Electromagnetic Spectrum and Wave Properties in Medical Imaging
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is Absorption?
the condition of light when the light photons are stopped by a substance.
What is Amplitude?
the height of a wave. A wave with a large amplitude is generally stronger than a wave with a small amplitude.
What does attenuated mean?
the conditions of light when some of the photons are absorbed but some are transmitted through a substance.
What is Electromagnetic Energy?
pure energy, rather than particles with mass. The term is used because rays of electromagnetic energy have properties of both electrical energy and magnetic energy.
What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
the range of electromagnetic energy in wavelengths, frequency or energy. It is a continuum of every possible frequency. Radio waves, light and x-rays are all terms for different ranges on this spectrum.
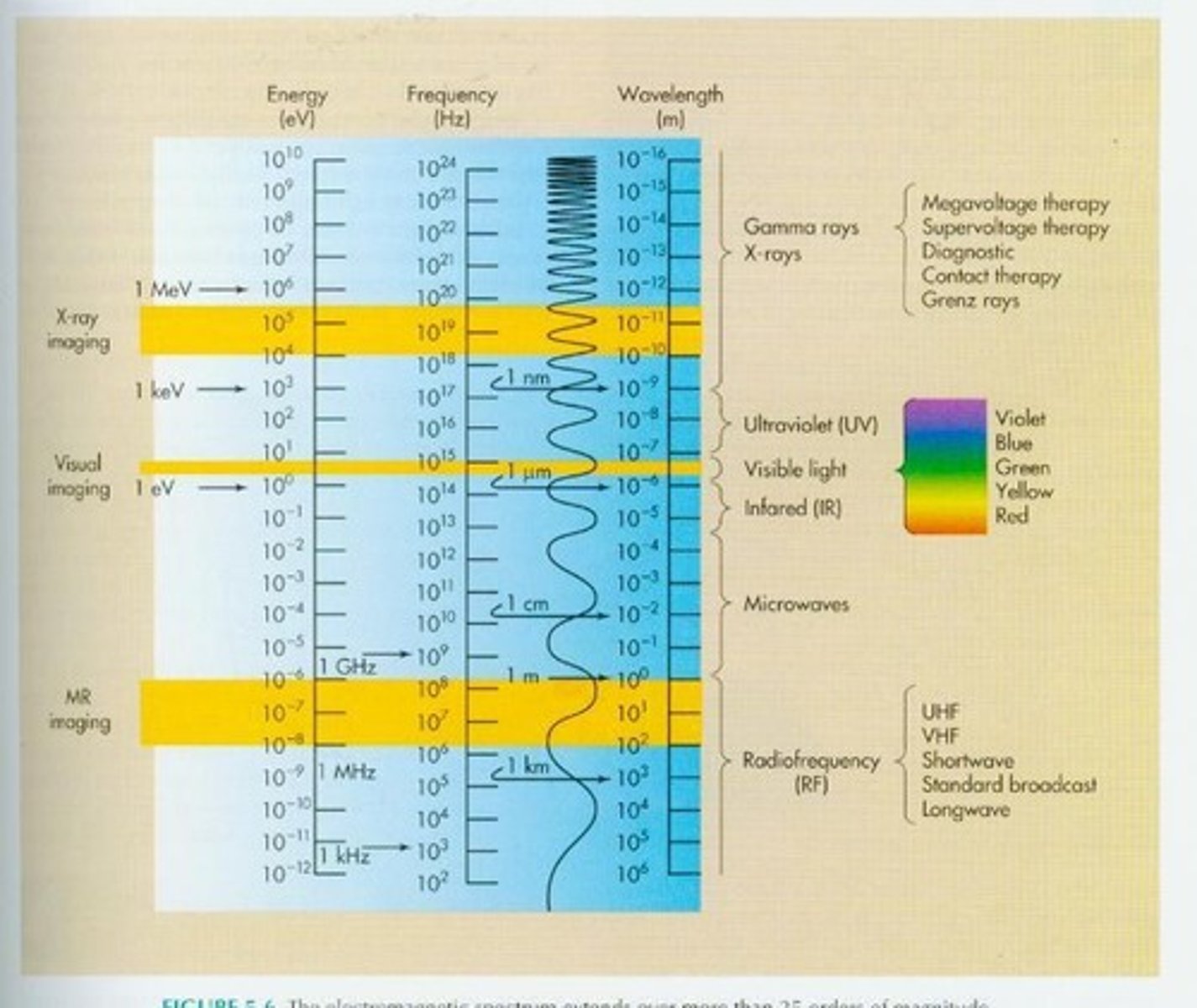
What is Frequency?
