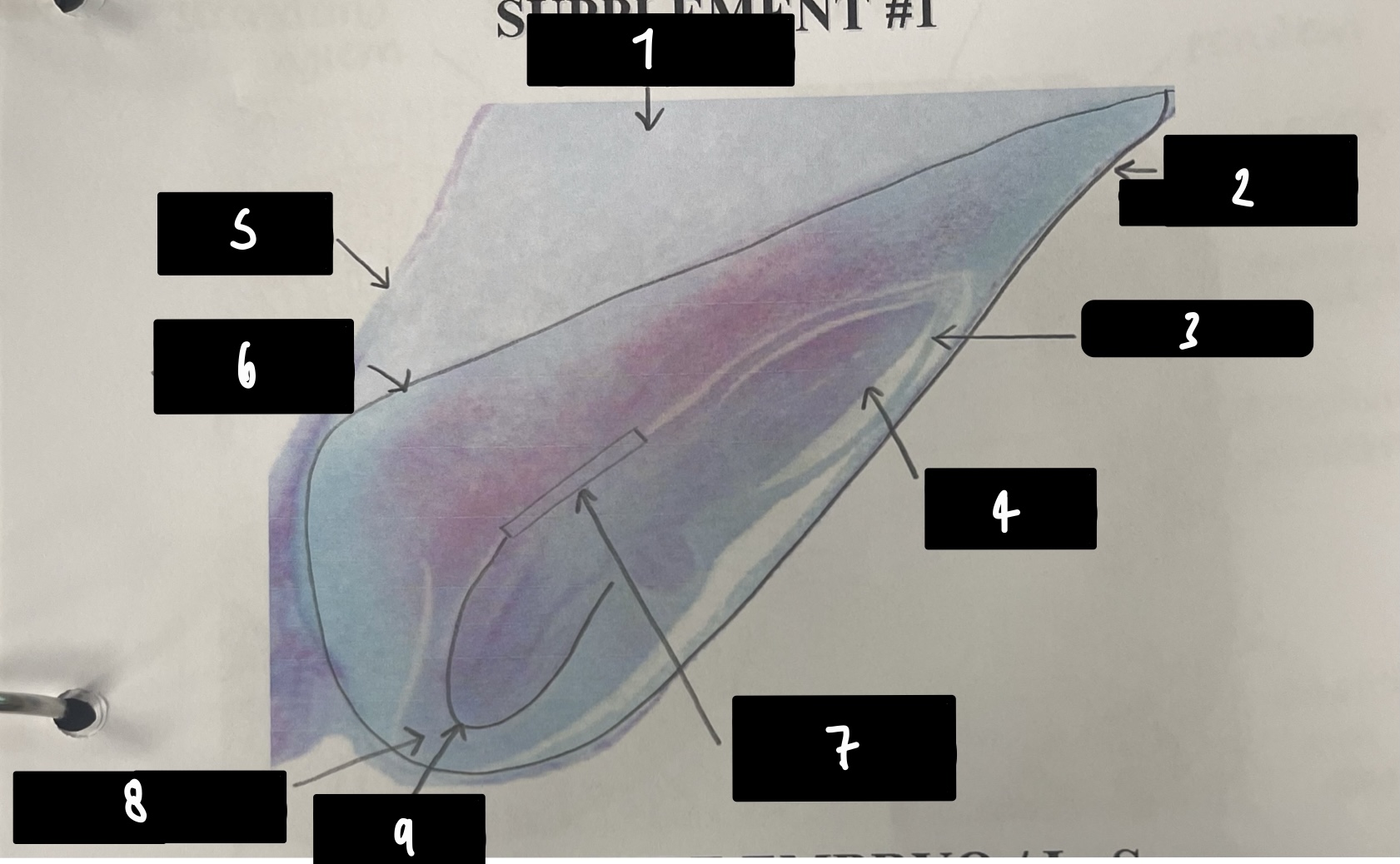
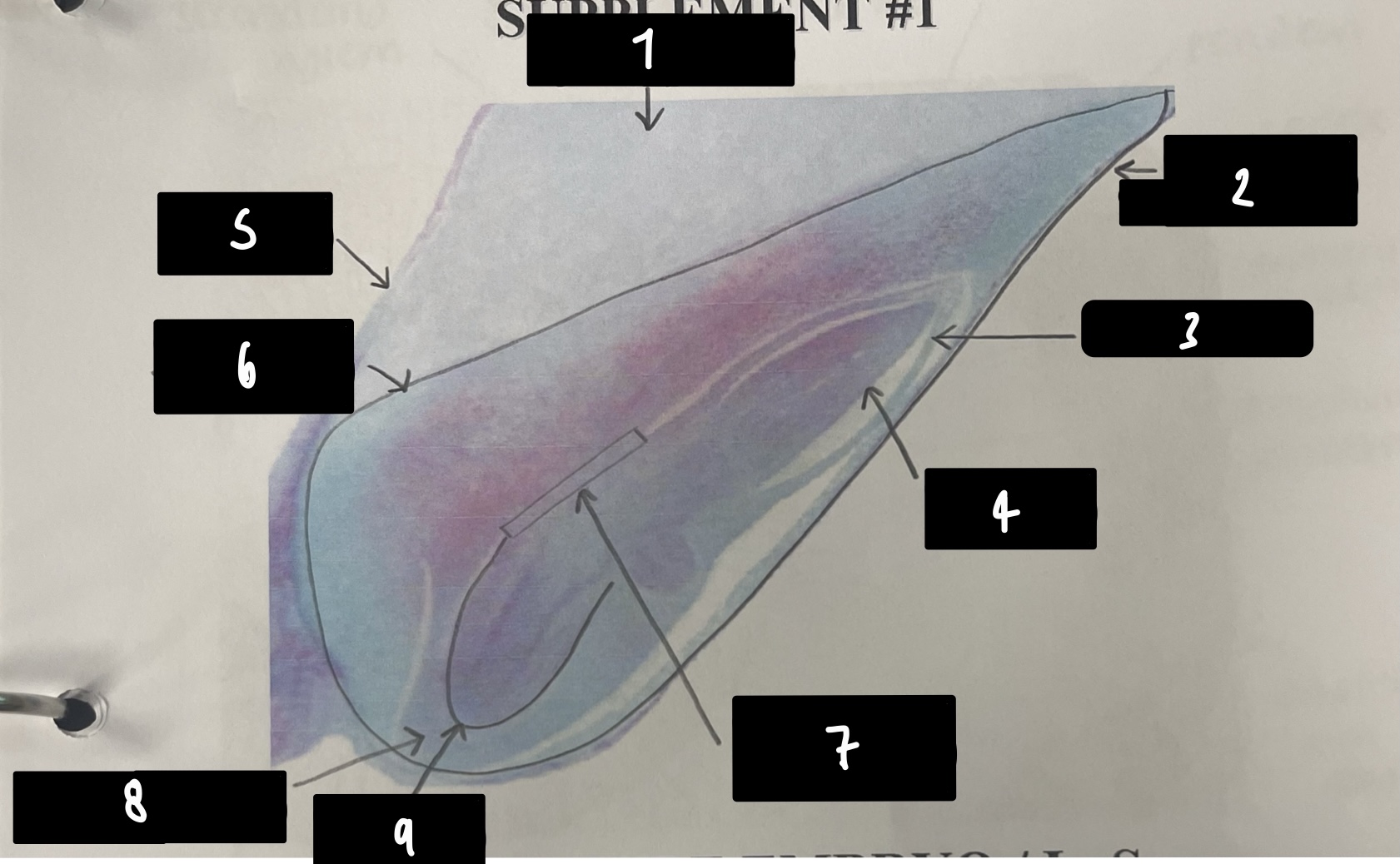
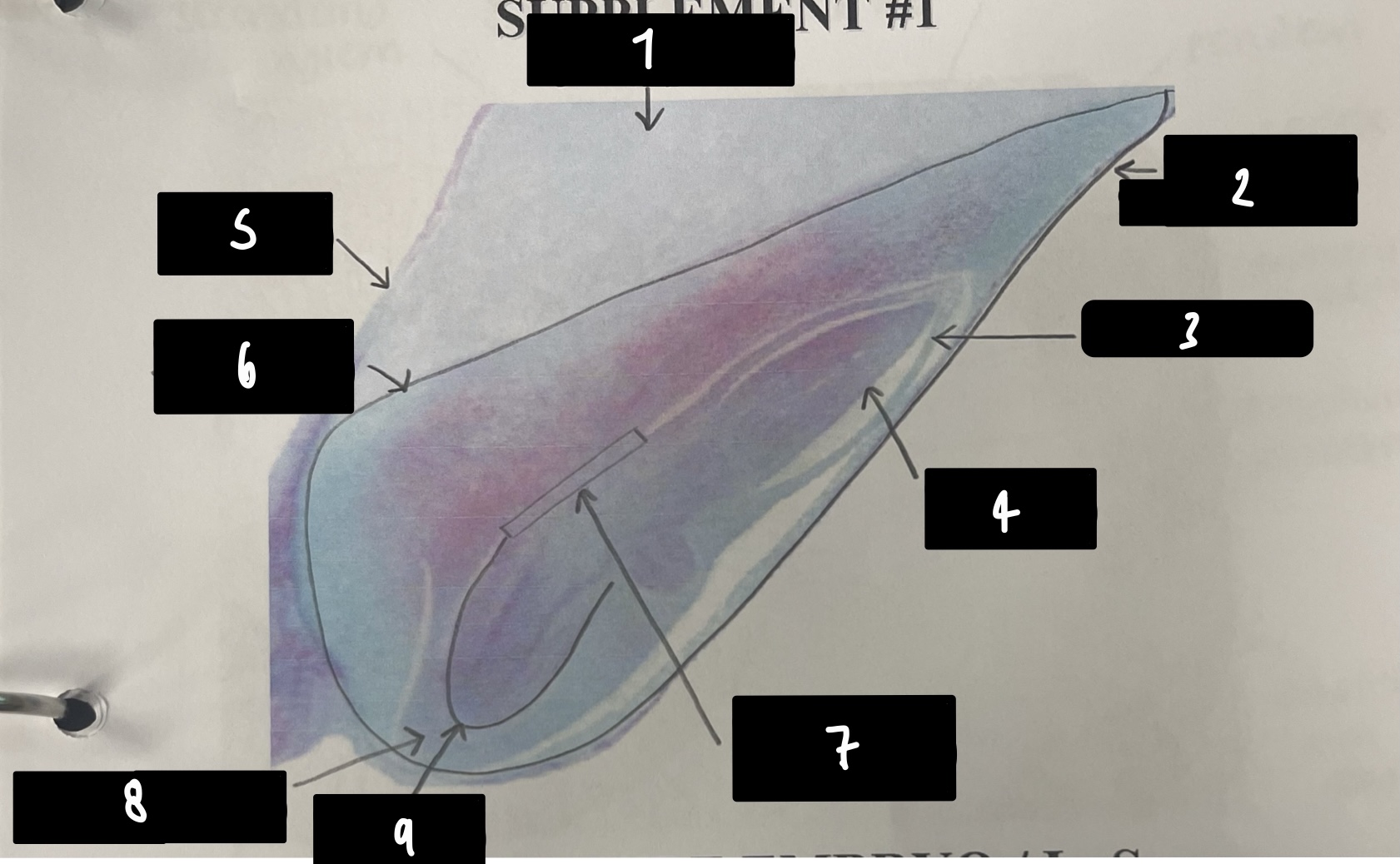
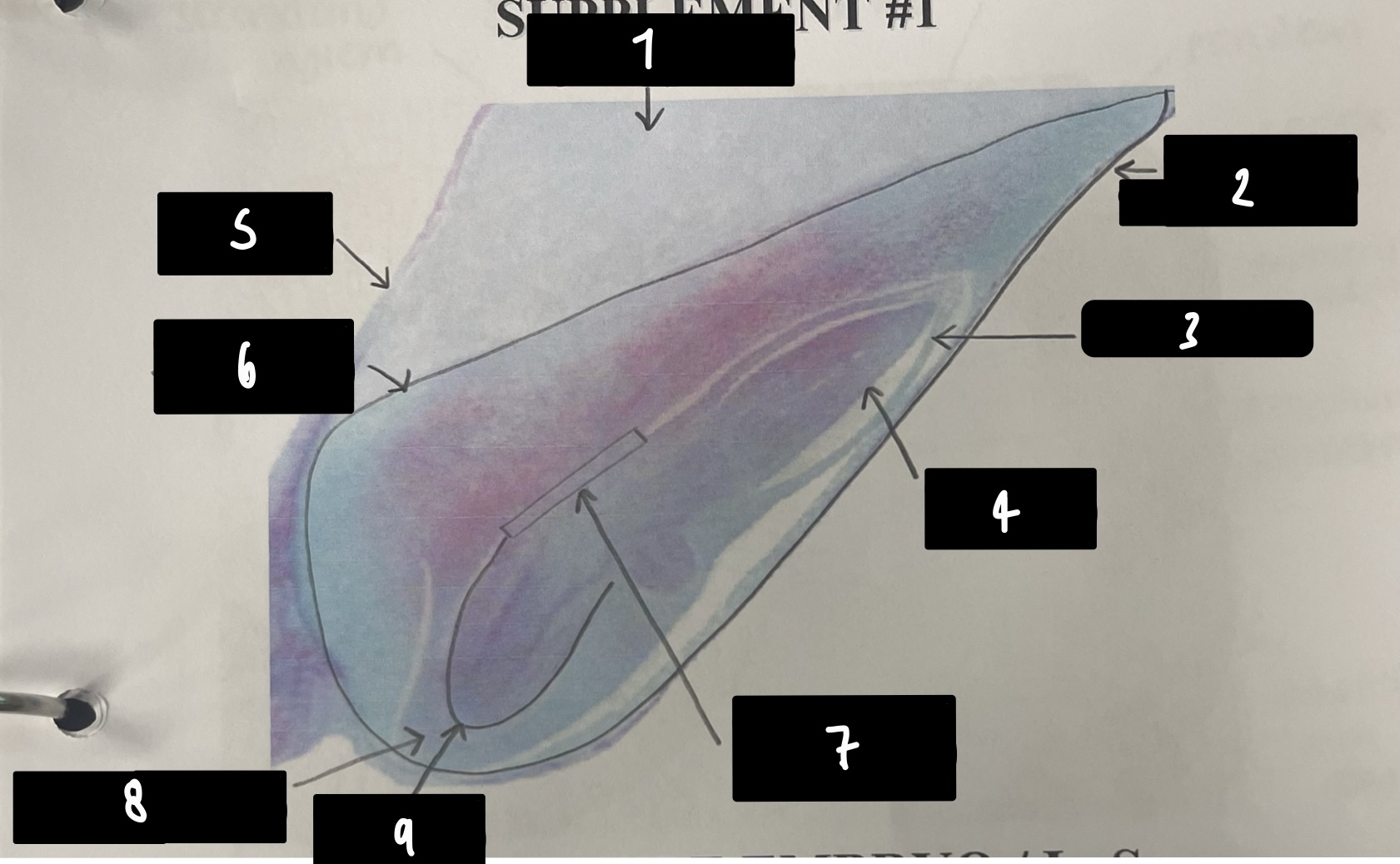
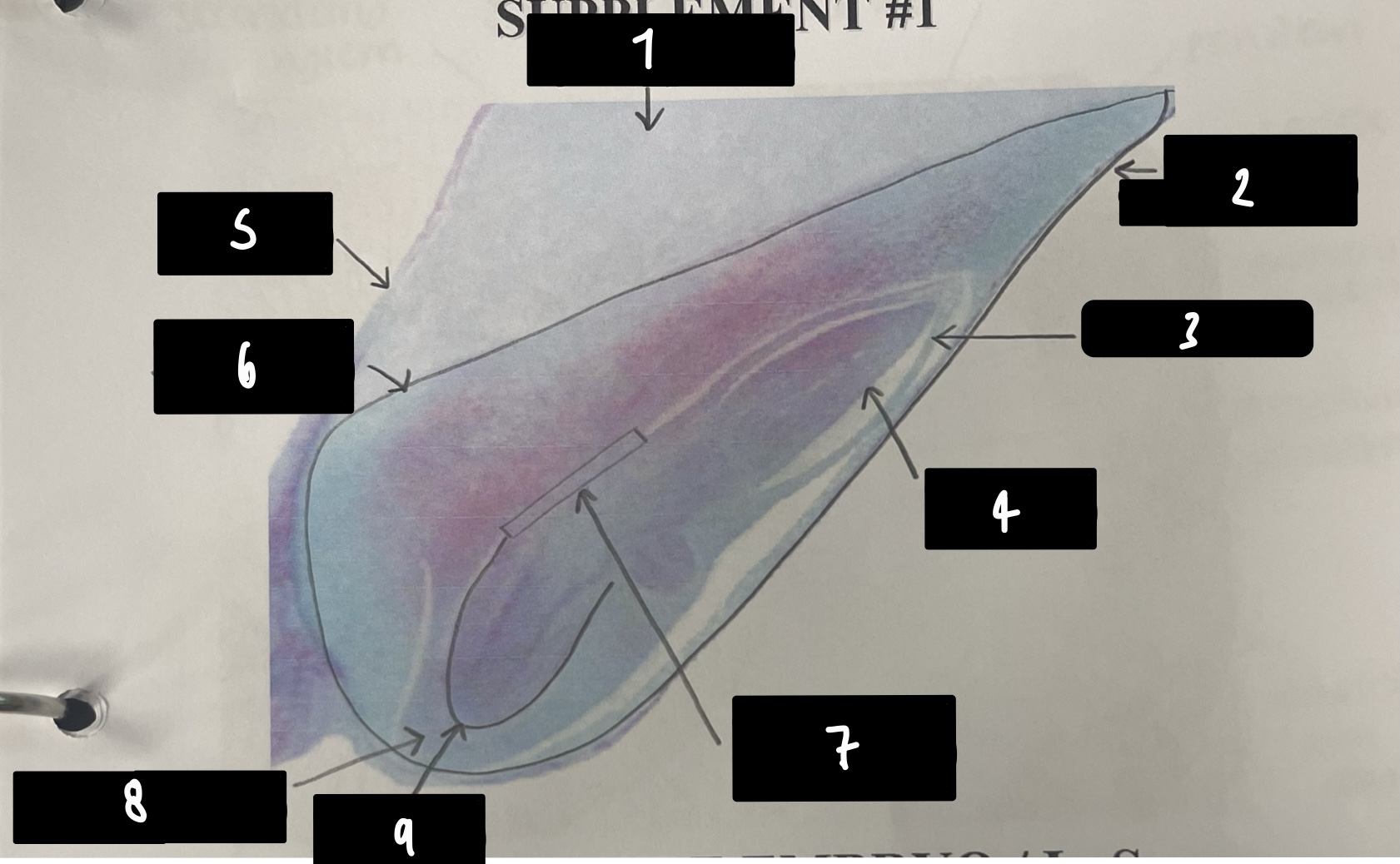
what specifically is the structure in this diagram
mature embryo
8
New cards
name the structure in label 1
root apical meristem (region of root growth)
9
New cards
name the structure in label 2
hypocotyl (stem axis below cotyledons)
10
New cards
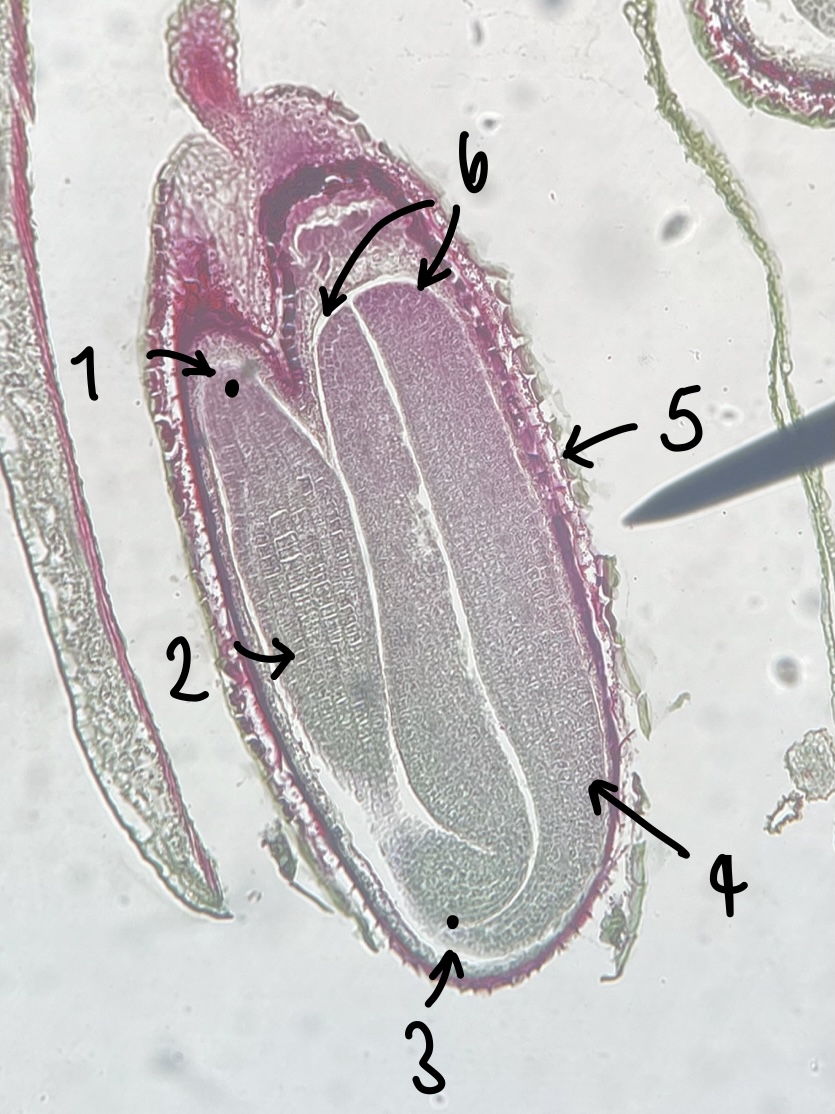
name the structure in label 3
stem apical meristem (region of stem growth)
11
New cards
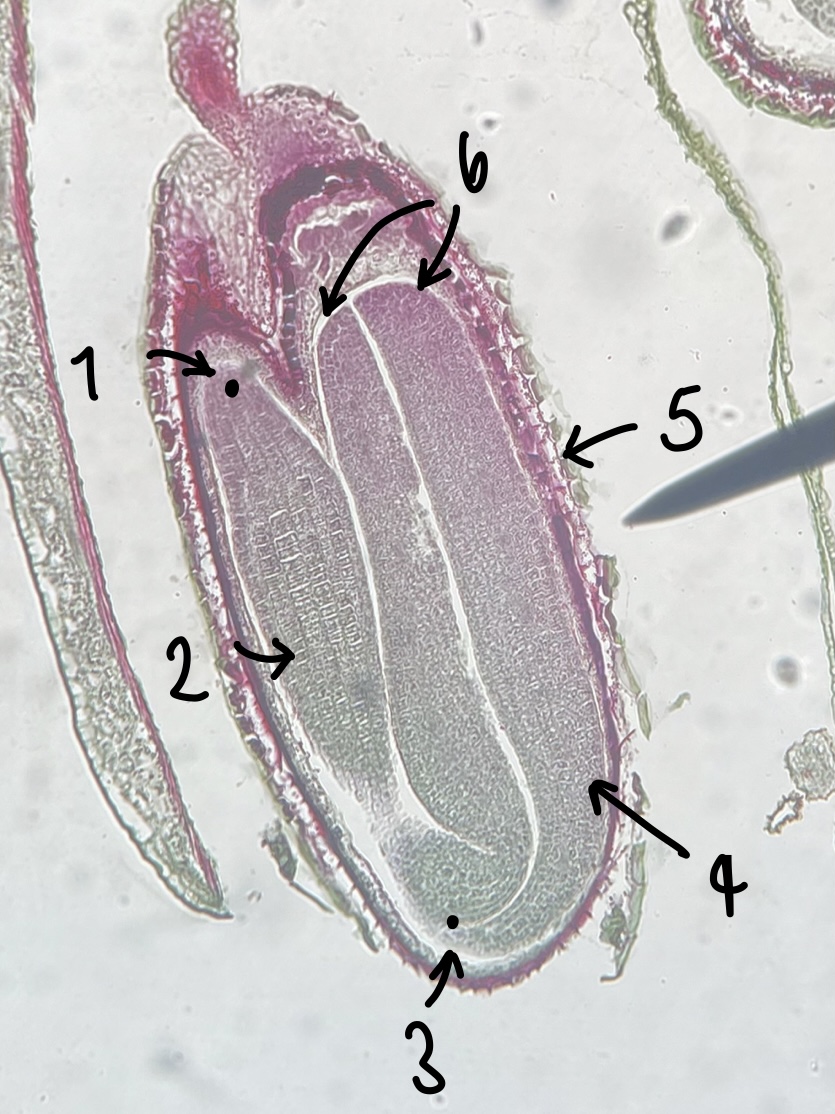
name the structure in label 4
mature embryo (both the hypocotyls and cotyledons)
12
New cards
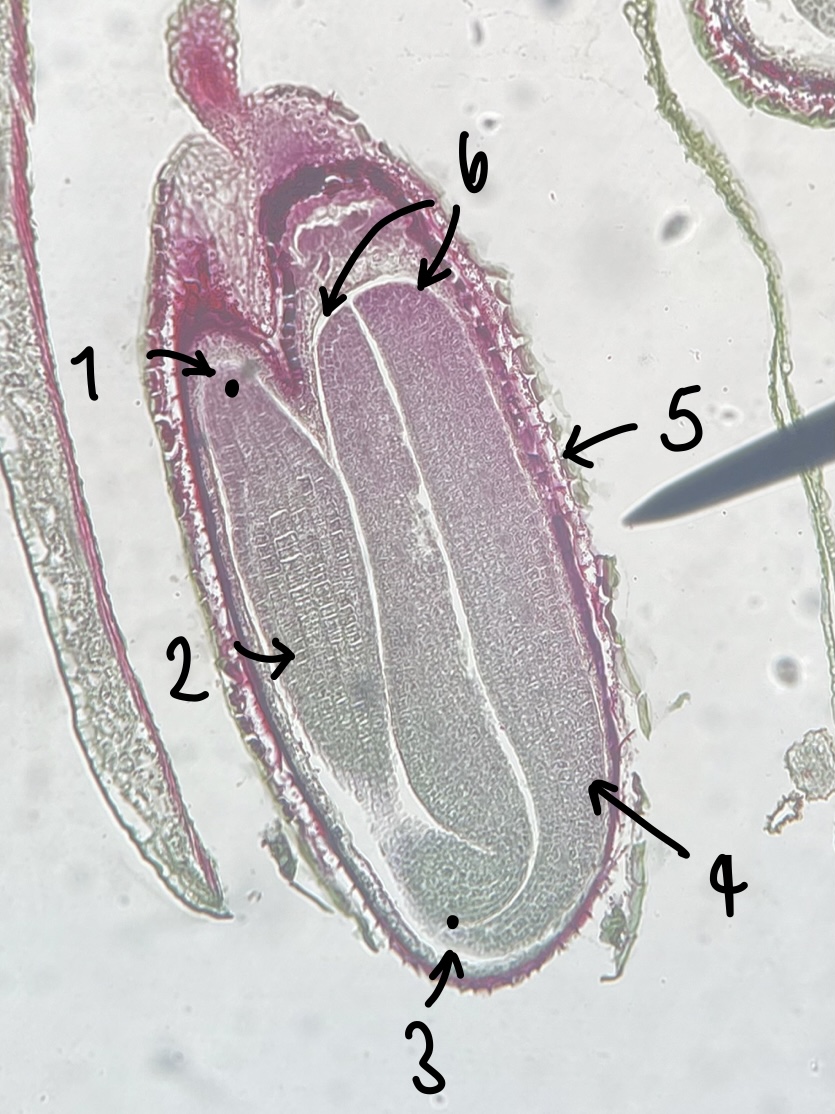
name the structure in label 5
testa (mature seed coat)
13
New cards
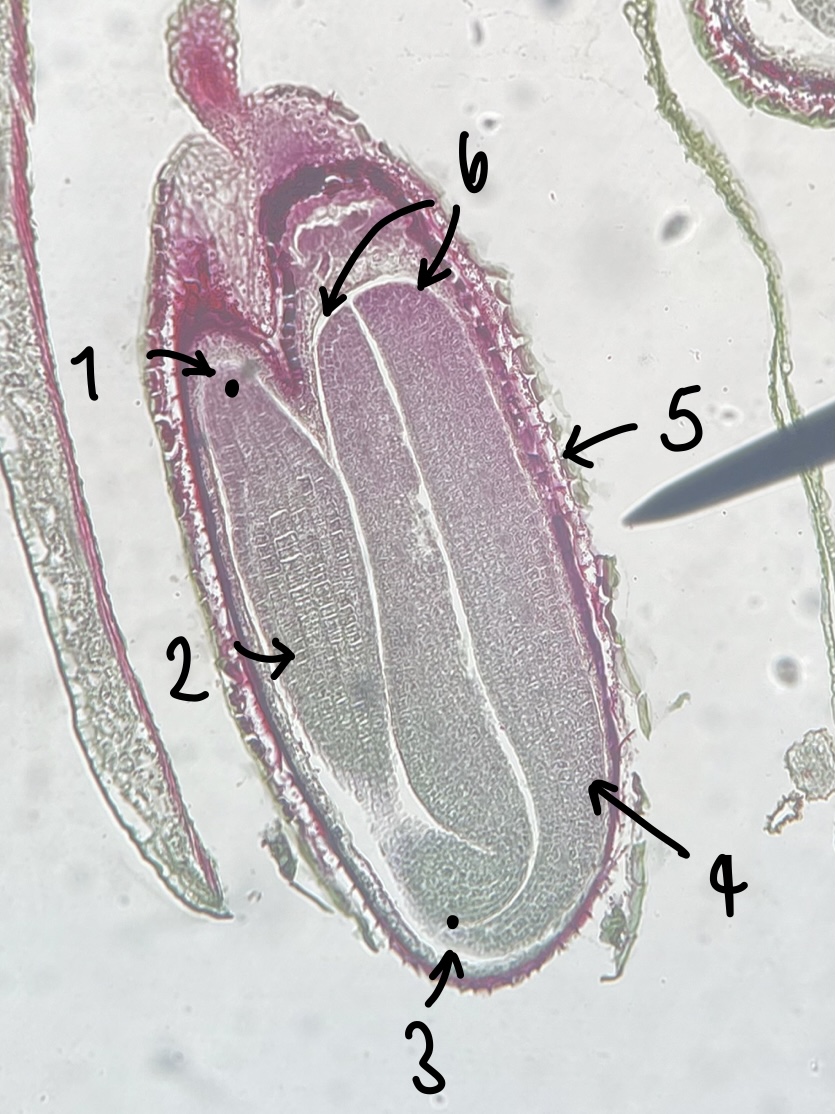
name the structure in label 6
cotyledons (embryo leaves)
14
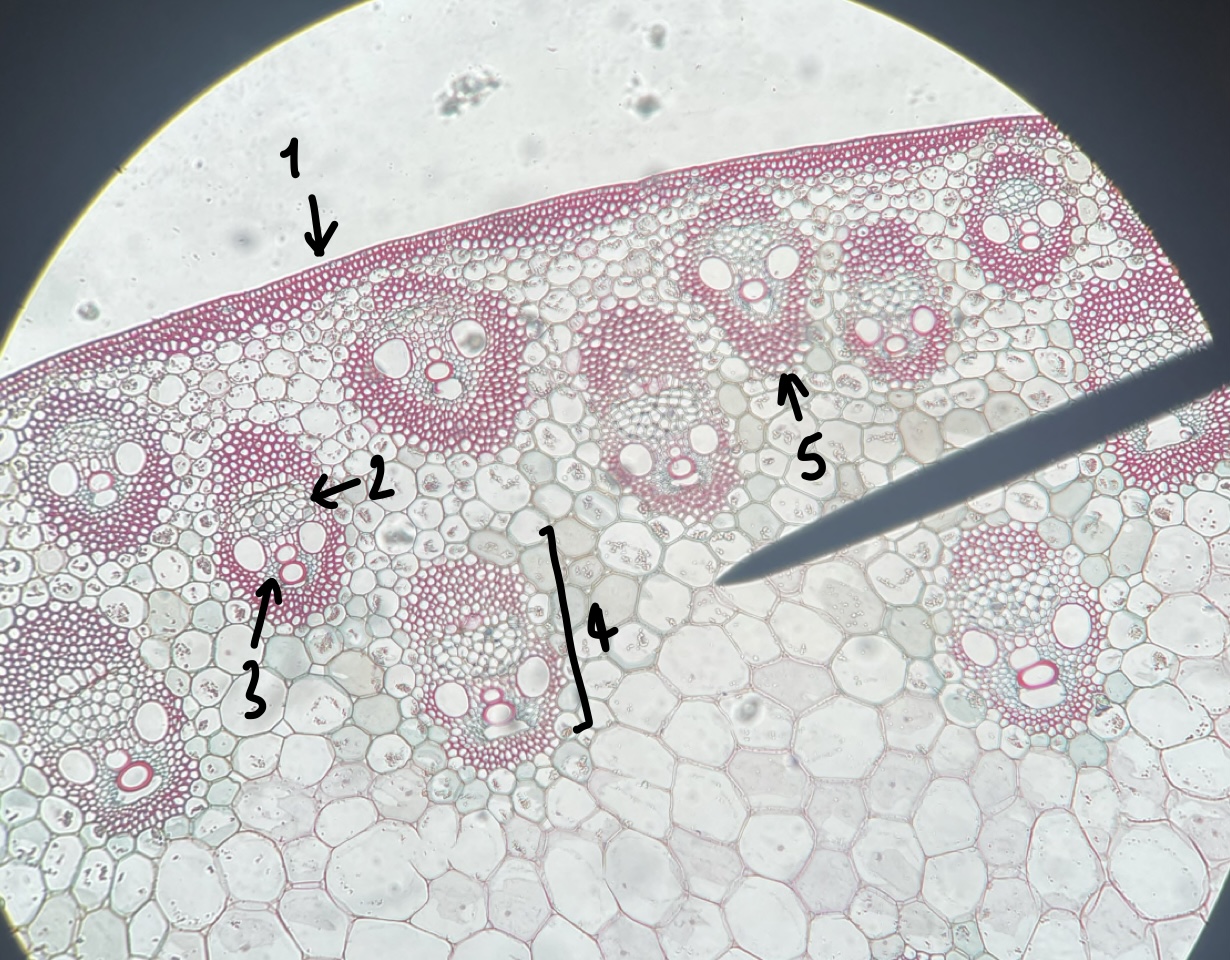
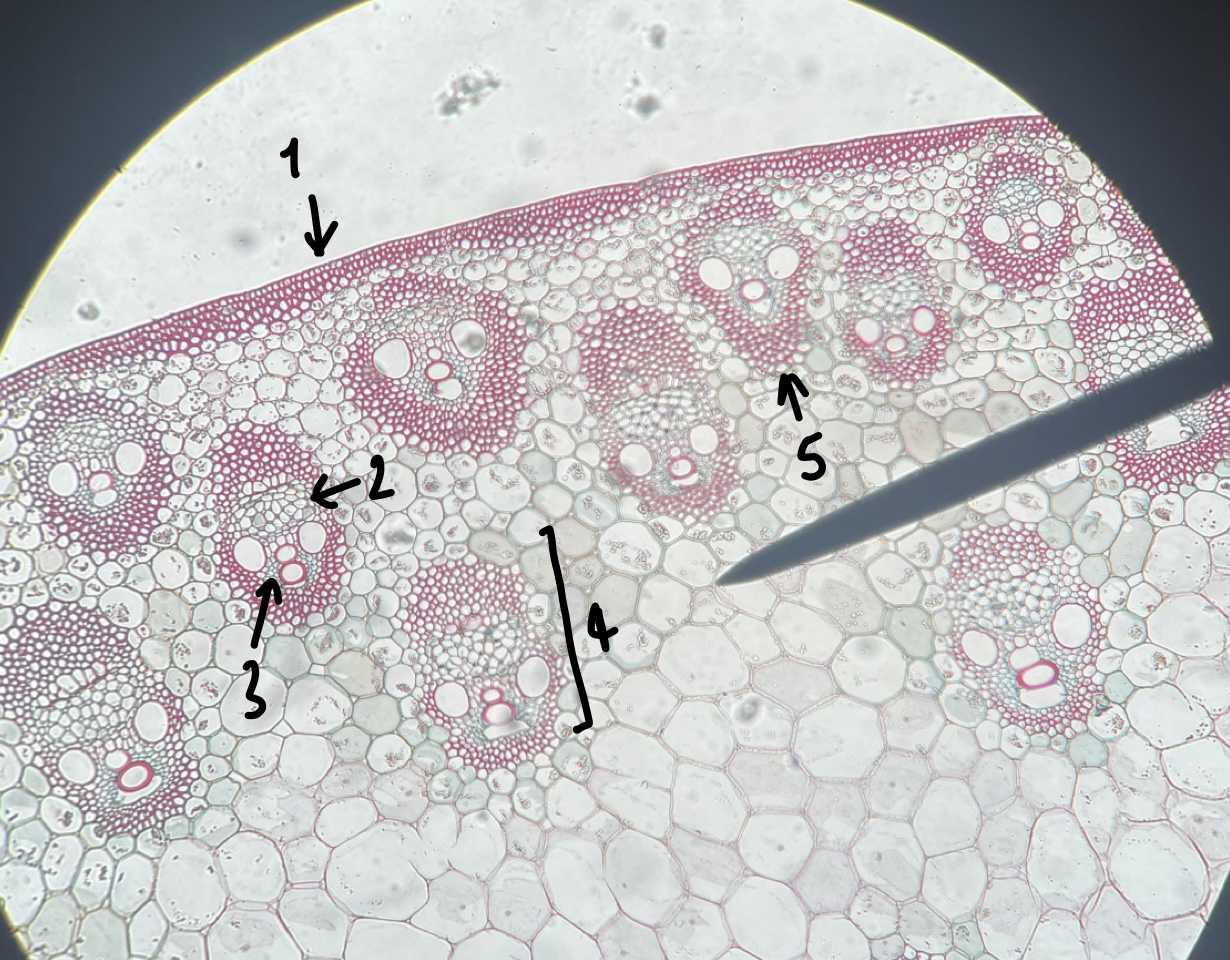
New cards
what genus of Liliopsida seed did we observe
__Zea__
15
New cards
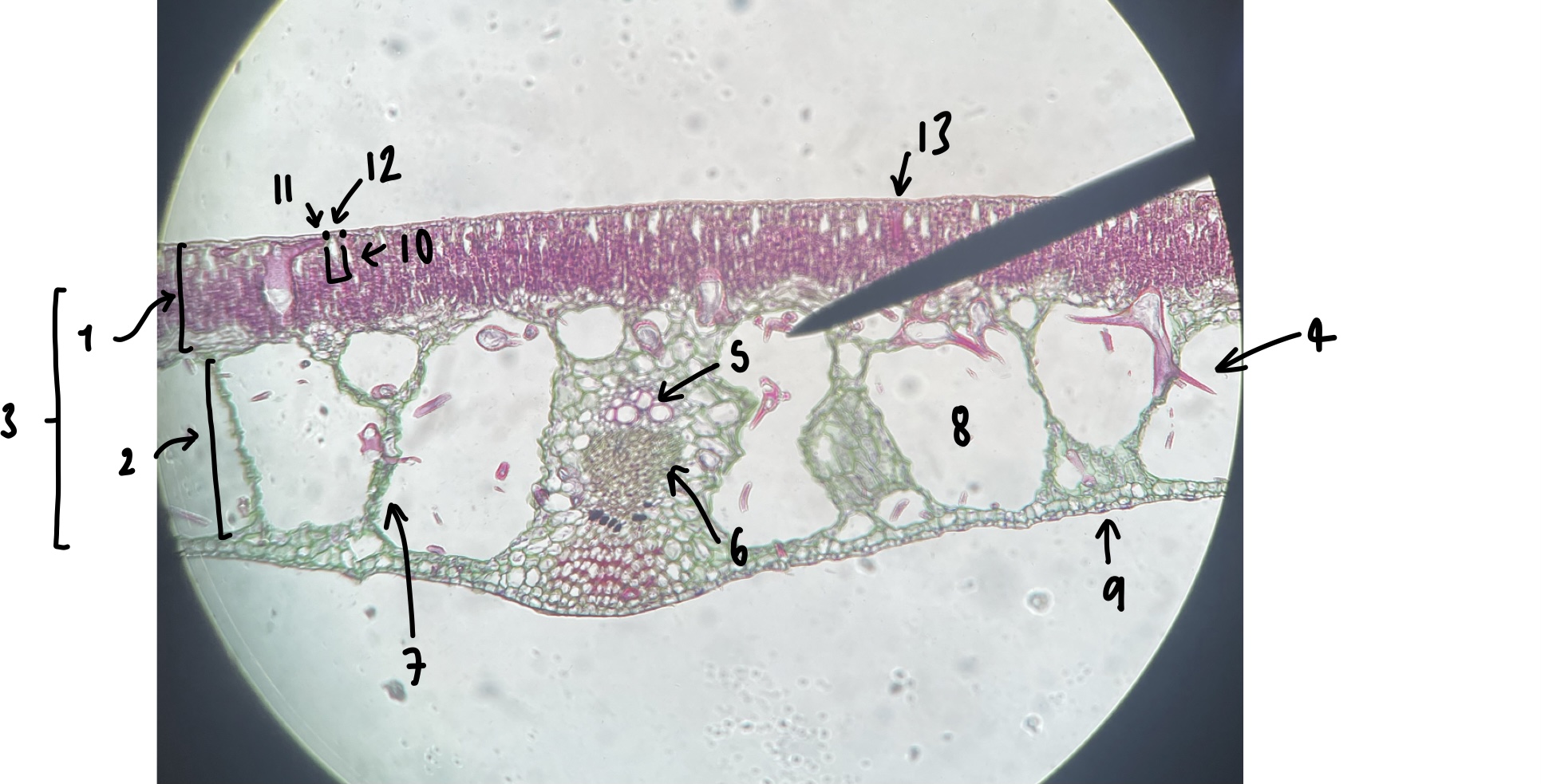
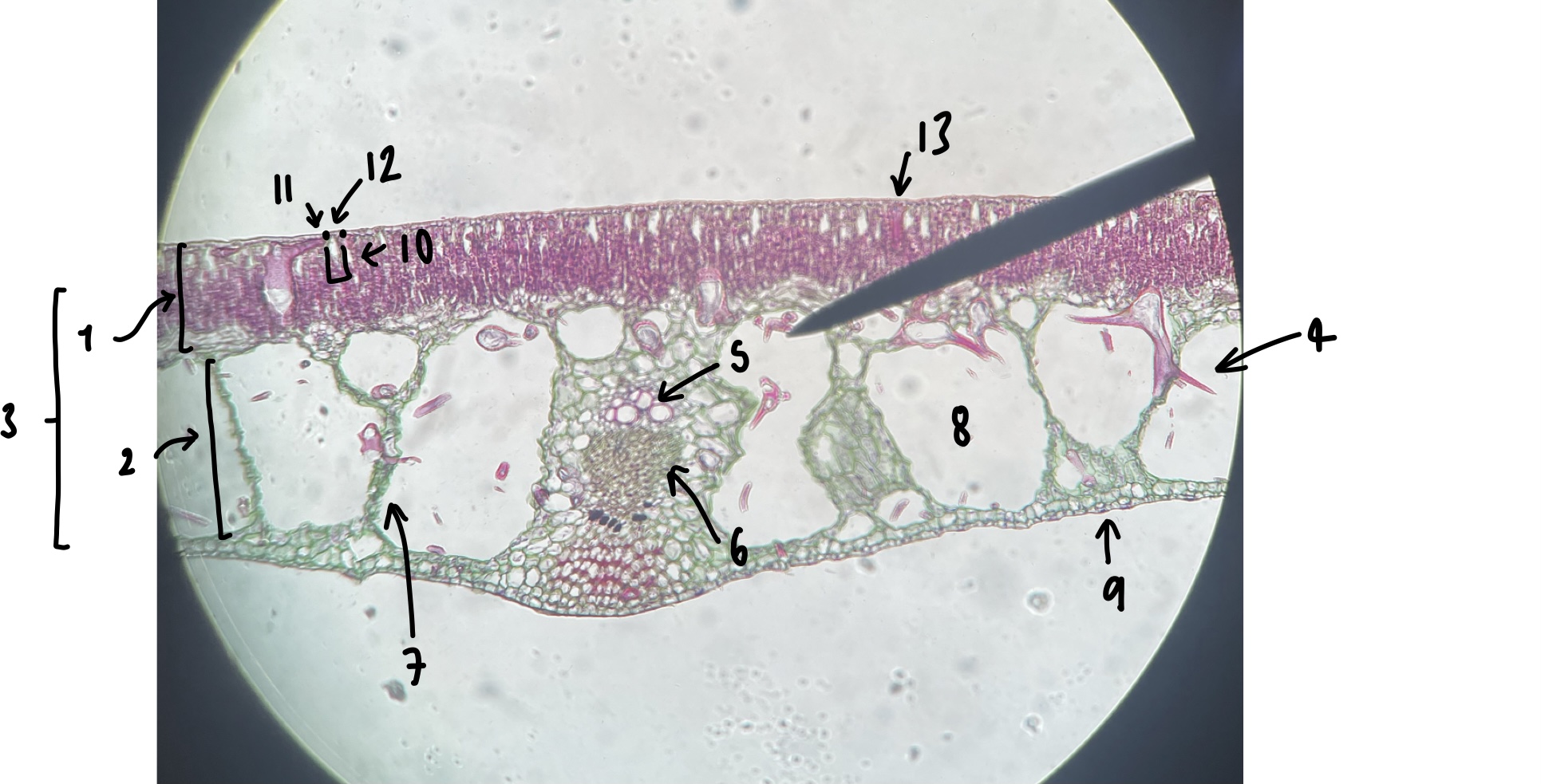
the majority of the __Zea__ seed consists of …
endosperm
16
New cards
what specifically is the structure in this diagram
mature embryo
