Photosynthesis ☀️💧→💨🌿
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What are the two steps of photosynthesis?
1.) Light-Dependent reaction
2.) Light-Independent reaction
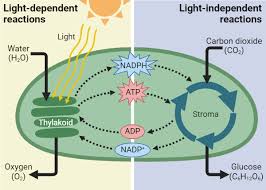
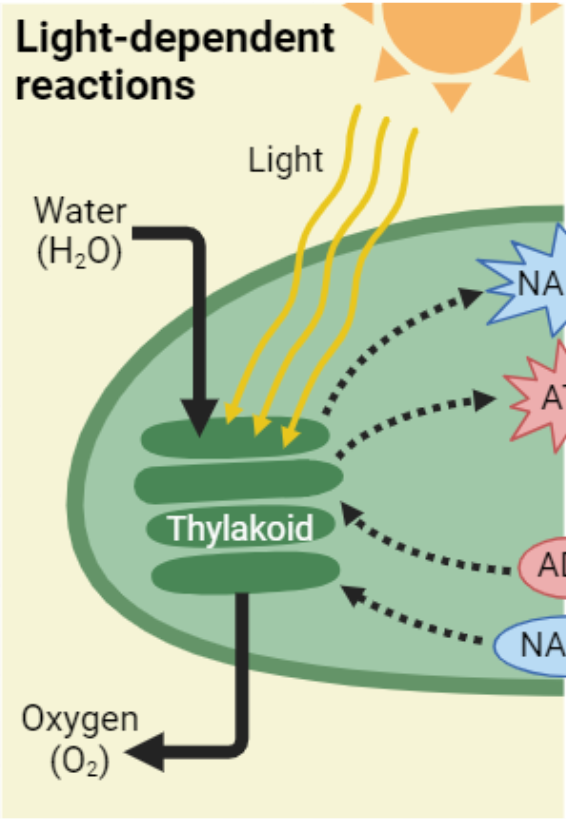
Light-Dependent reaction?
In thylakoid
light energy is converted into biochemical energy (ATP + NADPH)
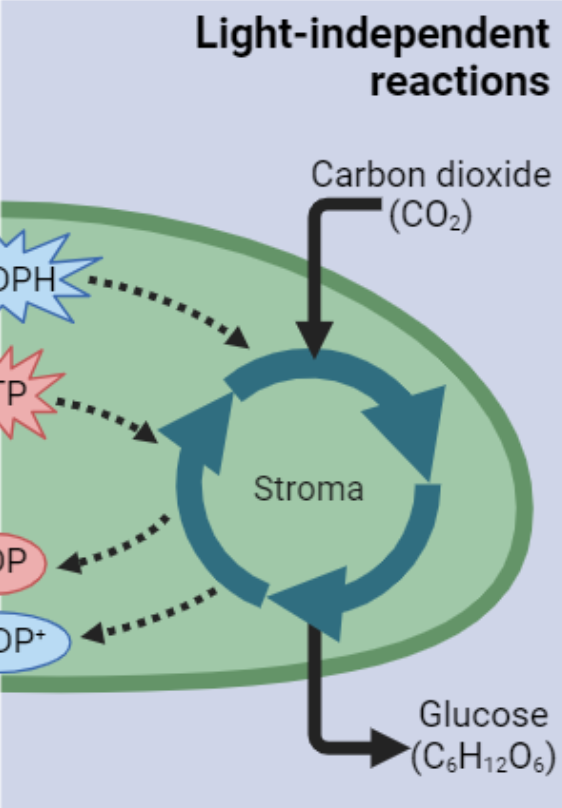
Light-Independent reactions
In Stroma
biochemical energy is used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose
What is the source of energy in the light reaction?
Light

