Campbell Biology Chapter 6
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
light microscopy
magnification of cellular structures up to 1000 X
scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
image of 3D surface coated with heavy metal like gold (100,000 X)
transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
image of ultra thin slice to view intracellular components (500,000 x)
cell fractionation
technique that breaks cells and separates their components
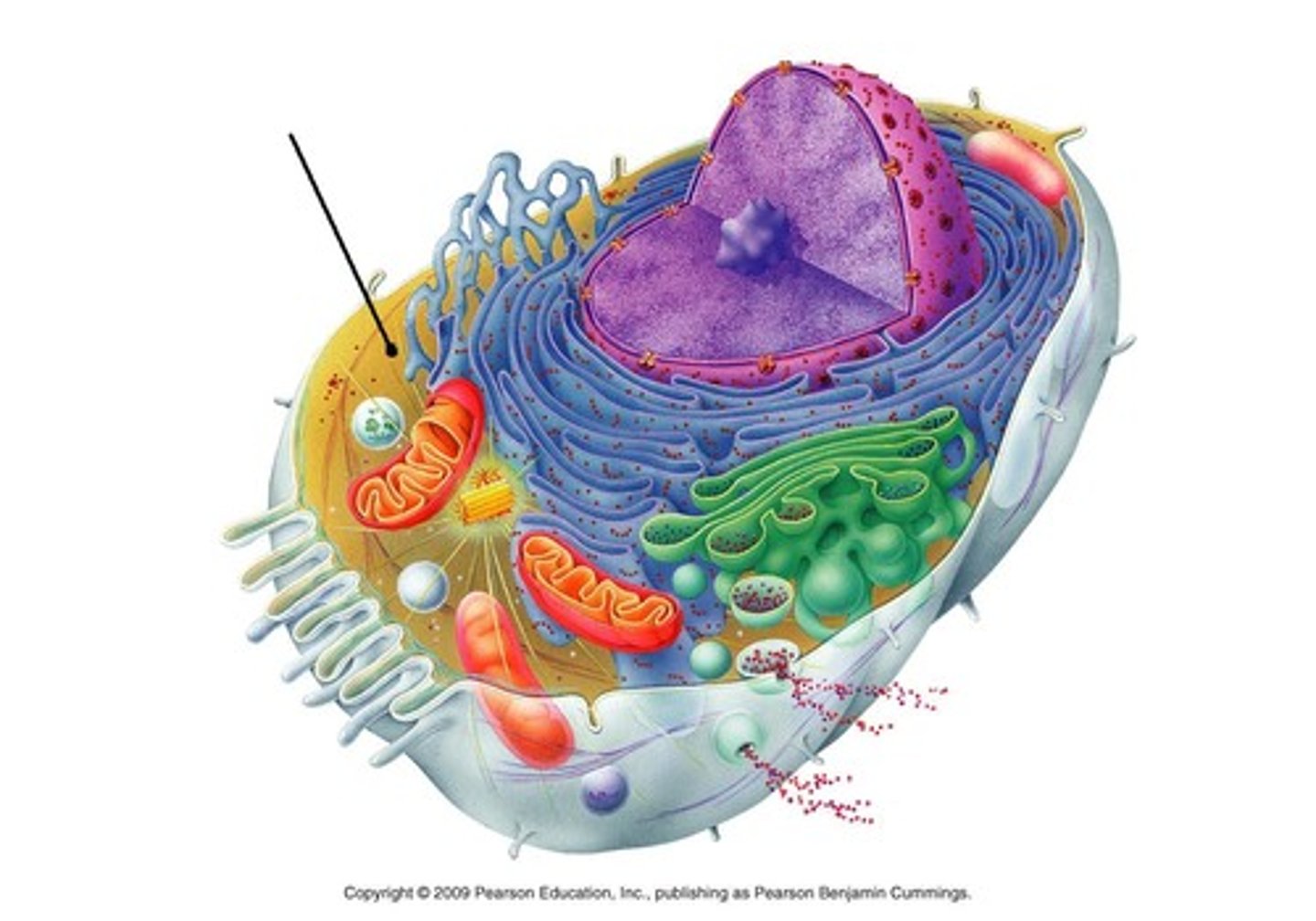
cytosol
aqueous part of cytoplasm within which particles and organelles are suspended
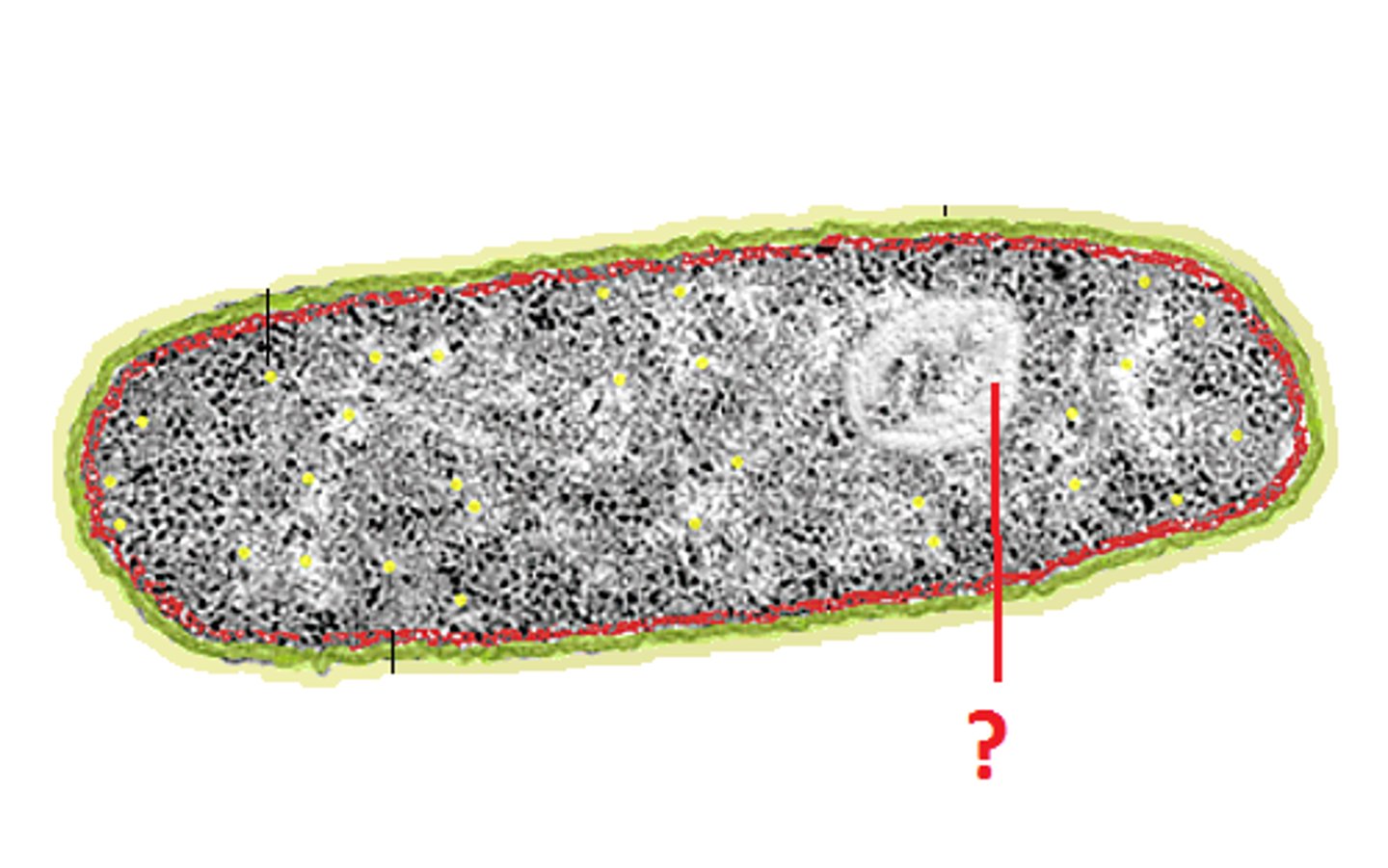
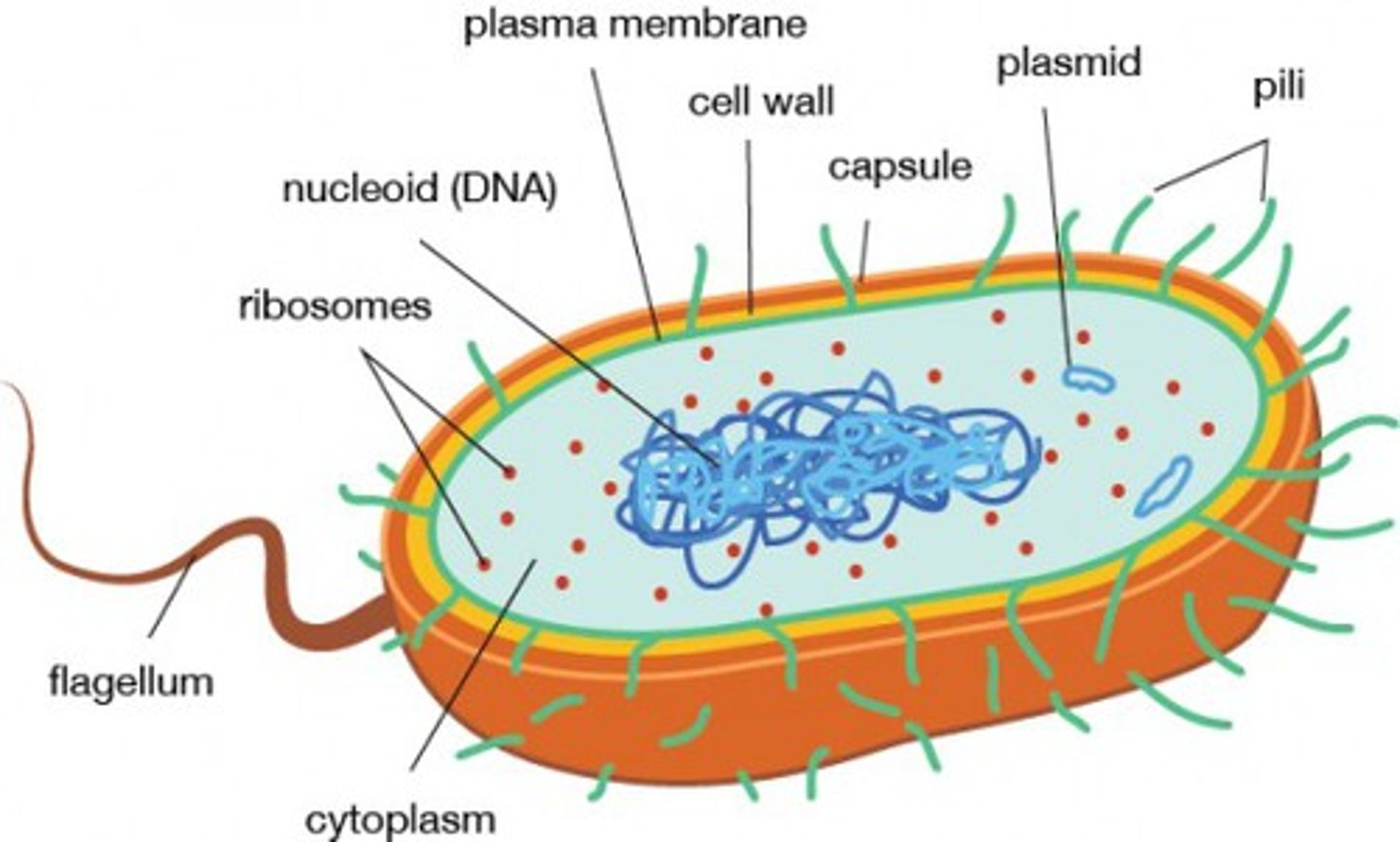
nucleoid
densly staining DNA region in a prokaryotic cell
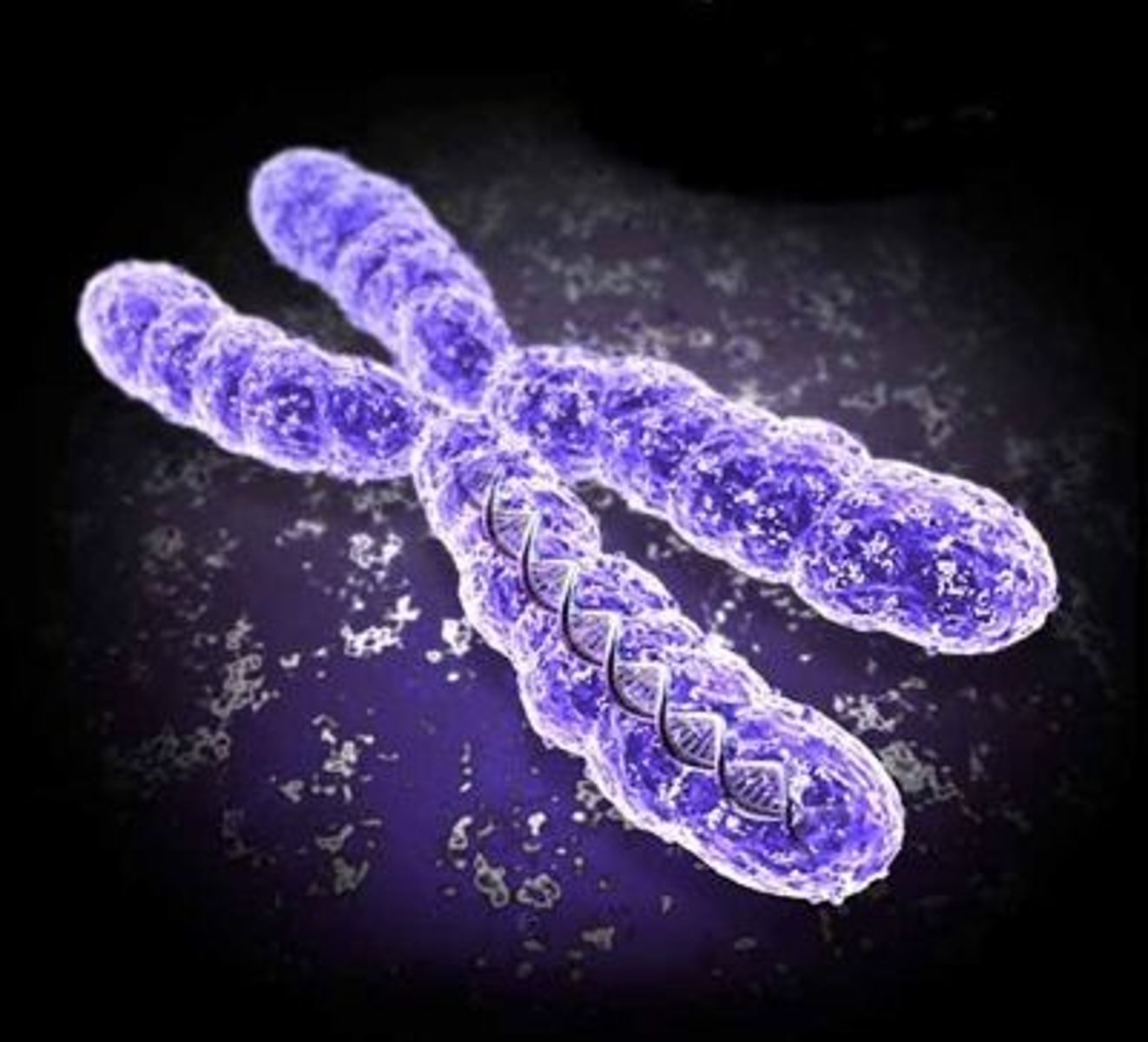
chromatin
uncondensed DNA wrapped around histones (used during transcription)
chromosome
condensed chromatin (used during cell division)
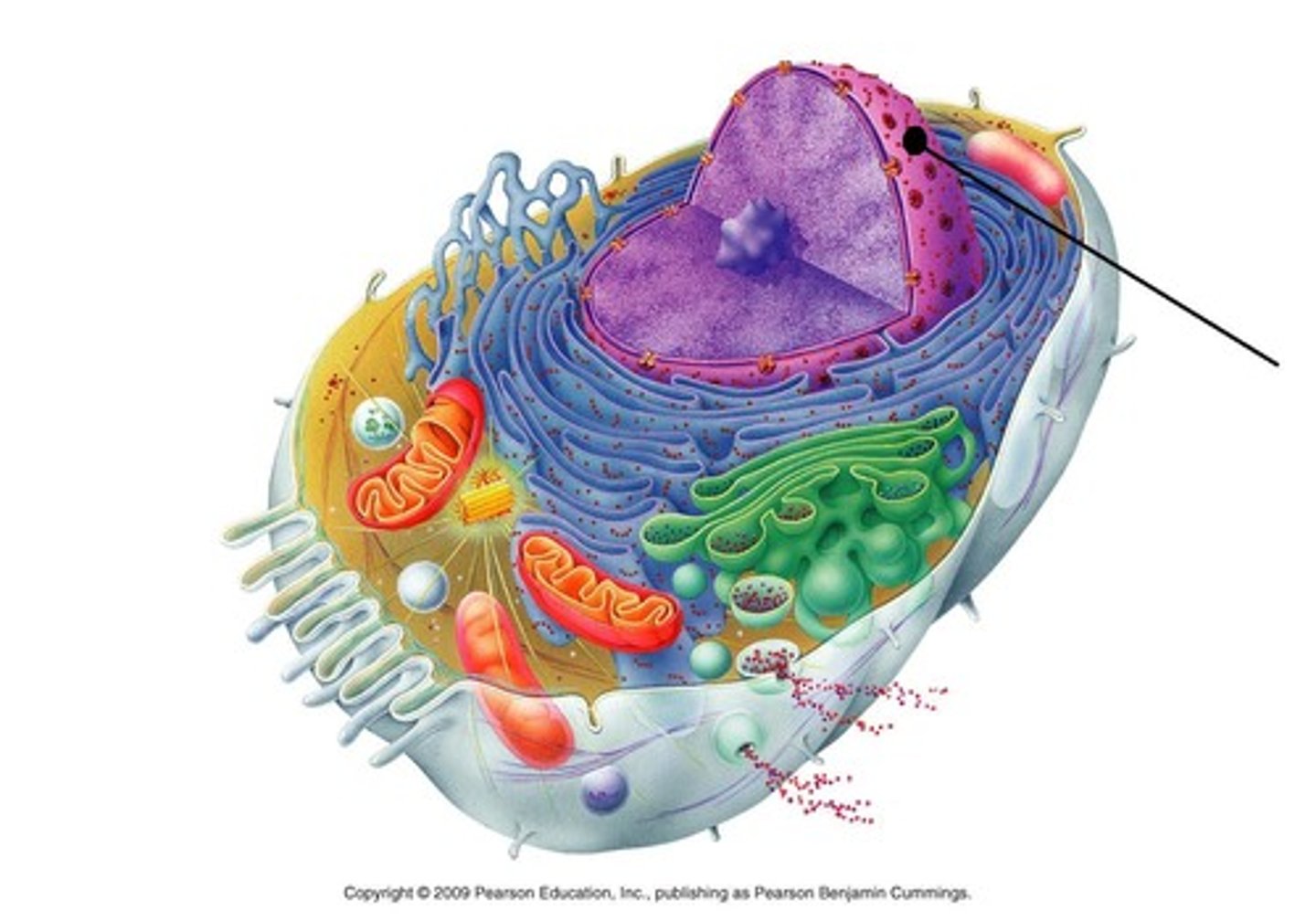
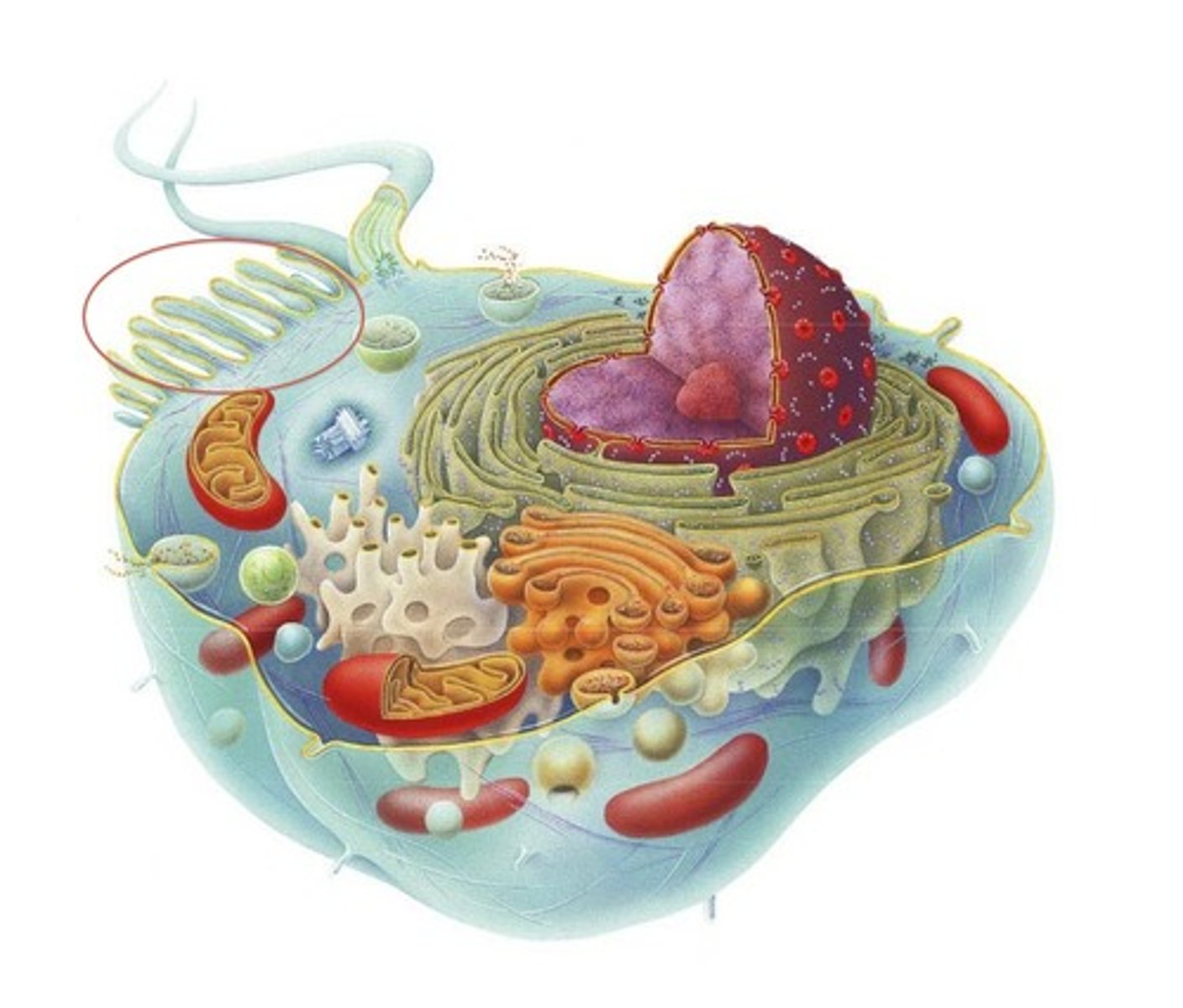
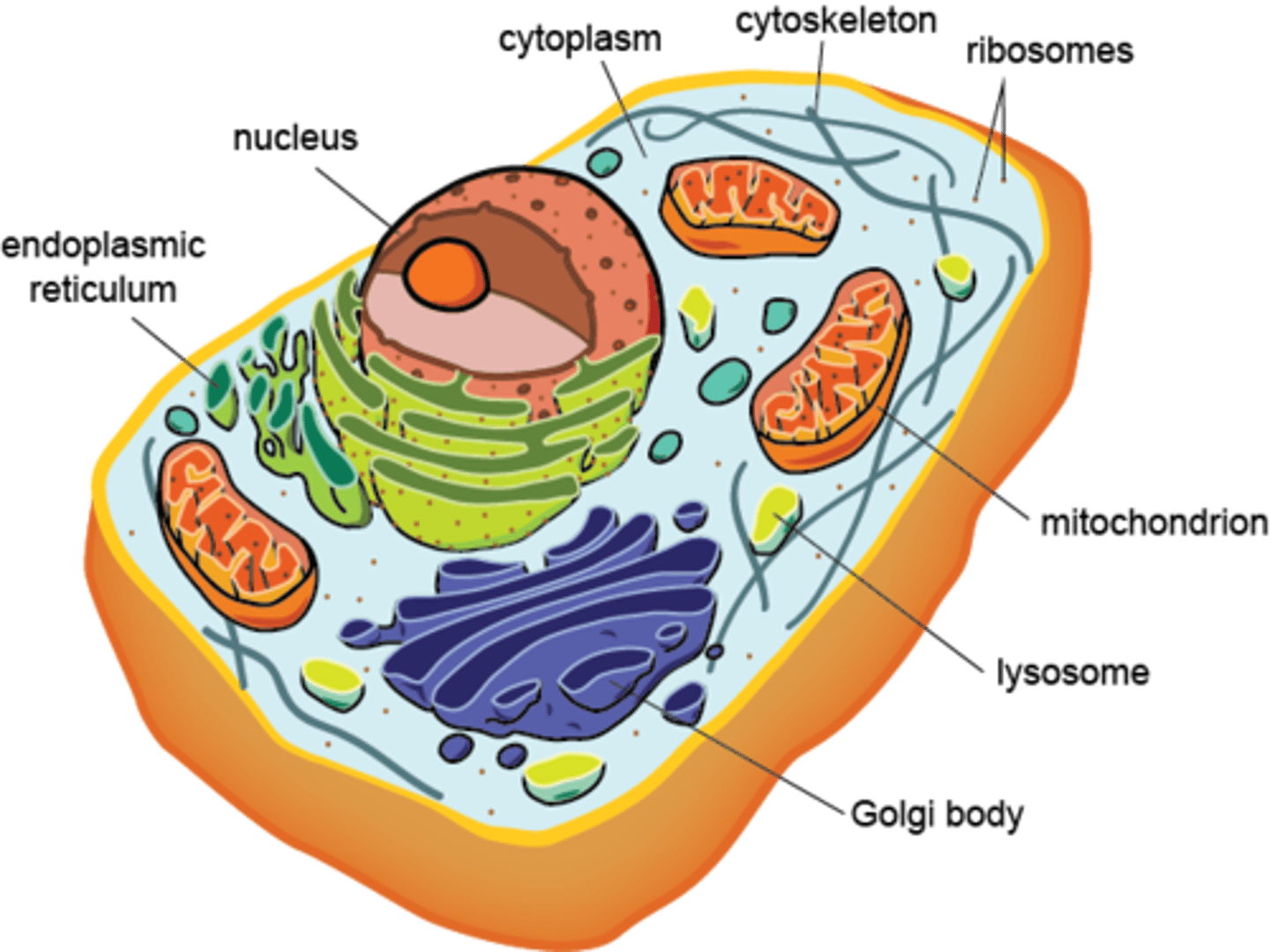
nucleus
organelle that contains DNA and controls processes of cell
nucleolus
