Embryo 12 - Pharyngeal Apparatus and Tongue Development
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
When does the pharyngeal apparatus begin developing?
During the 4th week of development in the most cephalic region of the embryo.
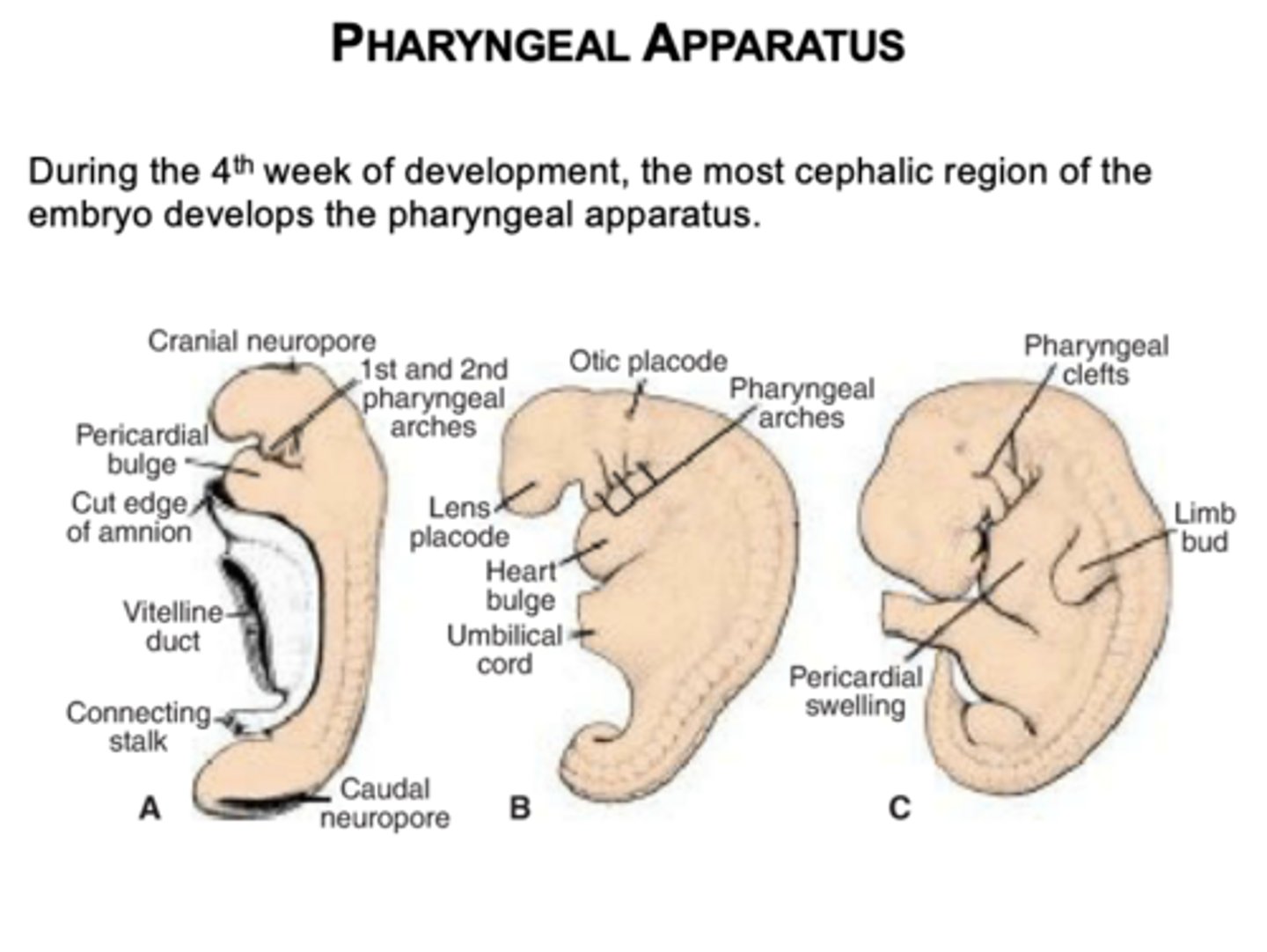
What four structures make up the pharyngeal apparatus?
Pharyngeal arches, pouches, grooves (clefts), and membranes.
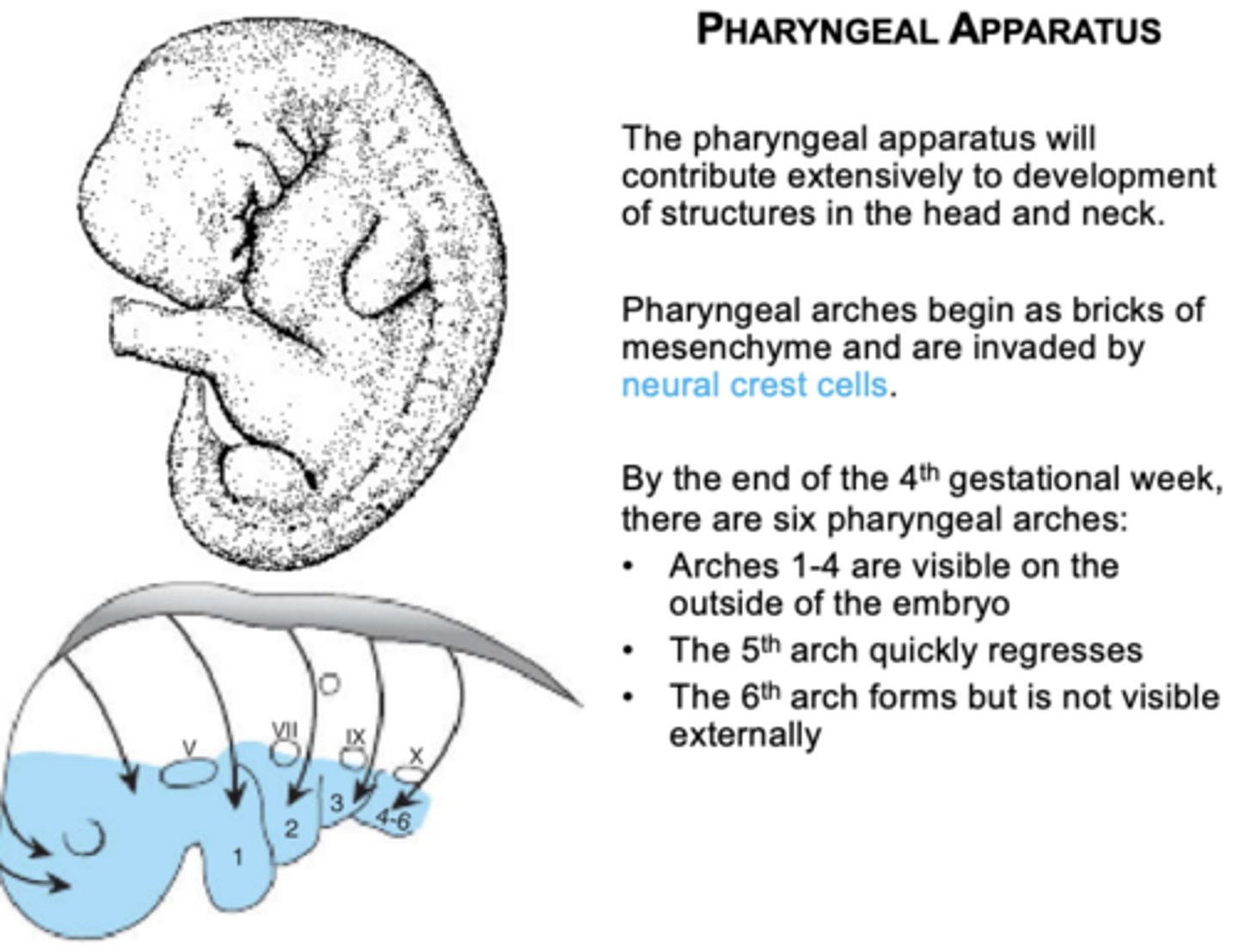
What will the pharyngeal apparatus contribute to the development of?
Structure in the head and neck region
How do the pharyngeal arches development start?
begin as bricks of mesenchyme and are invaded by neural crest cells
What lines the pharyngeal pouches?
Endoderm.
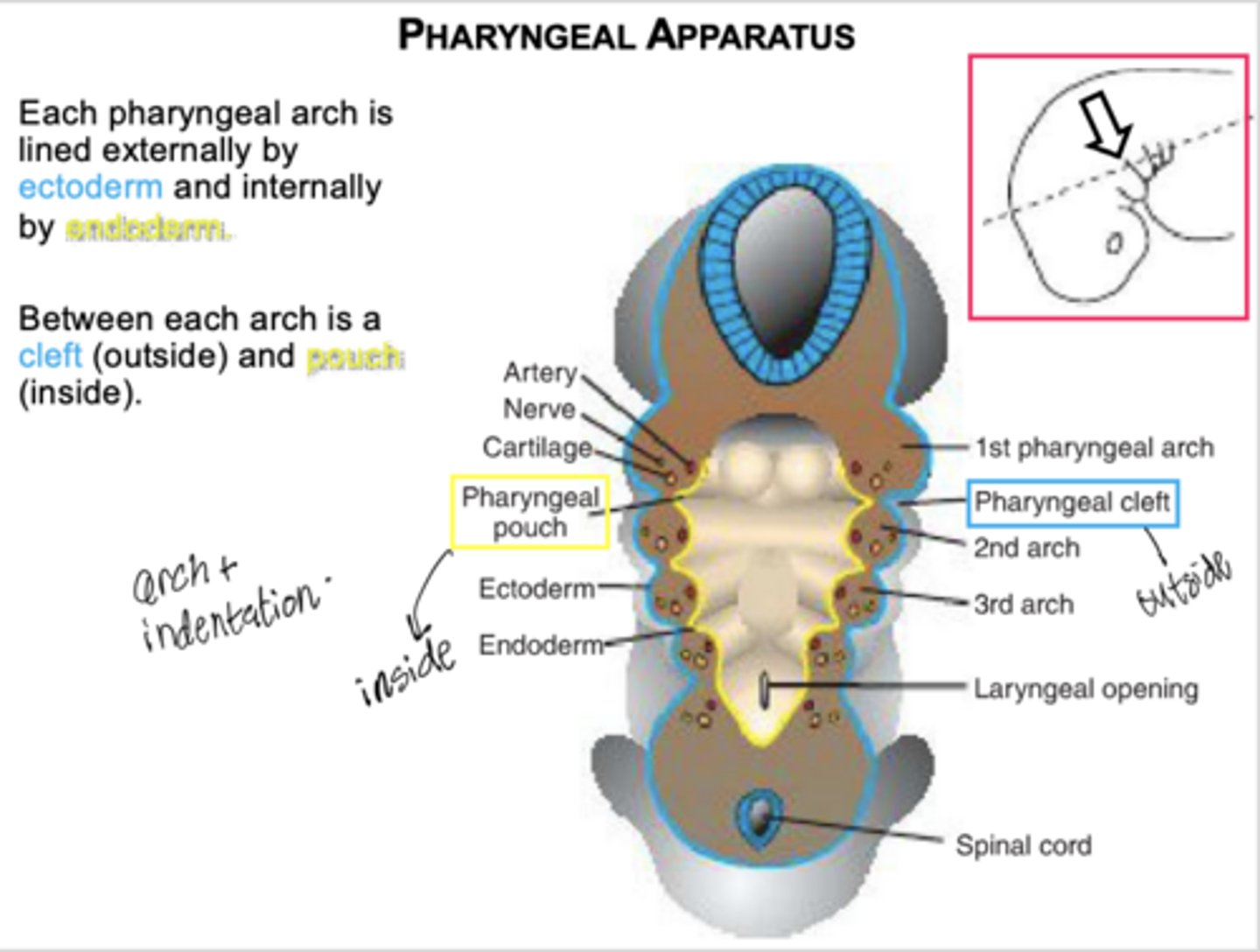
What lines the pharyngeal grooves (clefts)?
Ectoderm.
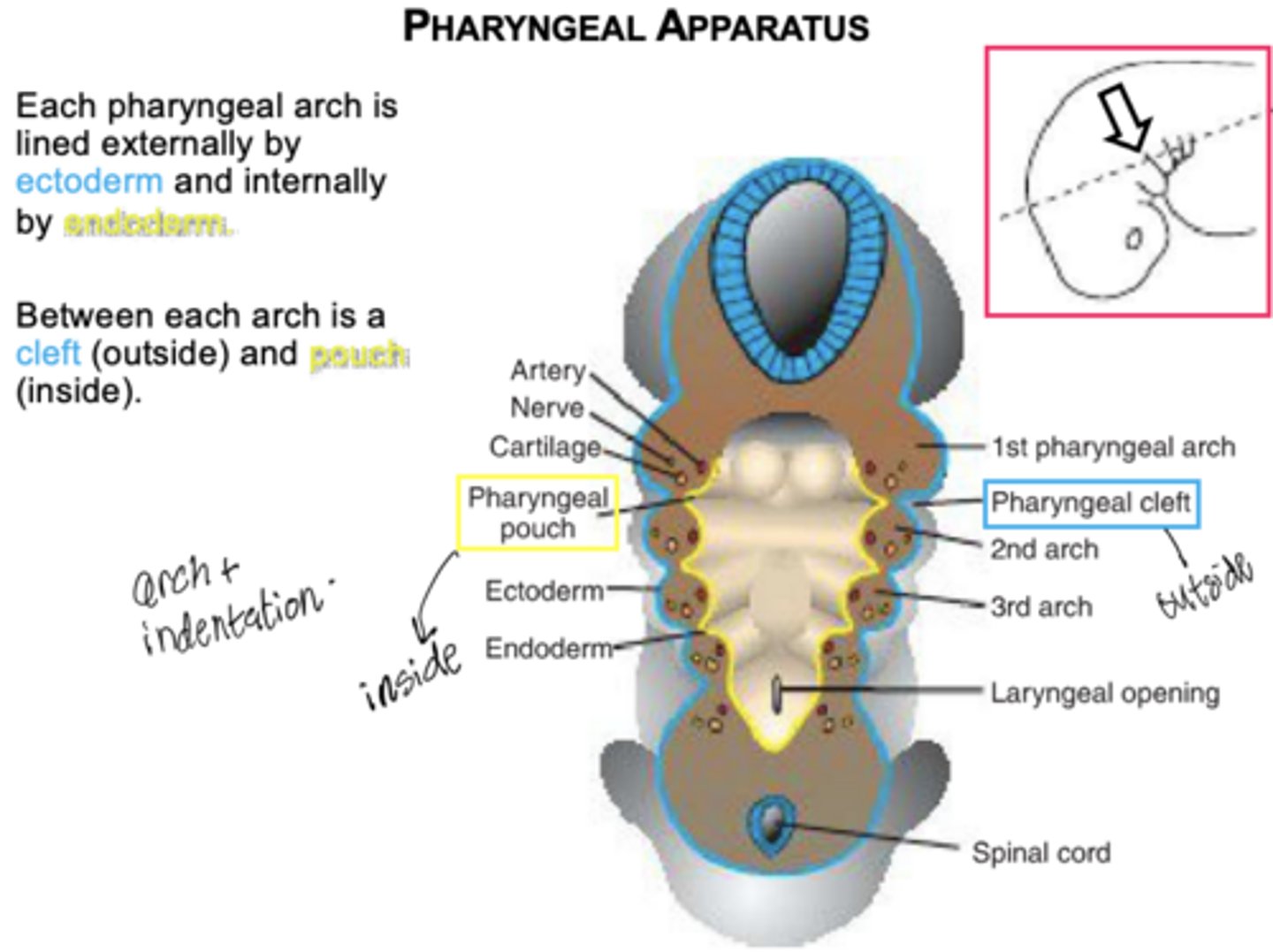
What are pharyngeal membranes?
Regions where a pouch meets a groove.