What is the source of energy in the Calvin cycle?
Biochemical Energy
What is ETC?
Electron Transport Chain
protein complexes and molecules embedded in a membrane
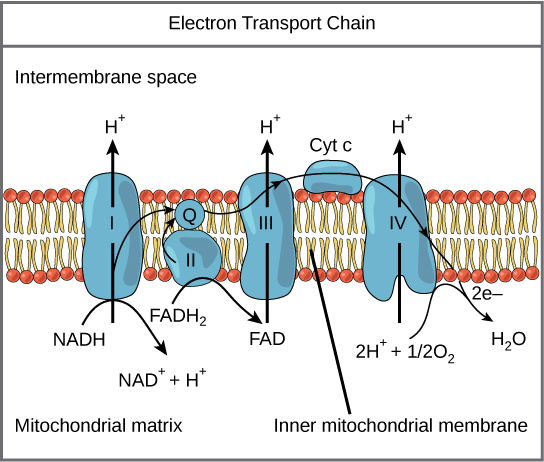
ETC Functions
transfer electrons through redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions
What is Photolysis?
break water molecules
using energy provided by light
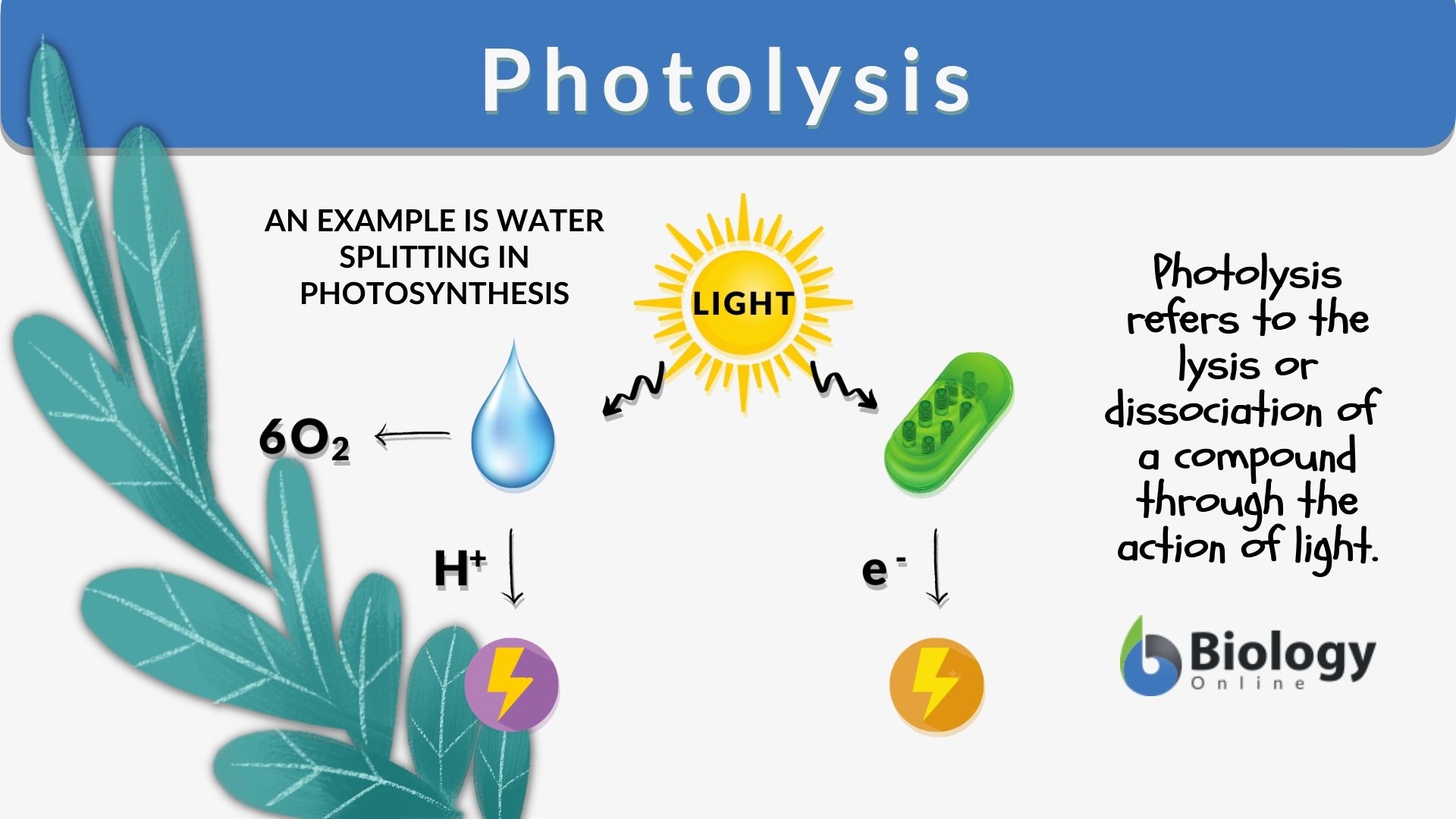
When and Where does Photolysis happen?
When: light hits molecules, causing them to split
Where: thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
How CO2 goes into Calvin cycle and used?
Rubisco fixation→ two 3-GPA→ sugar
Which step makes sugar?
Reduction Phase
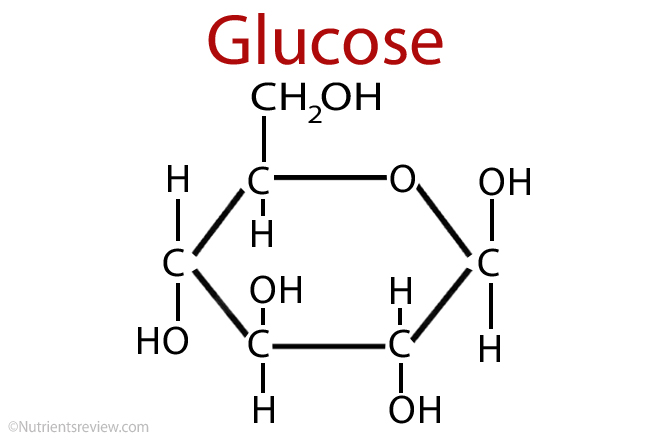
