Comprehensive Micro Review
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
NF on skin
coag neg staph
corynebacterium
cutibacterium acnes
micrococci
strep viridans
(transient/colonizers of skin)
vaginal NF
lactobacilli
low numbers of anaerobes and skin flora
normal GI flora
enterobacterales
anaerobes
enterococcus
lactobacilli
respiratory NF
anaerobes
saprophytic neisseria
strep viridans group
GPC (staph, rothia, nutritionallu varient strep)
corynebacterium
strep penumoniae, moraxella, H. influenzae, and yeast (in small amounts)
should there be NF in the blood
no
should there be NF in the body fluids
no
should there be NF in the urine
no (but it’s often contaminated)
common pathogens in urine cultures
enterobacterales
enterococci
S. aureus
S. saprophyticus (young females)
Pseudomonas
pathogens in the genital cultures
clue cells caused by bacterial vaginosis
N. gonorrhoeae, Group B Strep, and yeast (in any amount)
pathogens in stool cultures
salmonella
shigella
campylobacter
pathogens in throat cultures (upper)
S. pyogenes
pathogens in lower respiratory cultures (sputum)
S. pneumoniae
H. influenzae
Moraxella catarrhalis
S. aureus, Enterobacterales, Pseudomonas, and Acinetobacter (when predominant)
pathogens in wound cultures
S. aureus
S. pyogenes (and other beta-strep)
Enterococcus
Anaerobes (esp B, fragilis, Prevotella, and Clostridium)
Enterobacterales
Non-fermenters
Candida spp.
pathogens in the body fluids (CSF)