17
New cards
name the structure in label 1
endosperm (embyro nutrient)
18
New cards
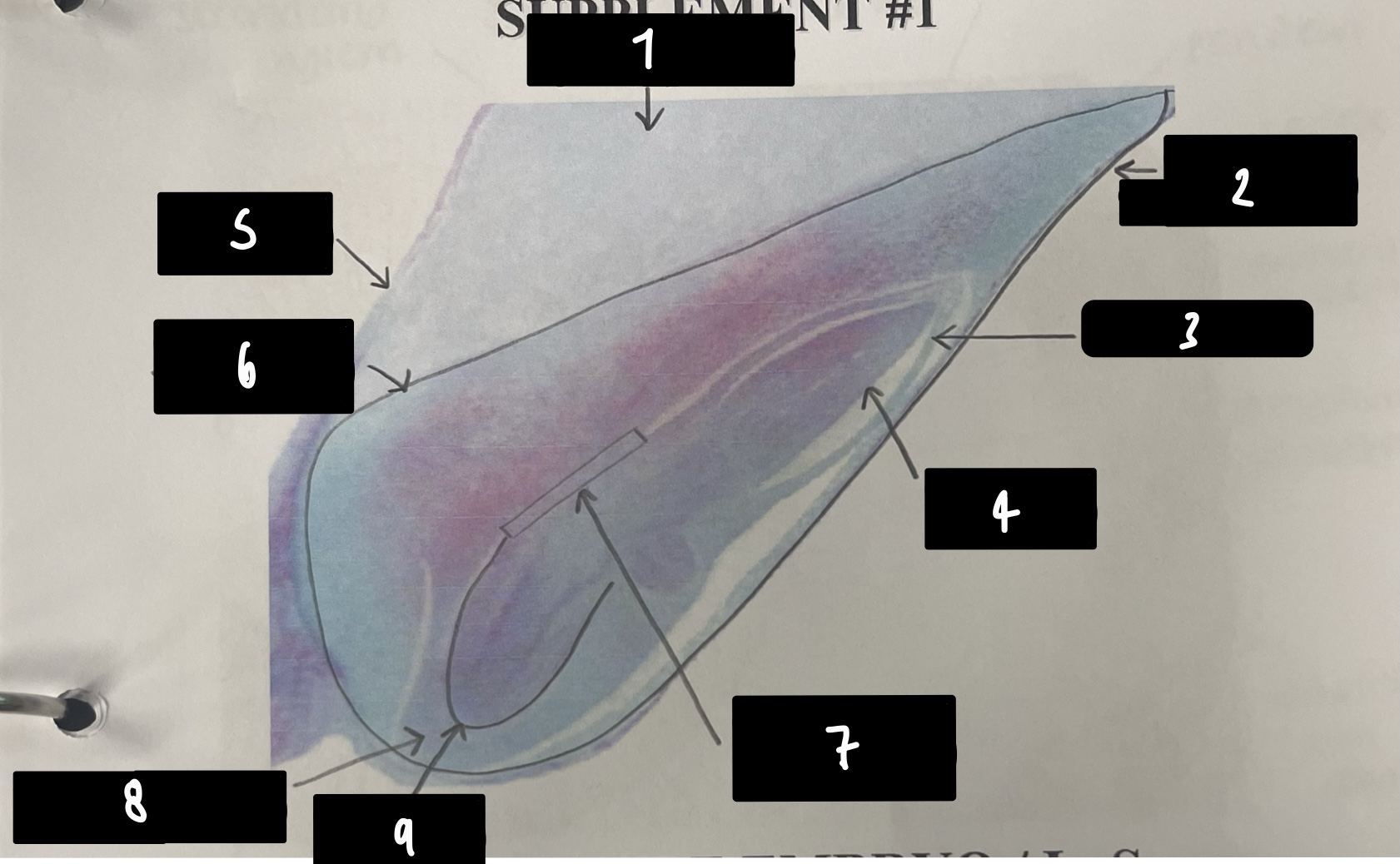
name the structure in label 2 (the whole structure)
mature embryo
19
New cards
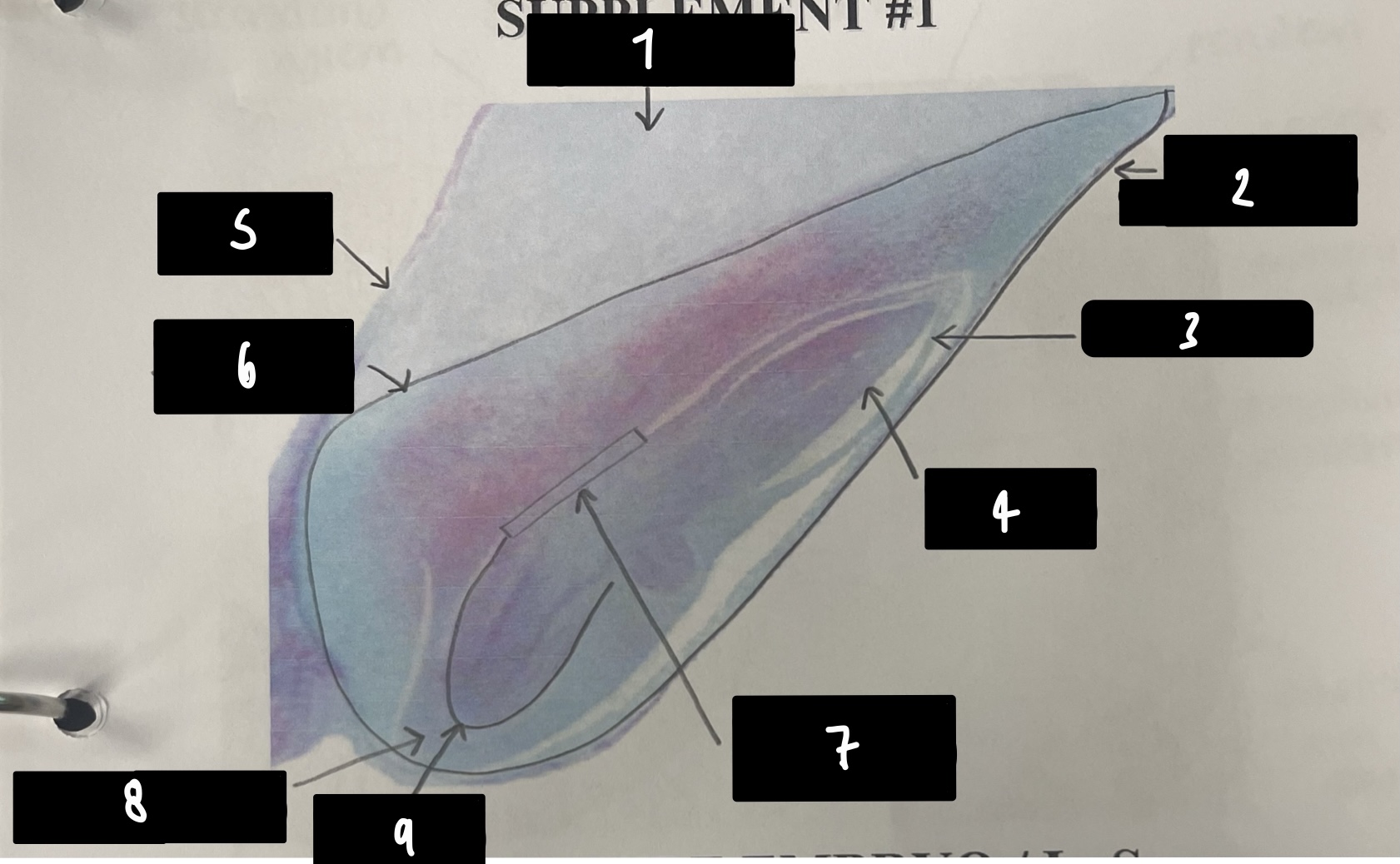
name the structure in label 3
coleoptile (sheath protects plumule)
20
New cards
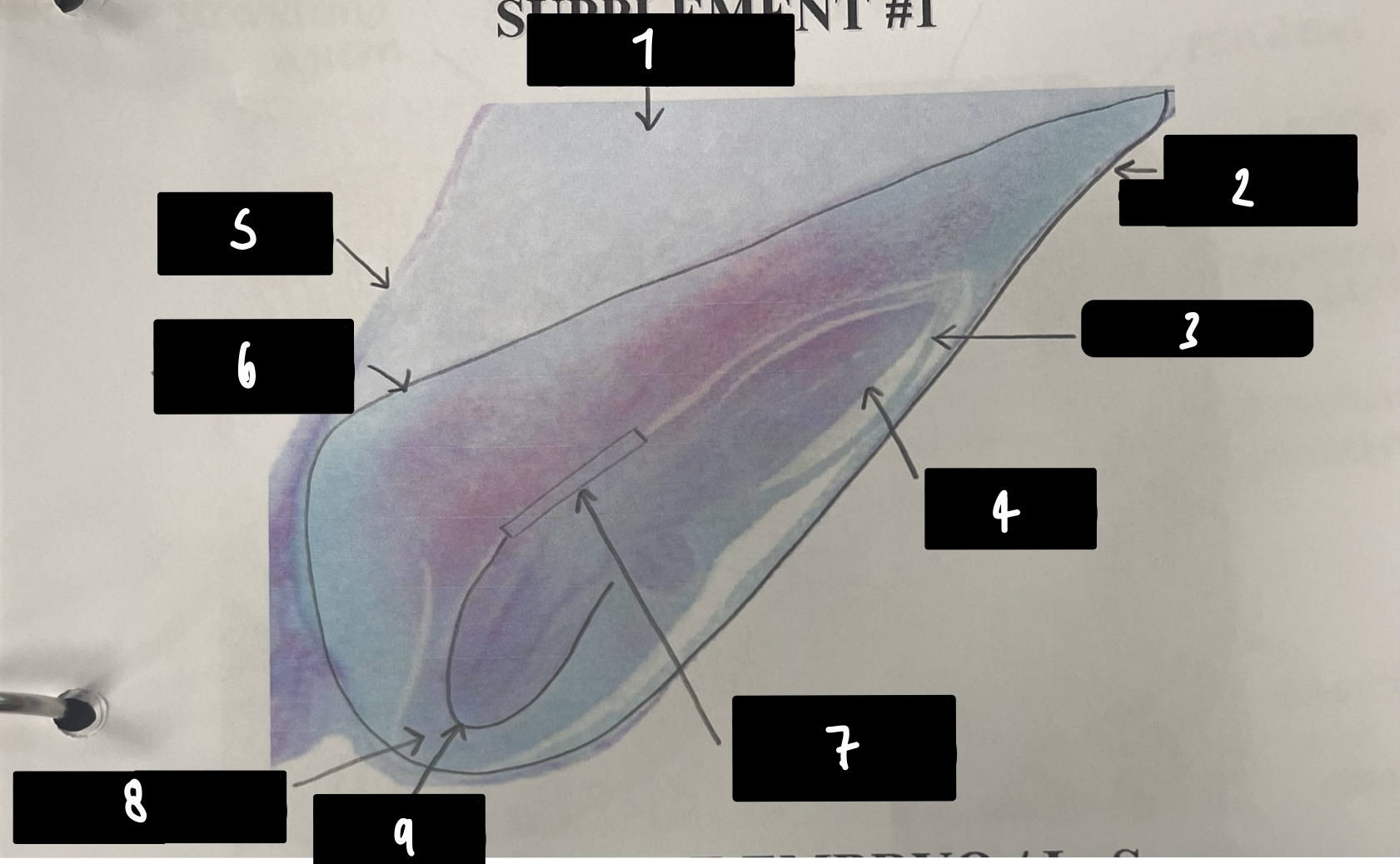
name the structure in label 4
plumule (embryonic shoot bearing steam apical meristem)
21
New cards
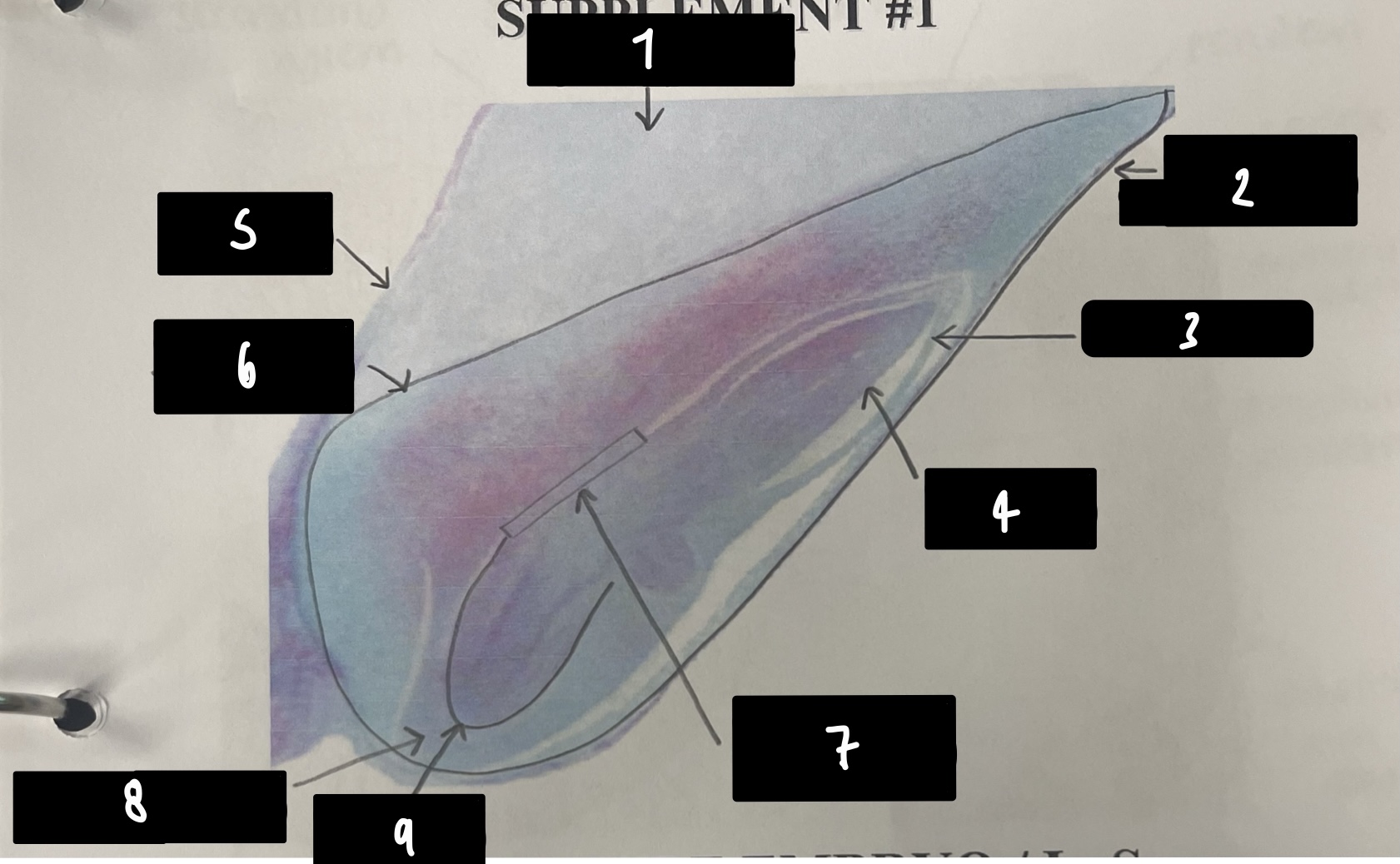
name the structure in label 5
pericarp (fruit wall)
22
New cards
name the structure in label 6
scutellum (cotyledon absorbs endosperm)
23
New cards
name the structure in label 7
mesocotyl (scutellum attachment point)
24
New cards
name the structure in label 8
coleorhiza (sheath protects radicle)
25
New cards
name the structure in label 9
radicle (embryonic root)
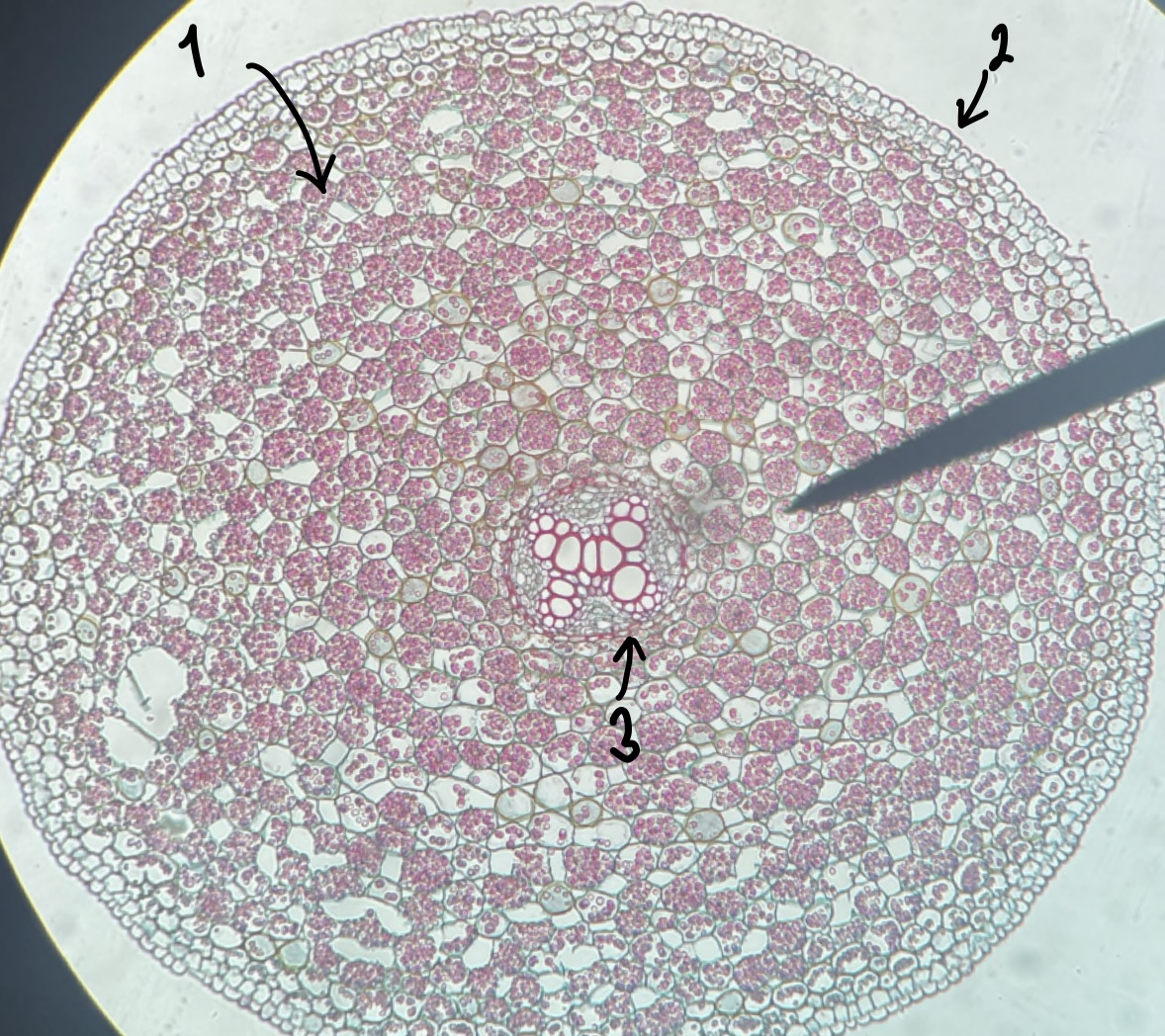
26
New cards
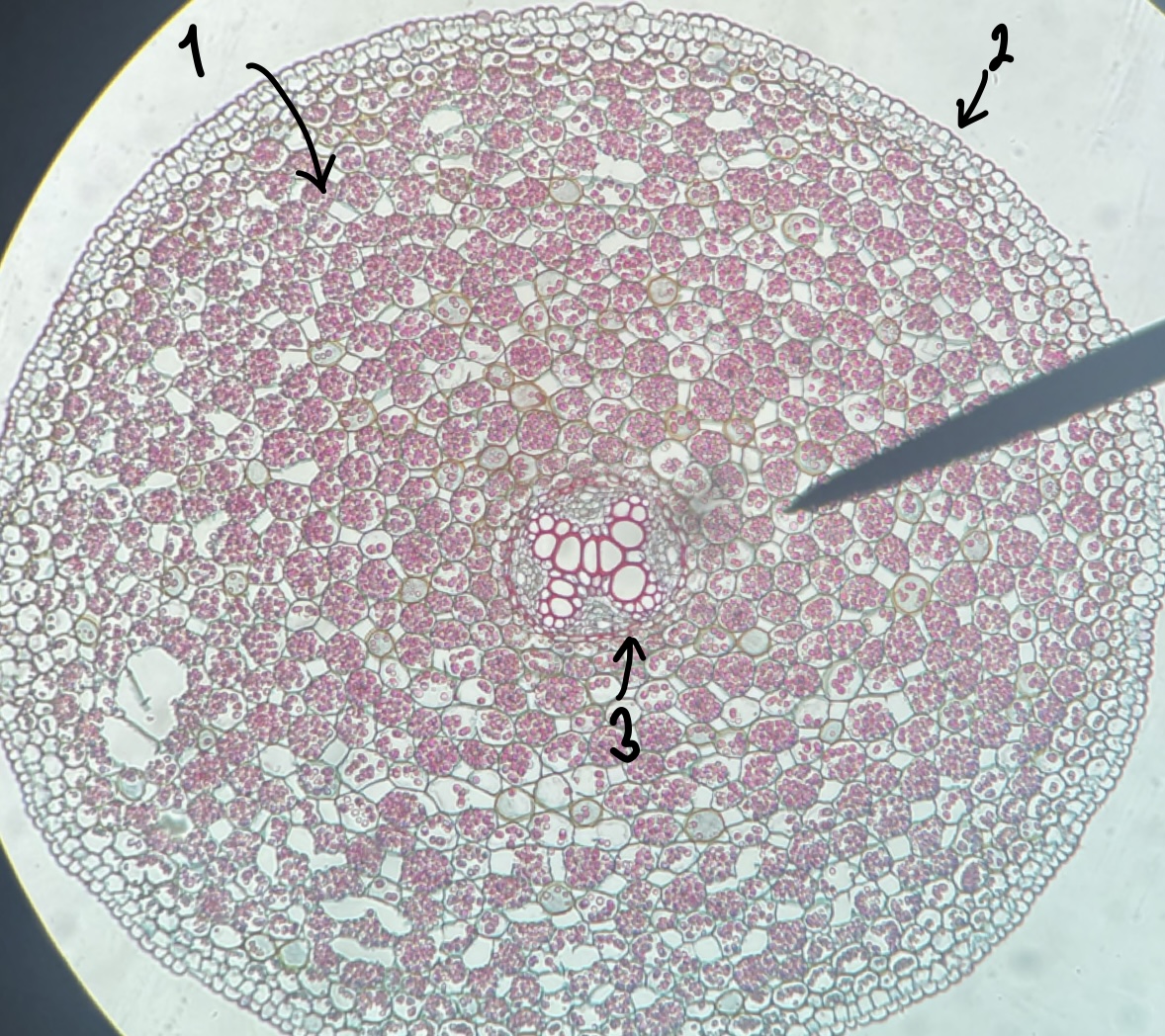
what genus of Magnoliopsida root did we observe
__Ranunculus__
27
New cards
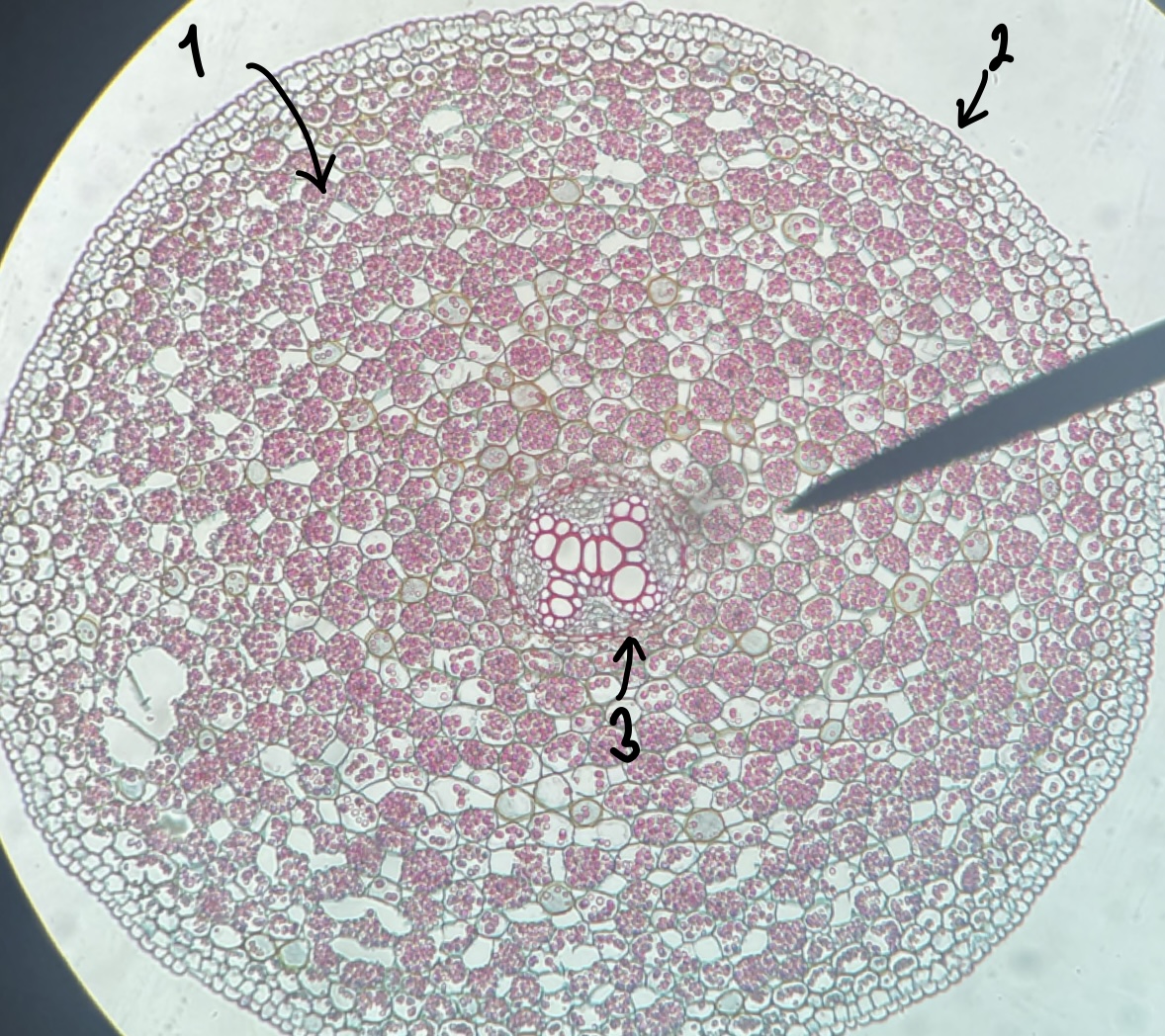
what type of root does a __Ranunculus__ plant have
dicot
28
New cards
what is the general and specific stele type of the __Ranunculus__ root
protostele
actinostele
actinostele
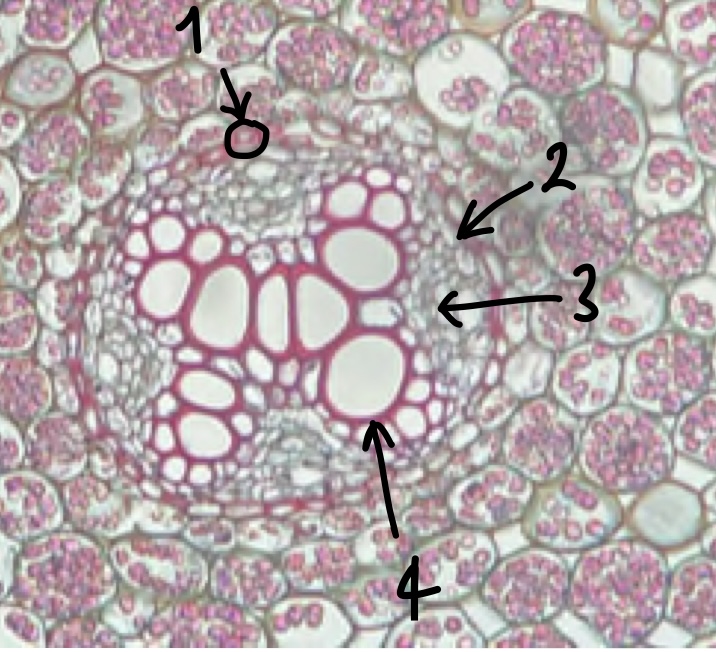