organelle where ribosomes are synthesized and partially assembled (within nucleus)
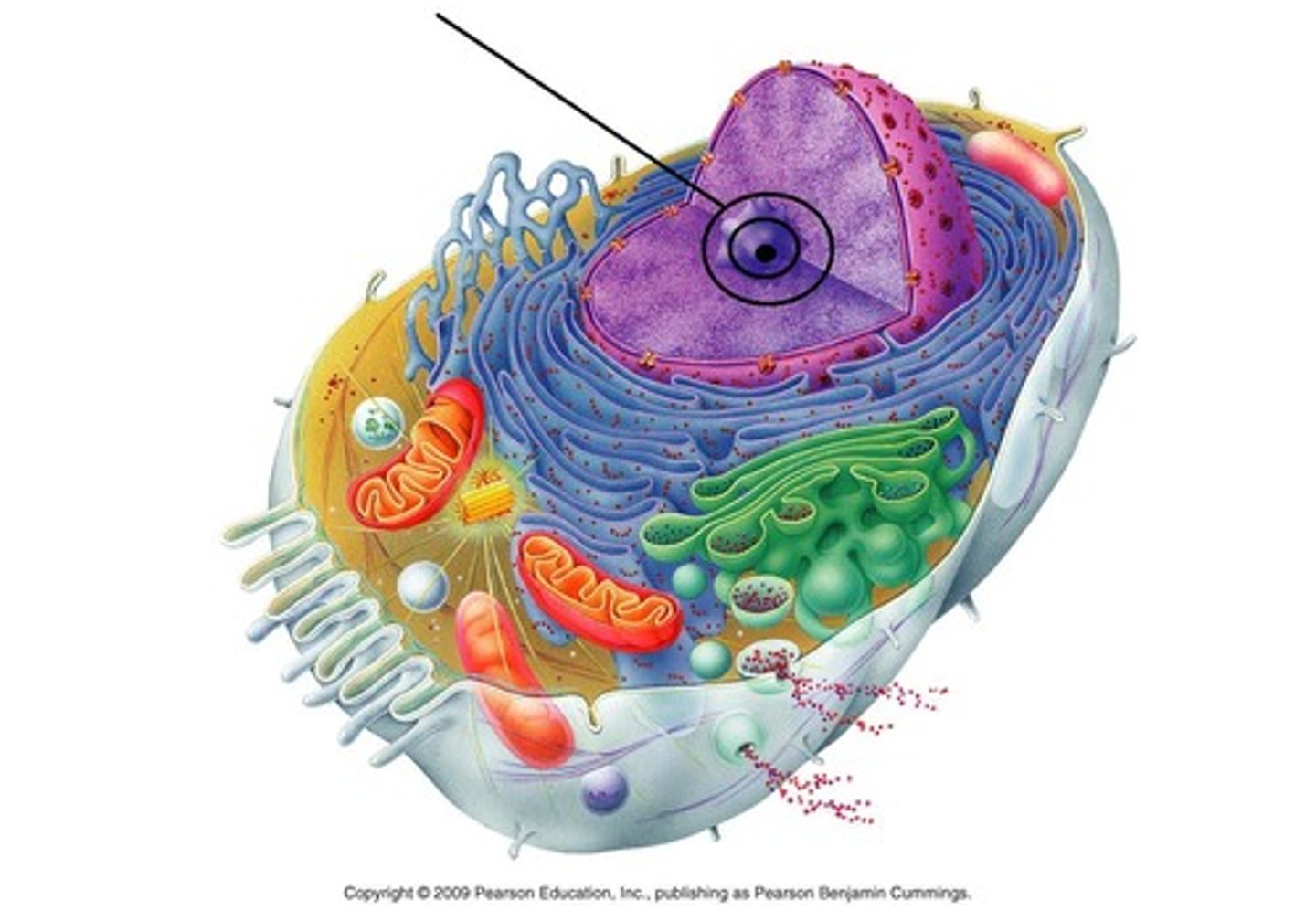
nuclear envelope
perforated double membrane that controls flow of materials (around nucleus)
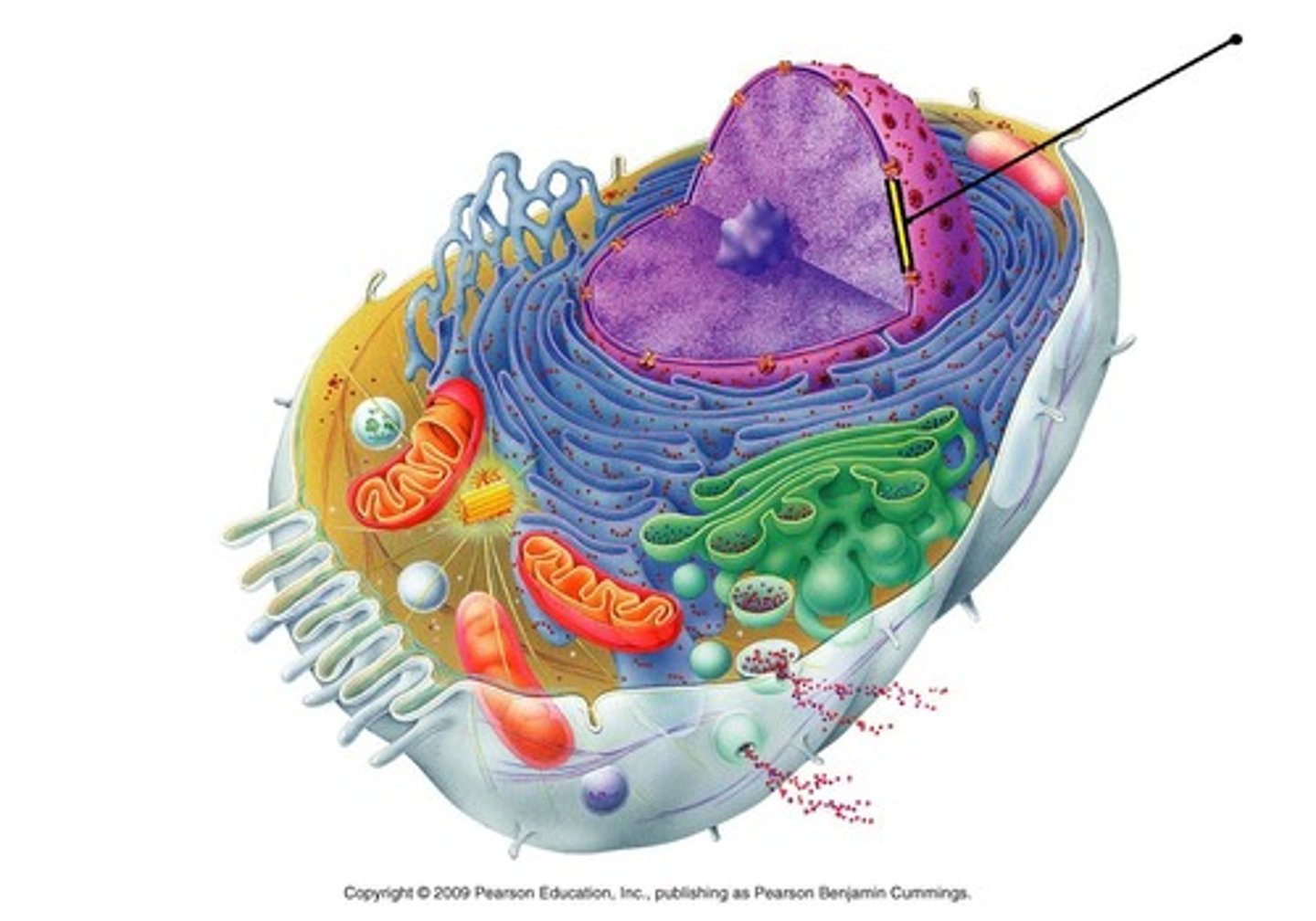
nuclear lamina
netlike array of intermediate filaments that maintains shape of nucleus
ribosomes
organelles made of protein and rRNA that direct protein synthesis (in cytoplasm or tethered to rough ER)
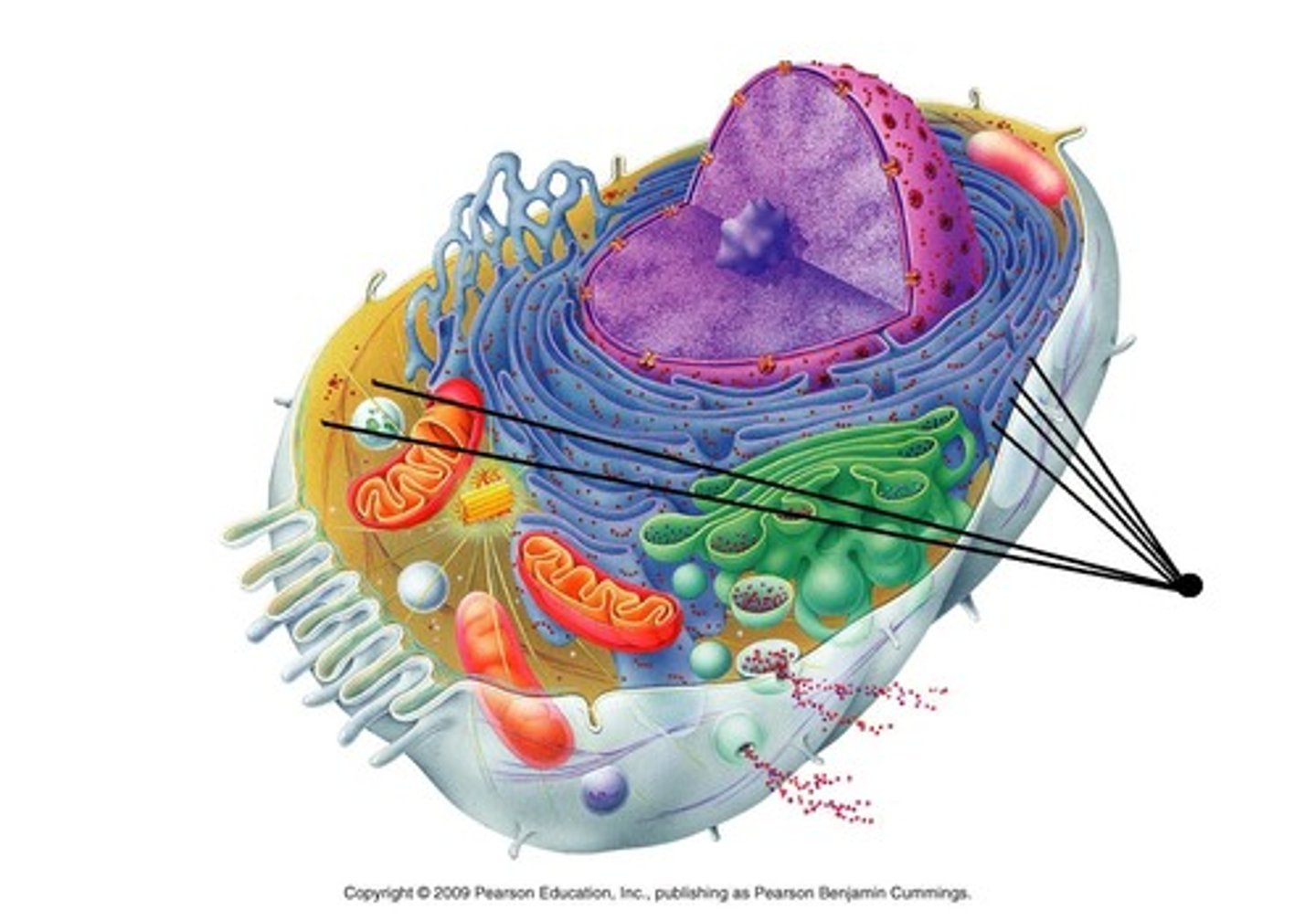
free ribosomes
suspended in the cytosol and synthesize proteins that function in the cytosol
bound ribosomes
bound to a Rough ER and synthesize proteins that will function in the membrane or will be sent outside the cell
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
internal membrane system in which components of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed
rough ER
organelle continuoues with nuclear membrane, to which ribosomes are tethered and proteins are synthesized for export
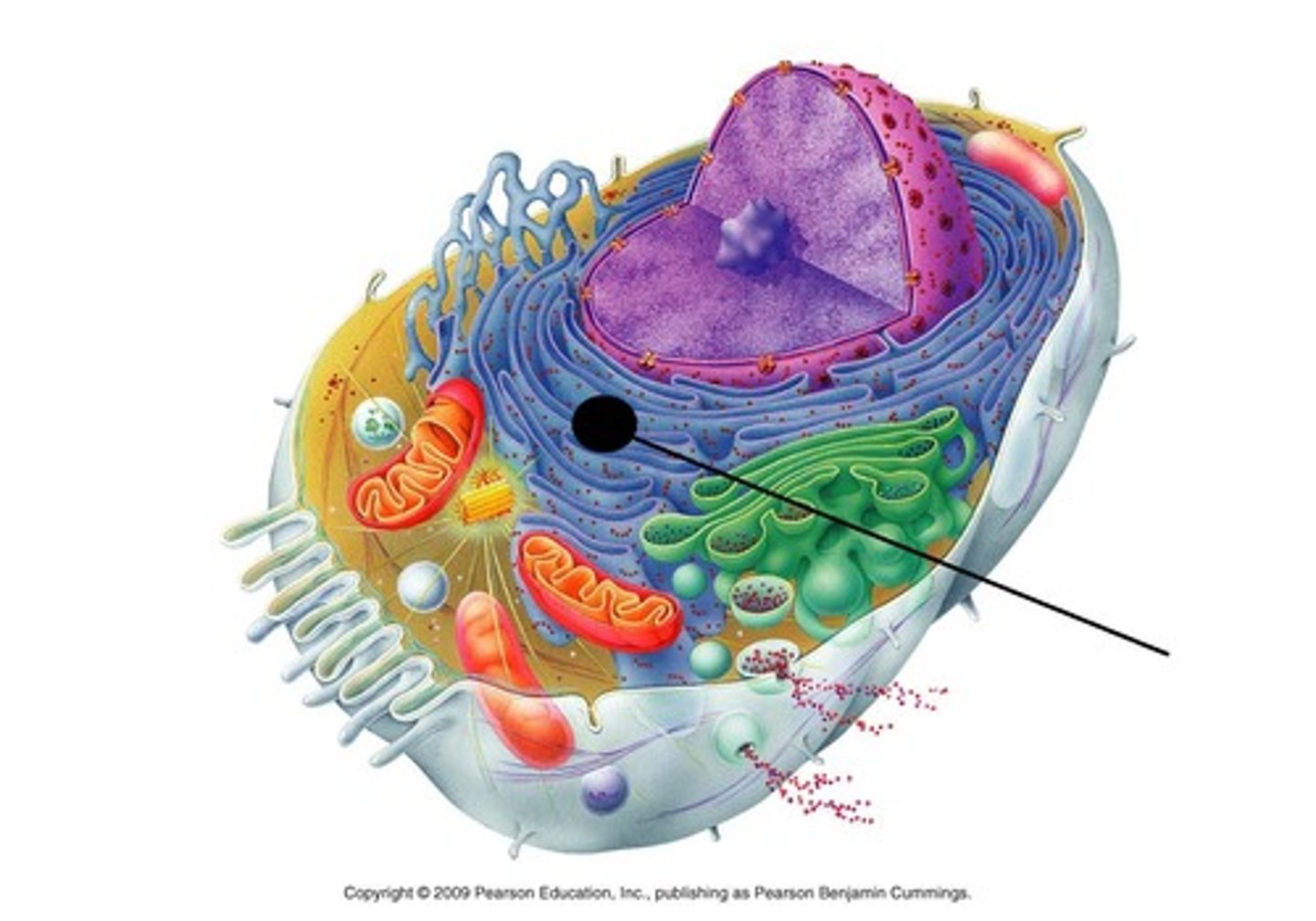
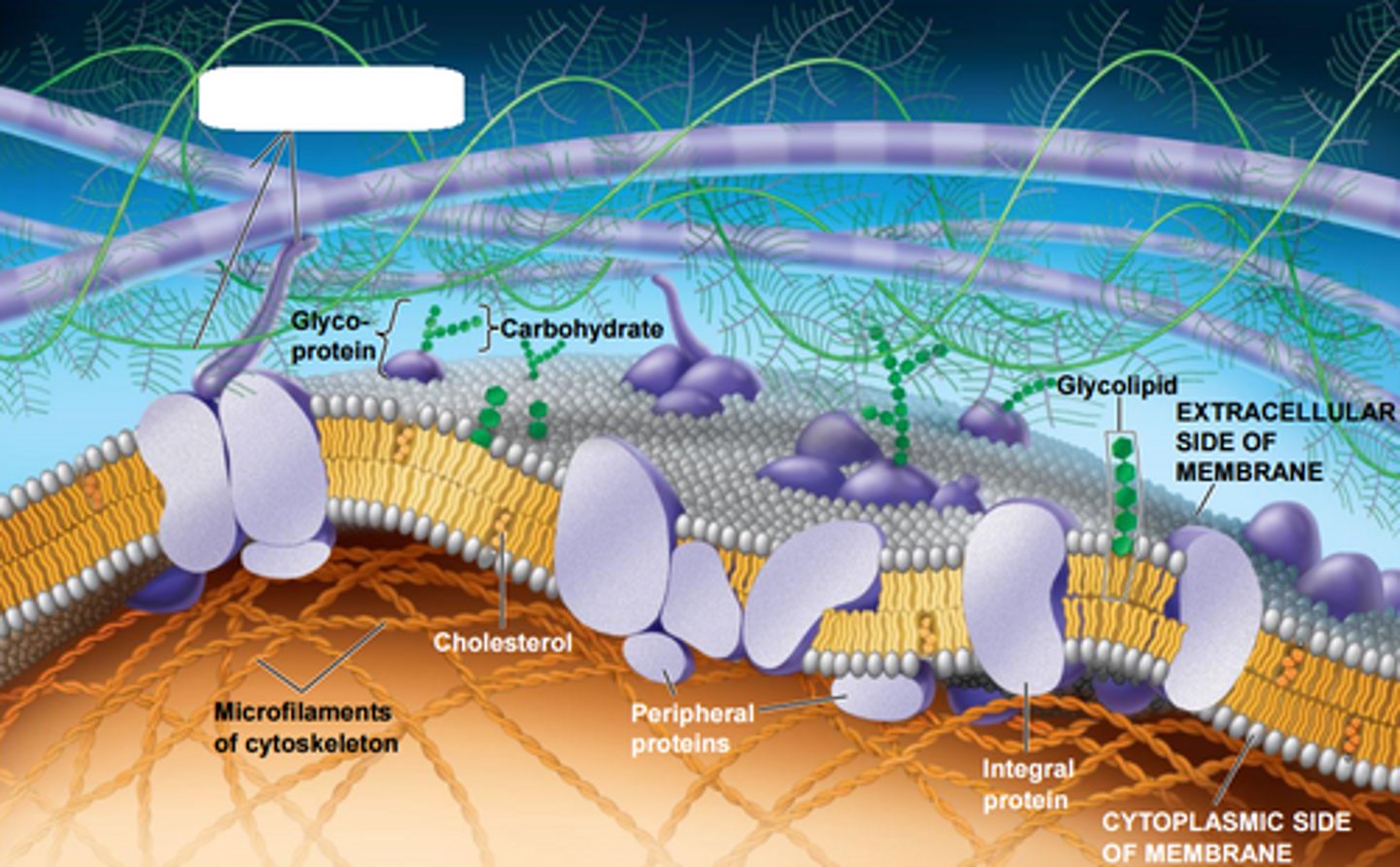
Glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
The Rough ER grows in place by...