Group B Strep (neonates)
N. meningitidis (young adults)
S. pneumoniae
Listeria
E coli
H. influenzae
Cryptococcus
pathogens in the body fluids (pleural fluid)
S. pneumoniae
S. aureus
H. influenzae
P. aeruginosa
pathogens in the body fluids (peritoneal fluid)
Enterobacterales
anaerobes
S. viridans group
Enterococcus
pathogens in the body fluids (pericardial fluid)
most often viral
S. aureus
Strep viridans group
pathogens in the body fluids (synovial fluid)
S. aureus
N. gonorrhoeae
coag negative staph
corynebacterium
cutibacterium
pathogens in the blood
coag negative staph
corynebacterium
cutibacterium acnes
micrococci
strep viridans group
bacillus
plates set up for wound culture
aerobic BAP, CHOC, PEA, and LKV
anaerobic ABAP, APEA, and LKV
plates set up for body fluids
BAP and CHOC
what plate do you set up if you’ve seen yeast on the gram stain
SAB plate
plates set up for sputum
BAP, CHOC, and MAC
why do we place an optochin disk on a BAP plate when doing a sputum culture
to identify Streptococcus pneumoniae ( it’s sensitive to optochin)
what plates do we set up for a blood culture
BAP, CHOC, and MAC if you see GNB in the blood smear
ABAP if you have an anaerobic bottle
what plates do you set up for a urine culture
BAP and MAC
what plates do you set up for a genital culture
BAP, CHOC, MAC, and TM
what plates do you set up for a stool culture
BAP, MAC, XLD, and CAMPY
what is a TM plate used to identify
Neiserria species
what is the PEA plate used for
