module 1 prokaryotes
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
free-living
independent of other organisms
Commensalism
one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
parasite
An organism that feeds on a living host
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food; obtains carbon from the atmosphere
Heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer
Chemotrophs
obtain energy from chemicals
Phototrophs
obtain energy from light
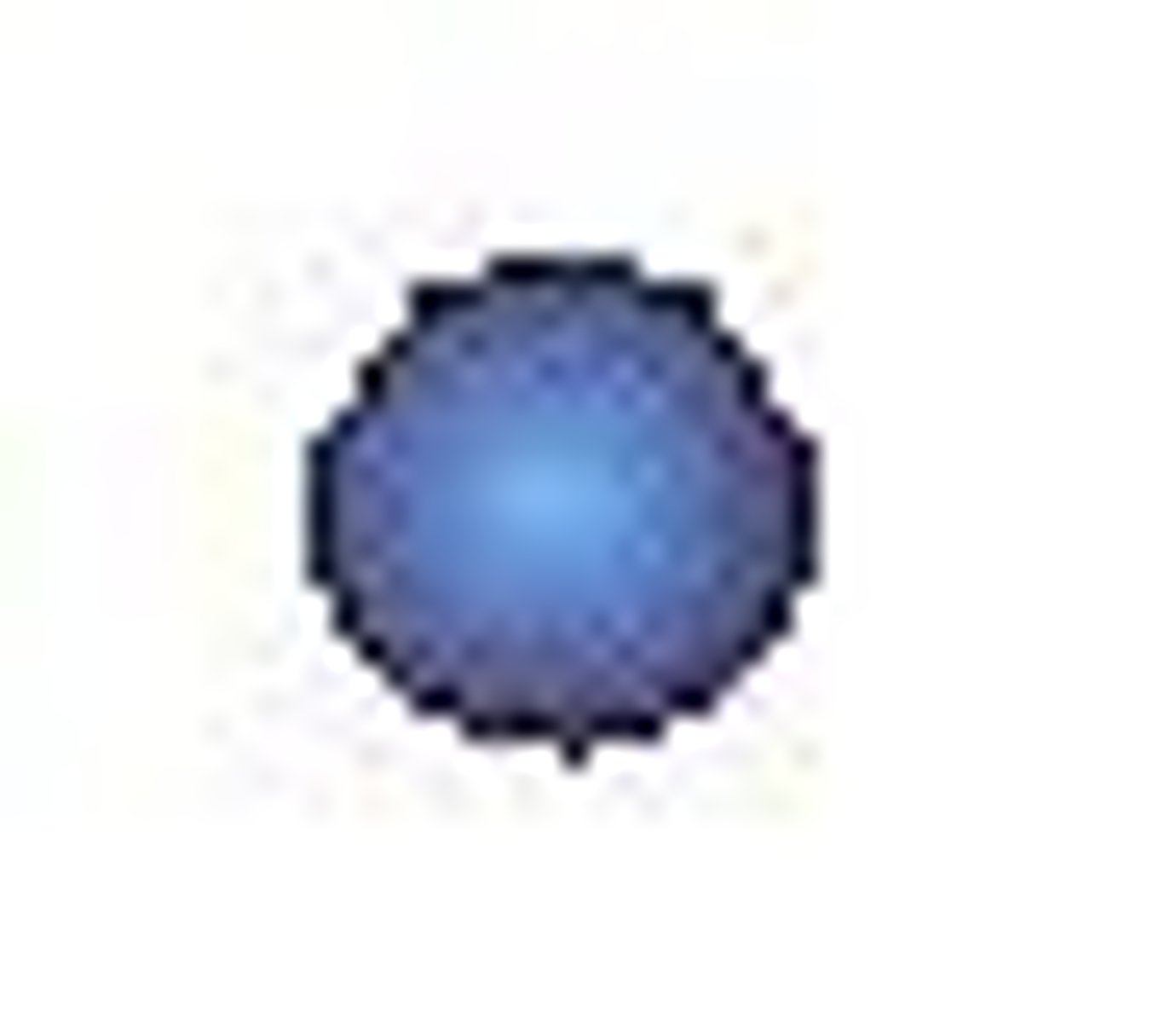
