Image Production - Acquisition & Technical Evaluation
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
DEL Pitch
the distance from the center of one DEL to the center of the next
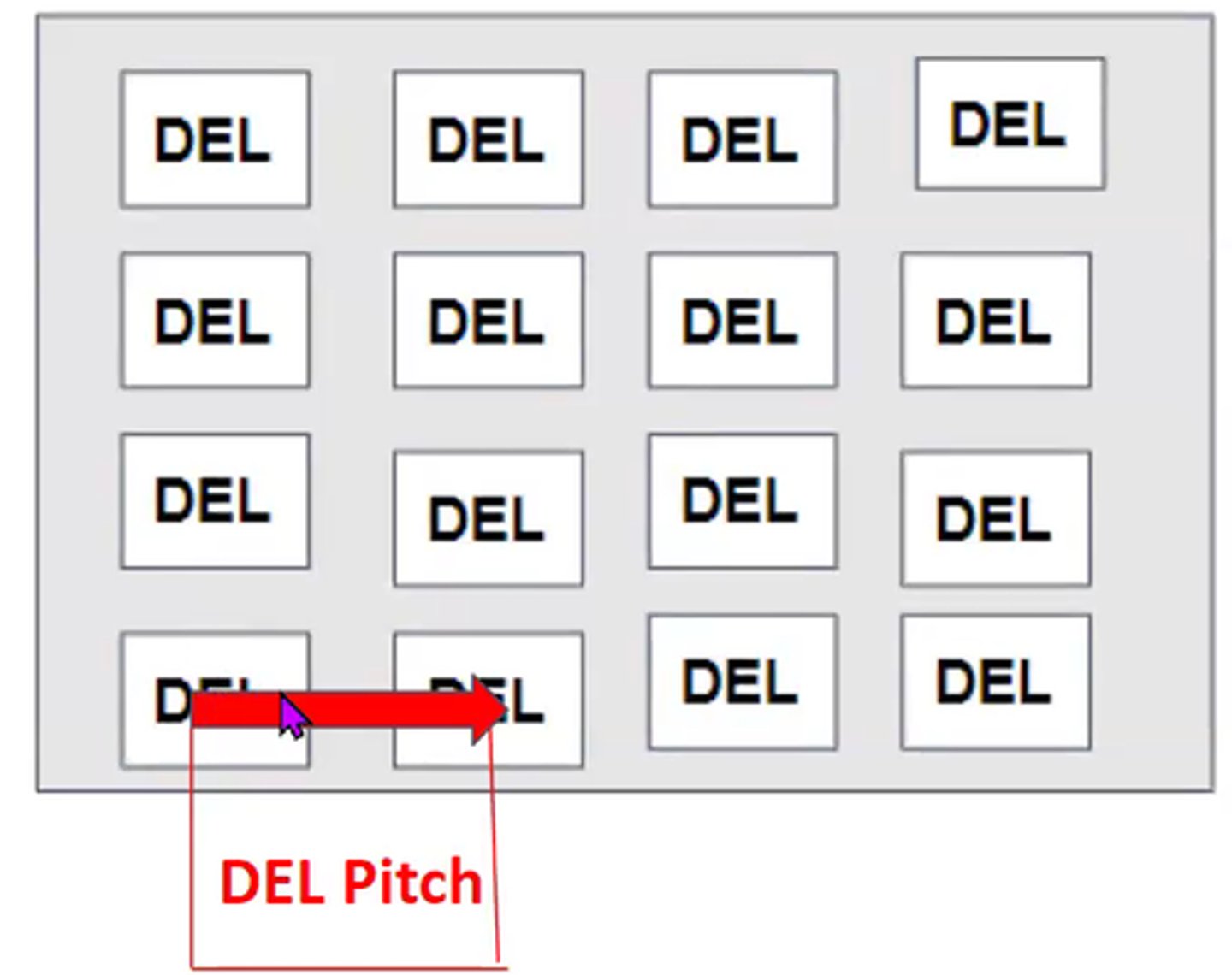
DEL Pitch vs Pixel Pitch
-DEL Pitch -> in detector
-Pixel Pitch -> in monitor
Quantization
takes electrical signal and turns them into digital bits of info. Occurs during ADC. Displays a specific brightness on screen

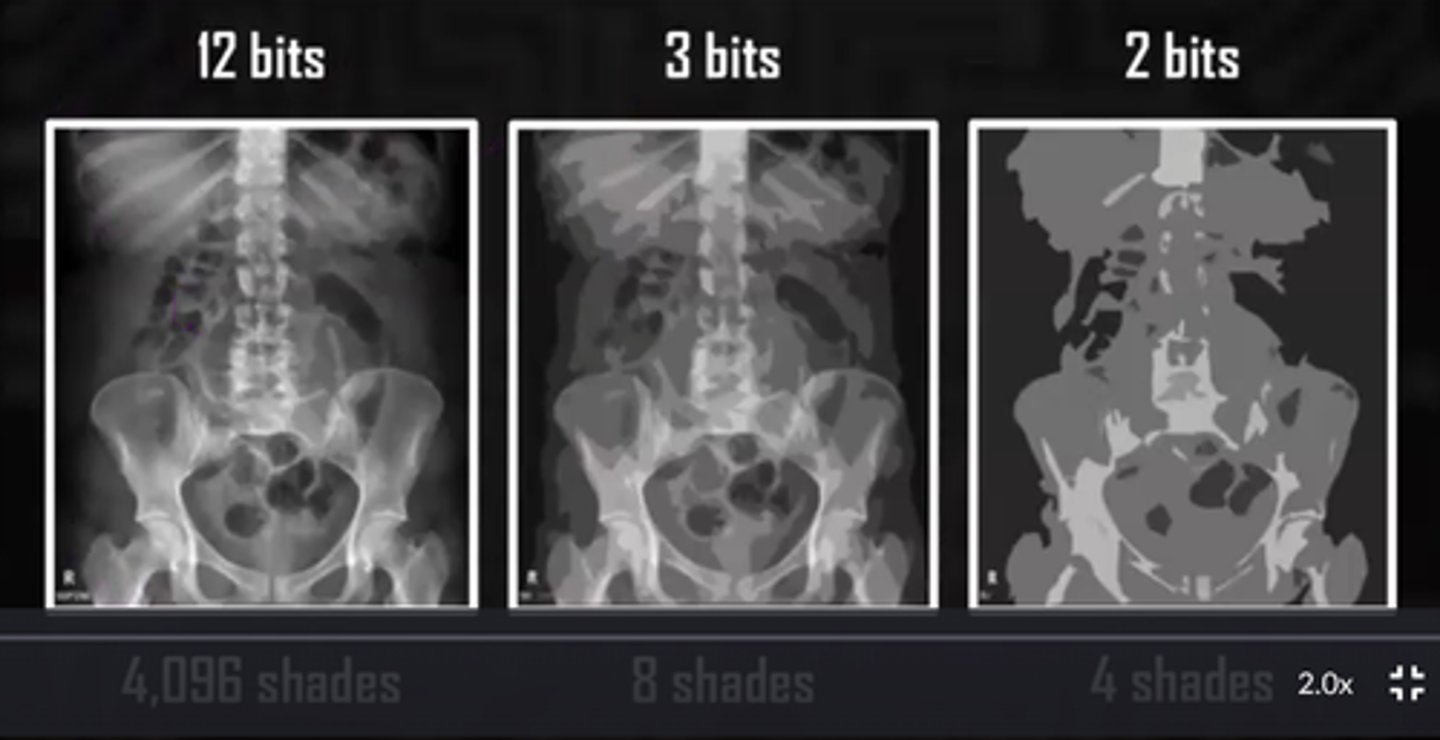
Bit depth
total number of possible brightness levels (shades of gray) that can be assigned to any individual pixel in the image
Detective Quantum Efficiency (DQE)
how efficient a system converts a input signal into a useful output image (measure QUALITY of digital image)

What has the highest DQE?
Direct DR (only 2 steps)
8 bits = ____ possible values for the density of each pixel
256
10 bits = ____ possible values for the density of each pixel
1024
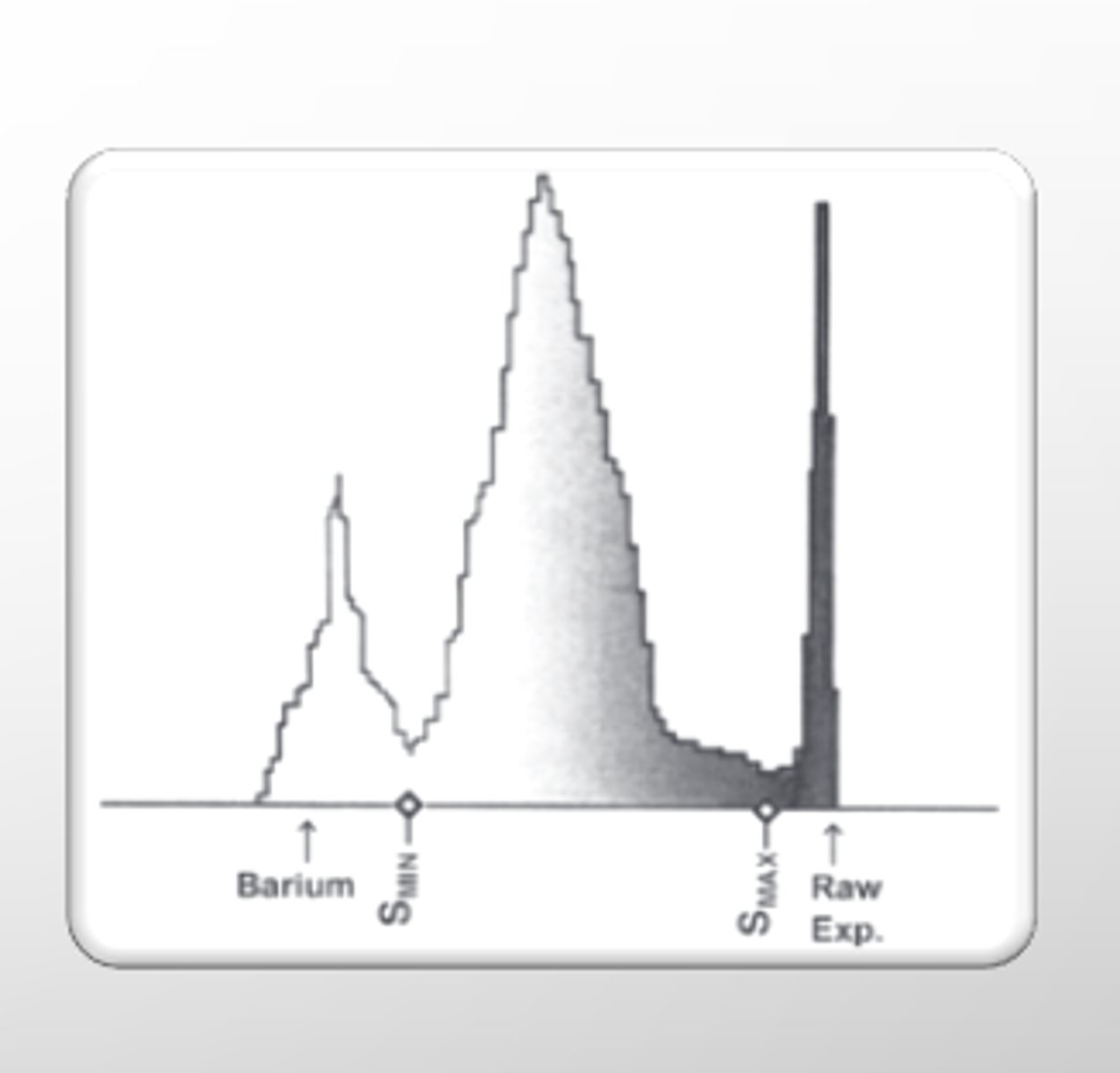
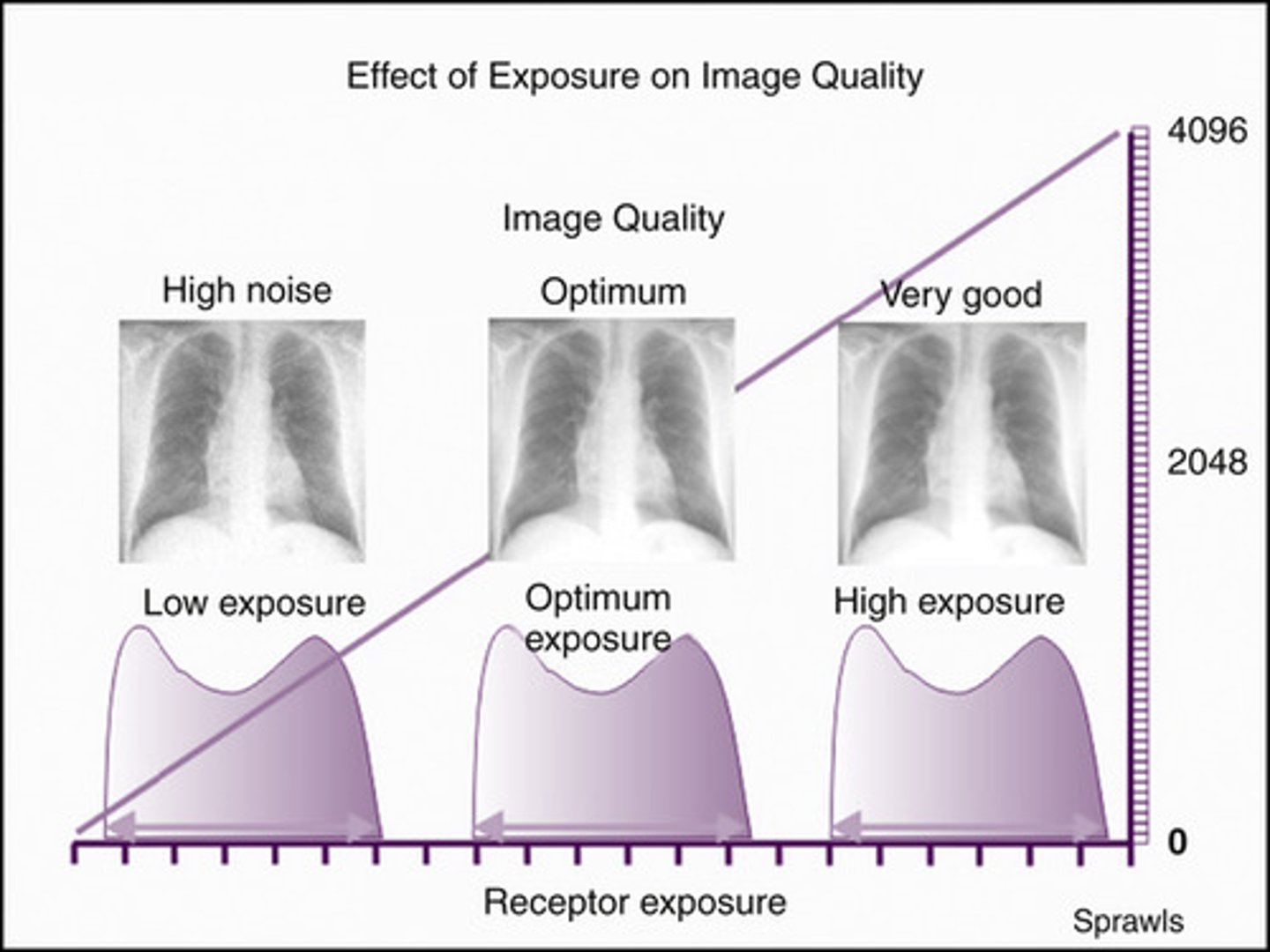
Histogram
-graphical display of the pixel intensity distribution for a digital image
-frequency of recorded exposure values
histogram analysis
A process in which a computer analyzes the histogram using an algorithms and compares it with a pre-established histogram specific to the anatomic part being imaged