After it grows, portions of the membrane are transferred to ______________ by...
adding membrane proteins and phospholipids to its own membrane.
other parts of the endomembrane system, transport vesicles
smooth ER
organelle where lipids are synthesized, detoxification occurs(in liver), and helps muscles contract
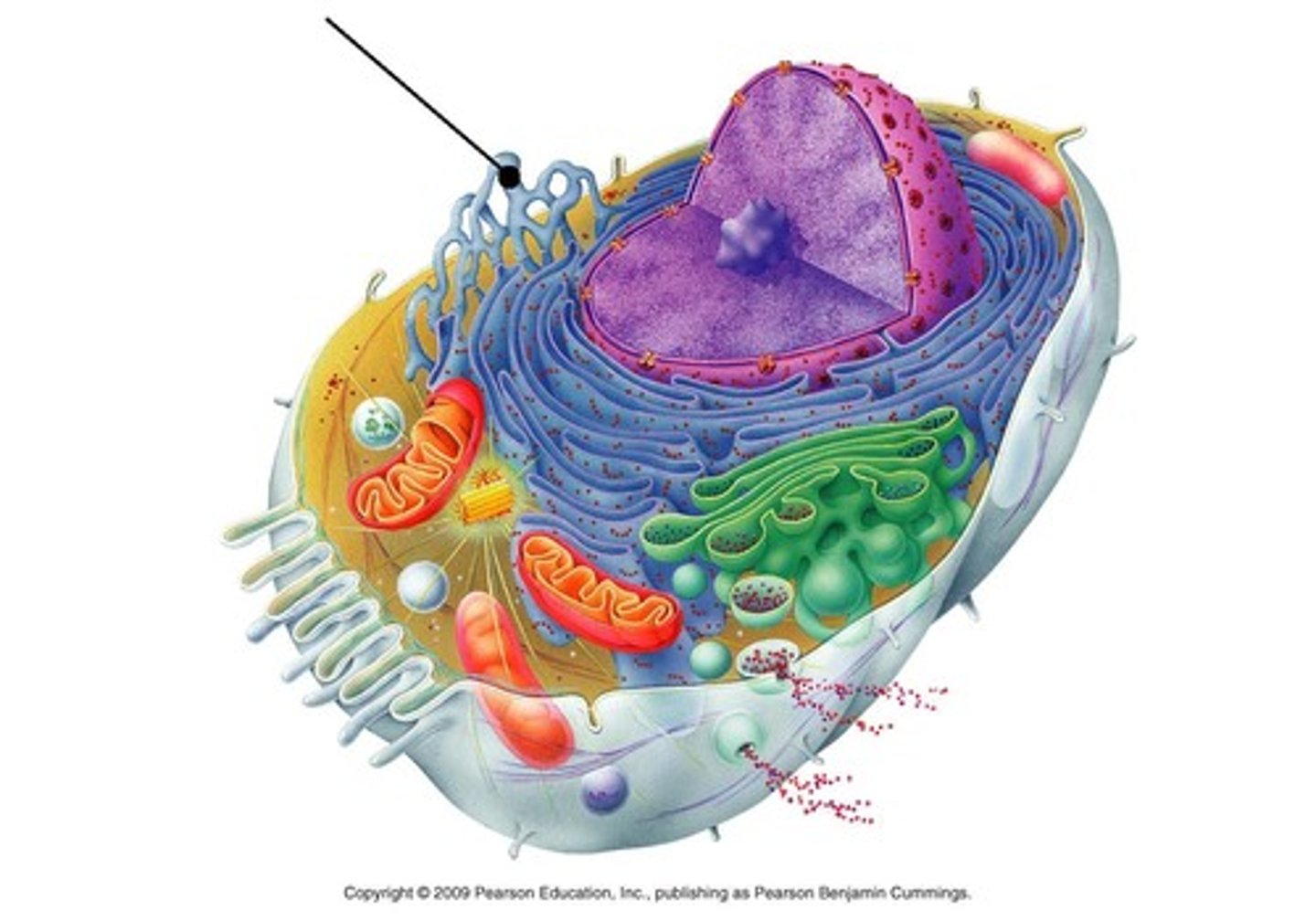
transport vesicles
A tiny membranous sac in a cell's cytoplasm carrying molecules from one place to another.
vesicles
small sacs surrounded by phospholipid bilayer that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
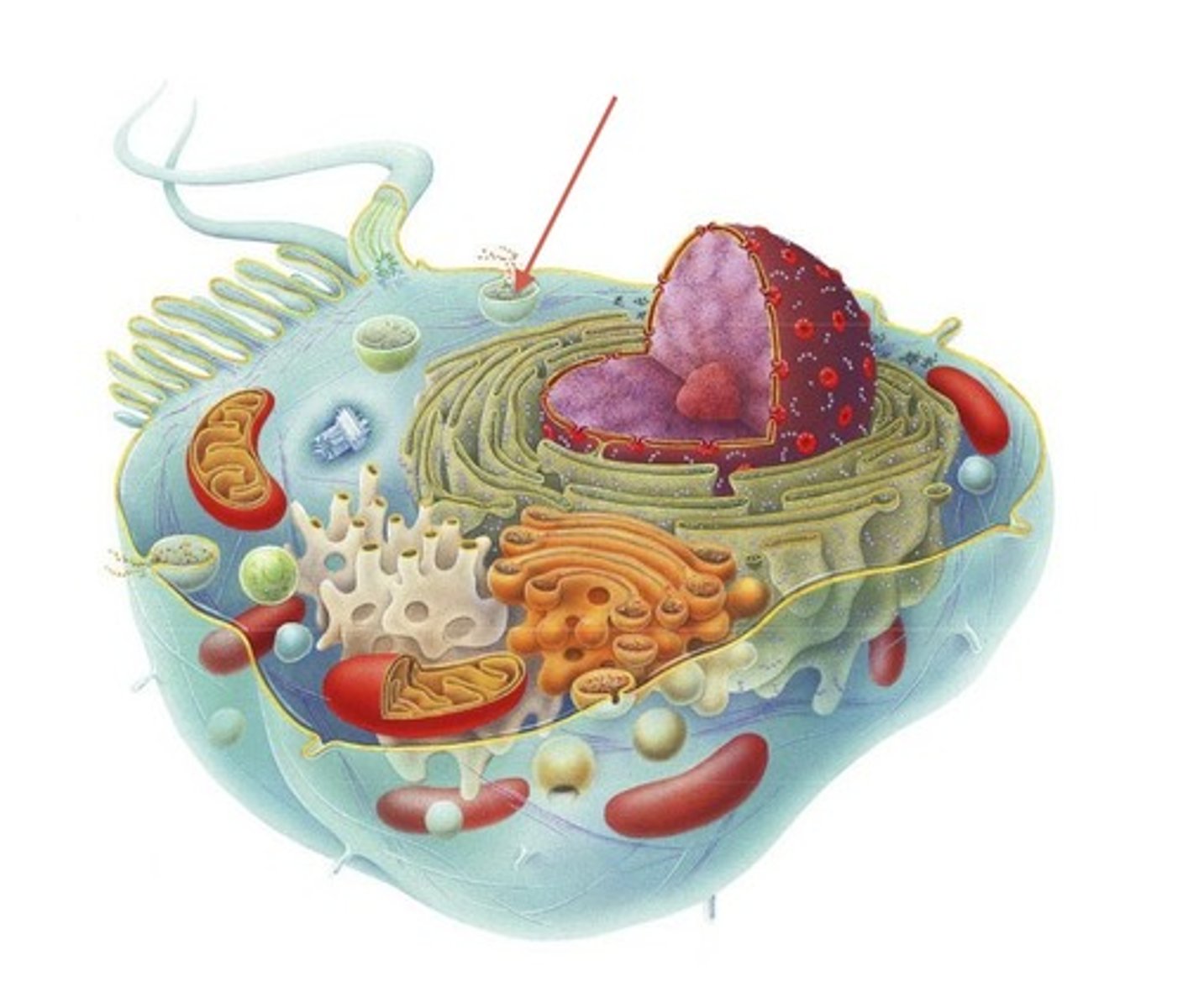
golgi apparatus
stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for transport
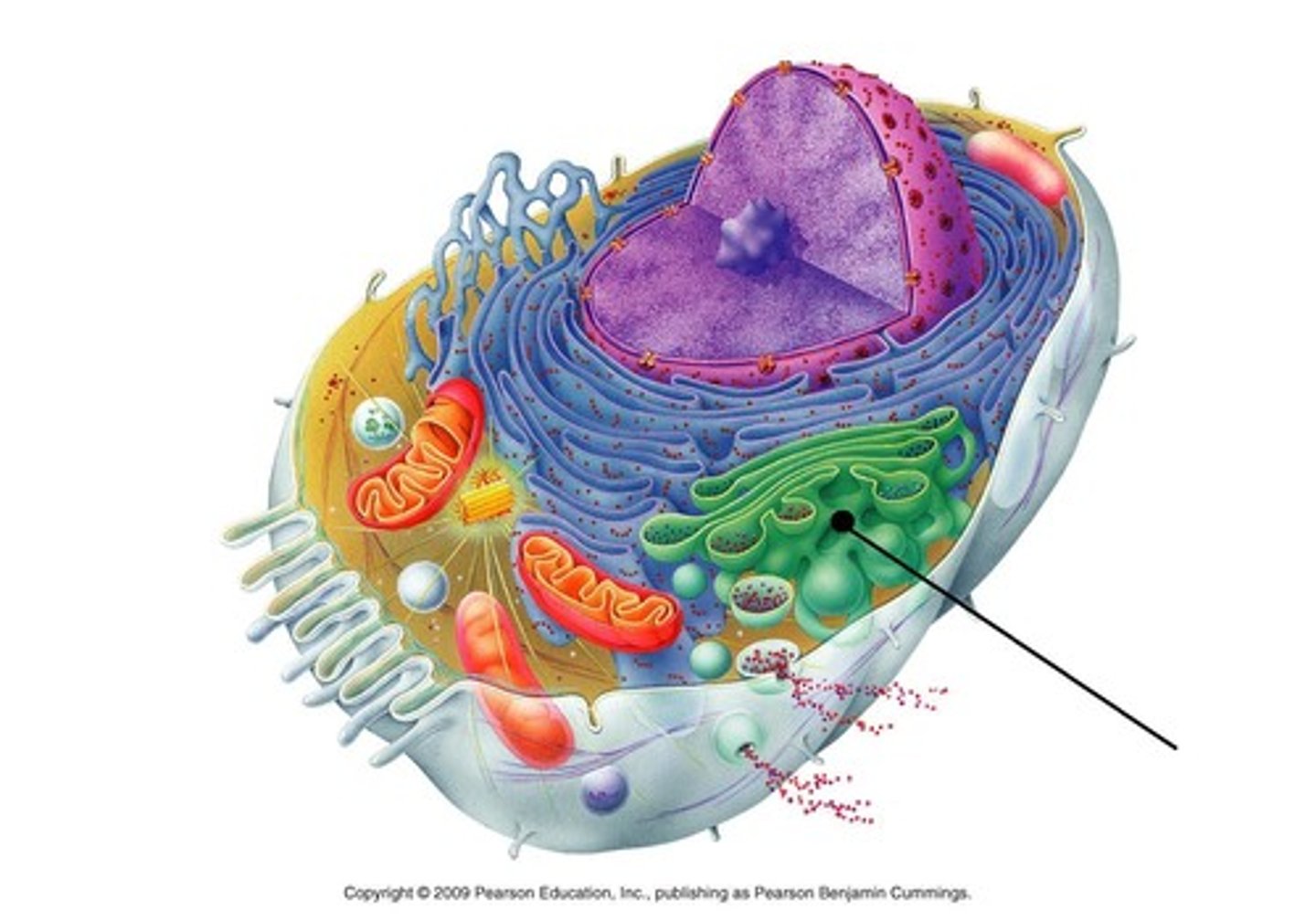
cis vs trans side of the golgi apparatus
The cis side faces the ER and receives materials by fusing with transport vesicles. The trans side faces away from the ER and vesicles bud off from their that travel to other sites.
When molecules leave the golgi apparatus ___________ are added to help with sorting.
identification tags(phosphate groups or other groups)
lysosome
organelle filled with enzymes that break down macromolecules
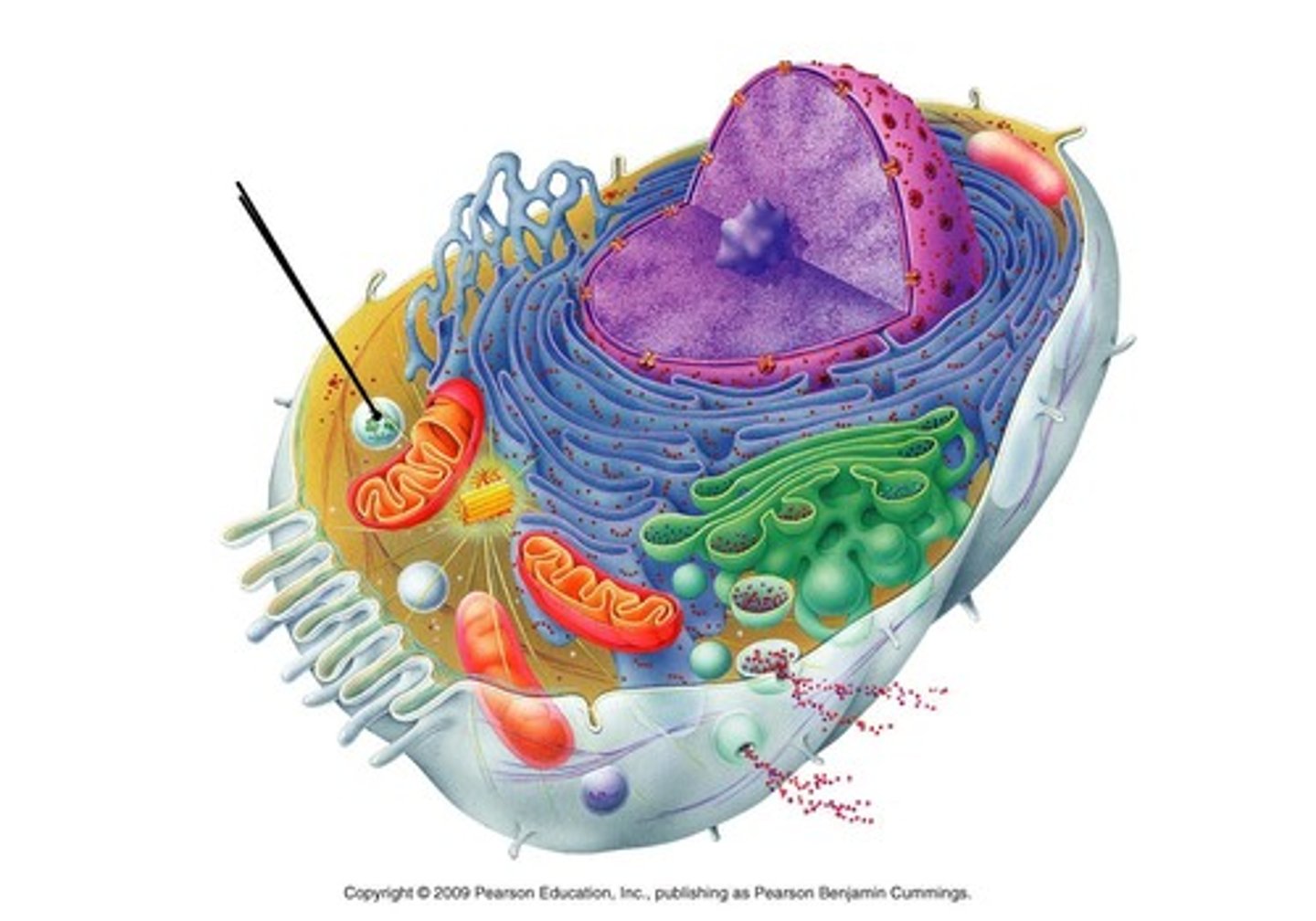
phagocytosis
when extensions of cytoplasm surround and engulf LARGE food particles
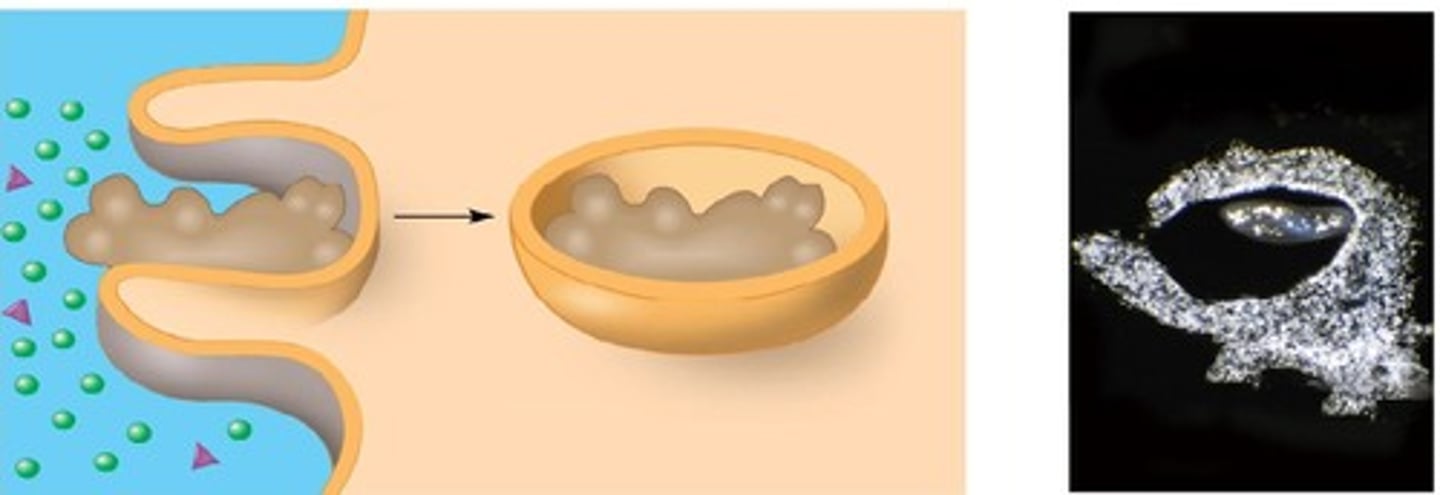
Autophagy
A process in which lysosomes decompose damaged organelles to reuse their organic monomers
Food vacuoles are formed by ________ and fuse with ____________.