29
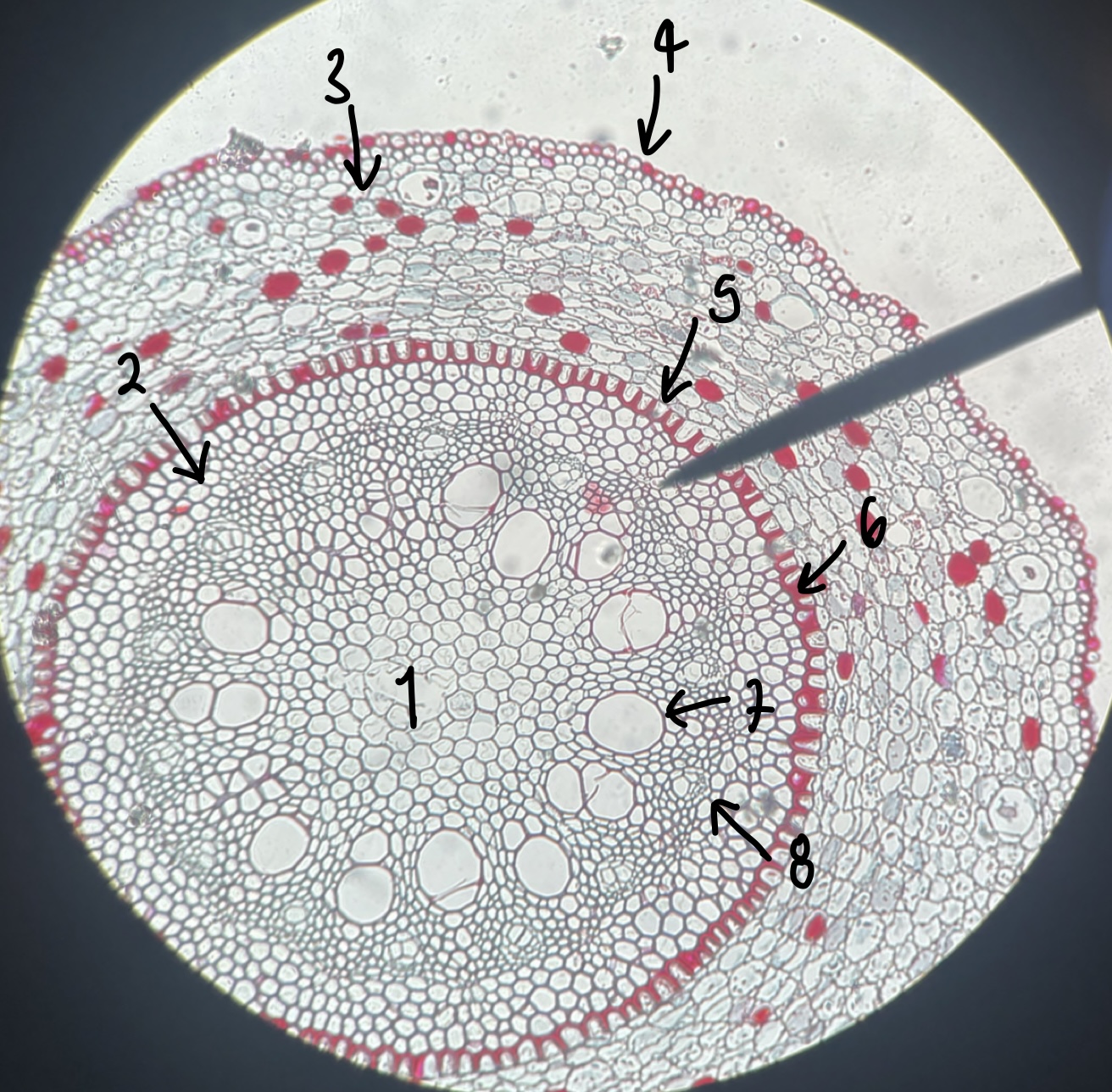
New cards
name the structure in label 1
cortex
30
New cards
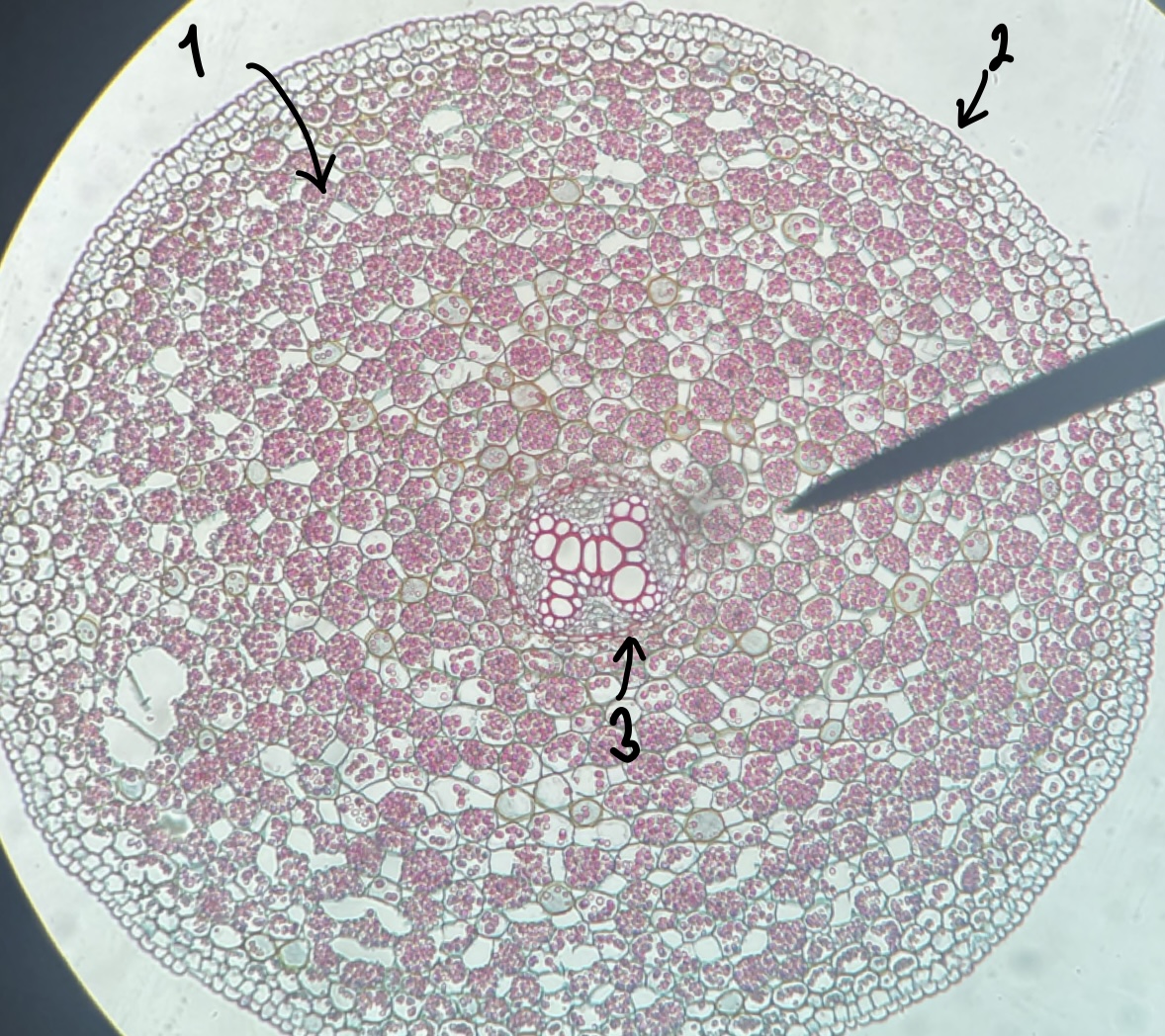
name the structure in label 2
epidermis
31
New cards
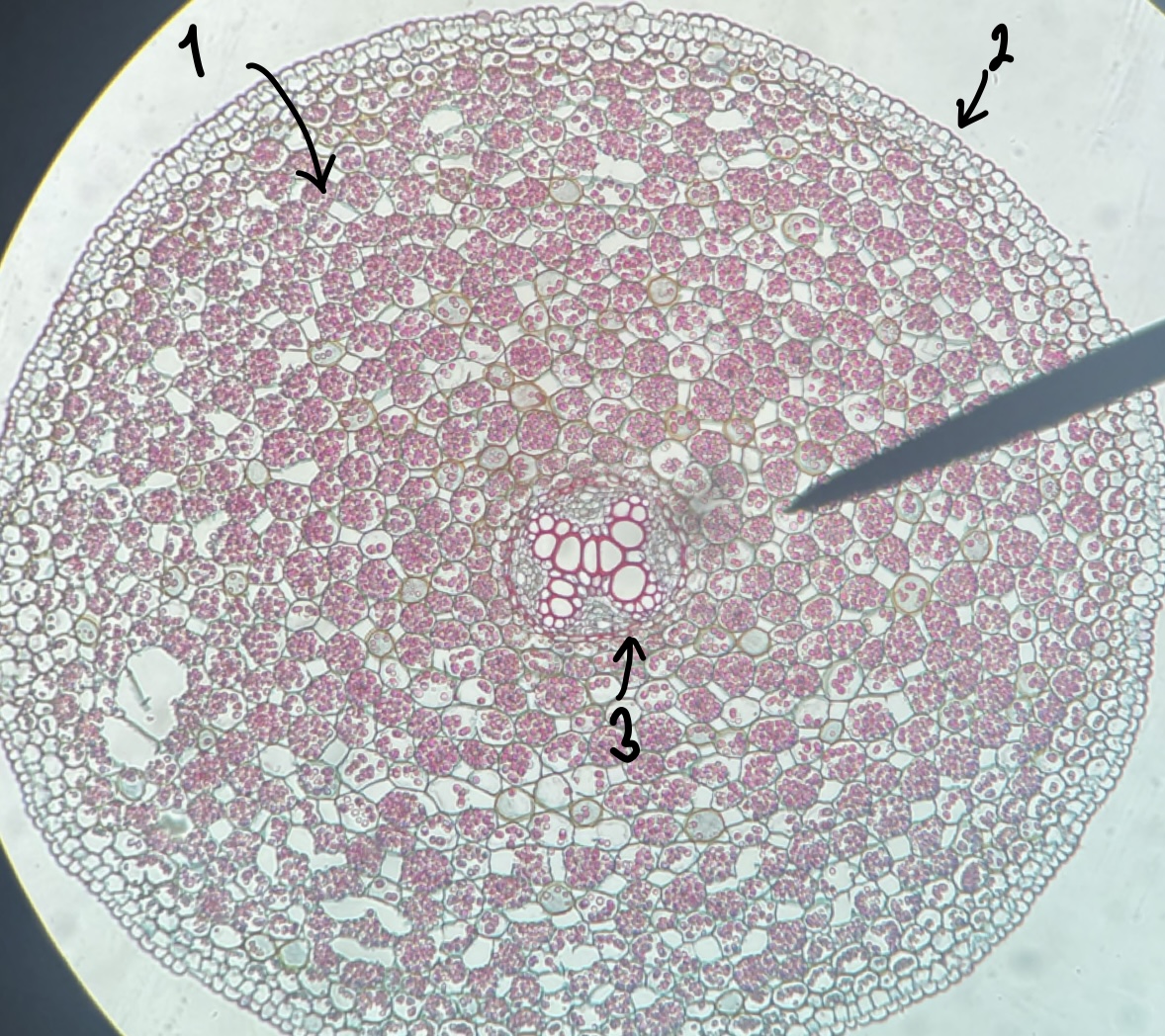
name the structure in label 3
endodermis
32
New cards
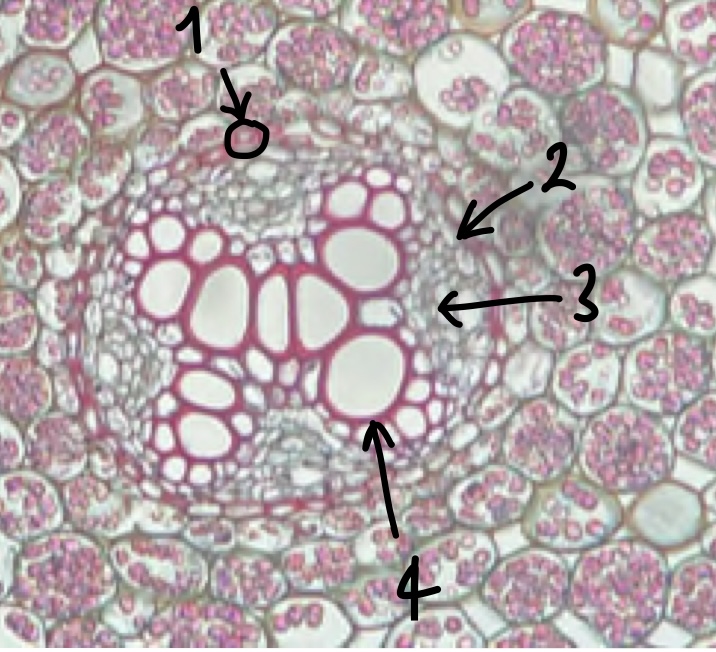
(zoomed in area inside the endodermis) name the structure in label 1
casparian strip (red strip between endodermis cells)
33
New cards
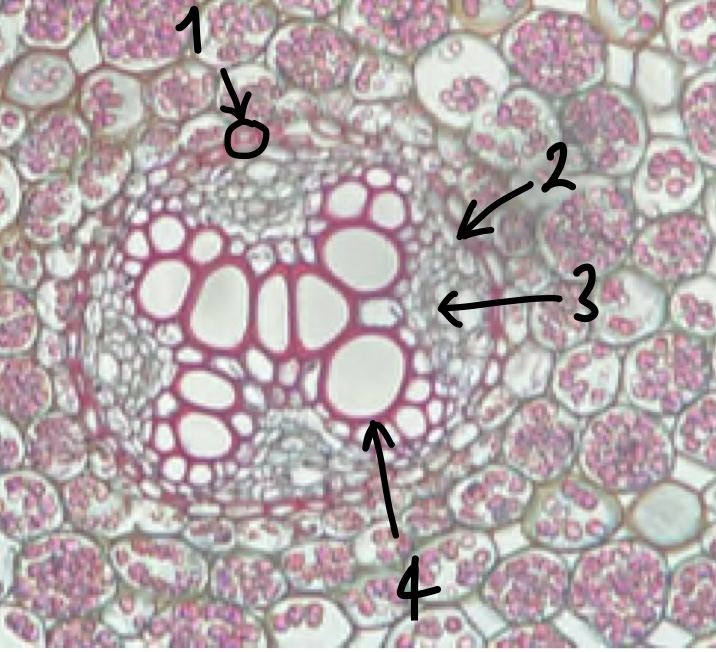
(zoomed in area inside the endodermis) name the structure in label 2
pericycle (cell layer beneath endodermis)
34
New cards
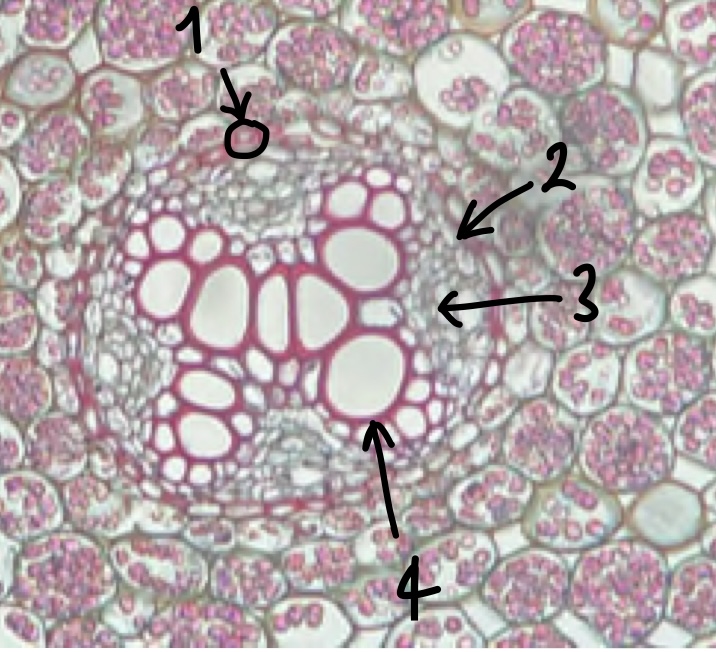
(zoomed in area inside the endodermis) name the structure in label 3
phloem
35
New cards
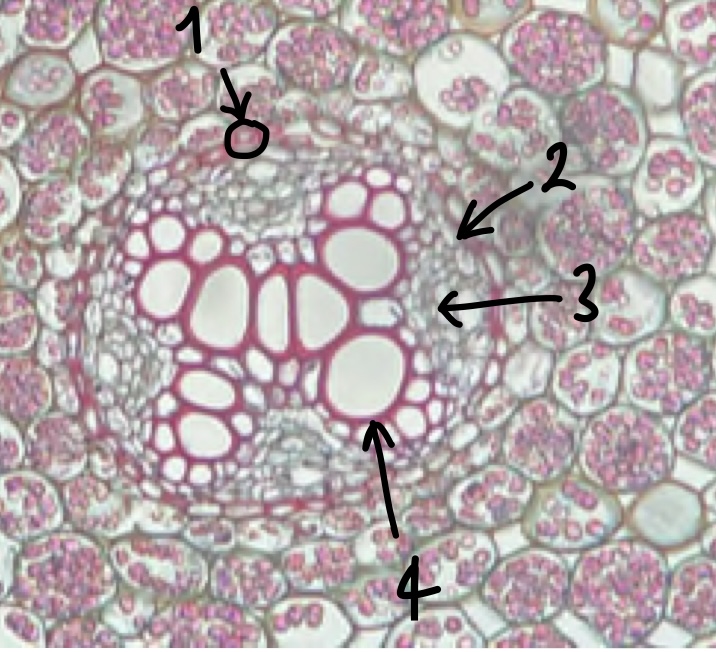
(zoomed in area inside the endodermis) name the structure in label 4
xylem
36
New cards
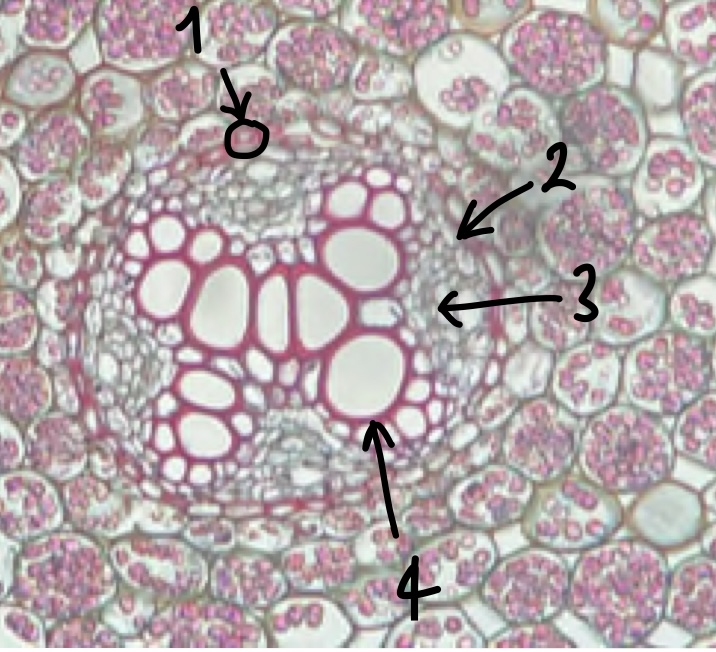
what is the cell layer called between phloem and xylem
vascular cambium
37
New cards
what genus of Liliopsida root did we observe
__Smilax__
38
New cards
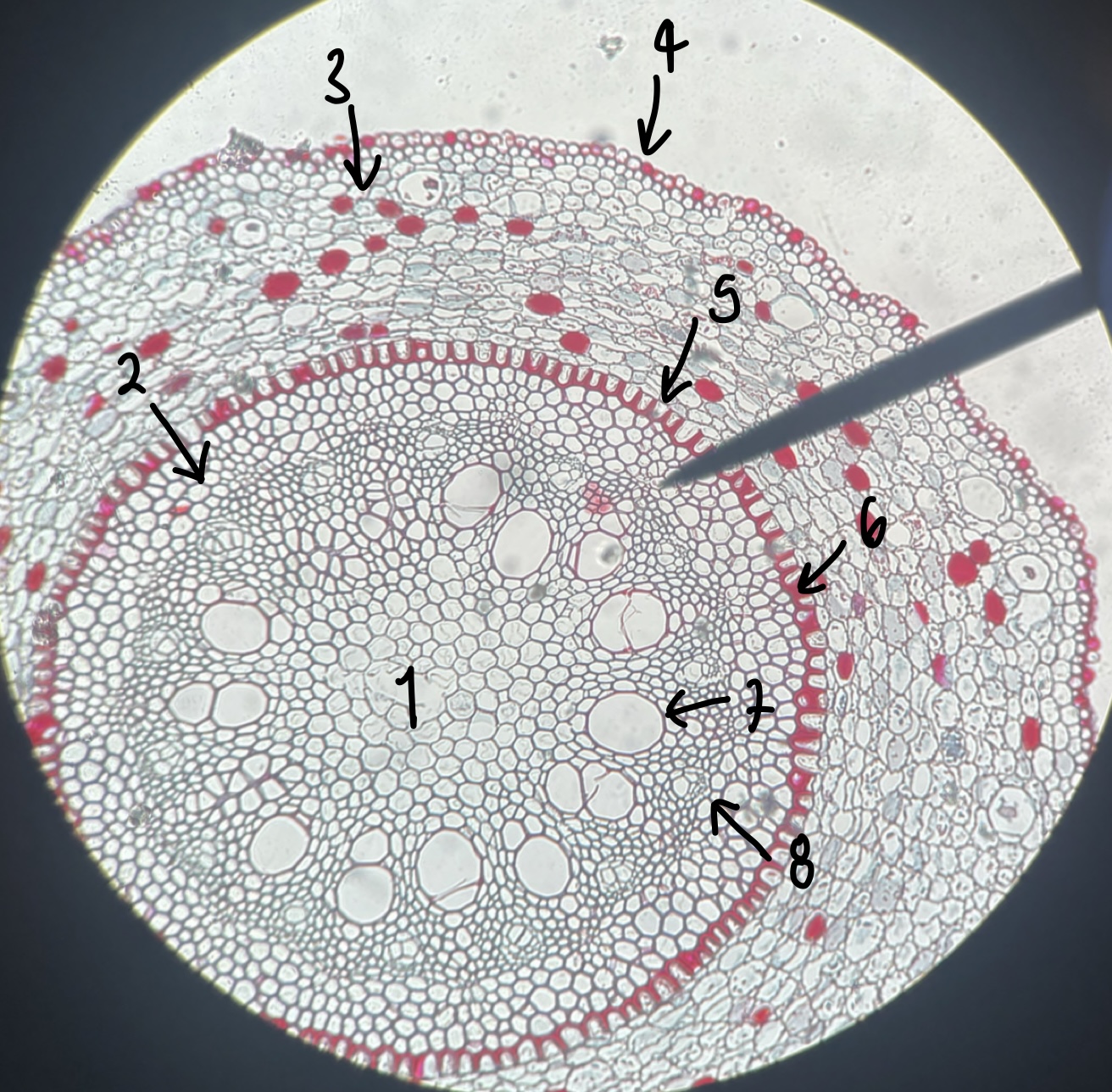
what type of root does a __Smilax__ root have
monocot
39
New cards
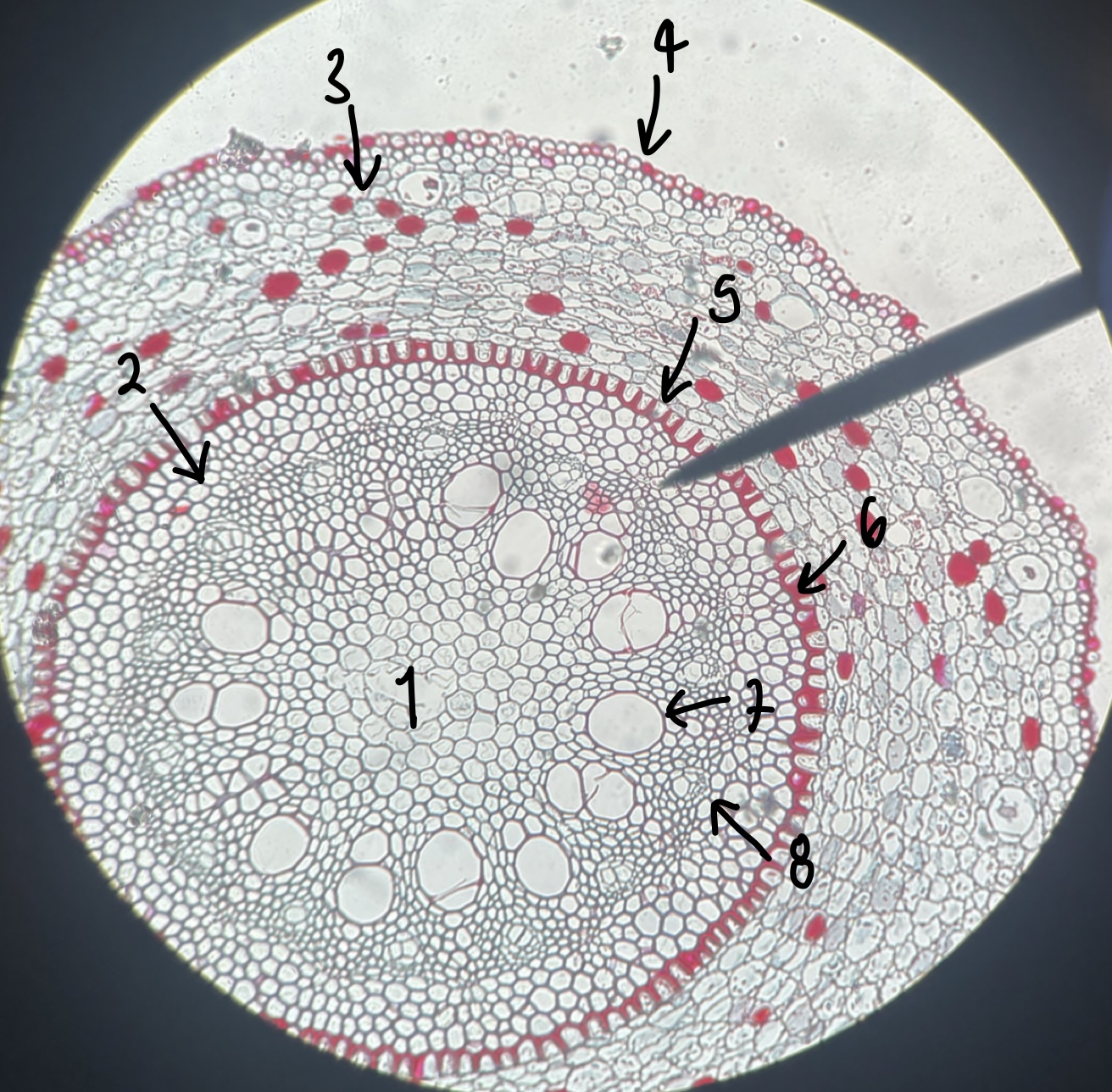
what is the general and specific stele type of the __Smilax__ root