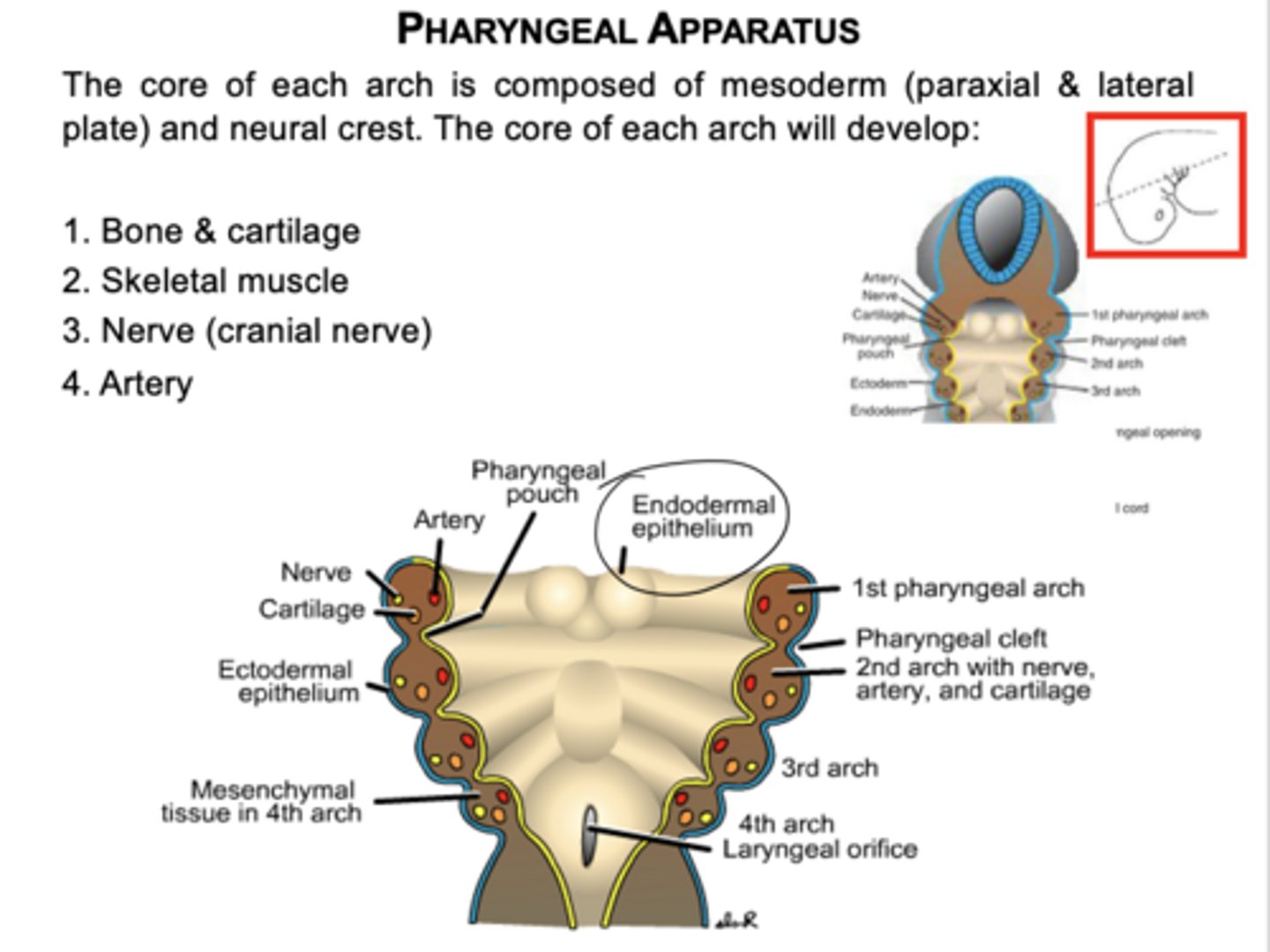
What germ layers form the core of each pharyngeal arch?
Mesoderm (paraxial and lateral plate) and neural crest cells.
What four components develop from each pharyngeal arch core?
Bone/cartilage, skeletal muscle, cranial nerve, and artery.
How many pharyngeal arches form initially?
Six arches form, but the 5th regresses and is not functional.
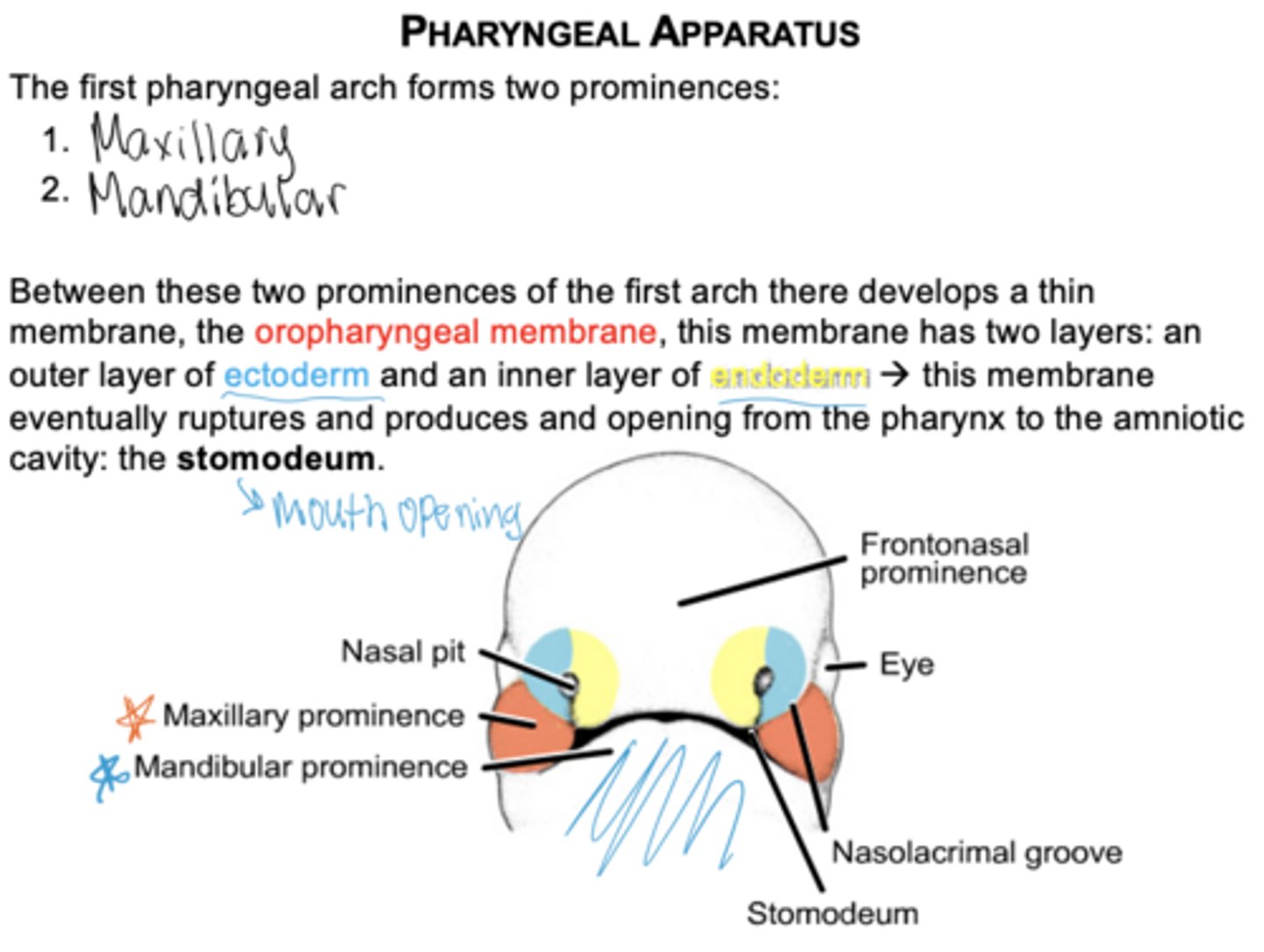
What two prominences arise from the first arch?
Maxillary and mandibular prominences.
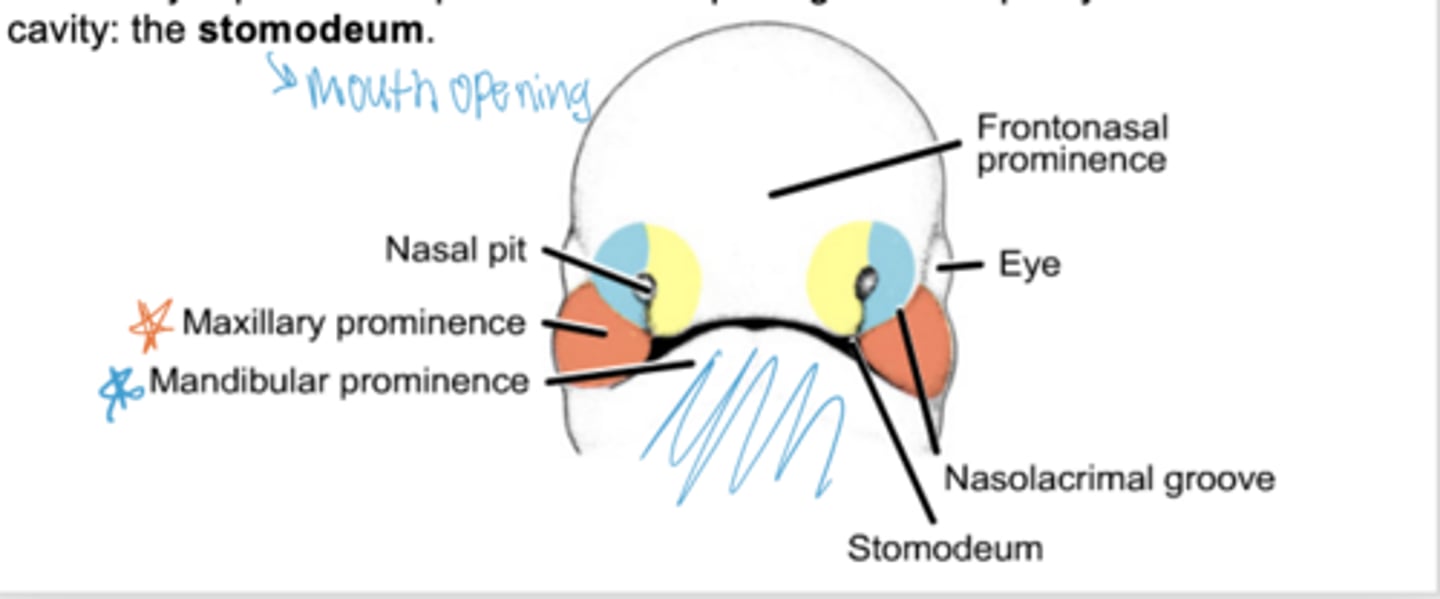
What membrane forms between the maxillary and mandibular prominences?
Oropharyngeal membrane which has two layers
outer layer of ectoderm
inner layer of endoderm
What happens to the oropharyngeal membrane?
It ruptures to create the opening of the mouth (stomodeum).
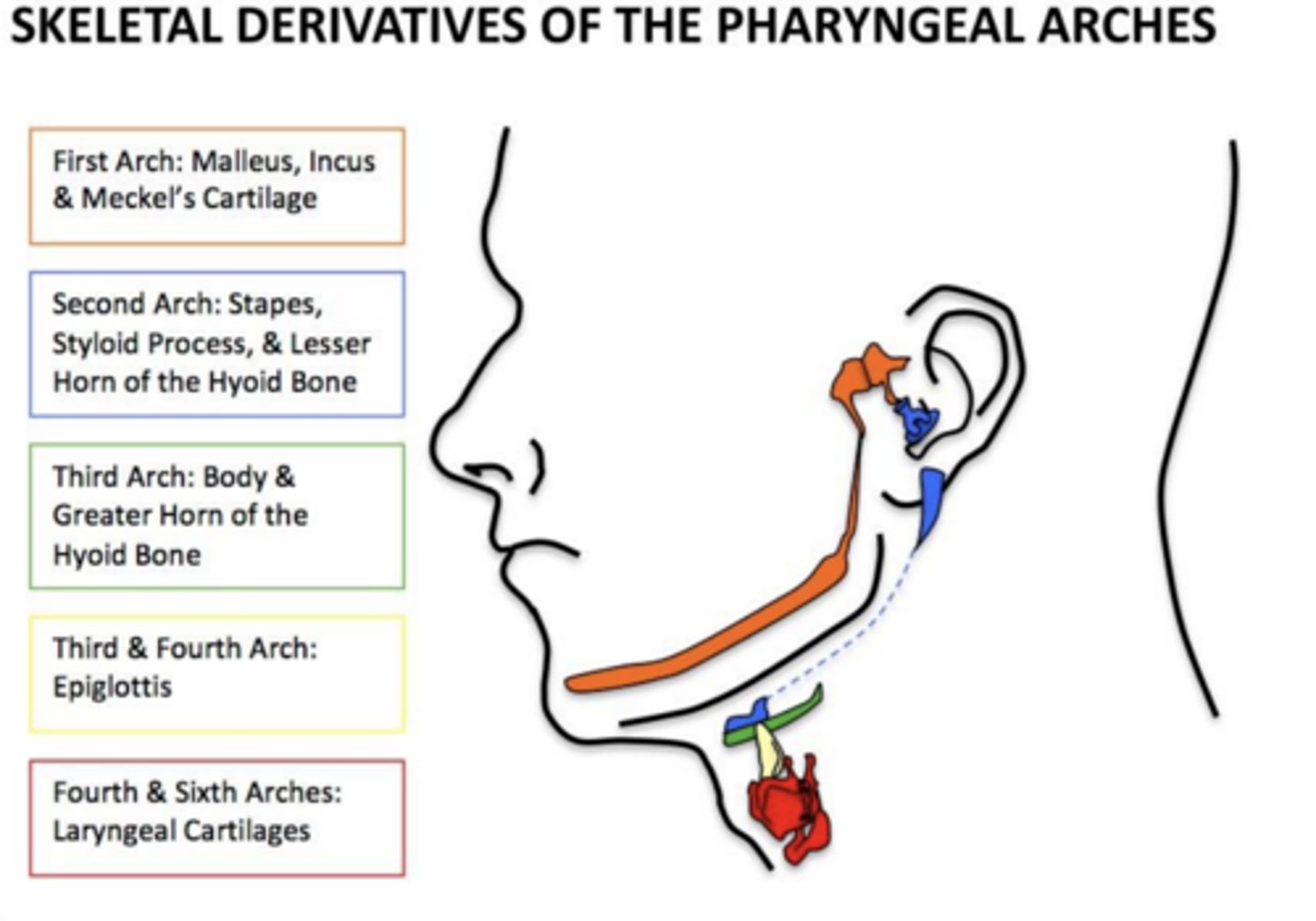
What is Meckel's cartilage?
Cartilage of the first arch.
What bones form from the dorsal part of Meckel's cartilage?
Malleus and incus.
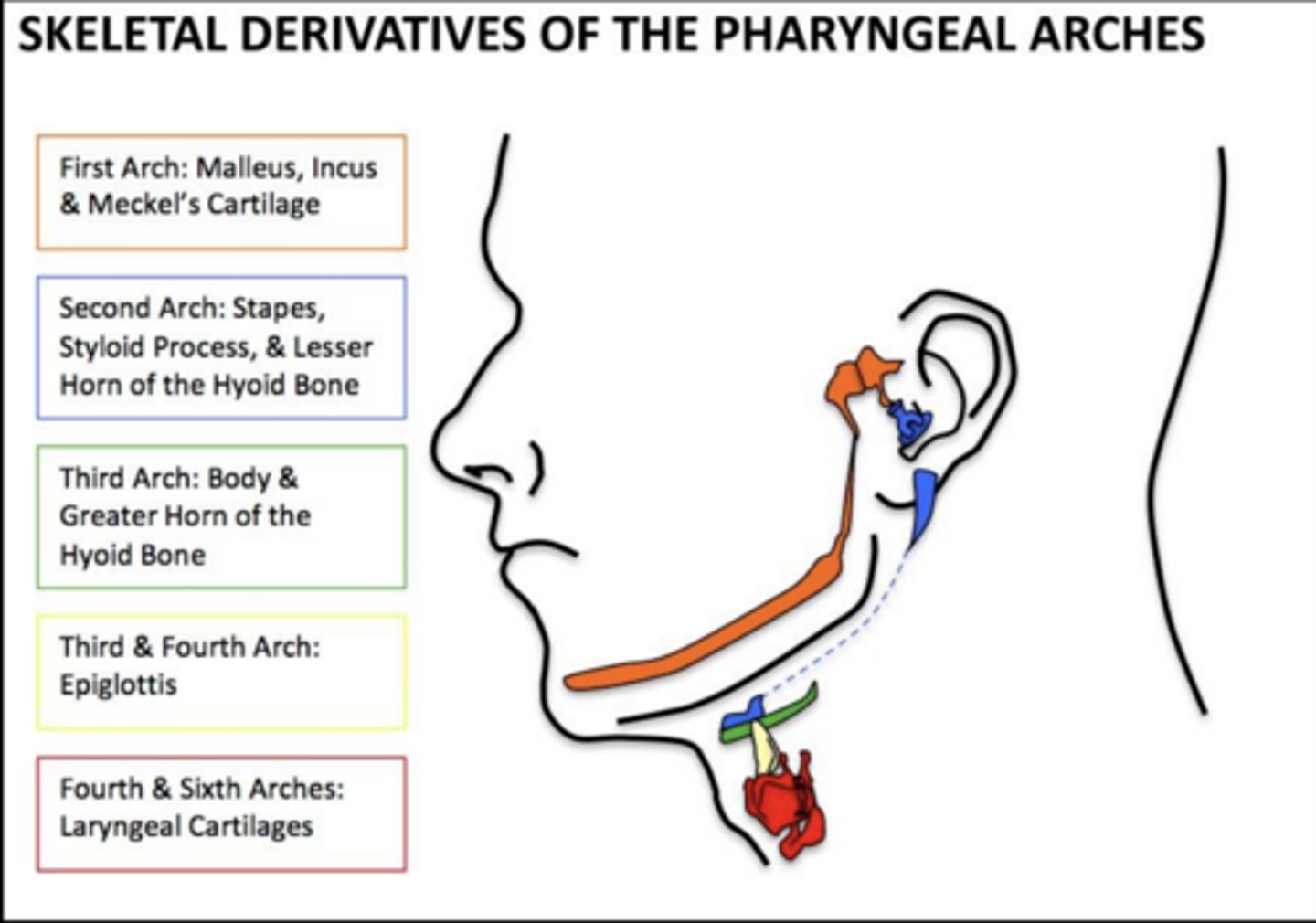
What ligaments arise from Meckel's cartilage?