phagocytosis, lysosomes
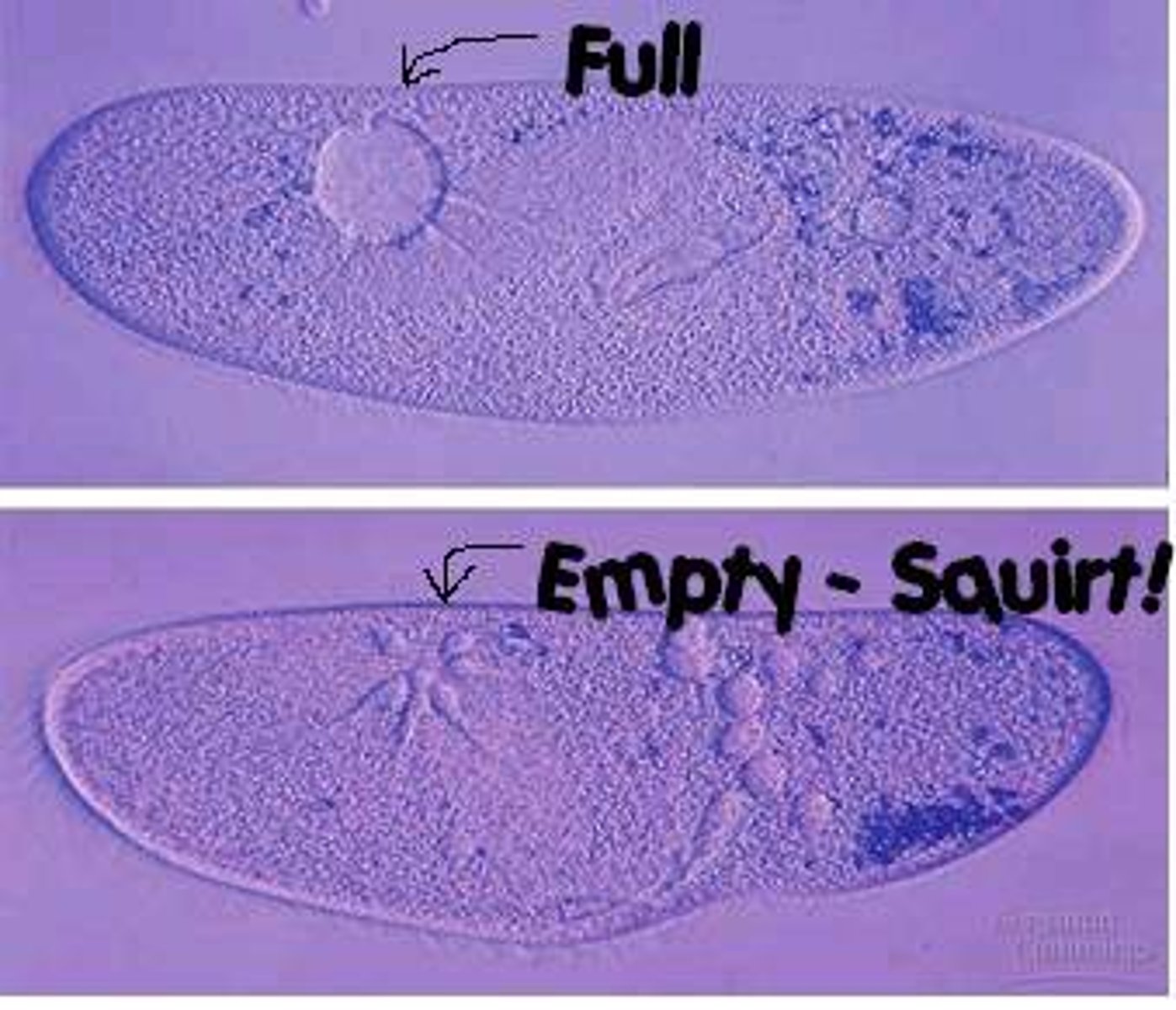
contractile vacuole
saclike organelles that expand to collect excess water and contract to squeeze the water out of the cell
central vacuole
membranous sac in plant cells with roles in reproduction, growth, and storage
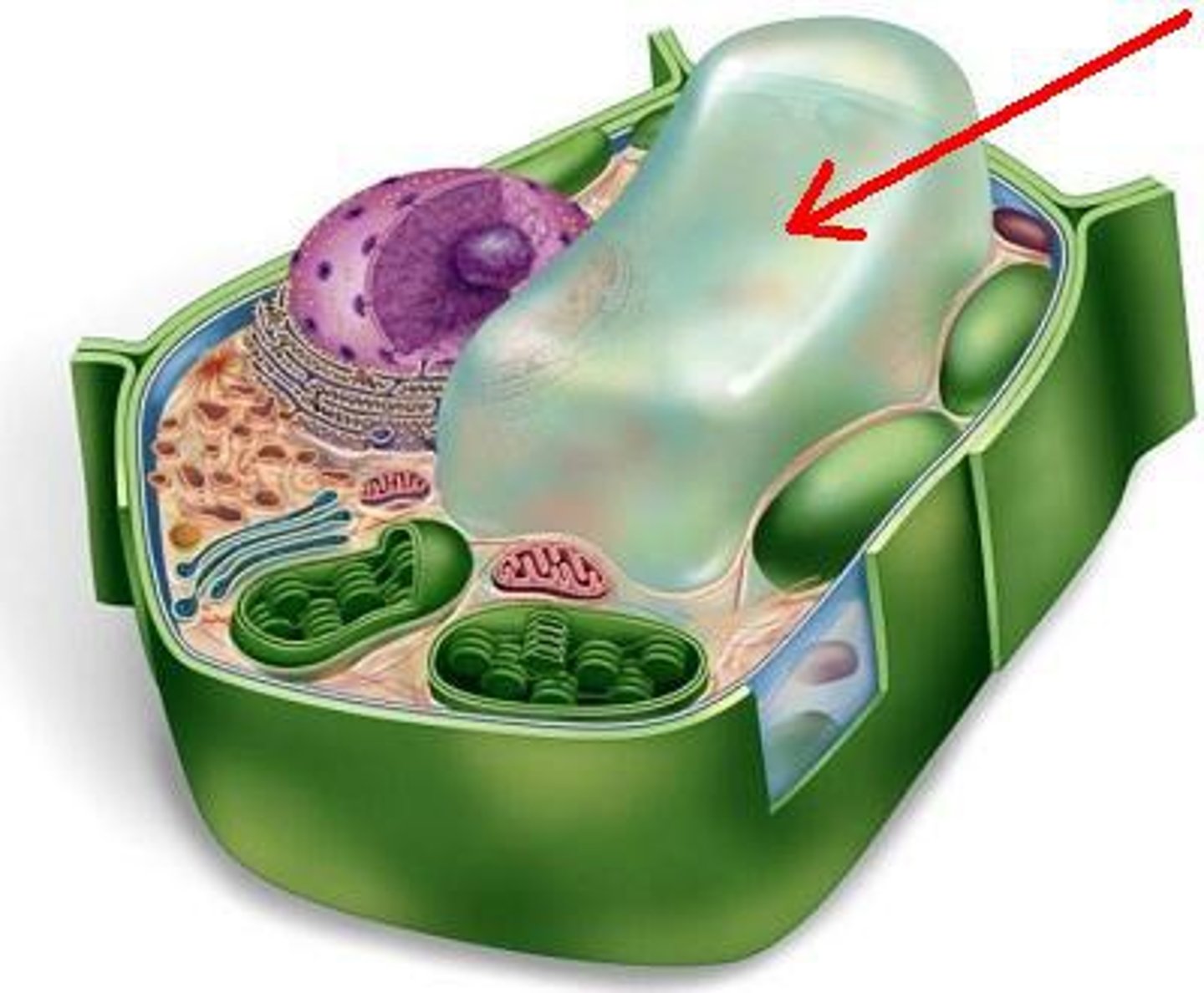
Tonoplast
A membrane that encloses the central vacuole in a plant cell that is selective in its transport of solutes through the membrane
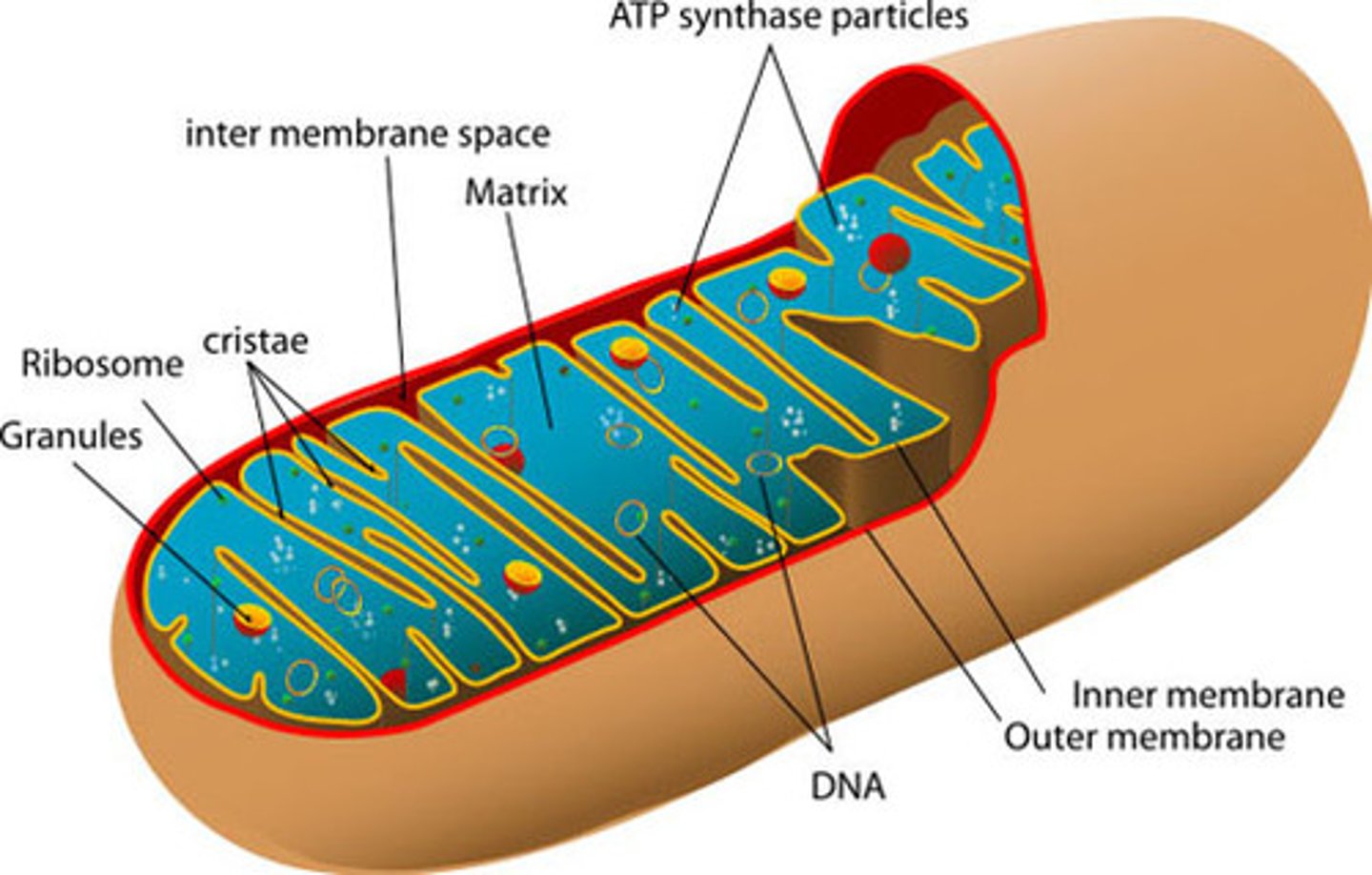
mitochondria
organelle in all eukaryotic cells where chemical energy in glucose and fats is transformed into ATP (cellular respiration SITE)
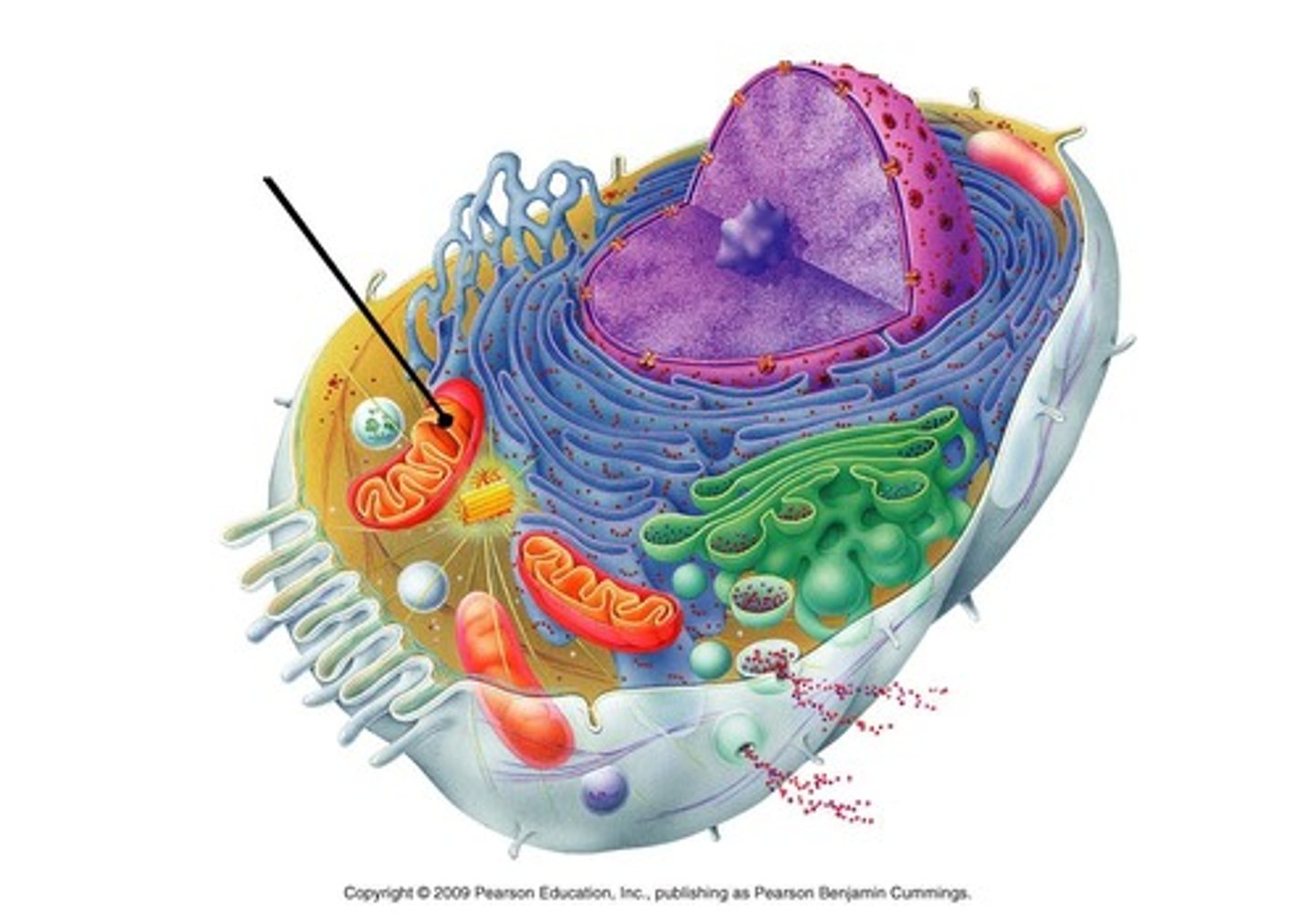
intermembrane space of mitochondria
space between inner and outer membranes
chloroplast
organelle in plants where sunlight energy is used to synthesize glucose (photosynthesis SITE)
endosymbiont theory
states that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as prokaryotic cells engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cell
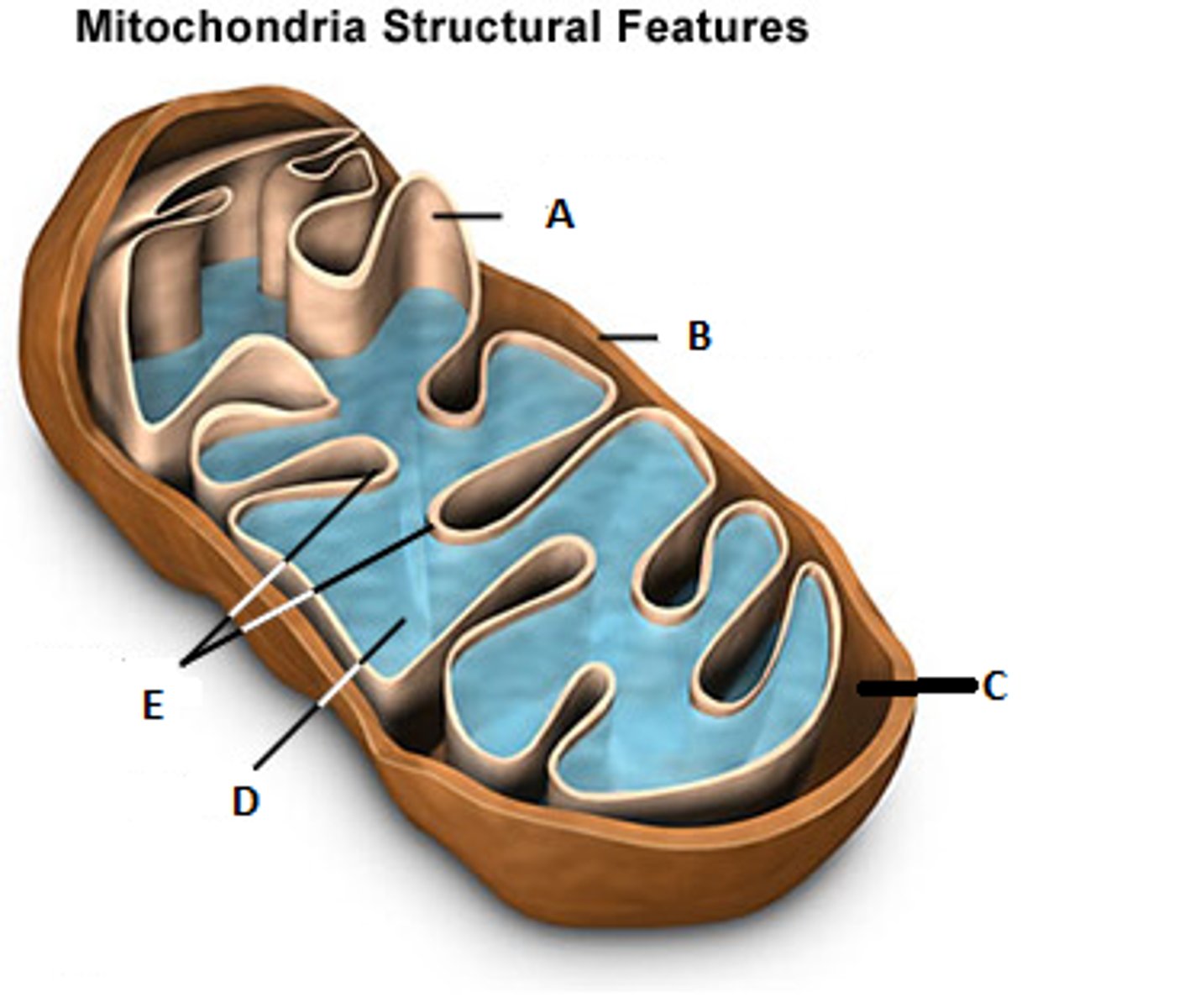
mitochondrial matrix
(D) internal compartment of mitochondria (Krebs cycle SITE)
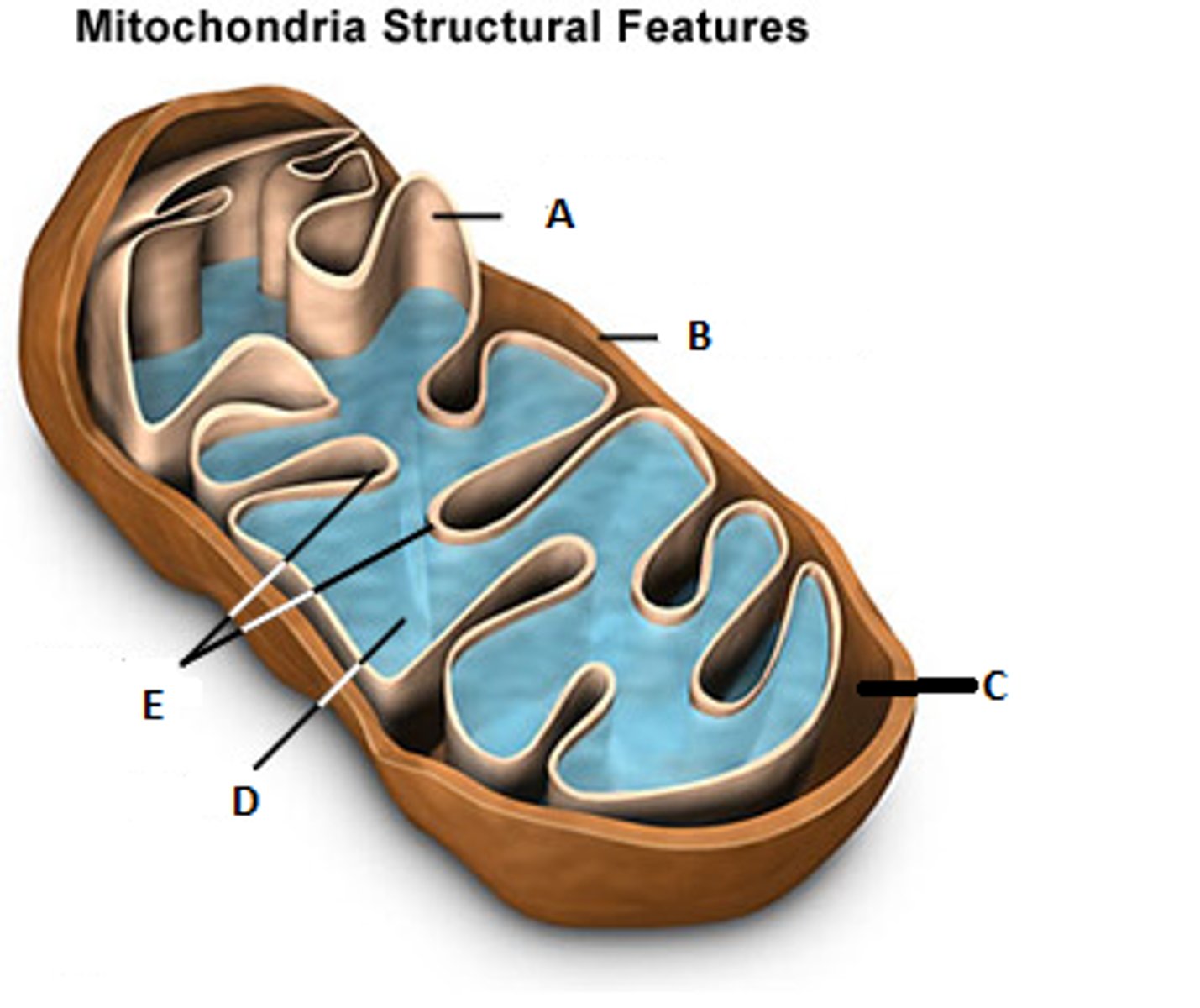
cristae
(E) inner membrane infoldinfgs of mitochondria that increase surface area (Electron Transport Chain and ATP synthase SITE)
Amyoplast
plastid that stores starch in roots
Chromoplast
a plastid that stores pigments for fruits and flowers
thylakoids
(C) flattened membrane sacs in chloroplast (Light Reactions SITE)
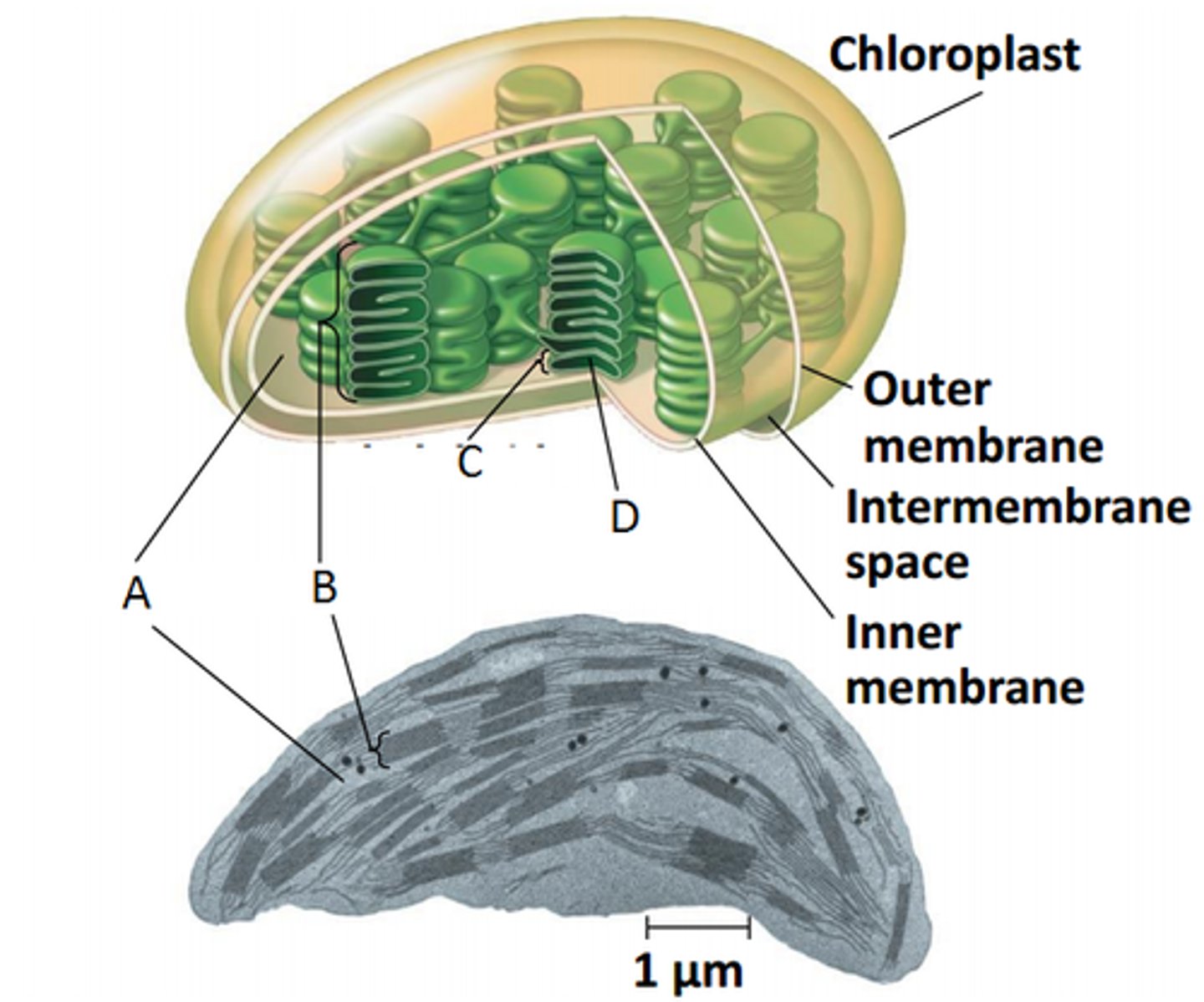
grana