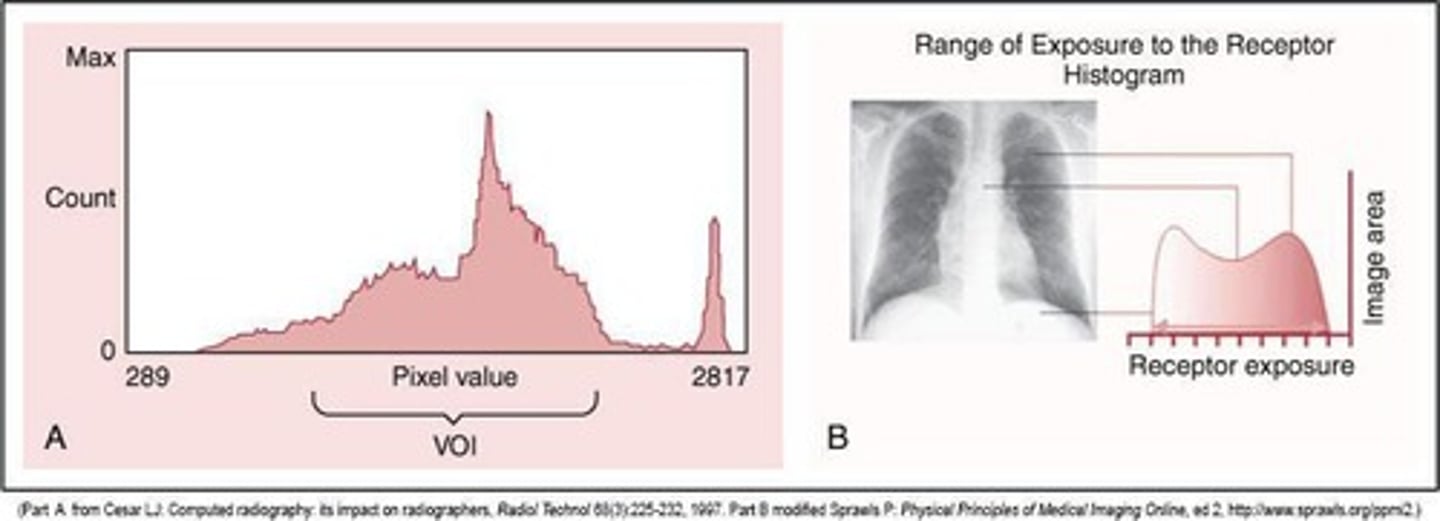
____ determine the range of the histogram data set that should be included in the display image
VOI - value of interest
Look up table (LUT)
a series of mathematical equations that are used for image processing in radiography
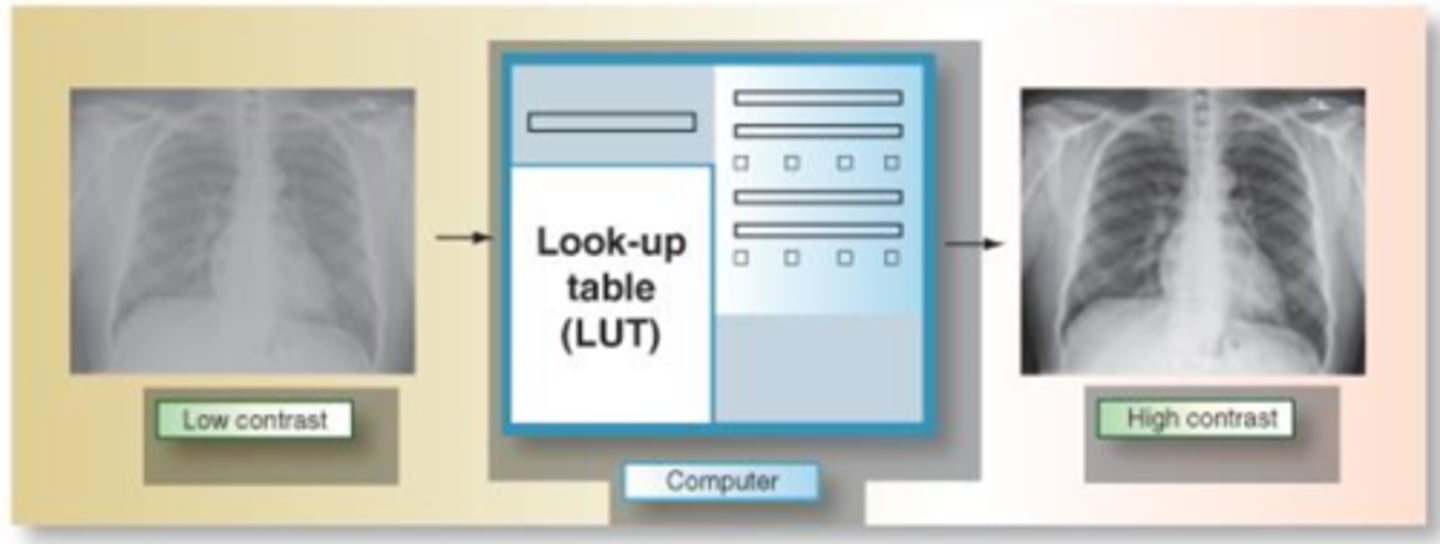
LUT is the controller of what?
digital contrast
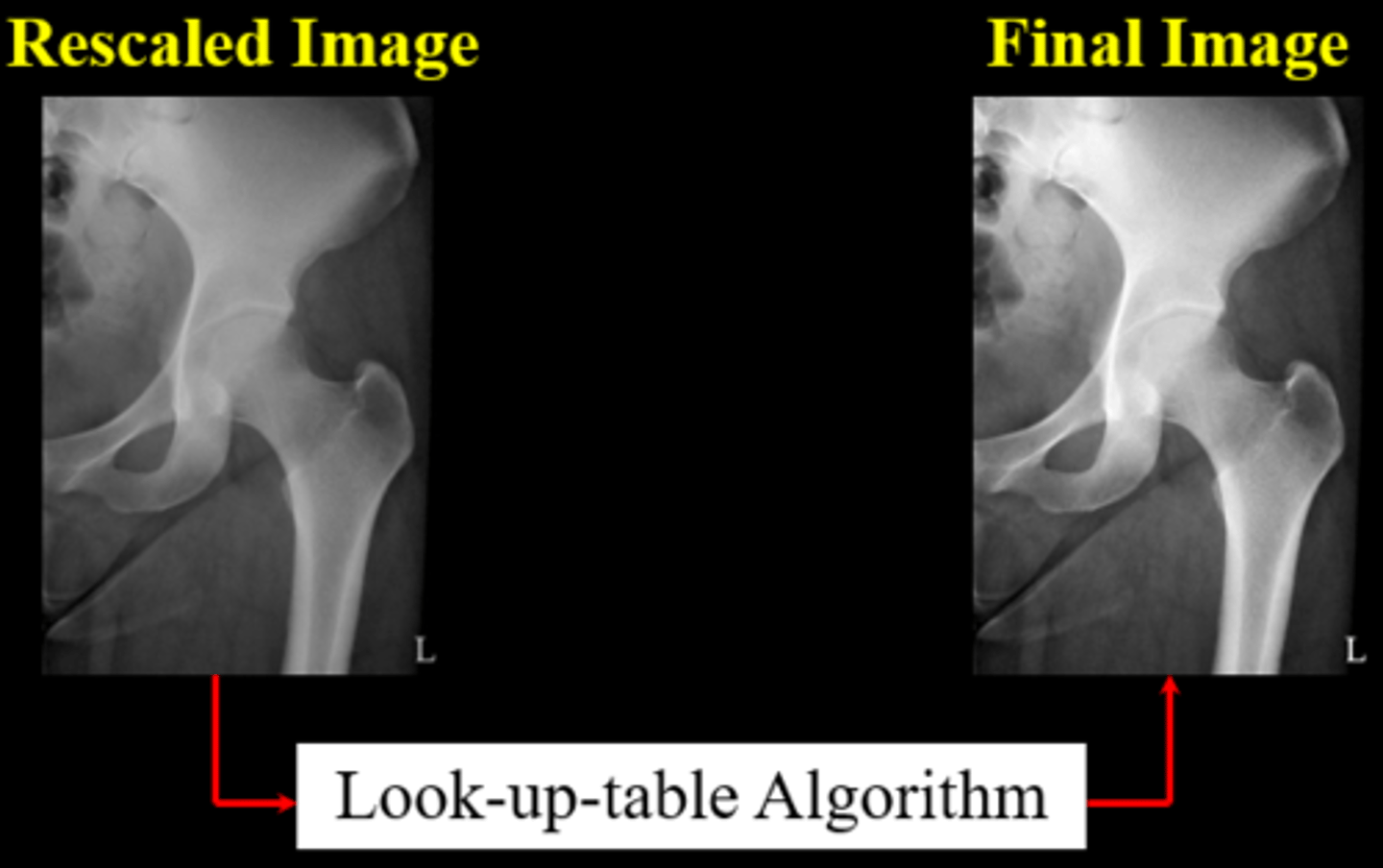
Rescaling
A digital processing technique that is used to modify an overexposed or underexposed image
Dead pixel
Pixel w/ a malfunction or sensor error

Dead pixel correction
using a software technique, dead pixels are identified in the matrix and then removed from all subsequent images
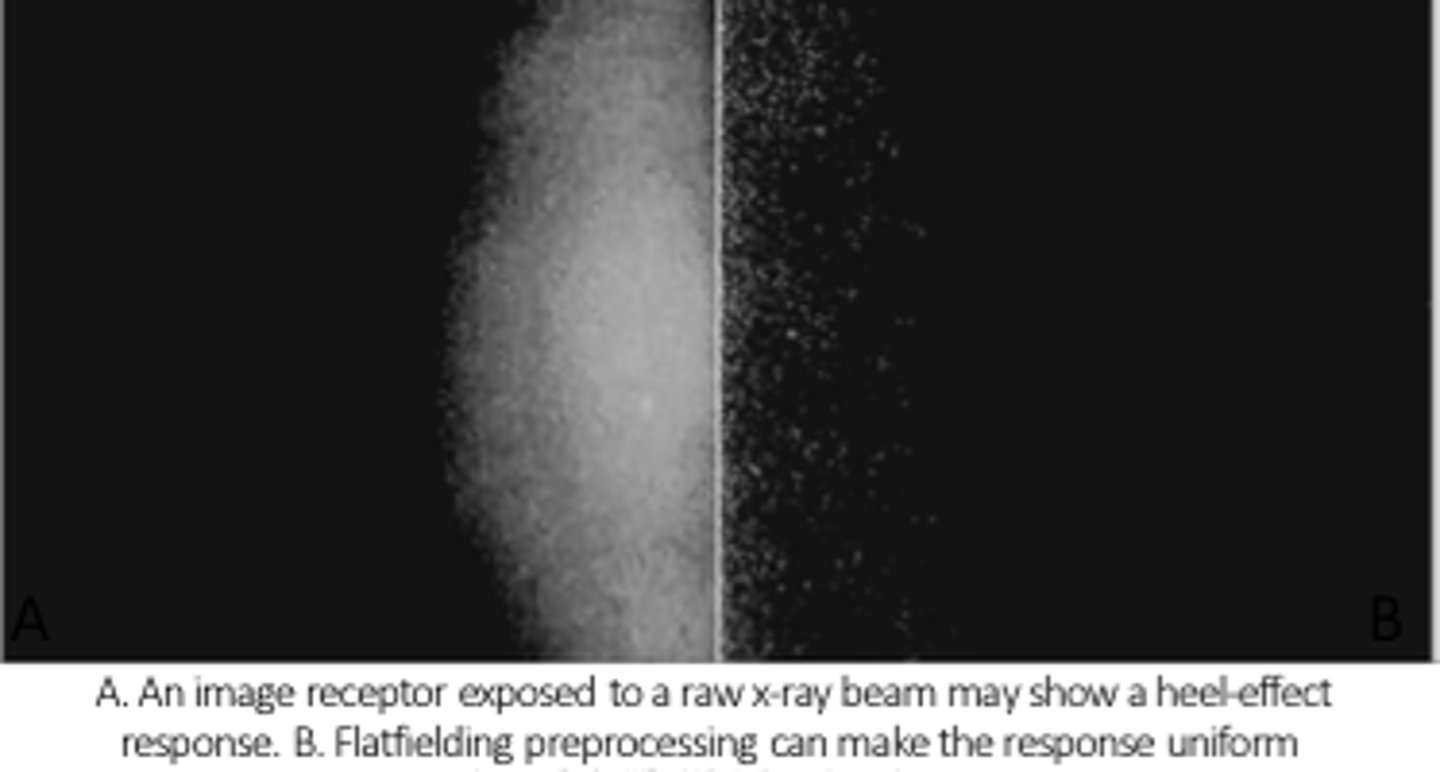
flat fielding
dead pixels are removed from the matrix by making a mask of the dead pixels
edge enhancement
increases the contrast along the edges of the structure
edge enhancement helps improve _________ _______. Excessive use can cause "_______ ________".
-visibiity of details
-halo artifact
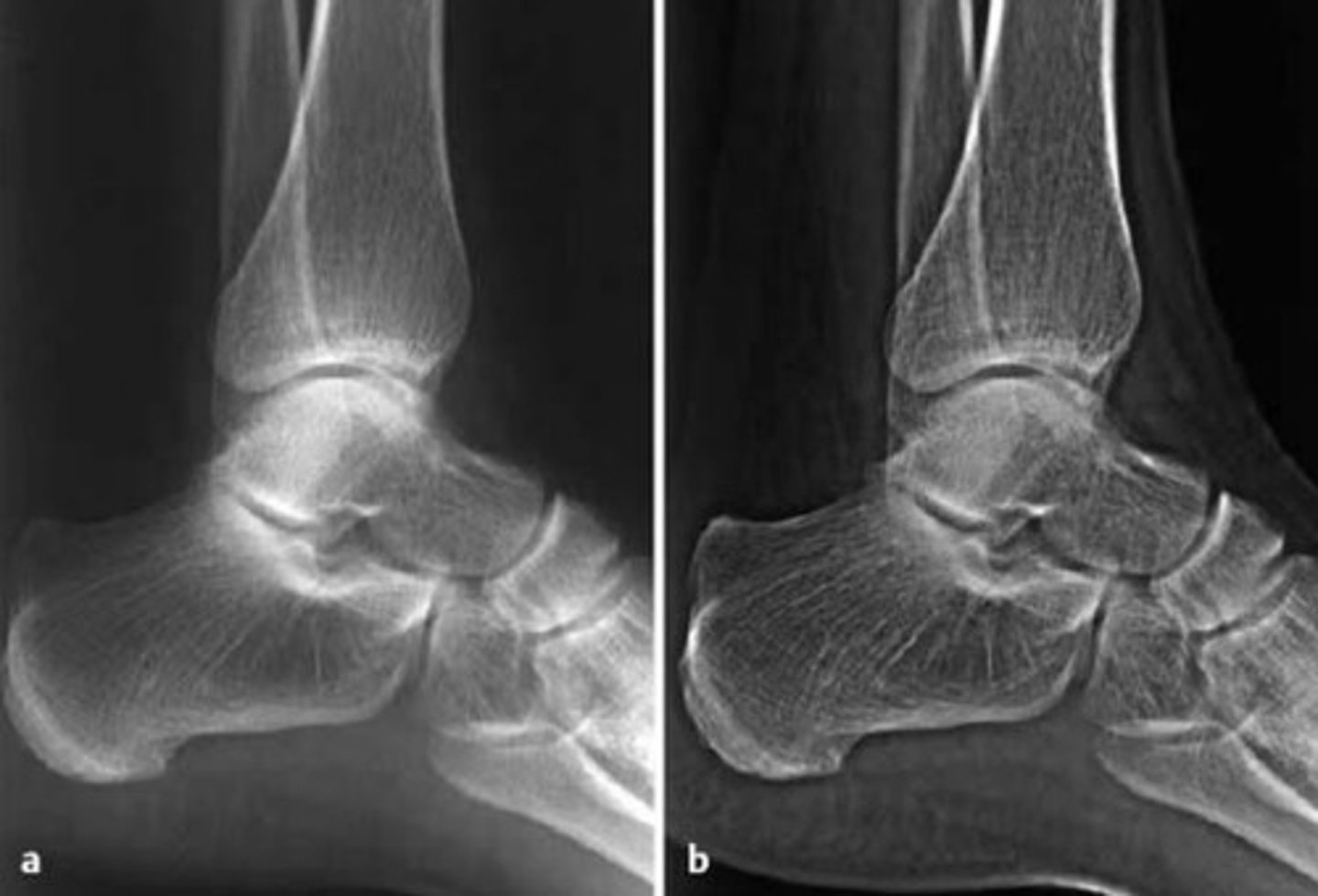
equalization
process by which soft tissue and bone are enhanced so all the information within a region of interest can be seen
smoothing: what does it do? what are other names for smoothing?