Anterior ligament of malleus and sphenomandibular ligament.
What does the ventral part of Meckel's cartilage contribute to?
Mandible via intramembranous ossification.
What structures arise from second arch cartilage?
Stapes, styloid process, stylohyoid ligament, lesser horn of hyoid.
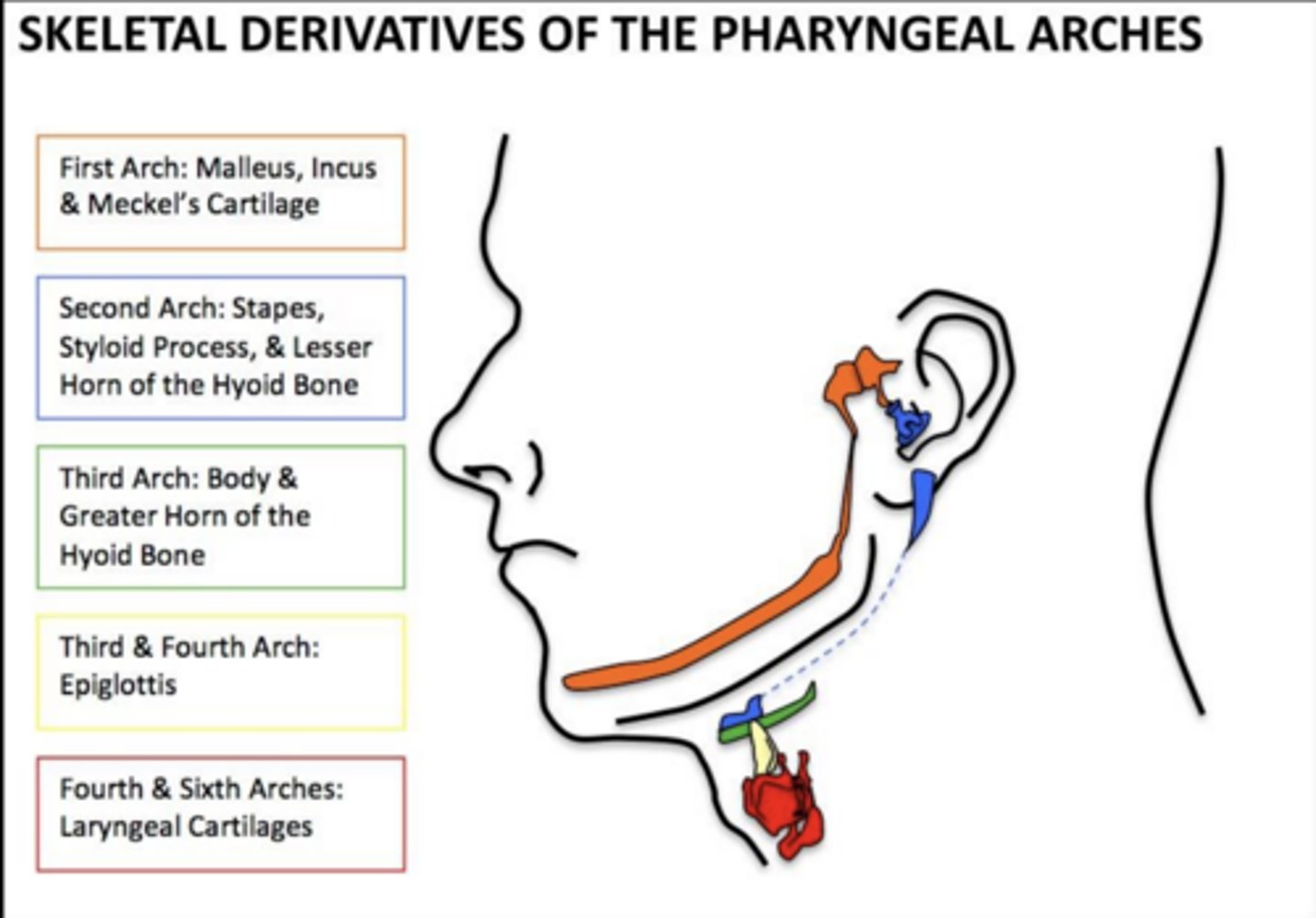
What arises from the third arch cartilage?
Greater horn and lower body of the hyoid.
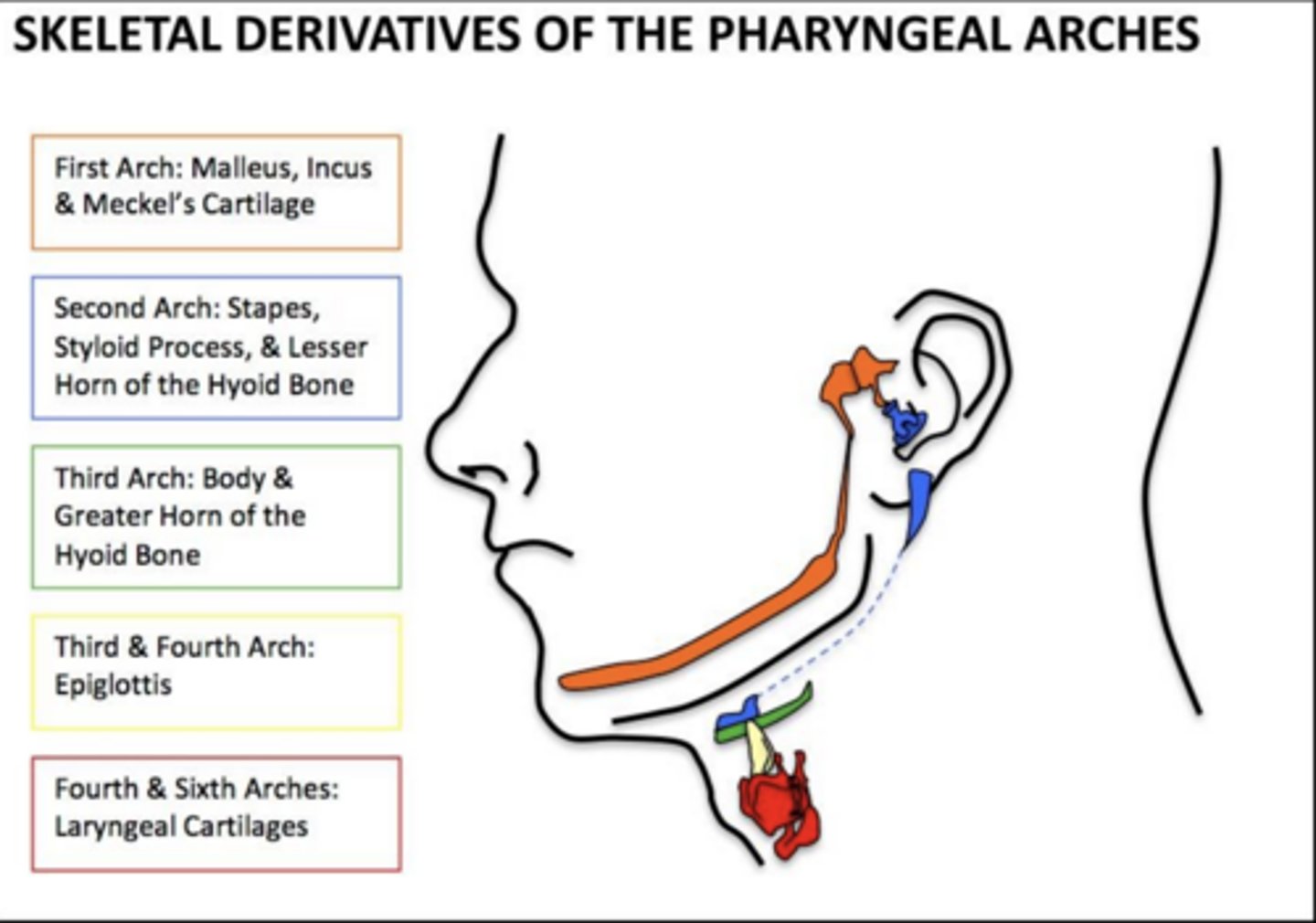
Which arches contribute to the epiglottis?
3rd and 4th arches.
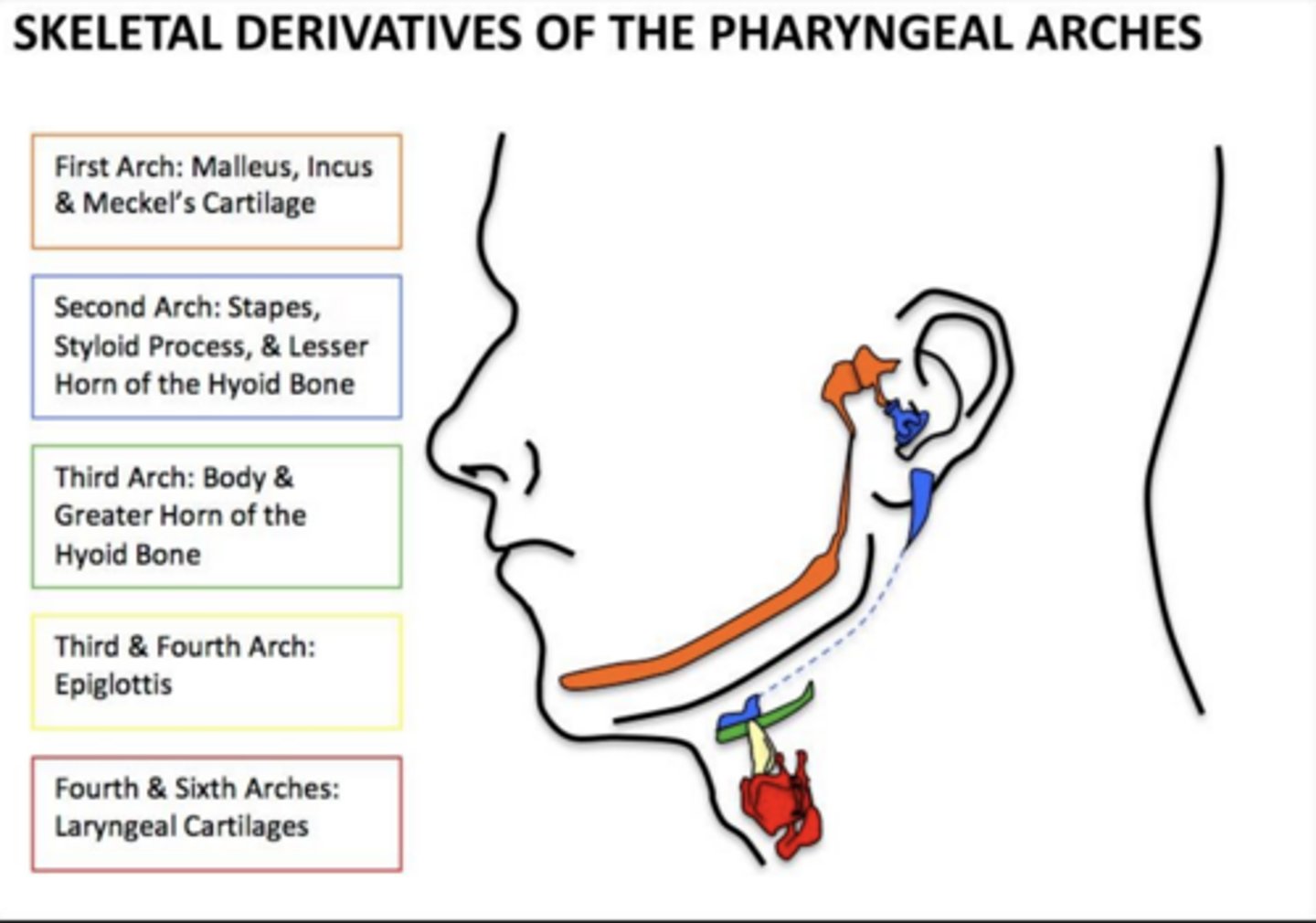
What do the 4th and 6th arches form?
Laryngeal cartilages.
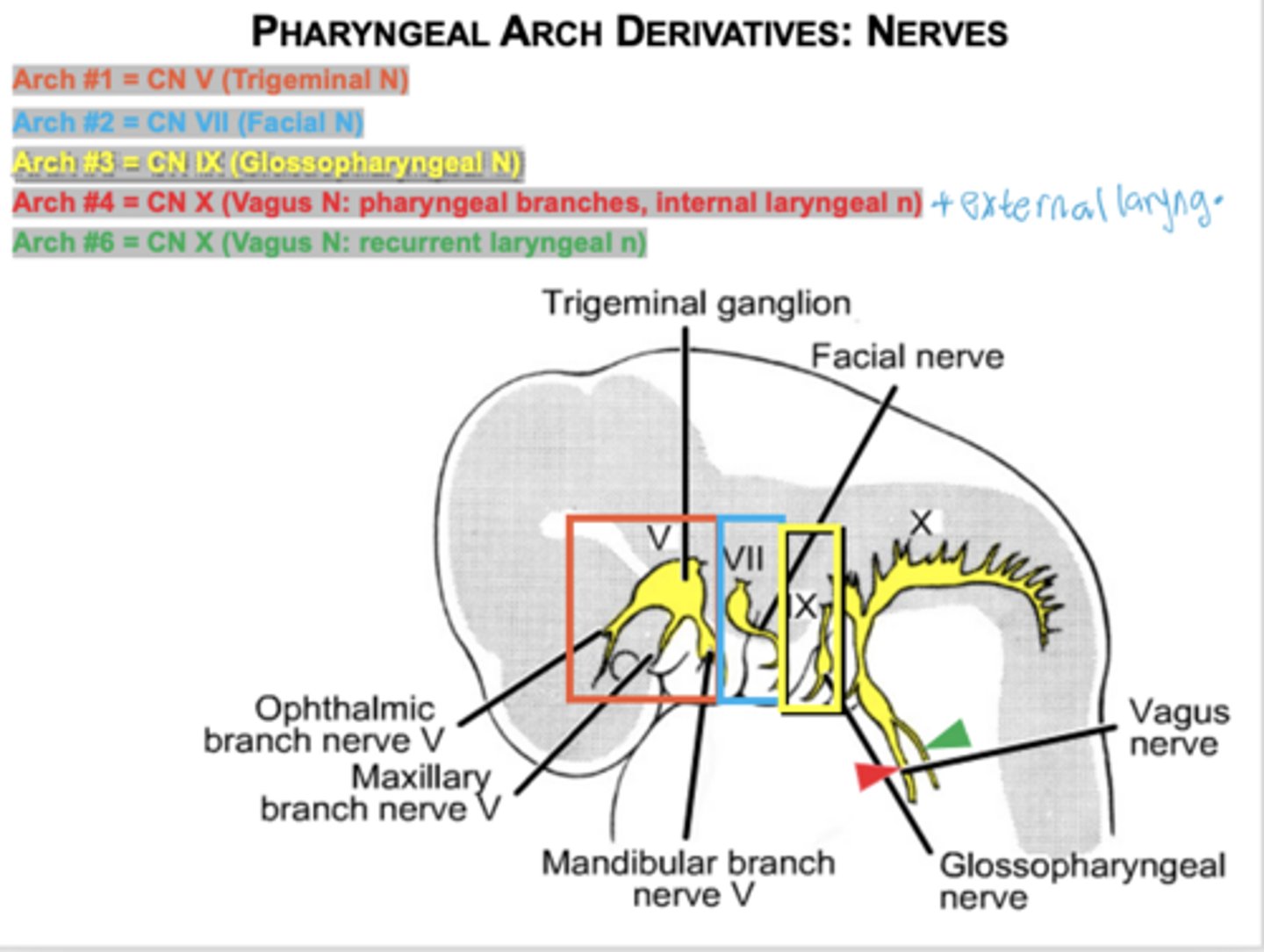
Which nerve innervates first arch muscles?
