Elements in the Periodic Table: Atomic Structure and Quantum Numbers
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary related to atomic structure, energy levels, quantum numbers, and fundamental principles from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Electron charge
Negative
Light (nature)
Exhibits properties of both a particle and a wave.
Niels Bohr
Scientist who visualized the diagram model of an atom.
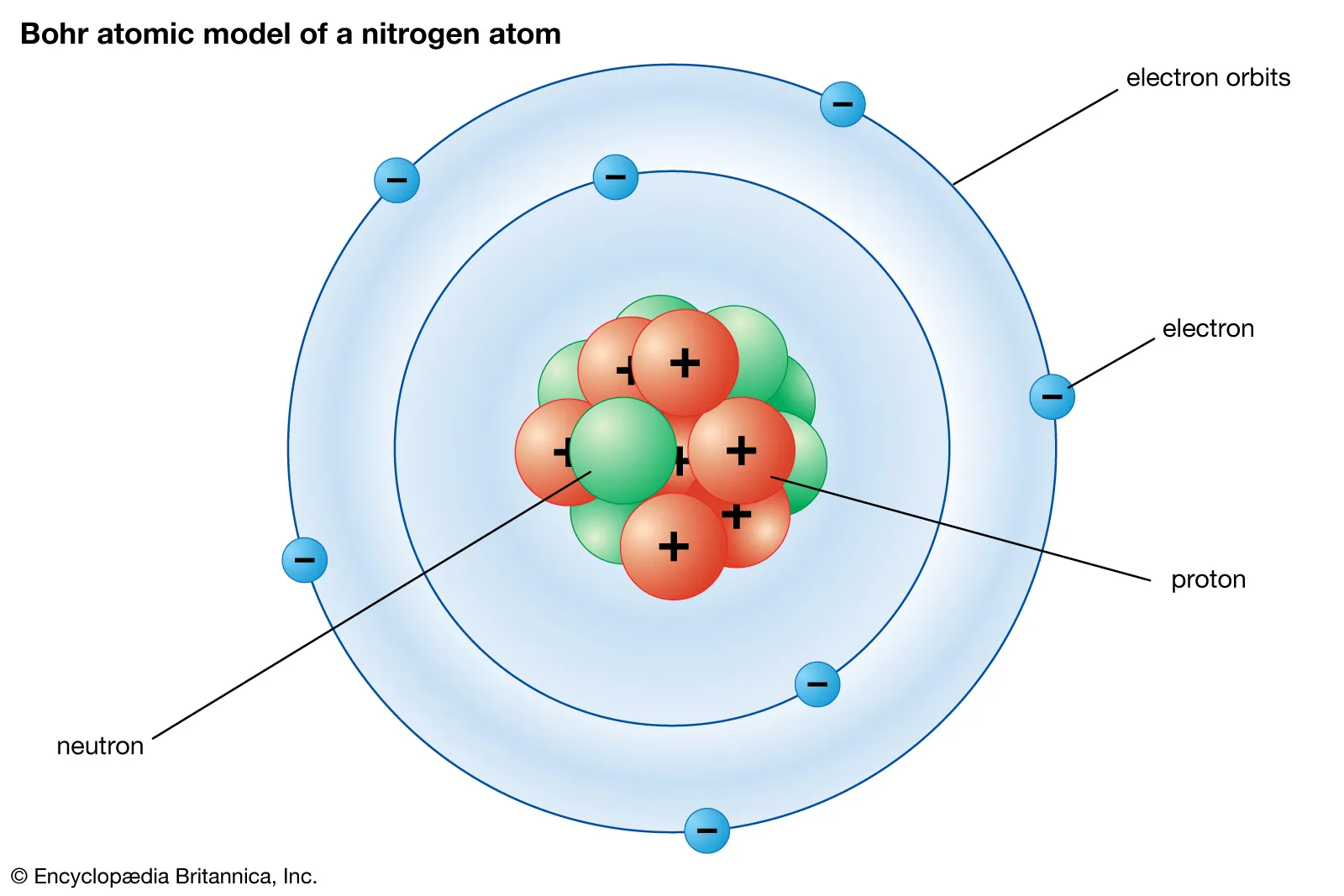
Valence shell
Another term for the main energy level, specifically the outermost occupied shell.
Ground state (electron)
The lowest energy level where electrons are usually found.
n (quantum number symbol)
The symbol used to represent the principal energy level.
Closest energy level to nucleus
Has a principal quantum number value of 1.
Maximum electrons per orbital
2 electrons.
Orbital
A region within a sub-energy level where an electron is most likely to be found.
Sub-energy level
A subdivision within a main energy level that contains one or more orbitals.
Wavelength
The distance between successive crests or troughs of a wave.
Amplitude
The maximum displacement or distance moved by a point on a vibrating body or wave measured from its equilibrium position.
Crest
The highest part of a wave.
Trough
The lowest part of a wave.
De Broglie's matter wave theory
Theory stating that particles like electrons can also exhibit wave-like properties, supported by electron diffraction experiments.
Wave-particle duality
The property of matter and light to exhibit both wave and particle characteristics.
Huygen's Principle
A method for analyzing wave propagation, used to demonstrate light as a wave, especially via Young's double-slit experiment.
Young's double-slit experiment
An experiment that clearly demonstrated the wave nature of light through interference patterns.
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
States that it is impossible to precisely know both the velocity (or momentum) and position of a particle at the same time.
Bohr's Atomic Model
A model depicting electrons orbiting the nucleus in distinct, quantified energy shells (K, L, M, N), each with a specific electron capacity.