-used to mask the quantum noise in an image.
-noise supression, low pass filtering
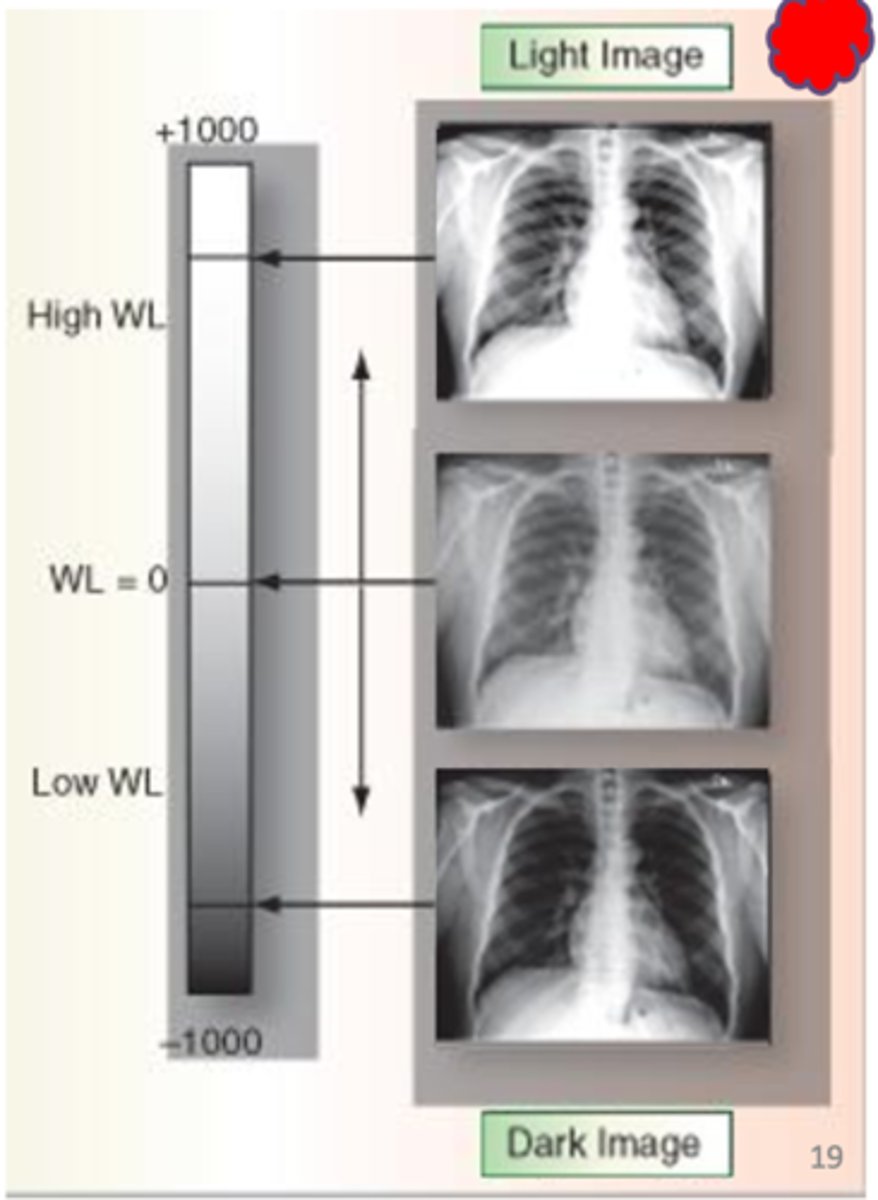
windowing
Ability to alter the brightness and contrast of a digital image, following processing
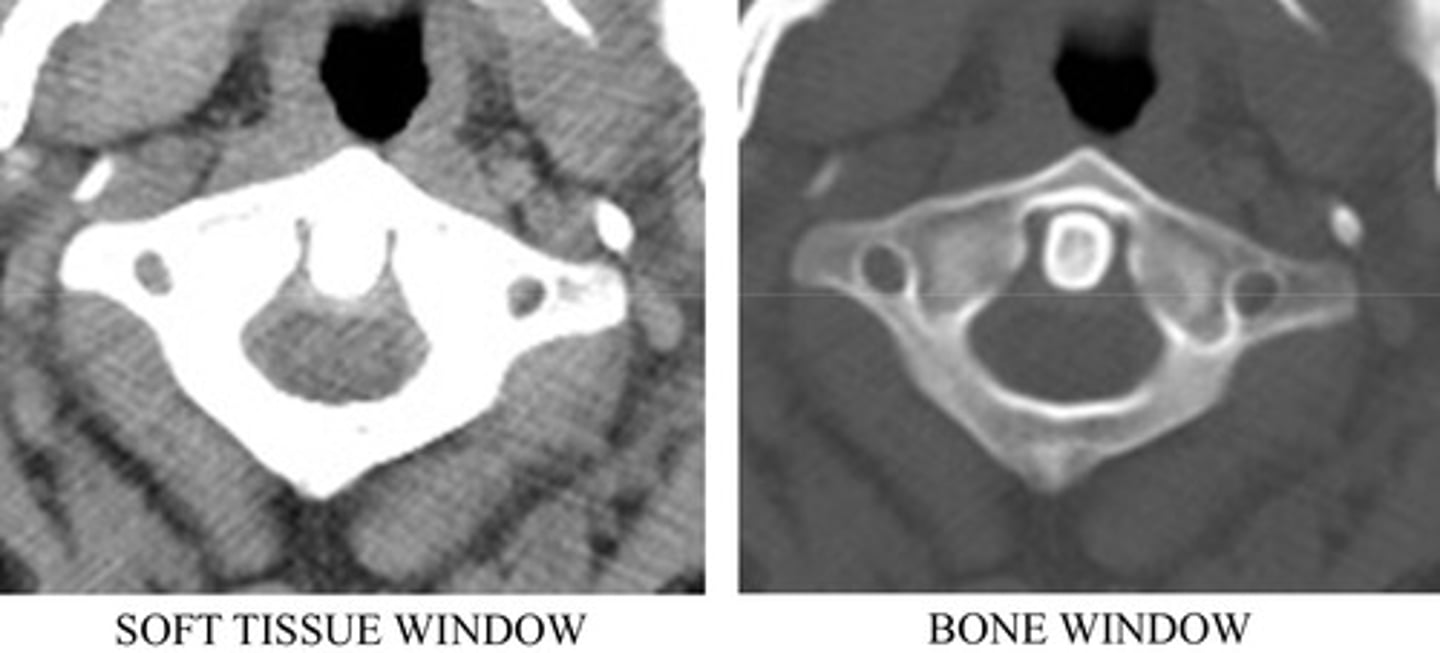
window level
Adjusts brightness of the displayed image.

window width
adjusts contrast of the digital image
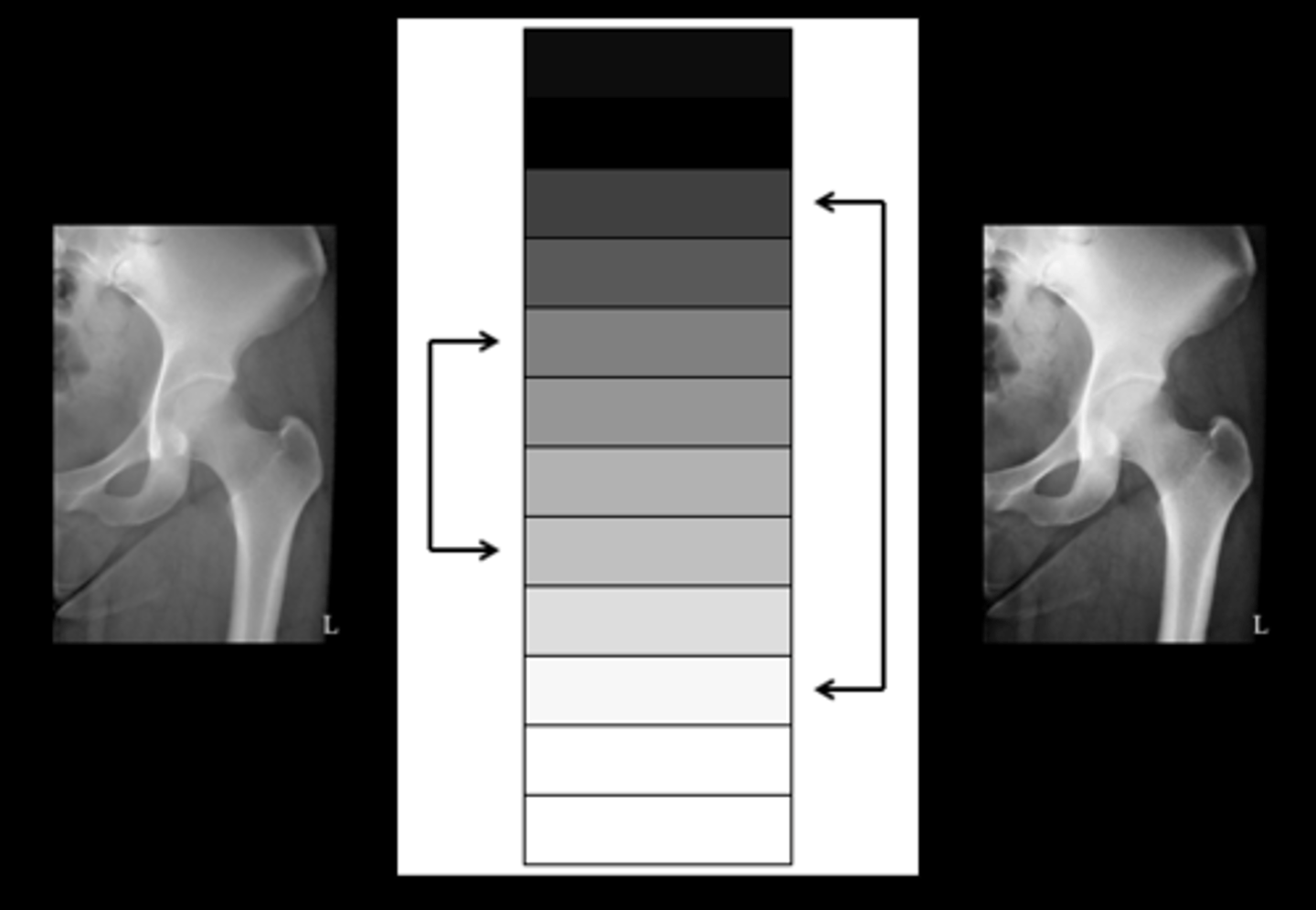
Wider the width, ______ the contrast
lower (long/more gray shades)(wide grey elephant)
narrow width, _____ the contrast
higher (short scale - more B&W) (short b&W penguin getting high)

shuttering
postexposure image manipulation that adds a black background to the original collimation edges
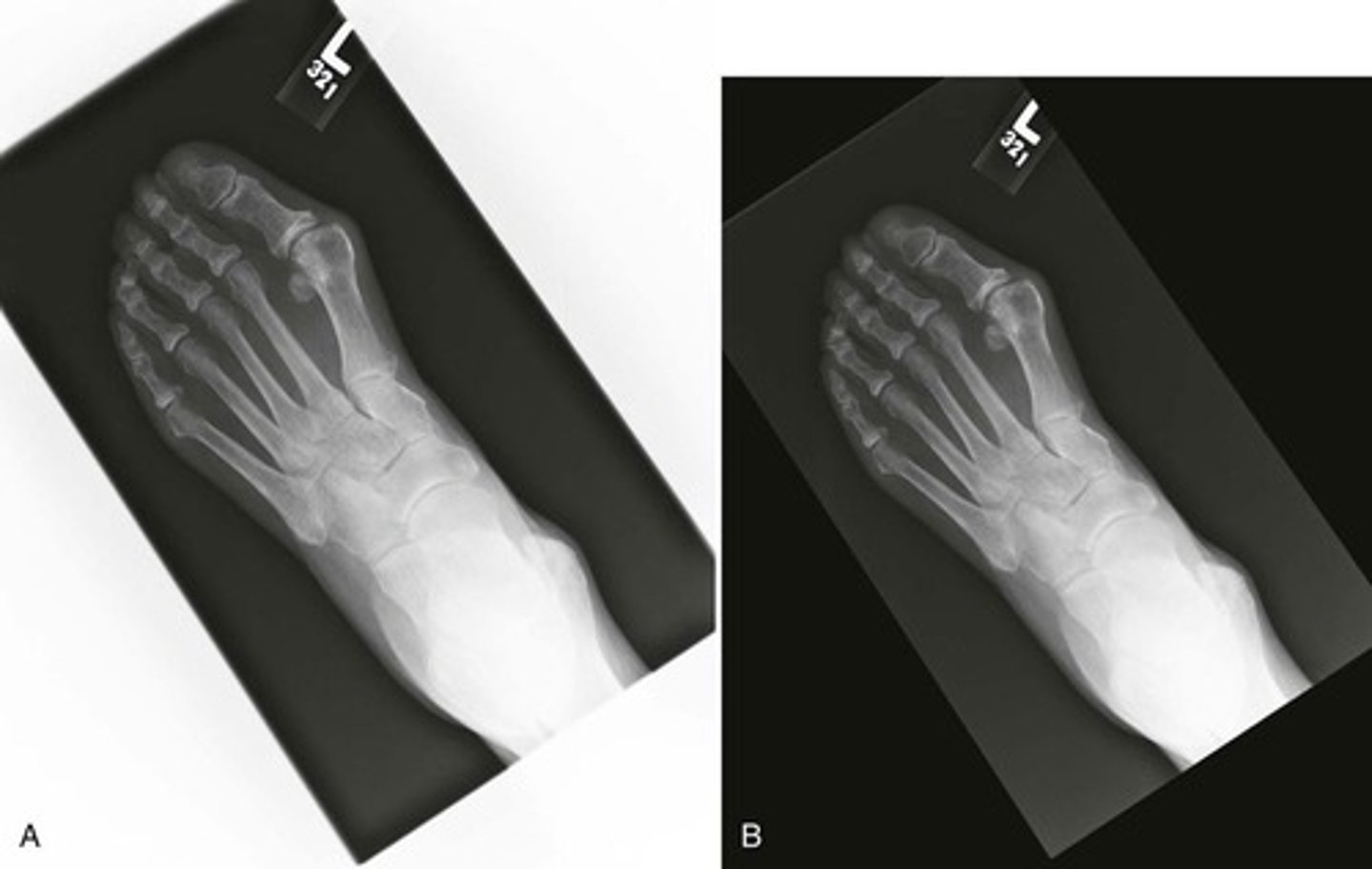
image inversion
Make white-black and black-white (used to view lines)
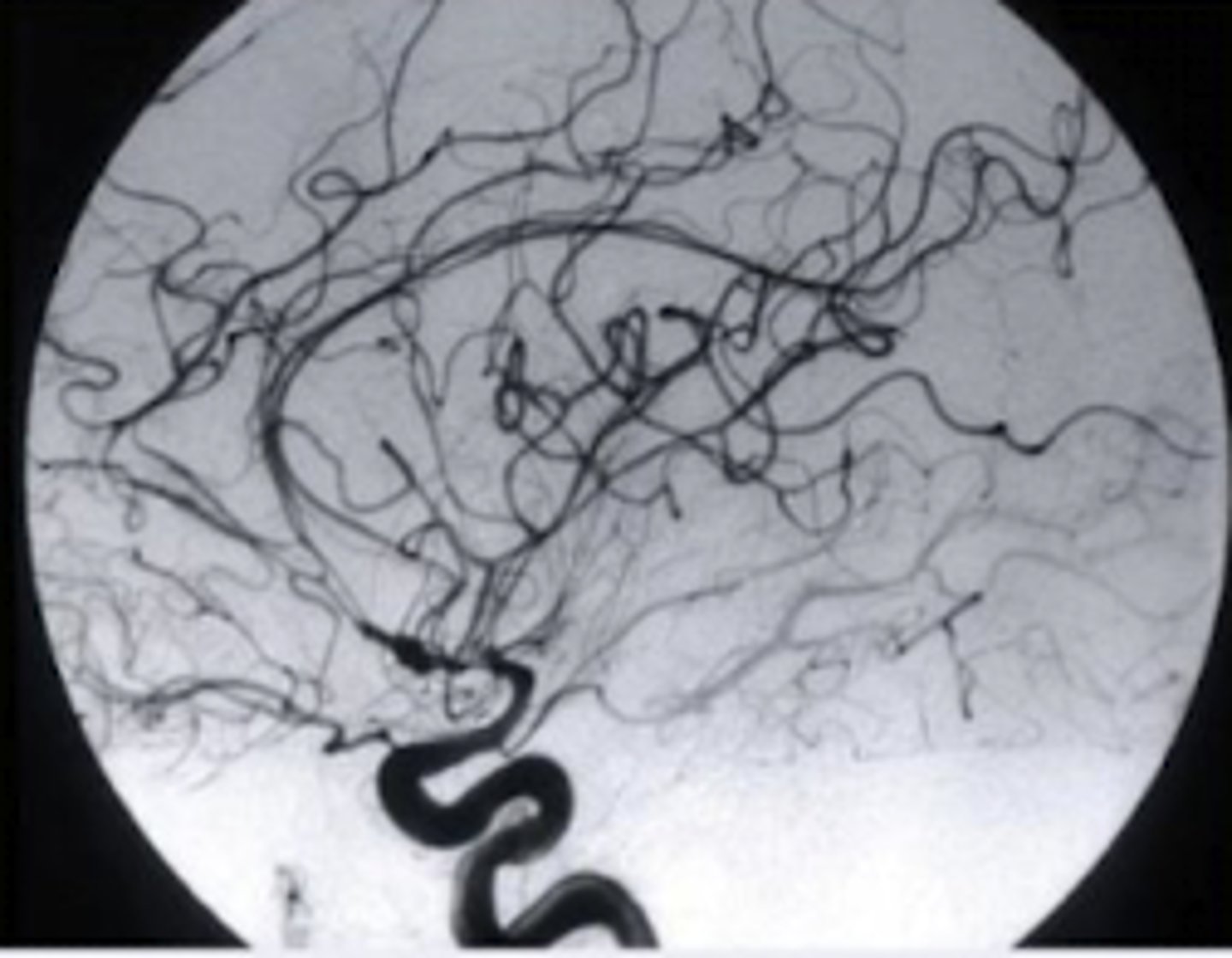
image subtraction
technique used in IR to clearly visualize blood vessels in a bony or dense soft tissue environment - removes bones
PACS (Picture Archival and Communication System in Medicine)