CN V (Trigeminal).
What muscles come from the first arch?
Muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior digastric, tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini.
Which nerve innervates second arch muscles?
CN VII (Facial).
What muscles derive from the second arch?
Facial expression muscles, stapedius, stylohyoid, posterior digastric.
Which muscle derives from the third arch?
Stylopharyngeus.
Which nerve innervates the third arch?
CN IX.
Which nerve innervates arches 4 and 6?
CN X (Vagus)
arch 4 - (superior laryngeal n -ext and int)
Arch 6 - (recurrent laryngeal nerve)
What muscles come from arches 4 and 6?
Laryngeal muscles, pharyngeal constrictors, levator veli palatini, skeletal esophagus.
(note slide should say external and internal laryngeal )
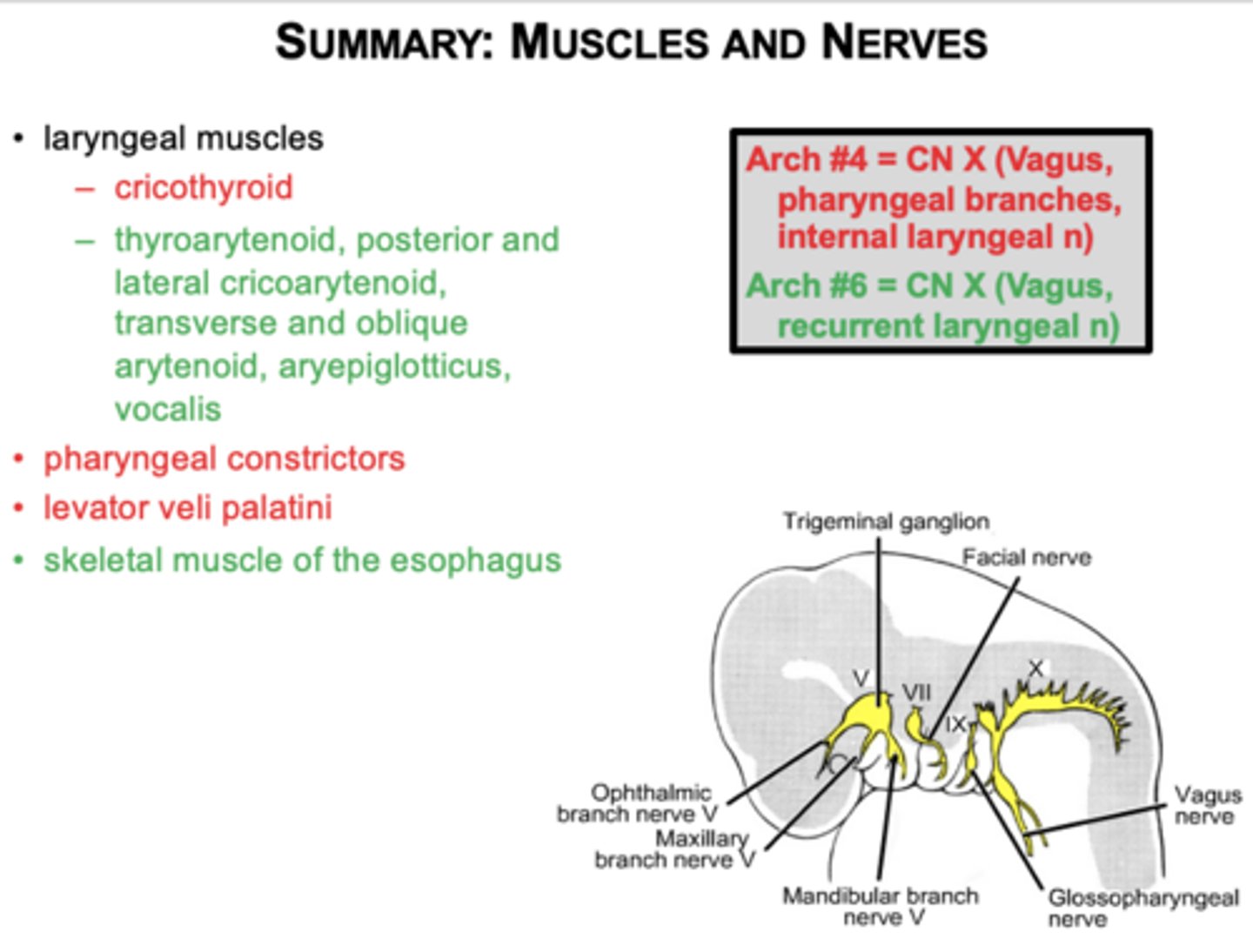
Know the derivatives of pharyngeal arch nerves
What artery persists from the first arch?
Maxillary artery.
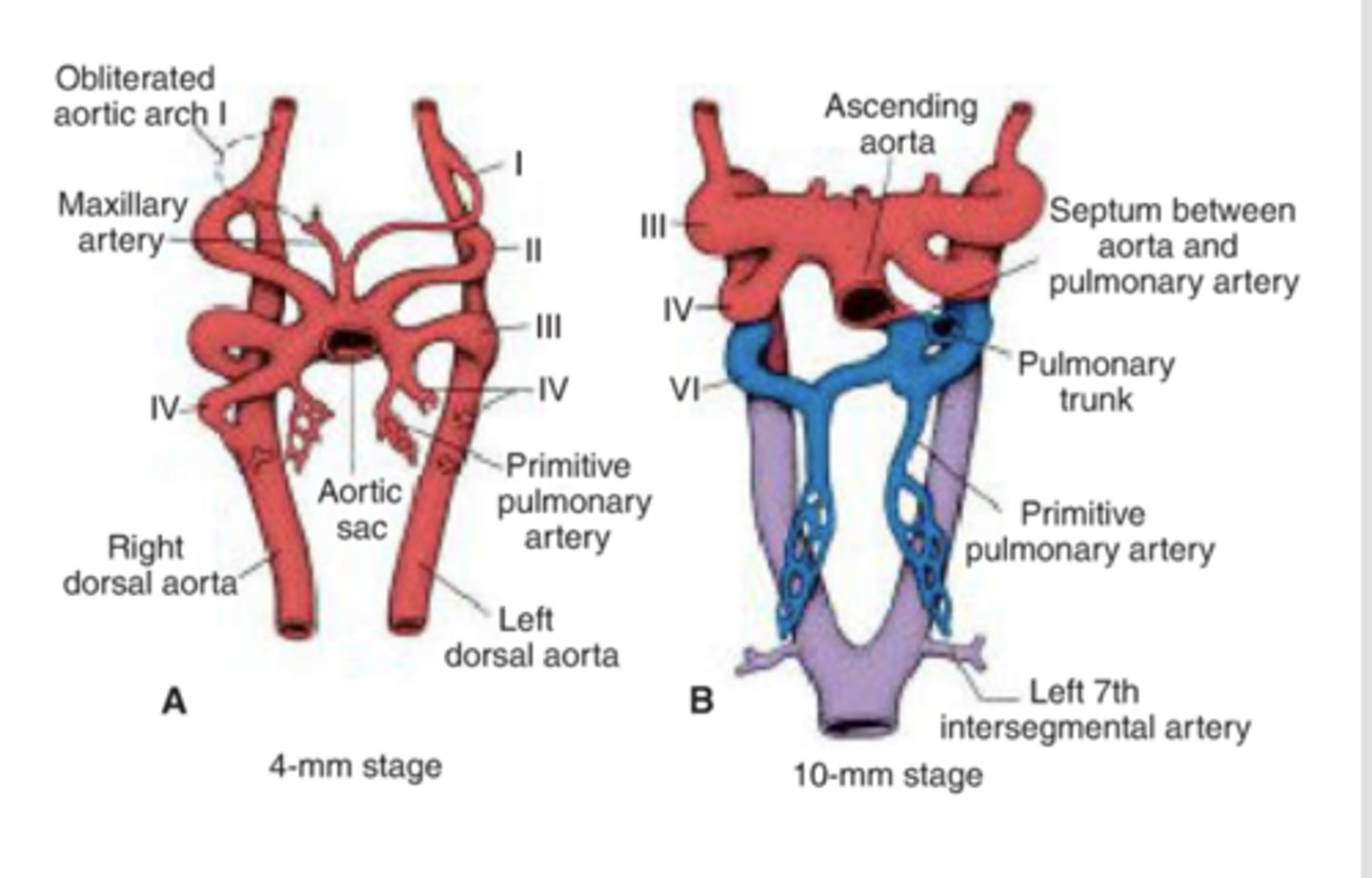
What arteries are formed from the second arch artery?
hyoid and stapes arteries
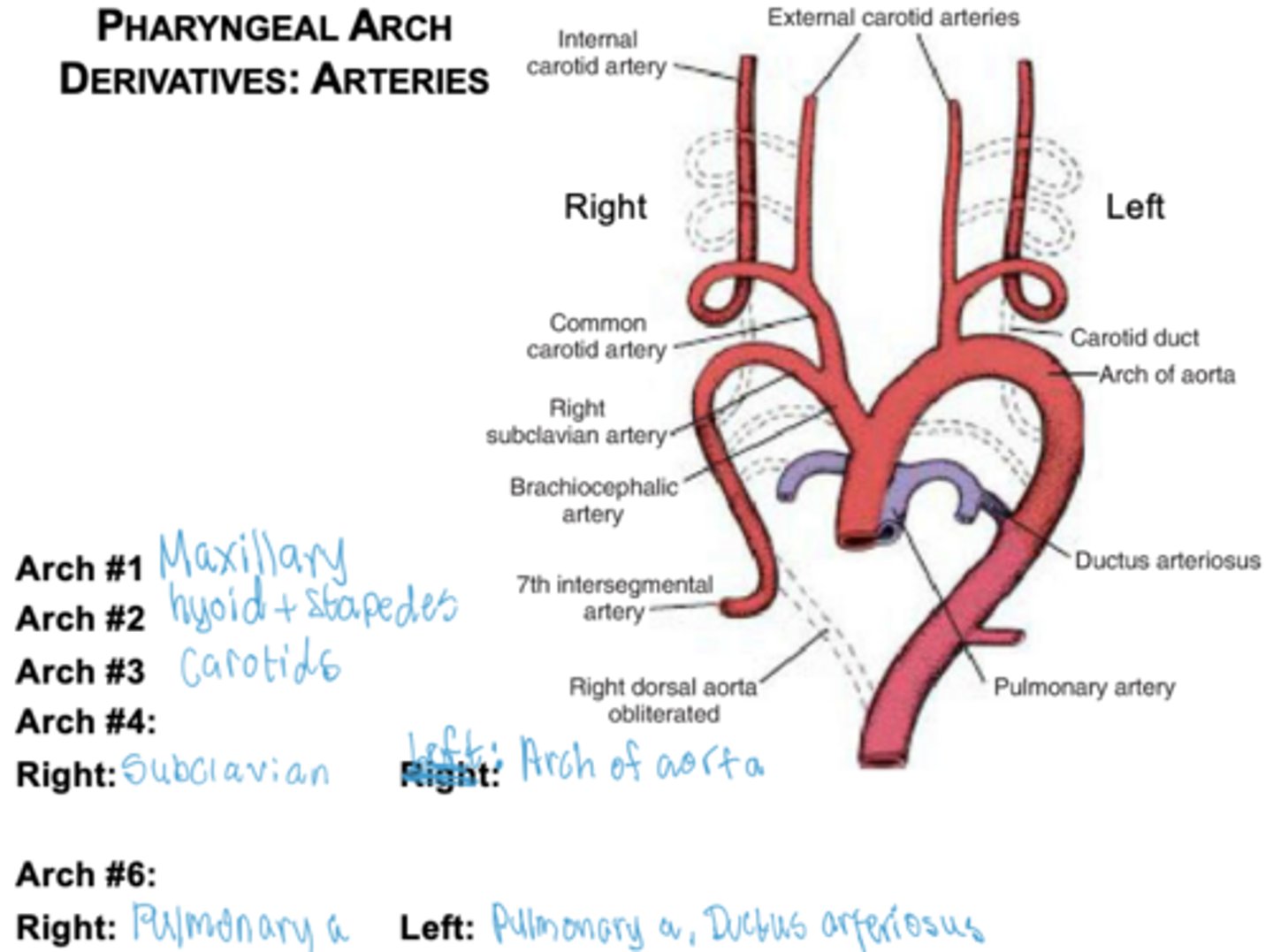
What does the third arch form?
Common carotid and internal carotid arteries.
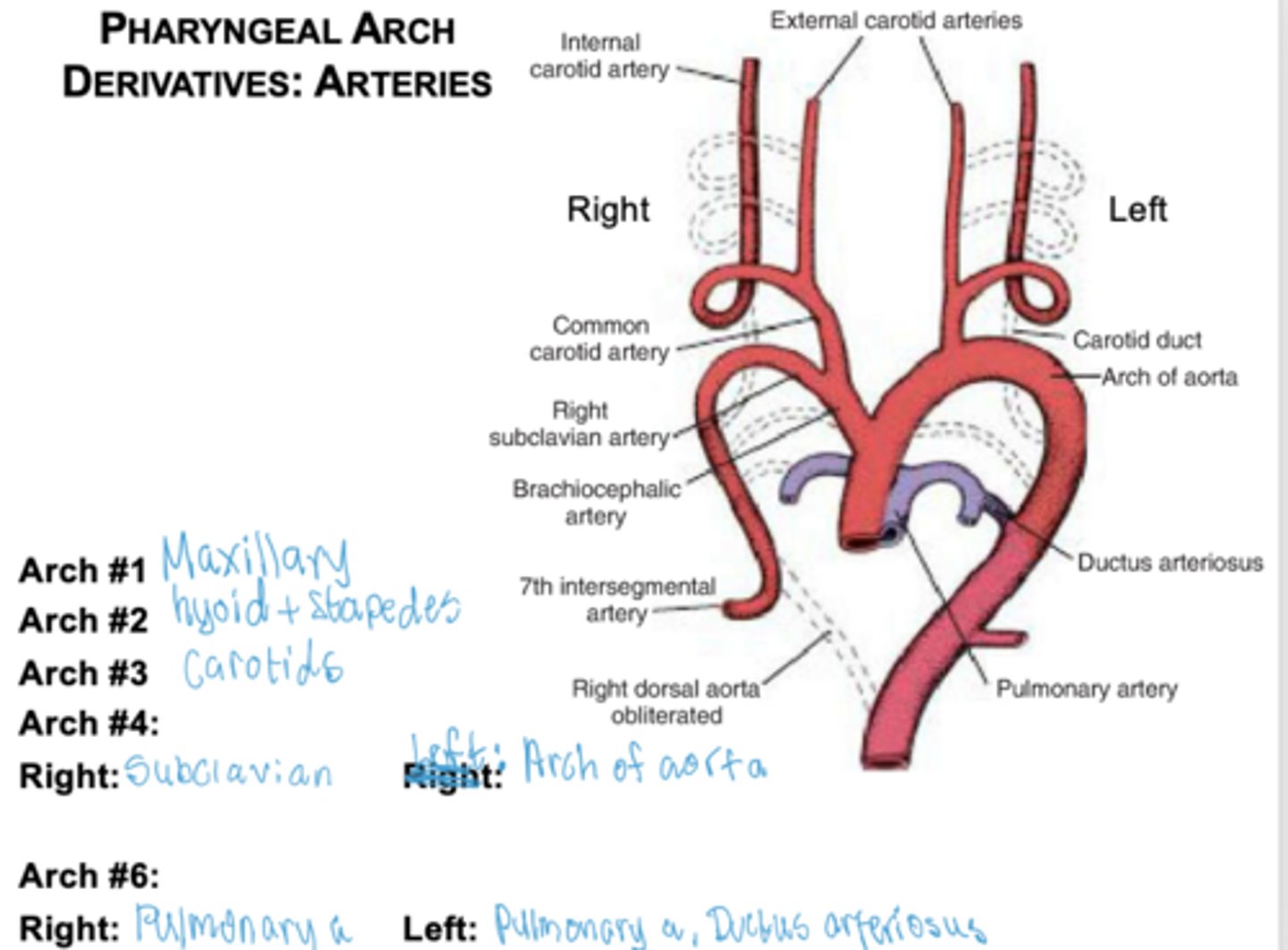
What does the right fourth arch form?