What’s main sugar in plants?
Glucose
Where energy is coming in and where it is flowing.
Light energy → Biochemical
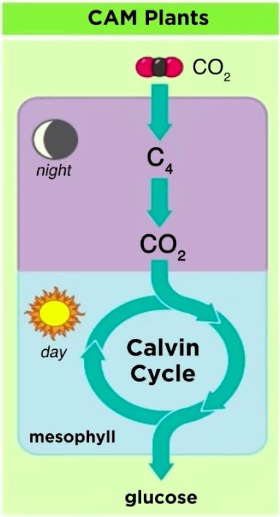
Difference in C3, C4 and CAM photosynthesis?
Enzyme
Spatial Separation
Temporal Separation
Why Rubisco make mistake in C4 photosynthesis?
Can’t recognize CO2 → O
Carbon dioxide consumes ATP
Is Rubisco in Mesophyll cells of C4 plants?
No
How is CAM photosynthesis a beneficial adaptation?
Saves water
Thrive Arid Environments
Photosynthesis at Night
Advantage of C3 photosynthesis?
costs less energy
inefficient due to photorespiration.
Advantage of C4 photosynthesis?
Plants handle Dry and Hot climates.
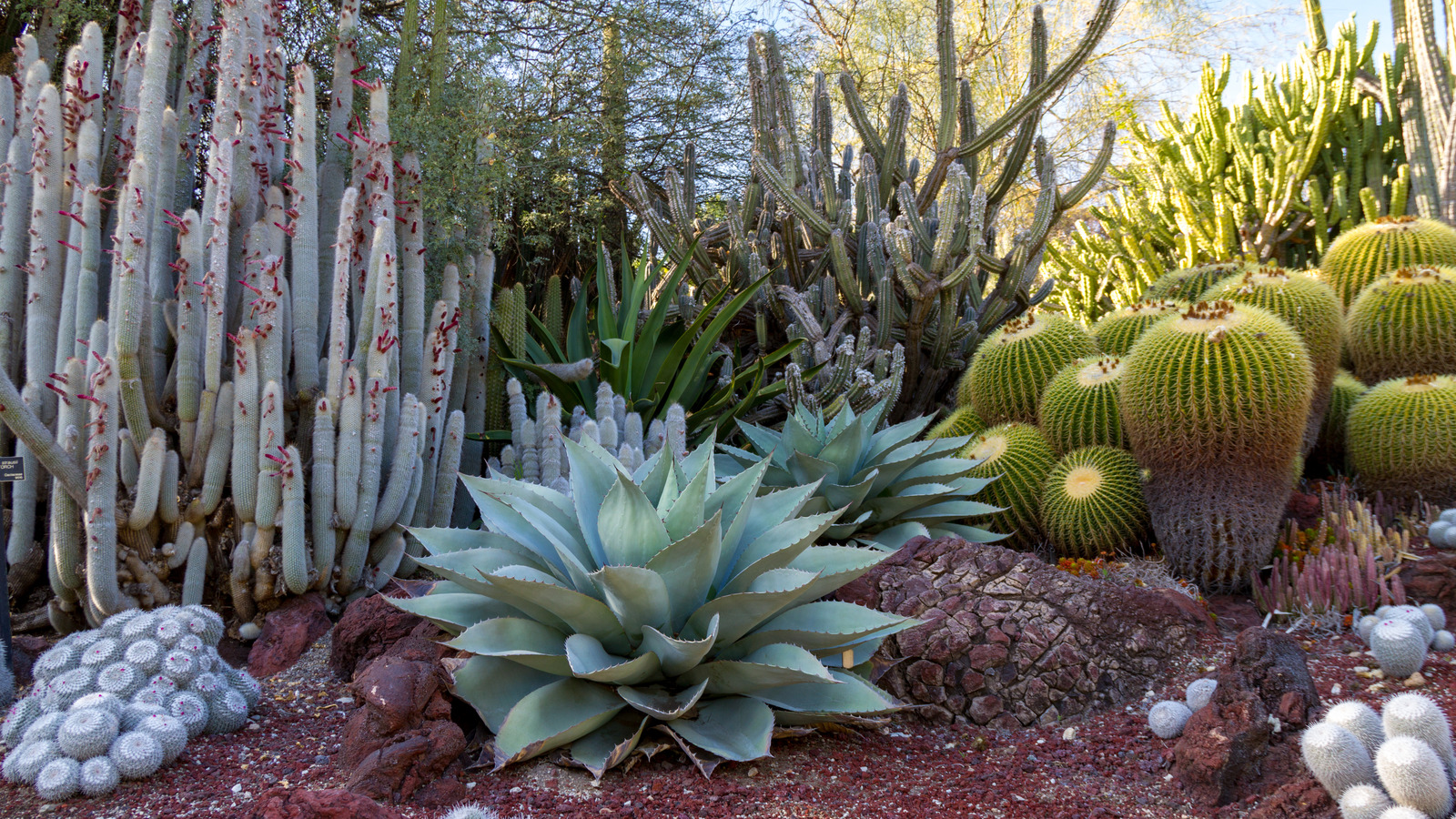