allows user to acquire, transmit, store, retrieve and modify digital images taken in all modalities of the radiology department
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine)
-enables integration of scanners, workstations, printers
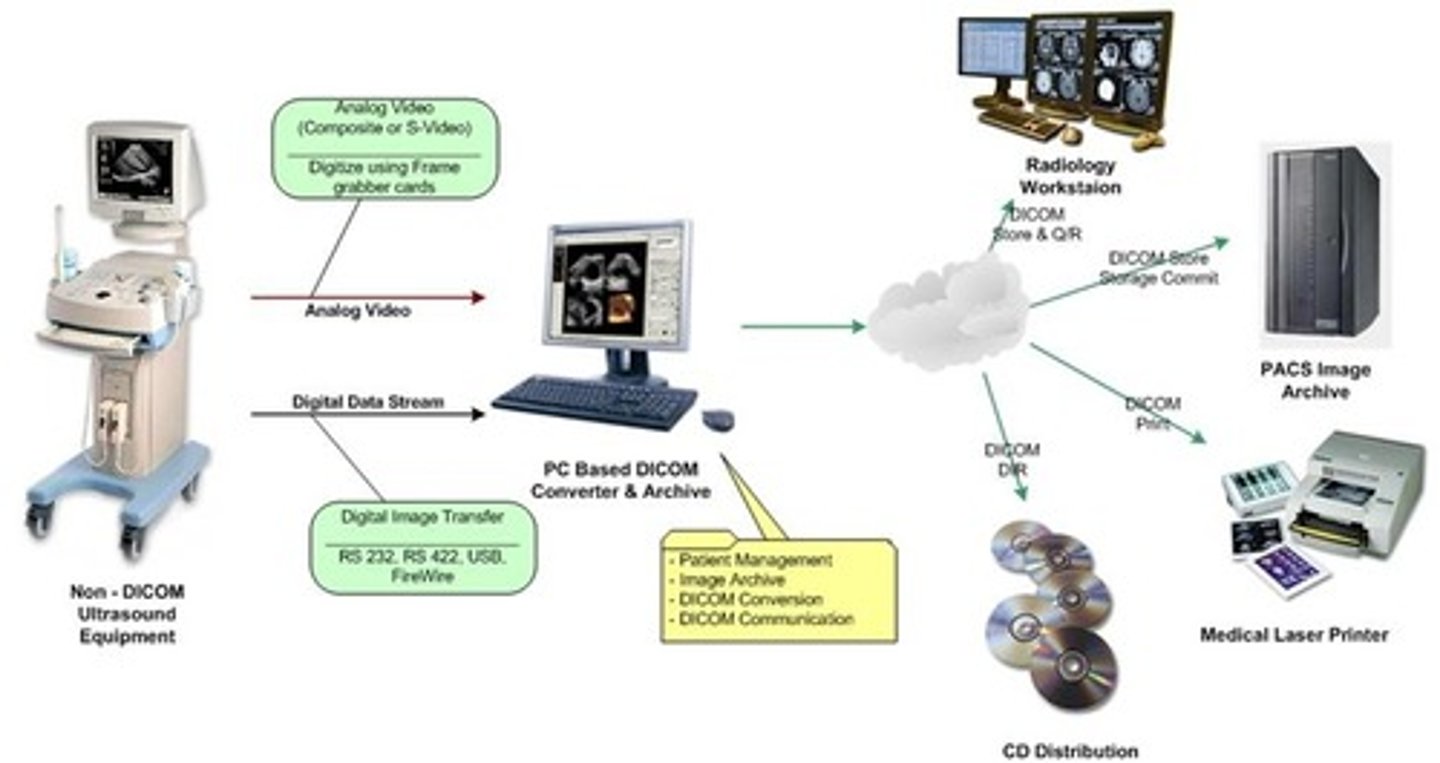
HIS (Hospital Information System)
patient information stored in hospital database
RIS (Radiology Information System)
radiology specific database
EMR (electronic medical record)
an electronic document that contains patient health information, gathered from different sources
geometric factors
Factors that affect the information recorded on the radiographic image receptor.
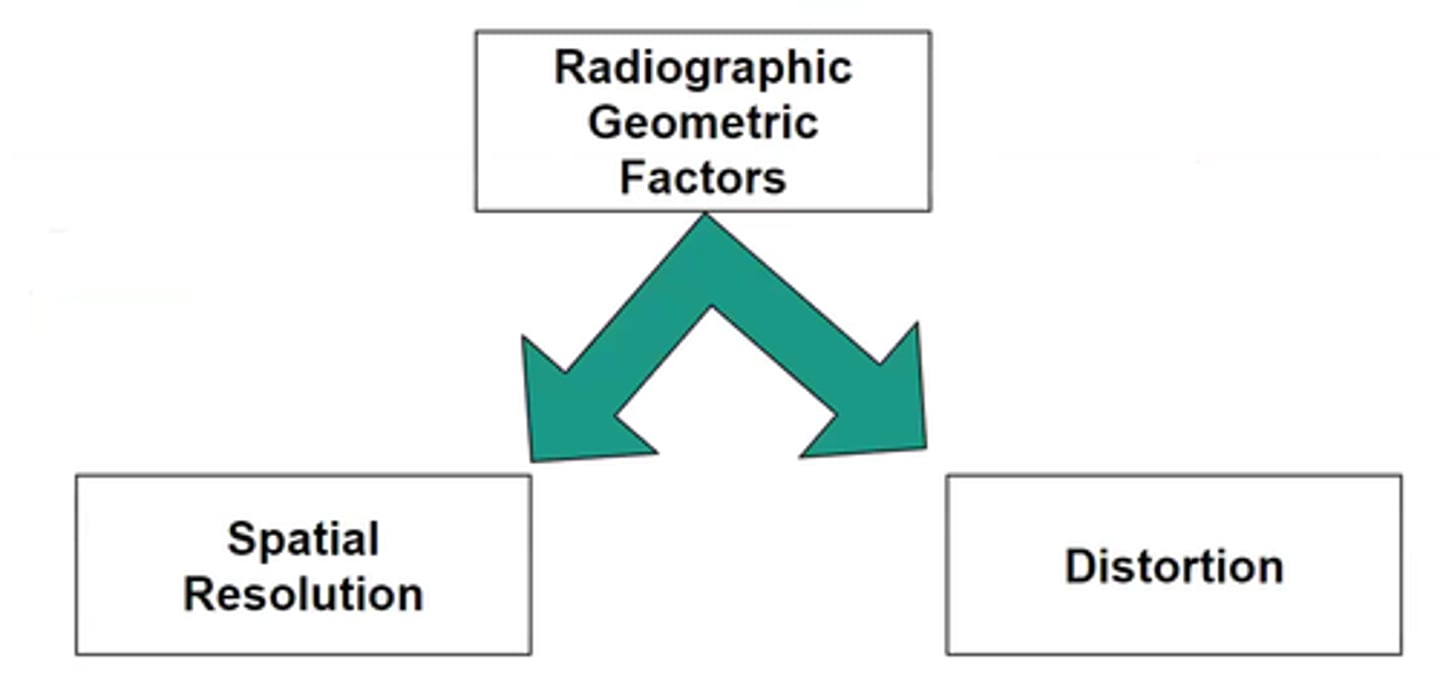
spatial resolution
ability of an imaging system to display two closely spaced objects as separate
Distortion
misrepresentation of the true size or shape of an object (size or shape)
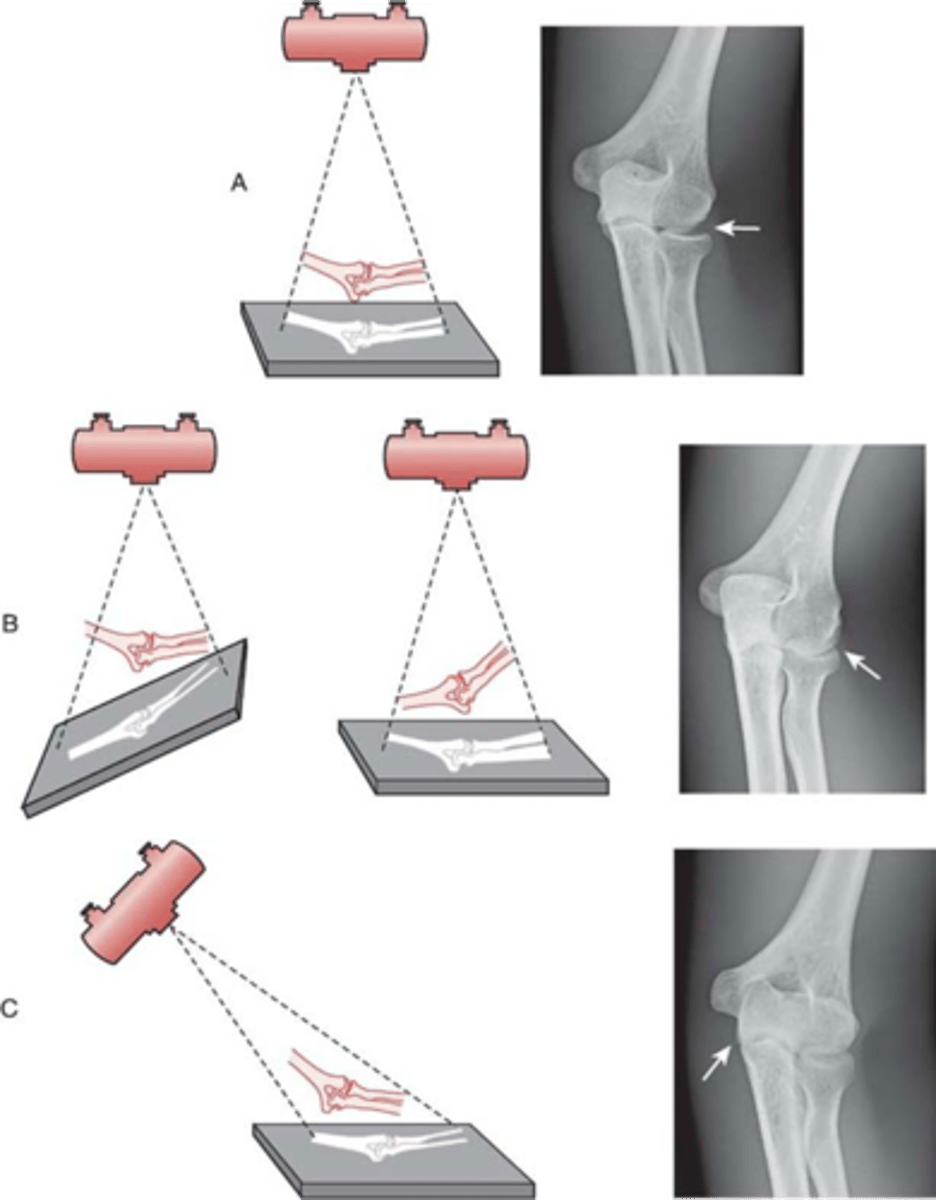
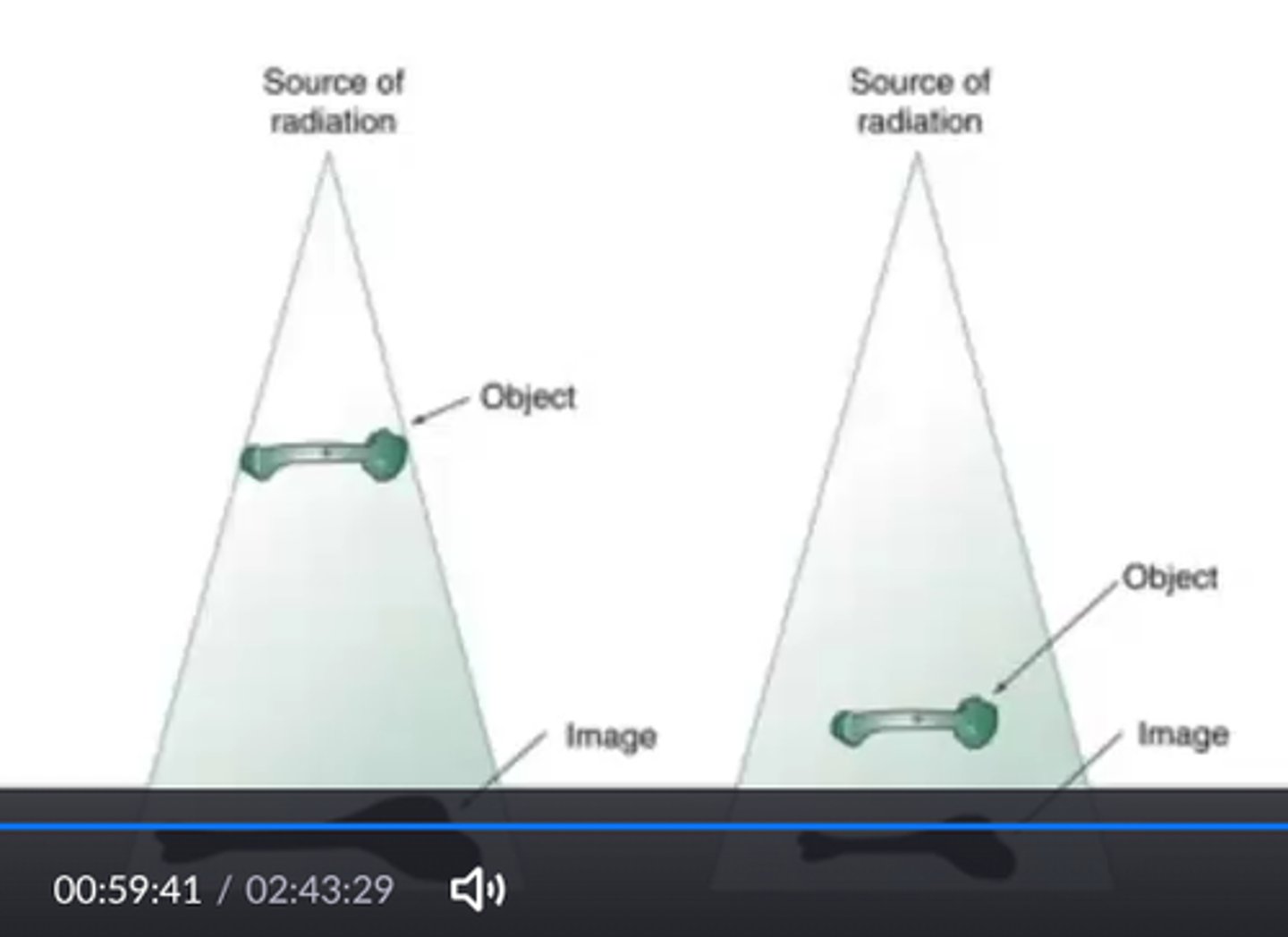
why do we use a 72" SID for lateral C-spine?