Right subclavian artery.
What does the left fourth arch form?
Part of the aortic arch.
What does the sixth arch form on the right?
Right pulmonary artery.
What does the sixth arch form on the left?
Left pulmonary artery and ductus arteriosus.
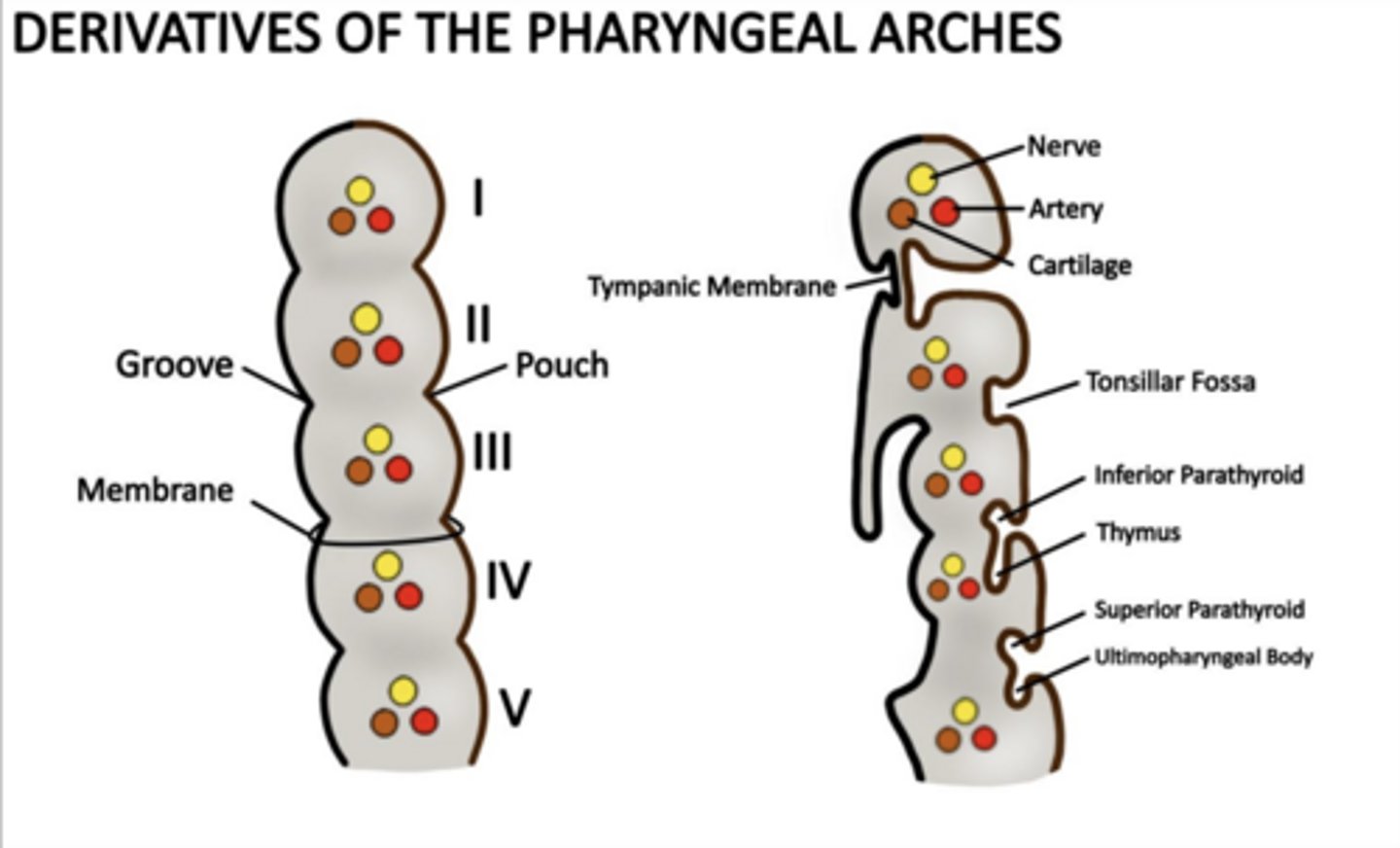
How many pharyngeal pouches form?
Four between each arch ALL lined by ENDODERM
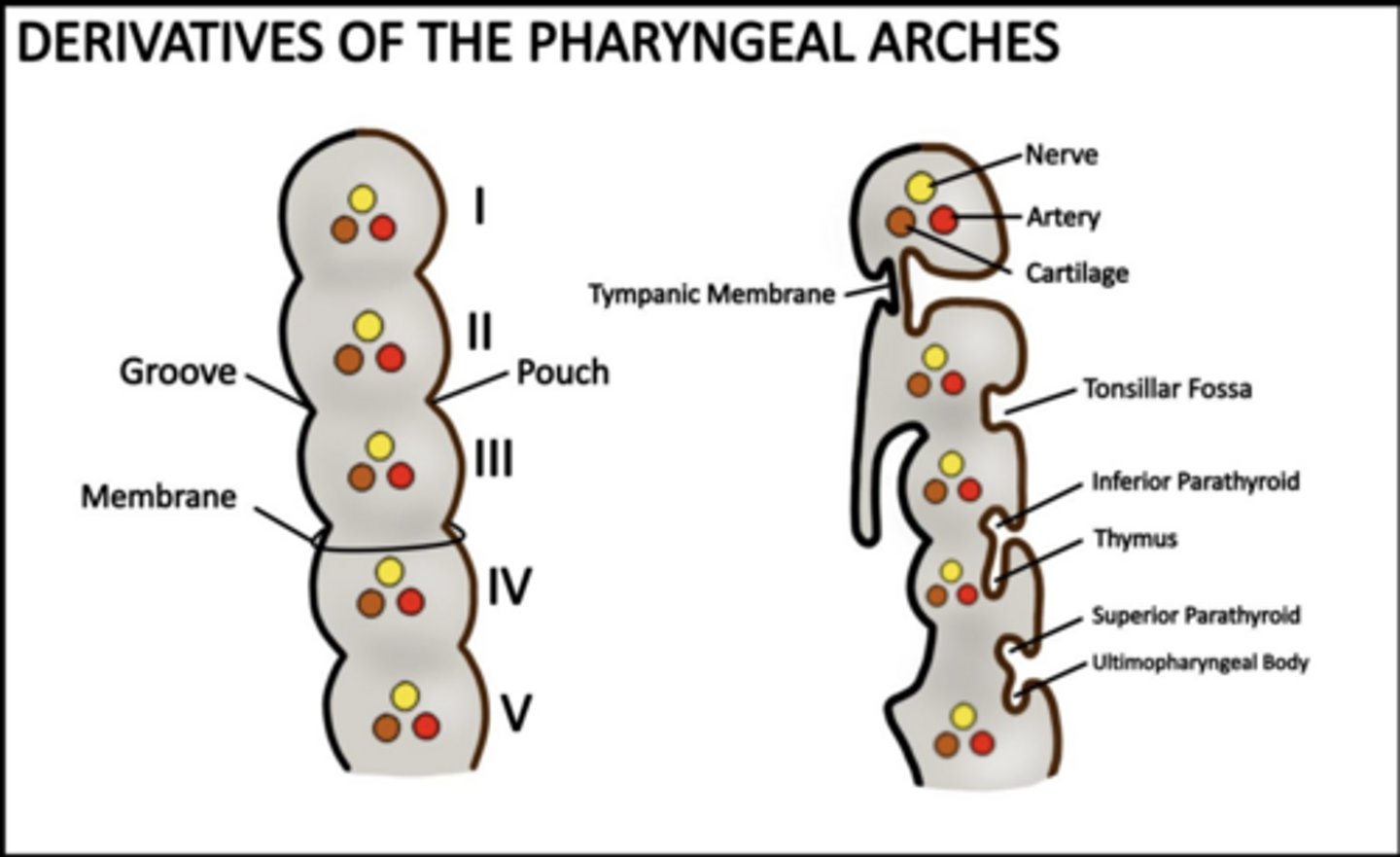
What does the first pouch form?
Tympanic cavity and auditory tube.
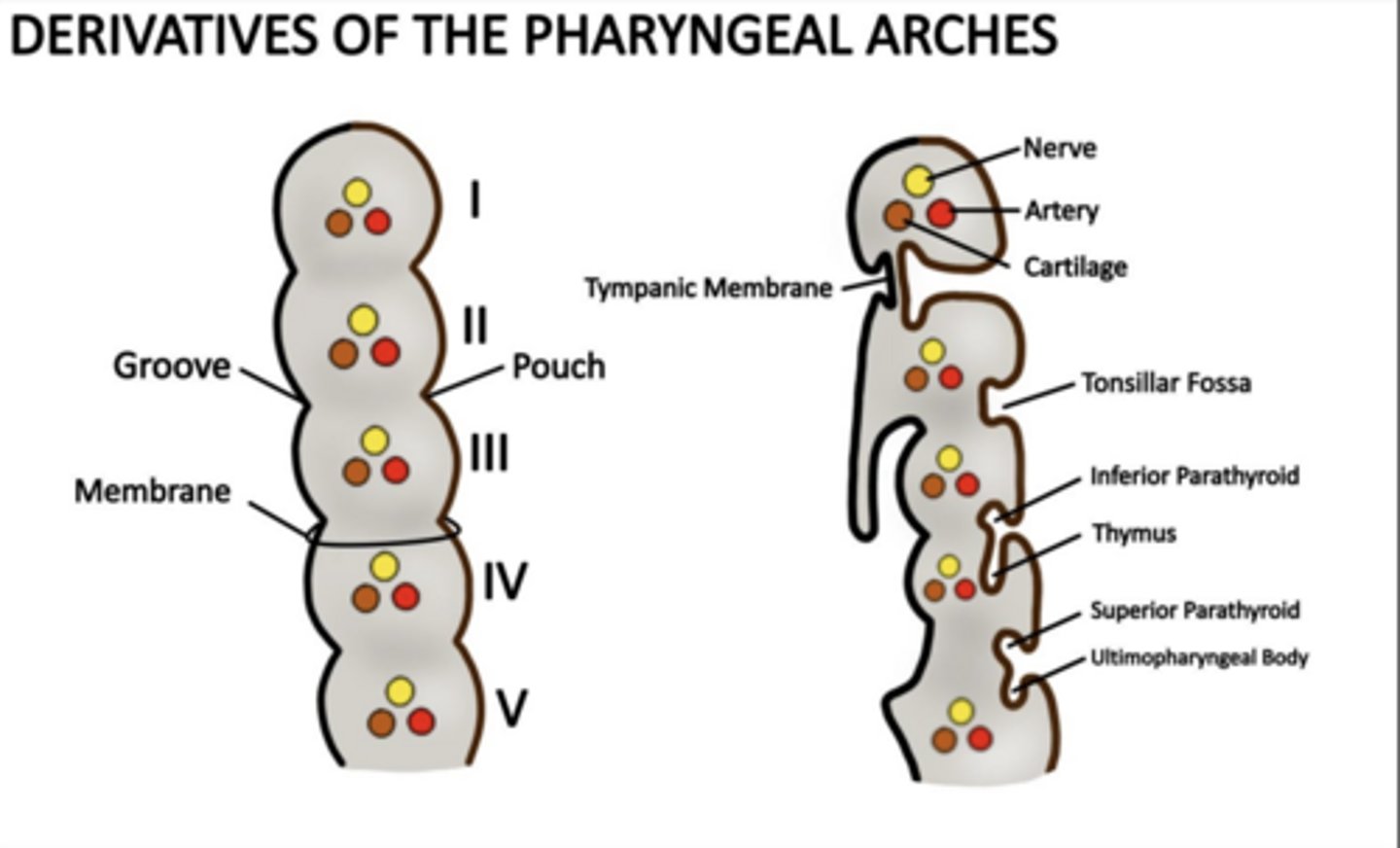
What does the second pouch form?
Palatine tonsils and tonsillar fossa.
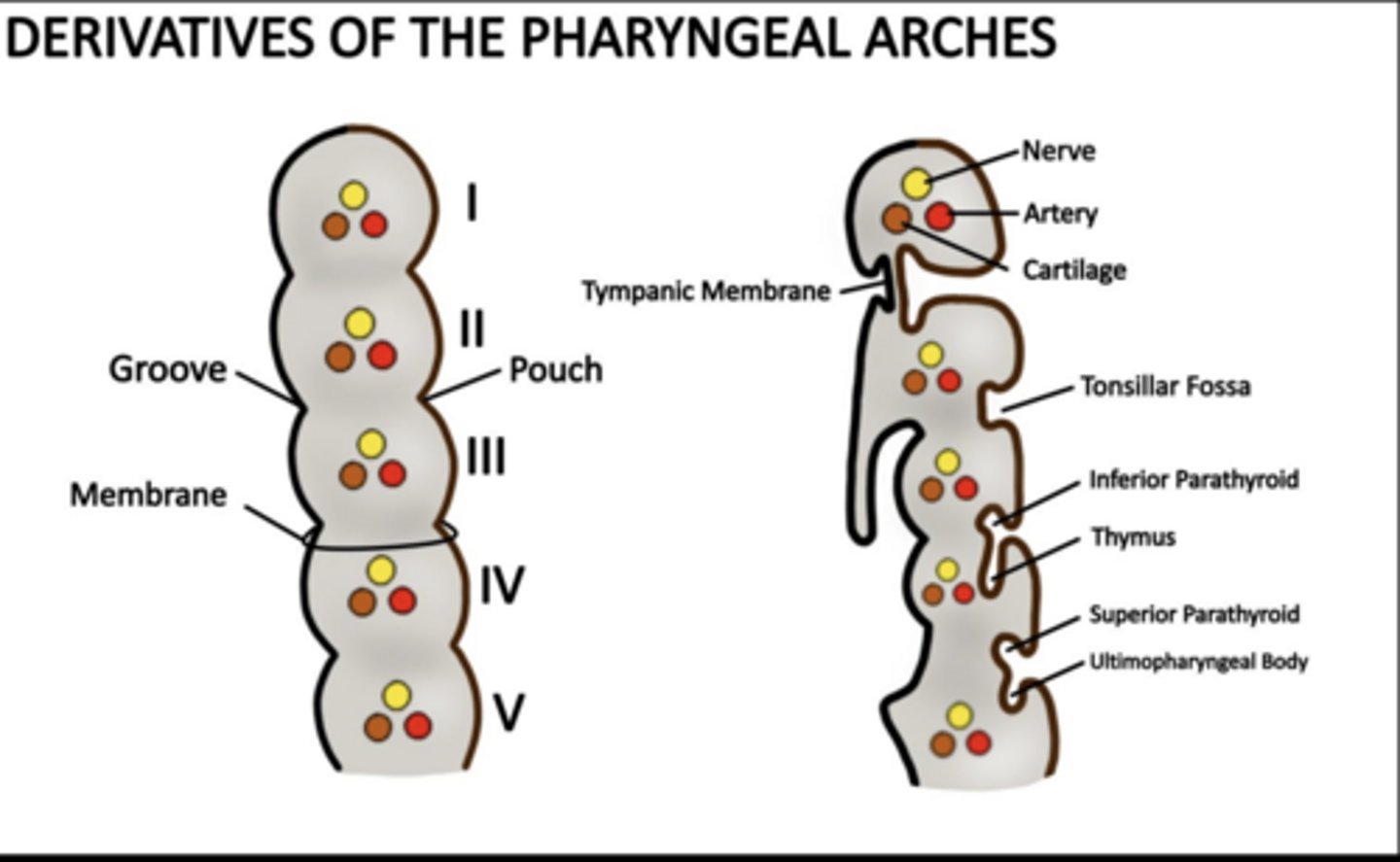
What does the third pouch form?
Inferior parathyroids and thymus.