the number of waves that go by in a second.
What is Hertz?
the SI unit of measurement for frequency (Hz). One Hz is 1 cycle per second.
What is Infrared Light?
a type of heat radiation; the infrared light in sunlight, for example, is what makes the sunlight feel warm upon one's skin. (Light greater than 700 nm.)
What is the Inverse Square Law?
a principle that states intensity of light diminishes by a factor of the square of the distance from its source.
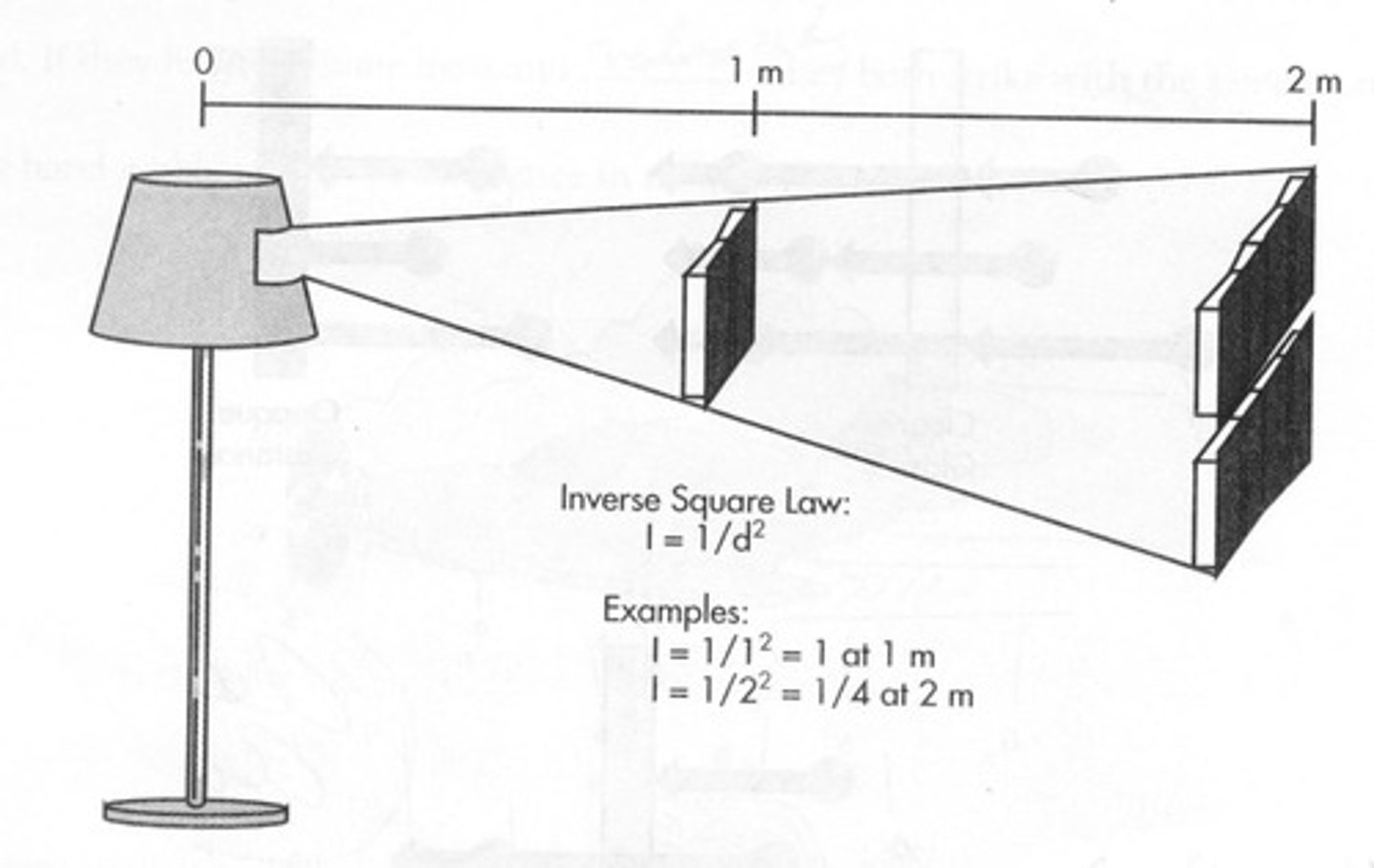
What is Light?
