LS4001 Genes, Cells and Tissues - Genes and Inheritance
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What does phenotype mean?
Physical appearance of a genetic trait
What is a mutation?
any change in the DNA sequence
What is a gene?
segment of DNA responsible for a trait
What is an allele?
an alternative version of a gene
What is genetic inheritance?
The way in which a trait is passed down generationally
Genes inhereited through mitosis/meosis?
Meosis!
What is the difference between a chromosone and a chromatid?
Chromosone is a fixed meal set of genes, a chomatid is how many copies of that fixed set of info there are
STAGE 1 ONE MEOSIS
PROPHASE (5)
the genetic information from the nucleus is condensed into chromosomes. The nuclear envelope breaks. The rest happens in the cytoplasm of the cell. Homogenous chromosones (similar in size shape and function [eye color etc clothes]) pair up (one from Mum, one from Dad). They then cross_over for genetic variation.
METAPHASE.
Recombinant homogeneous chromosomes line up two-by-two in the middle of the cell thanks to spindle fibers.
ANAPHASE.
The spindle fibers pull each of the homogolous pairs to opposite sides of the cell.
TELOPHASE.
New nuclear envelopes form one each side.
CYTOKENESIS.
Eponymous
STAGE 2 MEOSIS, NORMAL MITOSIS
PROPHASE (2)
Genetic information condenses into chromosomes. Nuclear envelope dissolves
METAPHASE.
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell attached at spindle fibers at centromeres
ANAPHASE.
The spindle fibers pull the chromosomes in half, to opposite size of the cell
TELOPHASE.
New nuclear envelopes form one each side.
CYTOKENESIS.
Eponymous
starting and finishing genetic material STAGE 1 MEOSIS
starts with 92 chromtids (2 sets of info)
ends with 46 genetically variant chromatids (One full set of info)
starting and finishing genetic material STAGE 2 MEOSIS
starts with 46 genetically variant chromatids (One full set of info)
ends with two haploid cells (with info from both parents)
starting and finishing genetic material - MITOSIS
starts with 92 identical chromatids (two sets of the same info)
ends with 2 identical full sets of the info, in separate cells.
Humans are diploid/somatic?
diploid, one set of info mum, one from dad, summimg to two, hence diploid
What is a dominant allele?
an allele that is fully expressed in the phenotype of a heterozygote
What is a reccesive allele?
an allele that will not show unless both alleles are reccesive
What does homozygous mean?
Possesing both homozygous, or both reccessive