reduces OID
size distortion = ___________. Controlled by OID & SID.
Magnification
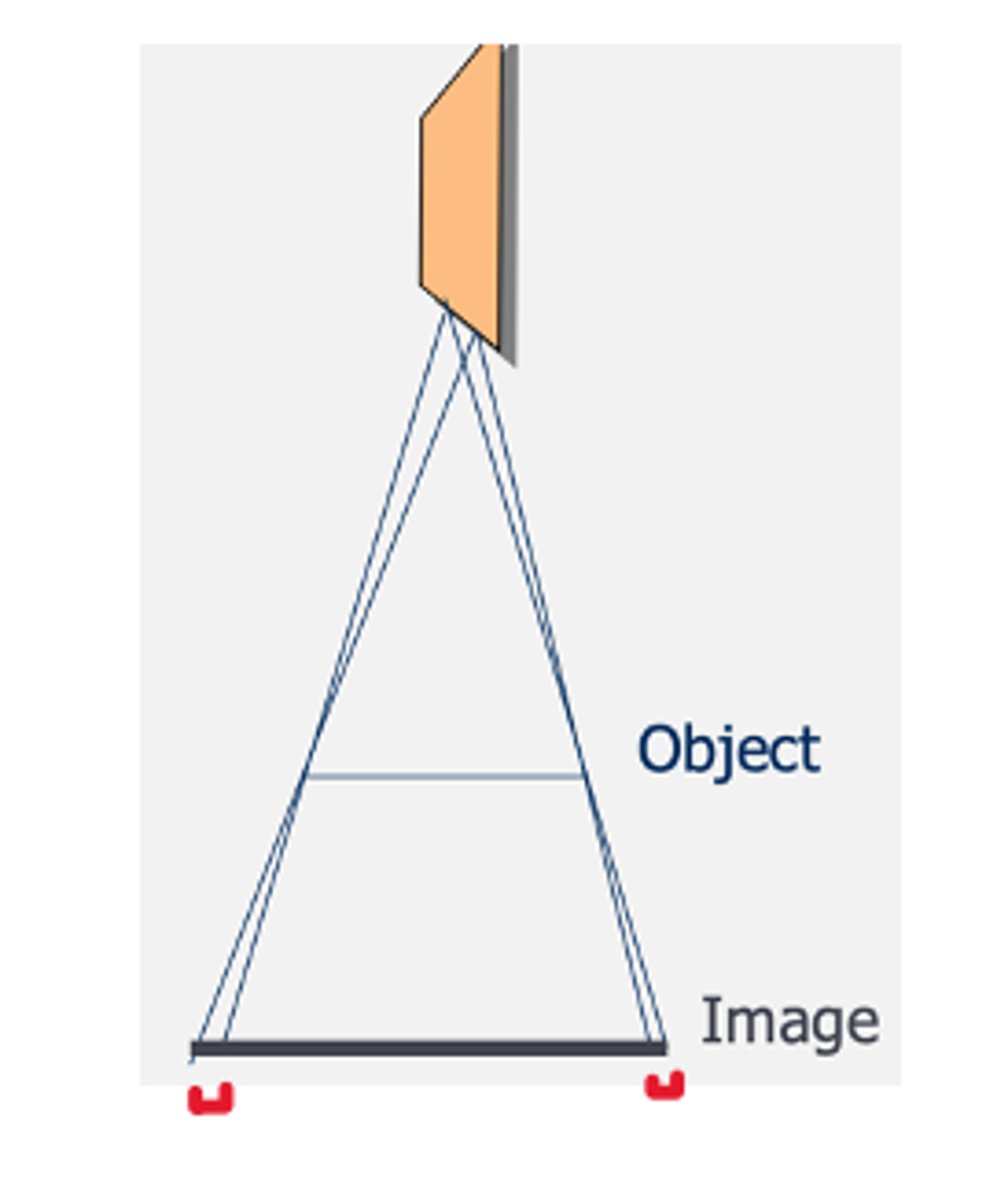
_______ is the main controlled of magnification
OID
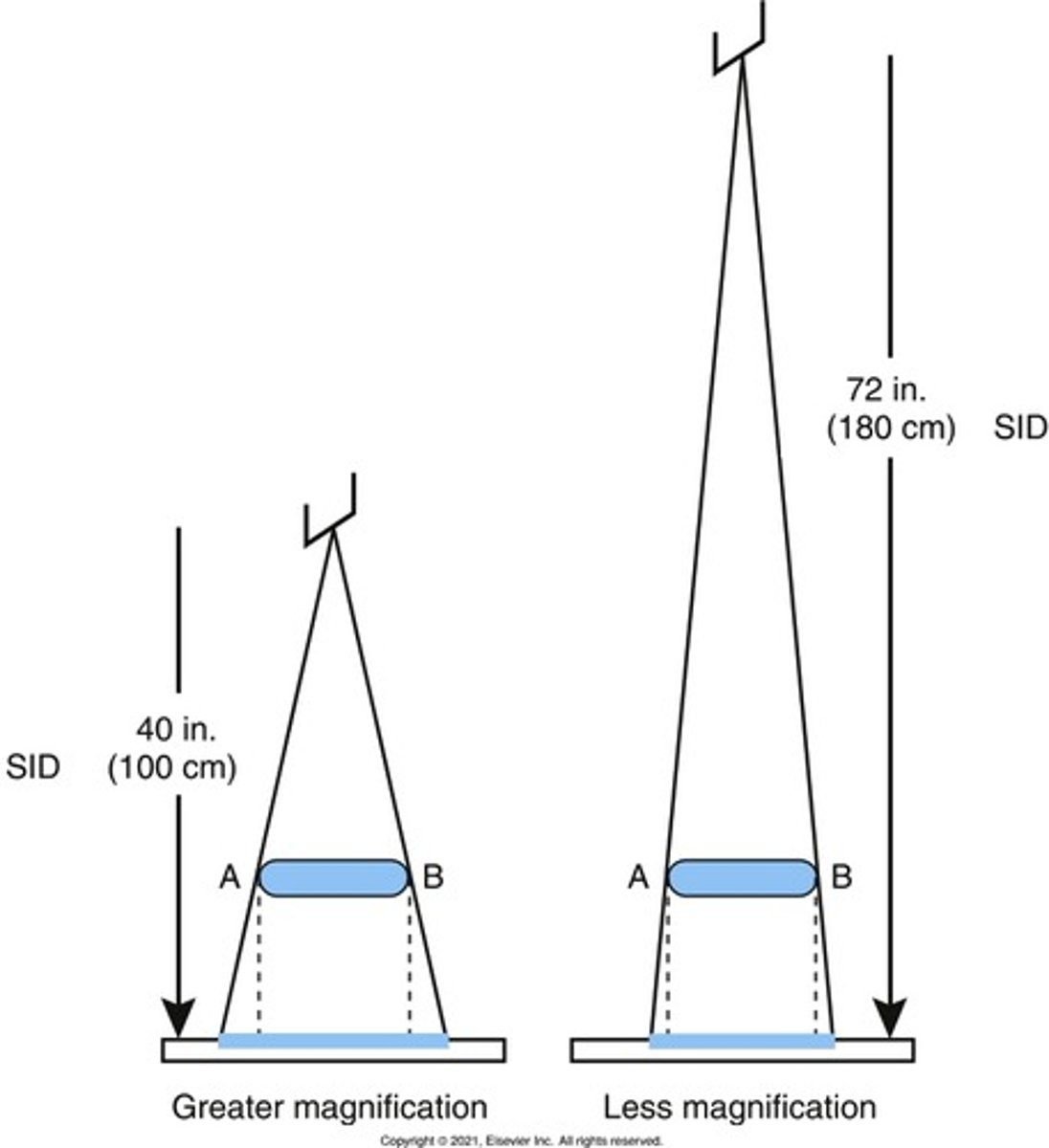
What SID helps reduce magnification? Examples of anatomical positioning that helps reduce magnification?
-72"
-PA Chest - reduces heart size
-PA skull - reduces magnification of orbits
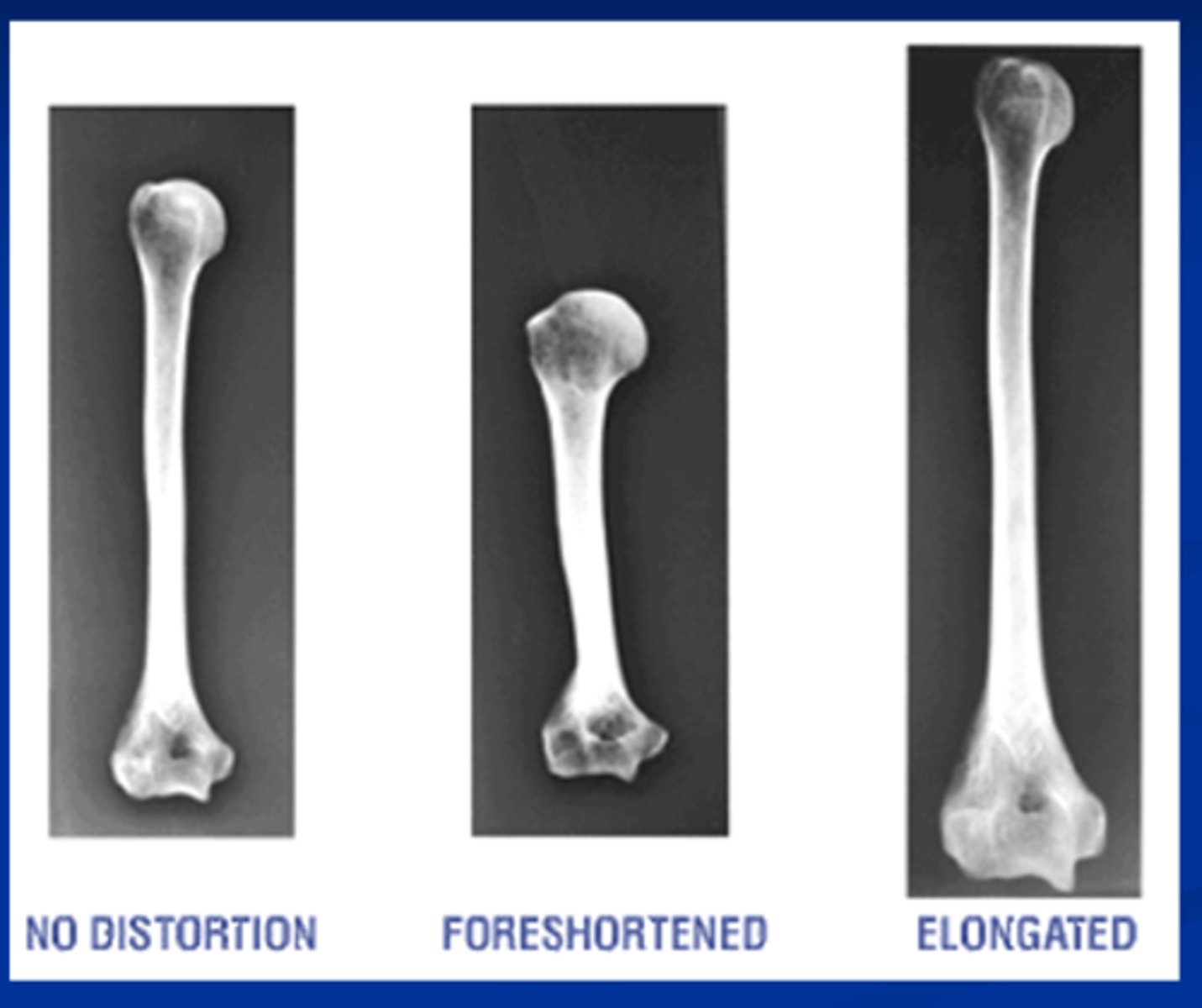
Shape distortion= _____________& ______________. Controlled by what?