the electromagnetic energy in a certain range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. It includes visible light, infrared light, and ultraviolet light.
What does it mean to be Opaque?
the property of a substance that totally absorbs light rays.
What does it mean to be Radiolucent?
the property of a substance that allows x-rays to partially pass through it.
What is Radiopaque?
the property of a substance that does not allow x-rays to pass through.
What is Refraction?
the "bending" of light photons as they pass through one clear medium to another. The amount of refraction varies, depending on wavelength.
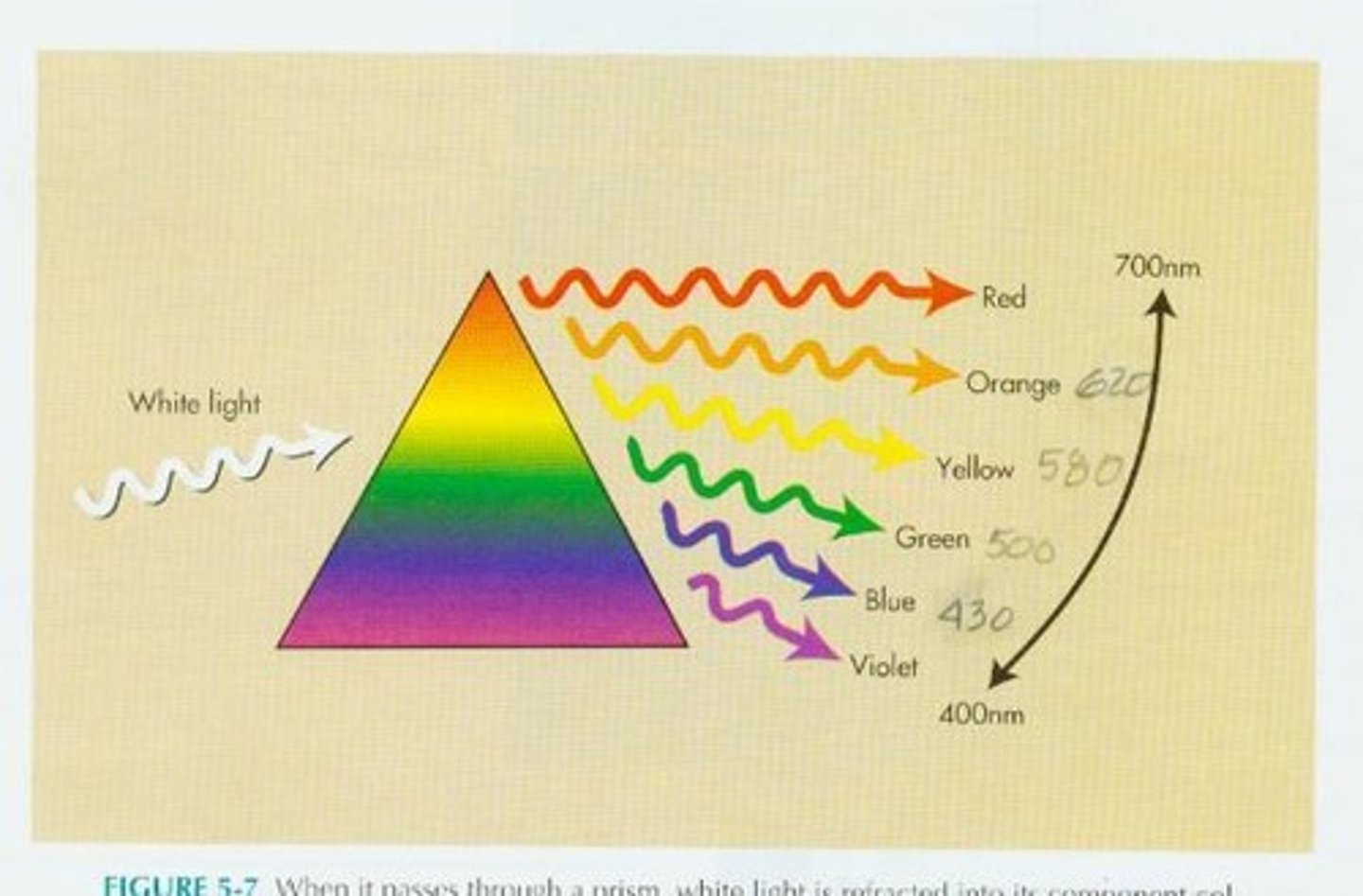
What is the Sine Wave?
the wave form of electromagnetic energy, the wave having regular characteristics such as a constant amplitude and wavelength.
What is the Speed of light?
approximately 3x10^8 m/sec, or 300 million meters per second. All electromagnetic radiation travels at the same velocity through space, the speed of sound.
What is Translucency?
the property of a substance that partially absorbs, or attenuates, light rays.
What does it mean for photons to be transmitted?
the state of light photons that have passed through a substance such as air, clear glass or the near vacuum of space.
What is Ultraviolet light?