siphonostele
eustele
eustele
40
New cards
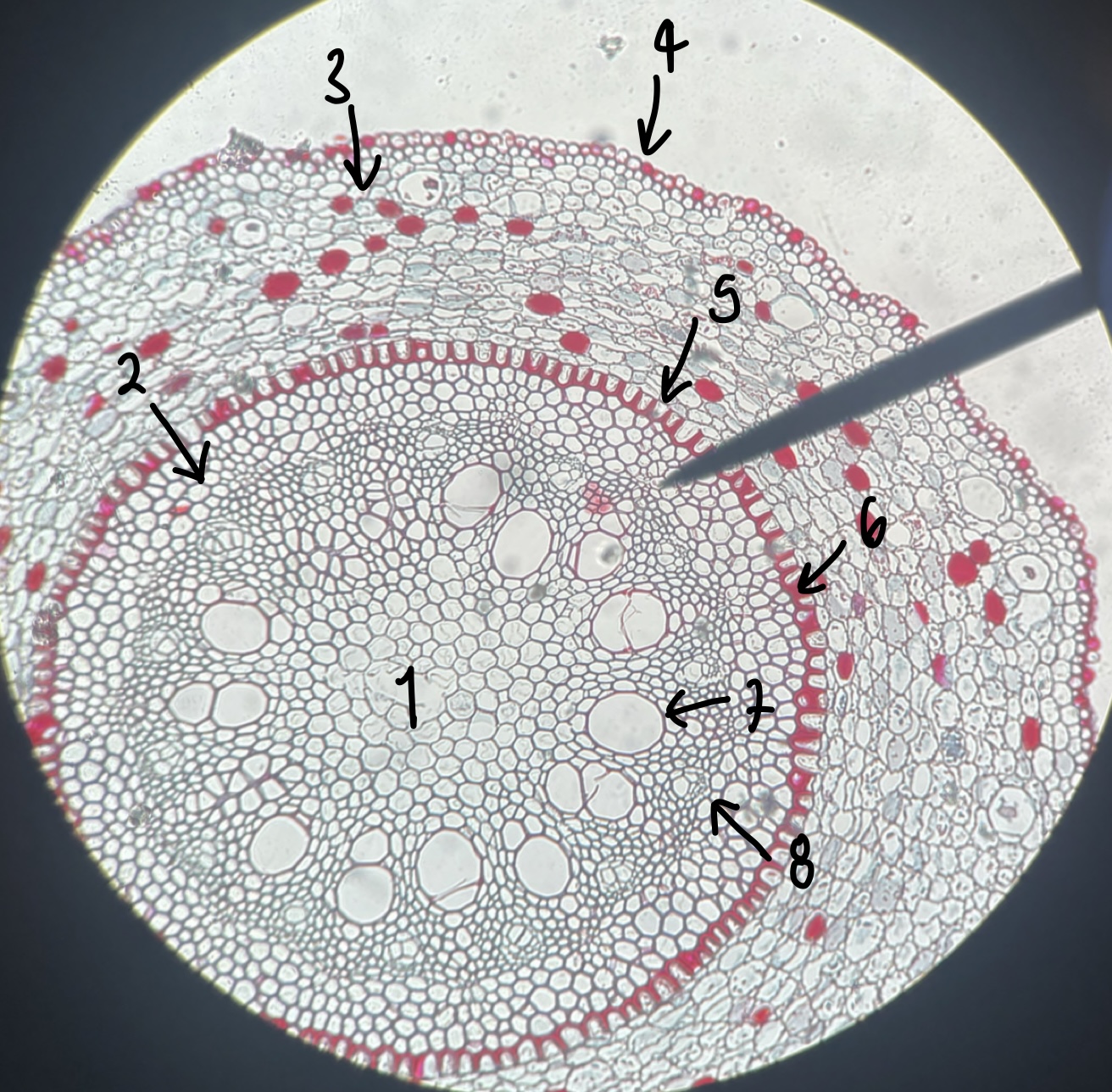
name the structure in label 1
pith
41
New cards
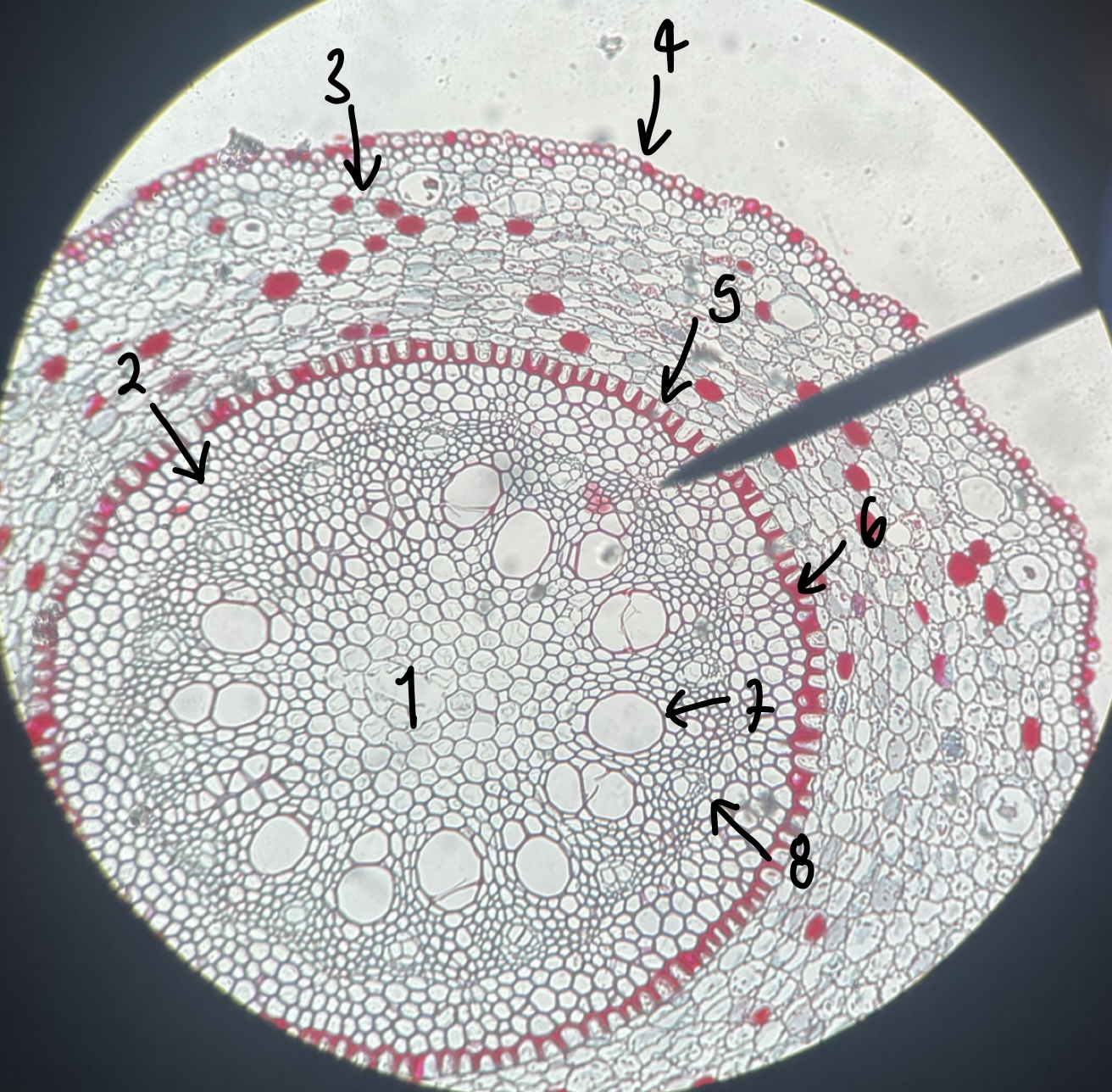
name the structure in label 2
pericycle
42
New cards
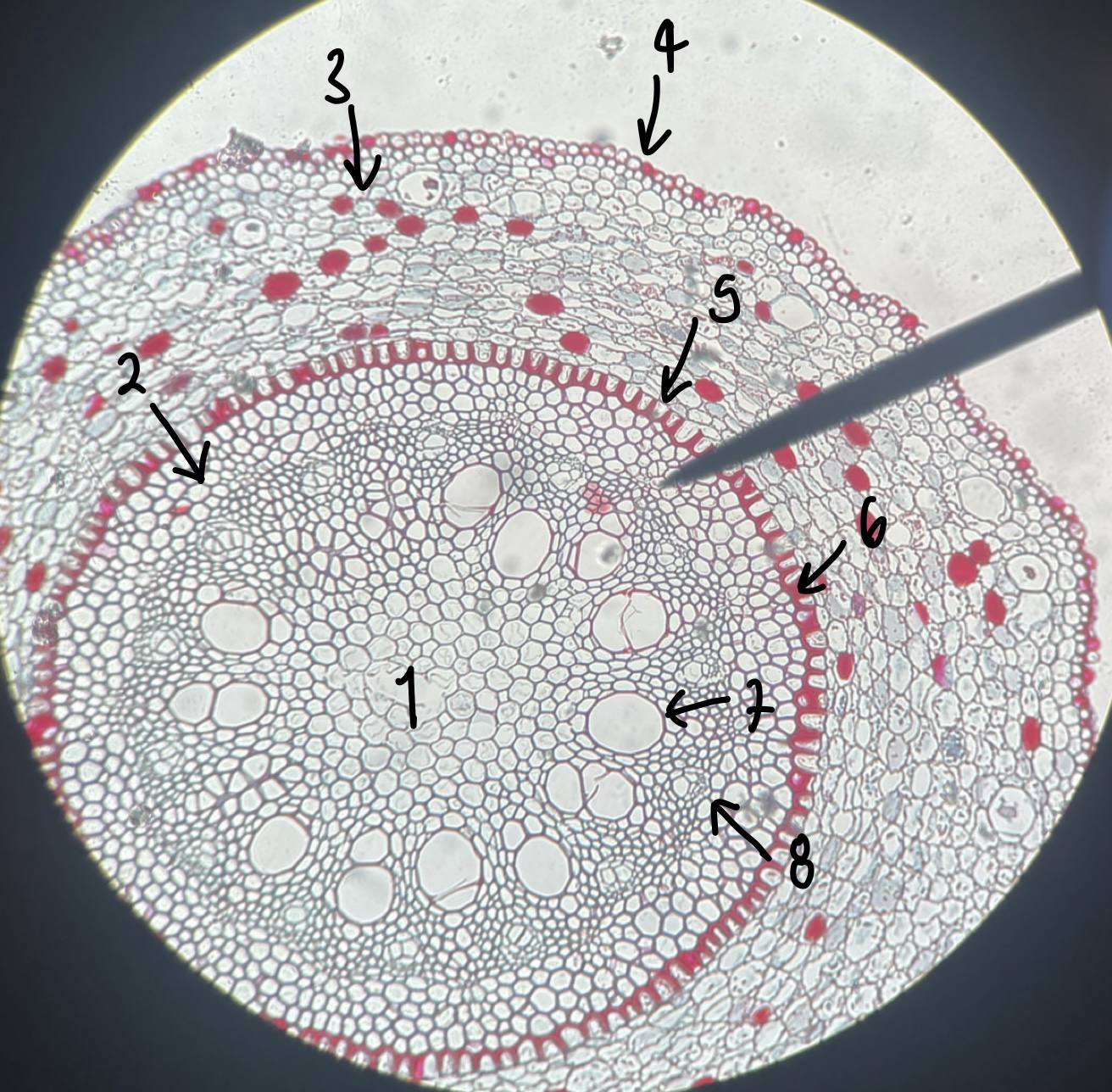
name the structure in label 3
cortex
43
New cards
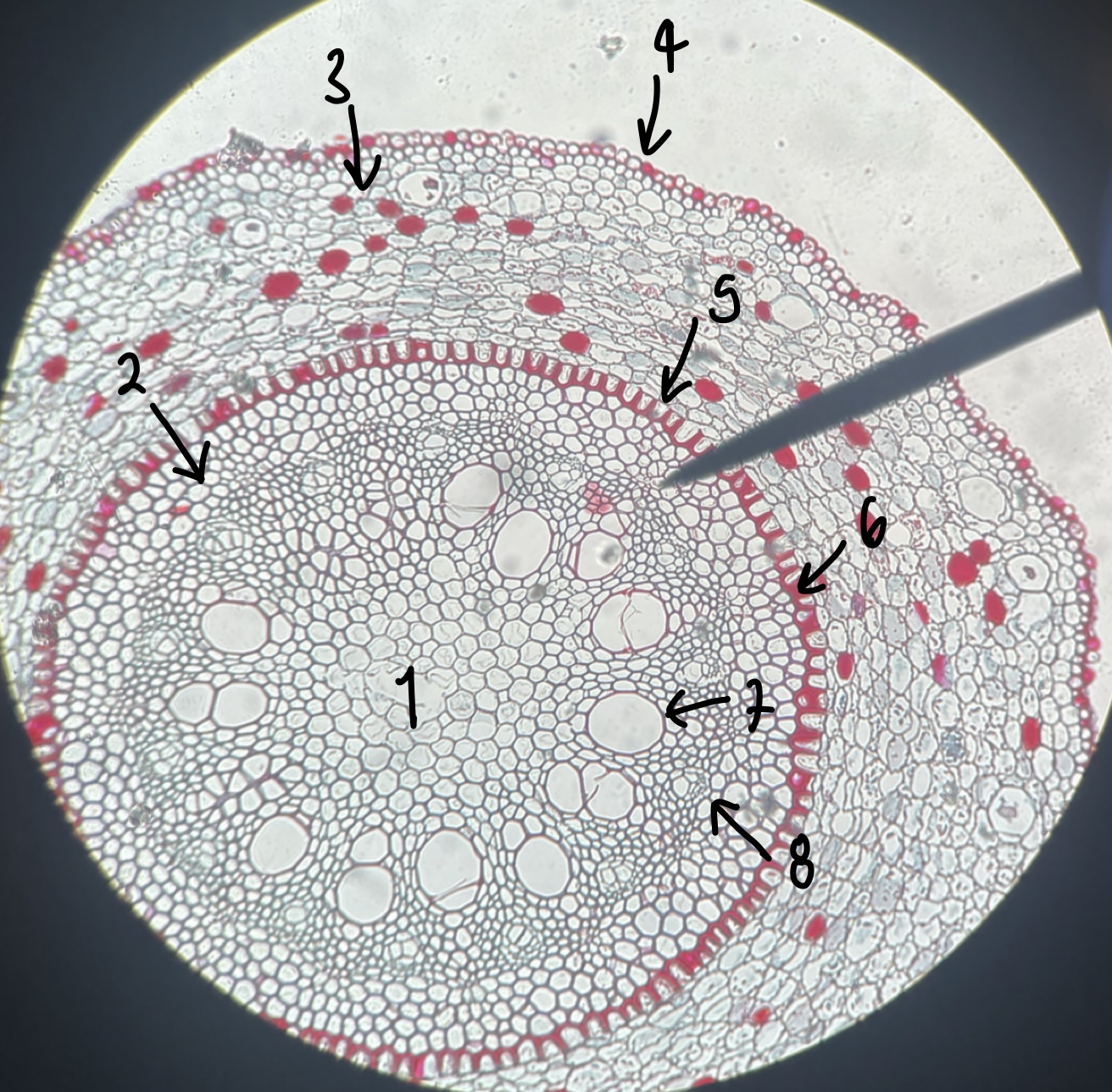
name the structure in label 4
epidermis
44
New cards
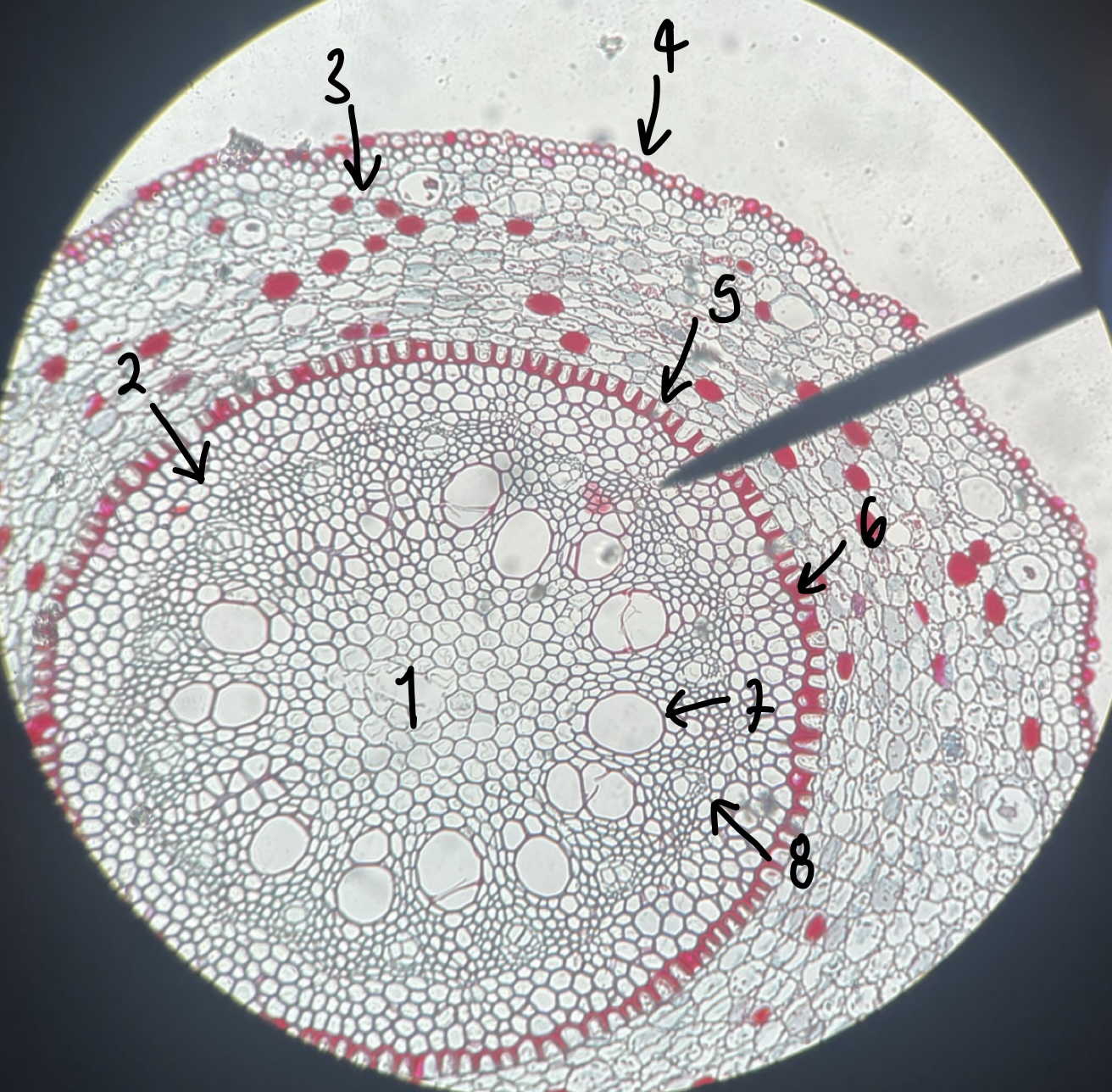
name the structure in label 5
endodermis
45
New cards
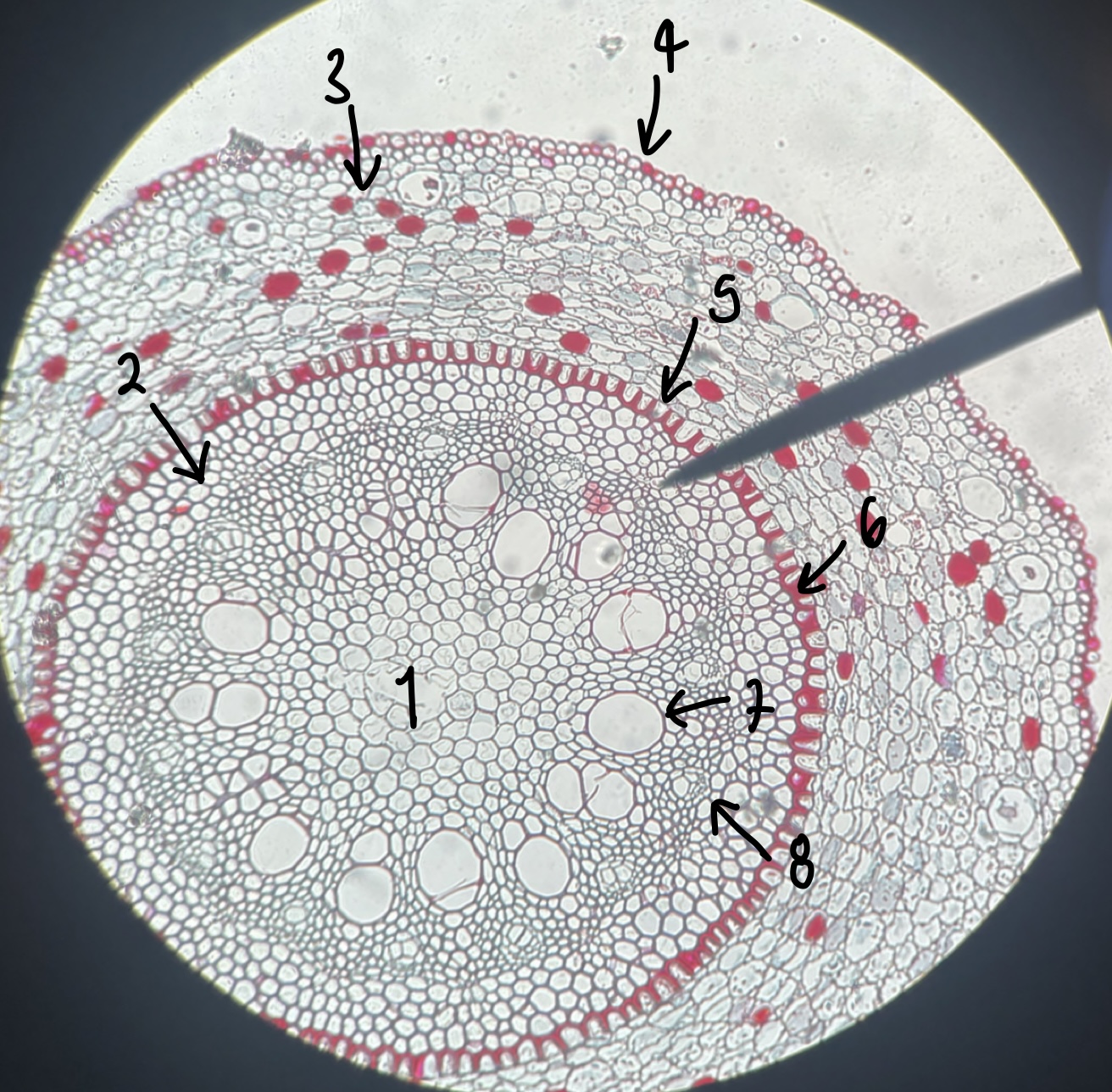
name the structure in label 6
casparian strip
46
New cards
name the structure in label 7
xylem
47
New cards
name the structure in label 8
phloem
48
New cards
what 2 genus of Magnoliopsida stem did we observe
__Medicago__
__Tilia__
__Tilia__
49
New cards
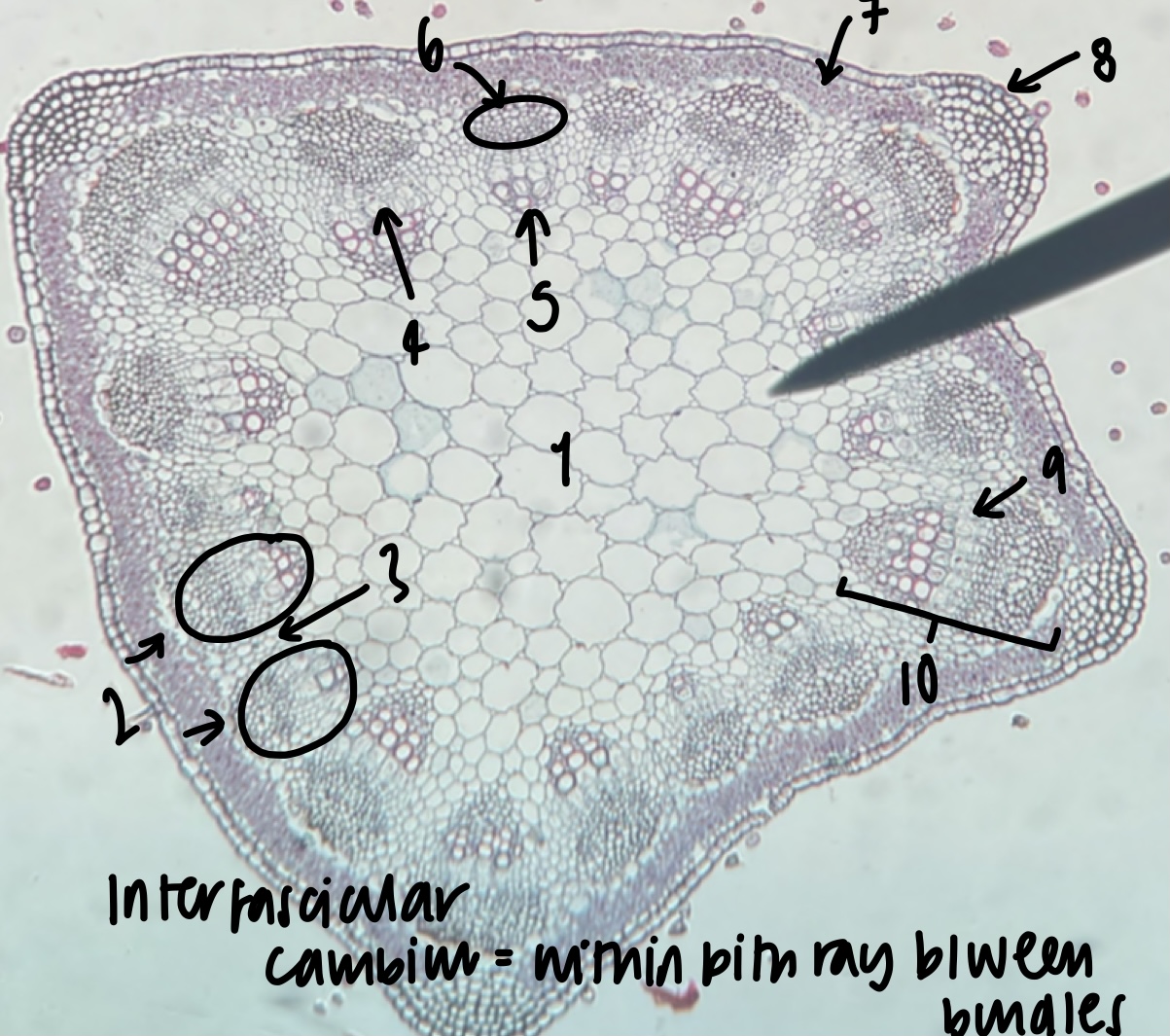
what kind of stem does a __Medicago__ plant have
dicot, primary growth
50
New cards
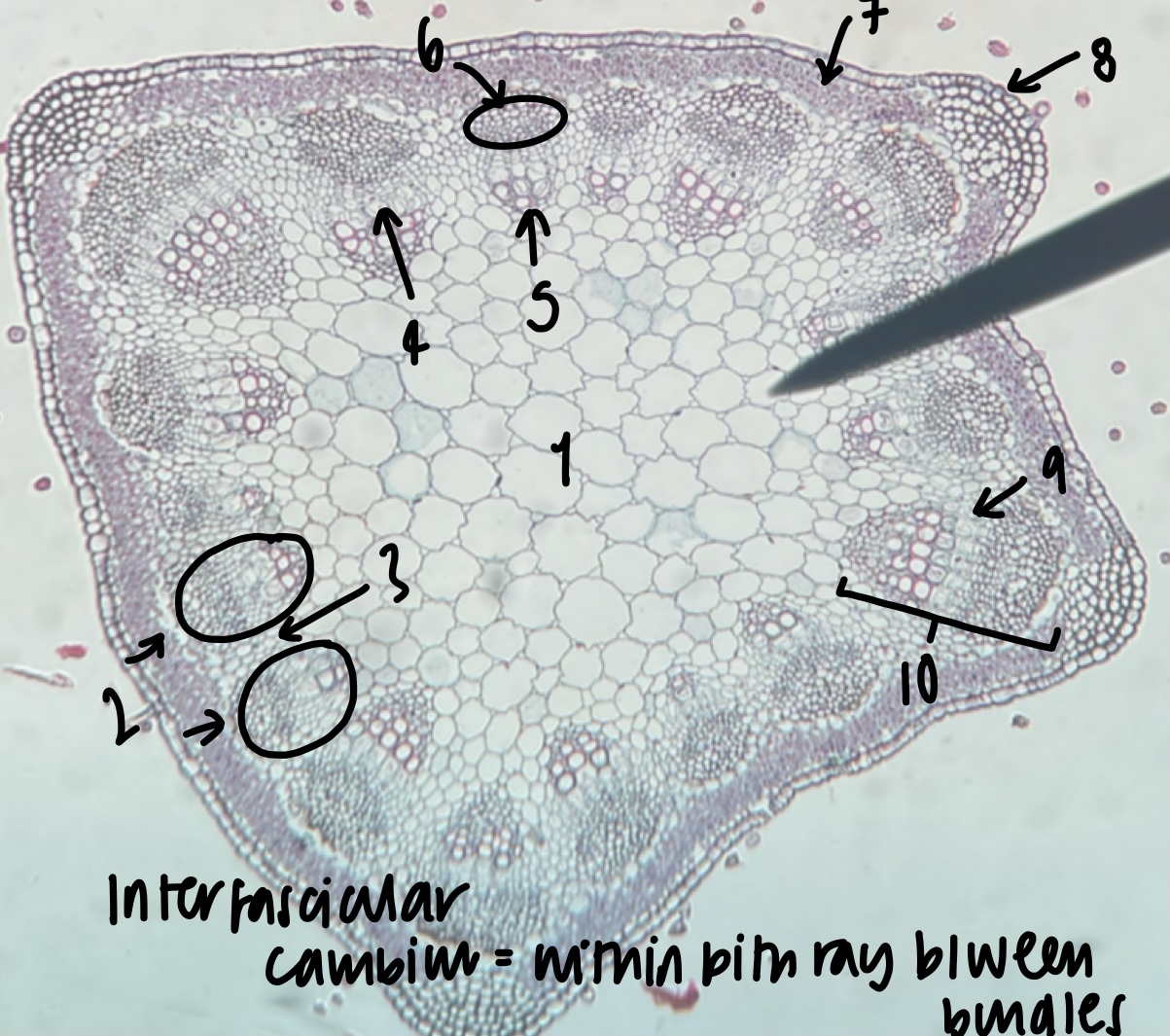
the stem of a __Medicago__ plant has vascular bundles in a …. (shape)
concentric ring
51
New cards
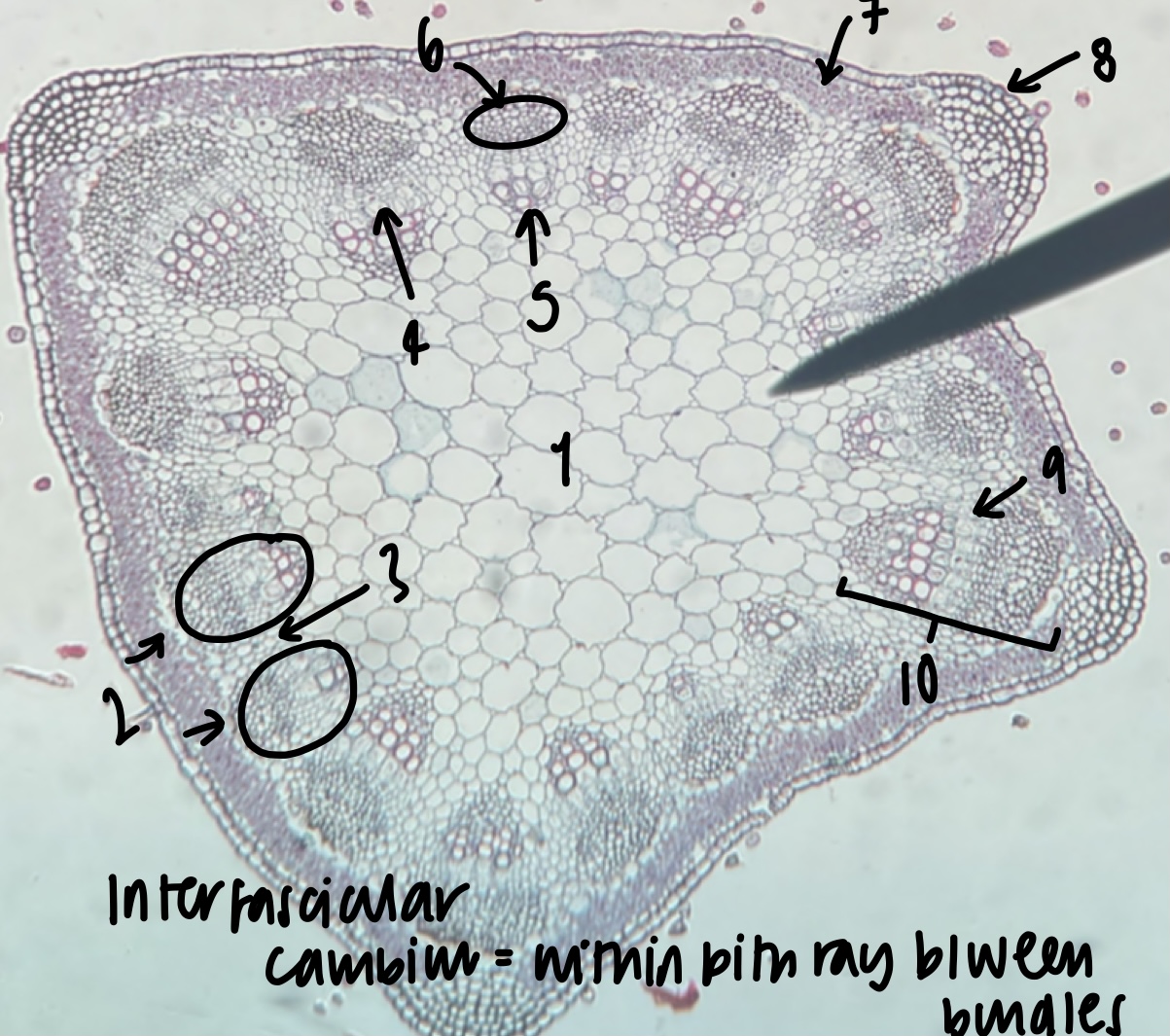
what is the general and specific stele type of a __Medicago__ stem
siphonostele
eustele
eustele
52
New cards
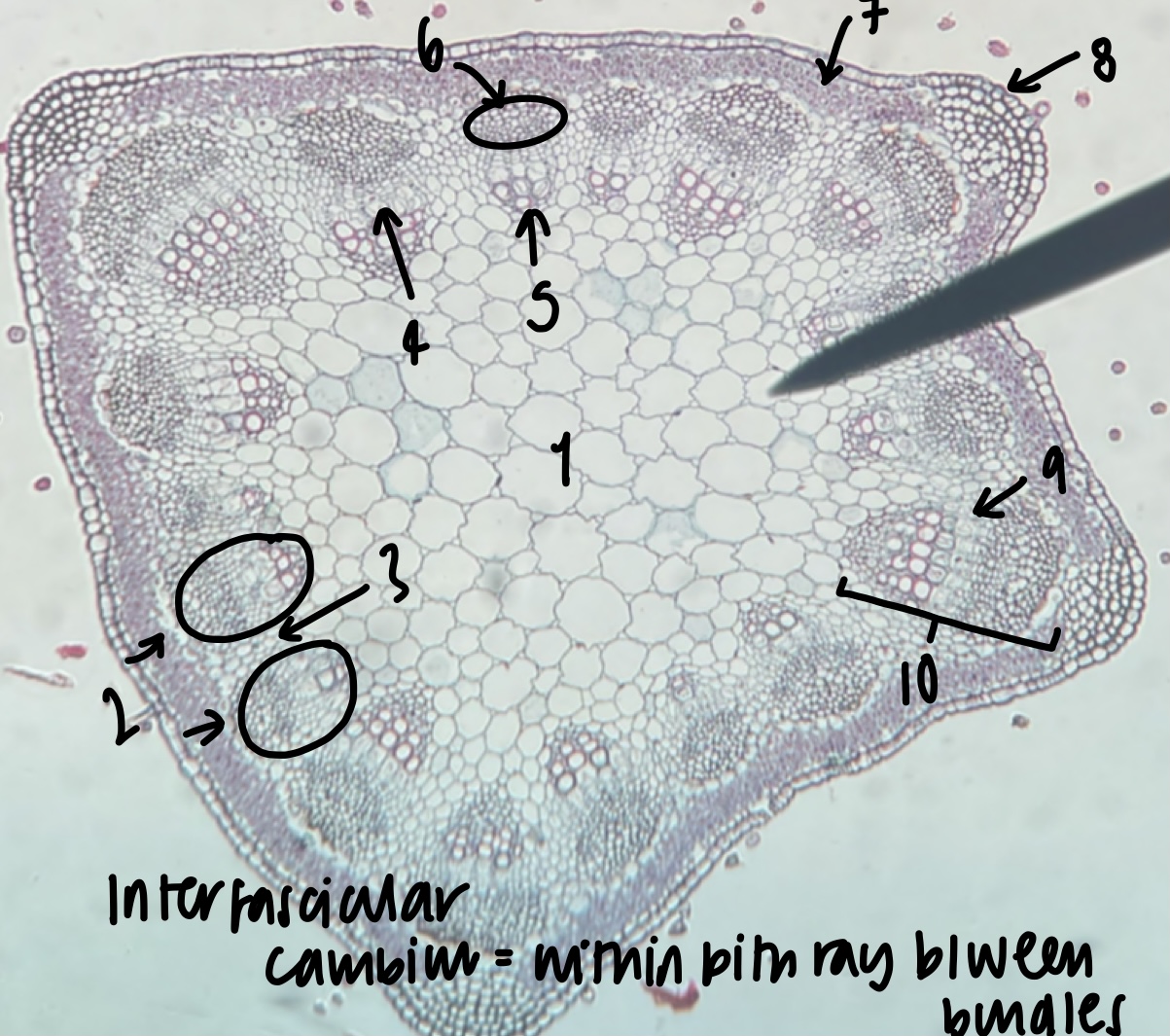
name the structure in label 1