coccus (cocci)
spherical shaped bacteria

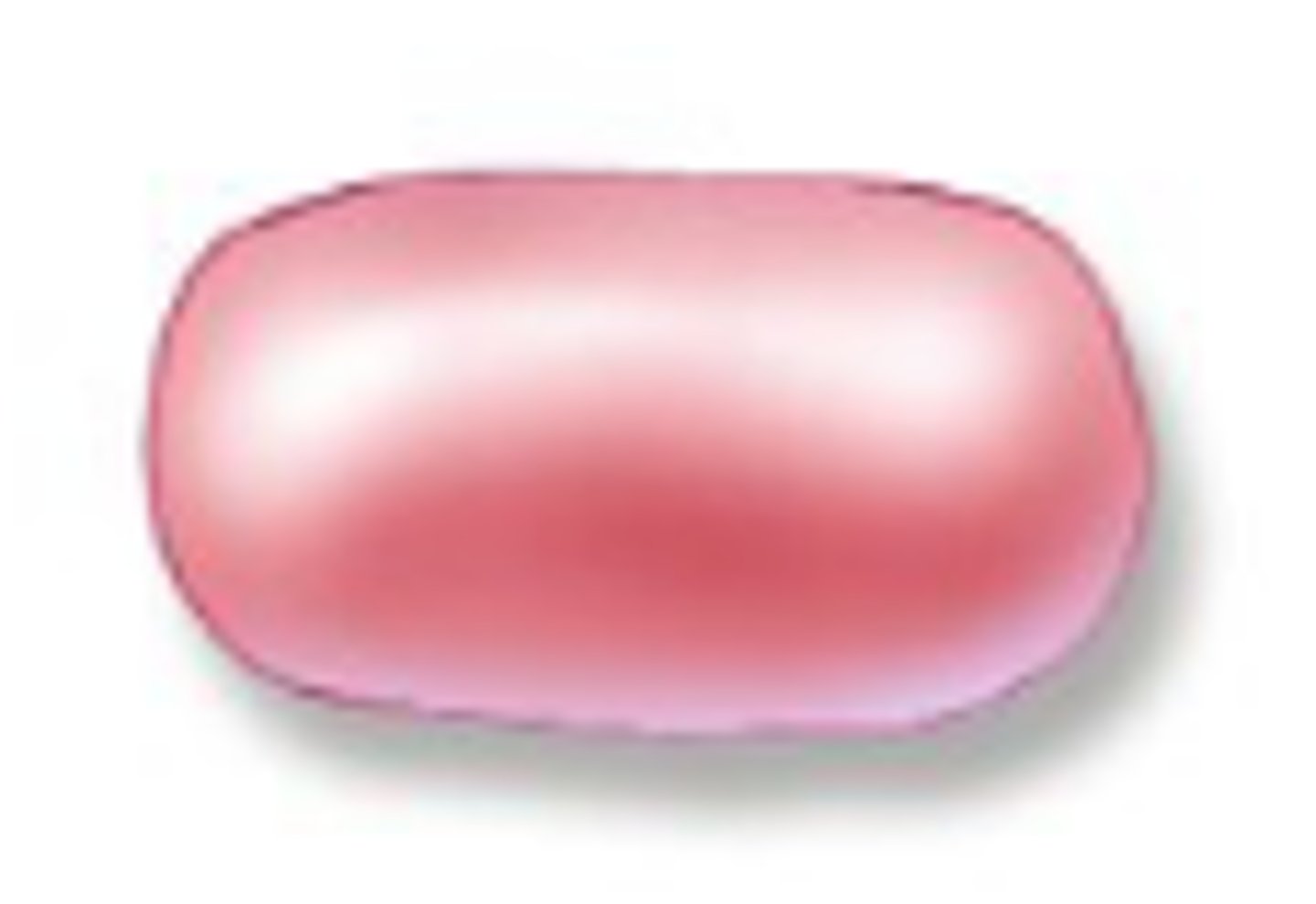
coccobacillus
short round rod

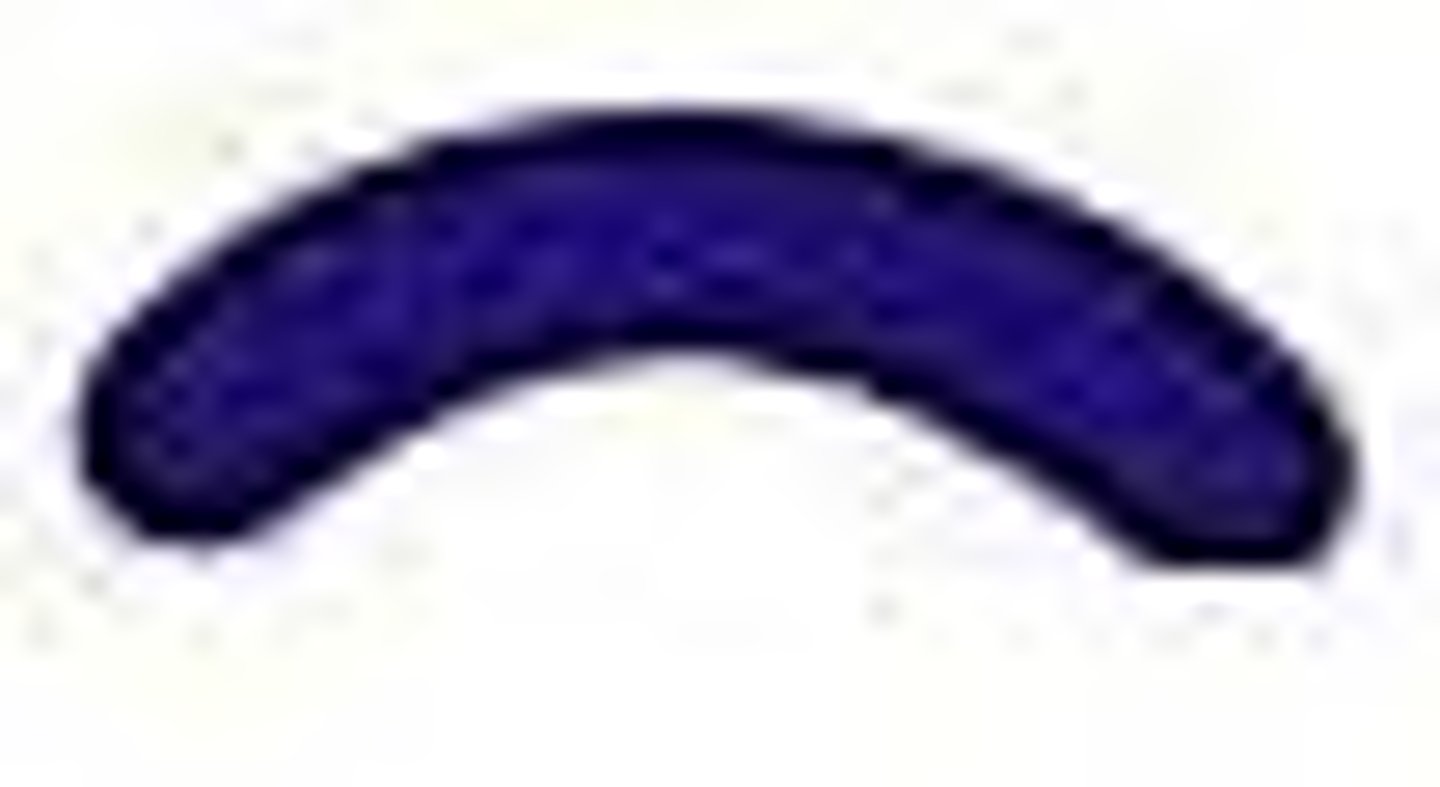
Vibrio
curved rod

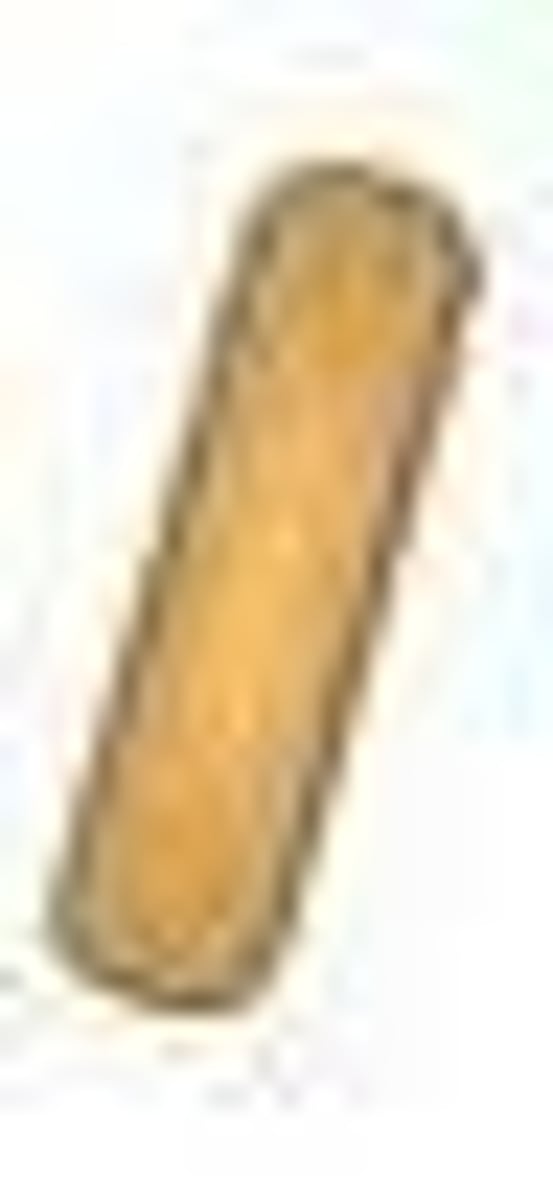
Bacillus