is energy at a higher frequency in the visible light spectrum that can interact with molecules in one's skin and cause sunburn or, over a long term, skin cancer. (Light less than 400 nm.)
What is Visible light?
the range of light that humans can see; the total range of visible light is less than a millionth of 1% of the electromagnetic spectrum. The frequencies above and below visible light, ultraviolet and infrared, are still considered light because they share other characteristics with visible light.
What is the Visible Light Spectrum?
a continuum of visible light that includes the frequency ranges of the various colors. Each color of the spectrum, as a prism or rainbow, is a different frequency.
What is Wavelength?
the length of one wave, measured from the top of one wave to the top of the next. To calculate wavelength, divide the velocity (300 million meters per second) by the frequency.
What are X-rays?
the result of fast moving electrons striking the atoms of certain metal. X-rays are not emitted naturally from atoms but are produced when kinetic energy outside the atom excites the electrons. X-rays are similar to gamma rays except that they originate in the electron shells of atoms rather than in the nucleus.
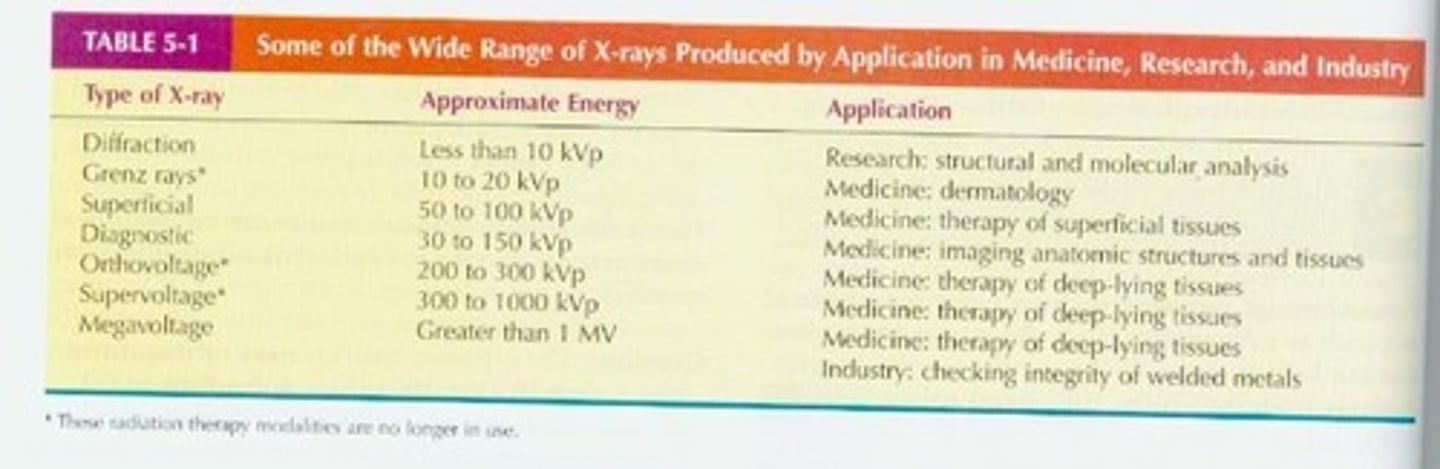
What is a Photon?
