3. DNA profiling
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
INTRONS
DNA made of both introns and exons
intron is a portion of a gene that does not code for AAs
when mRNA is made during transcription the introns have to be removed before translation can happen- splicing
EXONS
leaves only the exon parts which contain mRNA codons
code for AAs so are used to make proteins
MINI AND MICRO SATELLITES
repetitive DNA sequences that appear in a huge proportion of genomic DNA
also called variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs)
distinguished from each other by no. of base pairs in the sequences
MINI SATELLITES
has a DNA repeating sequence which is 10 to 60 base pairs in length
can be repeated between 10 and 1000 times and this varies widely among individuals
rich w/ G and C nucleotides
MICRO SATELLITES
section of DNA which has simple sequence repeats of 1 to 9 base pairs long
often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs)
rich w/ A and T nucleotides
DNA PROFILING
also known as genetic or DNA fingerprinting
compares introns (non-coding regions) and exons (coding regions) w/in DNA
compares repeated sequences (mini- and micro- satellites) within introns
same satellites appear on pairs of homologous chromosomes but no. of repeats could be diff as chromosomes may be maternal or paternal
more closely related two individuals= more similar DNA
HOW DNA PROFILE IS MADE
DNA sample extracted- could be from body fluids, tissue samples or a mouth swab
DNA is amplified using PCR
fragments of diff lengths are produced by cutting up DNA using restriction endonuclease enzymes
fragments are separated and visualised using gel electrophoresis
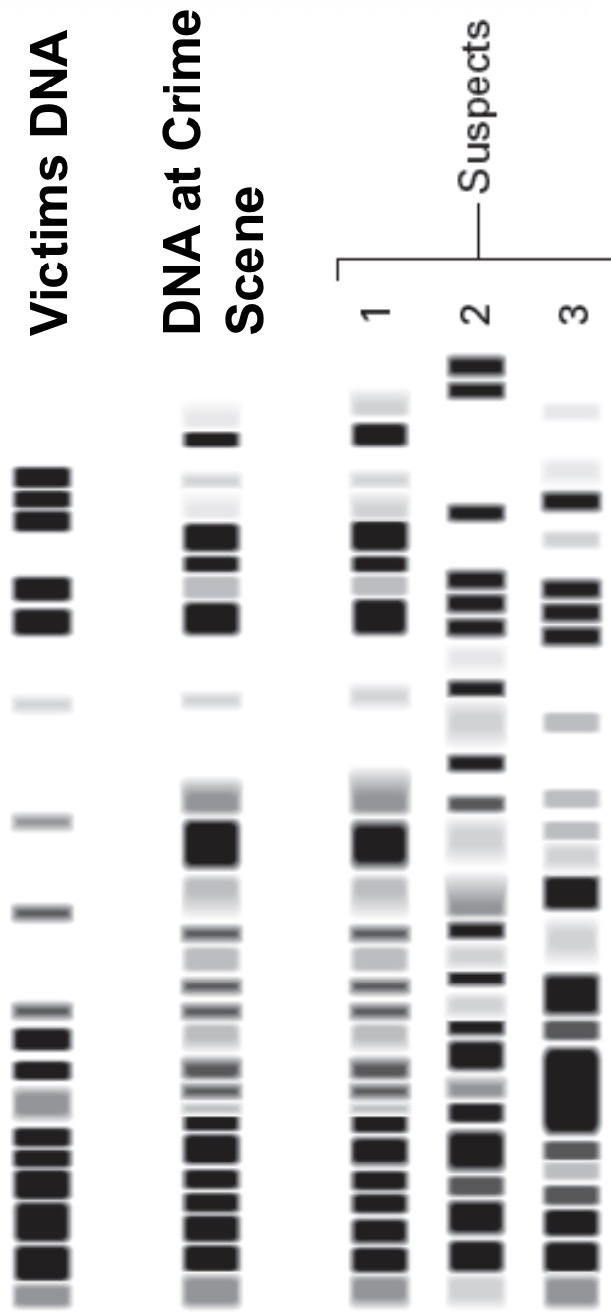
DNA PROFILING- CRIME
DNA Fingerprint is simply a ‘pattern’ produced on a piece of photographic film
can we say 100% that suspect 1 committed the crime?