rod shaped

Spirillum
spiral shaped cell

Spirochetes
spiral-shaped bacteria that have flexible walls and are capable of movement; corkscrew

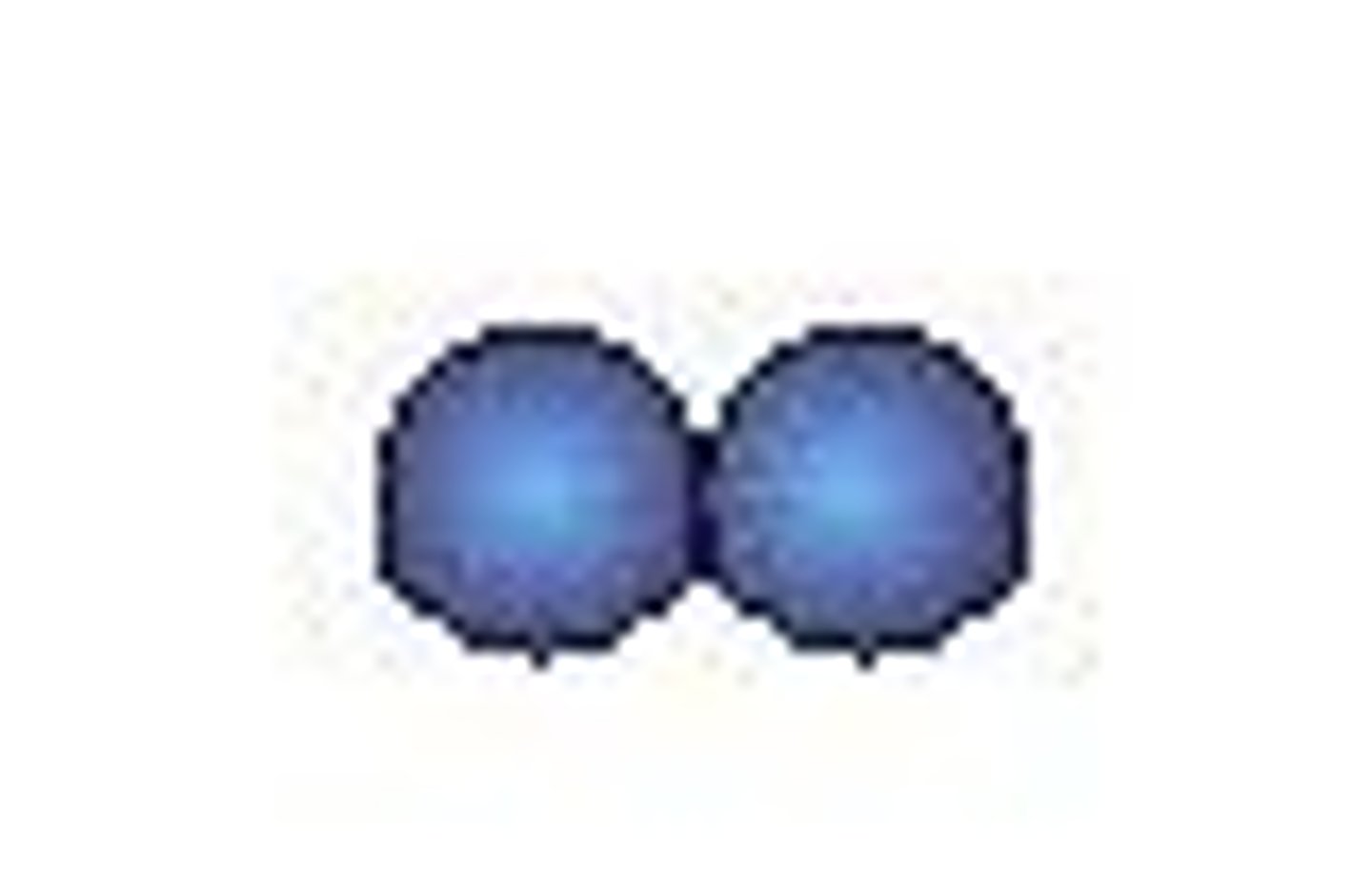
diplo
two (diplococci, diplobacilli)

strepto