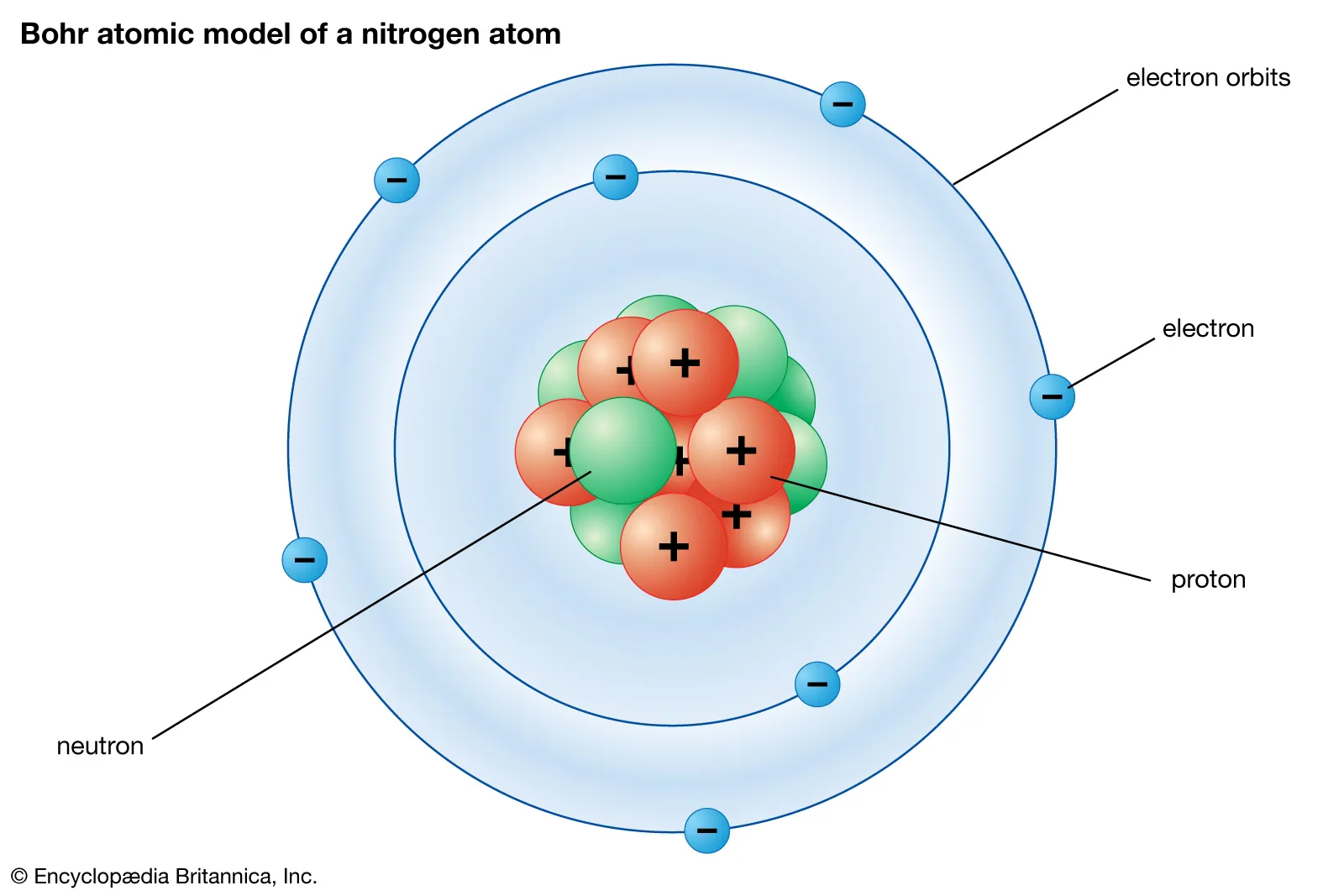
Quantum (of energy)
The discrete amount of energy required for an electron to move from one energy level to another.
Neutron
An uncharged subatomic particle located in the nucleus.
Proton
A positively charged subatomic particle located in the nucleus.
Quark
Fundamental particles that make up protons and neutrons.
Electron shells
Concentric paths or regions around the nucleus where electrons orbit, also known as energy levels.
High energy electrons
Electrons in outermost shells, requiring more energy to extract due to greater distance from the nucleus.
Excited state
Any energy level above the ground state where an electron can reside after gaining energy.
Quantum numbers
A set of numbers used to describe the state of an electron in an atom, acting like an 'address'.
2(n)²
The formula used to calculate the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a given energy level 'n'.
Sublevels (s, p, d, f)
Divisions within an energy level, classified by shape and defining the types of orbitals present.
s sublevel
Contains 1 orbital and can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
p sublevel
Contains 3 orbitals and can hold a maximum of 6 electrons.
d sublevel
Contains 5 orbitals and can hold a maximum of 10 electrons.
f sublevel
Contains 7 orbitals and can hold a maximum of 14 electrons.
Quantum theory
The mathematical description of the wave properties of electrons and other small particles, providing probabilities of electron location.
Principal Quantum Number (n)
The first quantum number, indicating the electron's main energy level and the approximate size of its orbital. Larger n means greater average distance from the nucleus.
Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
The second quantum number, defining the shape of an electron's orbital (l=0 for s, l=1 for p, l=2 for d, l=3 for f). Its value ranges from 0 to n-1.
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
The third quantum number, specifying the orientation of an orbital in space around the nucleus. Its value ranges from -l to +l.
Spin Quantum Number (ms)
The fourth quantum number, describing the intrinsic angular momentum (spin) of an electron, with possible values of +1/2 (spin up) or -1/2 (spin down).
Photon
A discrete packet of electromagnetic energy, emitted when an electron transitions from a higher to a lower energy orbital.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
States that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers; if two electrons occupy the same orbital, they must have opposite spins.