to identify gram positive bacteria
what is XLD used to identify
salmonella or shigella
what is a CAMPY plate used to identify
Campylobacter species
what is an LKV plate used to identify
anaerobic species
what is a BBE plate used to identify
B. fragilis
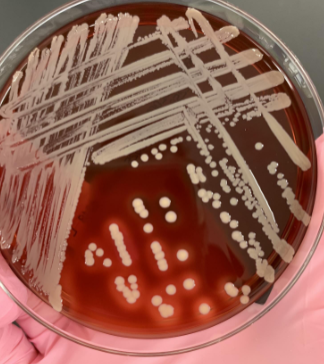
what would you do next
gram stain or do the catalase test
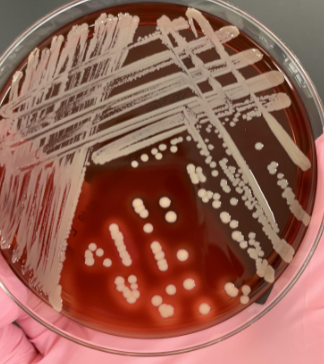
if you catalase is (+) and the gram stain shows GPC what next step would you take
do the coagulase
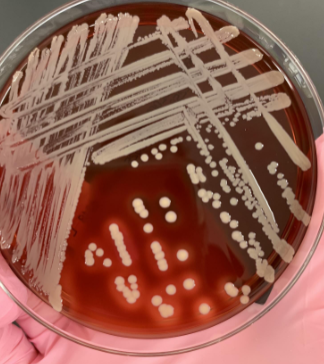
if your catalase is (+) and the gram stain shows GPC, and coagulase is (+) what organism would this be
Staphylococcus aureus
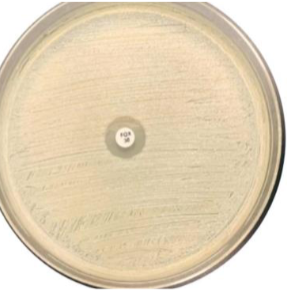
what suspectibility testing could you do for S. aureus
penicillin or cefoxitin
if your cefoxitin is resistant what organism would that be
MRSA
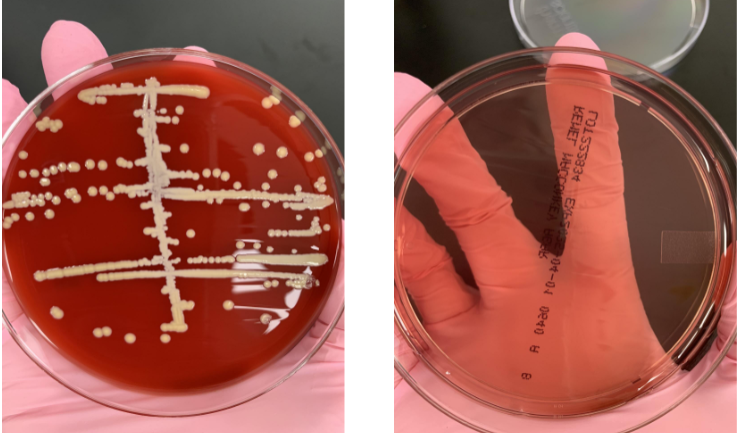
what next steps would you take
gram stain or preform catalase
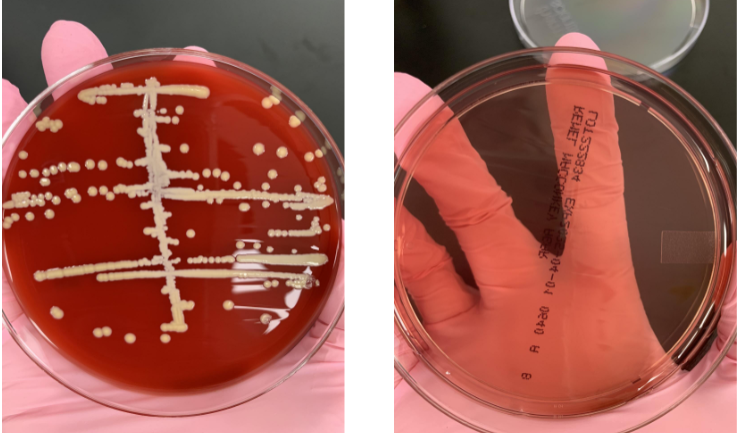
if your catalase is (+) then what next step would you take
coagulase
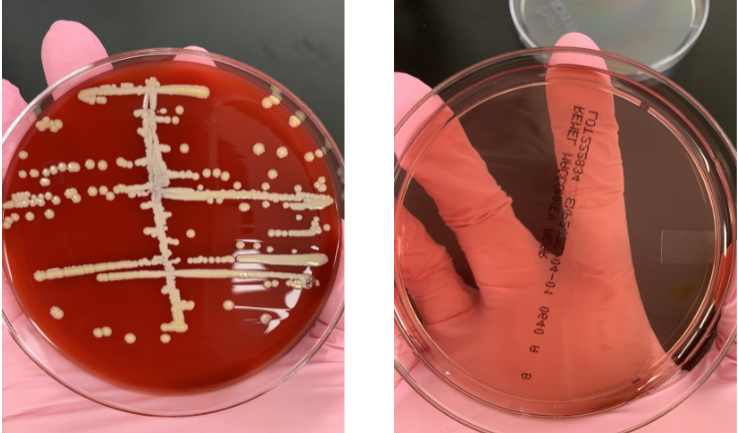
if your catalse is (+) and coagulase is (-) what would the organism be
coag negative staph
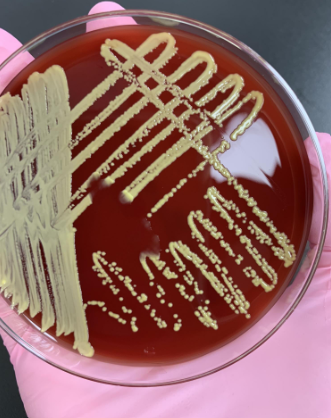
what would you do next
gram stain to look for tetrads and do catalase
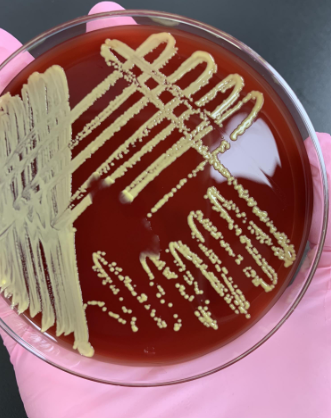
if you see tetrads and the catalase is (+) what would you do next
microdase test (should be blue or purple for +)