chains (streptococci, streptobacilli)
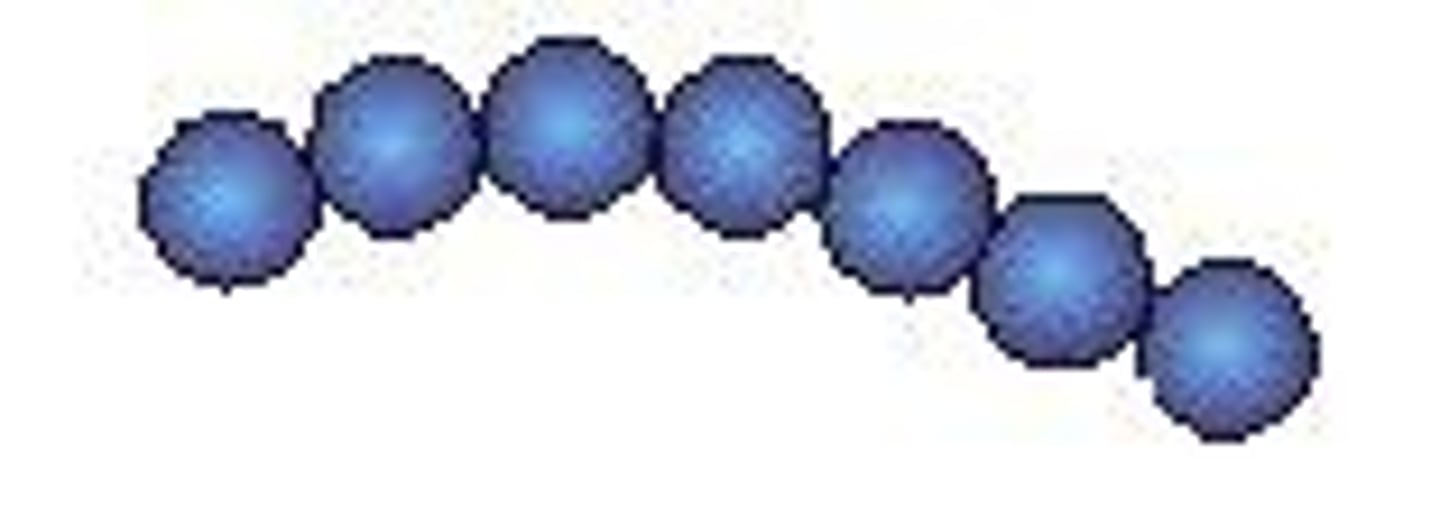
Tetrads
4 cocci in a square
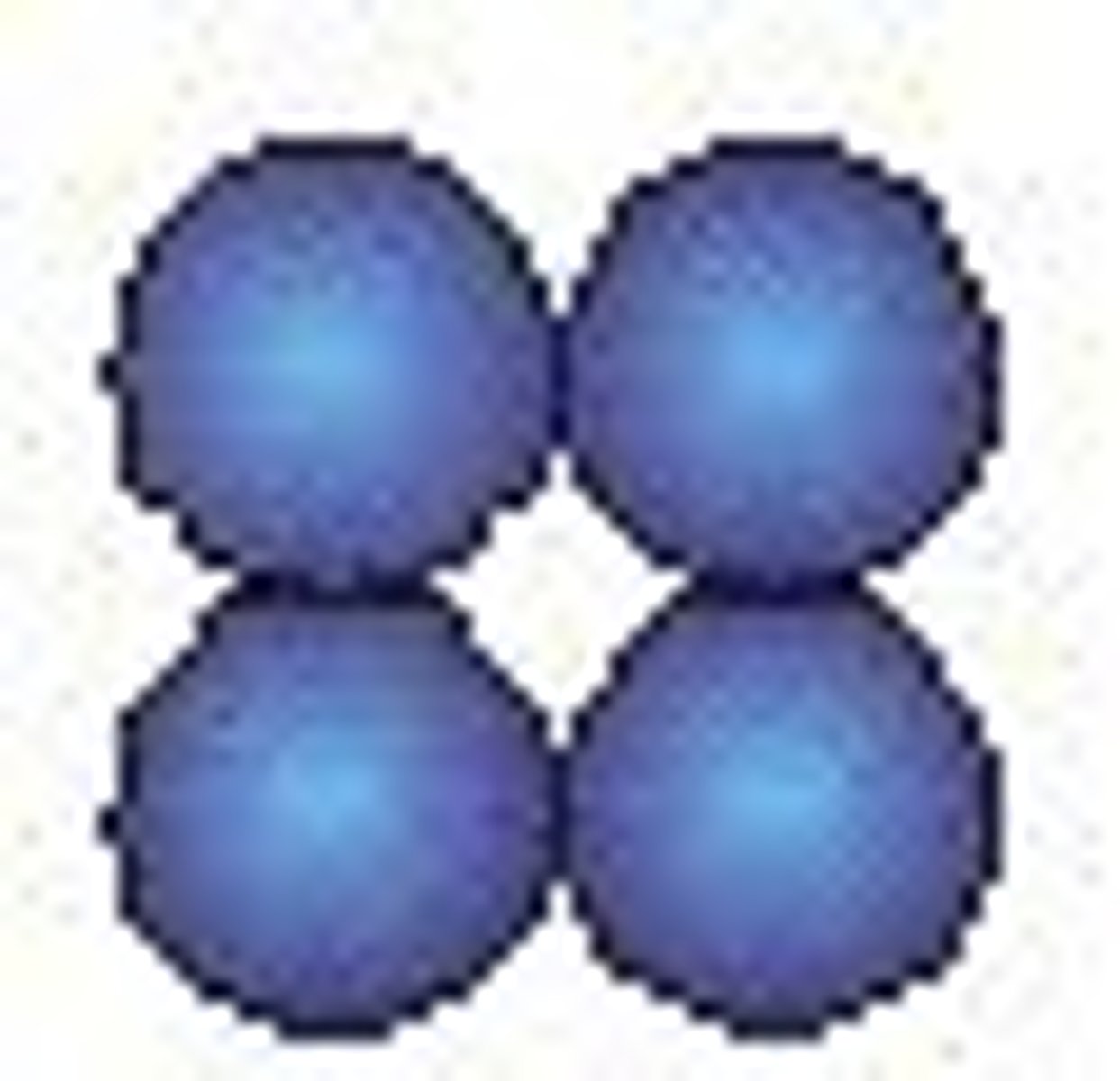

sarcinae
pack of 8 cocci together; cube-like
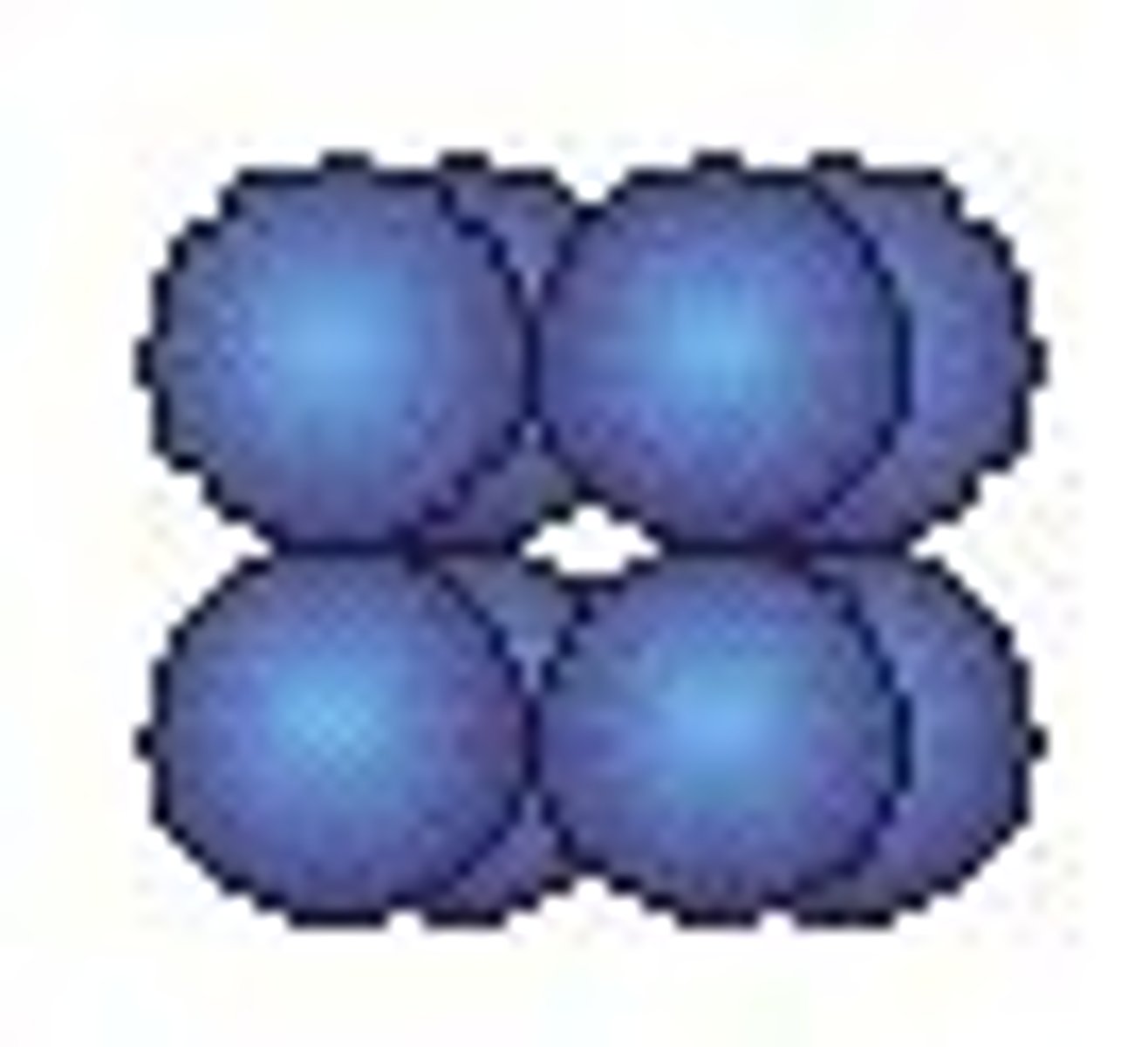
Staphylococci
grape-like clusters