pith
53
New cards
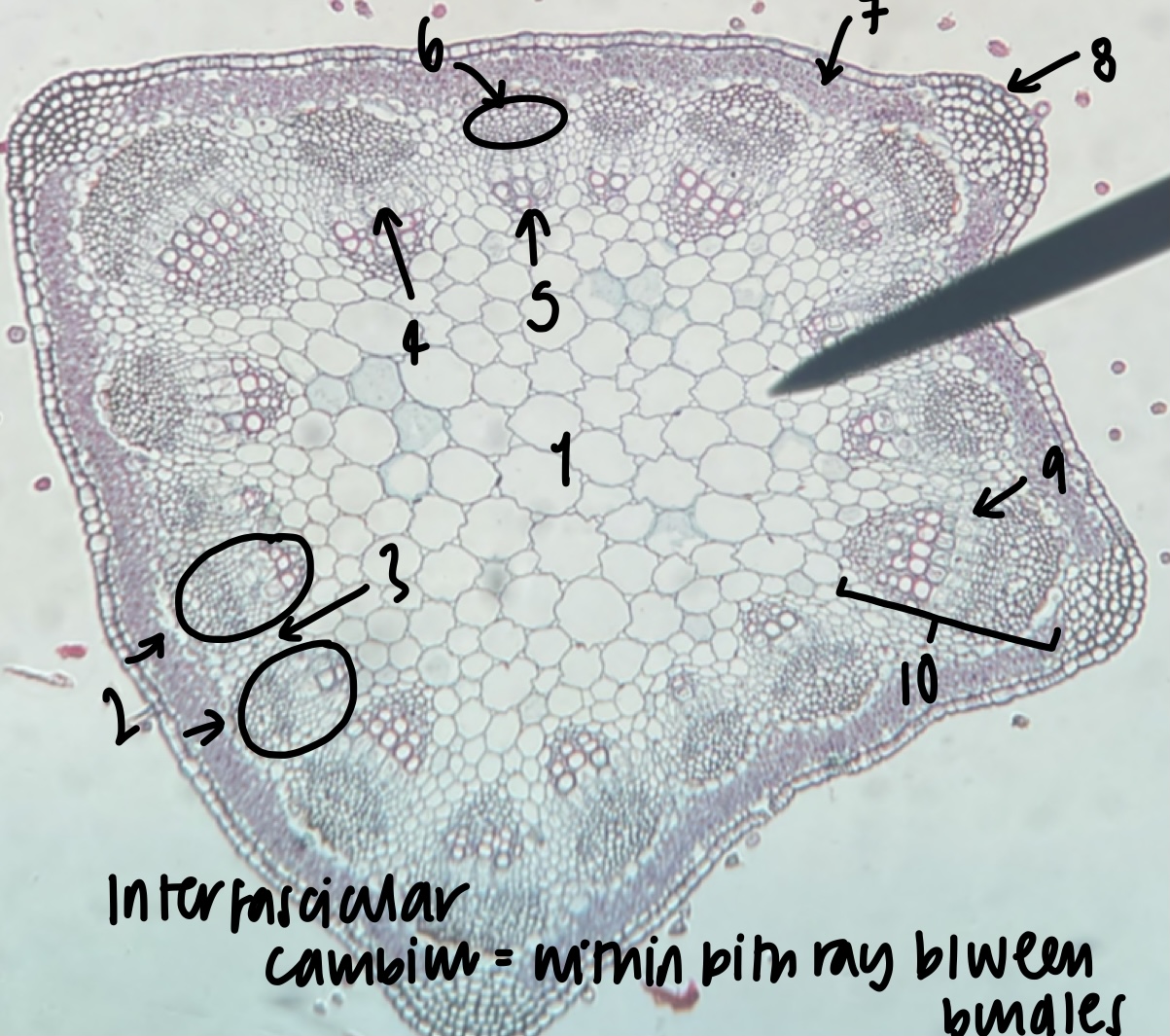
name the structure in label 2
vascular bundles (location of xylem and phloem)
54
New cards
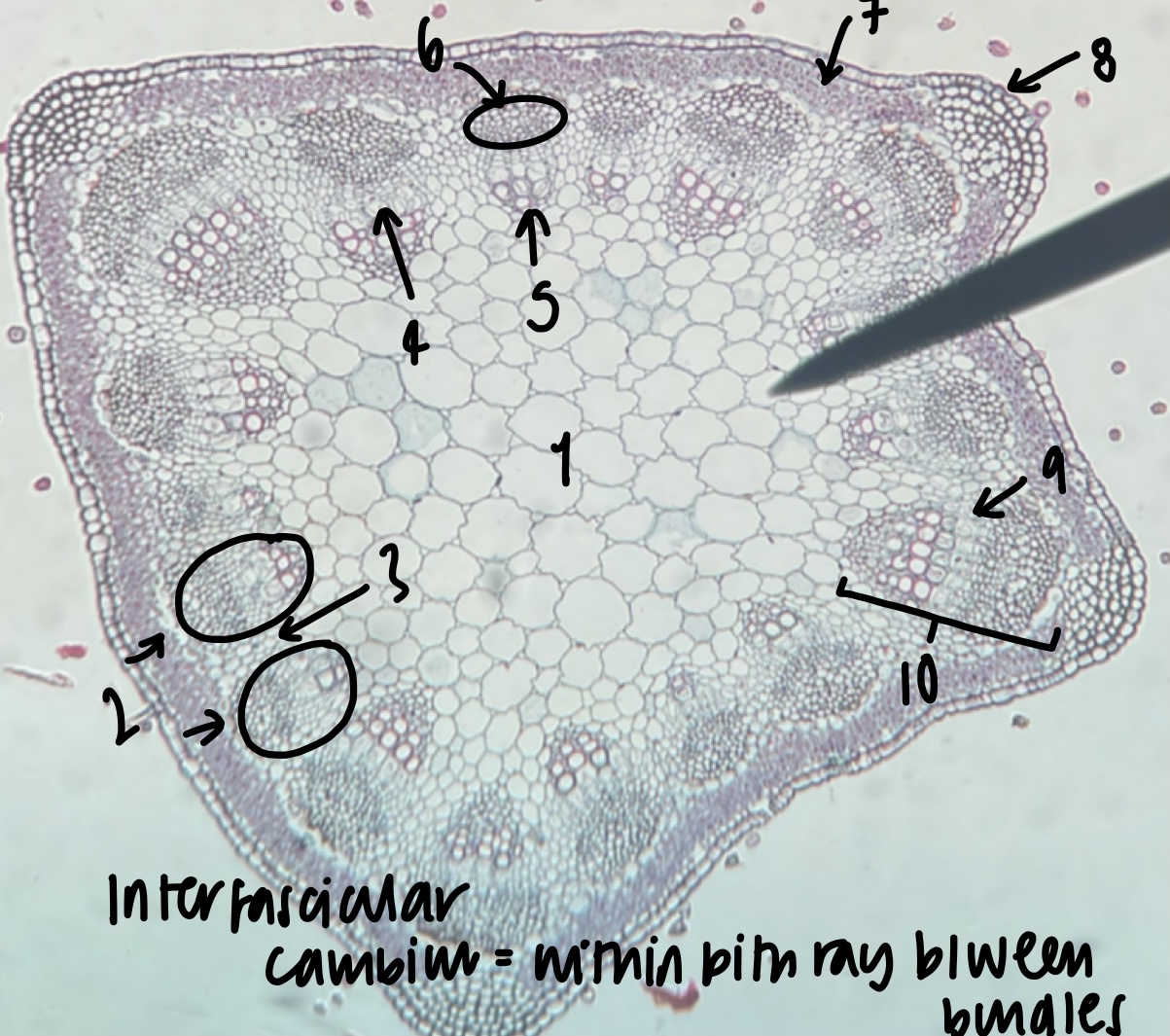
name the structure in label 3
pith ray (area between vascular bundles)
55
New cards
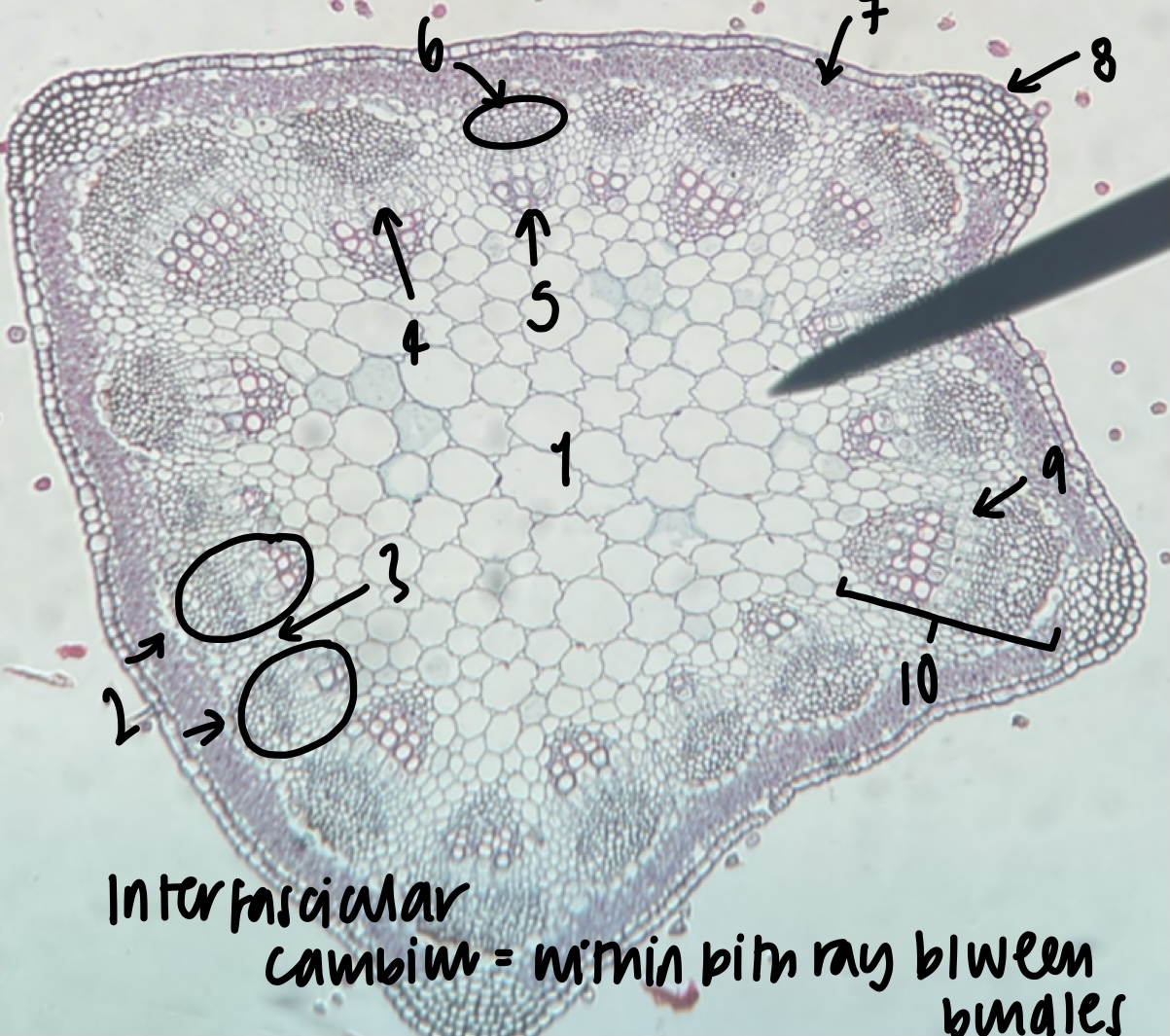
name the structure in label 4
phloem
56
New cards
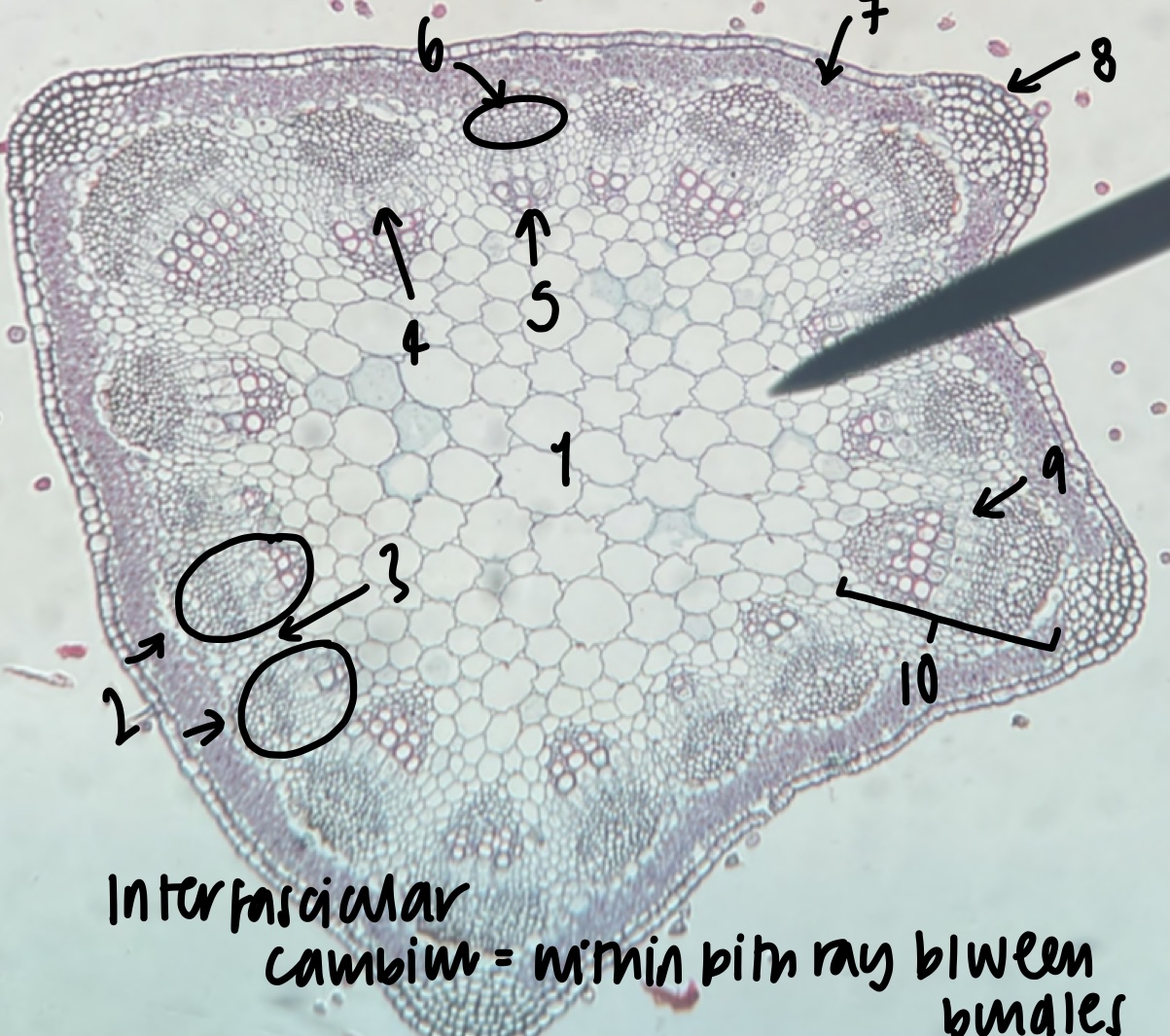
name the structure in label 5
xylem
57
New cards
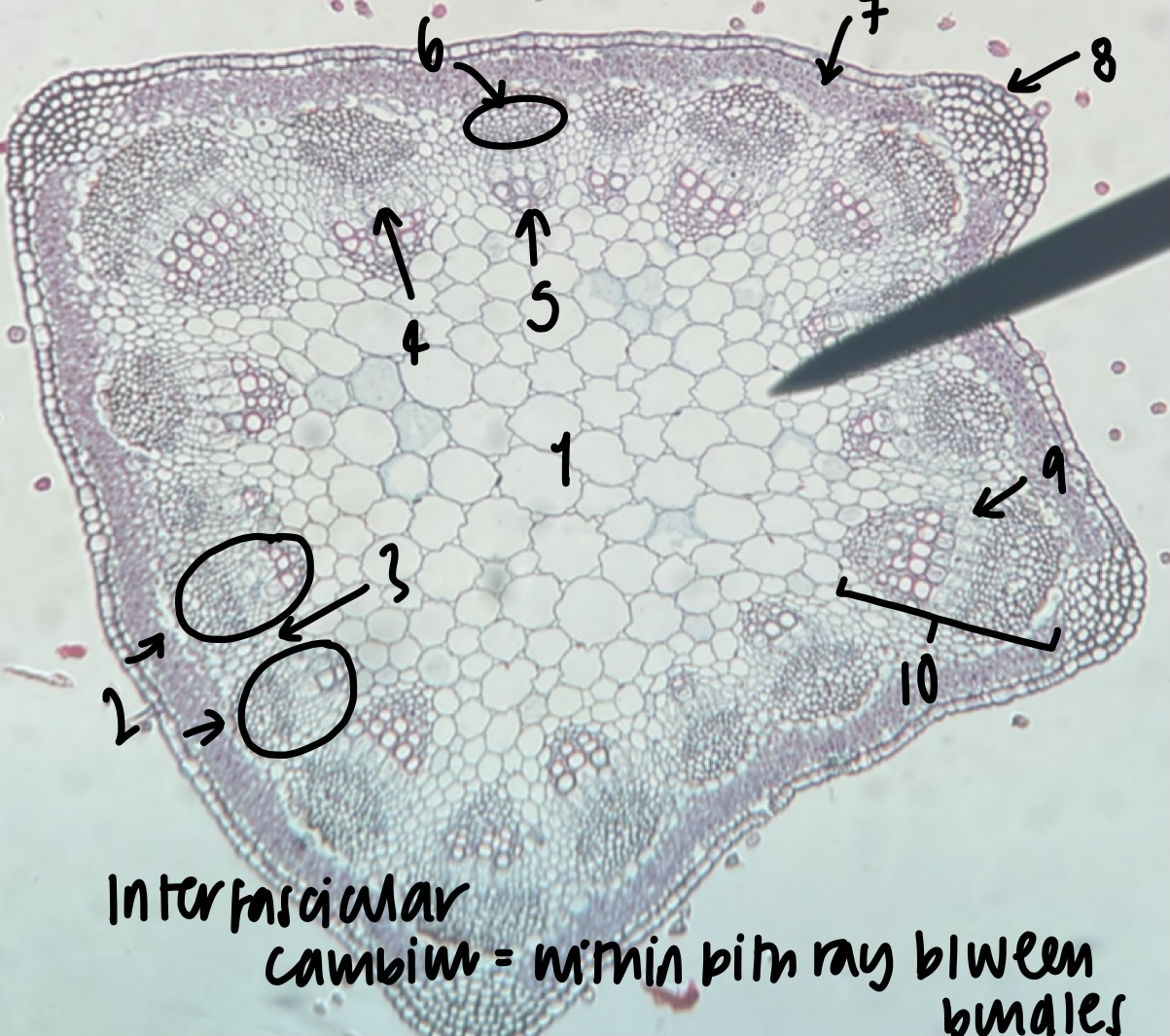
name the structure in label 6
fiber cap (outermost vascular bundle cell region)
58
New cards
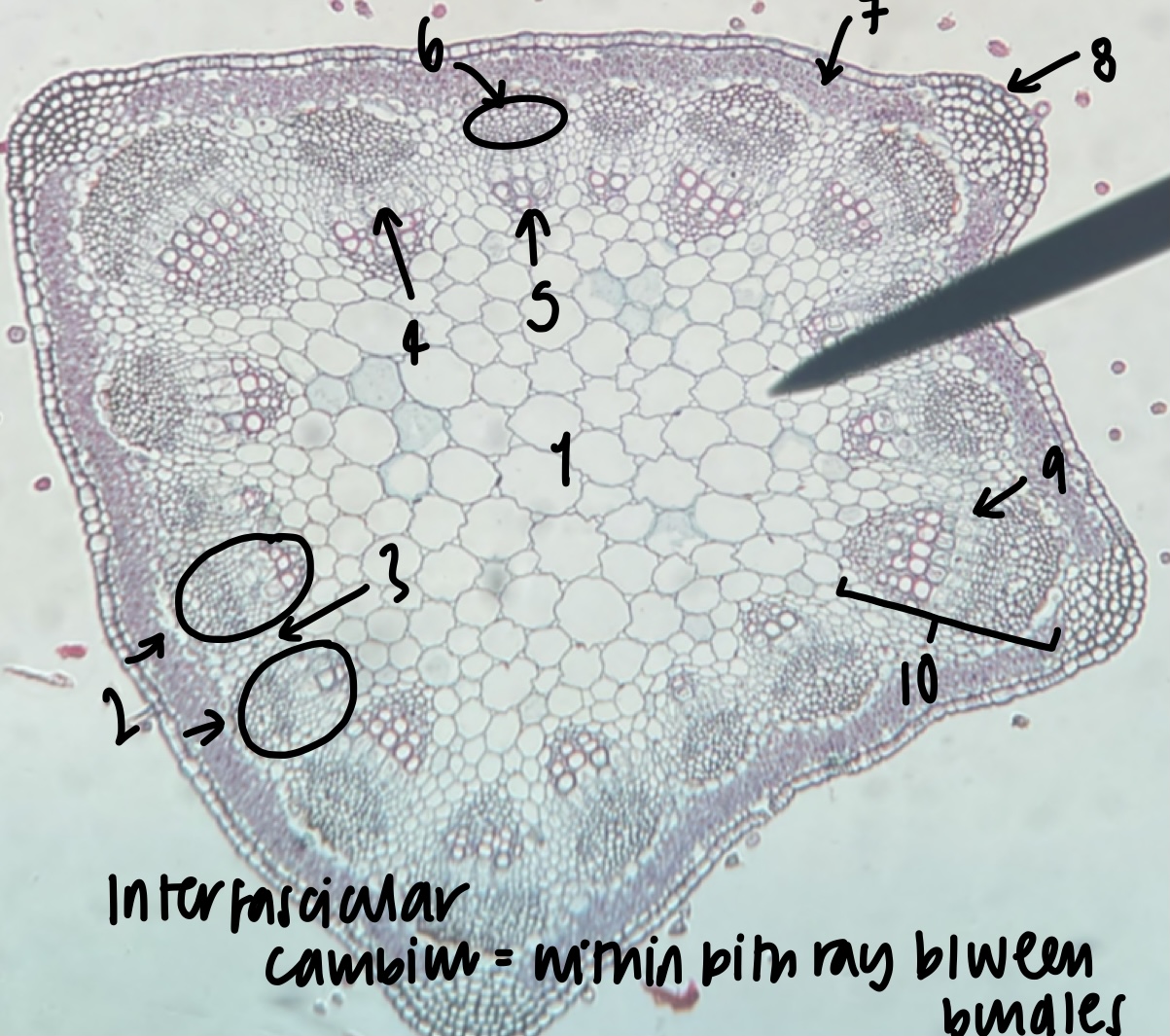
name the structure in label 7
cortex
59
New cards
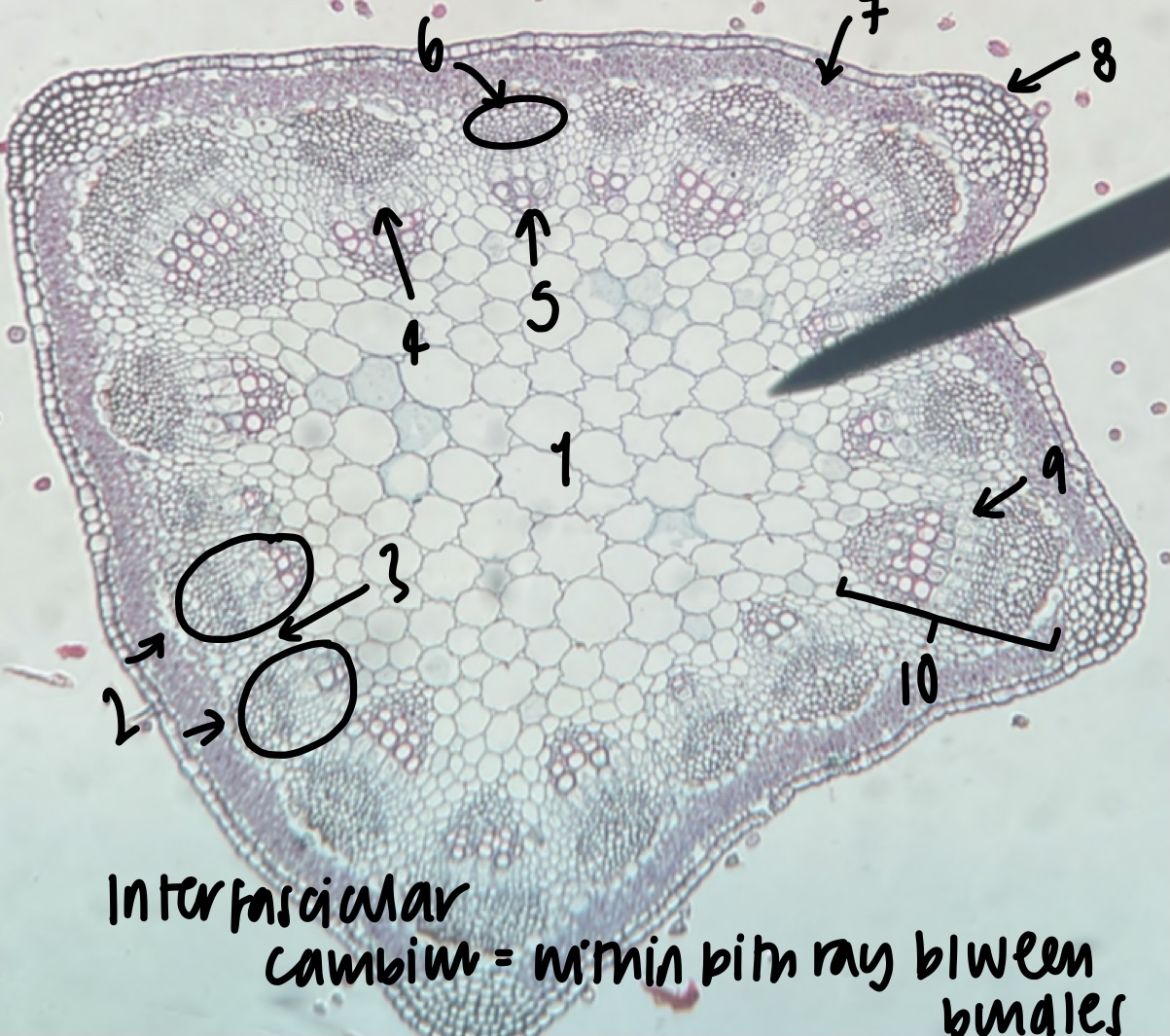
name the structure in label 8
epidermis
60
New cards
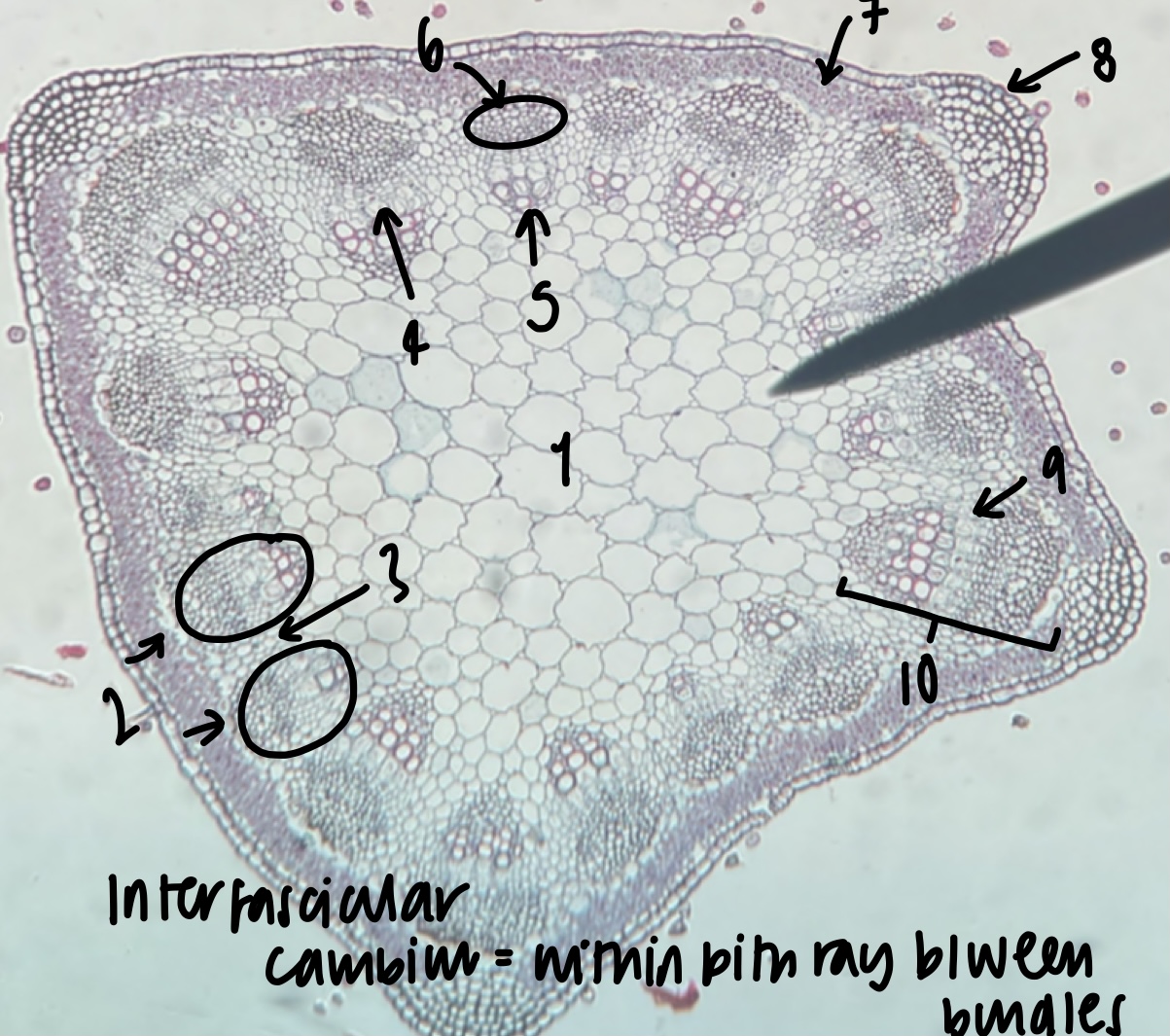
name the structure in label 9
fascicular cambium (within bundle)
61
New cards
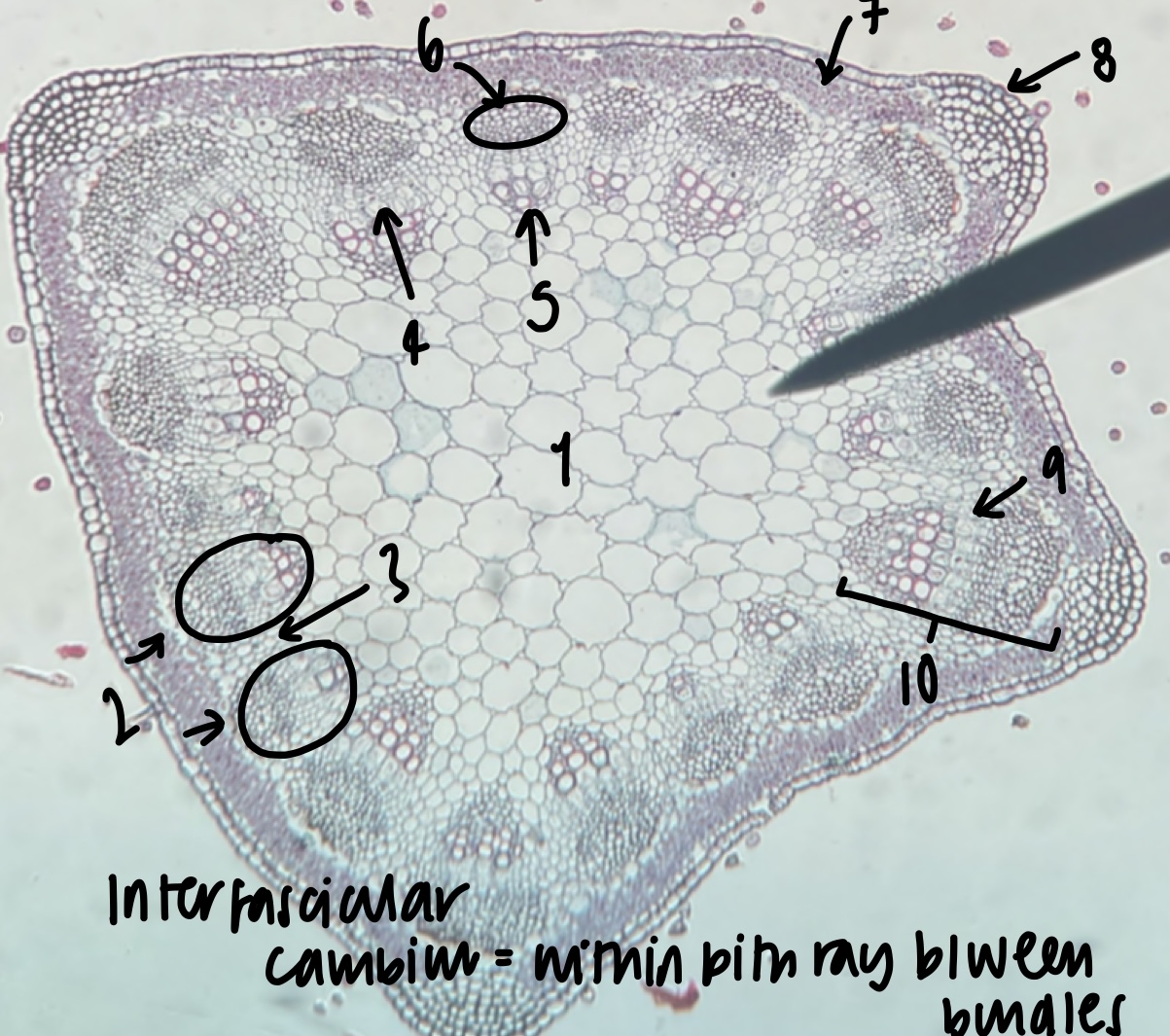
name the structure in label 10
vascular cambium (both inter-fascicular and fascicular)
62
New cards
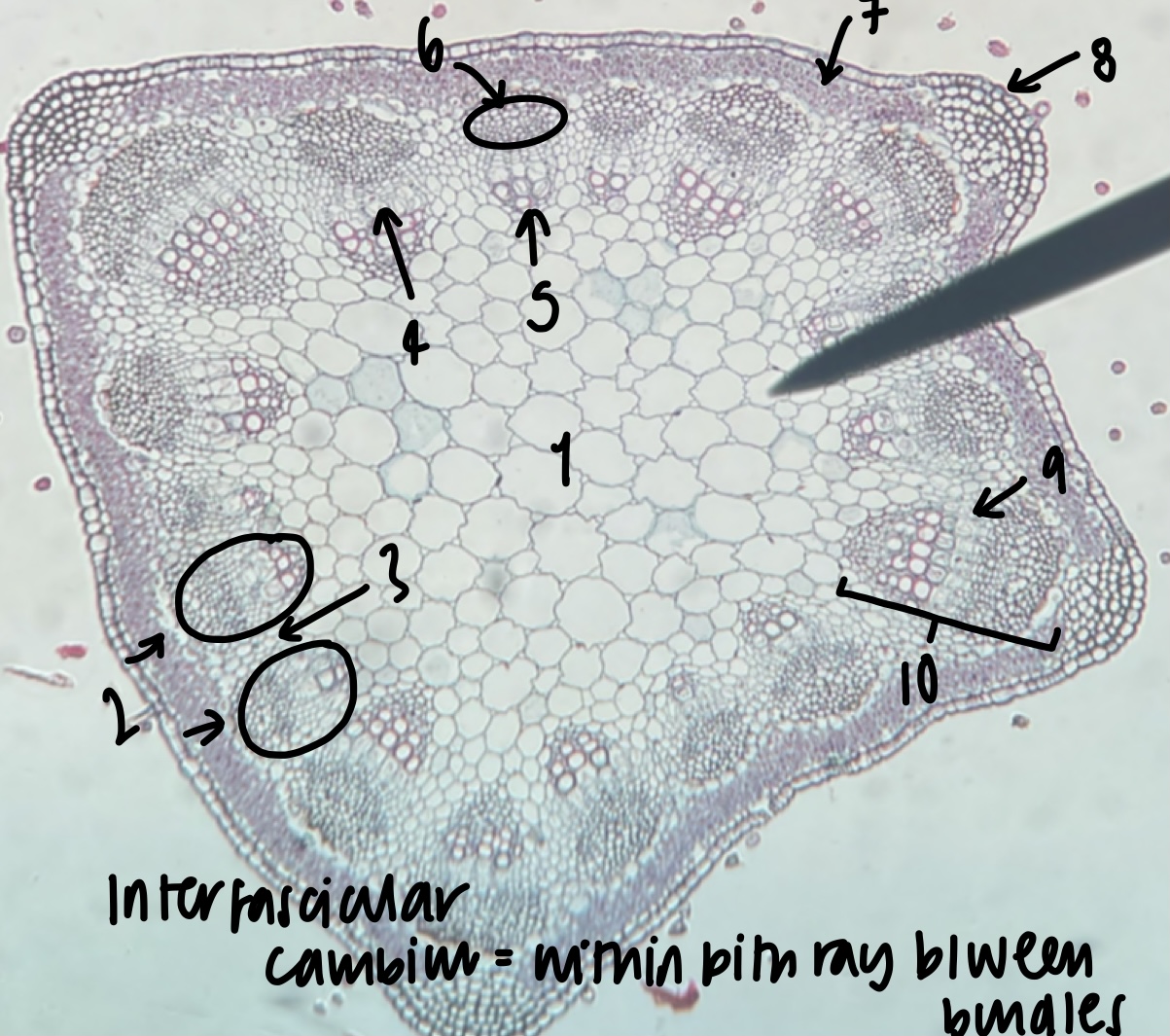
what structure is found within the pith ray between bundles
inter-fascicular cambium
63
New cards
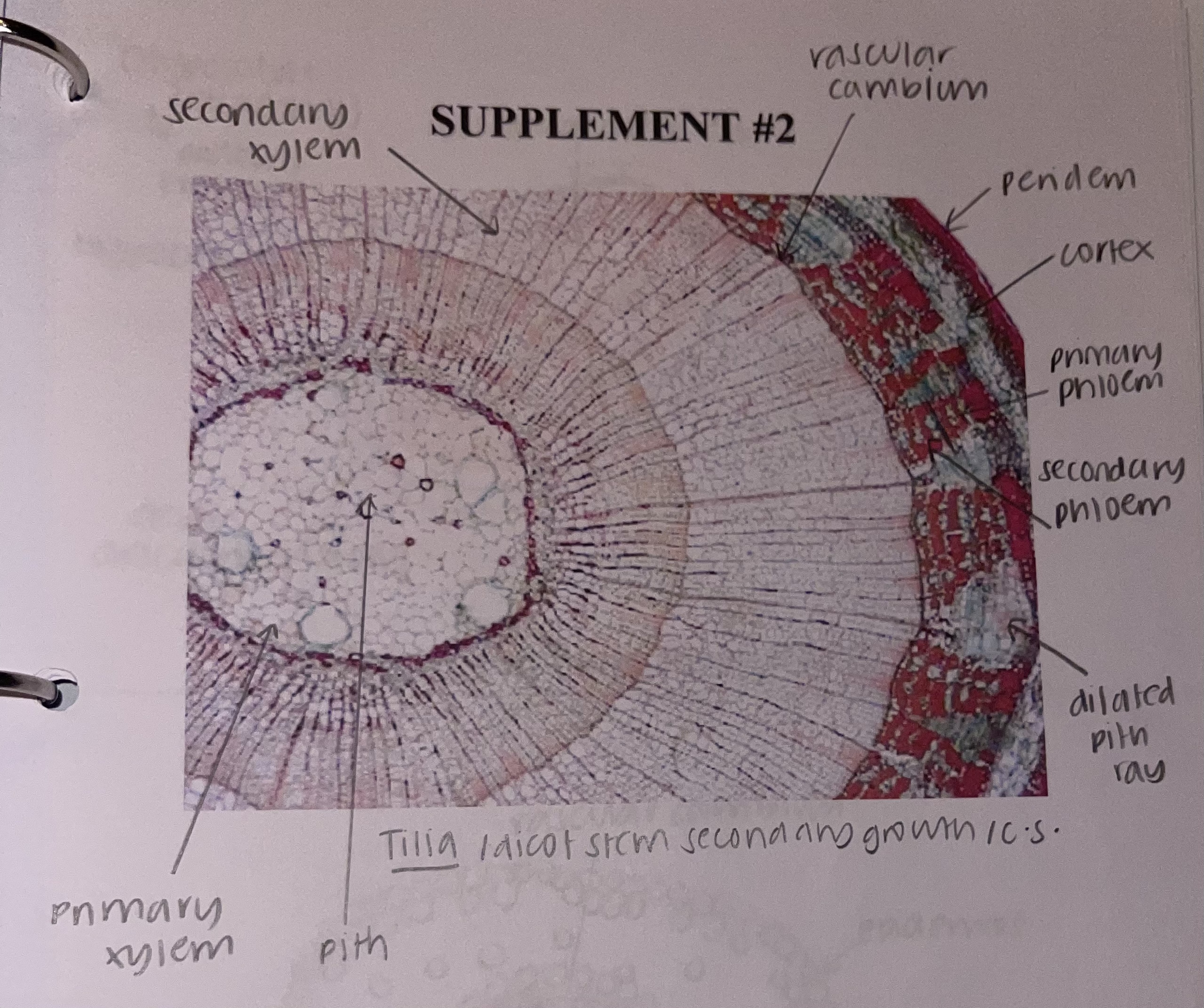
what kind of stem does a __Tilia__ plant have
dicot, secondary growth