Advantage of CAM photosynthesis?
Plants survive in Arid Environments.

Differences between light quality, intensity, and duration?
Quality: color/wavelength
Intensity: brightness or amount of photons
Duration: length of time plants receive light
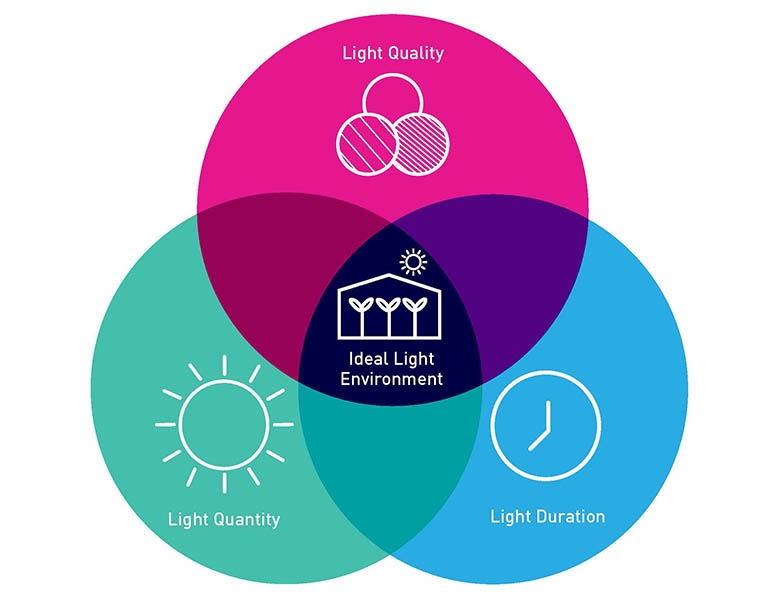
What is PAR?
Photosynthetically Active Radiation
range of light (approximately 400–700 nm)
plants used for photosynthesis.
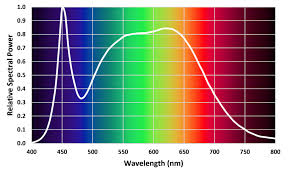
What is Photosynthetic Efficiency?
Amount of light energy plants and algae → chemical energy through photosynthesis
Environmental factors affect light quality?
Weather Conditions (Cloudy or Clear),
Seasonally and latitude (North – South)

Light Saturation Point?
light intensity plant's photosynthetic rate reaches its maximum
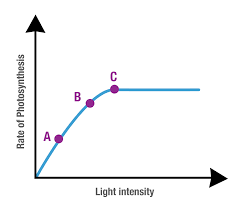
How is Light Saturation Point different in Shade Plants versus Sun Plants?
Shade plants: lower saturation point
Sun plant: higher saturation point