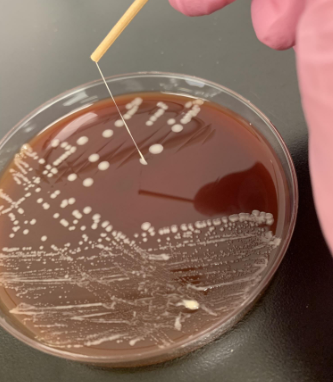
what organism is this
Rothia mucilaginosa
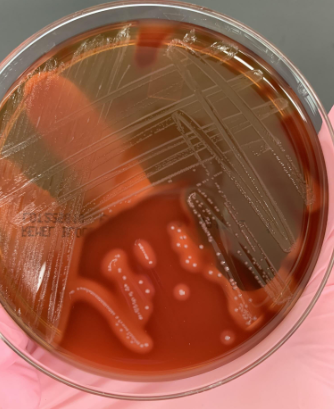
what next steps would you take
beta hemolysis so catalase and then Lancefield Grouping (probably Group A)

what next steps would you take
know it’s alpha so bile solubility
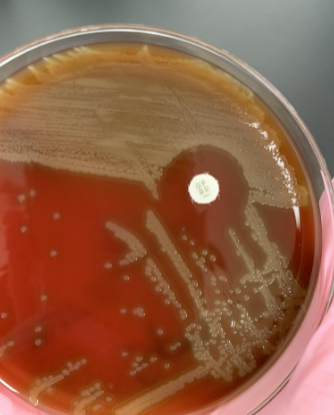
if bile solubility is (+) meaning the colonies lyse what organism is this
S. pneumoniae
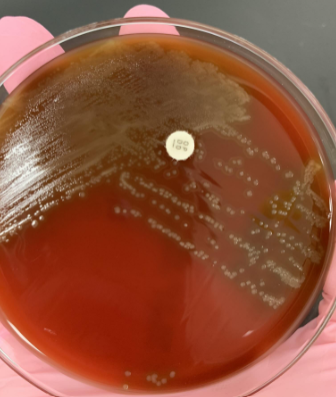
lets say you subbed alpha hemolysis to a new plate and put an optochin disk on the plate, and did bile solubility and it was (-) , what does this result tell you
optochin resistant so most likely S. viridans which is normal flora
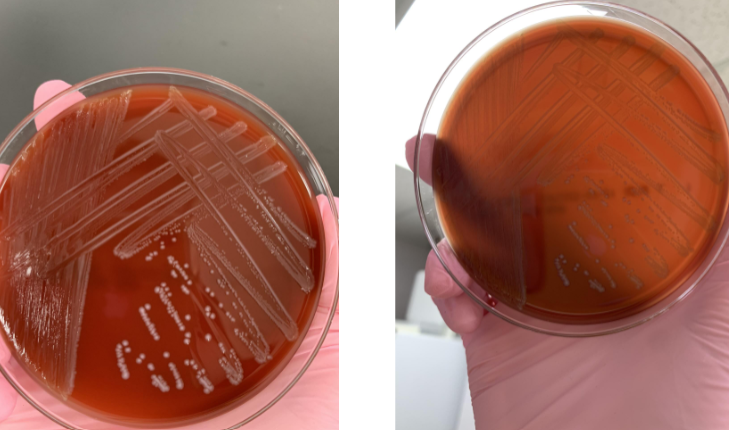
what next steps should you take
beta hemolysis so gram stain and catalase
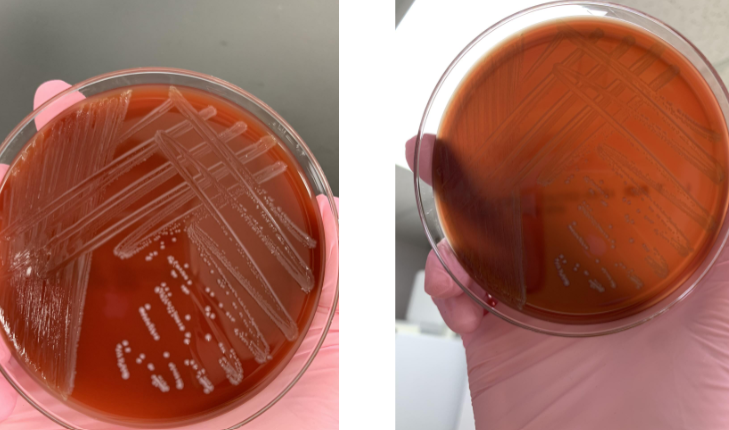
lets say the gram stain showed GPC and was catalase (-) what should you do next
PYR
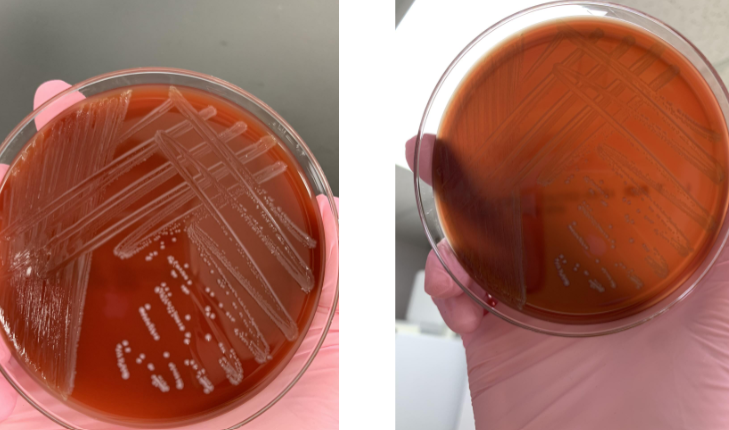
lets say the gram stain showed GPC, was catalase (-), and was PYR (+), what would the organism be
Enterococcus (if you did bile esculin it would show black)
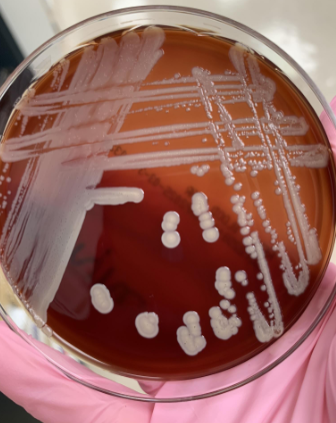
what would you do next
gram stain
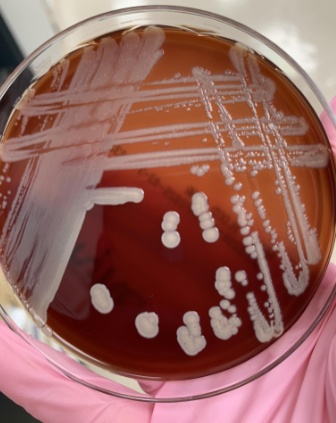
lets say the gram stain showed GPB that were stacking, what organism would this be
Corynebacterium
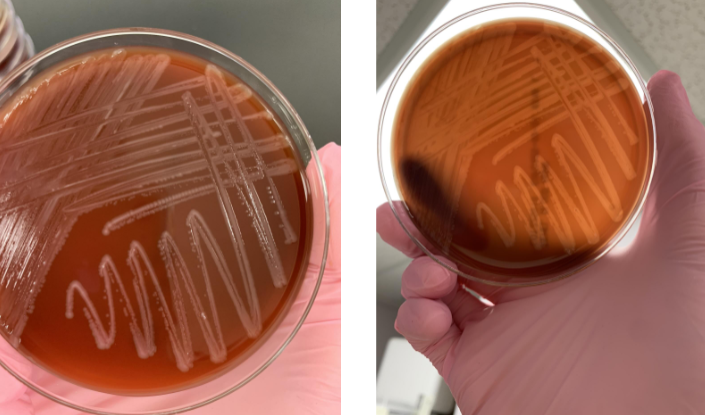
what would you do next
beta hemolysis so gram stain and catalase