64
New cards
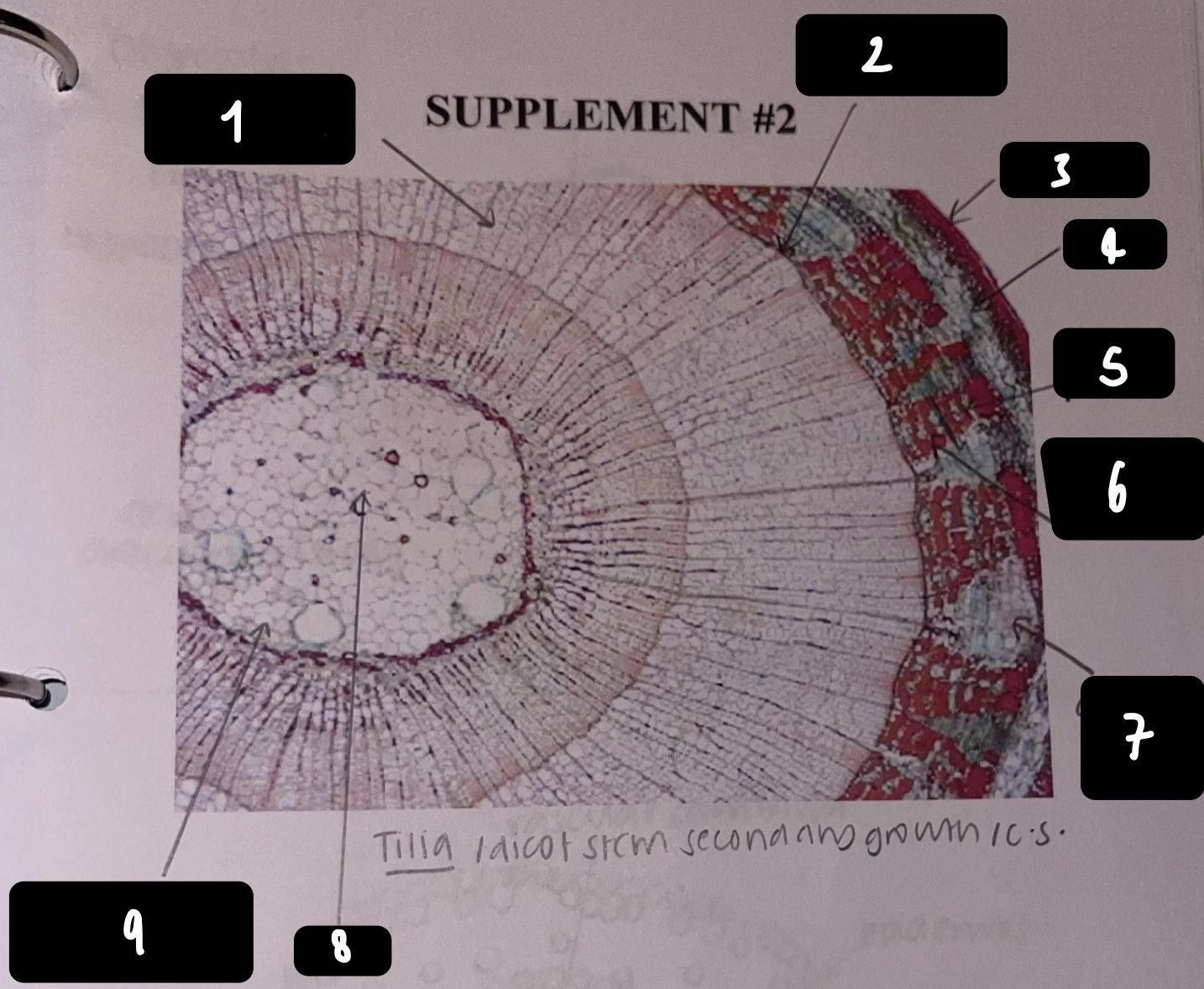
name the structure in label 1
secondary xylem
65
New cards
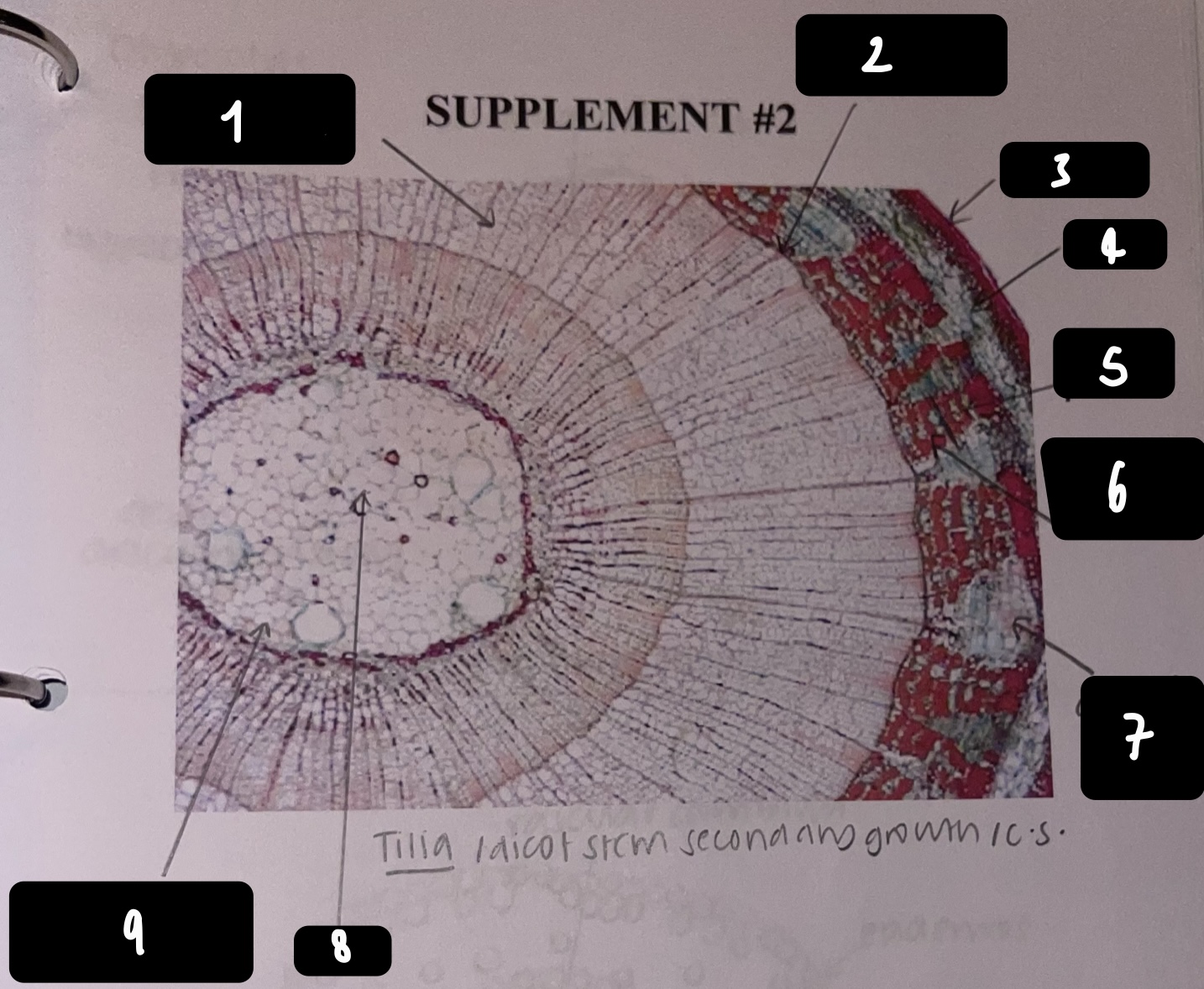
name the structure in label 2
vascular cambium
66
New cards
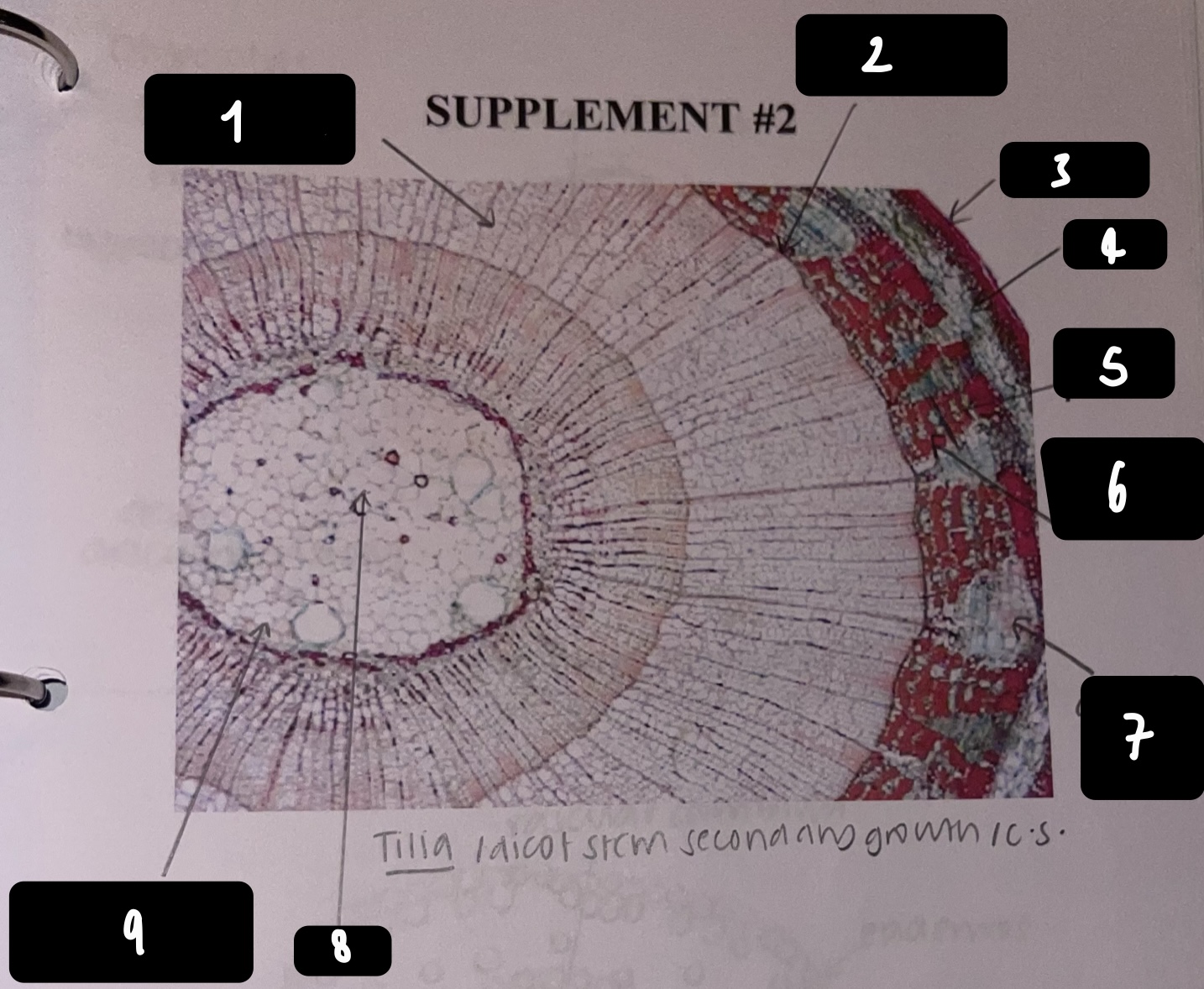
name the structure in label 3
periderm
67
New cards
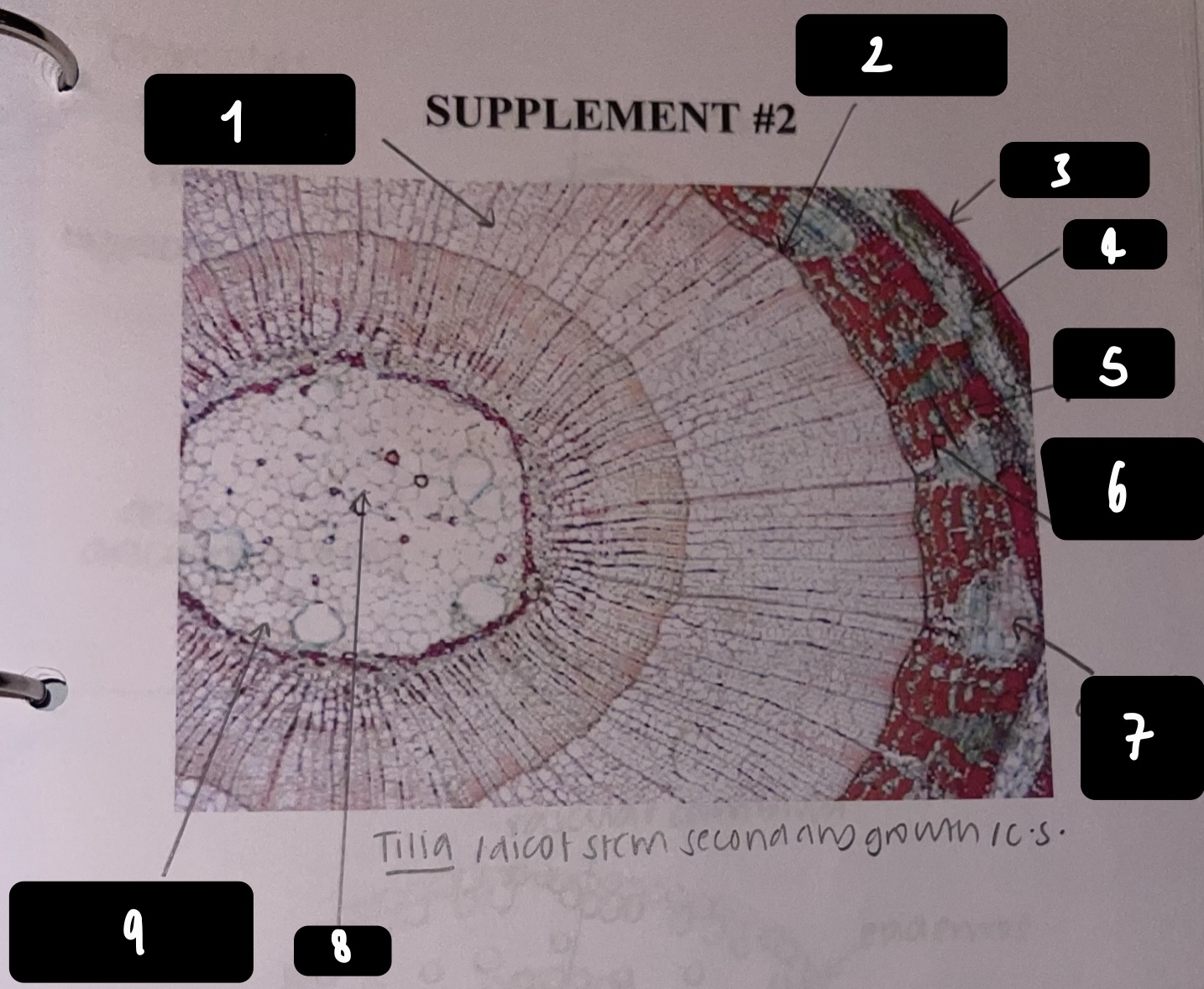
name the structure in label 4
cortex
68
New cards
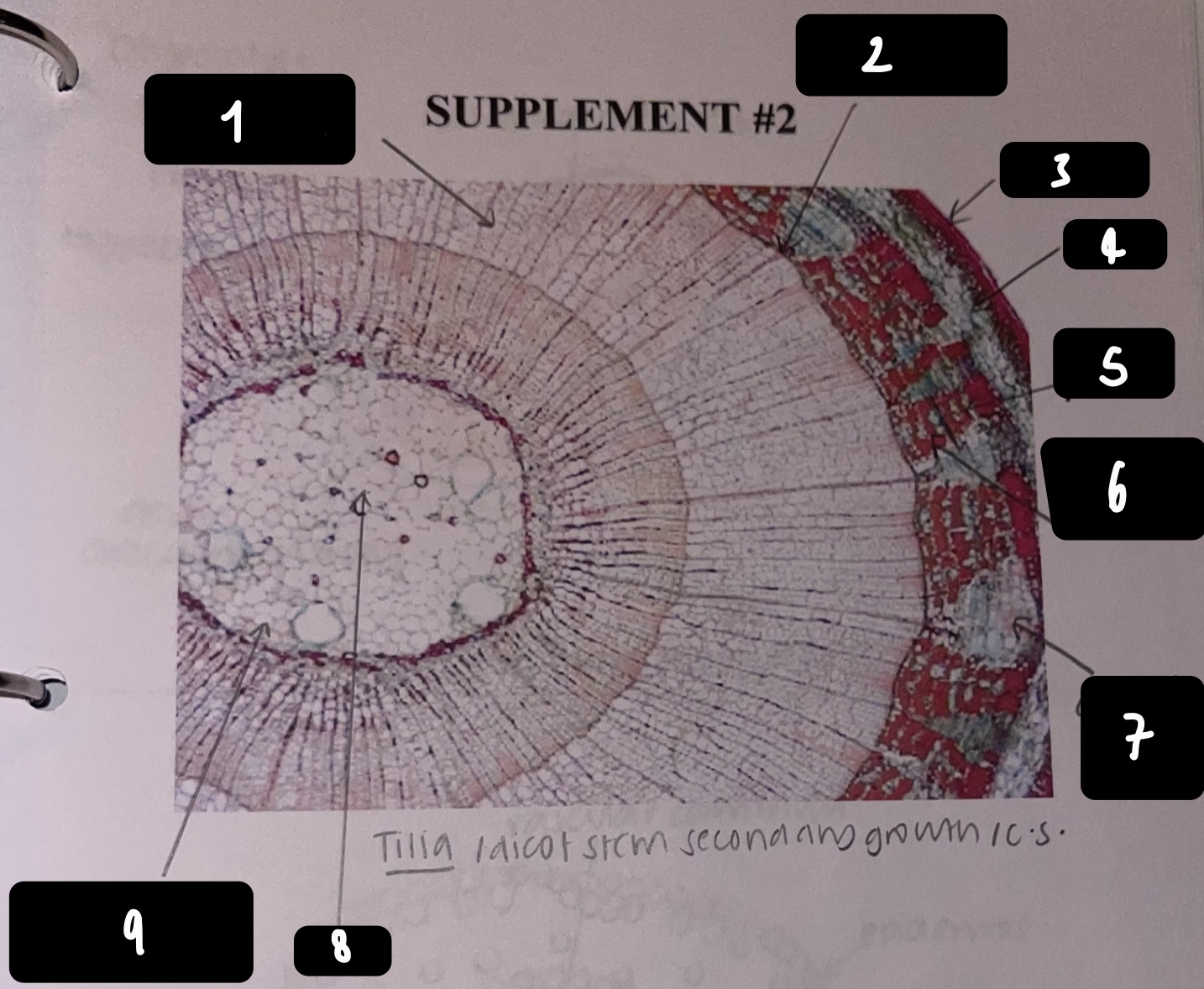
name the structure in label 5
primary phloem
69
New cards
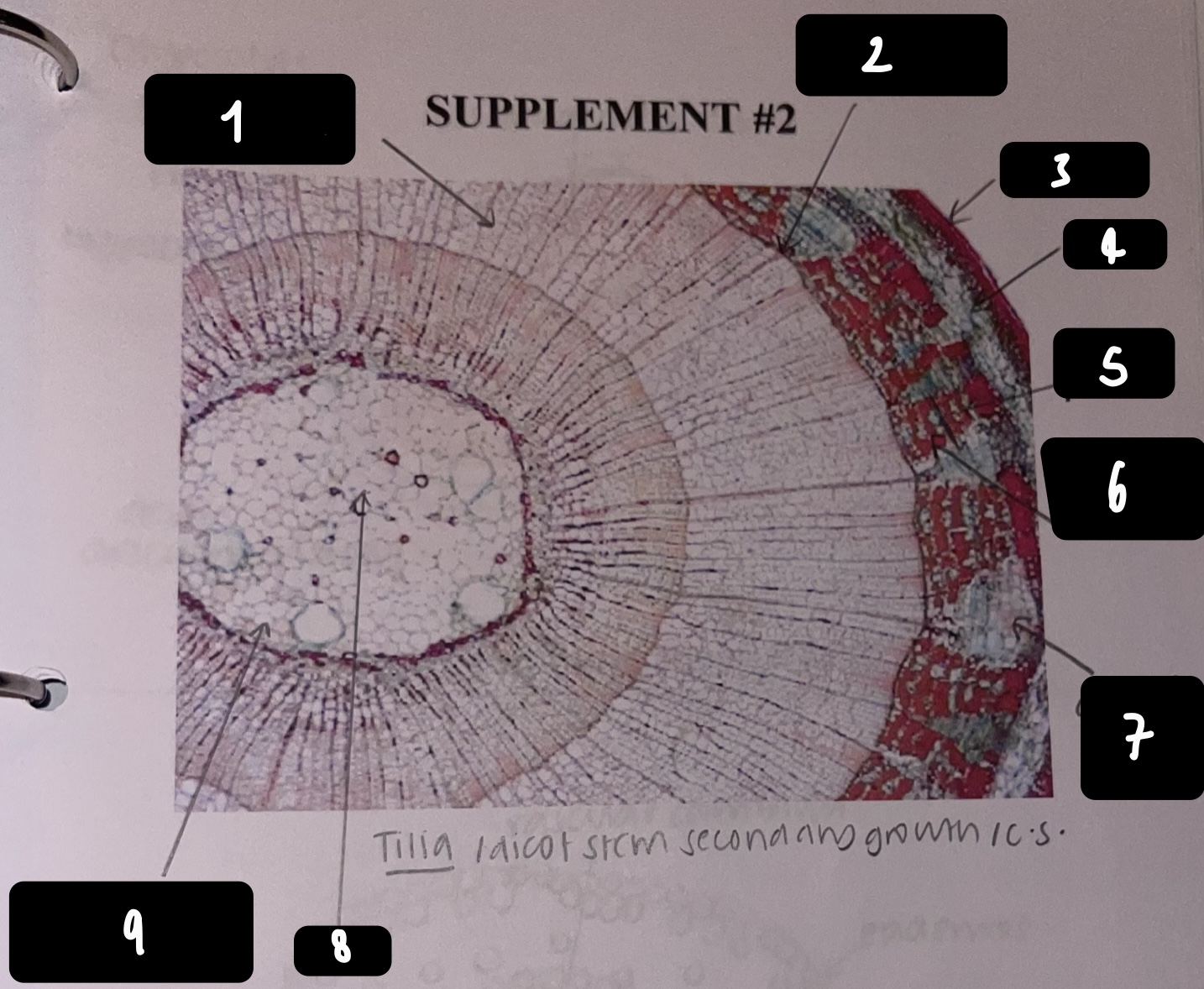
name the structure in label 6
secondary phloem
70
New cards
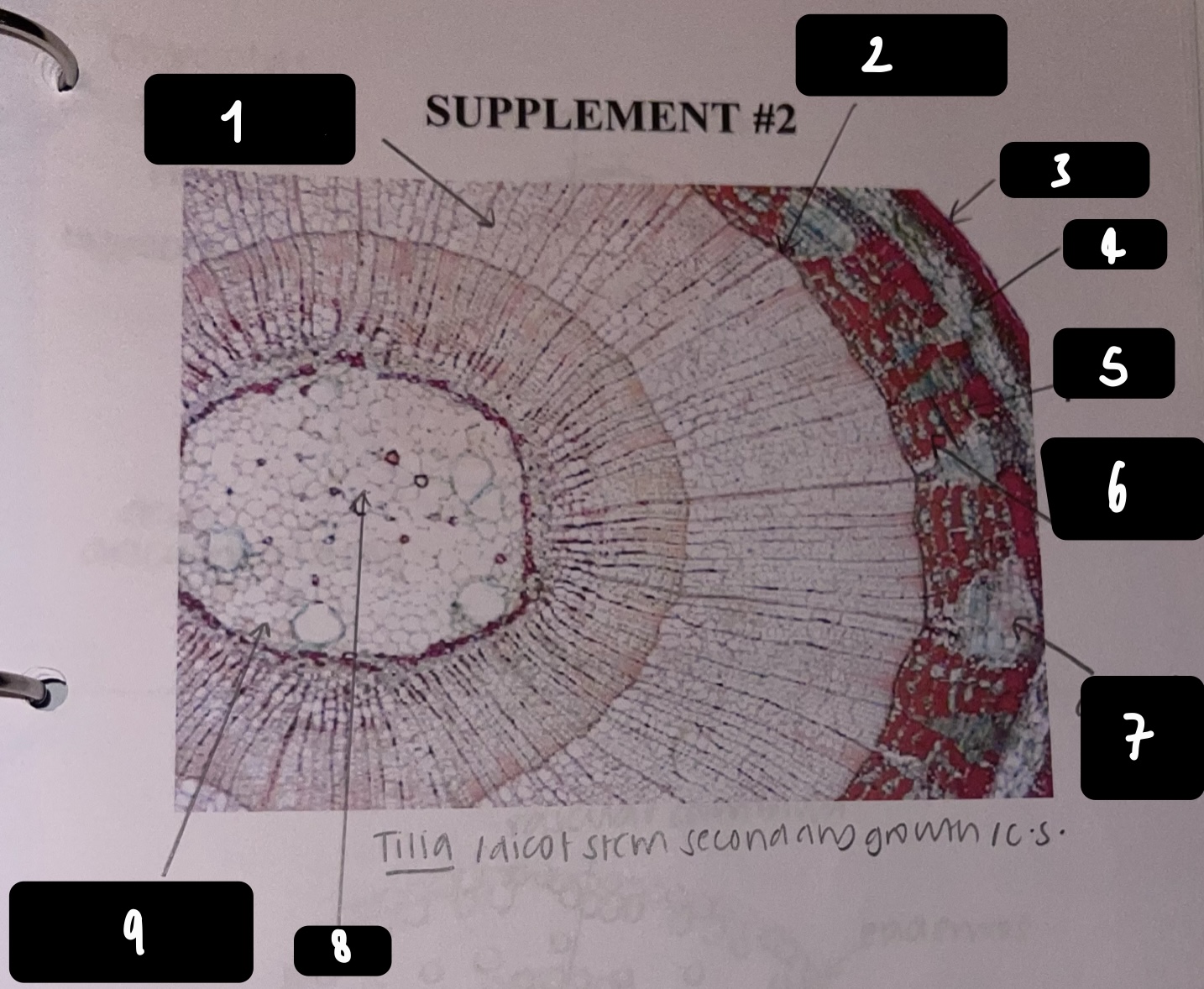
name the structure in label 7
dilated pith ray (area between phloem)
71
New cards
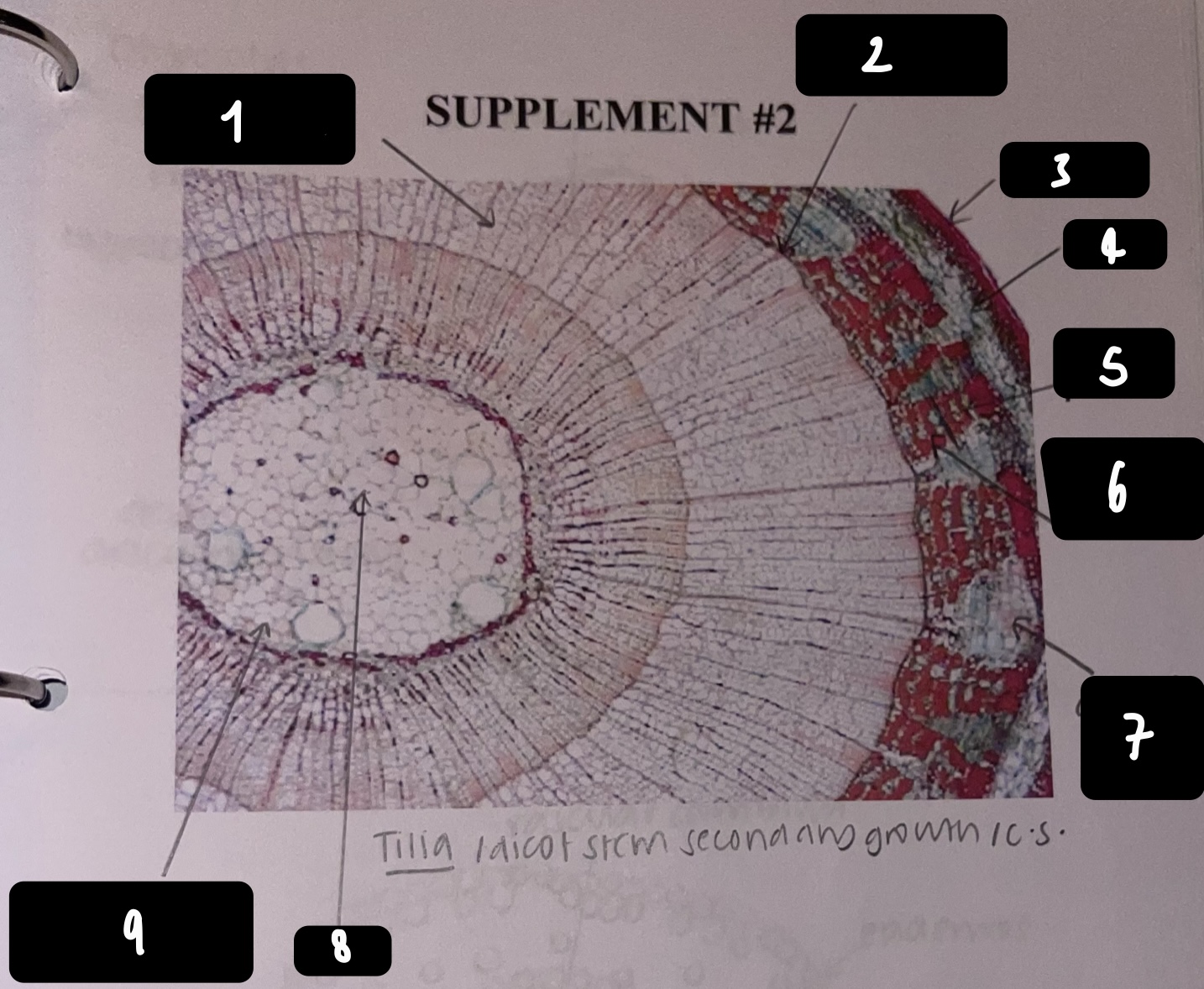
name the structure in label 8
pith
72
New cards
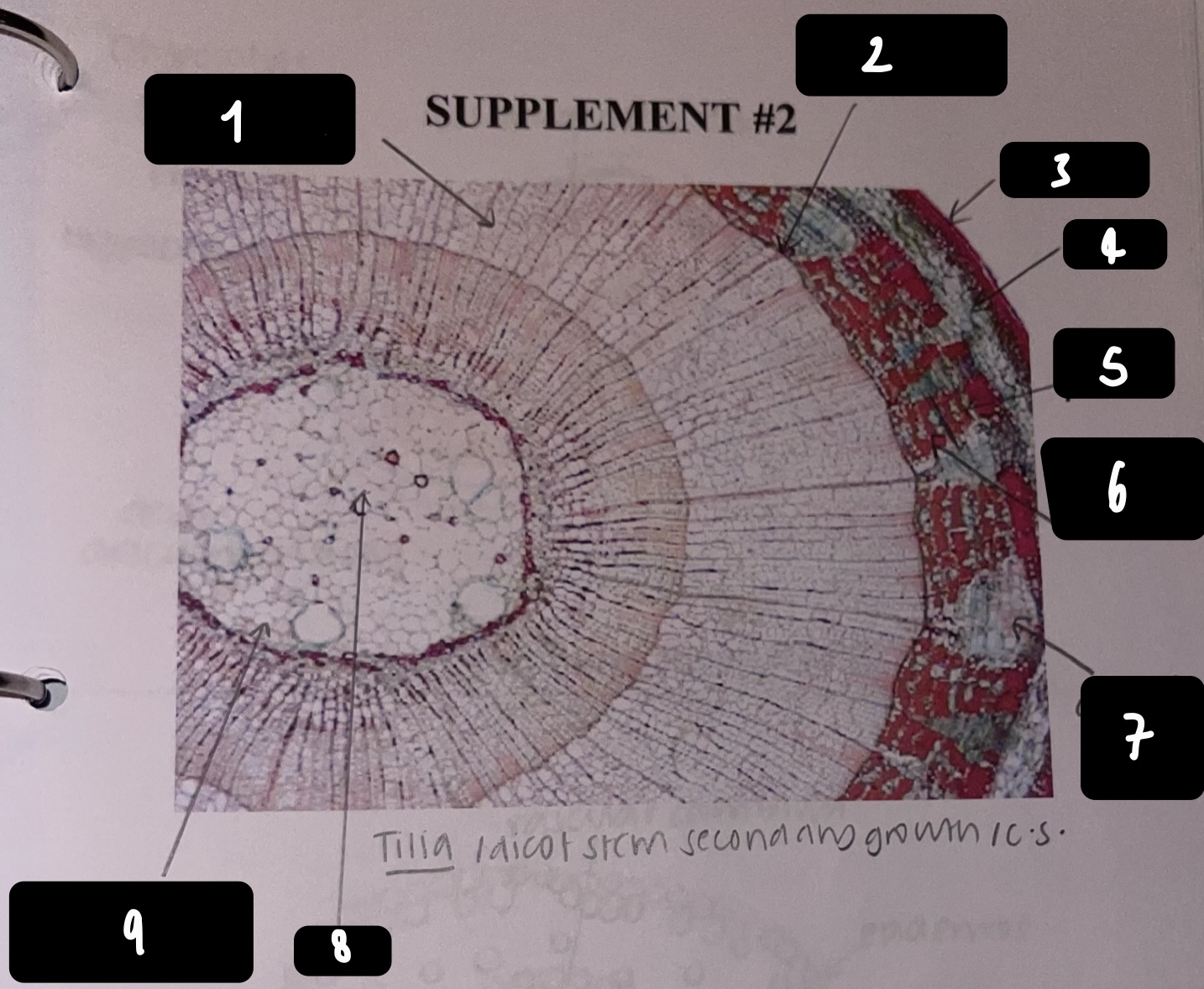
name the structure in label 9
primary xylem
73
New cards
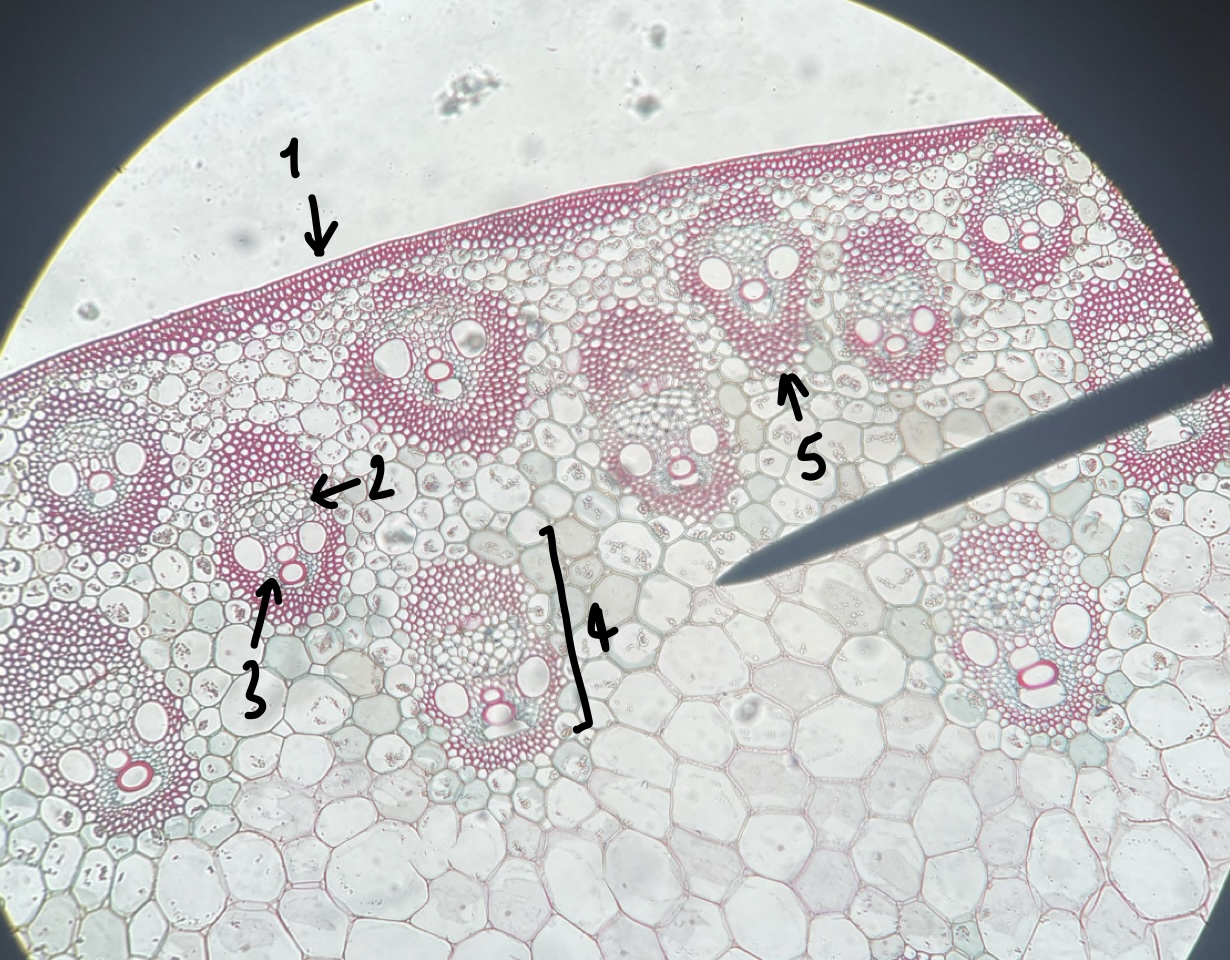
what genus of Liliopsida stem did we observe
__Zea__
74
New cards
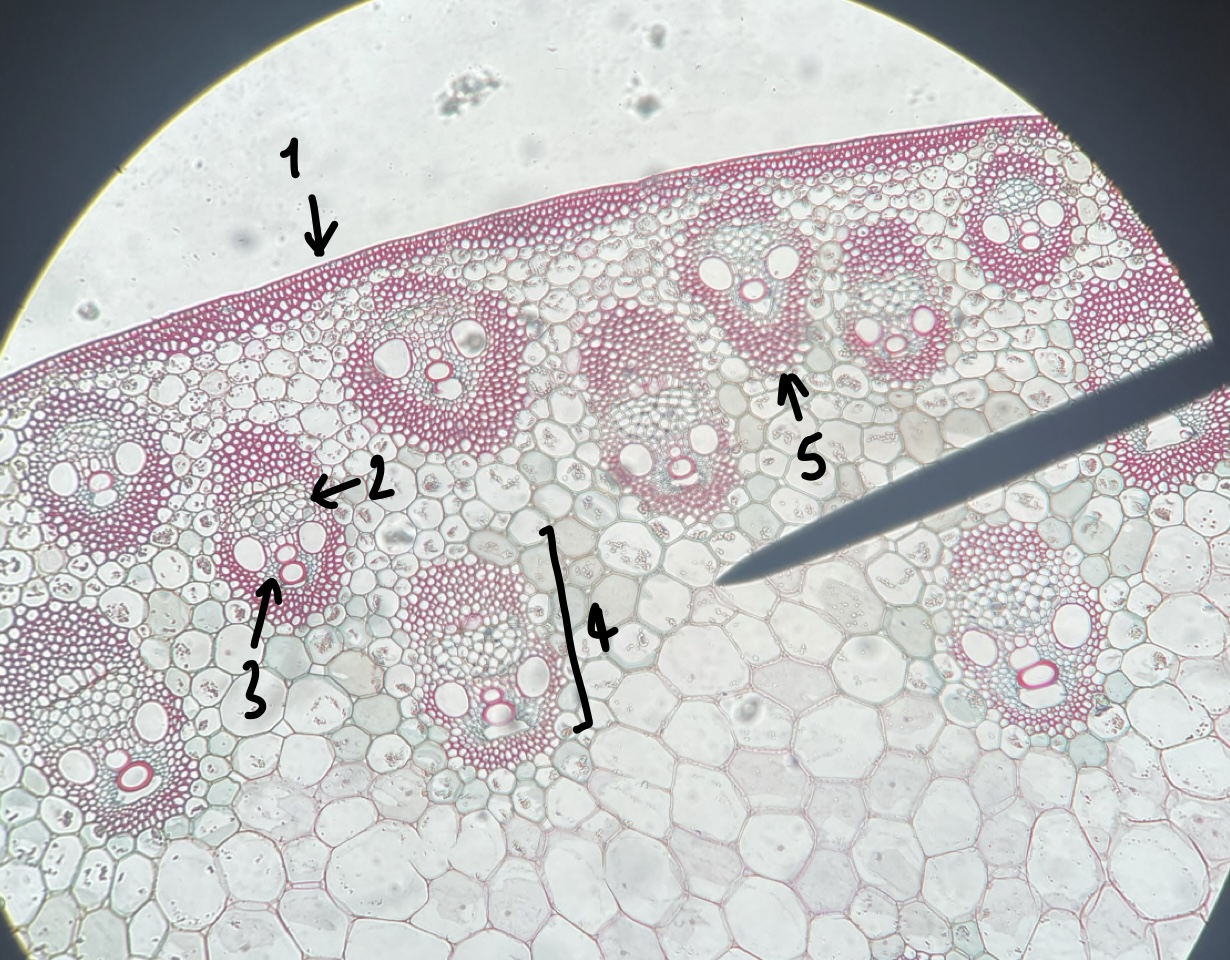
the stem of a __Zea__ plant has numerous vascular bundles which are …
scattered
75
New cards
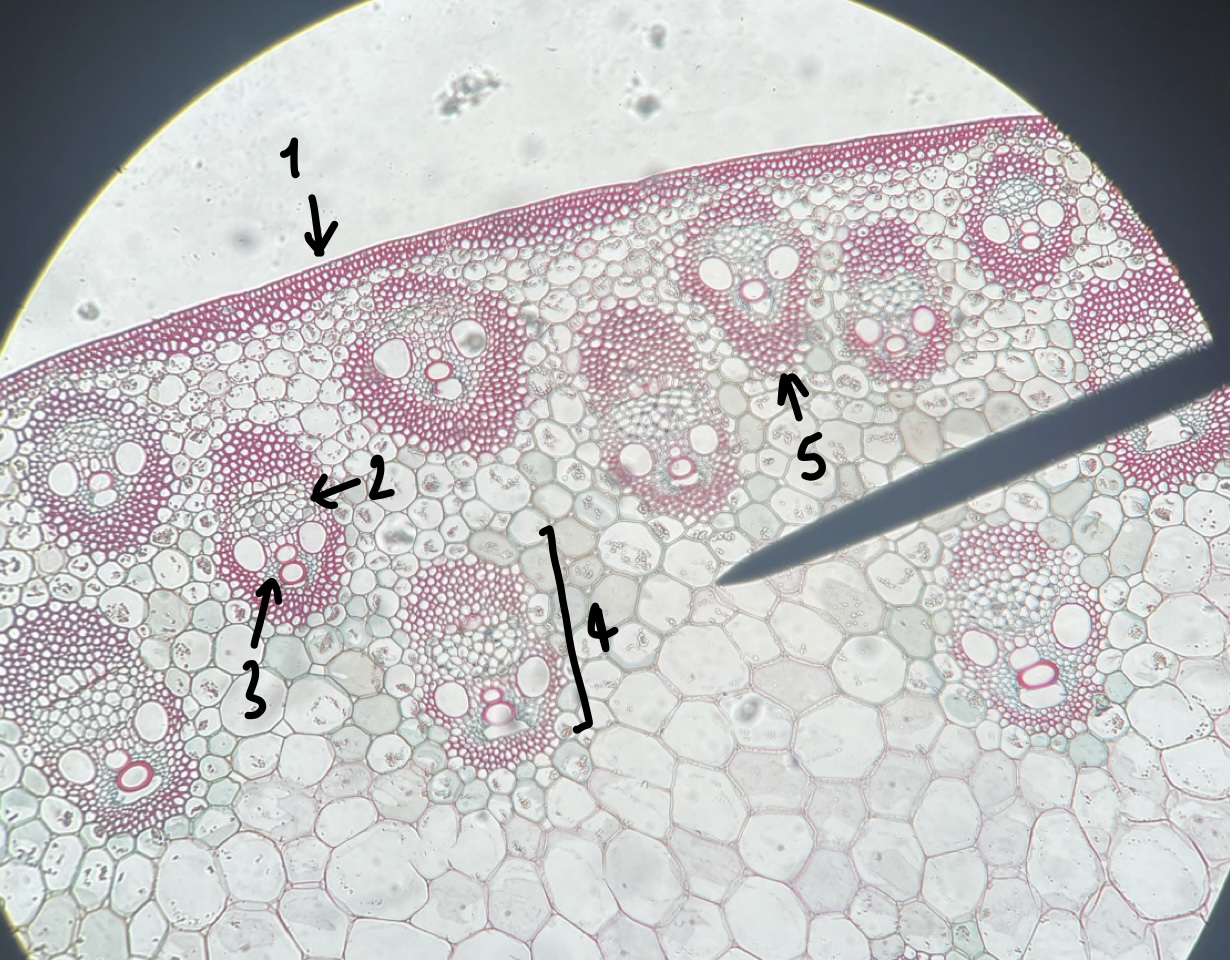
what type of general and specific stele type does a __Zea__ stem have
actatostele
76
New cards