A quantum of electromagnetic energy and the smallest quantity of any type of electromagnetic radiation (EM radiation).
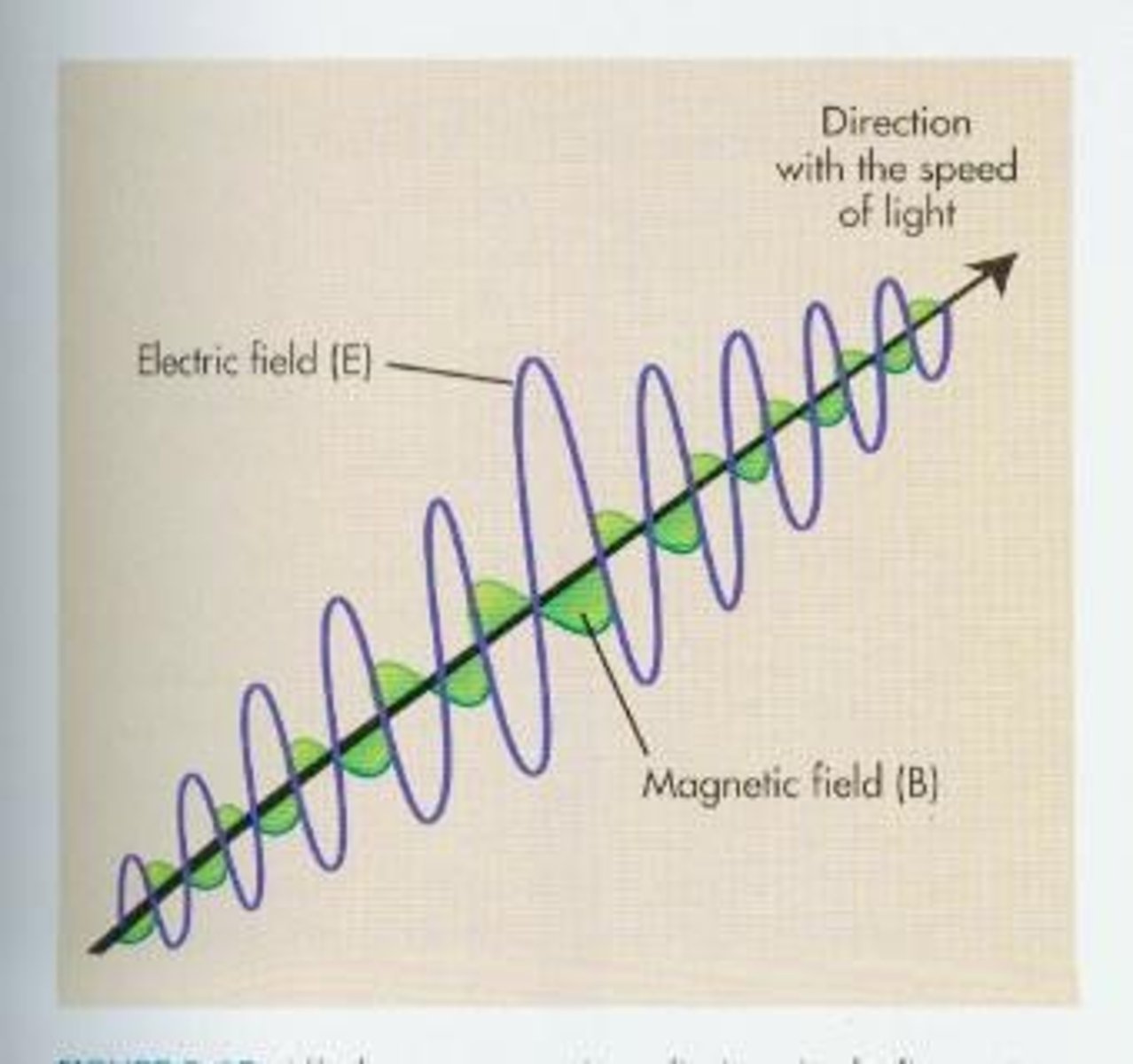
What is Electromagnetic radiation?