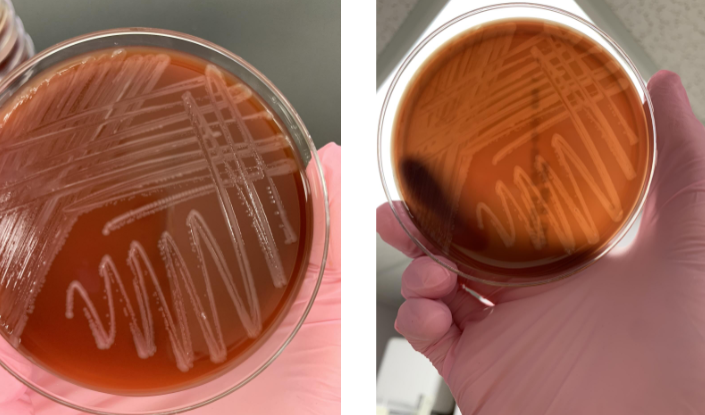
lets say the gram stain showed GPB with beta from a blood culture and was catalase (+) what is most likely the organism
Listeria monocytogenes
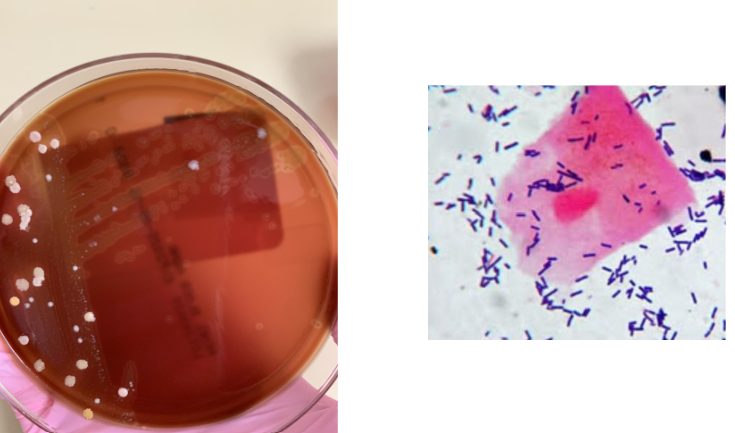
what organism is this most likely
alpha hemolysis and GPB so Lactobacillus
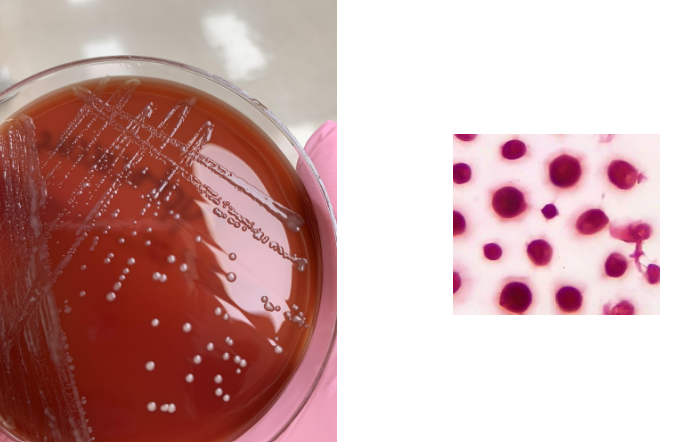
what does this CSF culture show
yeast
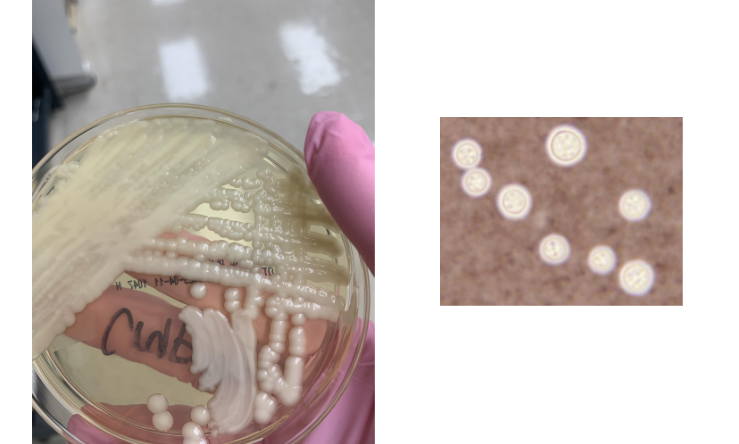
you saw yeast in your gram stain from your BAP so you put it onto an SAB plate and saw this, what next step would you take
india ink to confirm Cryptococcus neoformans
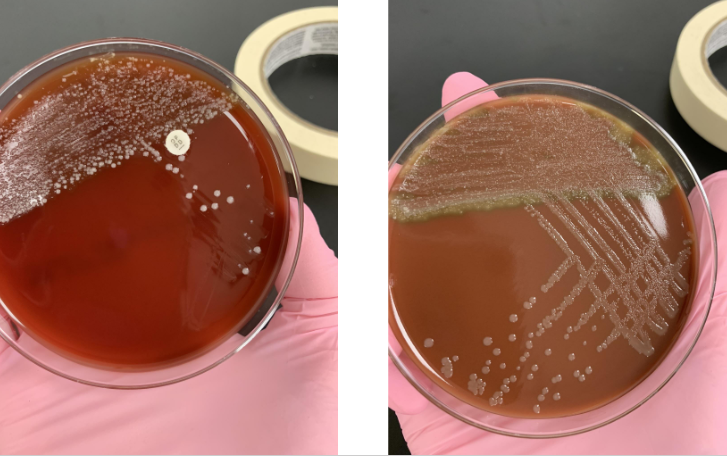
this is from a respiratory culture so what would you do next
there’s more growth on CHOC so gram stain the CHOC

lets say you gram stained your respiratory culture and saw GNCB, what next step would you take
subculture to a quad plate
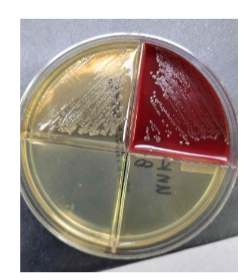
lets say you subcultured from you respiratory plate onto a quad plate and saw this, what is most likely the organism
H. influenzae
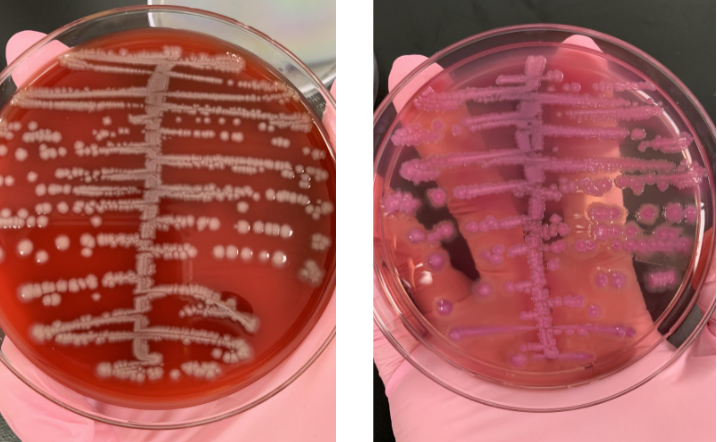
what next steps would you take
know it’s a lactose fermenter so indole
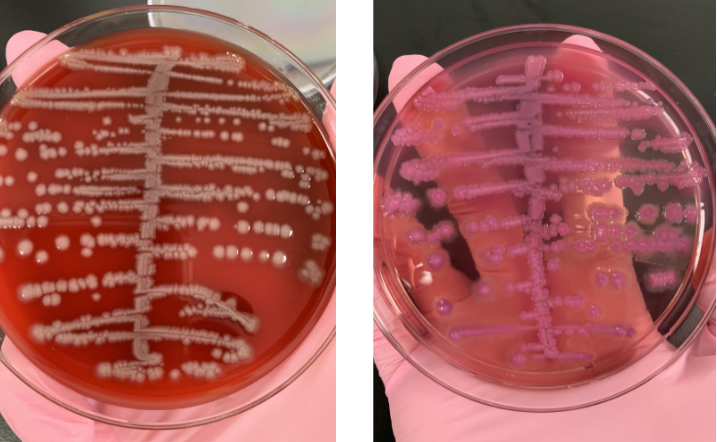
lets say the indole was (+) and you ended up doing a citrate tube and it was (-), what organism would this be
E. coli
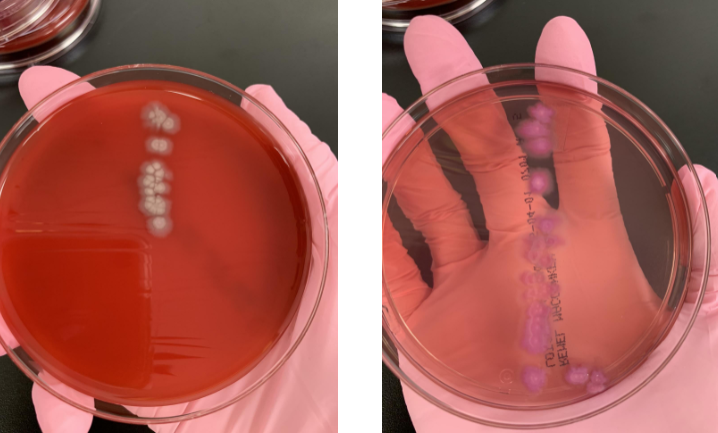
is this a UTI
noa UTI is characterized by specific symptoms and typically involves the urinary tract.