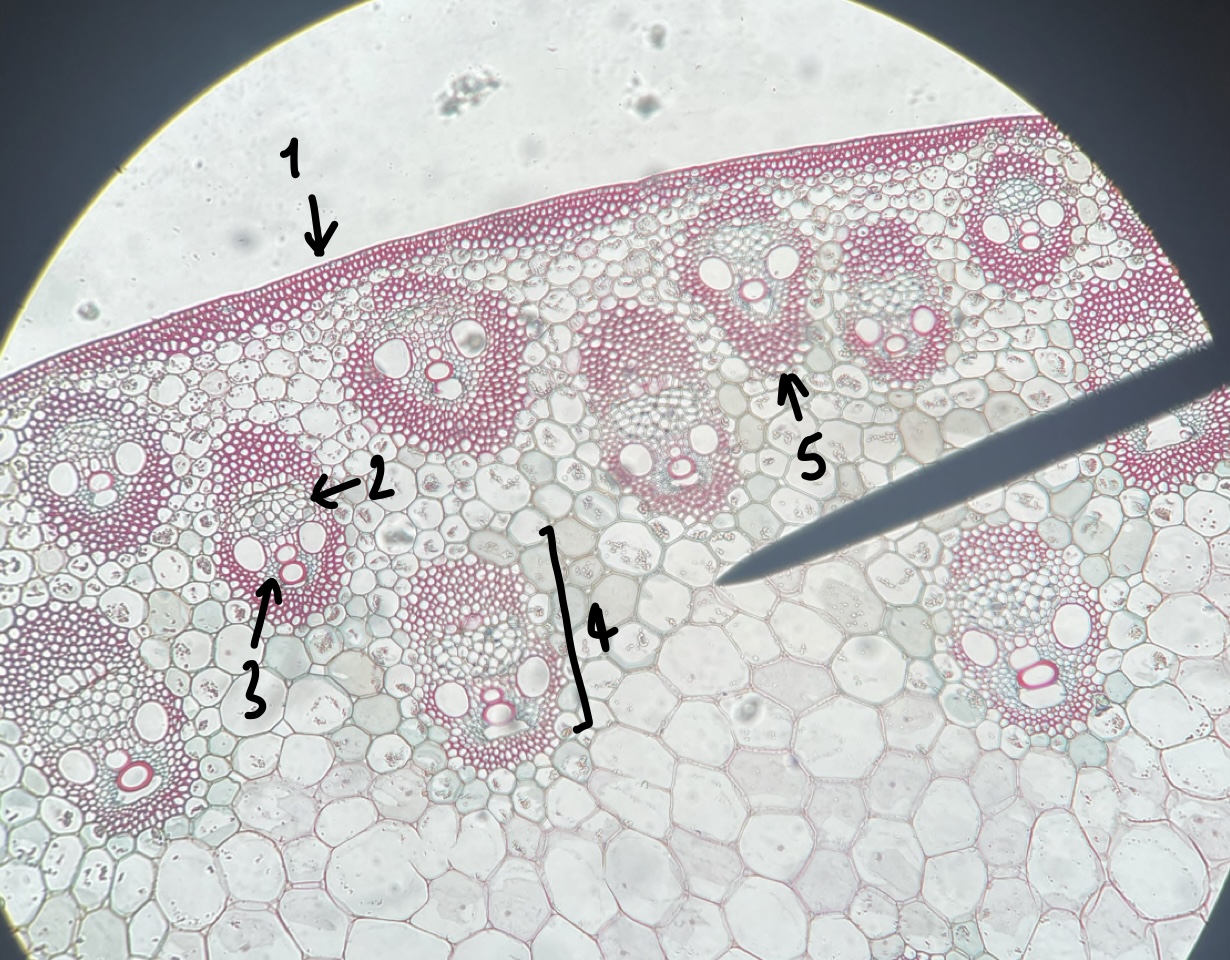
name the structure in label 1
epidermis
77
New cards
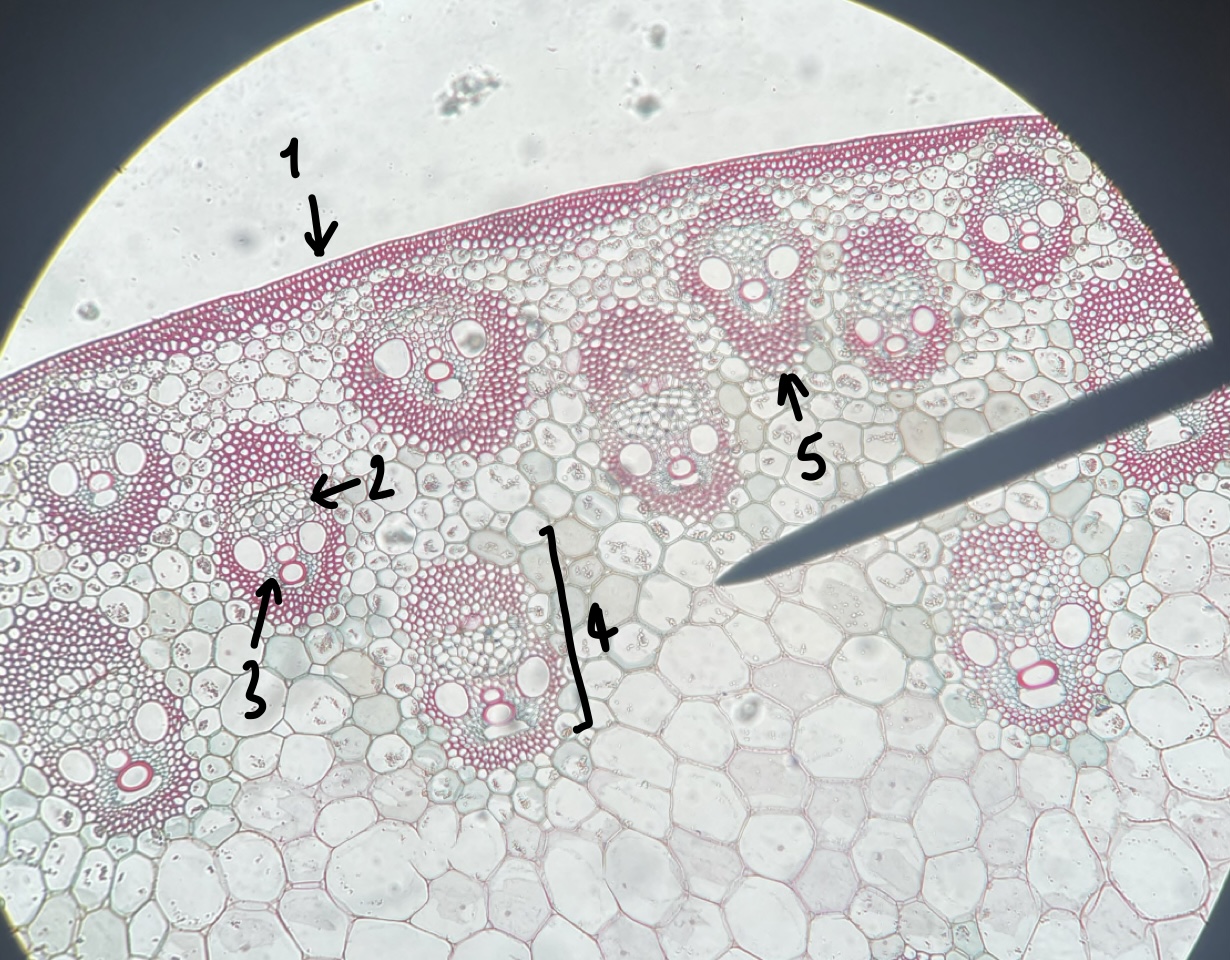
name the structure in label 2
phloem
78
New cards
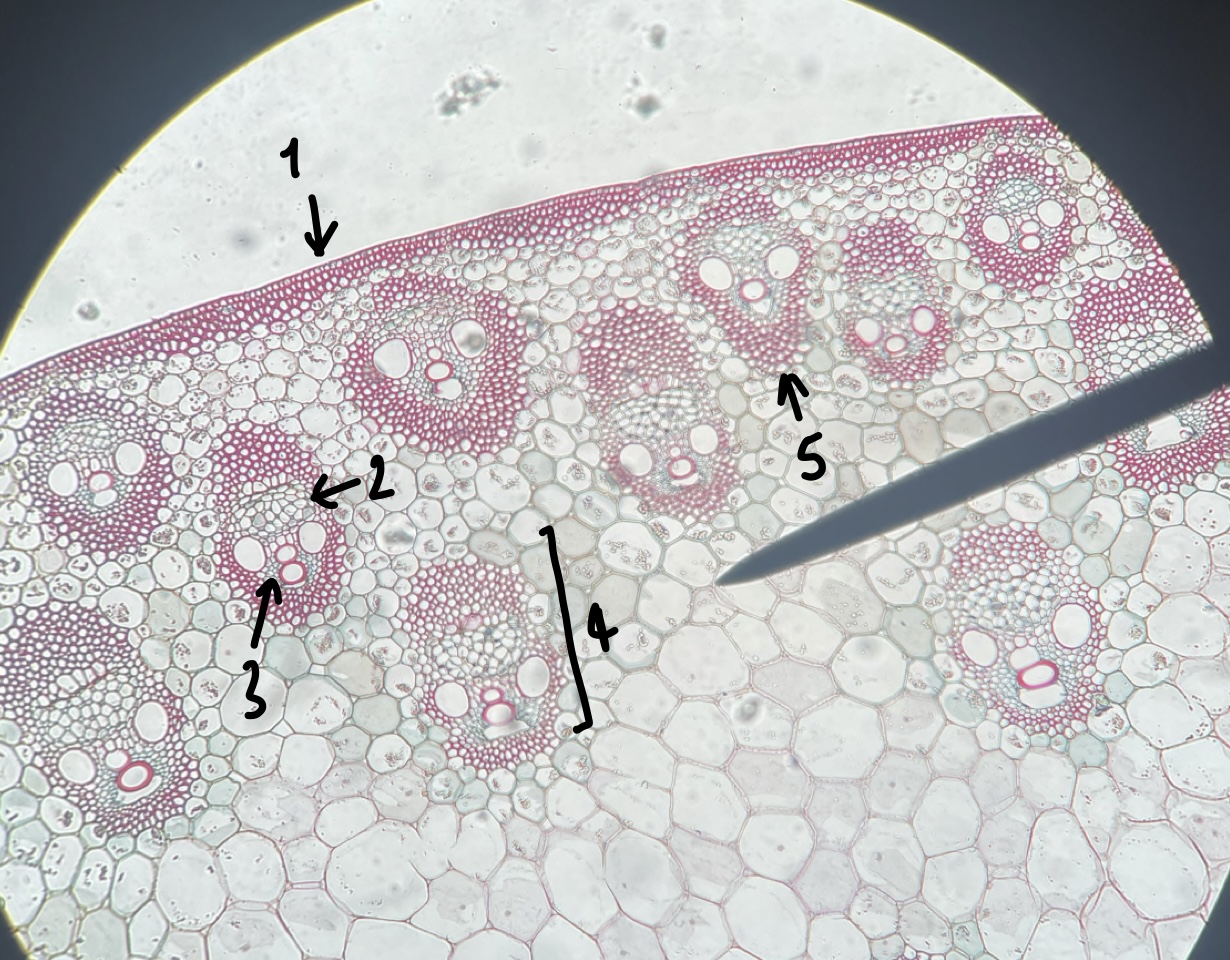
name the structure in label 3
xylem
79
New cards
name the structure in label 4
vascular bundle
80
New cards
name the structure in label 5
bundle sheath
81
New cards
what are the three type of Magnoliopsida leaves did we observe
Hydrophyte
Mesophyte
Xerophyte
Mesophyte
Xerophyte
82
New cards
a hydrophyte leaf is known to be adapted to
aquatic habitats with abundant moisture
83
New cards
what genus of Magnoliopsida possess hydrophyte leaves
__Nymphea__
84
New cards
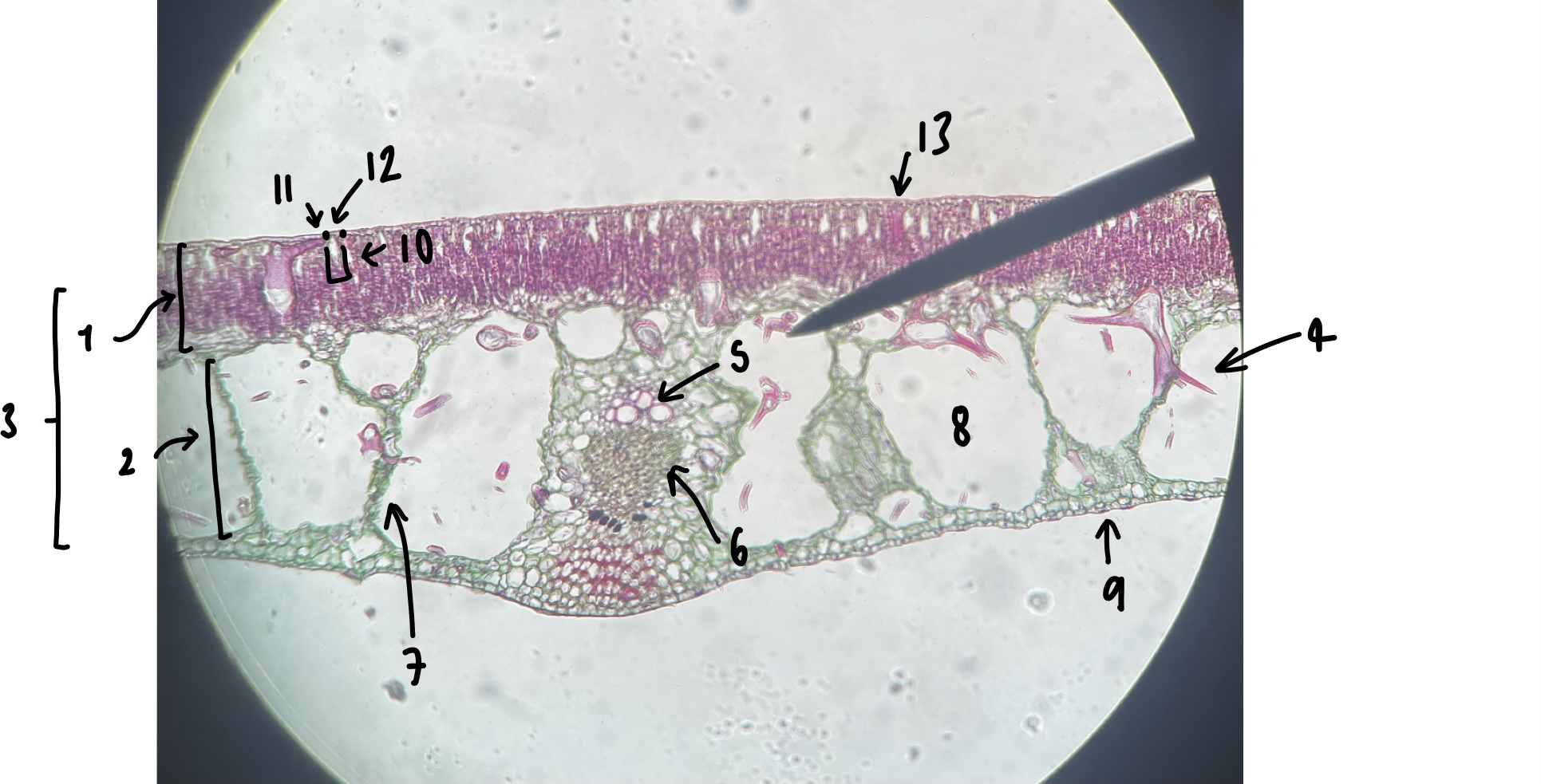
name the structure in label 1
palisade mesophyll (uppermost layer)
85
New cards
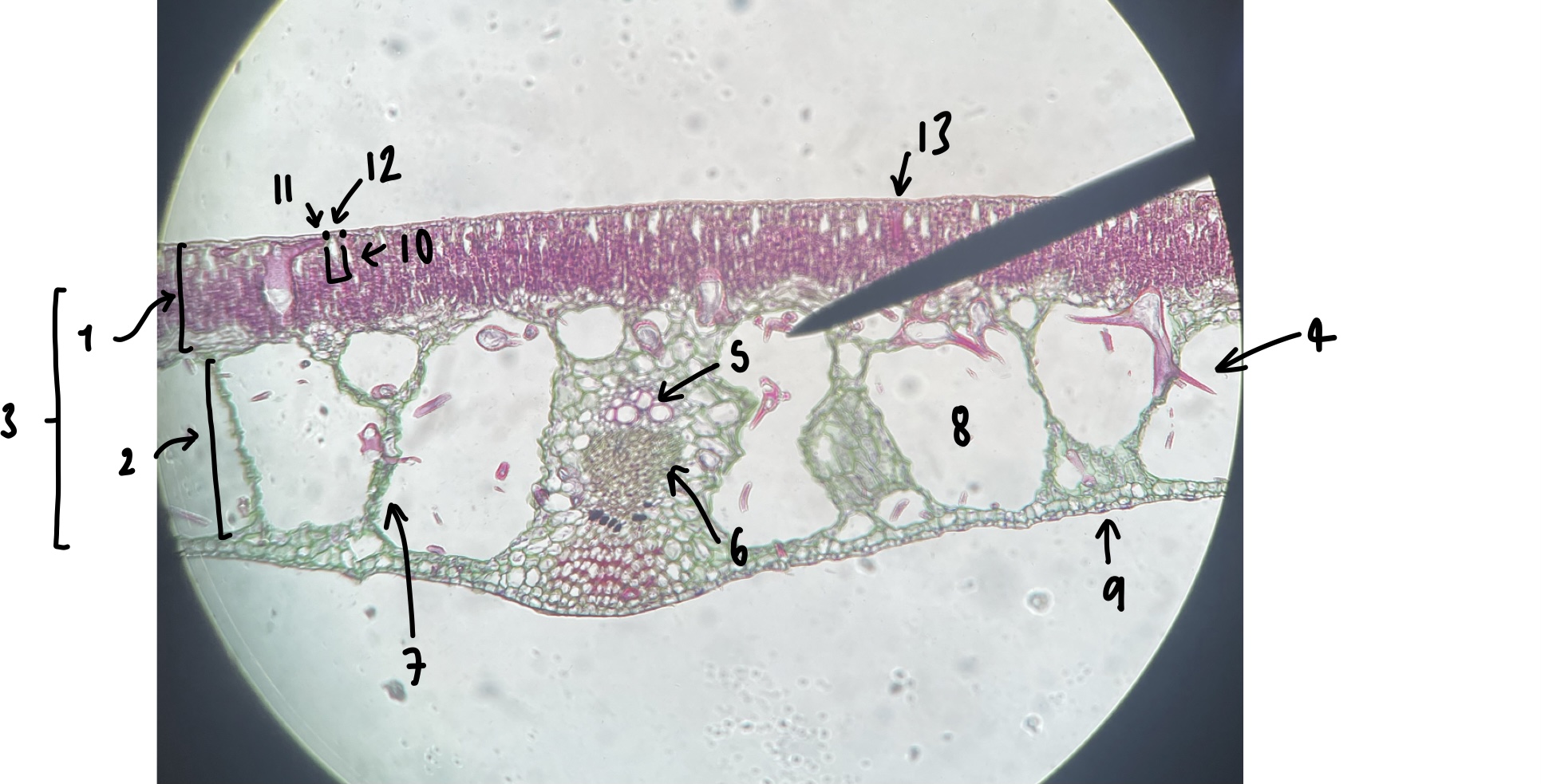
name the structure in label 2
spongy mesophyll (lowermost layer)
86
New cards
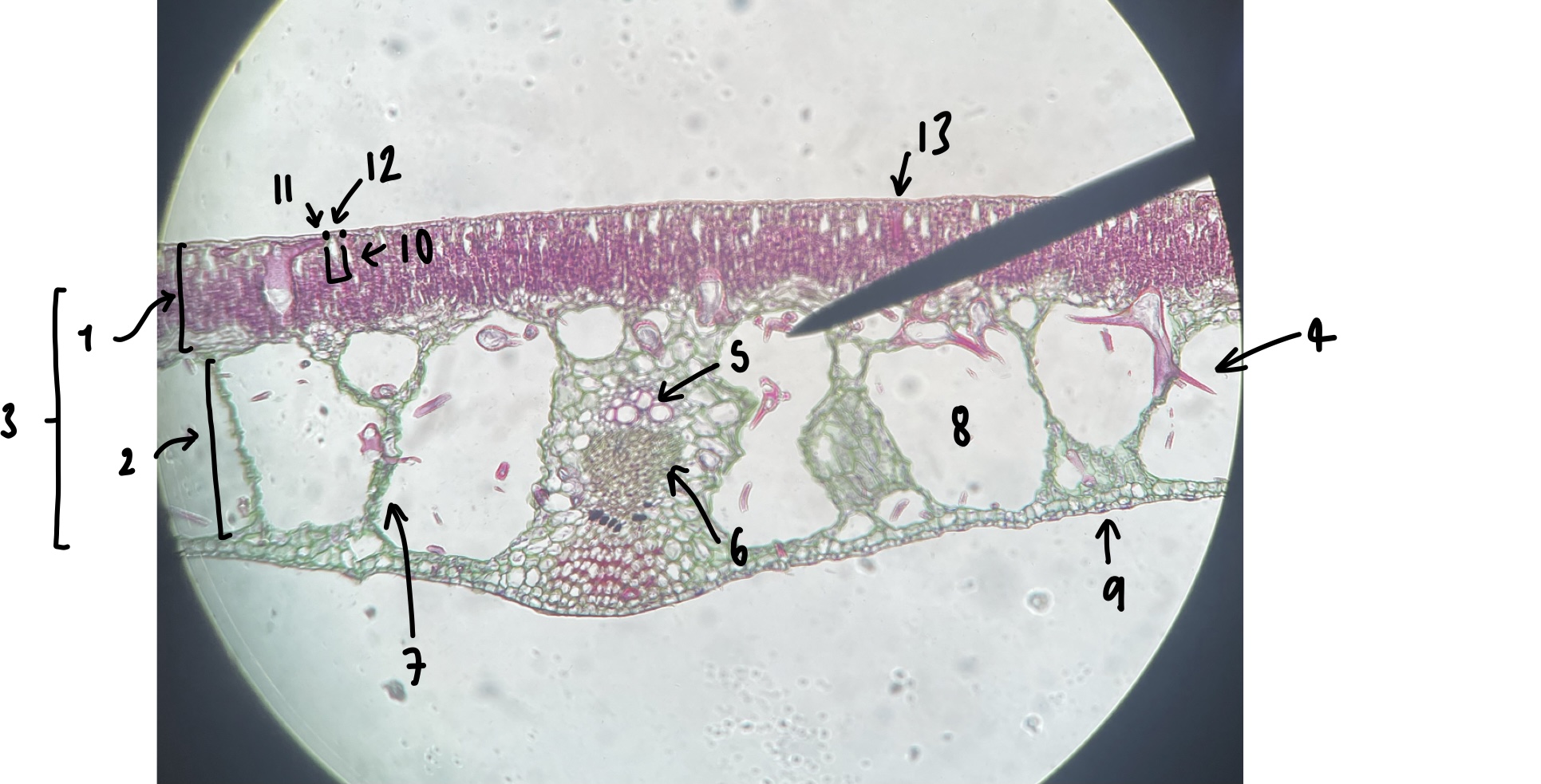
name the structure in label 3
mesophyll
87
New cards
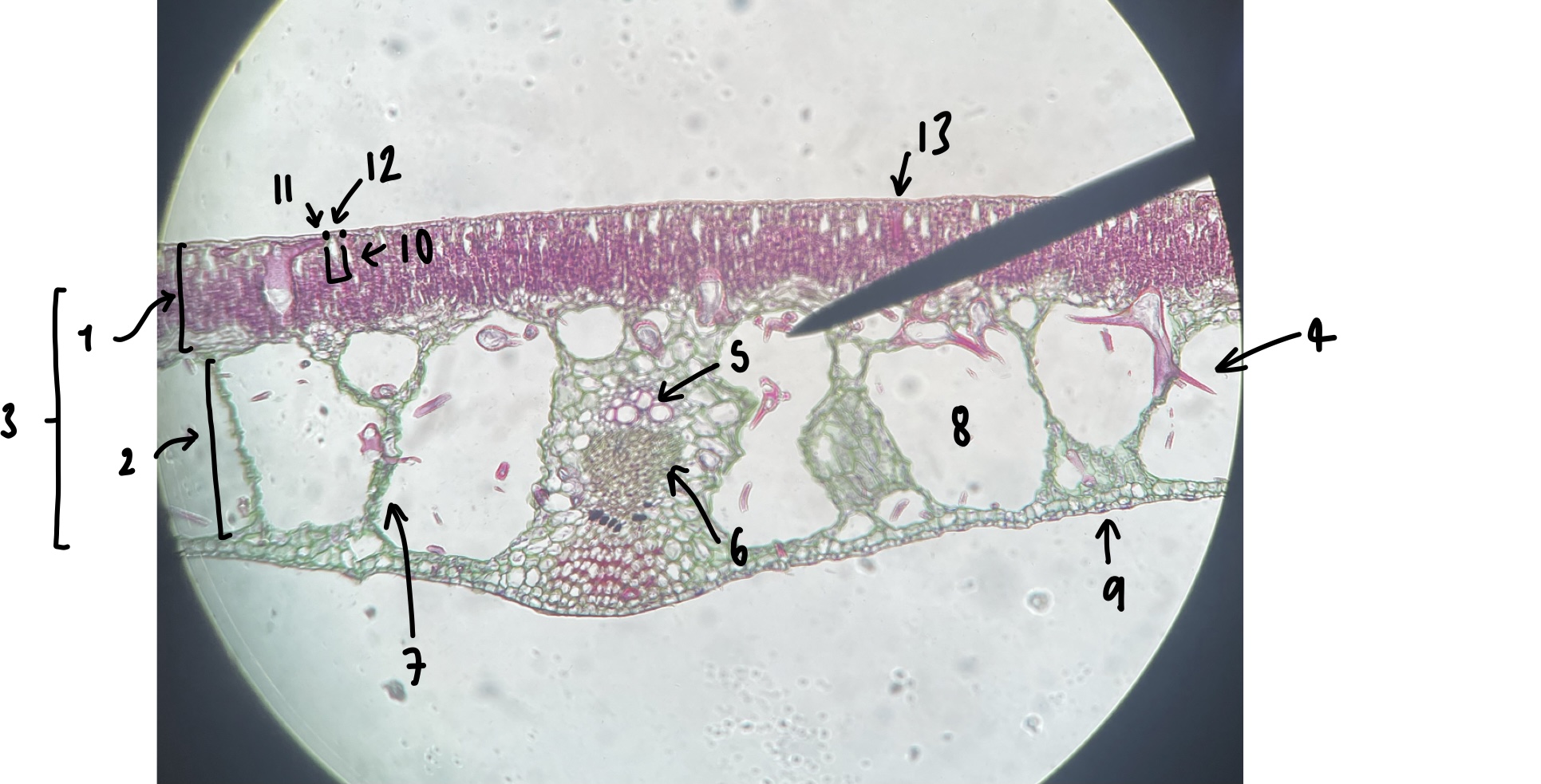
name the structure in label 4
Trichosclereid (large irregular shaped mesophyll cell)
88
New cards
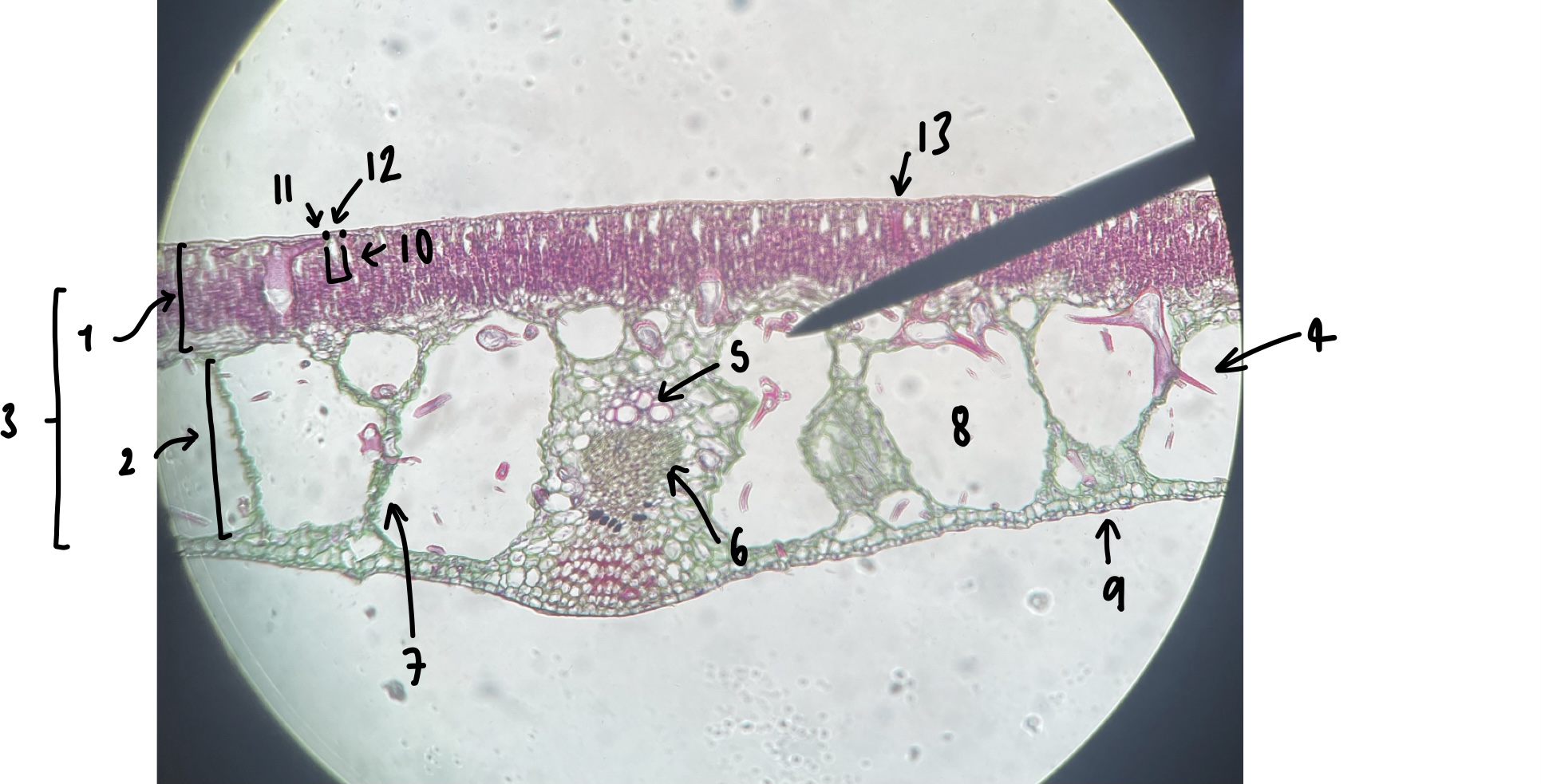
name the structure in label 5
xylem
89
New cards
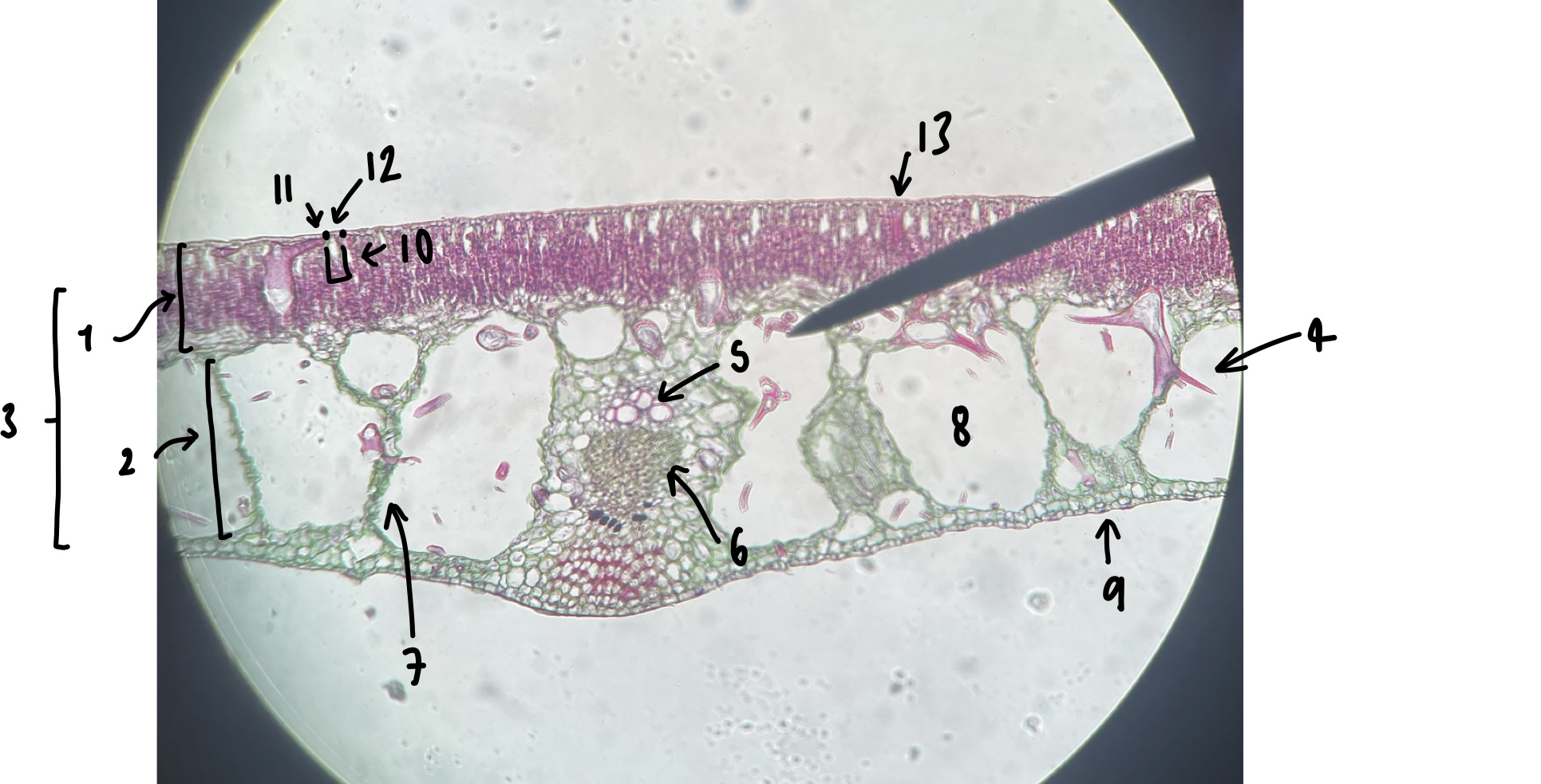