(B) stacked thylakoid membranes in chloroplast
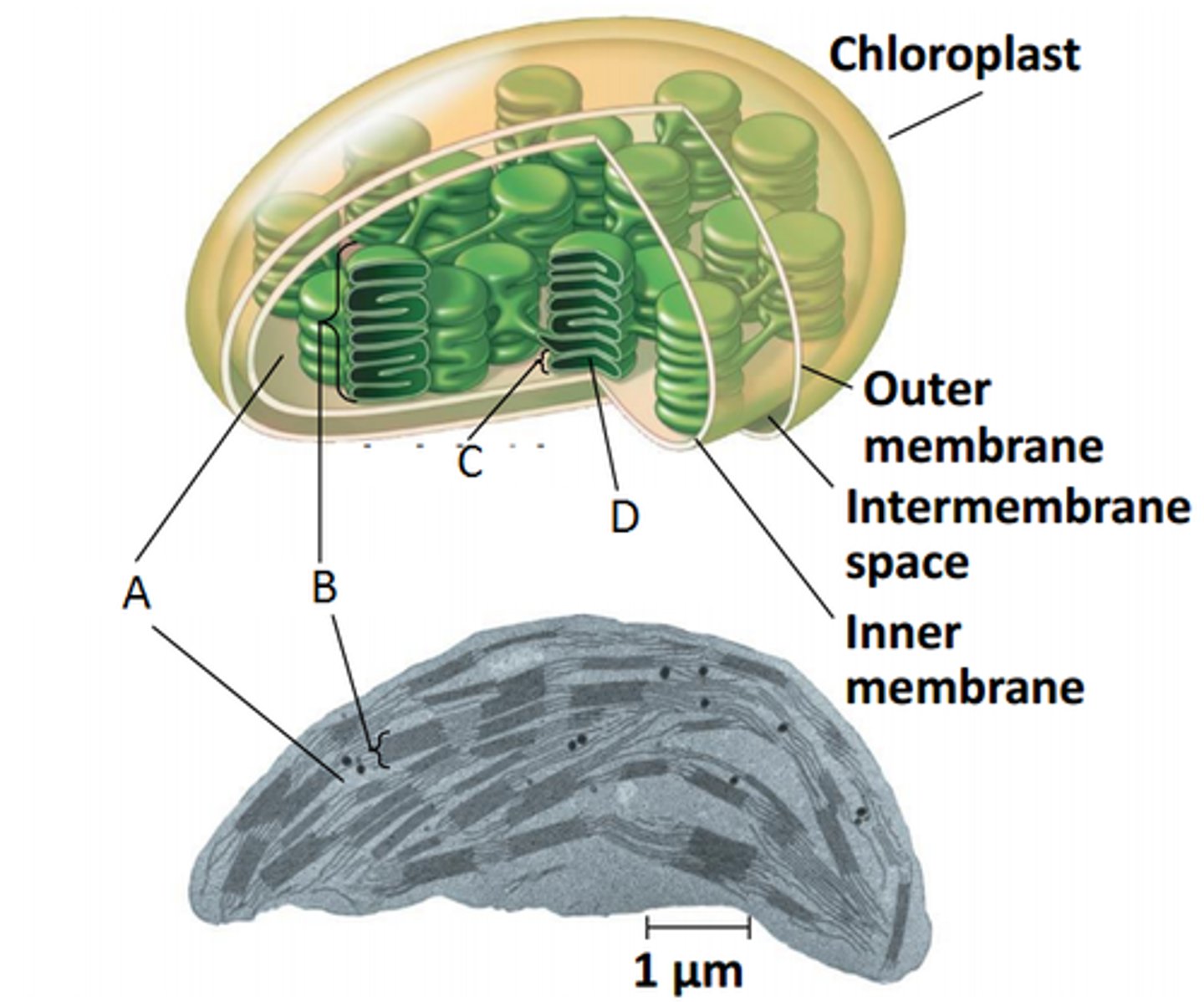
stroma
(A) innermost compartment of chloroplast (Calvin cycle SITE)
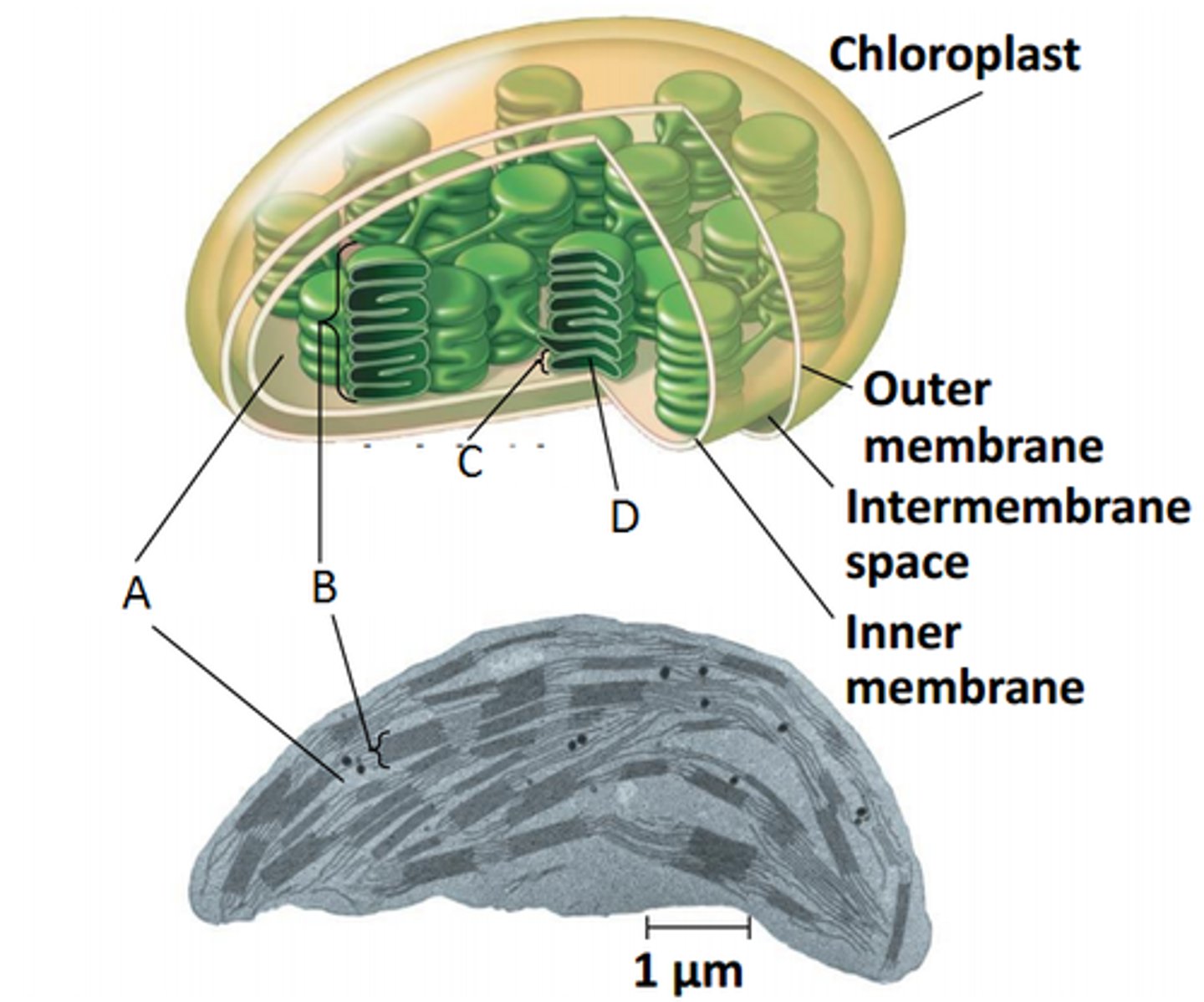
plastids
plant organelles surrounded by double membrane with their own DNA, that make and store food and pigments
peroxisomes
animal organelles that contain enzymes that detoxify alcohols, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals
A by product of the reactions that the peroxisomes do is __________
hydrogen peroxide
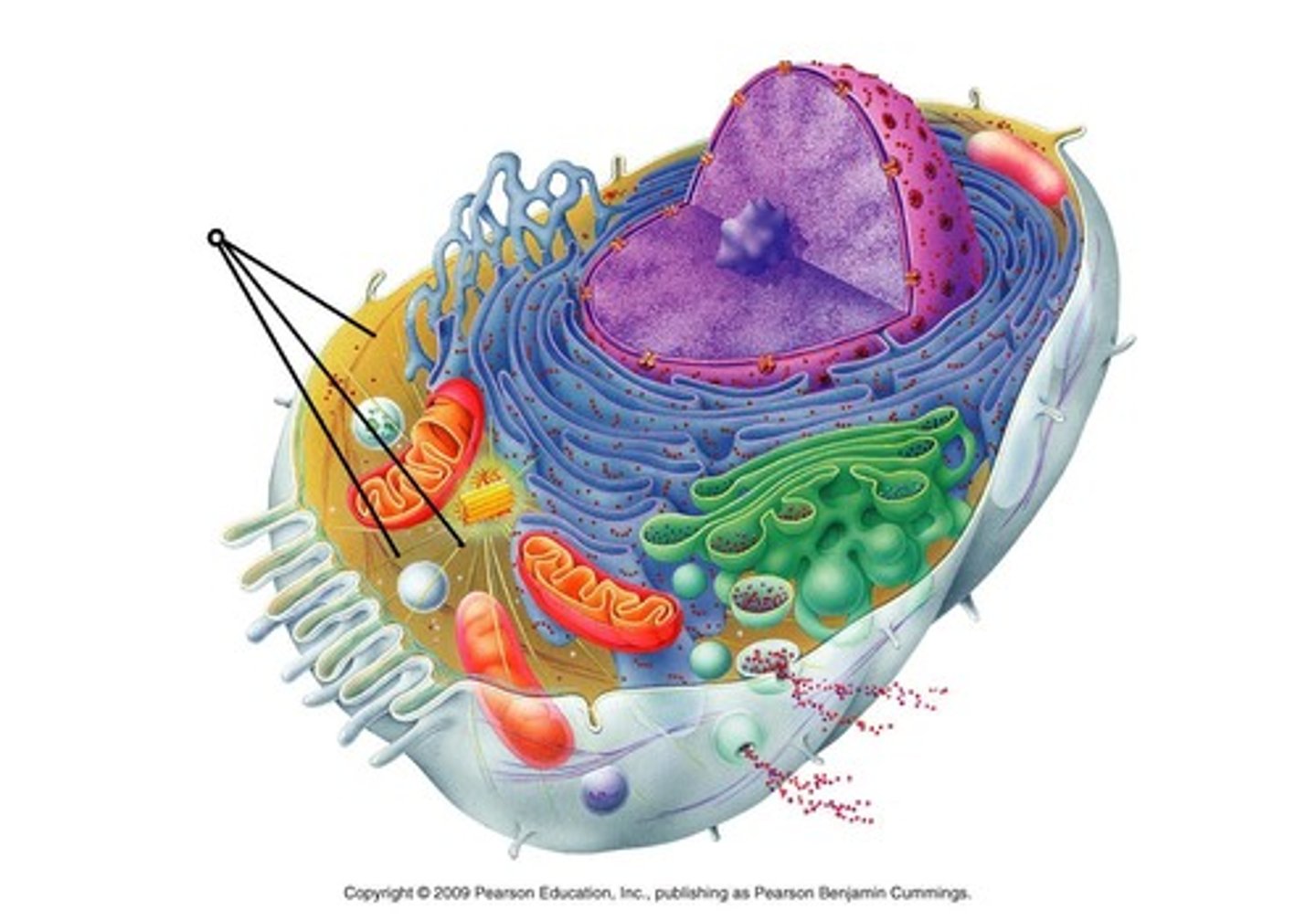
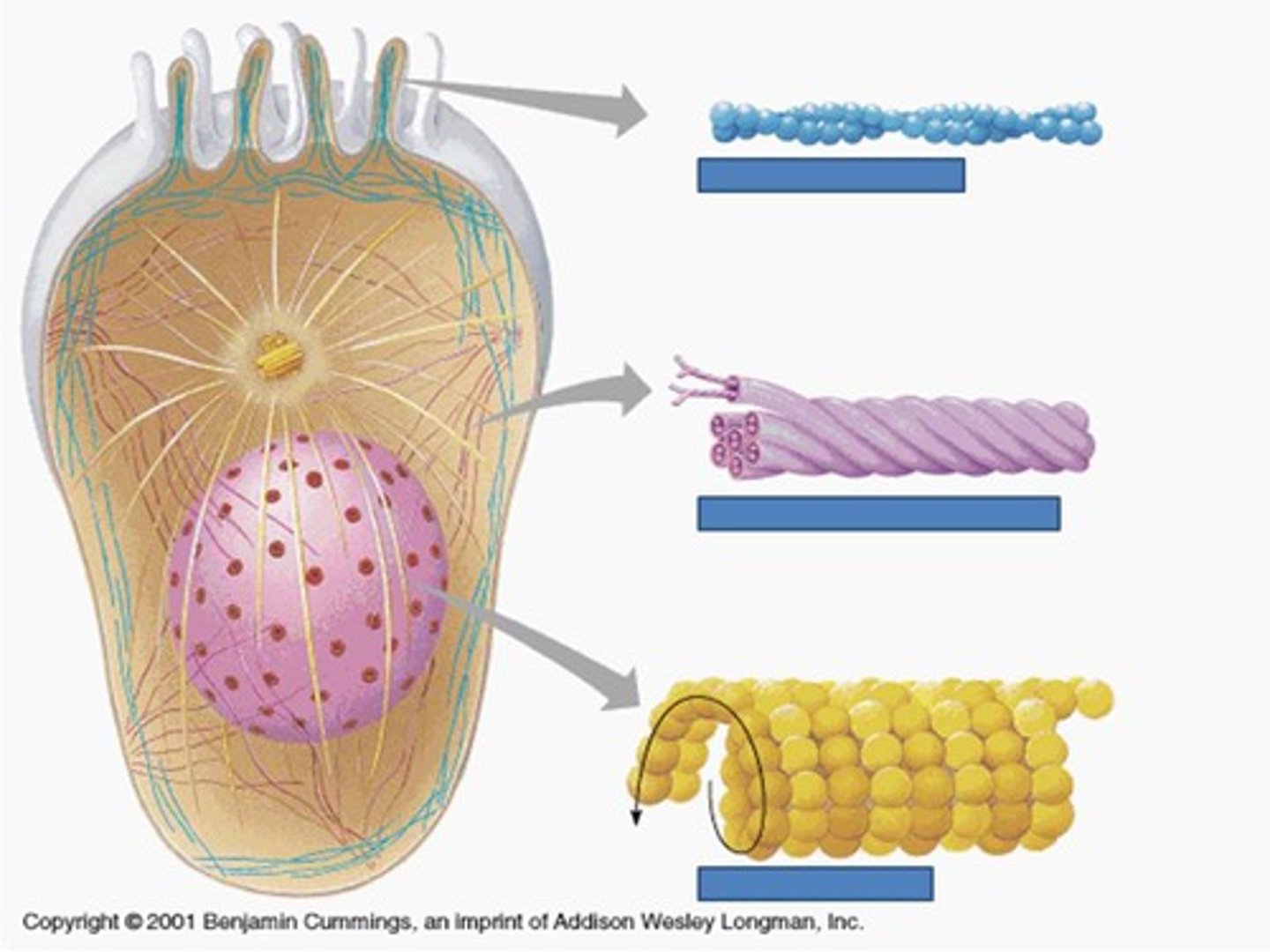
cytoskeleton
microscopic network of protein fibers within cytoplasm that gives shape to cell
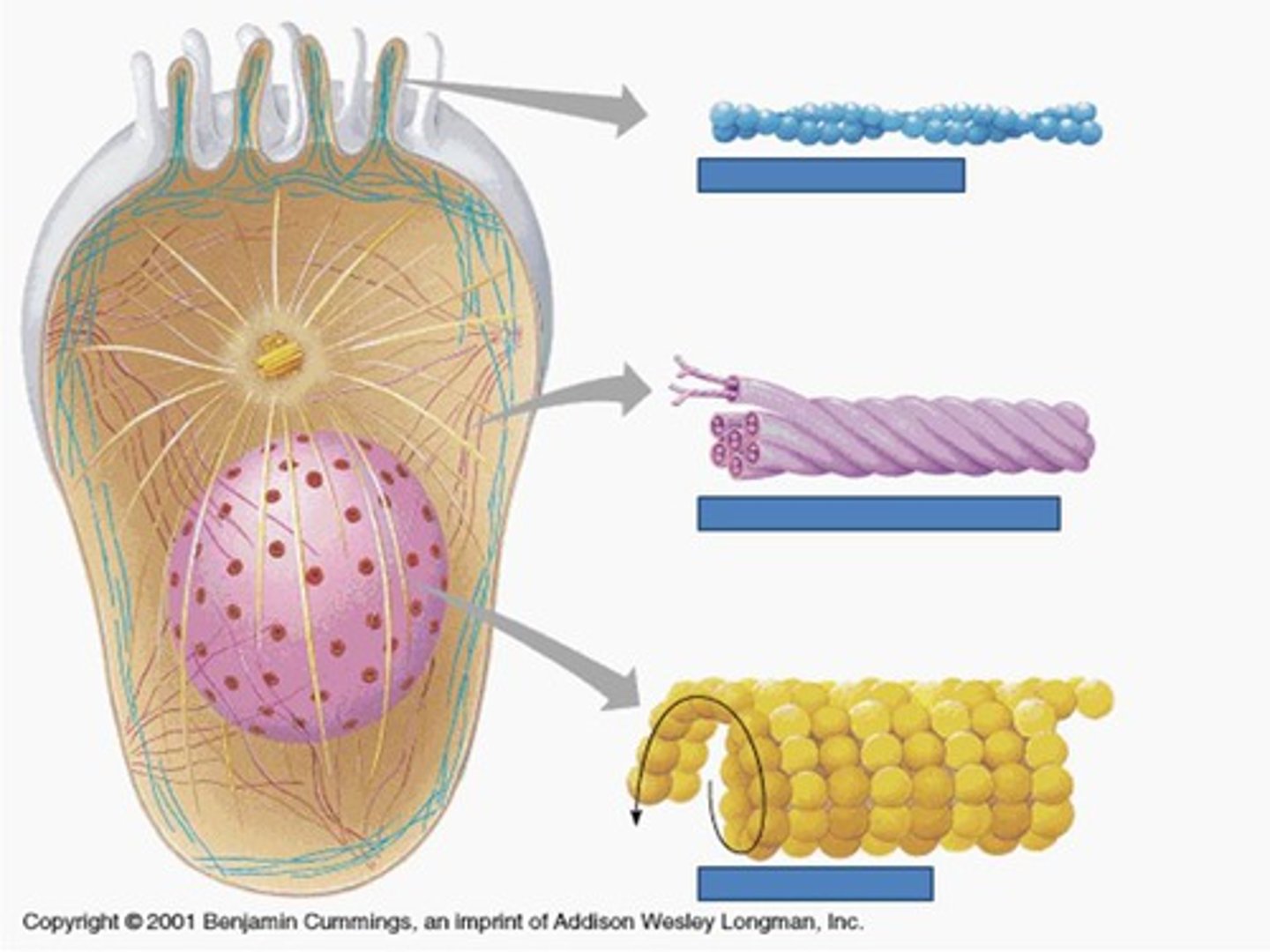
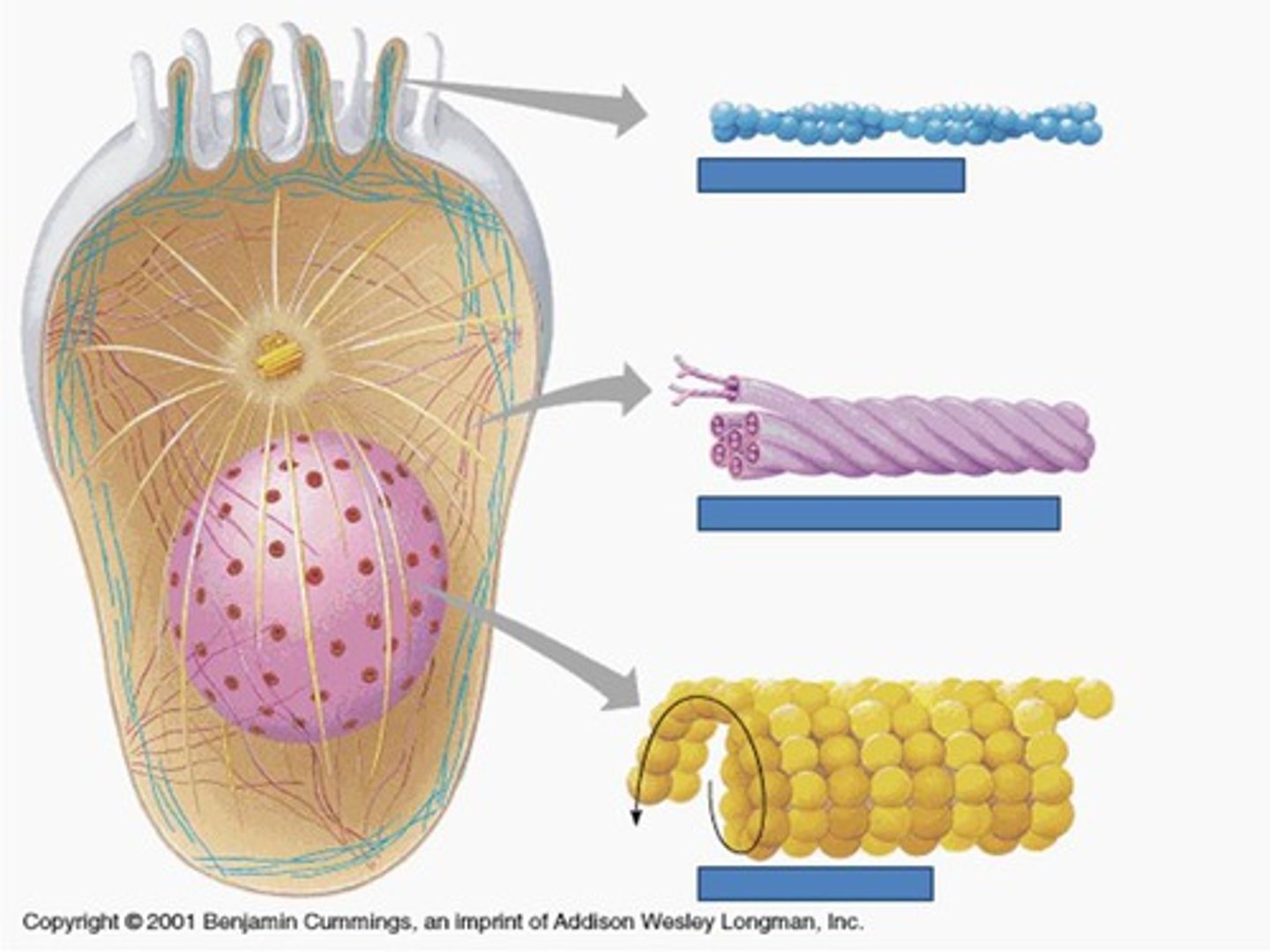
microtubule functions
(bottom) thickest, hollow tubes of tubulin proteins that make up cilia, flagella, and mitotic spindle
- organize the position of organelles
- direct intracellular transport
- also some movement(cilia and flagella)
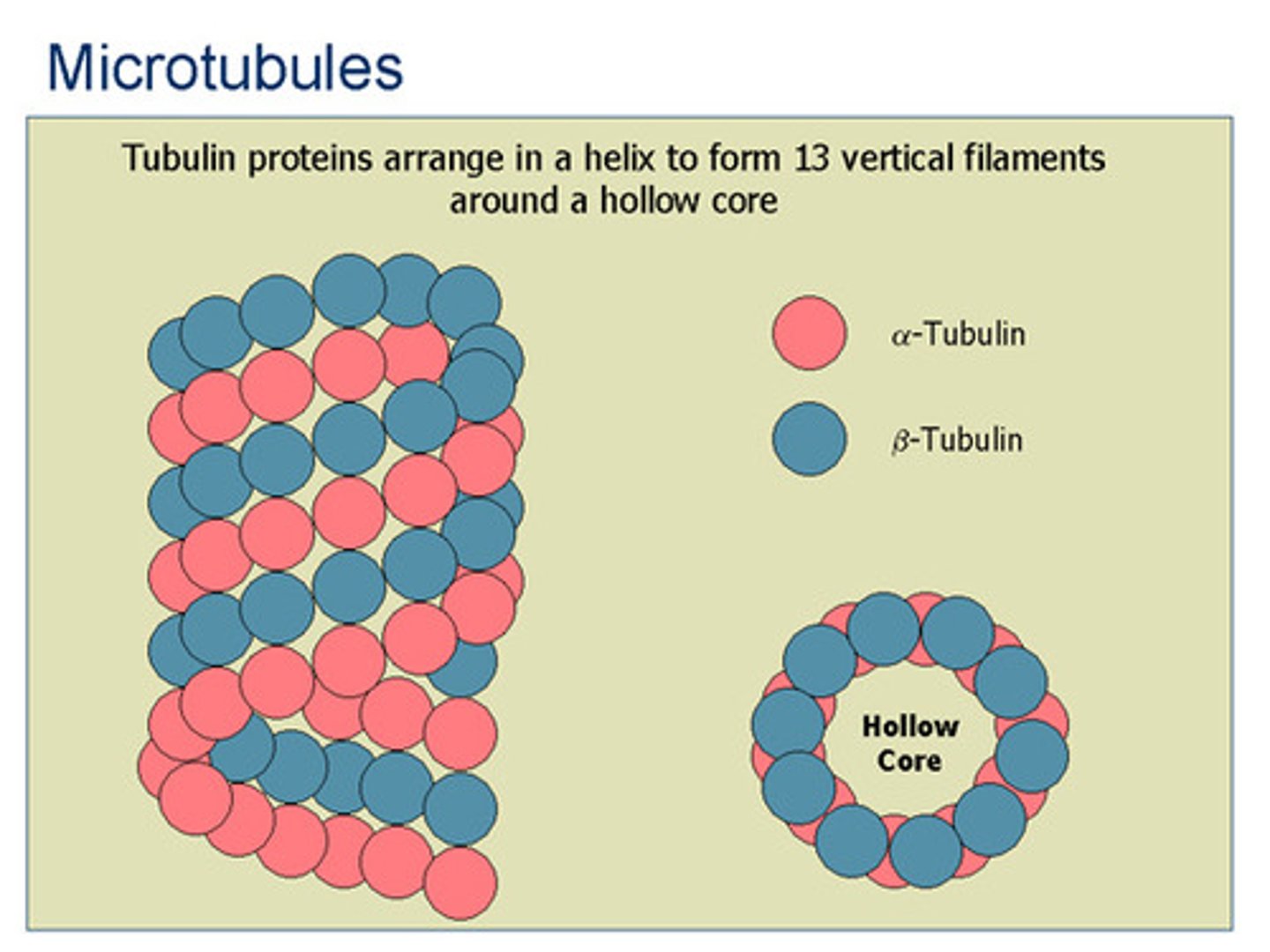
microtubule structure
alpha tubulin and beta tubulin proteins organize into a hollow tube shape
dimer
a molecule or molecular complex consisting of two identical molecules linked together.
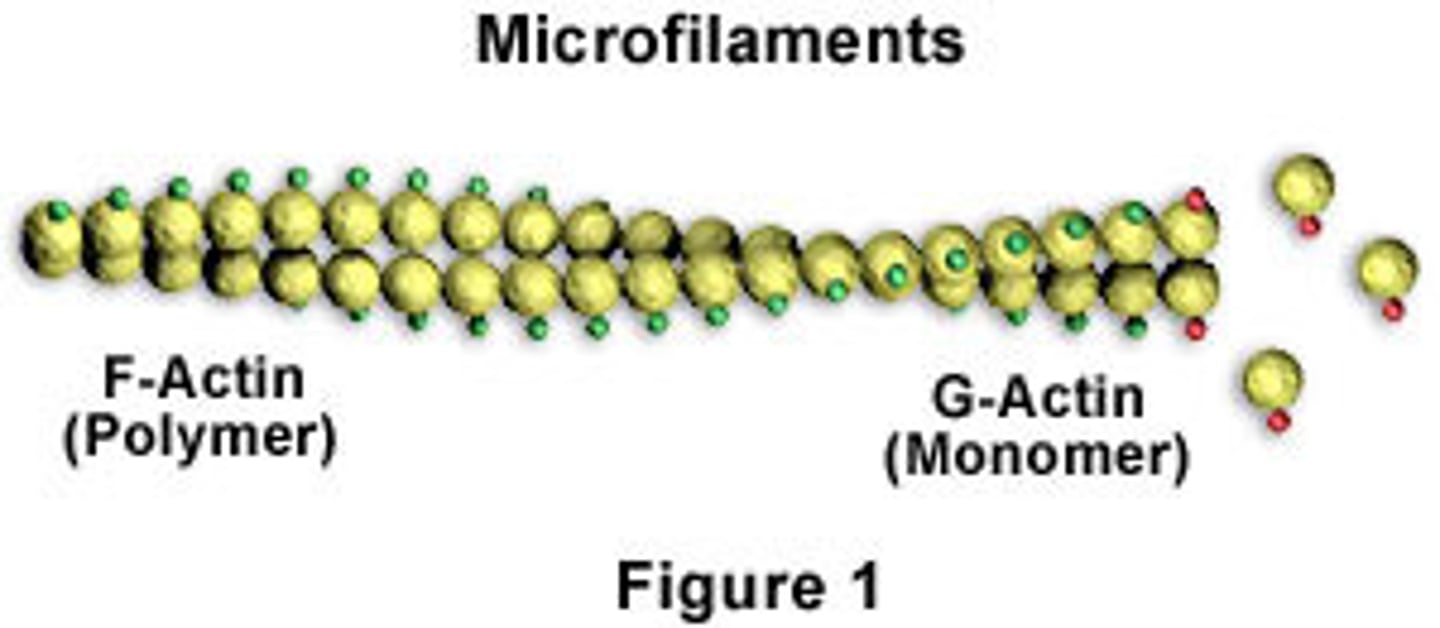
microfilaments
- control the outer shape of the cell(resist tension)
- (motility)muscle cell stretching and shrinking(movement like pseudopod arms)
- microvilli
microfilament structure
two intertwined strands of actin
pseudopodia