-elongation & foreshortening
-IR , X-ray tube, anatomical part
Magnification Factor formula: MF=
-SID/SOD (SOD = SID-OID)
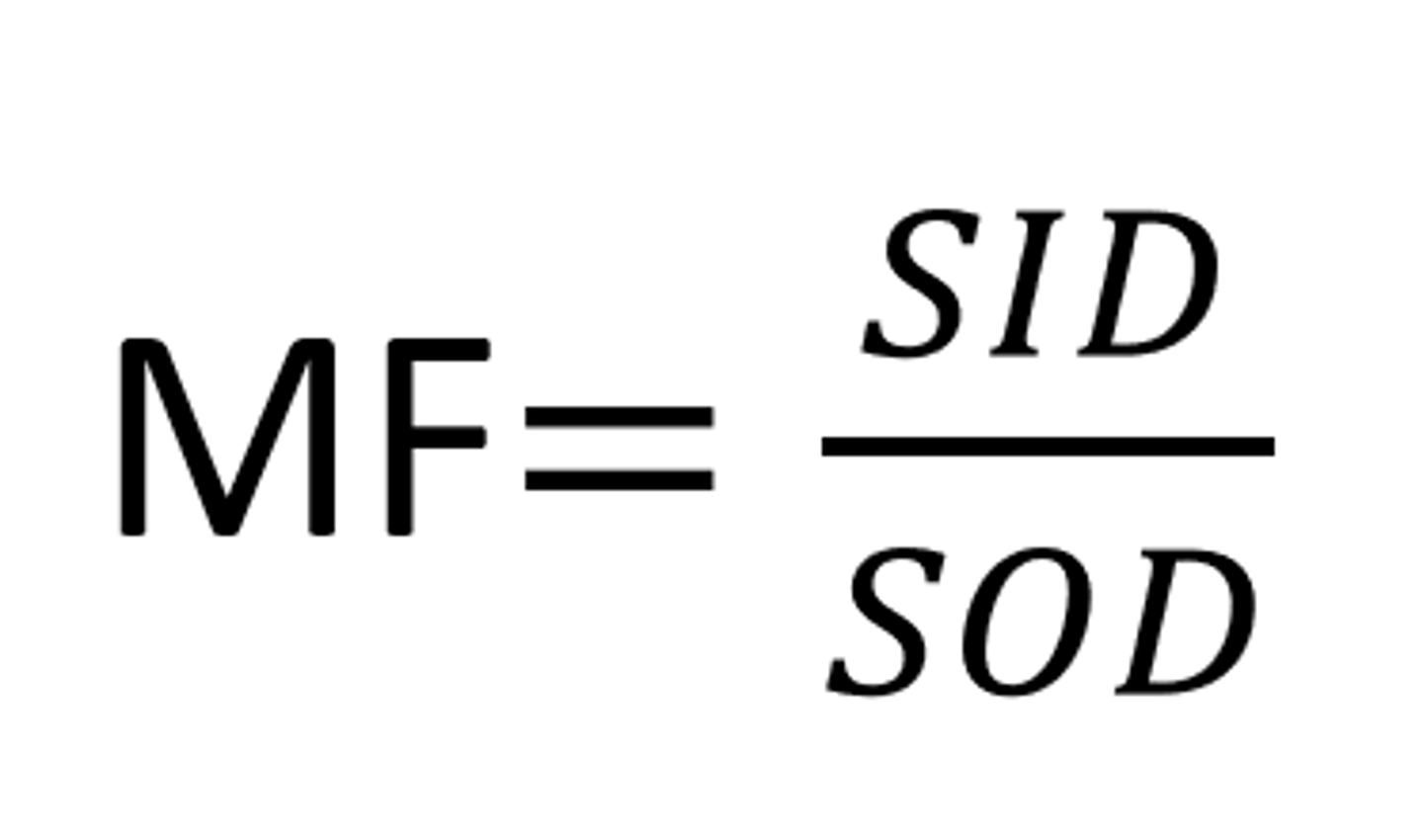
Formula for calculation for object size or image size
image size/ object size = MF
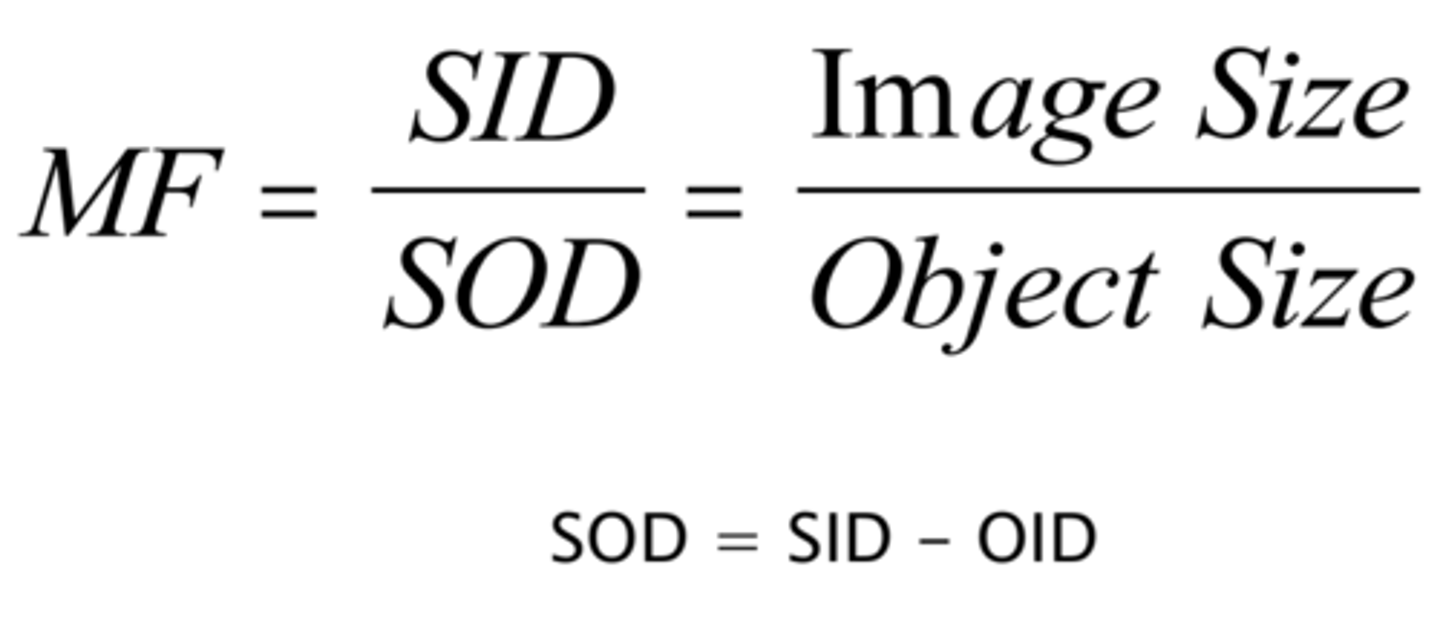
Elongation - part will appear _____. Results from angling the _____ & ____.
-longer
-tube & IR
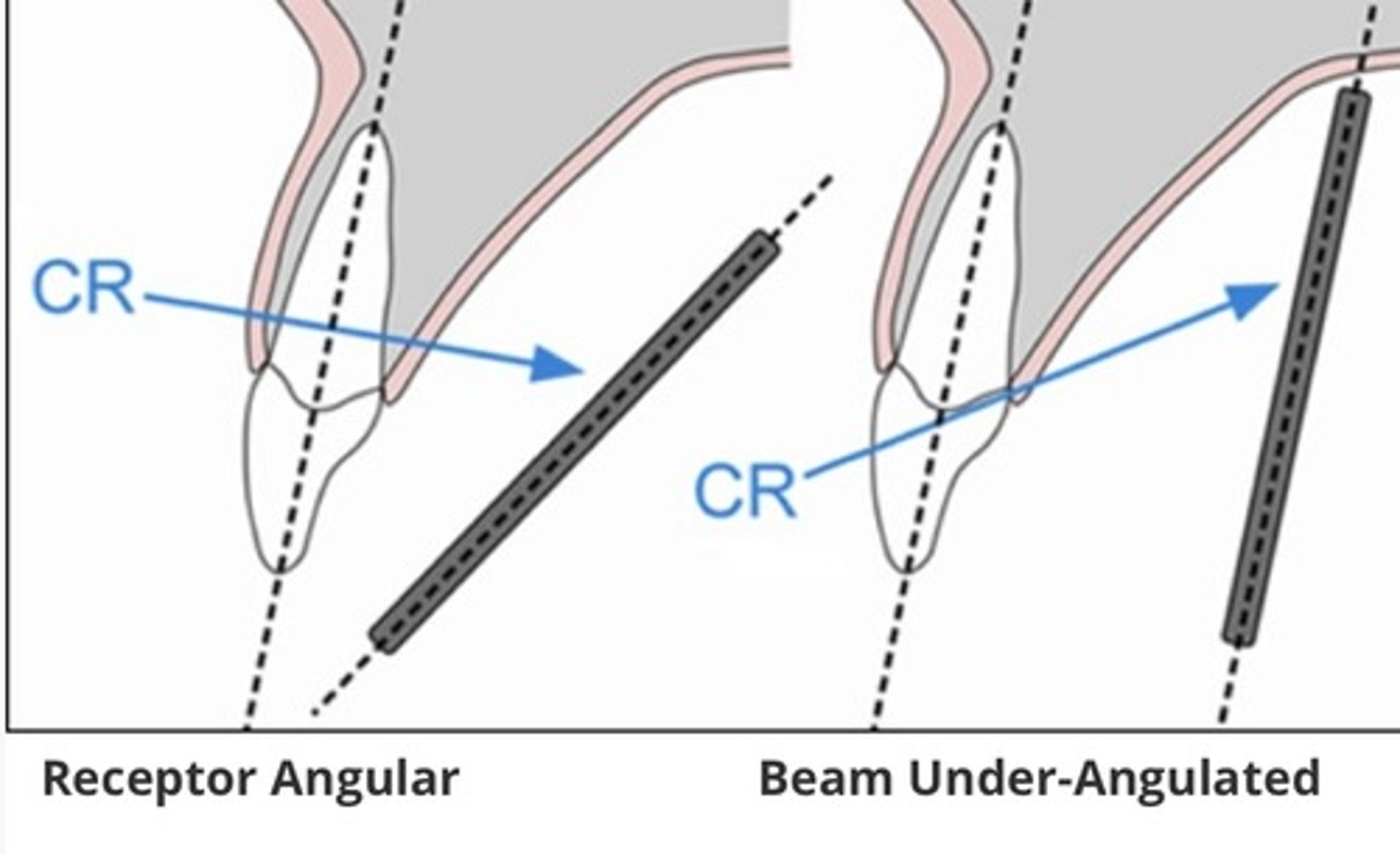
Foreshortening - the part appears __________. Results from angulation of the ________.
-shorter
-anatomy/part
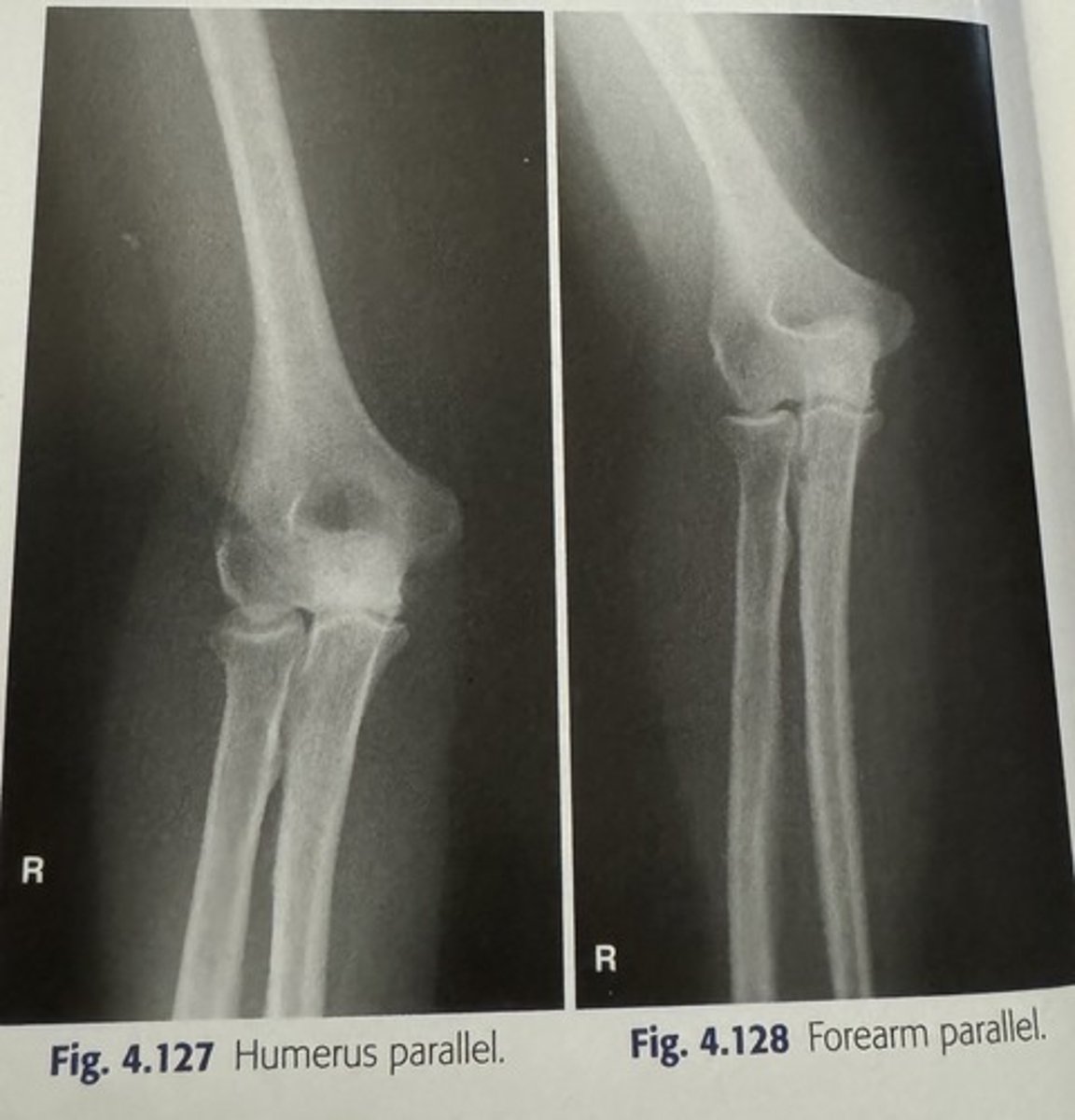
Elongation used with what two projections to help visualize anatomy?
-AP Towne Skull
-axial calcaneus
what would be used to minimize size distortion?
Decrease OID & Increase SID
3 multiple choice options
If OID is decreased, what is the effect on spatial resolution? what is their relationship?
-Spatial resolution increases
-inverse relationship
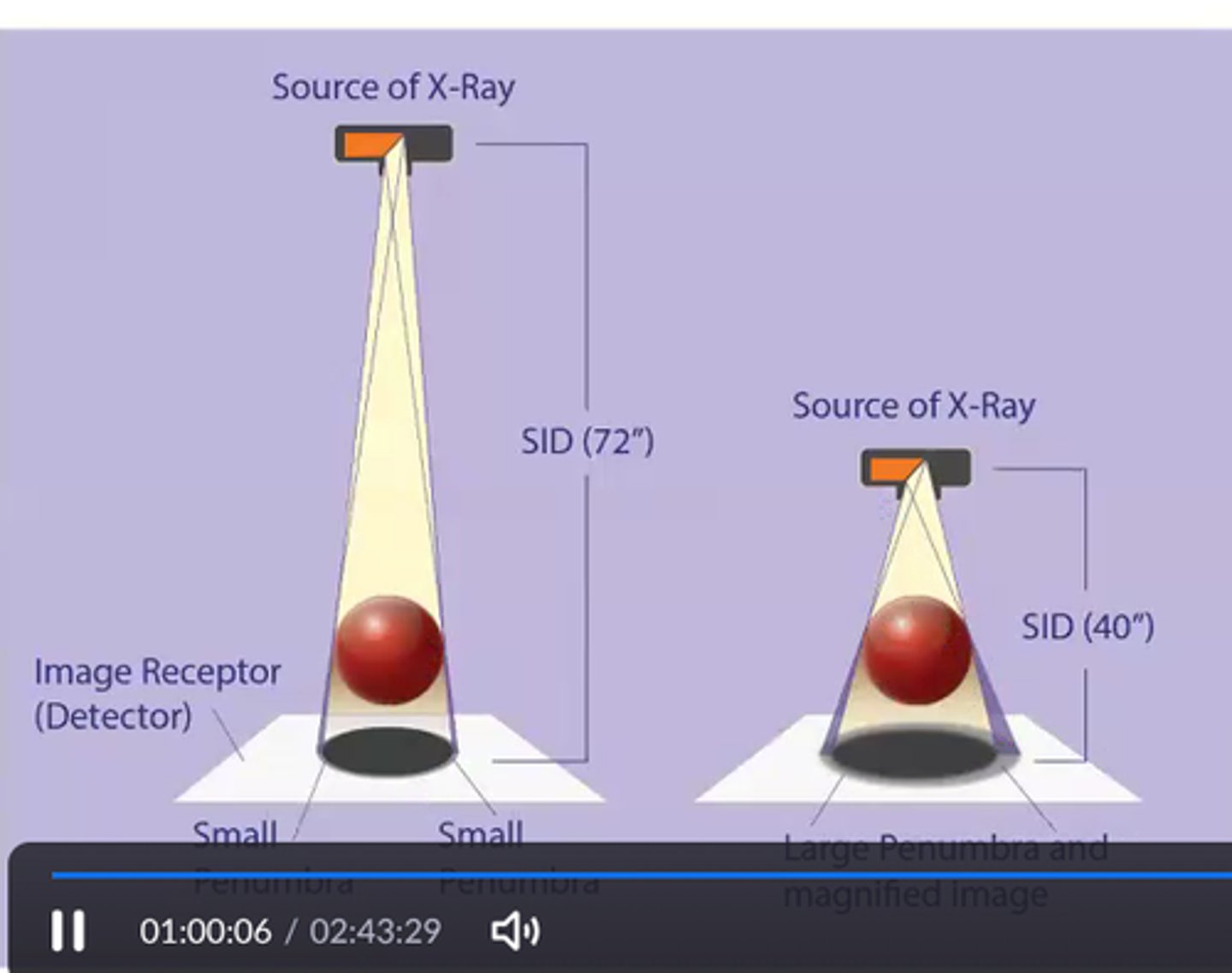
IF SID is increased, what is the effect on spatial resolution? what is their relationship?