no fingerprint just establishes whether a suspect is likely to have been present at a crime scene
STEP 1- DIGESTION
(PCR is completed first to make multiple copies of DNA)
DNA sample is digested i.e. cut into fragments by restriction endonuclease enzymes
cuts DNA at a specific recognition sites close to diff VNTRs (mini and micro satellite) sequences
DNA fragments produced will be diff lengths depending on how many repeats satellites contain
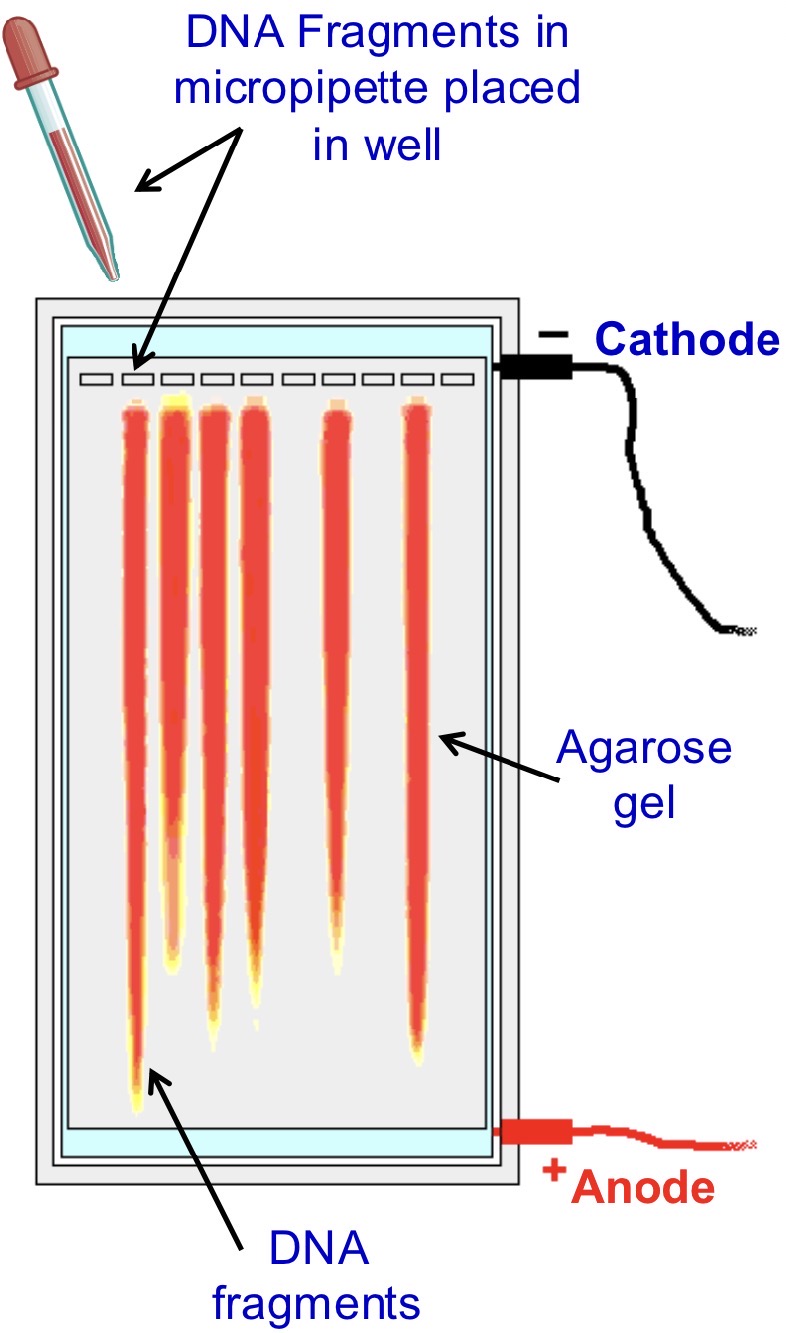
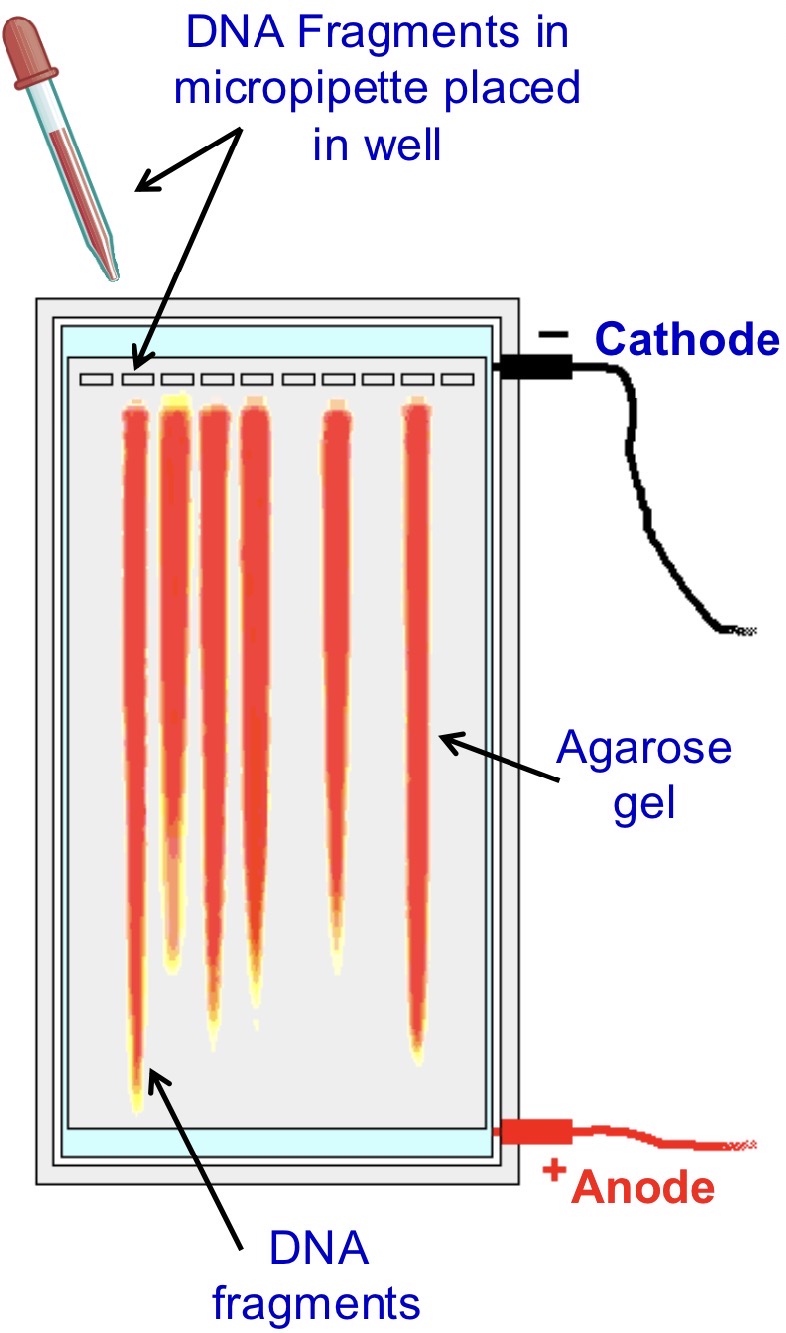
STEP 2- SEPARATION
DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis
loaded into a ‘well’ in agarose gel containing a buffering solution to maintain pH
gel contains a dye which binds to DNA fragments
fluoresces when placed under UV light
STEP 3- SOUTHERN BLOT
alkaline buffer is added to the gel and nylon filter paper is placed over it
dry absorbent paper is used to draw the solution containing DNA from gel to nylon filter leaving them as ‘blot’
pos charged Nylon binds DNA irreversibly under alkaline conditions
will be permanently in the same relative position they occupied on gel
alkaline solution also denatures DNA fragments so strands separate and base sequences are exposed
needs to happen as gel is too fragile handle

STEP 4- ADDITION OF PROBES
as DNA is now single stranded, large quantities of gene probes are now added
bind w/ complimentary DNA strands in a process called hybridisation
gene probes are short pieces of DNA that have complimentary sequences to parts of DNA being sought
each probe is labelled w/ a fluorescent molecule or radioactive isotope
DNA profile can then be produced as a graph with each peak representing no. of repeats at each VNTR
IDENTIFYING INDIVIDUALS- FORENSICS
to develop a DNA profile in criminal investigations, gene probes used to pick out short tandem repeats (micro-satellites widely used in DNA identification)
the more micro-satellites used to make up a DNA profile the more accurate it will be
family members are more likely than unrelated individuals to have micro-satellites in common
statistically, chances of two people matching on 11 or more sites is so small that it is counted as reliable evidence in court
IDENTIFYING INDIVIDUALS- PATERNITY
specific micro satellite markers are used to make matches between the child's DNA and potential fathers
each child's micro satellite has to have come from either their father or mother
if some come from neither then paternity is disproved