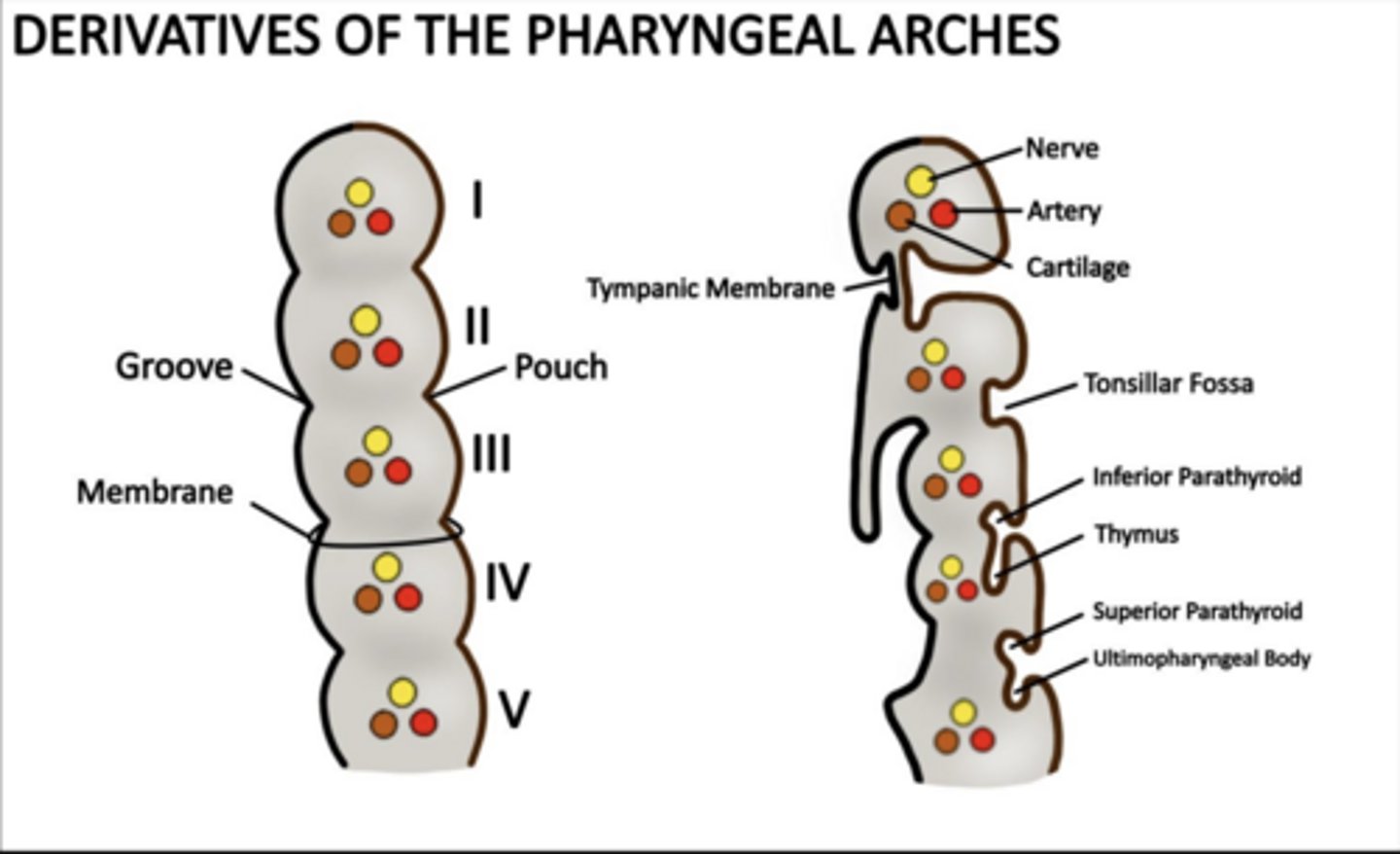
What does the fourth pouch form?
Superior parathyroids and ultimopharyngeal body (C cells).
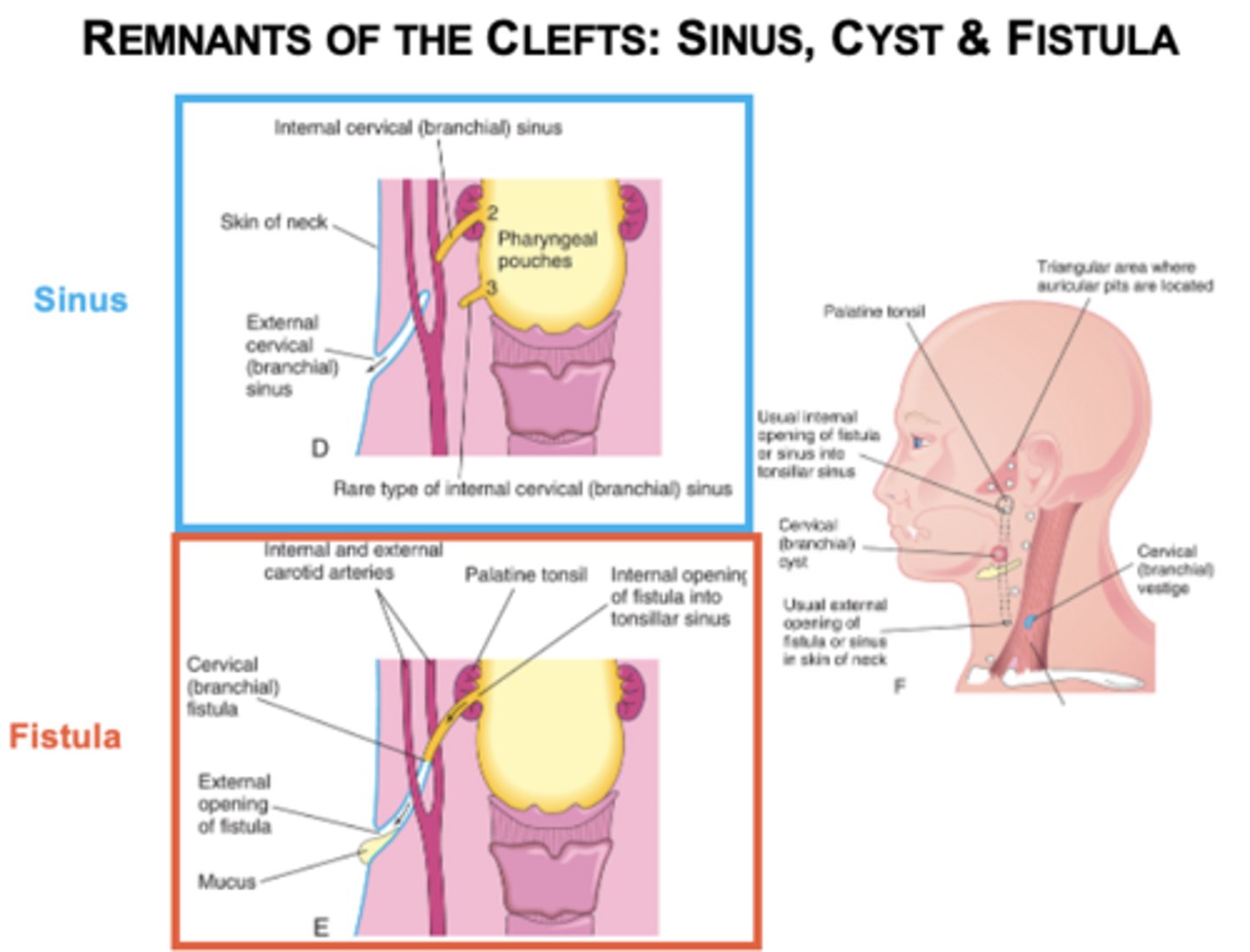
What does the first cleft form?
External auditory meatus.
What do clefts 2-4 normally do?
Disappear.
What results if clefts persist?
Sinus, cyst, or fistula.
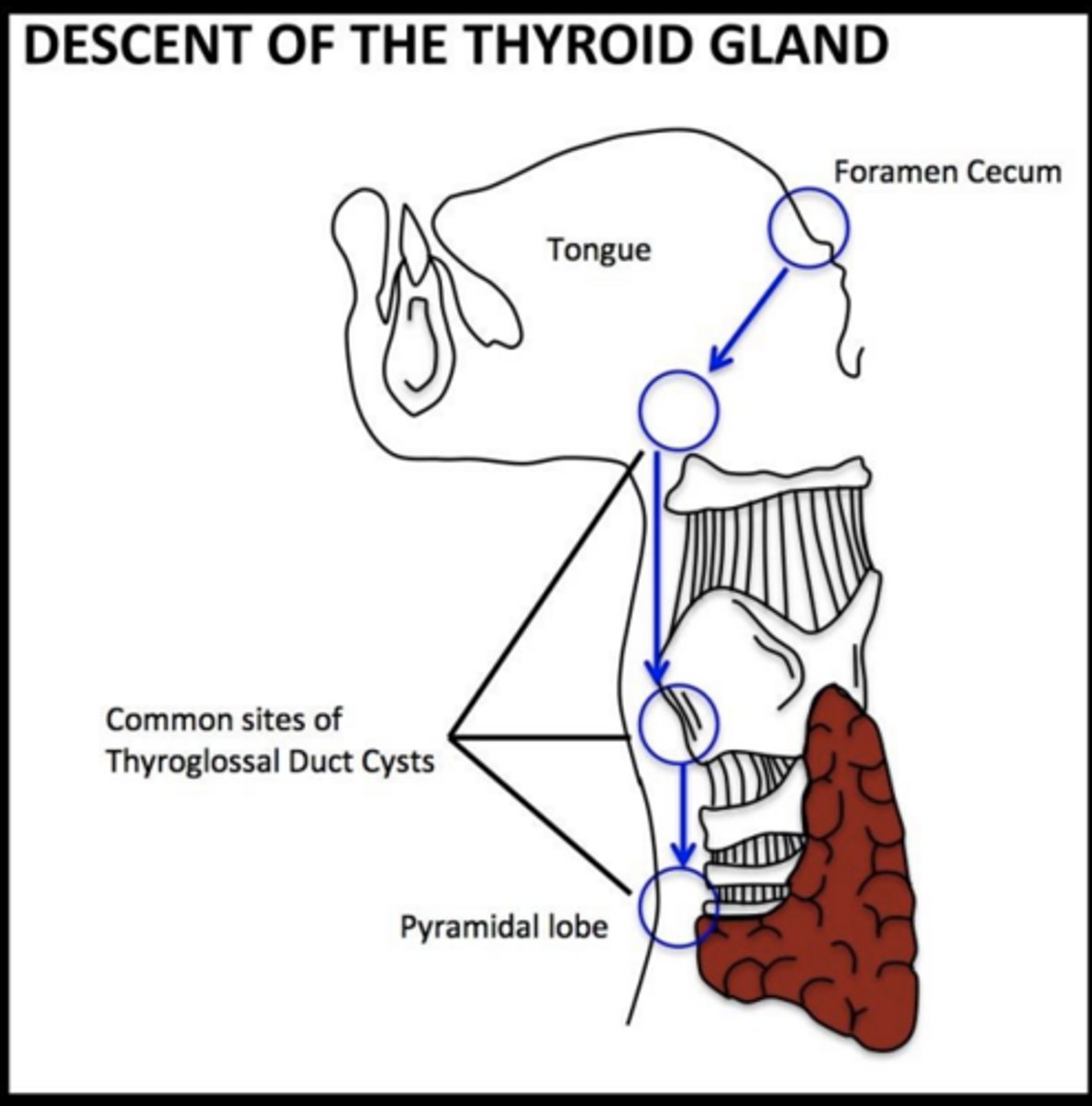
Where does the thyroid originate?
Median endodermal thickening at the foramen cecum.
What is the foramen cecum?
tube in tongue where the thyroid will descend through.
What connects the thyroid to the tongue during descent?
Thyroglossal duct.
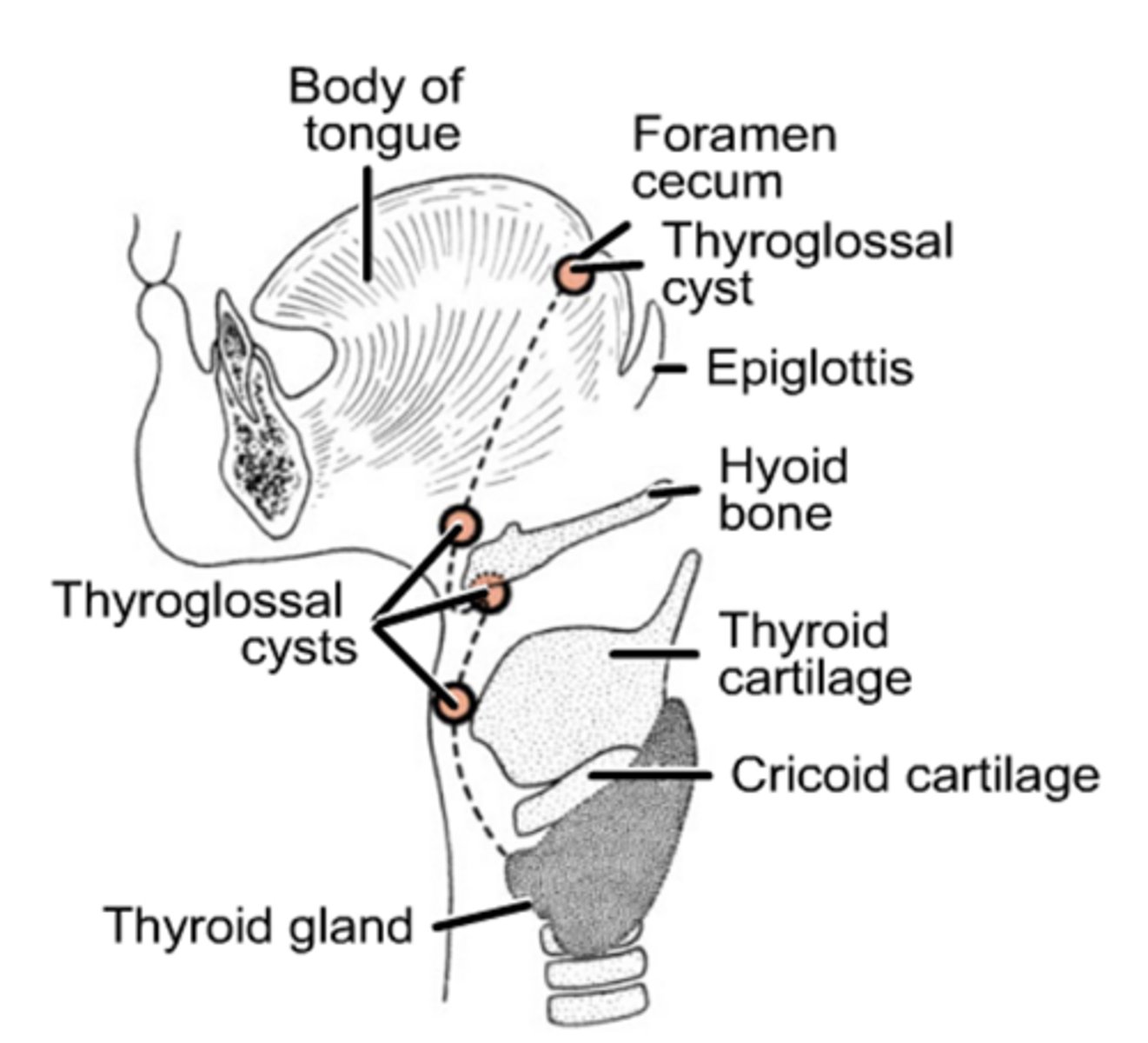
What is the pyramidal lobe?
Remnant of the thyroglossal duct present in ~50% of people.