-Spatial resolution will increase
-direct relationship
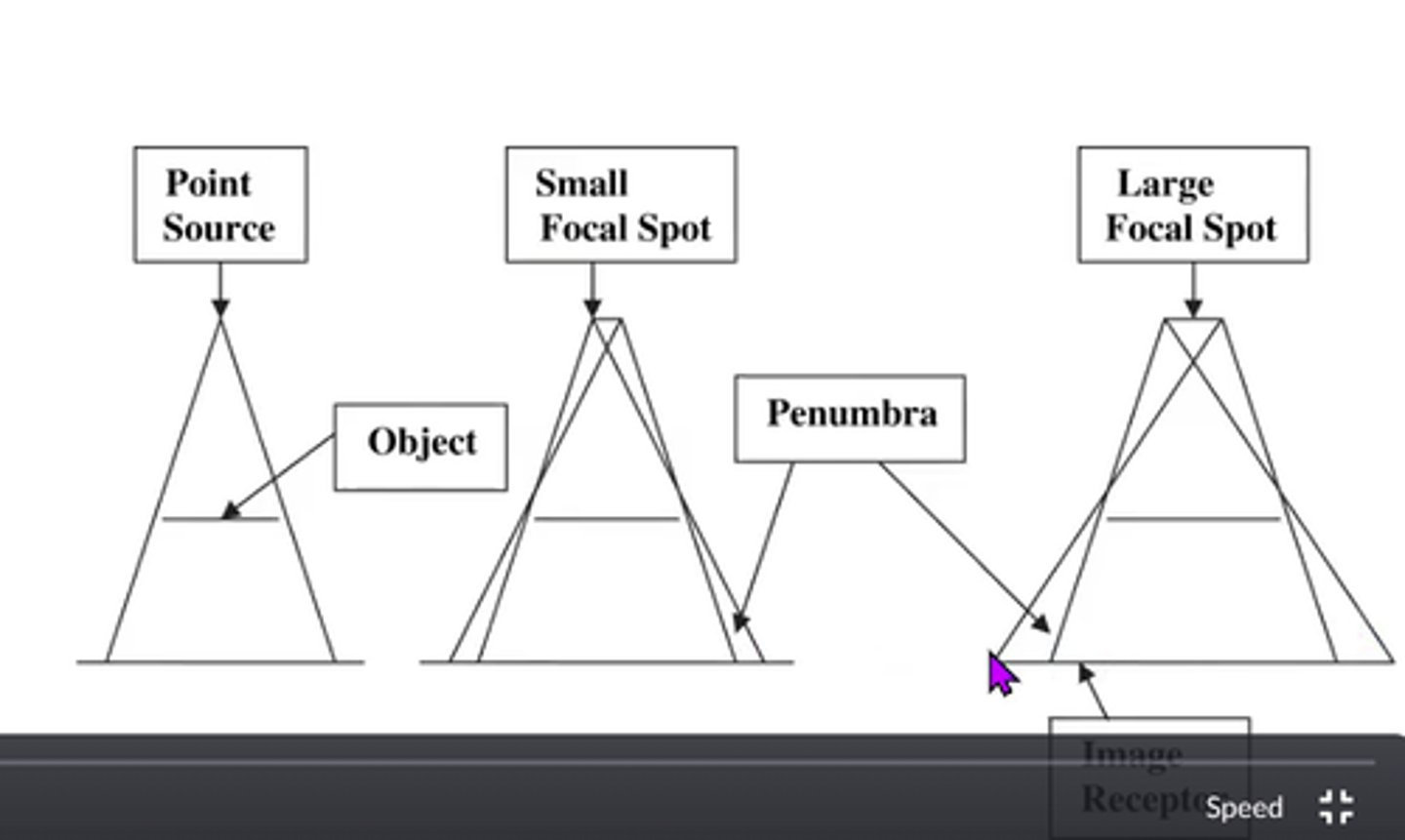
If the FSS is decreased, what is the effect on spatial resolution? What is their relationship?
-increased spatial resolution
-inverse relationship
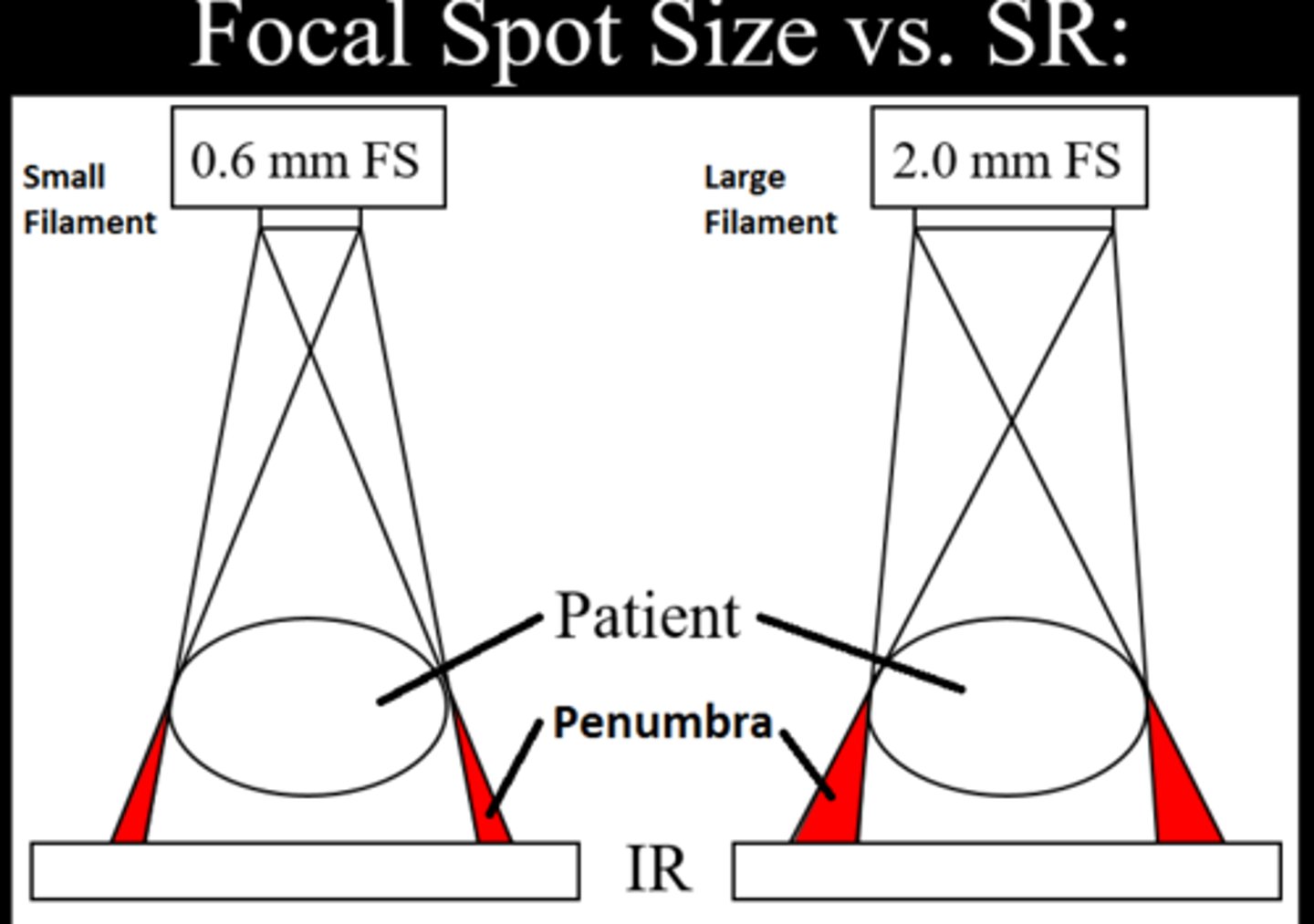
Penumbra
unsharpness or blurring at the edges of an object
Penumbra more significant at what SID? (40" or 72")
40"
what is voluntary motion? how is it reduced?
-Motion under the control of the patient (breathing)
- effective communication
what is involuntary motion? how is it reduced?
-motion patient is unable to control (cardiac)
-short exposure times
Why would an increase in pt size decrease spatial resolution?
-larger pt = larger OID
-larger OID = magnification
-larger pt = increased thickness/size = scatter
Tube, part or IR angulation will result in a form of distortion. If you decrease the angle of the part, what happens to spatial resolution?
-spatial resolution increased
Increasing Pixel size does what to Spatial resolution?
decreases
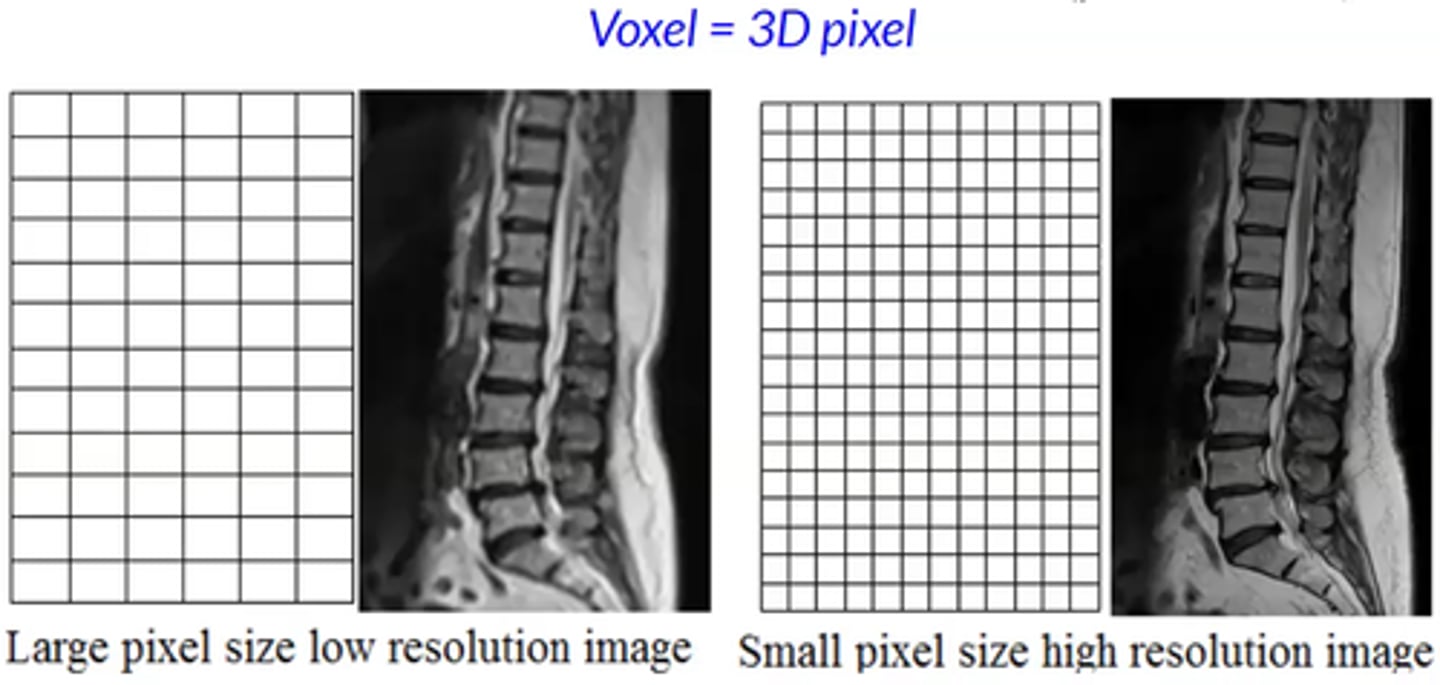
Increasing DEL size does what to Spatial resolution?
decreases
Increasing PSP plate (CR plate) size does what to Spatial resolution?
decreases

When using CR its important to select the ________ IR possible for the part. Why?
-smallest
-improves spatial resolution
Increasing Sampling frequency (done by laser in CR equipment) does what to Spatial resolution?
increases
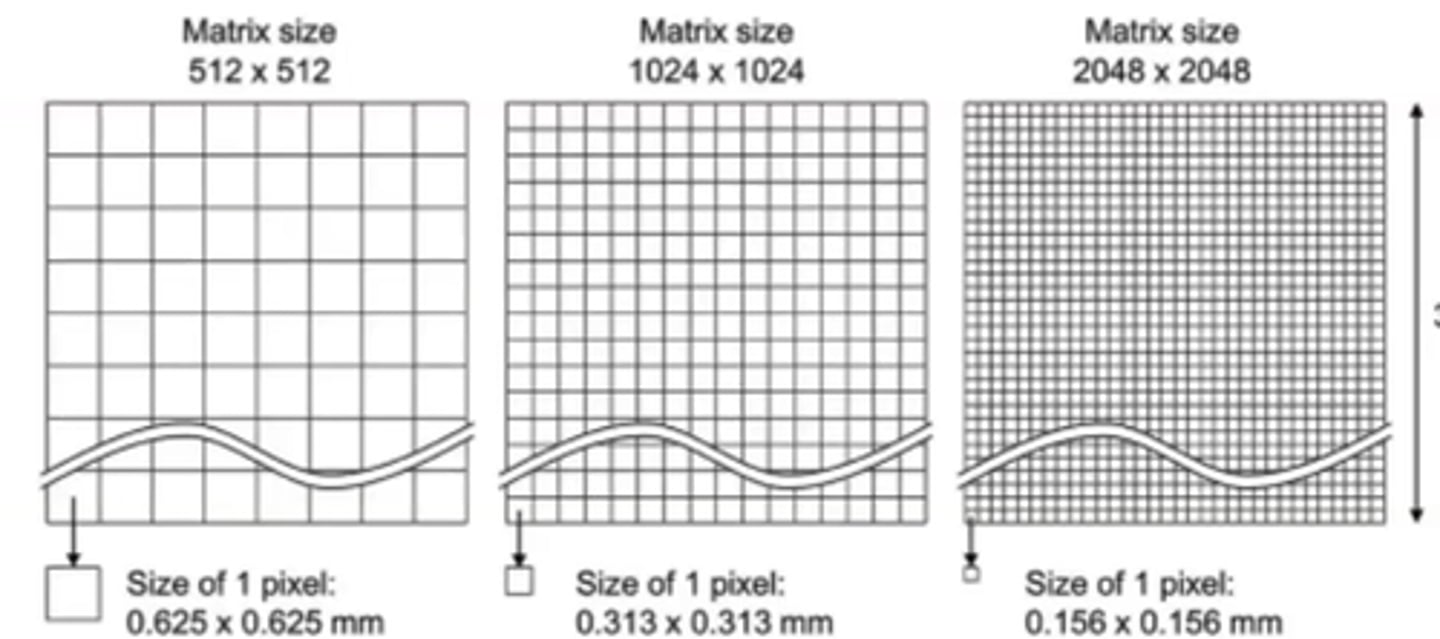
Increasing matrix does what to Spatial resolution?