What does heterozygous mean?
one dominant and one recessive allele
What does diploid mean?
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
What does somatic mean?
only onse set of chromosones
What does haploid mean?
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes (gametes)
What is a genotype?
genetic makeup of an organism
Mendel's Peas
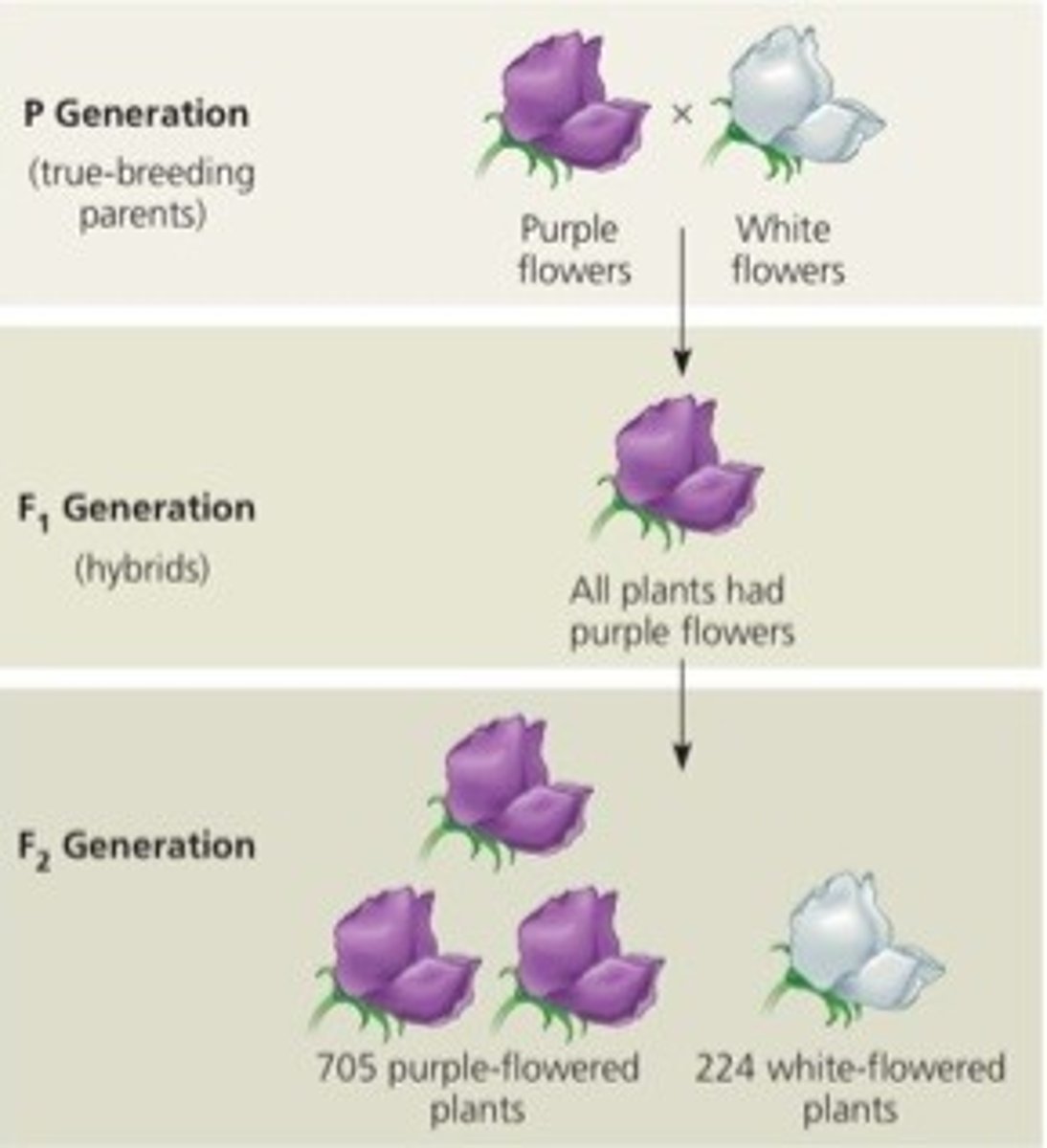
What is incomplete dominance?
when one allele is not completely dominant over the other leading to a blending of traits. (Red+White=Pink)
What is codominance?
Bpth alleles are equally dominant
What does autosome mean?
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
how many autosome pairs of chromosones in us? how many sex chromosone pairs?
22 autosome pairs of chromosones. 1 pair of sex chromosones.
What is sex linkage?
genes that are located on either the X or Y chromosome
What is a gene pool?
the sum total of all variations of this gene possesed by a specific species at a specific time
What is genotype frequency?
number of individuals with this genotype / total number of individuals in population
What is allele frequency?
number of individuals with this allele / total number of alleles of this gene
What does the Hardy-Weinberg principle assume? So what does it mean if the results deviate from the equation?
Assumes the opposite of Deviations which are:
-genetic drift
-bottle neck effect
-natural selection
-mutations
-migration
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
Genes travel on _____________?
Chromosones
What is crossing over?
the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring.
What is independent assortment?
Random distribution of homologous chromosomes!!!!
What are linked genes?
genes on the same chromosome
What are unlinked genes?
genes on different chromosomes
What is a genetic cross-test?
A test used t determine the genotype of an individual, where they could be homozygous dominant, or heterozygous. The indivual is bred with a homzygous reccesive individual, and their offspring are observed
What is the cross-test result for a homozygous dominant individual?
All of the offspring are are dominant.
What is the cross-test result for a heterzyous individual?
50% of the offpring are dominant, 50% of the offpring are reccesive
How many genes were used in the cross-test used for the discovery of gene linkage
Two different genes
How are the distance between genes and frequency of recombinance related.
each estra map unit if ditnce between two genes, increases thise genes' chance(FREQUENCY) of recombinance by 1%