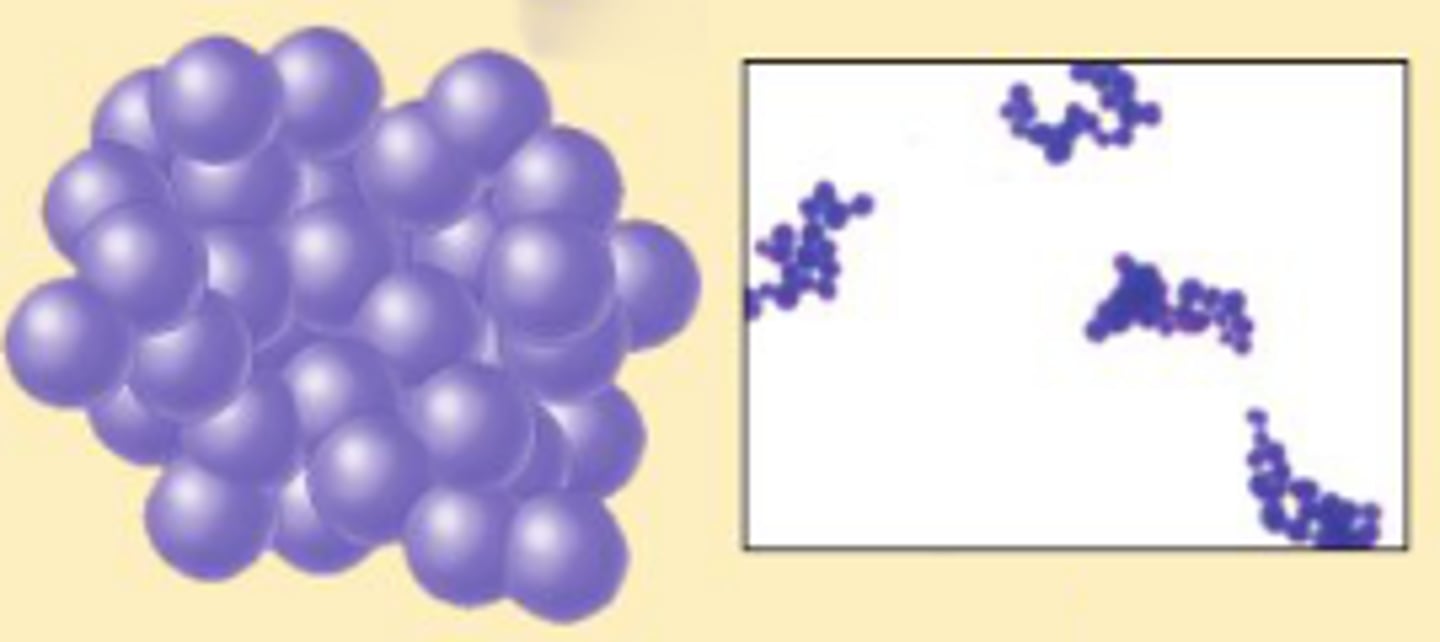
flagella in prokaryotes
Made of flagellin, rotates like a propeller (360 degrees)
Pilus
A hollow tube that SOME bacteria can make and use to transfer DNA to another cell which is called conjugation.