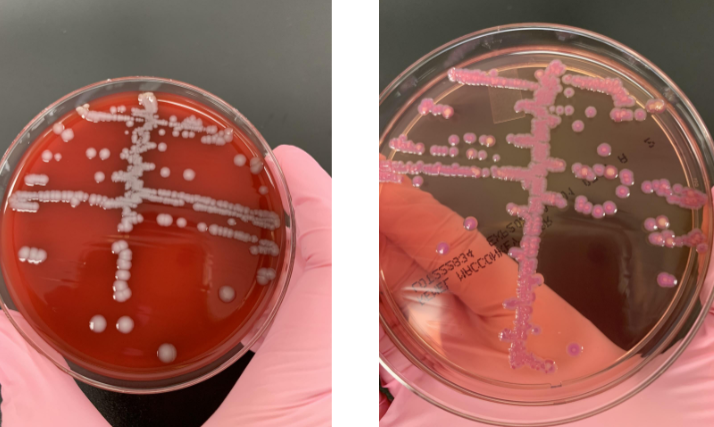
what next steps would you take
lactose fermenter so would do indole
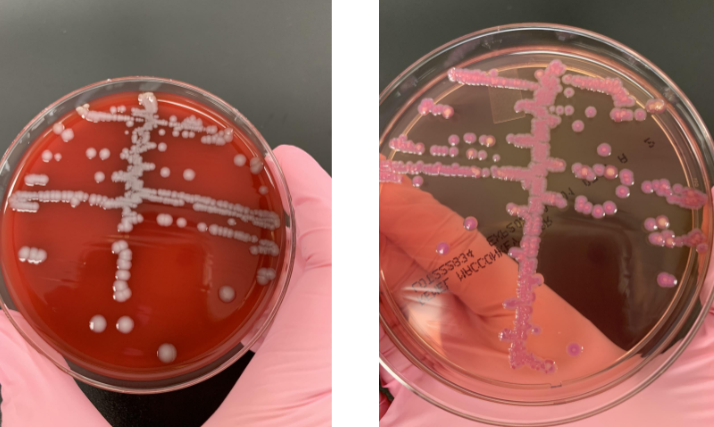
lets say your indole was (-), what next step would you take
API strip
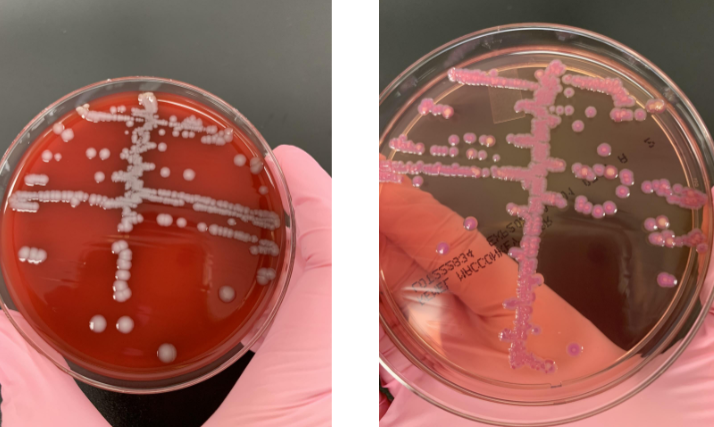
lets say your API strip showed indole (-), citrate (+) and urease (+), what organism would it be
Klebisiella pneumoniae
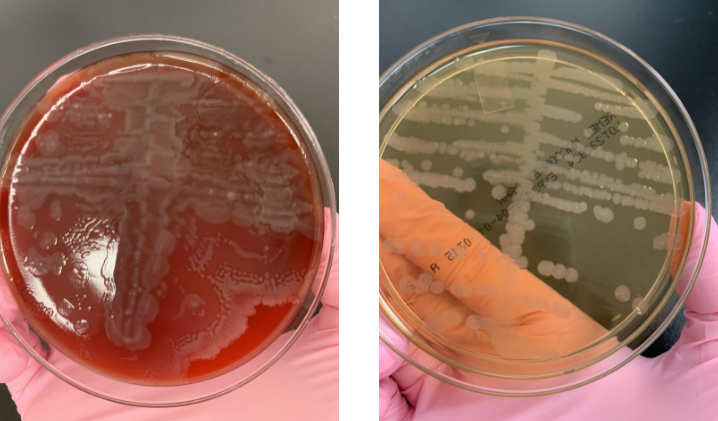
what next steps would you take
swarming present and non-lactose fermenter so oxidase
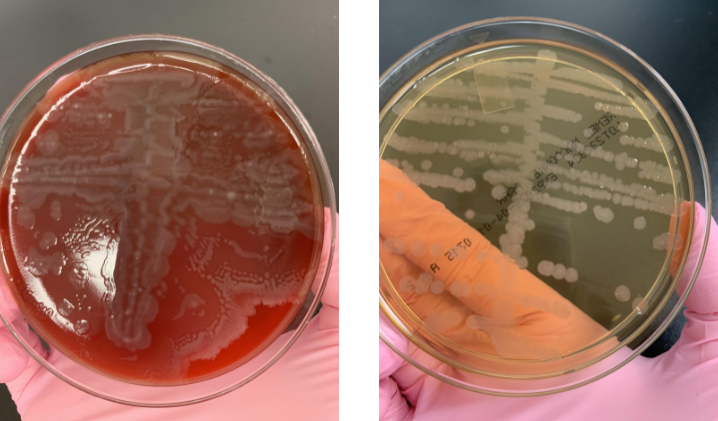
lets say the oxidase was (-), what next steps would you take
API strip
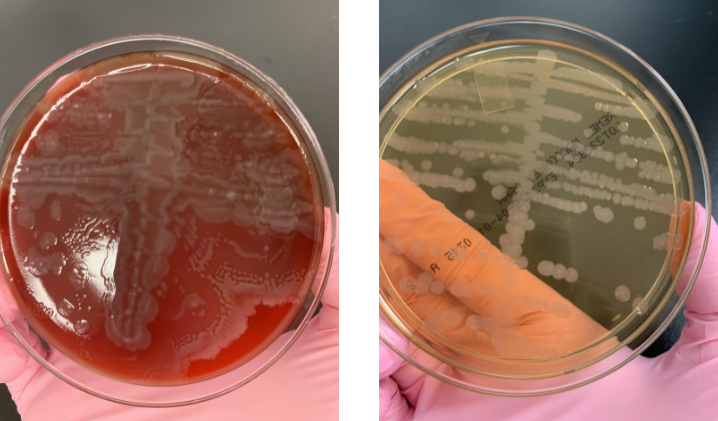
your oxidase is (-) and lets say your API strip showed H2S (+), urease (+), and TDA (+), what organism is this most likely
Proteus mirabilus
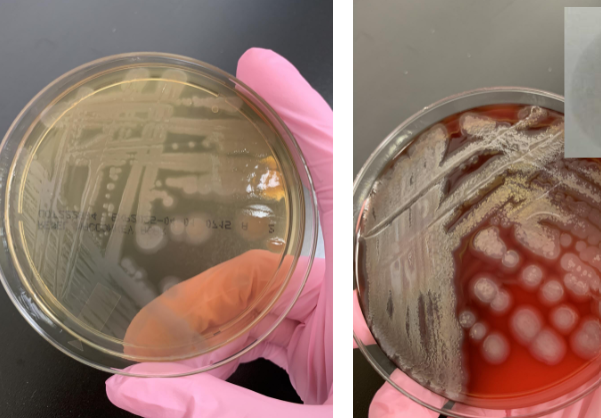
what next steps would you take
preform an oxidase because the organism doesn’t ferment lactose
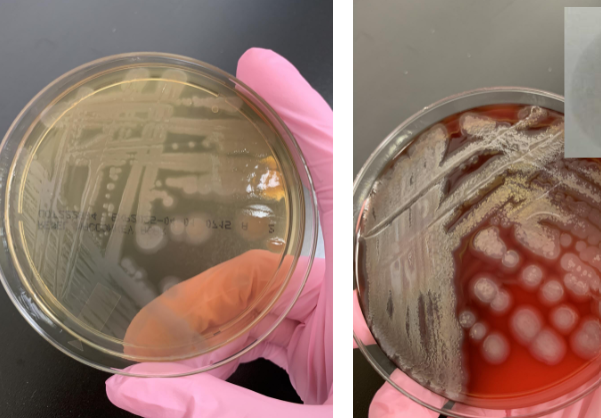
lets say your oxidase is positive and it’s also motile, what organism is this
P. aeruginosa
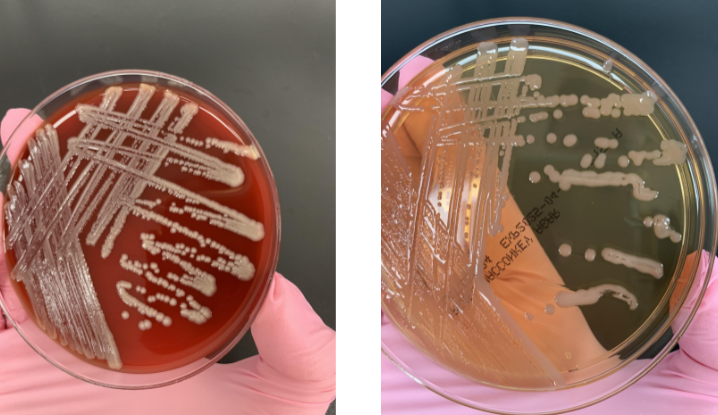
what next steps would you do
gram stain
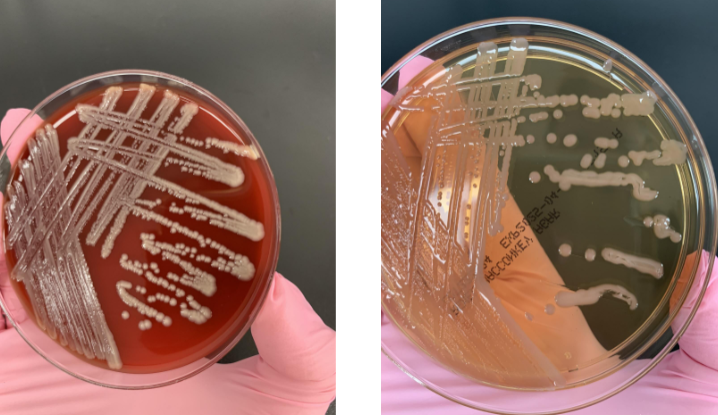
lets say the gram stain showed GNB, what step would you take next
oxidase and API strip
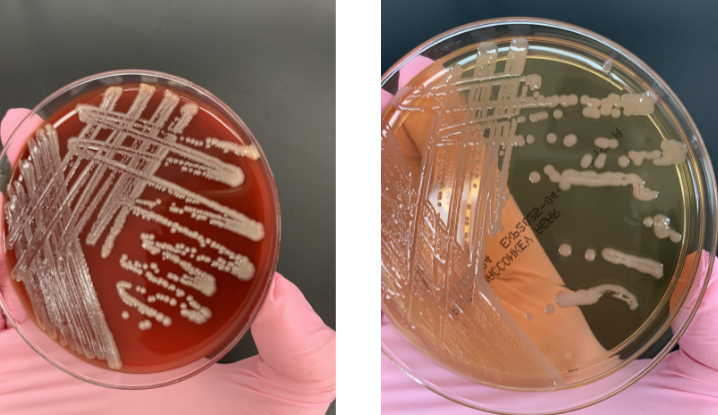
lets say your GNB was oxidase (-) and your API strip showed glucose (-), what organism is this
Acinetobacter lwoffi