Covers the frequencies existing below broadcast radio up to and including gamma rays.
What is Velocity?
The speed a wave travels in a medium; EM waves travel at the speed of light and can travel in a vacuum.
What are the Wave equations?
Velocity = frequency x wavelength; or Wavelength = velocity / frequency; or Frequency = velocity / wavelength.
As density decreases, speed
increases for sound waves
What are the Regions of interest for rad techs?
The three regions are visible light, x-radiation, and radiofrequency.
What is Ultrasound?
A form of radiation that is not EM radiation and requires a medium of molecules to propagate.
What is Planck's quantum equation?
Energy is directly proportional to frequency and inversely proportional to wavelength.
What is White light?
Composed of light of various wavelengths, including Violet (400 nm), Blue (430 nm), Green (500 nm), Yellow (580 nm), Orange (620 nm), and Red (700 nm).
What is Radiofrequency (RF)?
Relatively speaking, RF has very low energy and very long wavelength compared to x-rays.
What is Standard AM radio band?
About 100 m wavelength (1 mHz); FM is much shorter in the range of 3 meters (100 mHz).
What is Microwave radiation?
Overlaps with RF and both are used with communications; cell phones operate in the lower microwave range.
What is MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)?
Based upon the RF given off by the hydrogen atom when precessed; F = 105 to 1010 Hz.
What is Ionizing Radiation?
Ionizing EM radiation, such as X-rays and Gamma Rays, is usually expressed as energy contained in the photons.
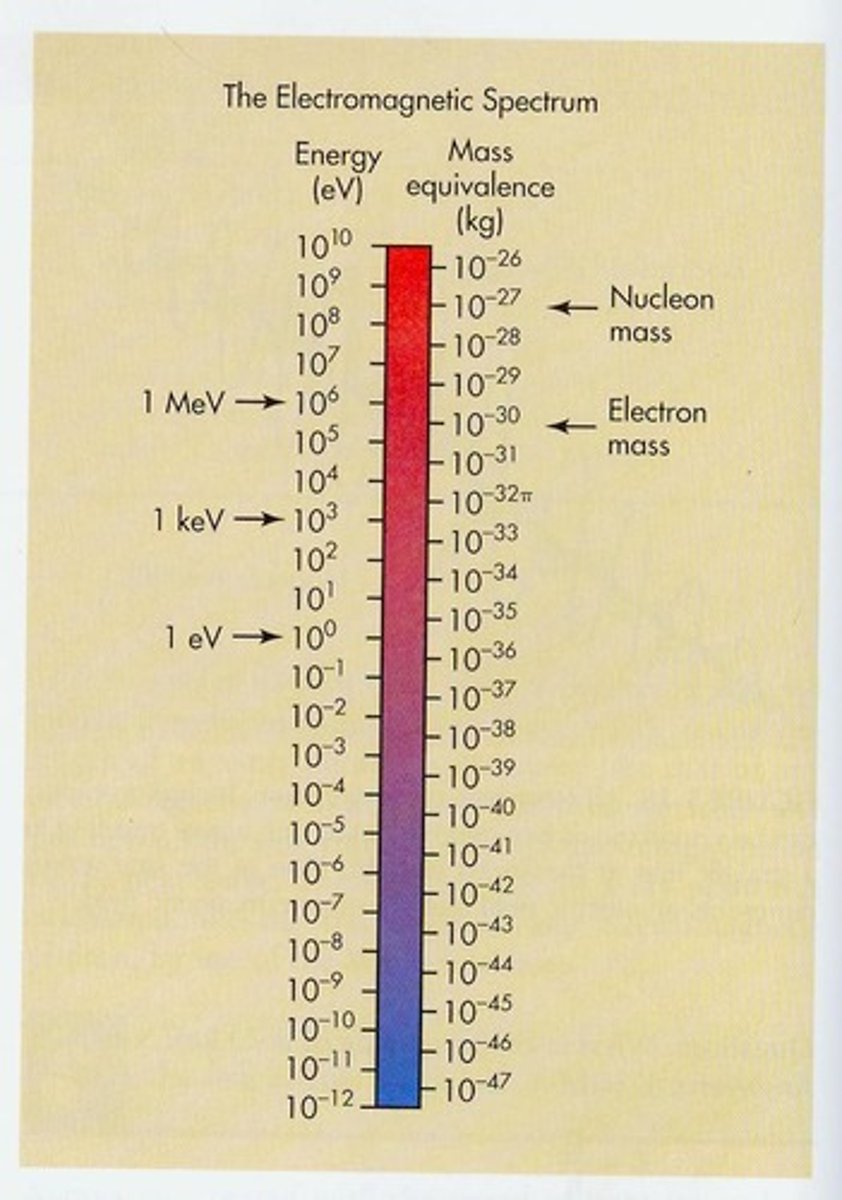
What is Wave-particle duality?
Behaving similar to waves and particles is called the wave-particle duality of radiation.
What are Photons?
Interact with matter most easily when the matter is approximately the same size as the photon wavelength.
What is absorbed light?
Energy is deposited in the substance & reappears as heat.
What is Transparency?
Incident light waves cause vibration in the substance and are re-irradiated almost without change.
What is the Inverse Square Law Formula?