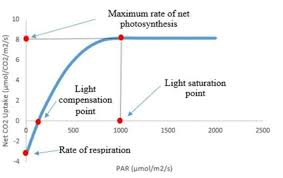
What is Light Compensation Point?
Light Intensity Plant's rate Photosynthesis = Rate of Respiration
Light Duration and Circadian Rhythms related to each other?
light duration synchronizes our circadian rhythm
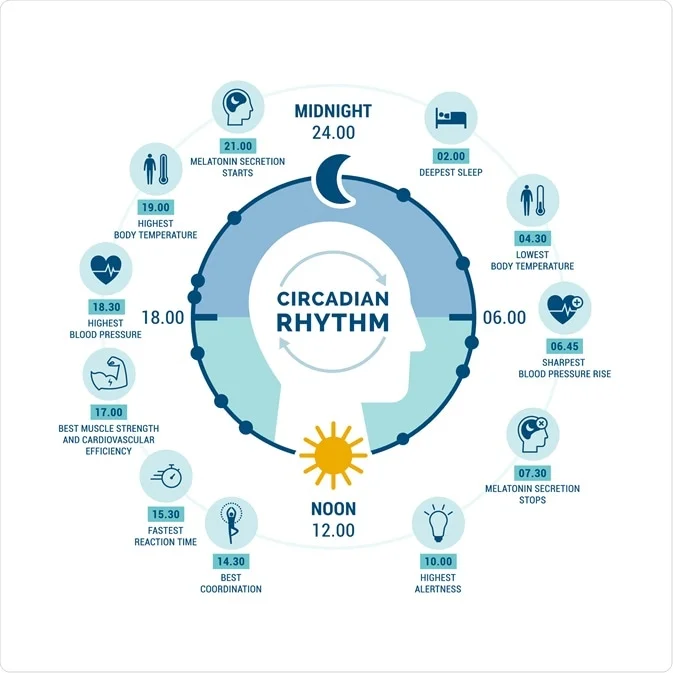
How affect Plant Behavior?
24-hour cycles
physical and behavioral changes

3 “light” in Photosynthesis Reaction Equation
1. Light Quality
2. Light Intensity
3. Light Duration

Light Quality
wavelengths of light in the visible spectrum

Light Intensity
quantity of light striking a leaf per unit time

Light Duration
amount of time plant receives light

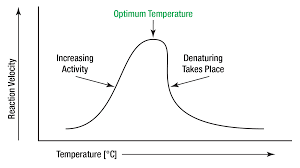
How temperature affect photosynthesis?
Cold = slower reactions
Warm = faster reactions
Too hot = denatured proteins.
What is Optimum Temperature?
Outcome of Evolution and Natural Selection relative to environment
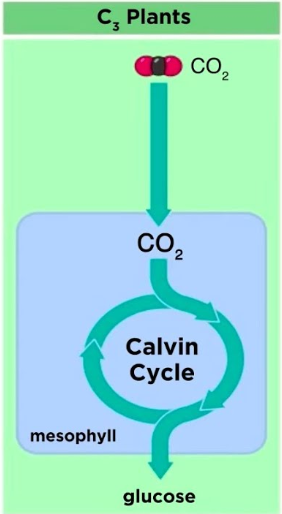
How we put C3 photosynthesis into practice?
(Wheat, Rice)
standard, Best in cool/moist areas
suffers photorespiration
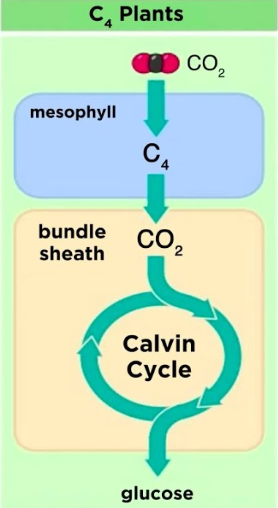
How we put C4 photosynthesis into practice?
(Corn, Sugarcane)
spatially separates CO2 fixation
(mesophyll/bundle sheath cells) for hot/sunny climates
How we put CAM photosynthesis into practice?
(Cacti, Pineapples)
temporally separates (night/day)
What happen to photosynthesis water is limiting & directly affected?
Leaves wilt, reducing light absorption.
Stomata close, limiting CO₂ for the Calvin cycle.
Photolysis stops, halting ATP and NADPH production.

If CO2 in atmosphere increased, no changes to light or water, what happen to photosynthesis that occurs?
boosts photosynthesis and plant growth
3 environmental features affect plants in winter and their photosynthesis?
Decreased Light Duration/ Intensity
Freezing Temperatures
Limited Water Availability