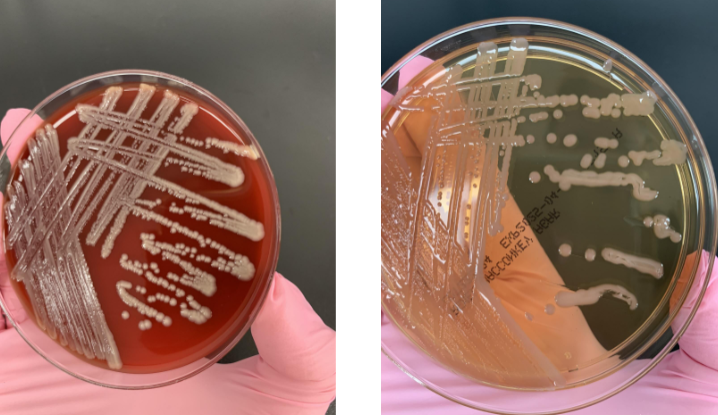
lets say your plate showed a GNCB that was oxidase (-), and nomotile but on the API strip it showed glucose (+), what organism is this
Acinetobacter baumanni
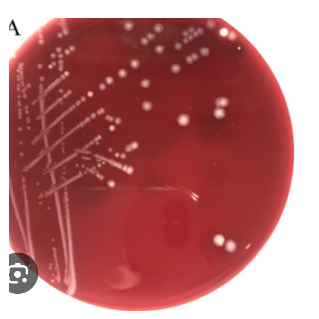
this is a wound culture that has grown on your ABAP and LKV but not your BAP, what does this mean and what next step would you take
it’s an obligate anaerobe, gram stain

lets say your gram stain showed GNB so you sub-cultured to a BBE plate and saw this, what organism would this be
B. fragilis

lets say your gram stain showed GNB so you sub-cultured to a BBE plate but instead of black you saw clear growth, what organism would this be
Prevotella
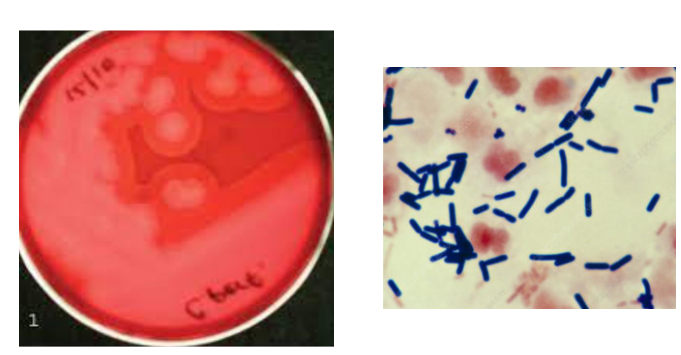
lets say you saw this on your ABAP, there was no growth on the LKV, and gram stained and saw GPB, what organism would this be
Clostridium perfringens
how would you work up S. saprophyticus
make sure the patient is a young female and it’s a urine culture
preform a catalase (+)
preform a coagulase (-)
preform novobiocin susceptibility (R)
how to work up N. gonorrhoeae
preform isolation on TM and look for growth or gram stain to see GNDC
if growth perform NH strip to confirm or NAAT
how to work up Salmonella
isolate on selective media (XLD) should be black because of H2S production
indole (-)
API strip
how to work up Shigella
isolate on selective media (XLD) should show red colonies
indole (V)
API strip