name the structure in label 6
phloem
90
New cards
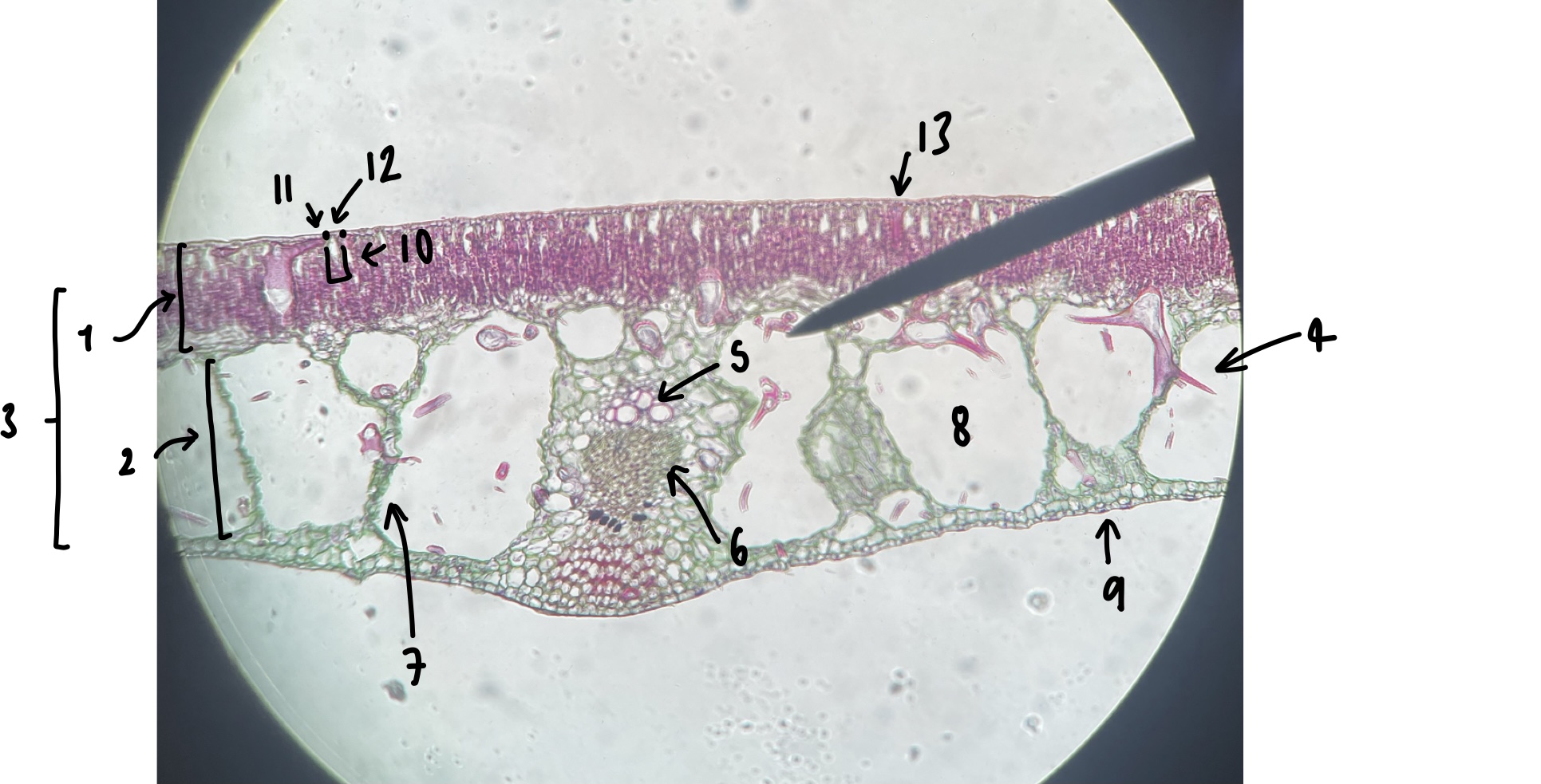
name the structure in label 7
vascular trace
91
New cards
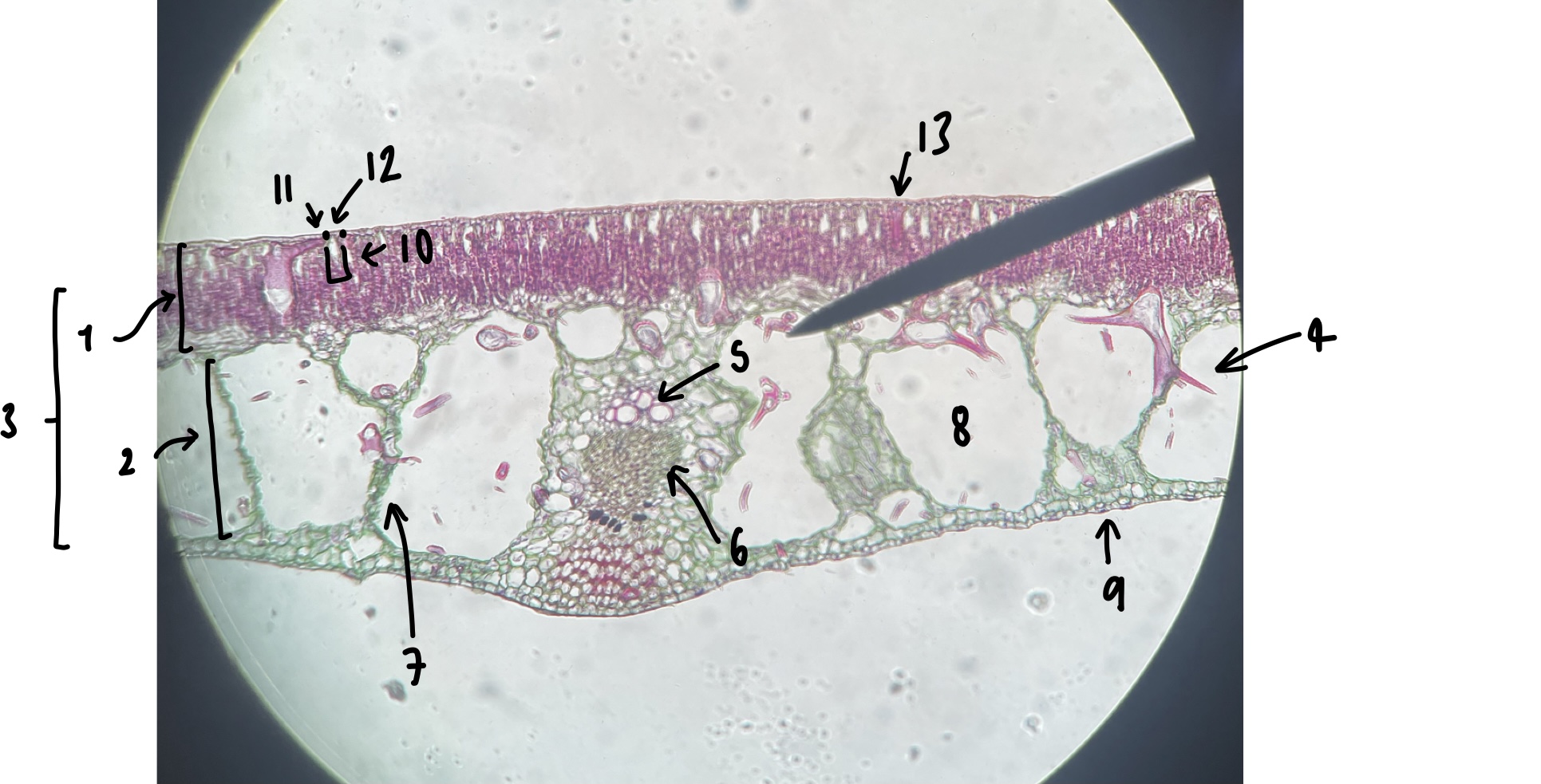
name the structure in label 8
air space (within spongy mesophyll)
92
New cards
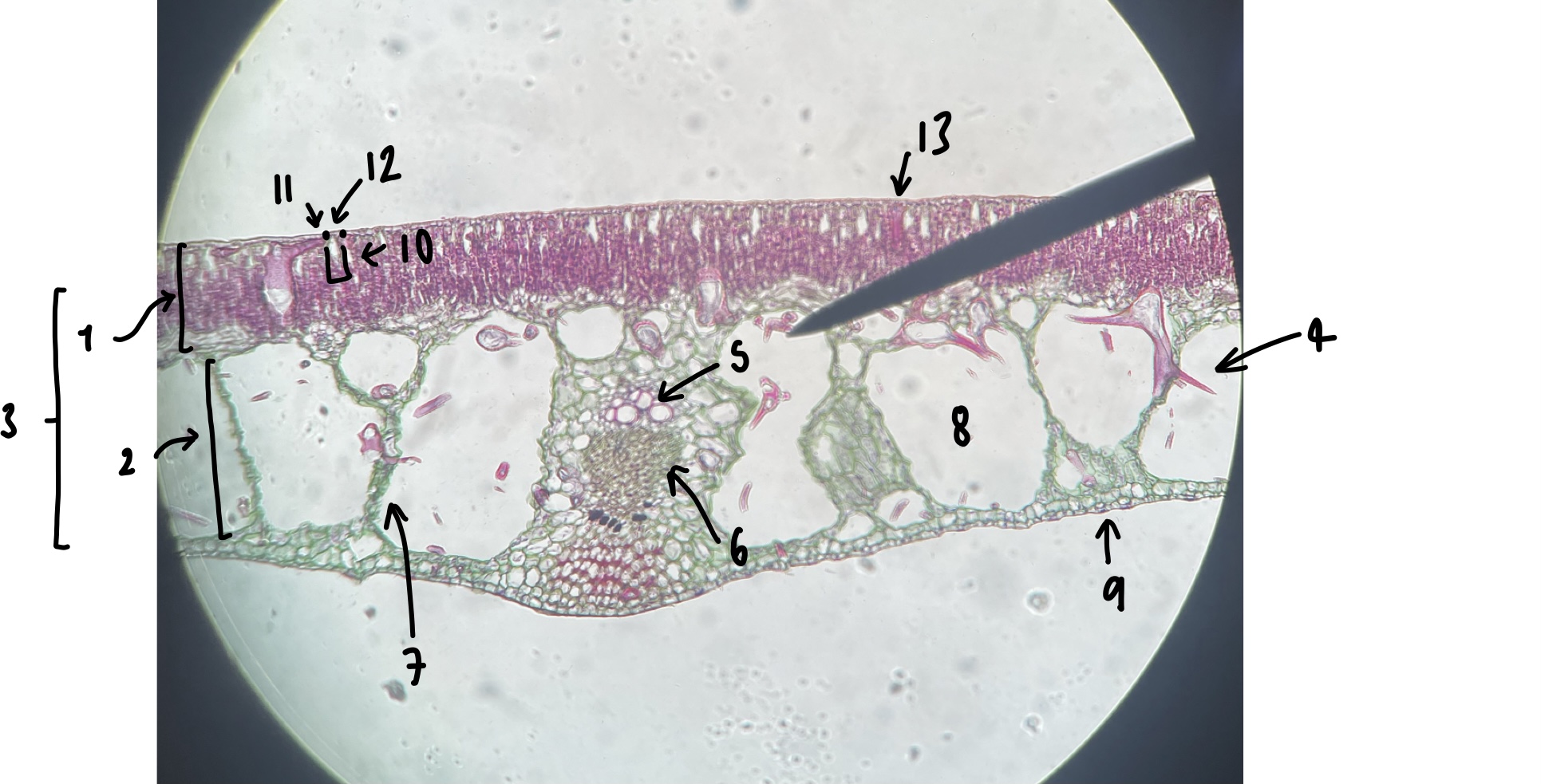
name the structure in label 9
abaxial epidermis
93
New cards
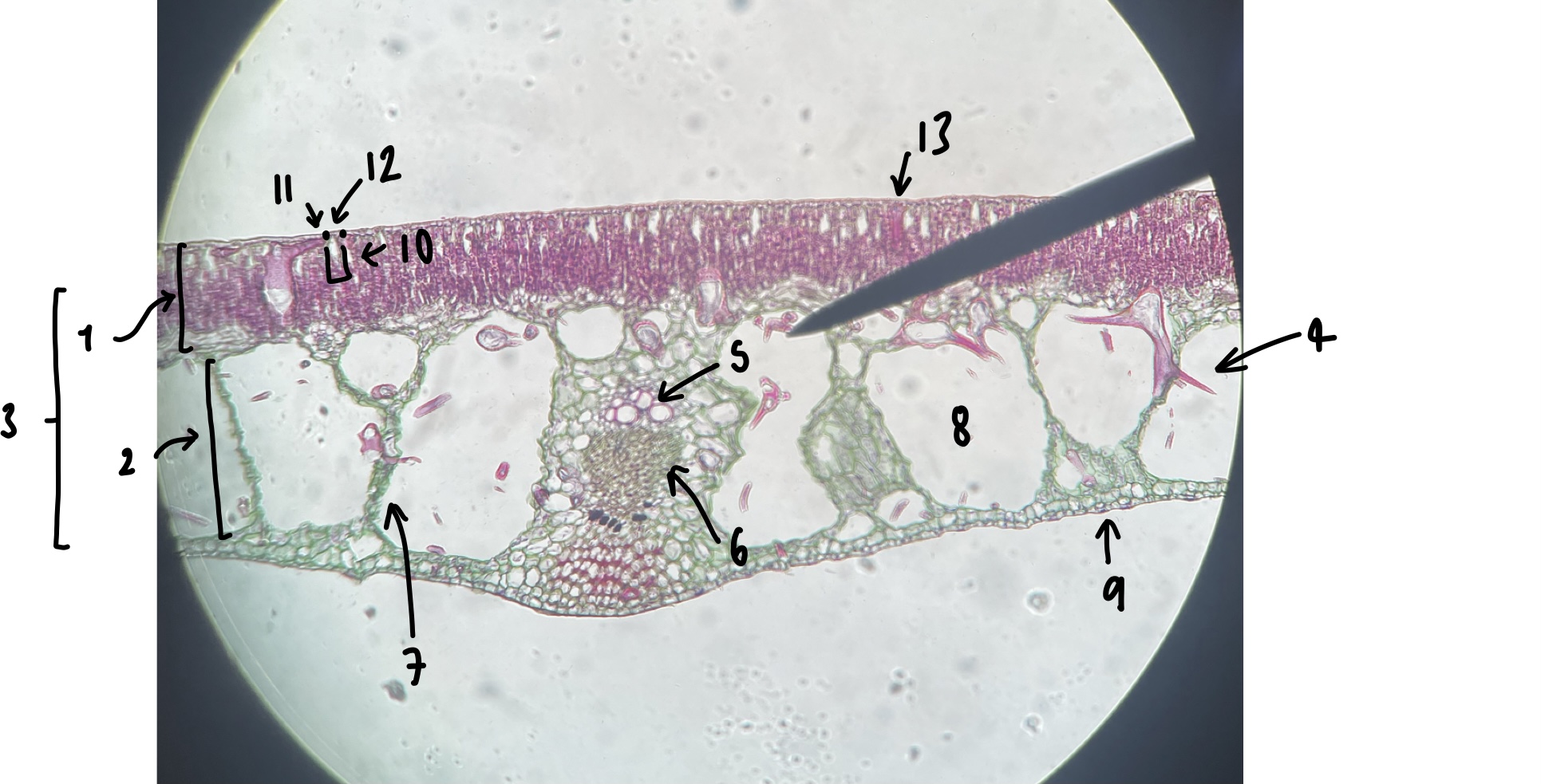
name the structure in label 10
stomatal chamber
94
New cards
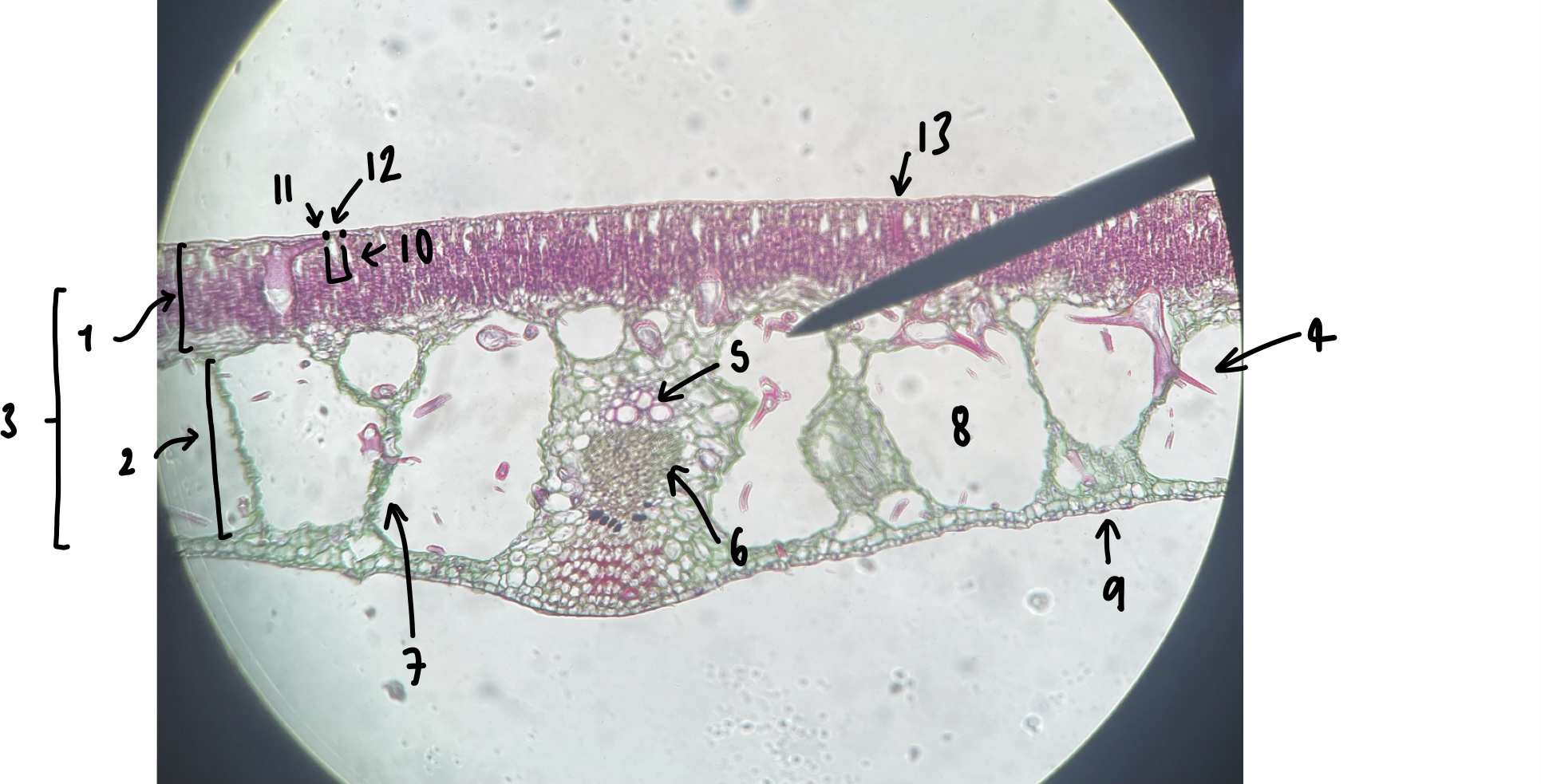
name the structure in label 11
guard cells
95
New cards
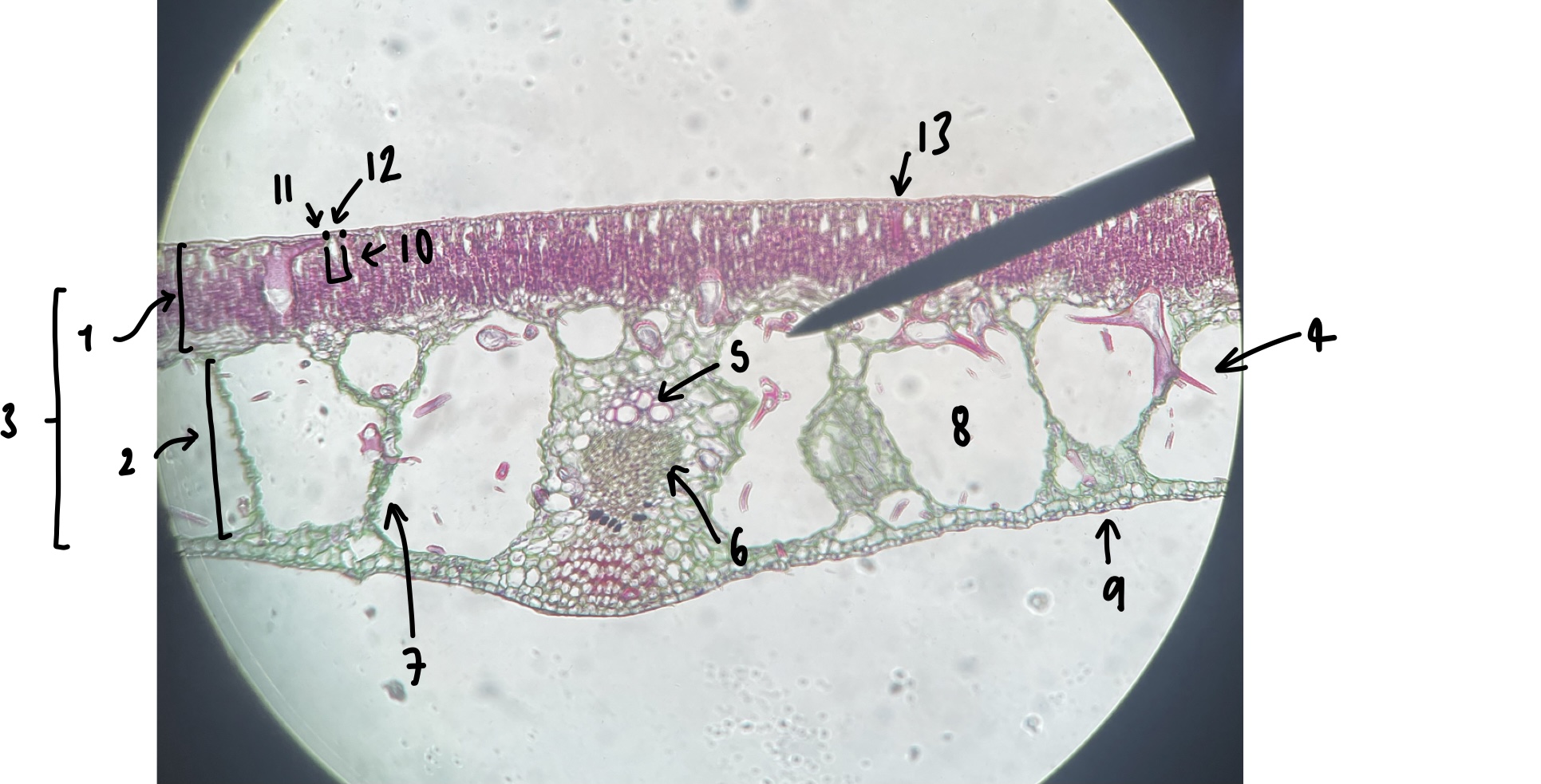
name the structure in label 12
adaxial stomate
96
New cards
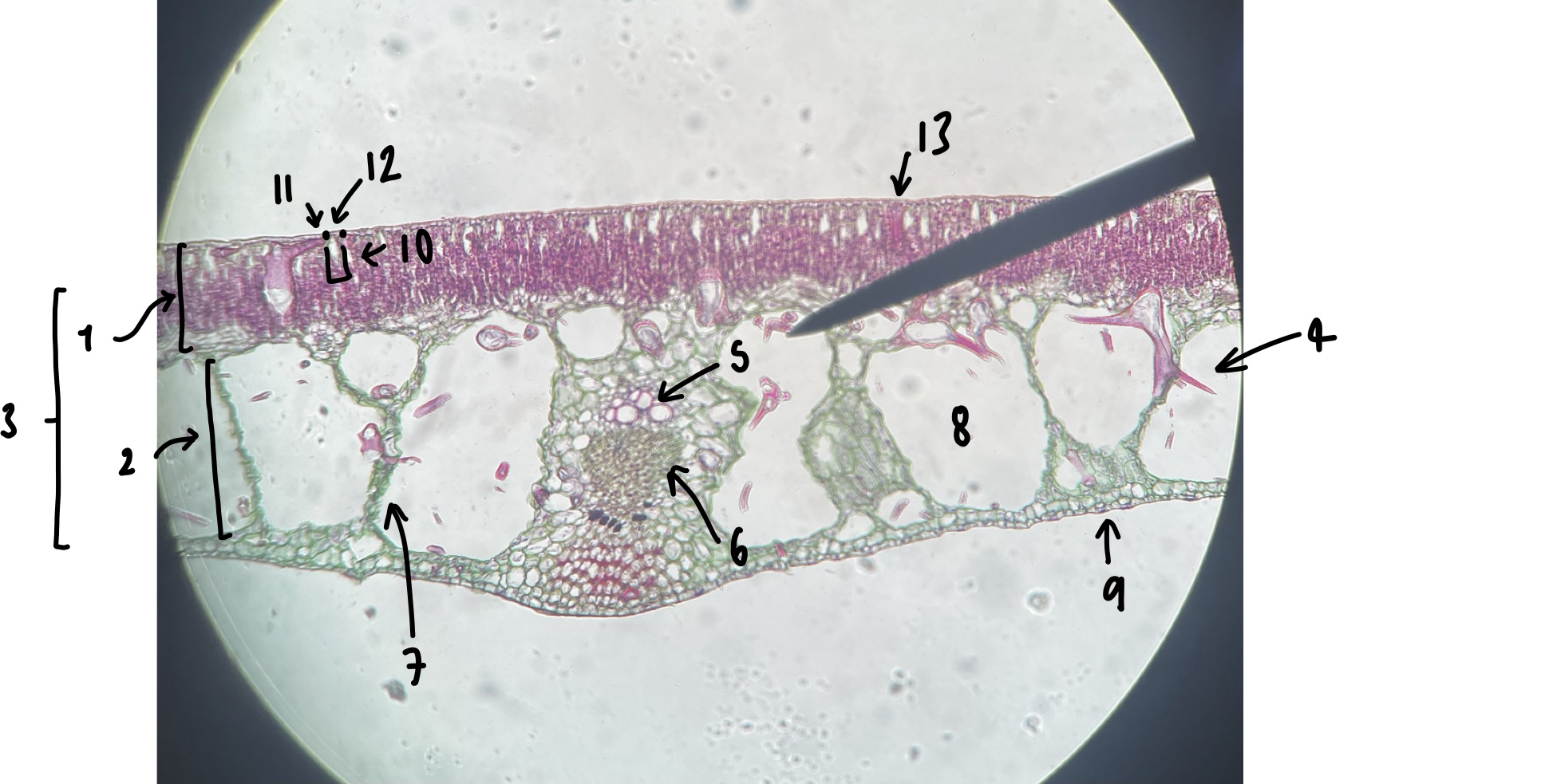
name the structure in label 13
adaxial epidermis
97
New cards
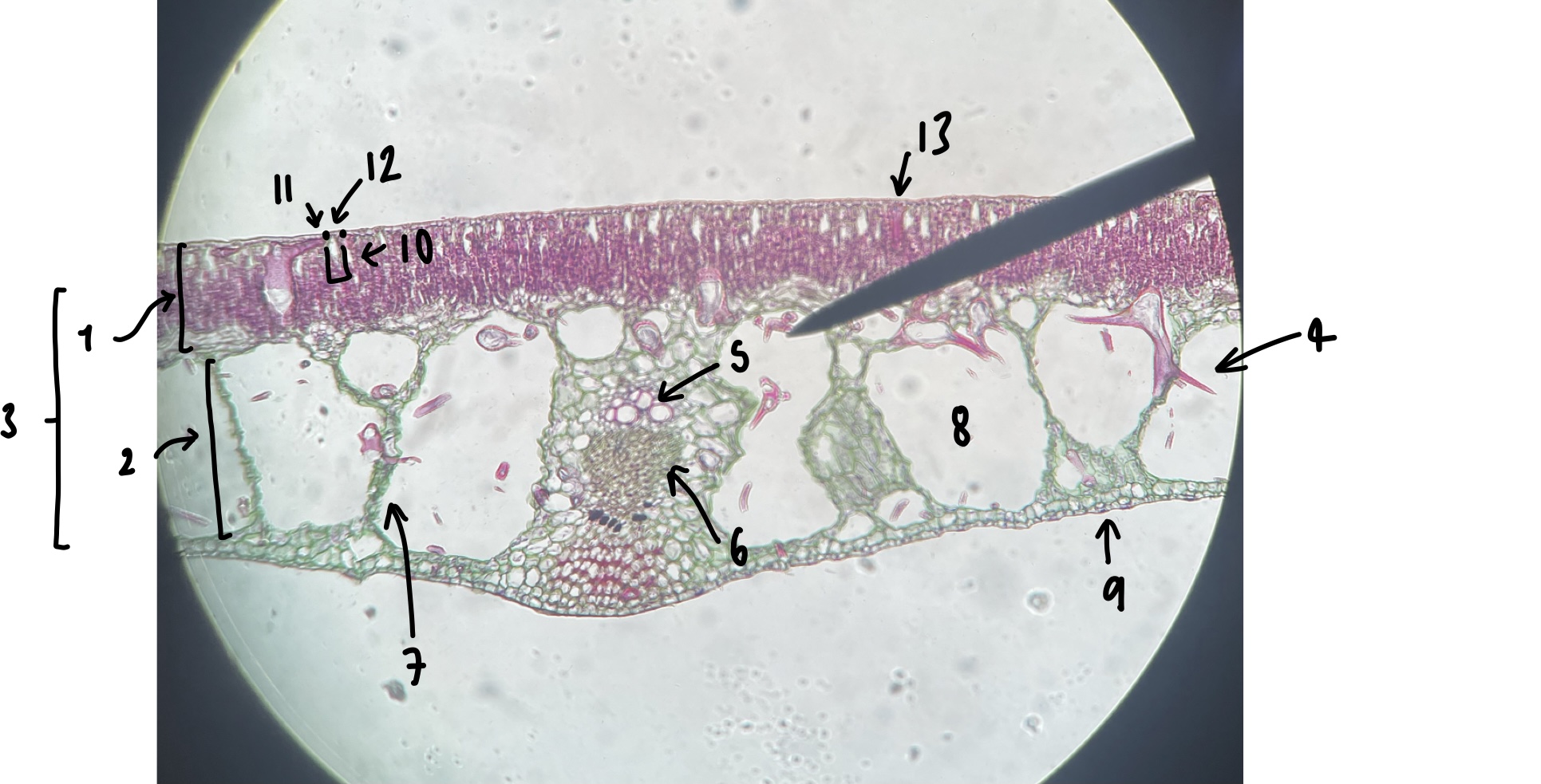
give three characters of a hydrophyte leaf we observed
little to no cuticle
large air spaces
adaxial stomates
large air spaces
adaxial stomates
98
New cards
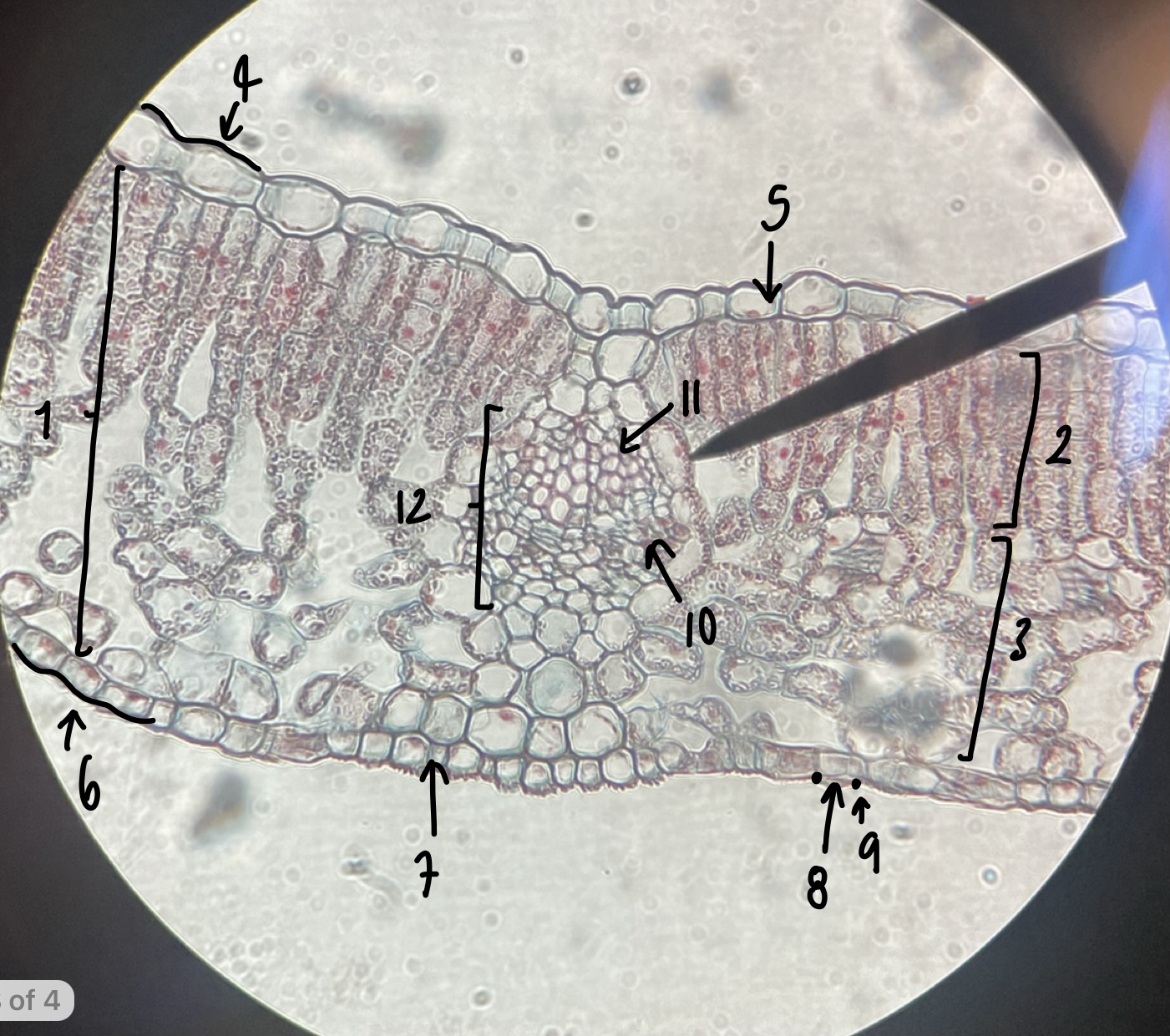
a mesophyte leaf is known to be adapted to habitats with
moderate moisture
99
New cards
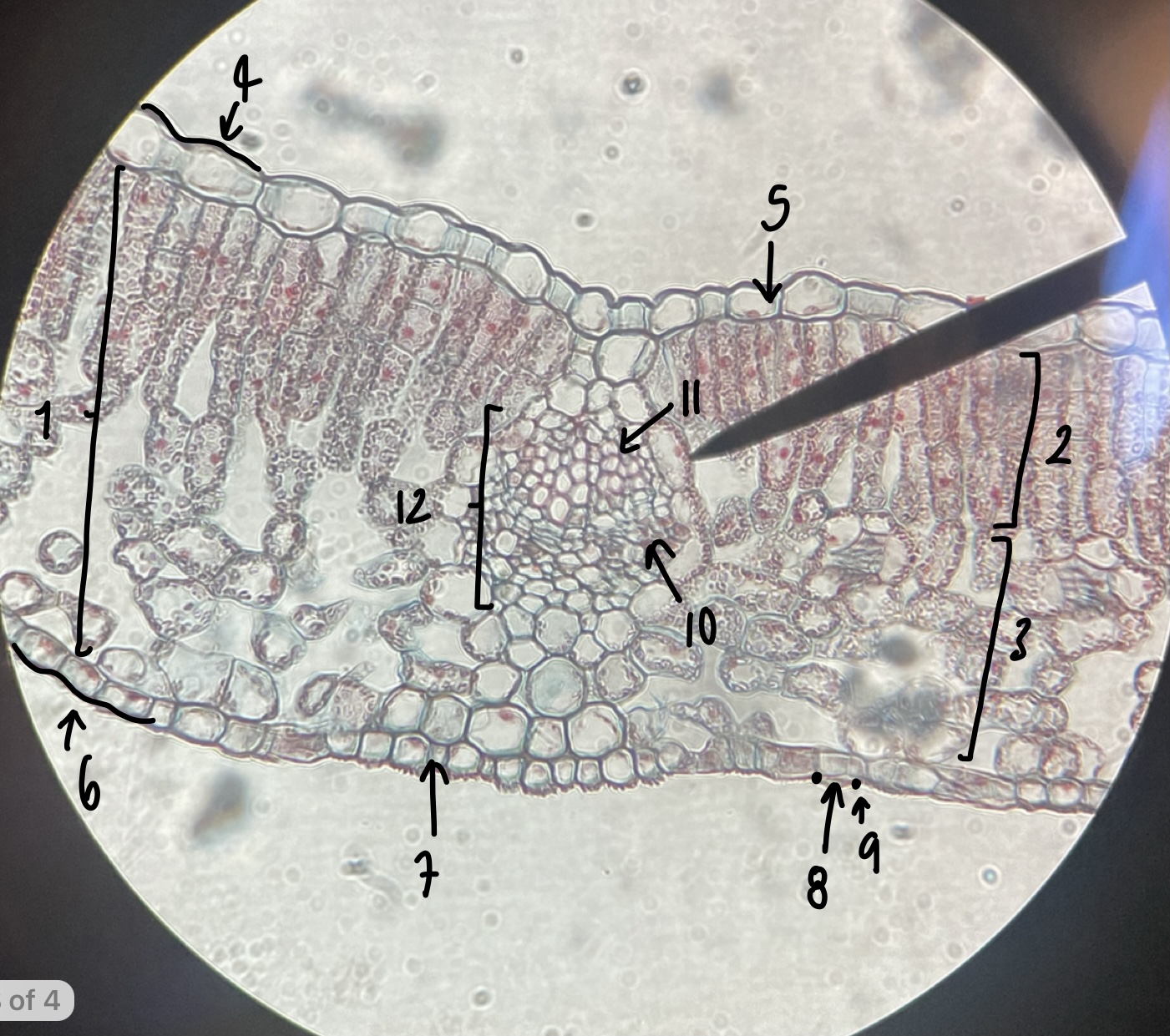
what genus of Magnoliopsida possesses mesophyte leaves
__Syringia__
100
New cards
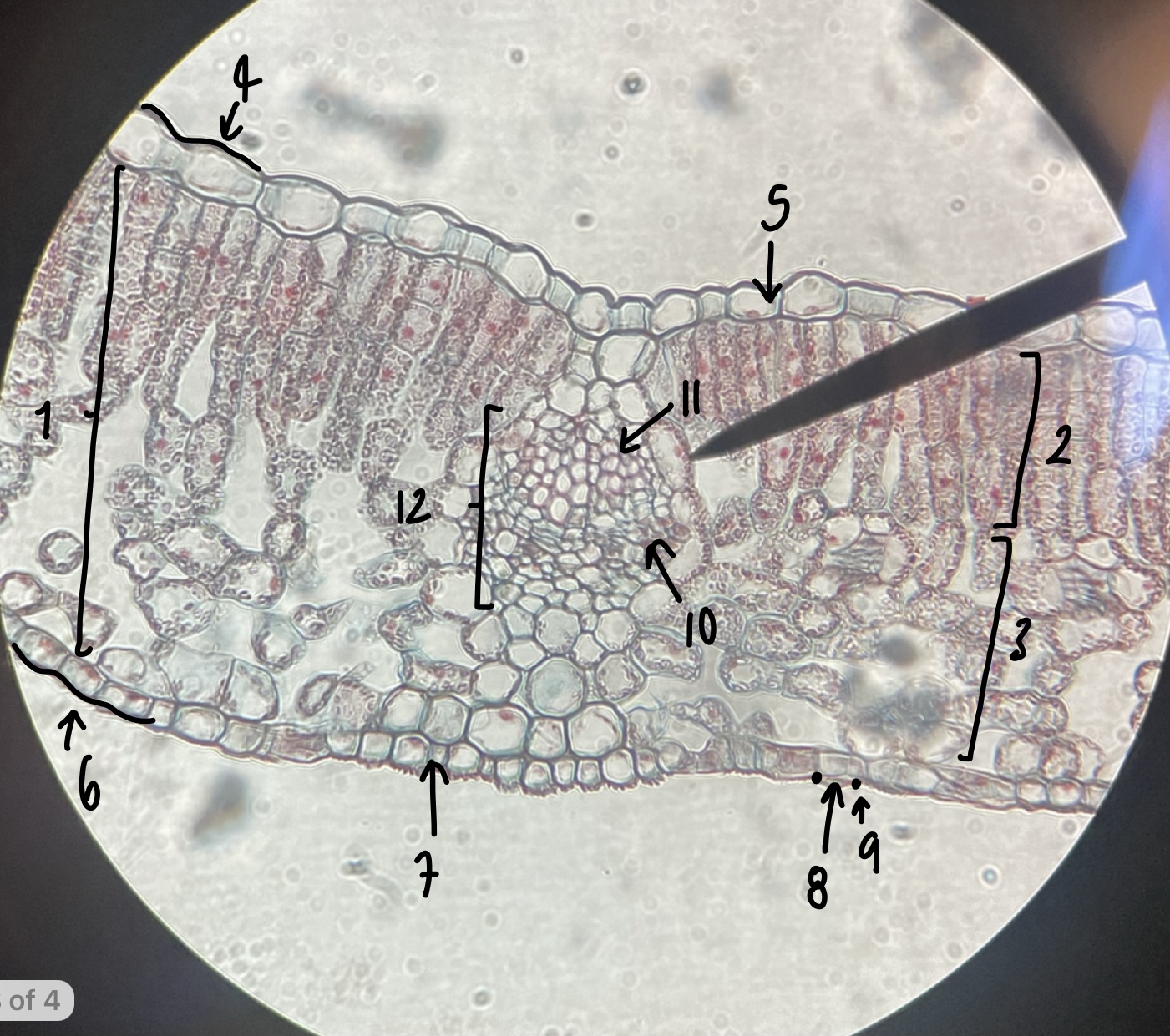
name the structure in label 1
mesophyll