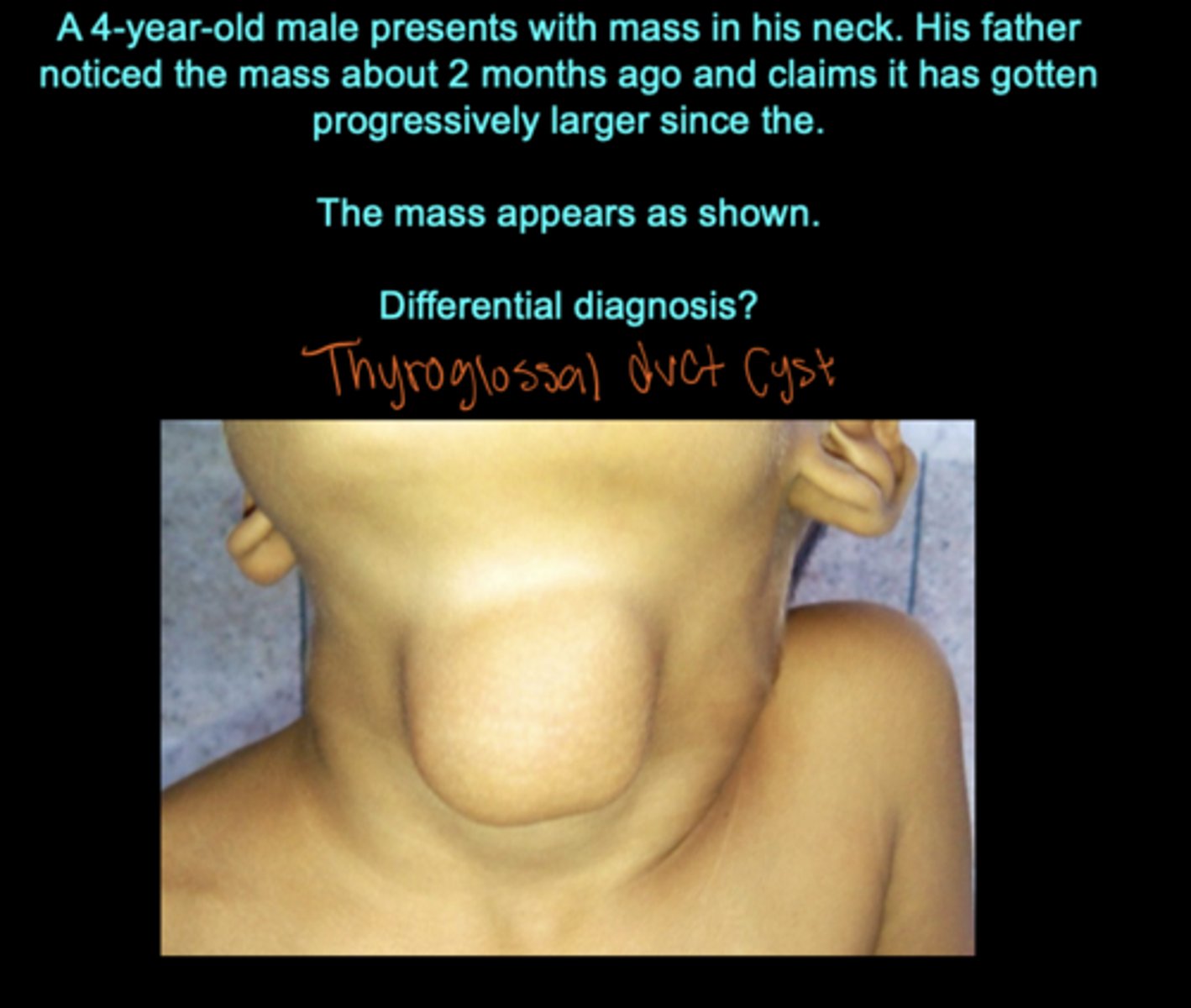
What results from persistence of the thyroglossal duct?
Thyroglossal cysts or sinuses seen at the center of the neck/most anterior
What forms the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
Lateral lingual swellings from arch 1.
What forms the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
Copula from arches 3 and 4.
What marks the division between anterior and posterior tongue?
Terminal sulcus.
What is the sensory innervation of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
CN V.
What is the sensory and taste innervation of the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
CN IX.
What is the root of tongue innervation?
CN X.
What nerve supplies most tongue muscles?
CN XII.
Which tongue muscle is NOT supplied by CN XII?
Palatoglossus (CN X).
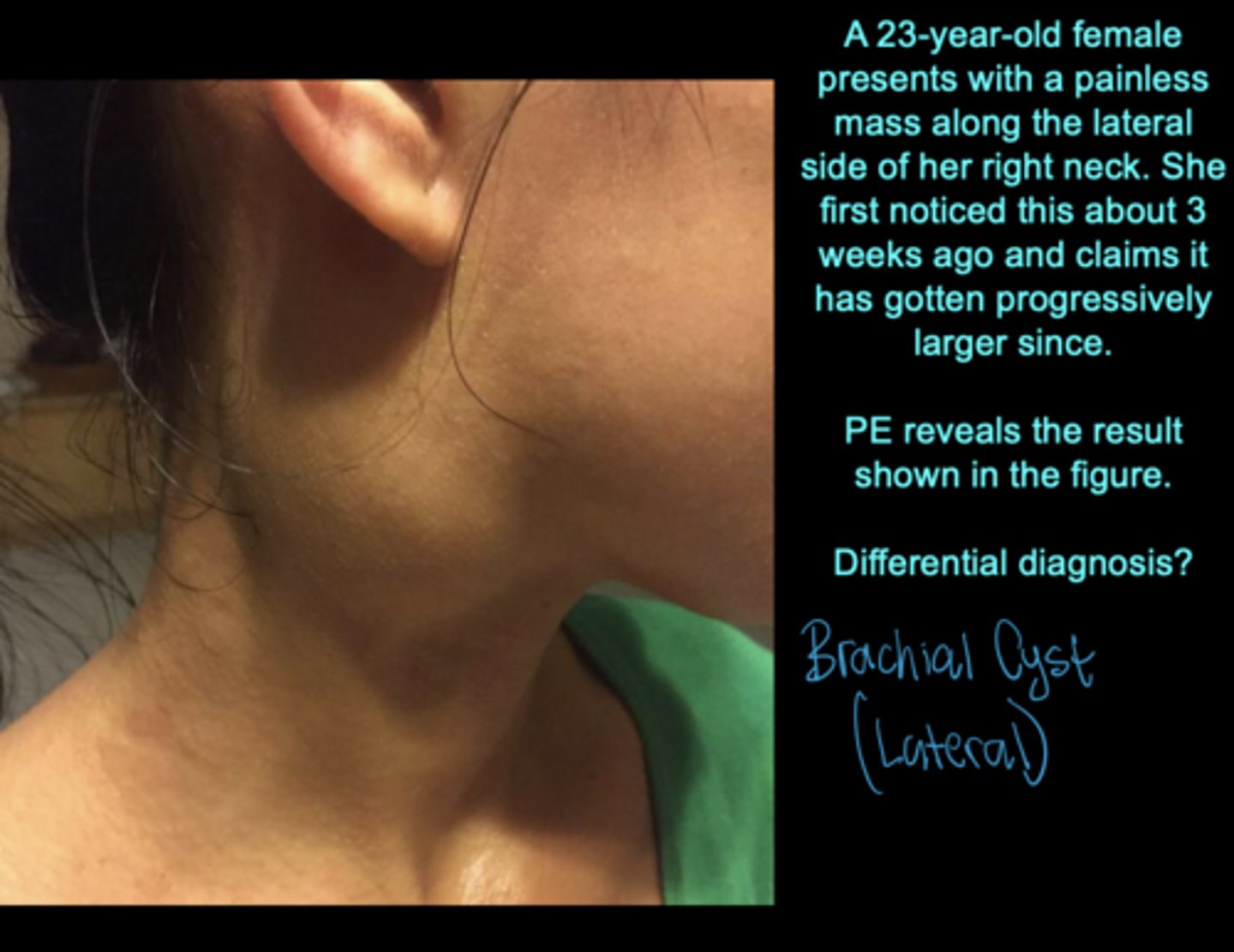
What causes branchial cysts/fistulas?
Persistence of pharyngeal grooves occur when the second arch fails to grow over the third and fourth arches. Such a defect results in the formation of a lateral cervical cyst; fistulas have an external opening on the lateral aspect of the neck
What is ectopic thyroid tissue?
Thyroid tissue along migration path (foramen cecum)
What is Treacher Collins Syndrome?
first arch defects - variable; may have any of the following: hypoplasia of the mandible, face; malformation of ears, eyelid defects, and faulty dentition
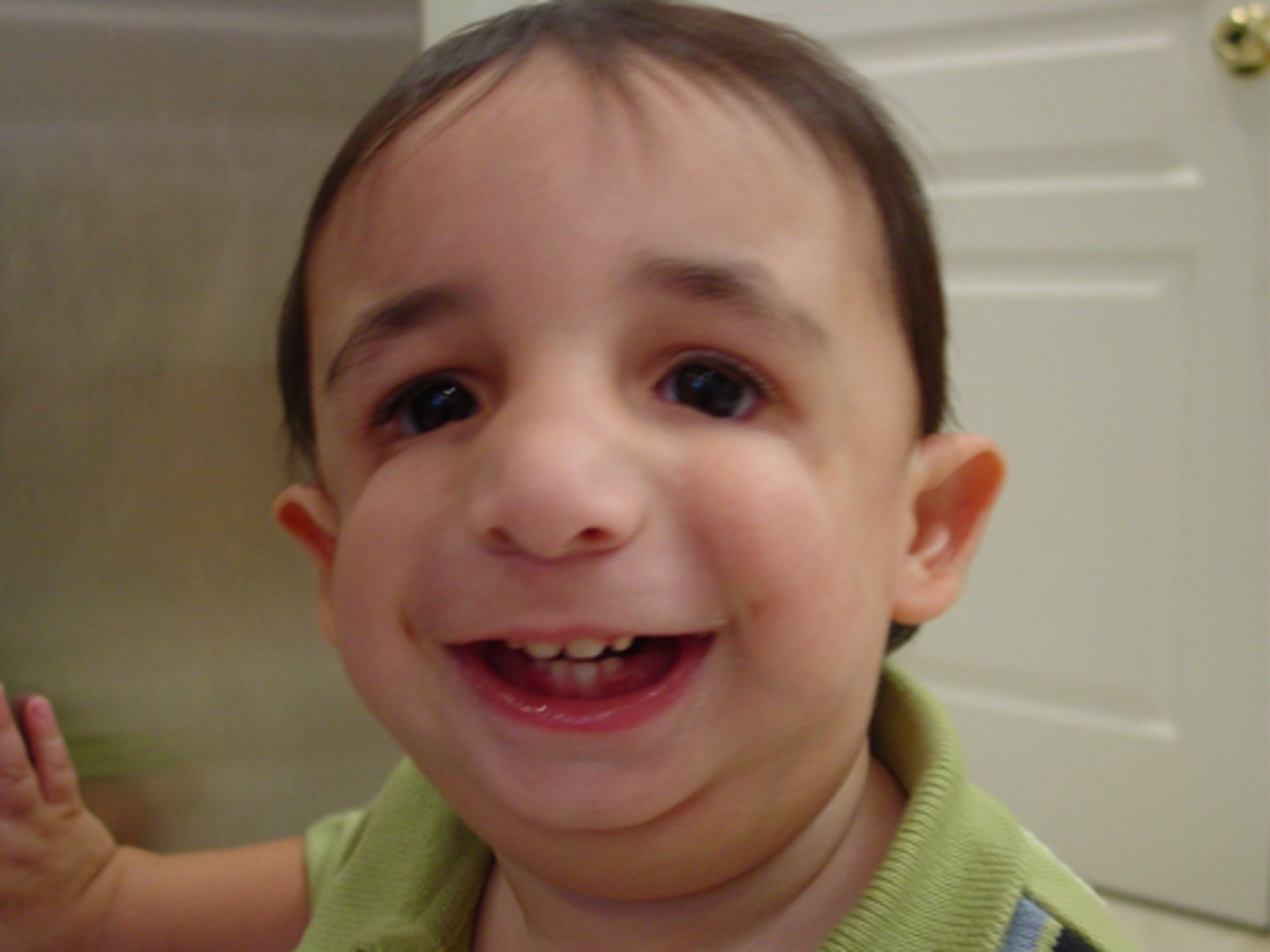
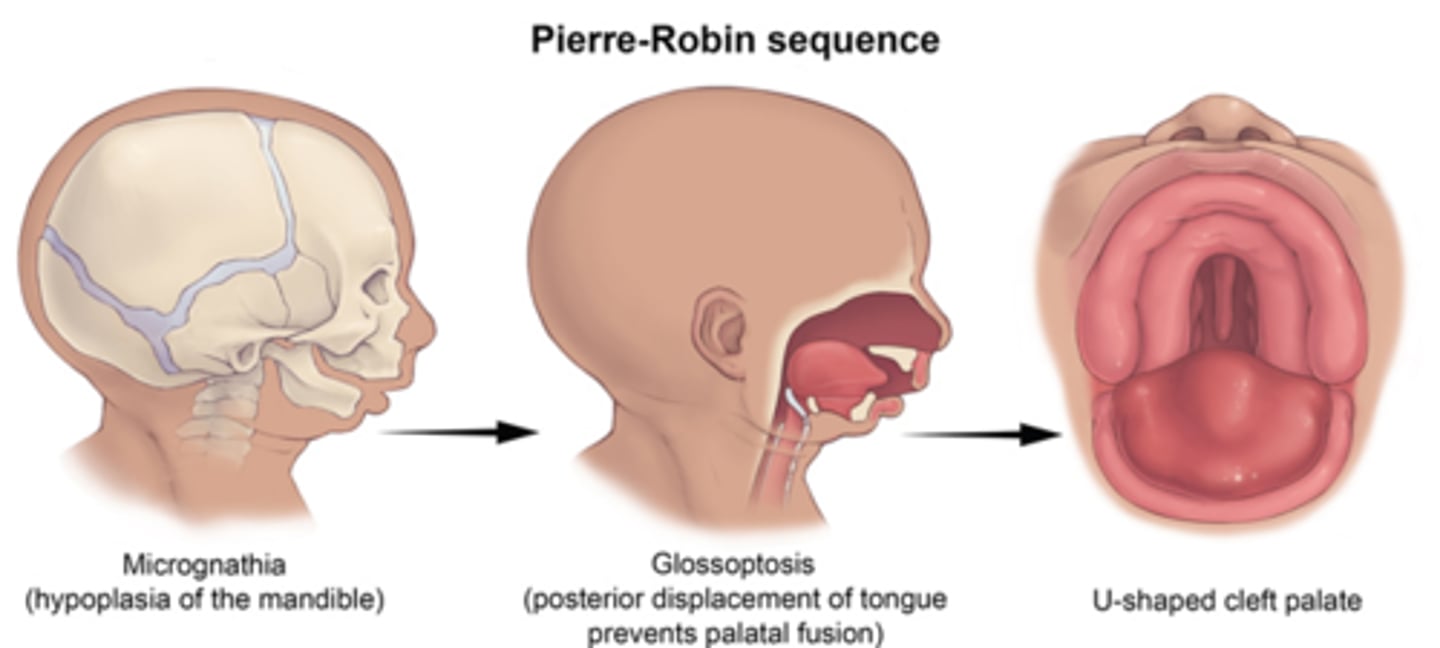
What syndrome involves micrognathia, external ear defects and cleft palate?
Pierre Robin Sequence involves the first arch
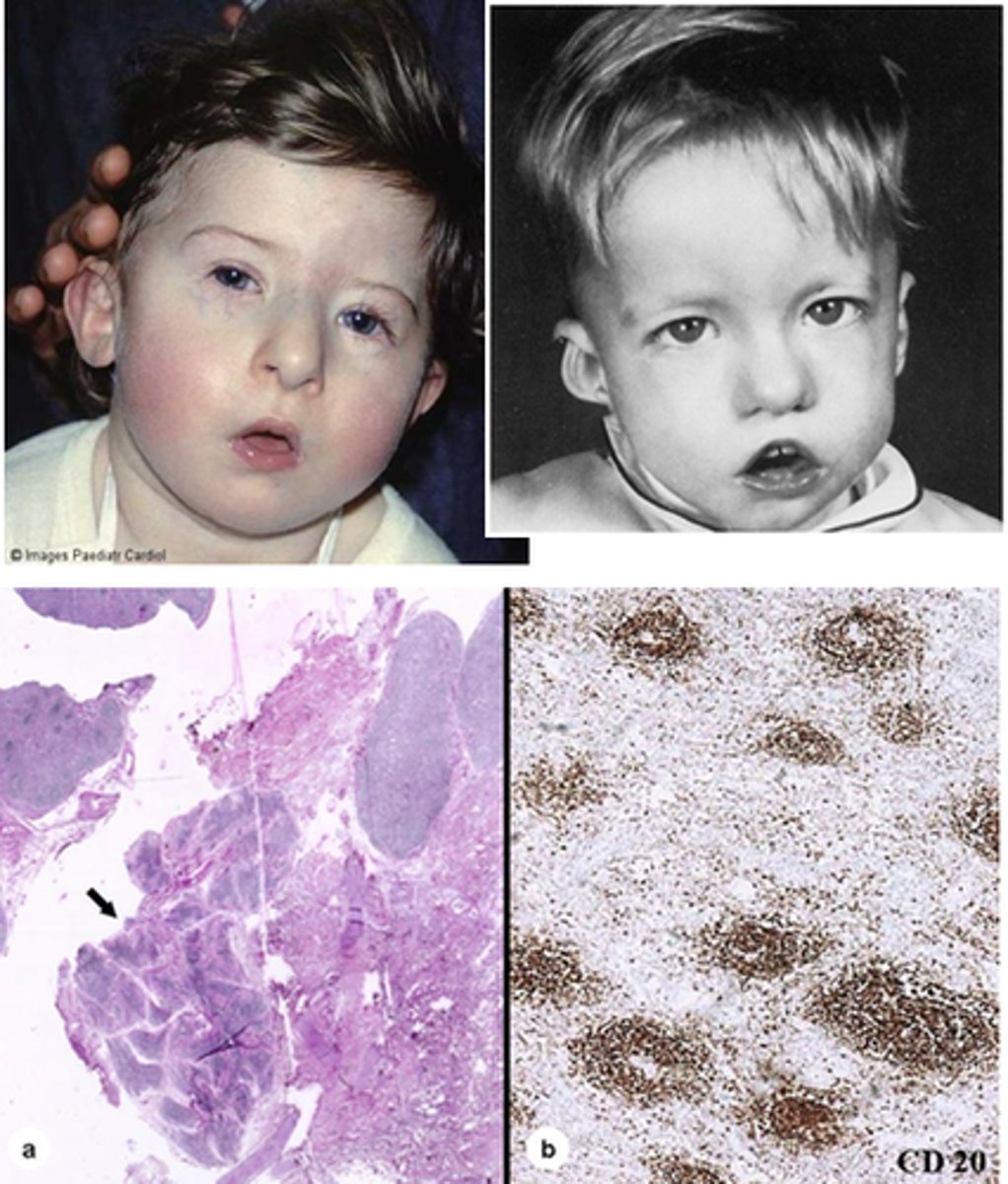
What is DiGeorge anomaly?