A cellular extension of cells used in moving and feeding that are controlled by microfilaments
intermediate filament function
- anchors organelles(keeps organelles in a stable position)
- provide mechanical strength
- forms nuclear lamina
intermediate filament structure
proteins coiled into cables
motor proteins
A protein that interacts with cytoskeletal elements and other cell components, producing movement of the whole cell or parts of the cell.
monorails
"Tracks" made by the cytoskeleton that vesicles can travel on
keratin
protein found in epidermis, hair, and nails
centrioles
organelles in animal cells from which mitotic spindle forms during cell division (resemble basal bodies)
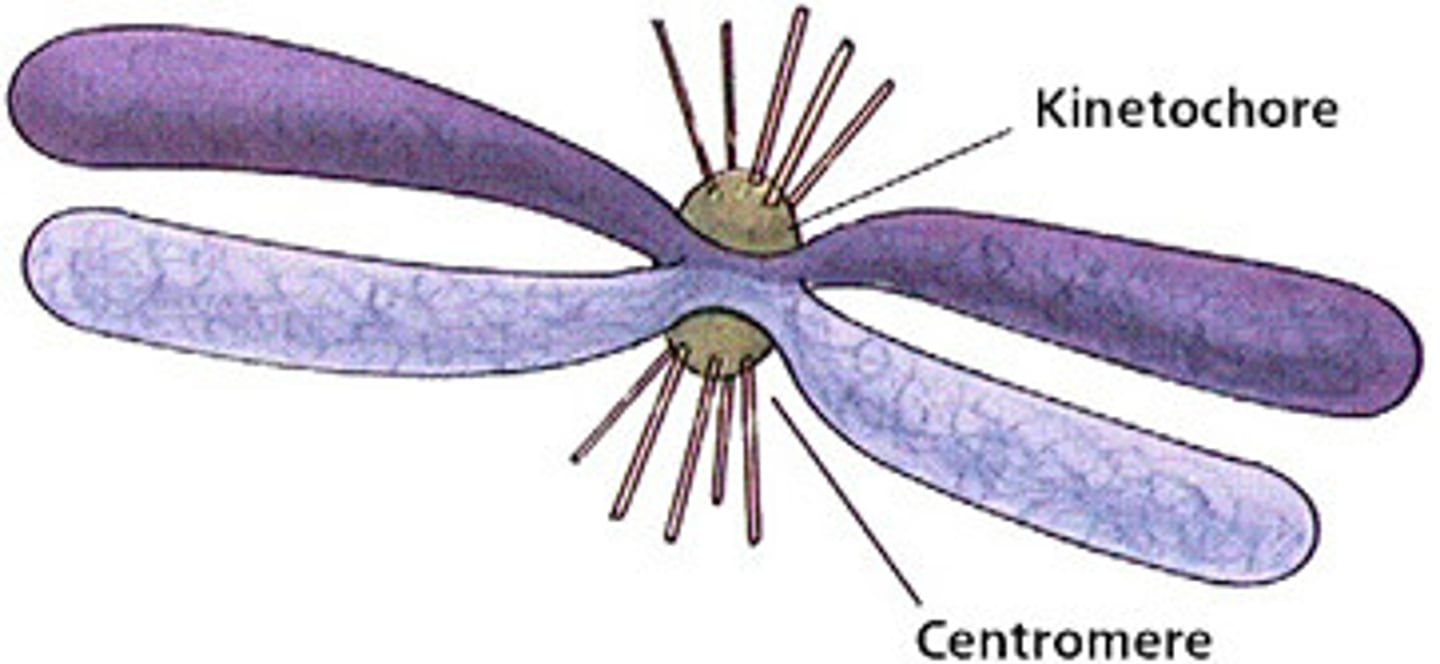
mitotic spindle
microtubules that attach to centromeres through kinetochore proteins of chromosomes and pull sister chromatids apart during cell divisions
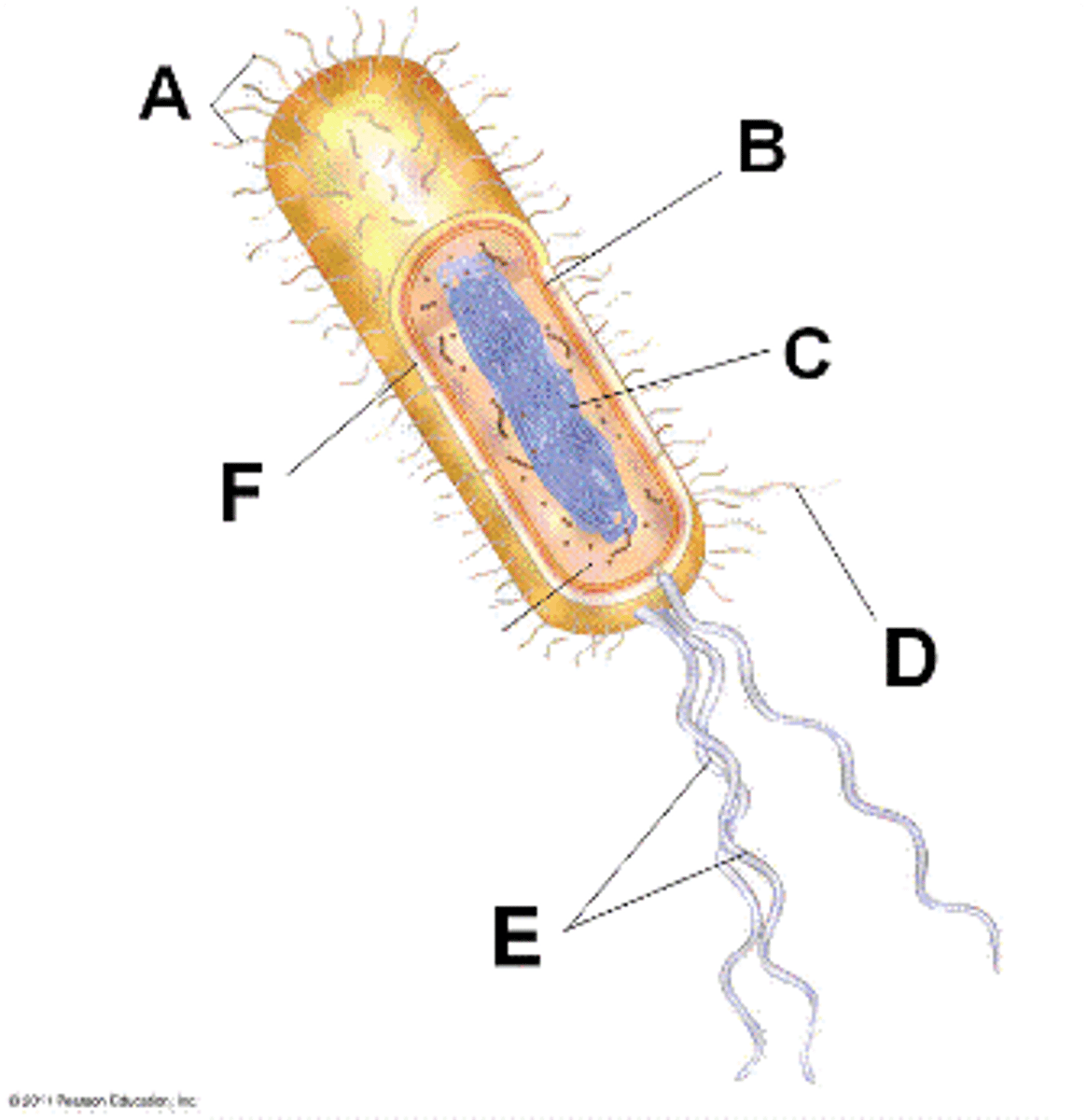
cilia
(A) short, many extensions of membrane-covered microtubules that move cell or materials past cell (ex. paramecium, trachea)
beating pattern like rowing
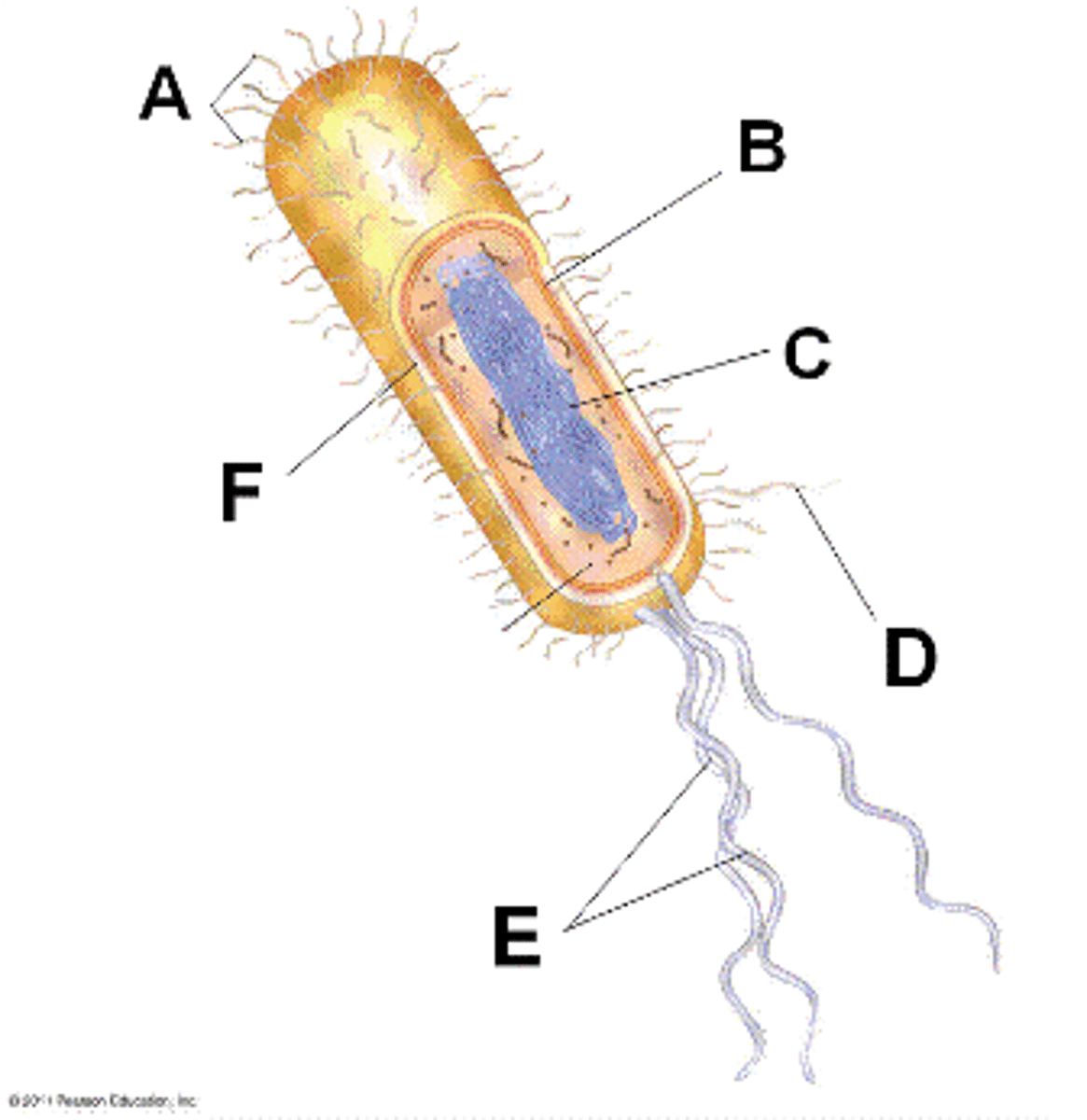
flagella
(E) long, few, whiplike tails of membrane-covered microtubules that move cells
beating pattern like snake
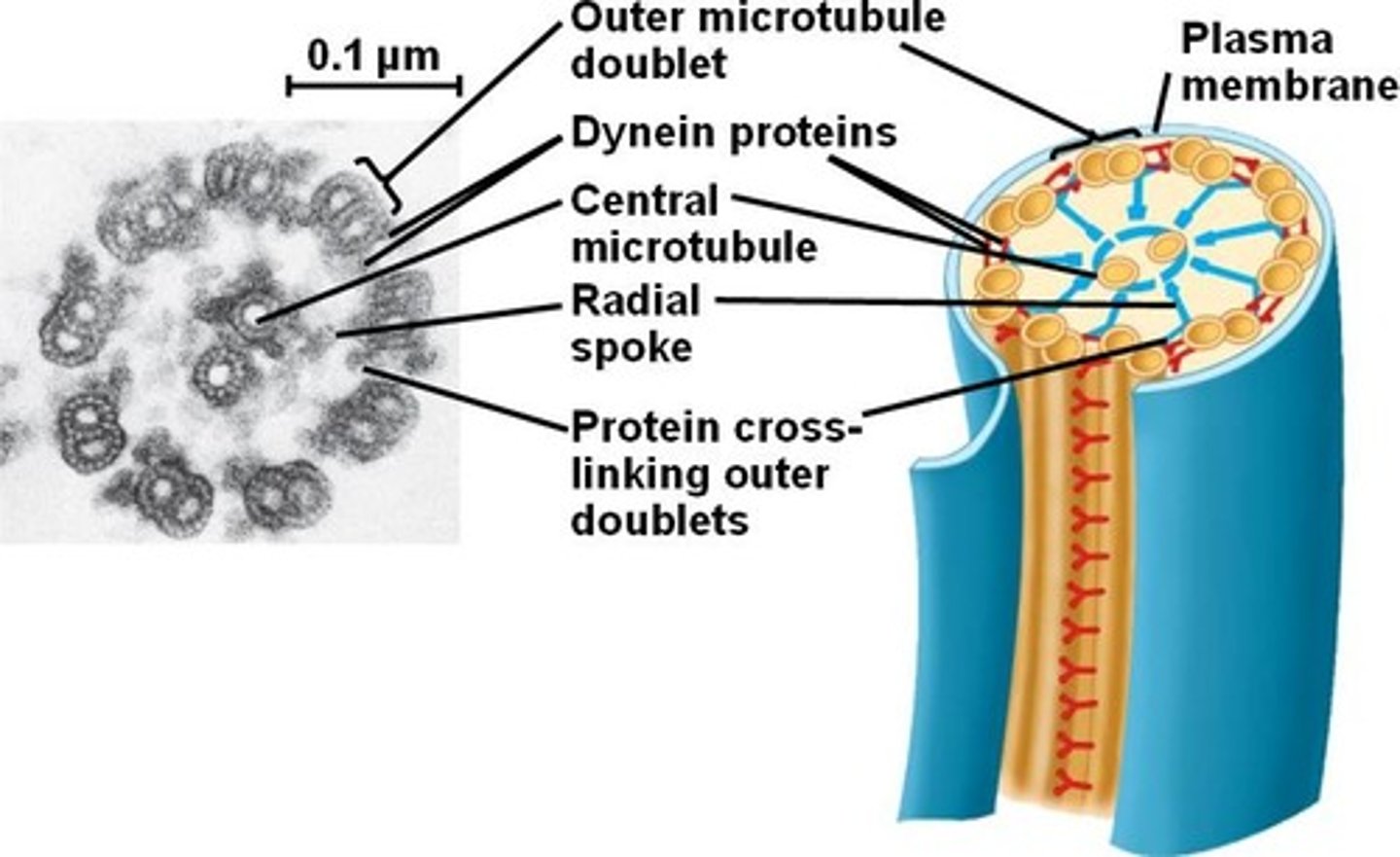
9+2 structure
cylinder of 9 microtubule doublets around a 1 doublet (make up cilia, flagella, mitotic spindle)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sVHUO89-sXg
basal body
star of 9 microtubules triplets that anchors cilia and flagella in membrane (resembles centrioles)
Where is the basal body located?