Fimbrae
Structural adaptation; spikes that allow bacteria to stick to the environment
Glycocalyx
A sticky carbohydrate coating around the cell wall that SOME bacteria have
cell wall of prokaryotes
made of peptidoglycan
Cell membrane (plasma membrane)
phospholipid bilayer that surrounds all cells and regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Nucleoid
A non-membrane-bounded region in a prokaryotic cell where the DNA is concentrated.
Chromosomes
double stranded DNA in a large folded circle. Bacteria usually contain only 1 copy of their circular chromosome.
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome; bonus
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis; made of protein and RNA (70S)
inclusions and granules
intracellular storage bodies
Endospores
bacterial spore that can survive harsh conditions
flagellum in eukaryotes
made of microtubules, which make the cytoskeleton and extend to form the flagella; move by sliding the microtubules back and forth, which makes a whip-like motion to push the cell
axial filaments
Also called endoflagella
Found in spirochetes
Anchored at one end of a cell
Rotation causes cell to move like a corkscrew
Monotrichous
one flagellum
Amphitrichous
flagella at both ends
Lophotrichous
bundle of flagella at one end
Peritrichous
flagella all over
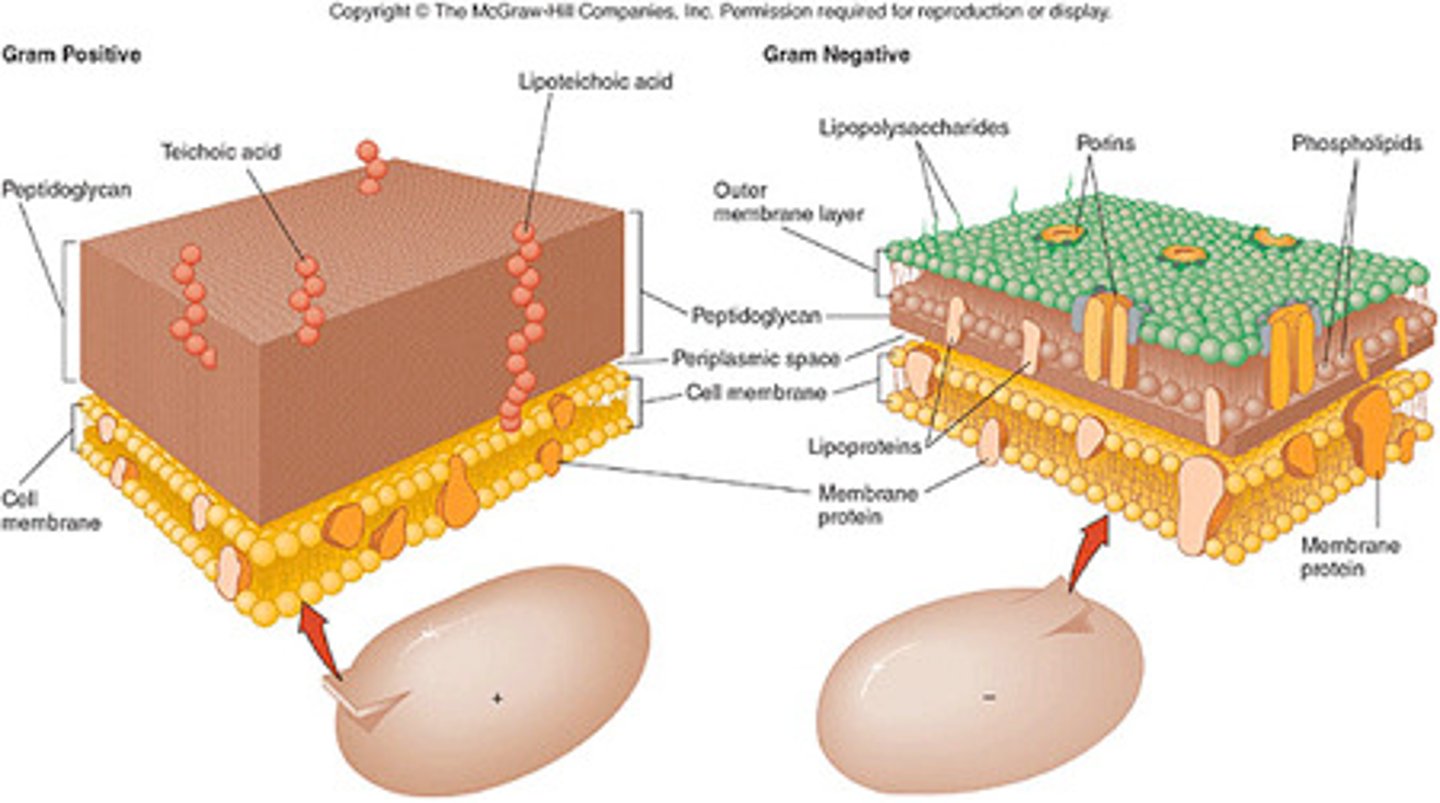
Gram positive cell wall
Thick peptidoglycan layer with teichoic and lipoteichoic acids (anchors to the cell membrane
- has cell membrane
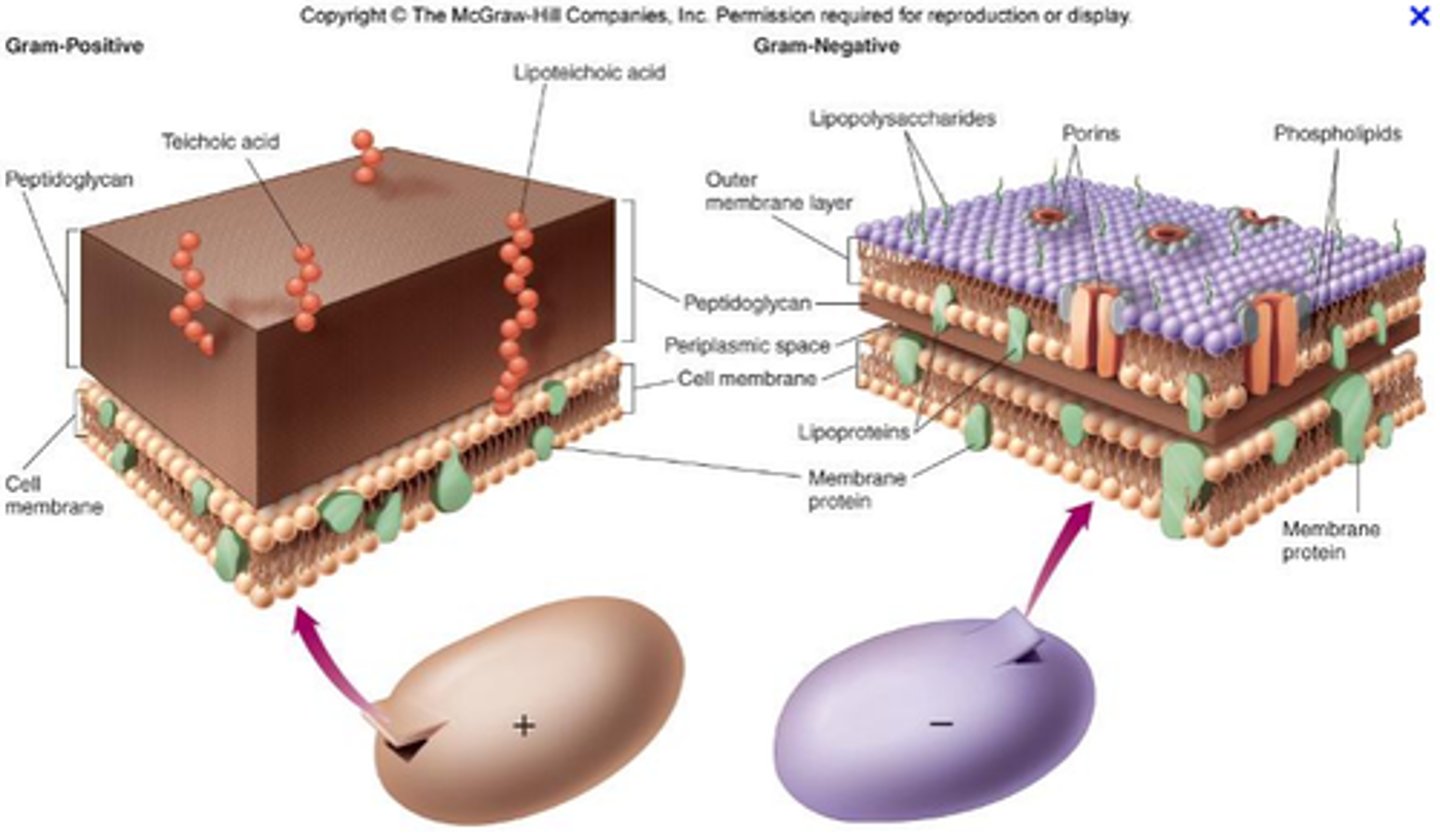
gram negative cell wall
Outer membrane w/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
thin peptidoglycan layer
Periplasmic space
inner membrane
Mycoplasma
no cell wall, no peptidoglycan (don't dye well)
- only bacteria with sterols
Mycobacterium
has a gram positive structure w/mycolic acids - allows the cell to stain "acid fast"