Involves abnormalities of the heart, parathyroid gland, face, and thymus gland.
Affected individuals will have congenital heart disease, unusual facial features with low-set ears, a small receding mandible, wide-set eyes and are born without parathyroid glands
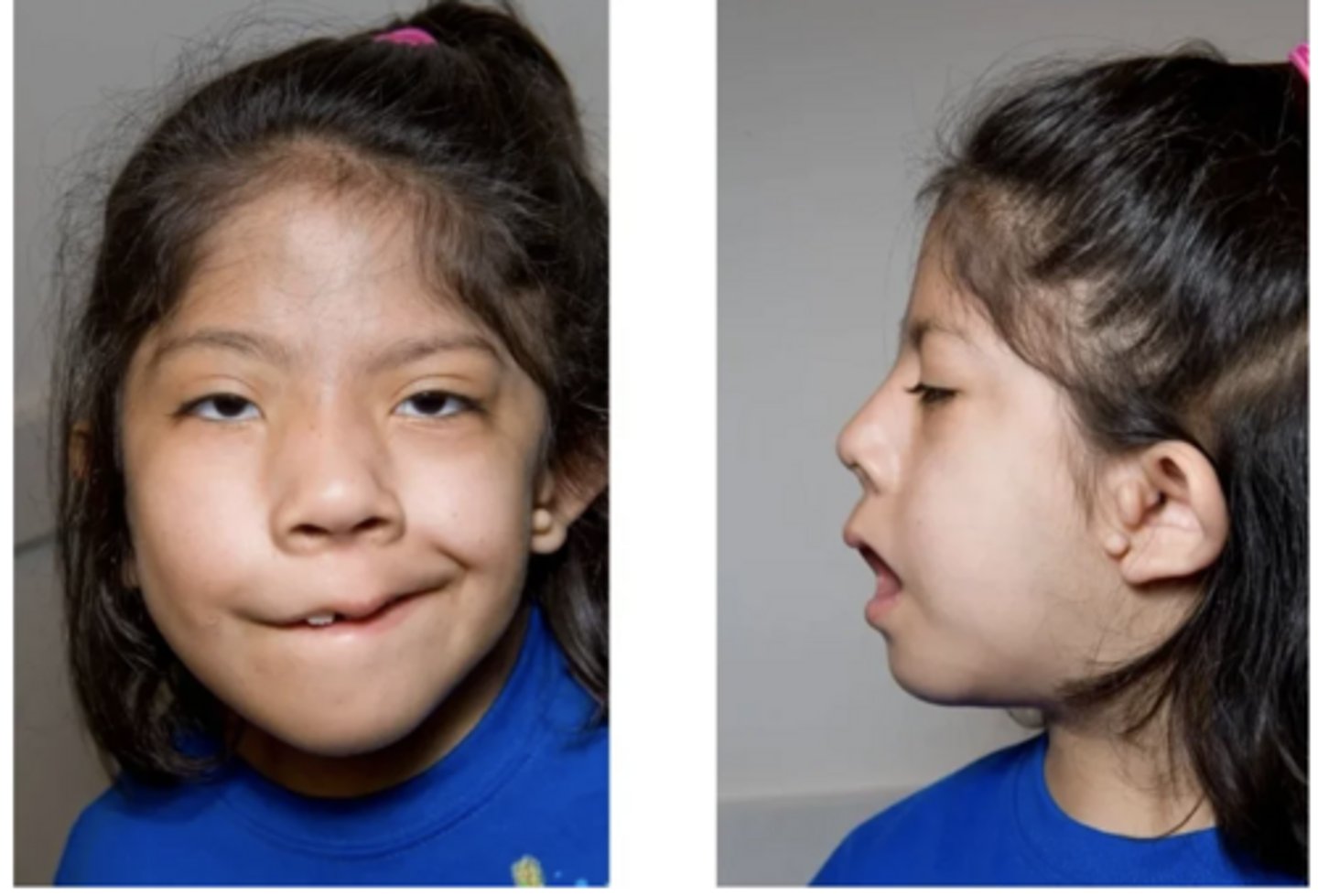
What Goldehar syndrome?
- Oculo-auricular-vertebral dysplasia
- abnormal development of 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches
- characteristic features: microtia, mandibular hypoplasia, microstomia, skin tags and vertebral anomalies
Which pharyngeal arch contributes the lateral lingual swellings?
Arch 1
What structures arise from Arch I to form the anterior 2/3 tongue?
Two lateral lingual swellings and the tuberculum impar
What structure is the tuberculum impar?
A median tongue swelling that contributes little to the final tongue
Which arches contribute to the copula?
Arches II, III, and IV (not much from 2)
Which arch contributes most to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
Arch III
Which arch forms the epiglottic swelling?
Arch IV
What does the terminal sulcus mark?
The border between anterior 2/3 and posterior 1/3 tongue regions.
What germ layers meet at the terminal sulcus?
Ectoderm anteriorly and endoderm posteriorly
Which arches are separated by the terminal sulcus?
Arch I (anterior 2/3) and Arch III (posterior 1/3).
What is the general sensory innervation of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
CN V (GSA, ectoderm).
What is the general sensory innervation of the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
CN IX (GVA, endoderm).
What is the taste innervation of the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
CN IX.
What is the sensory and taste innervation of the tongue root?
CN X.
What is the embryologic origin of tongue muscles?
Occipital somites.
What is ankyloglossia?
Abnormally short lingual frenulum restricting tongue movement (tongue tied)
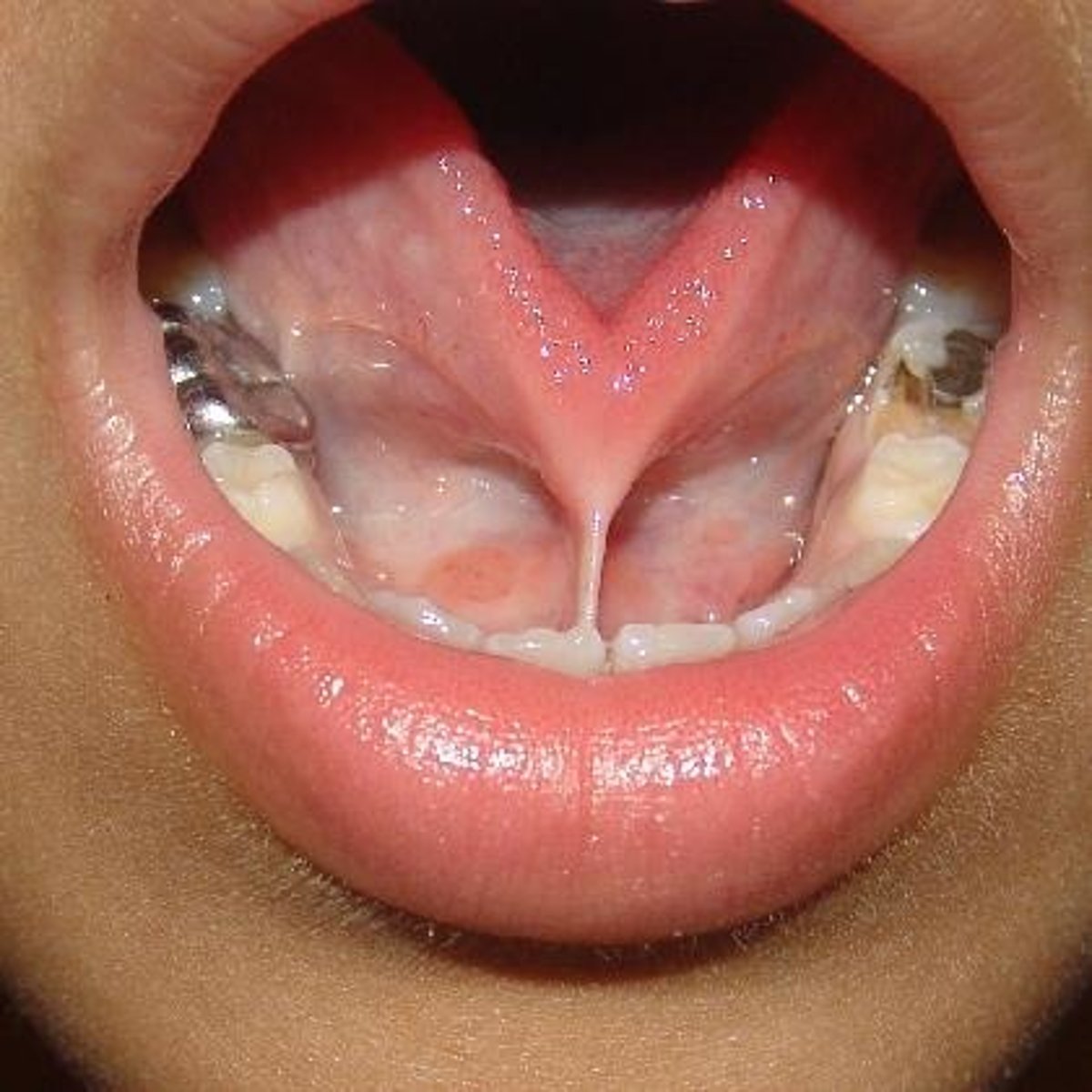
What is macroglossia?
Abnormally large tongue.
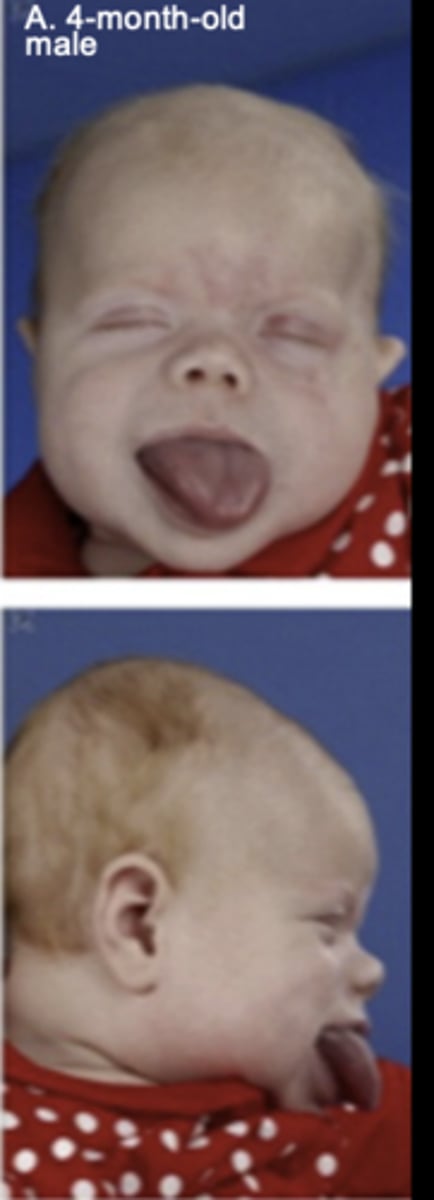
What is microglossia?
Abnormally small tongue.
What is aglossia?
absence of a tongue
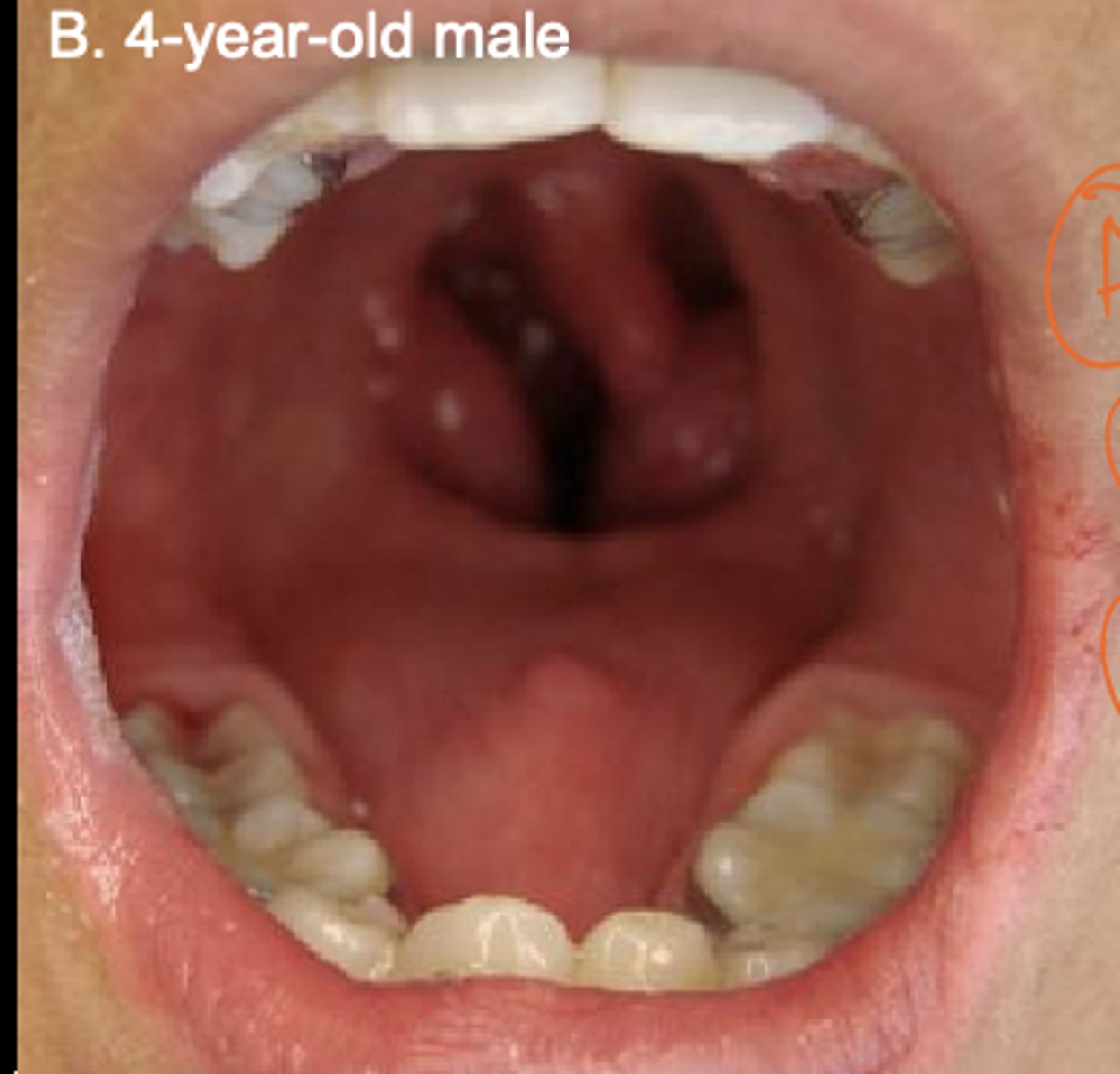
What is a bifid tongue (glossoschisis)?
Failure of tongue swellings to fully fuse.