LOCATED AT THE BOTTOM OF THE STRUCTURE INSIDE THE CELL AND IT ANCHORS THE CILIA/FLAGELLA
dyneins
proteins that connect microtubules in the 9+2 structure AND attach organelles to microtubules; when they contract, flagella/cilia move AND organelles "walk"
cytoplasmic streaming
circular flow of cytosol using myosin and actin filaments that speeds up distribution of materials within cells
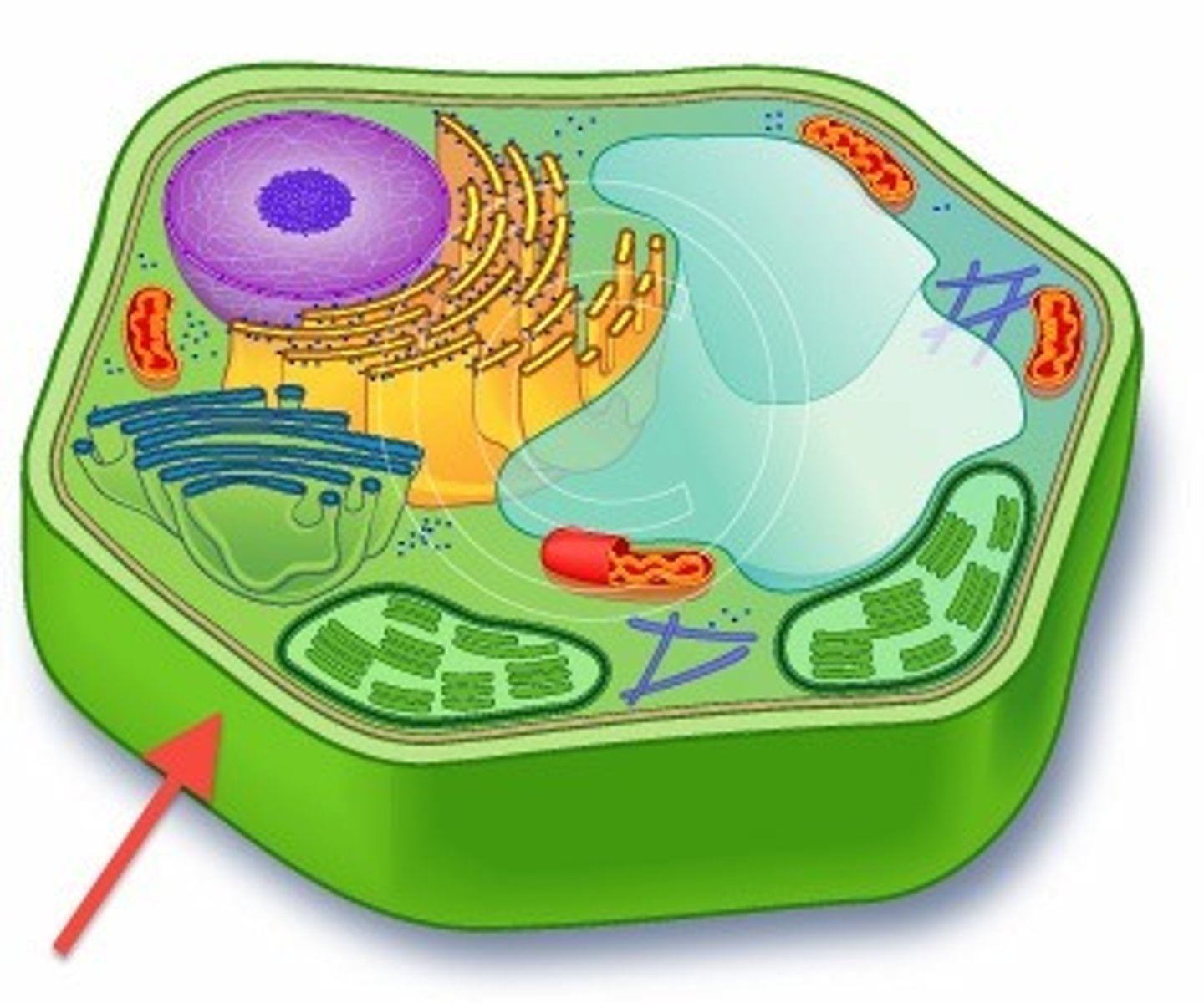
What is the cell wall and what is its function?
a strong supporting layer of cellulose, chitin, or peptidoglycans around cell membrane in plants, fungi, or bacteria
function is to maintain cell shape, protect it, and prevent excess water uptake
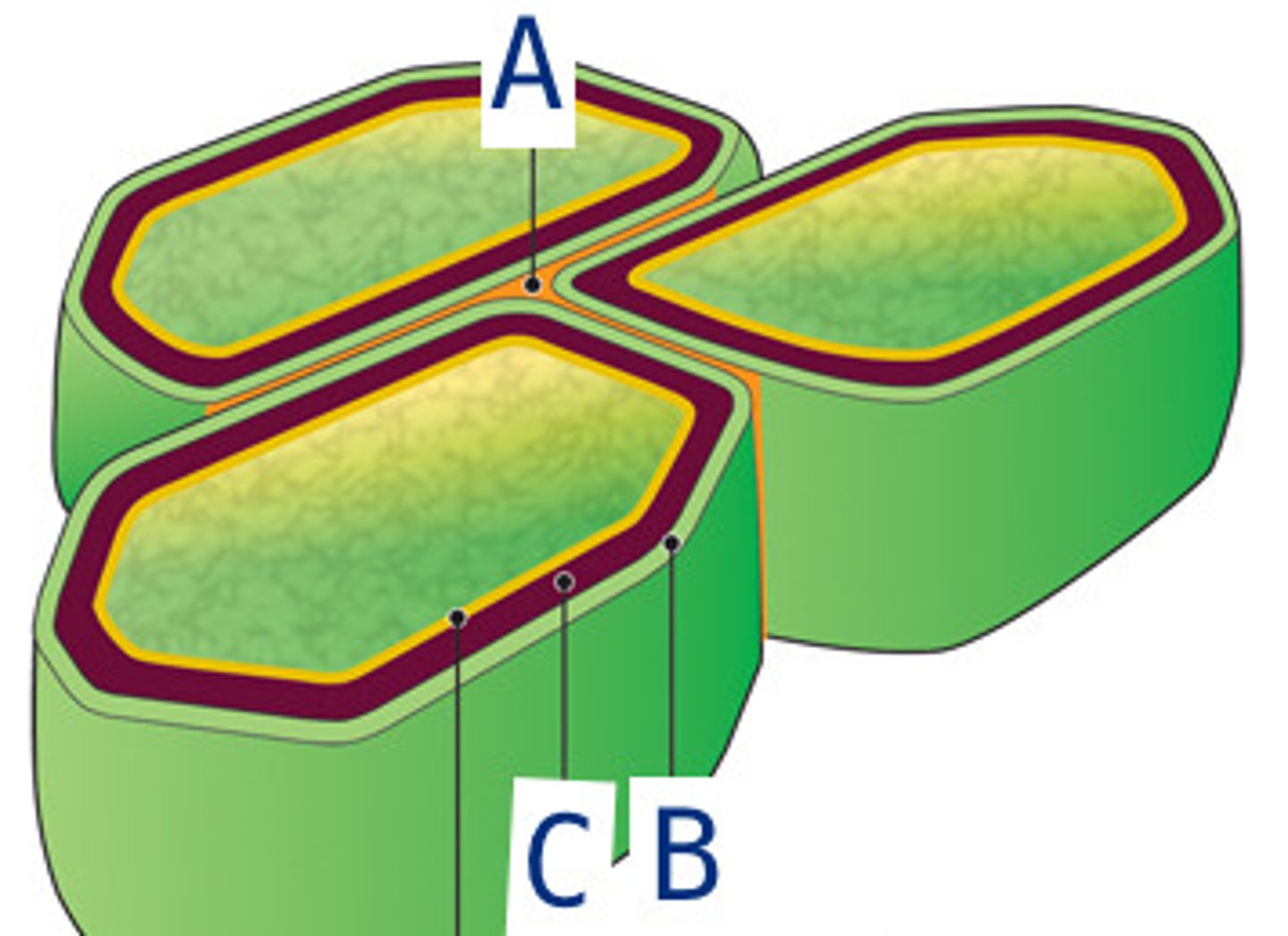
middle lamina
(A) thin layer of adhesive extracellular material (pectins) between primary walls of adjacent young plant cells
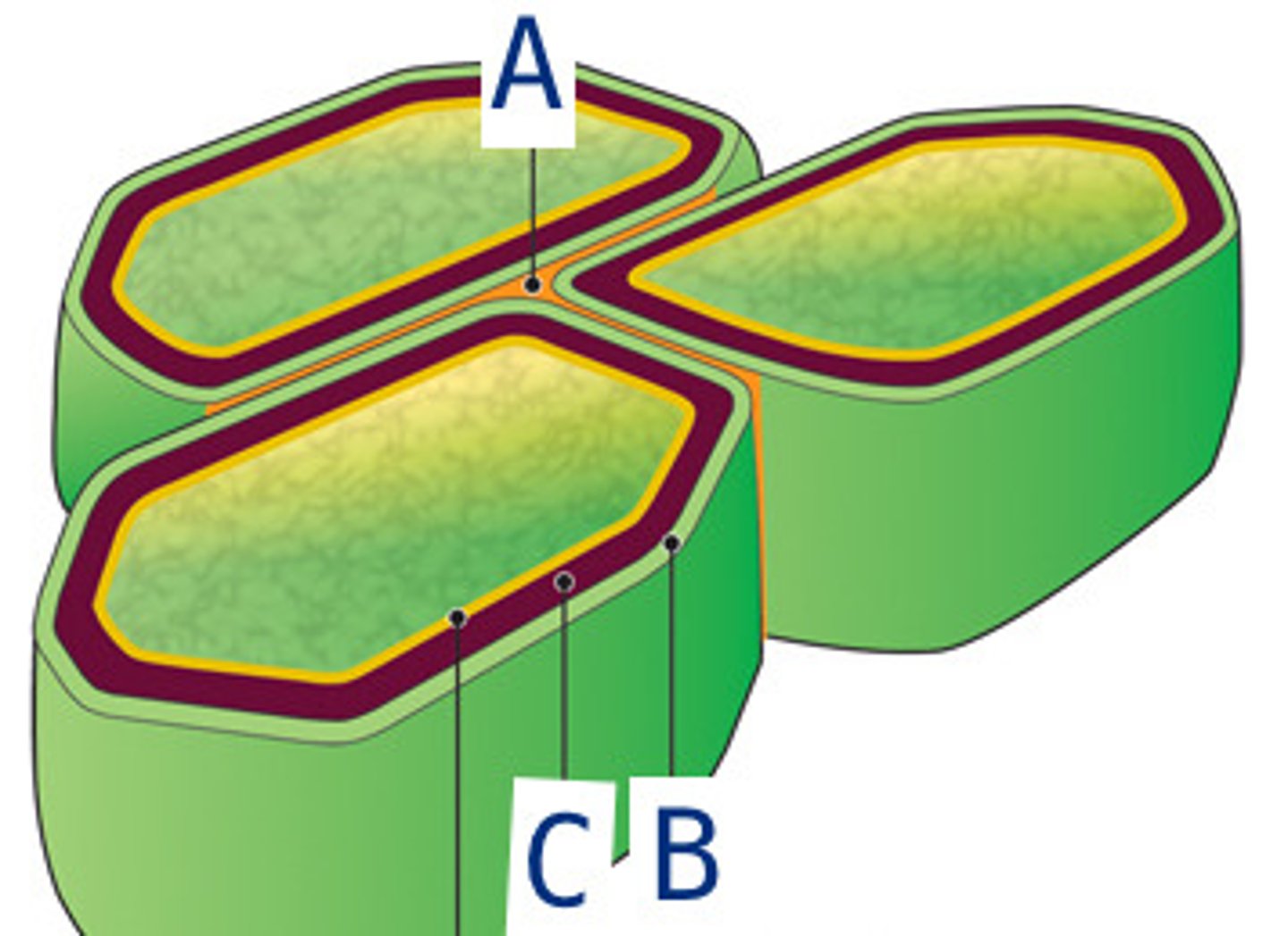
primary cell wall
(B) thin, flexible and furthest out because it is secreted first
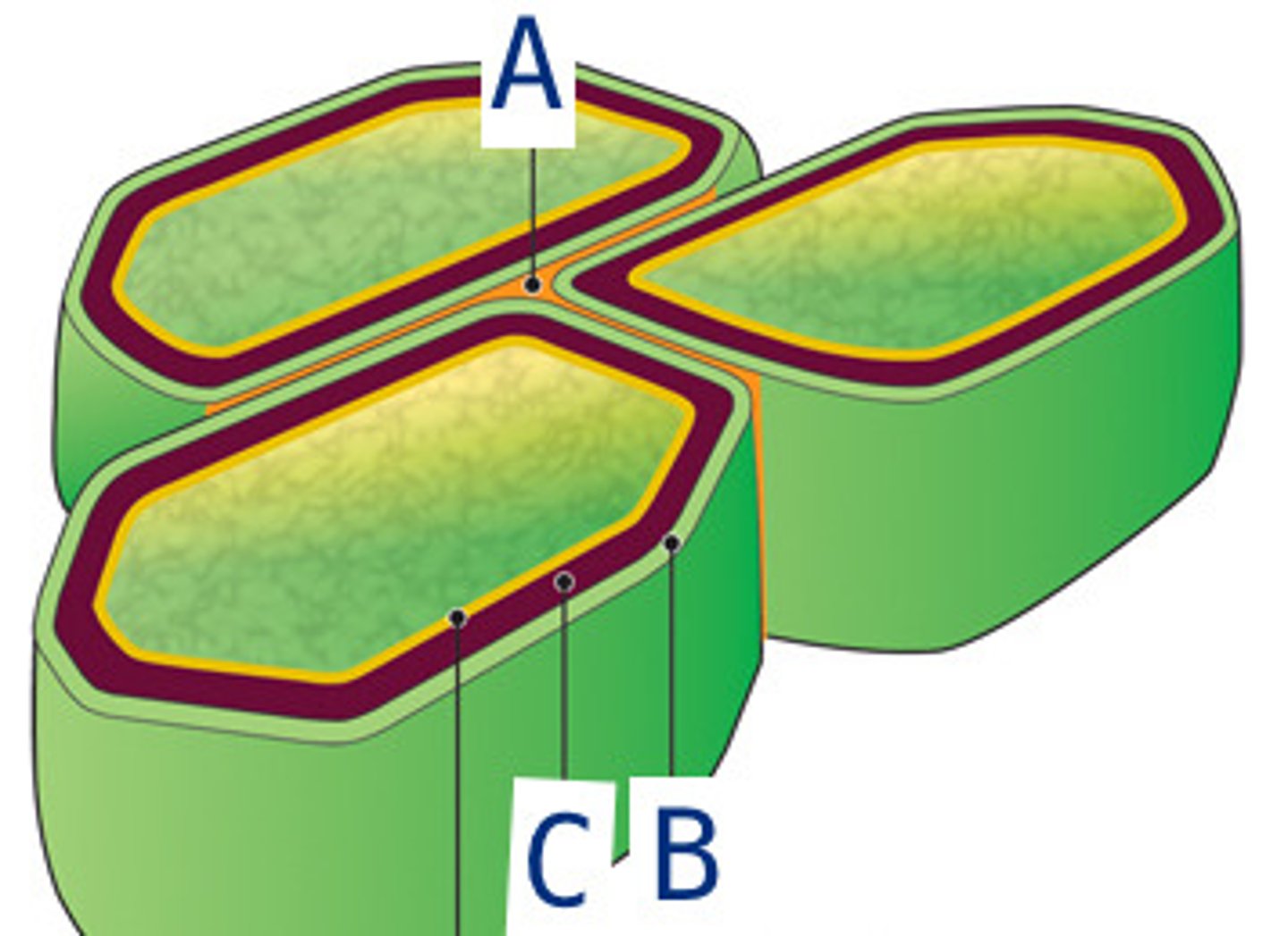
secondary cell wall
(C) strong, durable matrix added between plasma membrane and outermost structure for structure and support
extracellular matrix (ECM)
substance in which animal cells are embedded, consisting of proteins and polysaccharides
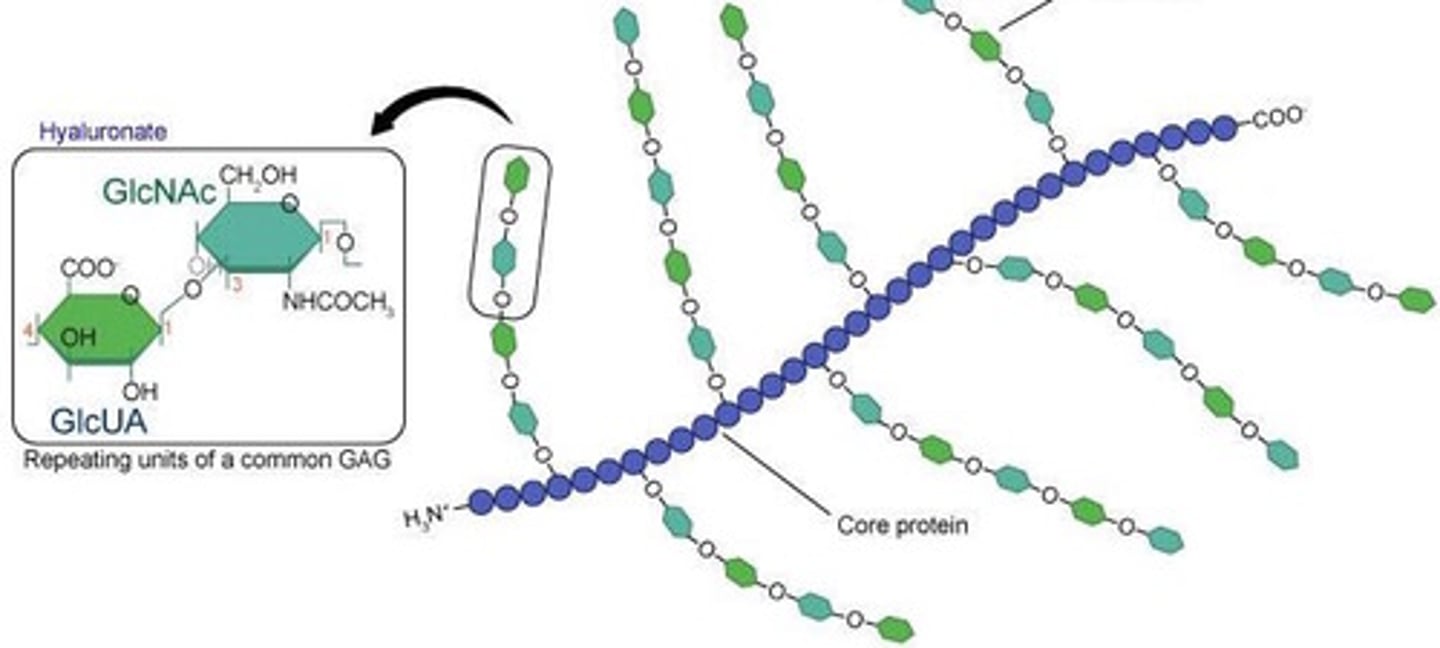
peptido/proteo-glycans
small core proteins with EXTENSIVE carbohydrate chains found in bacterial cell walls and animal ECM
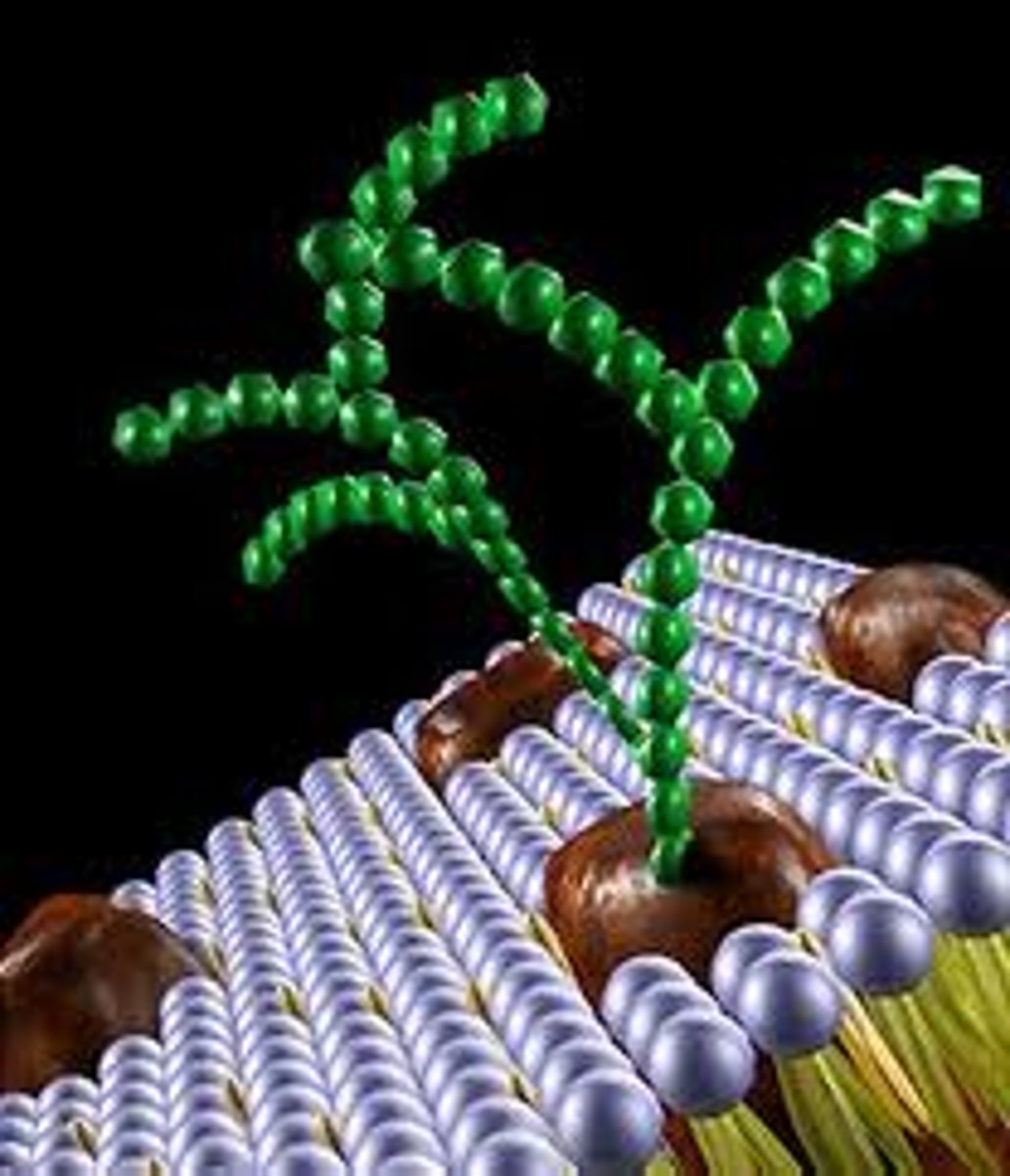
glycoproteins
transmembrane proteins with SHORT carbohydrate chains that identify the cell
fibronectin
a glycoprotein that helps cells attach to extracellular matrix
integrins
transmembrane proteins that connect both to outside extracellular matrix and inside cytoskeleton of animal cells.