how to work up Campylobacter
isolate on CAMPY
gram stain (shows seagull shape)
motility and oxidase (+)
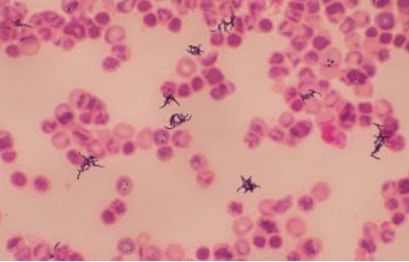
what organism is this
Cutibacterium acnes
lets say you’re given these results:
oxidase (-)
nonmotile
glucose oxidizer
on BAP it looks yellow-white, on MAC it’s clear
Acinetobacter
how would you work up Acinetobacter
isolate on BAP and MAC, perform oxidase test and motility test
clue cells are indicative of
garderella vaginalis
lets say your given these results:
lower respiratory culture
GNCB
butyrate esterase (+)
Moraxella cattarrhalis
lets say you’re given these results:
BAP has white growth, MAC has pink
indole (-)
citrate (+)
urease (+)
Klebsiella pneumoniae
lets say you’re given these results:
BAP has white growth, MAC has pink growth
indole (+)
citrate (-)
E. coli
lets say you’re given these results:
obligate anaerobe
beta on ABAP, growth on APEA, and no growth on LKV
GPB
Clostridium perfringens
what test can you preform to rule out/in S. pneumoniae
bile solubility
let’s say you’re given these results:
shiny/metallic on BAP, clear on MAC
oxidase (+)
motile
P. aeruginosa
lets say you’re given these results:
BAP has white growth
MAC has clear growth
XLD has black growth with hot pink background
Salmonella
lets say you’re given these results:
BAP has yellow-white growth and is beta
catalase (+)
coagulase (+)
S. aureus
Proteus mirabilus is indole
negative
Proteus vulgaris is indole
positive