I1/I2 = (d2/d1)2.
What is the Mass-energy equivalence equation?
E = mc2; where E is energy in joules, m is mass in kilograms, and c is velocity of light in meters/s (3 x 10^8).
What is the Law of conservation of matter?
Matter can be neither created nor destroyed.
What is the Law of conservation of energy?
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed.
What is the Theory of Relativity?
All three of the above laws are part of the Theory of Relativity.
What can cause electromagnetic energy to deflect from its straight-line course?
Both magnetic and electric fields.
What happens to sunlight when it passes through a prism?
It is refracted, creating colors that correspond to different frequencies in the visible light spectrum.
What does the term 'spectrum' refer to in the context of energy types?
It refers to a continuous array of energy types, where one type merges into the next without discrete boundaries.
What is required for an electron to jump to a higher energy state?
Energy is required for the electron to make the jump.
What occurs when an electron returns to its normal state?
It gives off energy, resulting in a lower energy level in the lower shell.
What is produced when an electron jumps to a higher state?
A photon is produced with each jump, and millions of photons together create visible light.
Why is radiation to reproductive organs particularly risky?
It can damage not only the individual but also genetic material that may be passed on to offspring as mutations or defects.
What material cannot be penetrated by X-rays?
Lead, which is completely radiopaque.
What does frequency refer to in wave terminology?
The number of waves that pass a given point in one second.
How many waves pass by in one second at a frequency of 300 MHz?
300 million waves.
What is the wavelength if the velocity is 300 million m/s and the frequency is 3 x 10^16 Hz?
100 meters, calculated using the equation: wavelength = velocity / frequency.
What is the frequency if the wavelength is 4 x 10^-7 m and the velocity is 3 x 10^8 m/s?
7.5 x 10^14 Hz, calculated using the formula: frequency = velocity / wavelength.