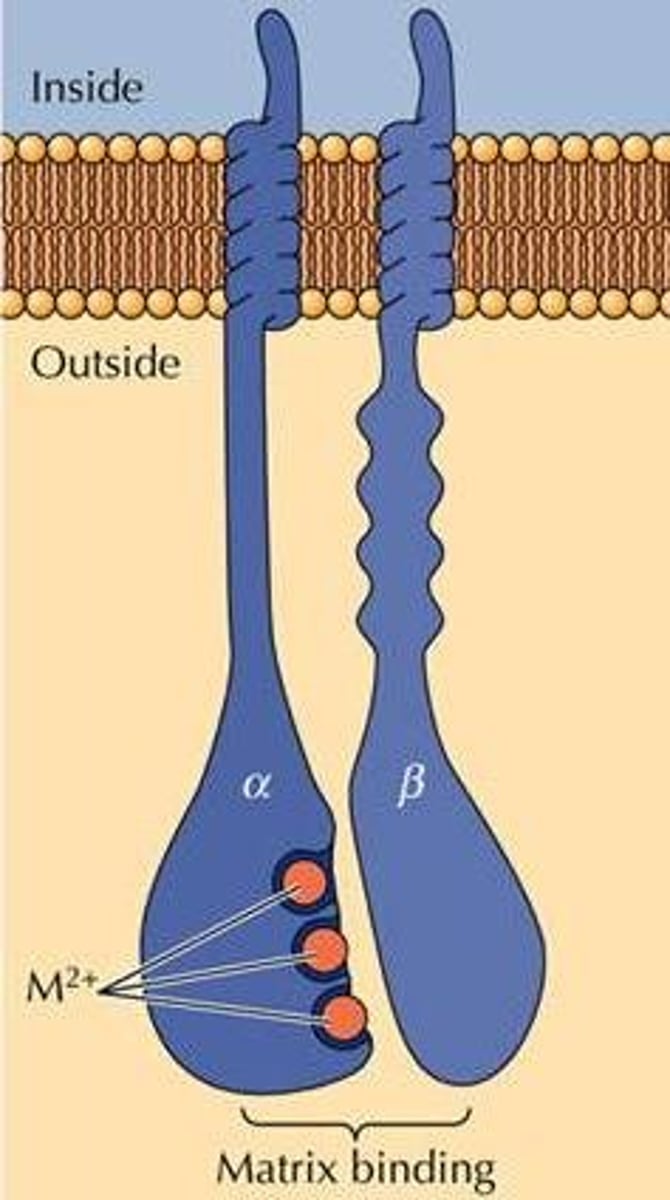
What is the purpose of fibronectin-integrin connections?
The link can help permit changes inside and outside the cell. It allows regulation of cell behavior.
plasmodesmata
(2) openings in plant cell walls through which strands of ER and cytosol connect adjacent cells
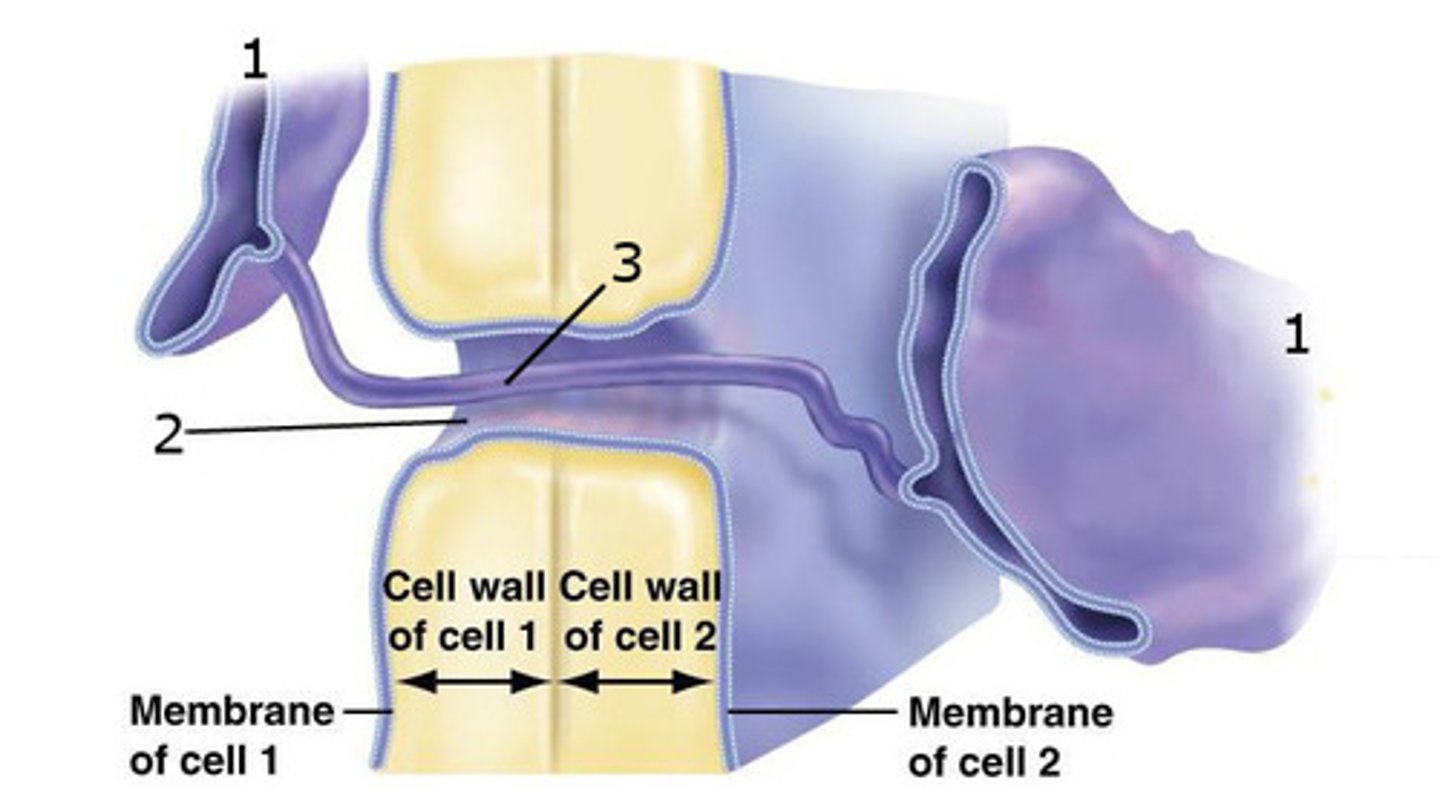
Plasmodesmata Function
Water and solutes can pass through. In some cases, RNA and proteins can also be exchanged.
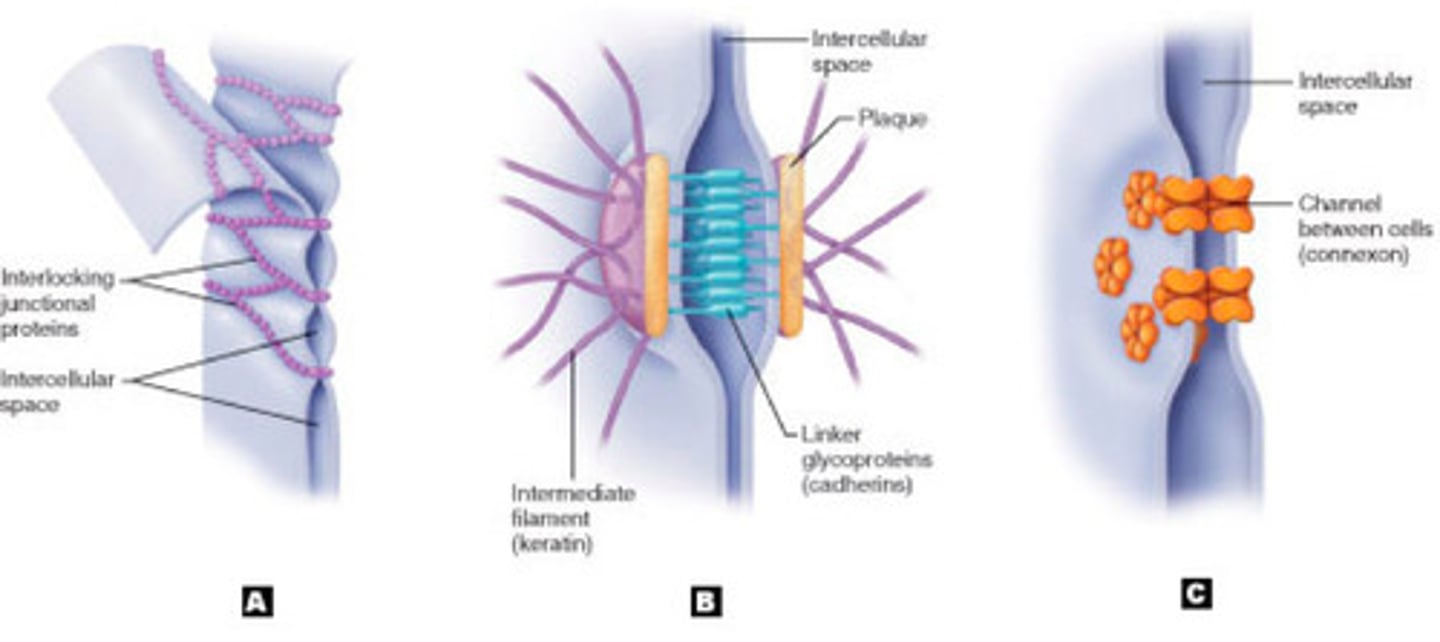
tight junctions
(A) membrane fusions of neighboring cells that prevent leakage of fluid between them
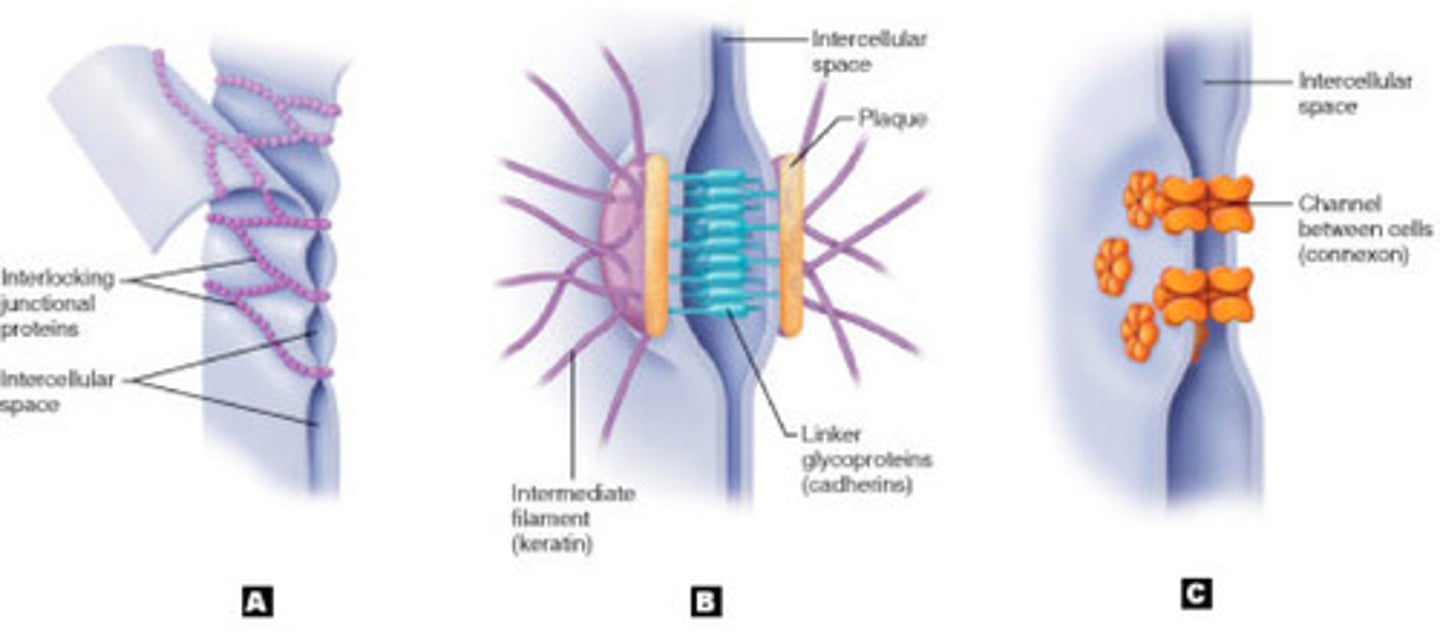
desmosomes
(B) anchoring junctions that prevents cells subjected to mechanical stress from being pulled apart
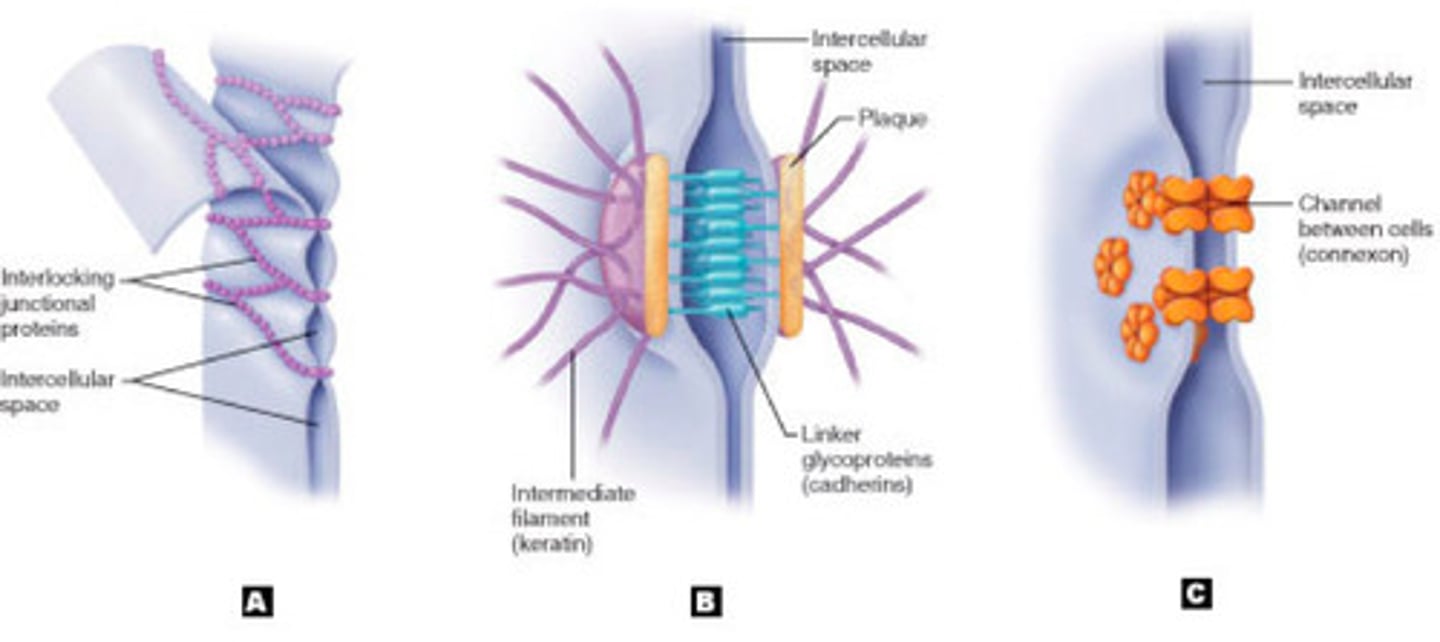
gap junctions
(C) cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells that allow movement of materials
microvilli
finger-like extensions of cells that increase surface area to increase absorption (ex. small intestine)
prokaryote
unicellular organism without nucleus and membrane bound organelles (archea and bacteria)
eukaryote
cells with nucleus and membrane bound organelles
collagen
fibrous protein found in connective tissues and ECM