increases
Nyquist frequency
Relationship between sampling frequency and Spatial resolution
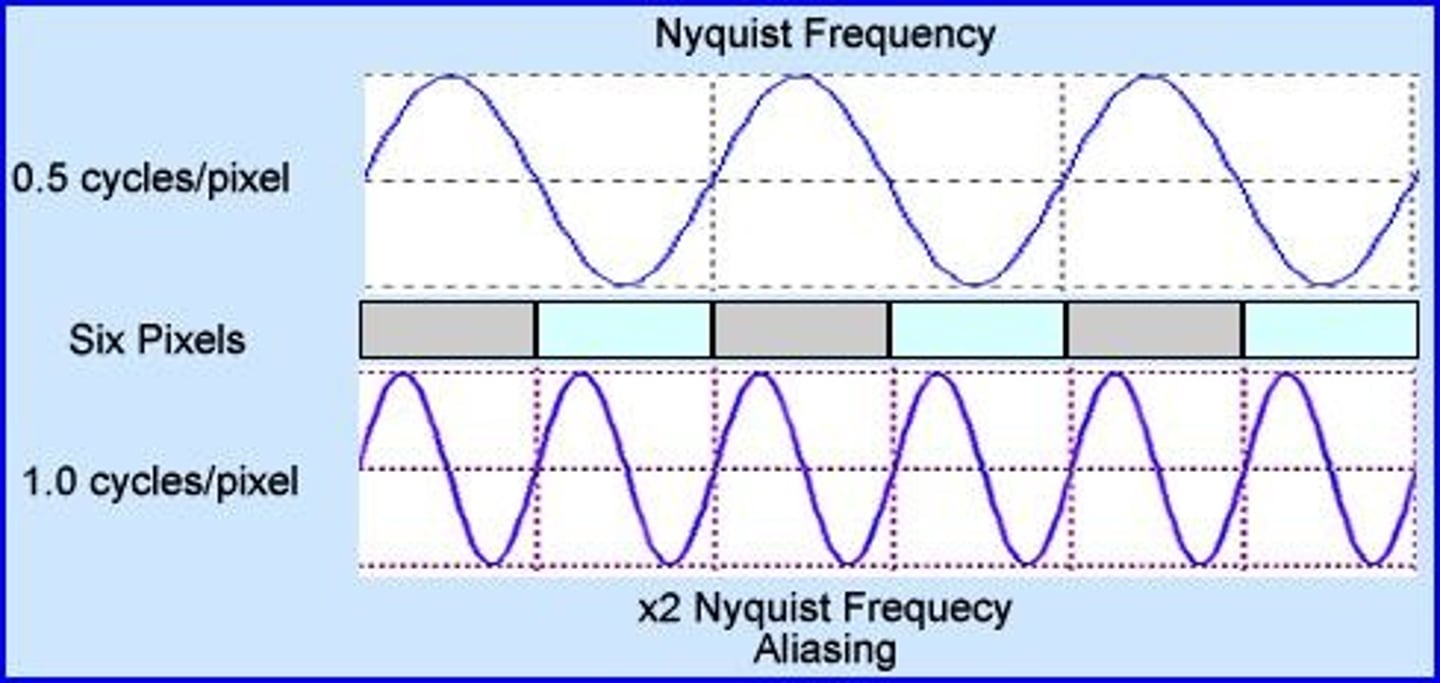
minimum of ____ lp/mm for diagnostic image quality
2.5
spatial resolution is _____ limited in DR
pixel
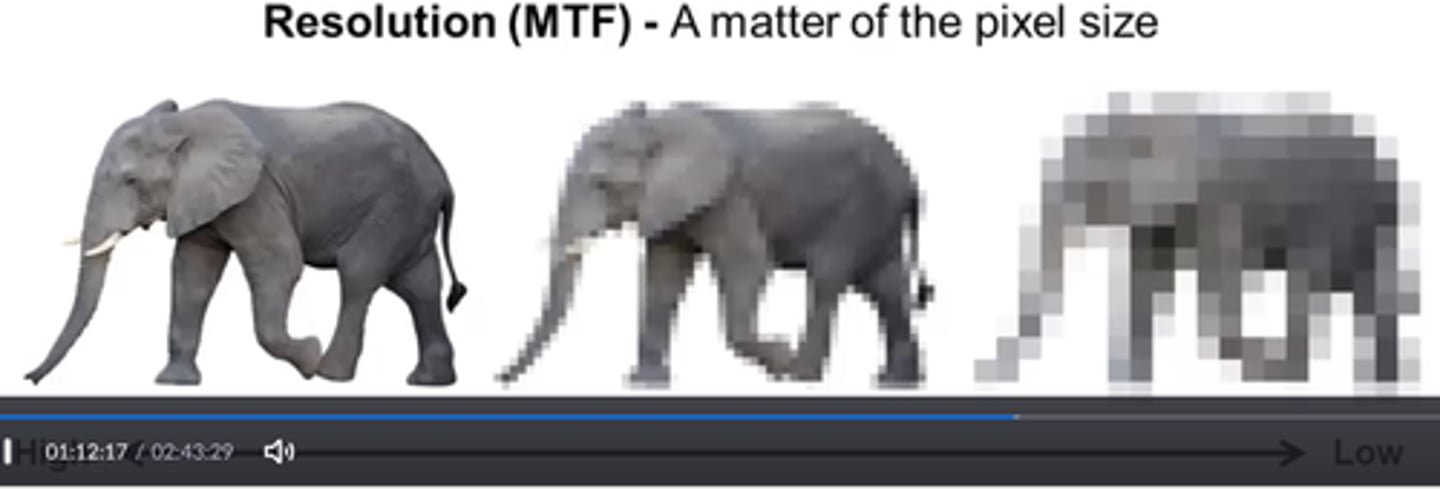
What is Modulator Tranfer Function (MTF)? Best measurement of what?
-ability of a system to record available spatial frequencies
-spatial resolution

contrast
difference in brightness levels between adjacent structures
Digital image contrast is primarily controlled by the _______________
Look up table (LUT)
Receptor exposure
amount of radiation passing through the patient and hitting the IR (both primary & secondary radiation)
Receptor exposure primarily controlled by ____
mAs
Short scale contrast
-mainly B&W
-low kVp
-High contrast
-"Short b&w penguin likes to get high"

Long scale
-lots of grays
-high KVp
-low contrast
-"Gray big elephant"
9 factors affecting subject contrast
1.kVp
2.Pt size
3.Part density
4.Pathology
5.Contrast media
6.Grids
7.OID
8.Filtration
9.Collimation
kVp has an _______ relationship with absorption
inverse
as kVp increases, ______ ________ decreases
differential absorption
increasing kVp results in increased ______
scatter
high scatter = _______ contrast
low (more gray)
attenuation
The reduction in the intensity of the x-ray beam as it passes through matter, as a result of absorption, scatter and divergence
differential absorption
different objects absorb radiation differently
actors that affect attenuation
-differential absorption
-thickness of the body part
-type of tissue (Atomic #)
-kVp
Additive disease: examples and how do we adjust technique?
-Pleural effusion
-Ascites
-osteopetrosis
-osteoscleoris
-Edema
-Increase technique
-*Fluid is heavier*
Destructive disease: examples and how do we adjust technique?
-Atrophy
-Pneumothorax
-Osteoporosis
-Decrease technique
-*air less dense*
Types of contrast agents:
positive and negative
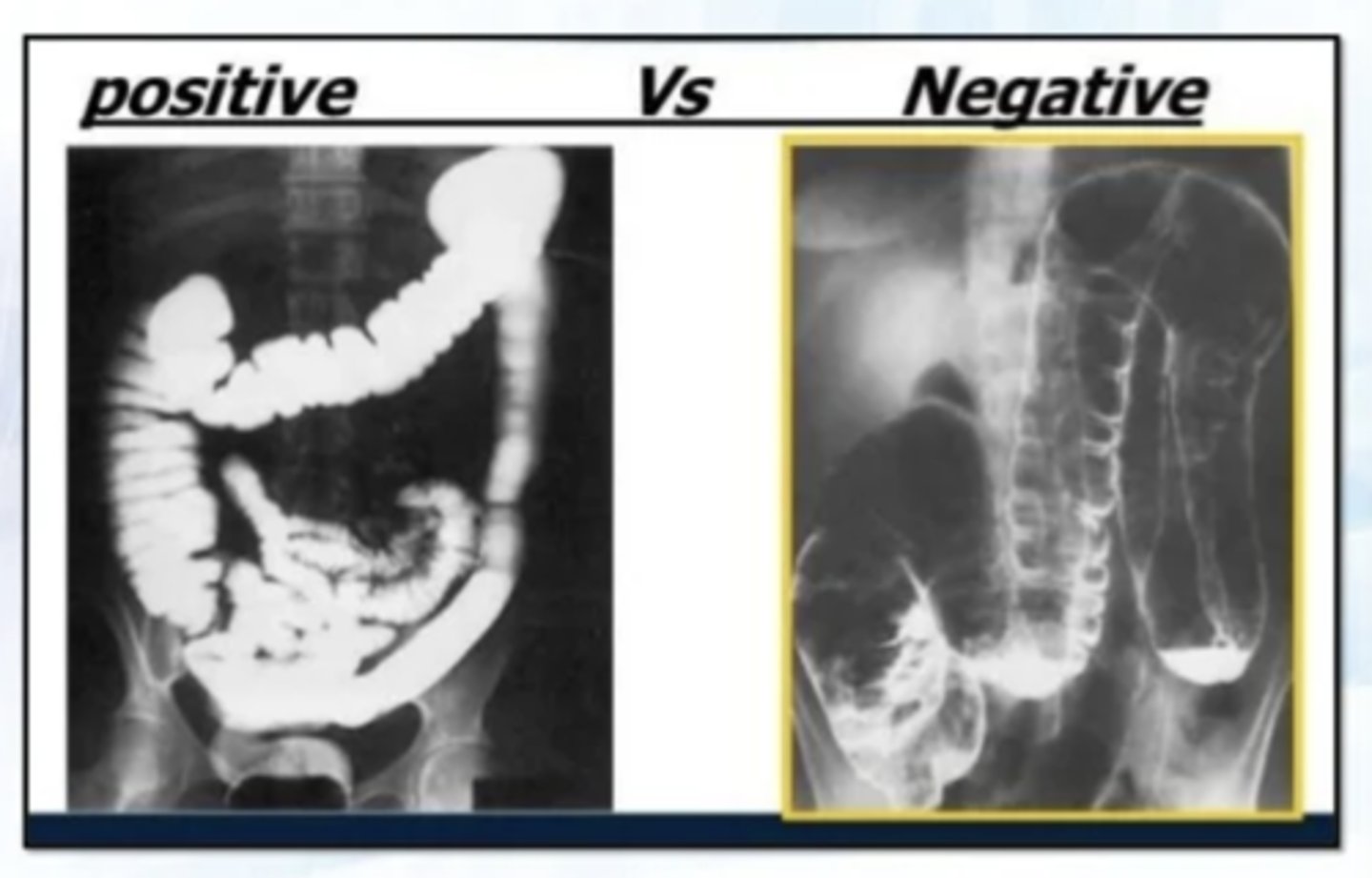
Positive contrast agent
-Barium
-higher atomic #
-appears white
-absorbs more photons
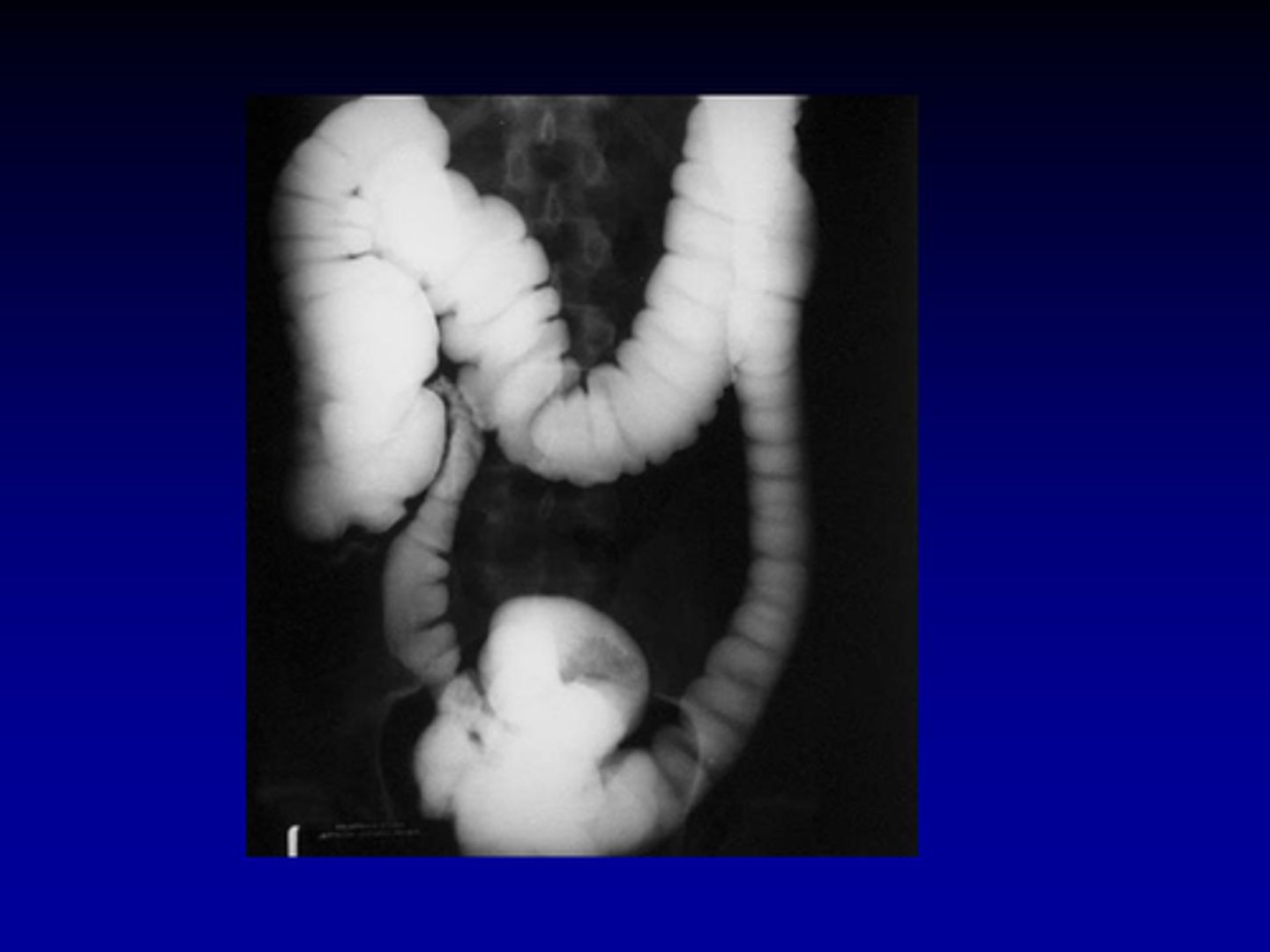
Negative contrast agents
-air
-lower atomic #
-appears black
-less absorption
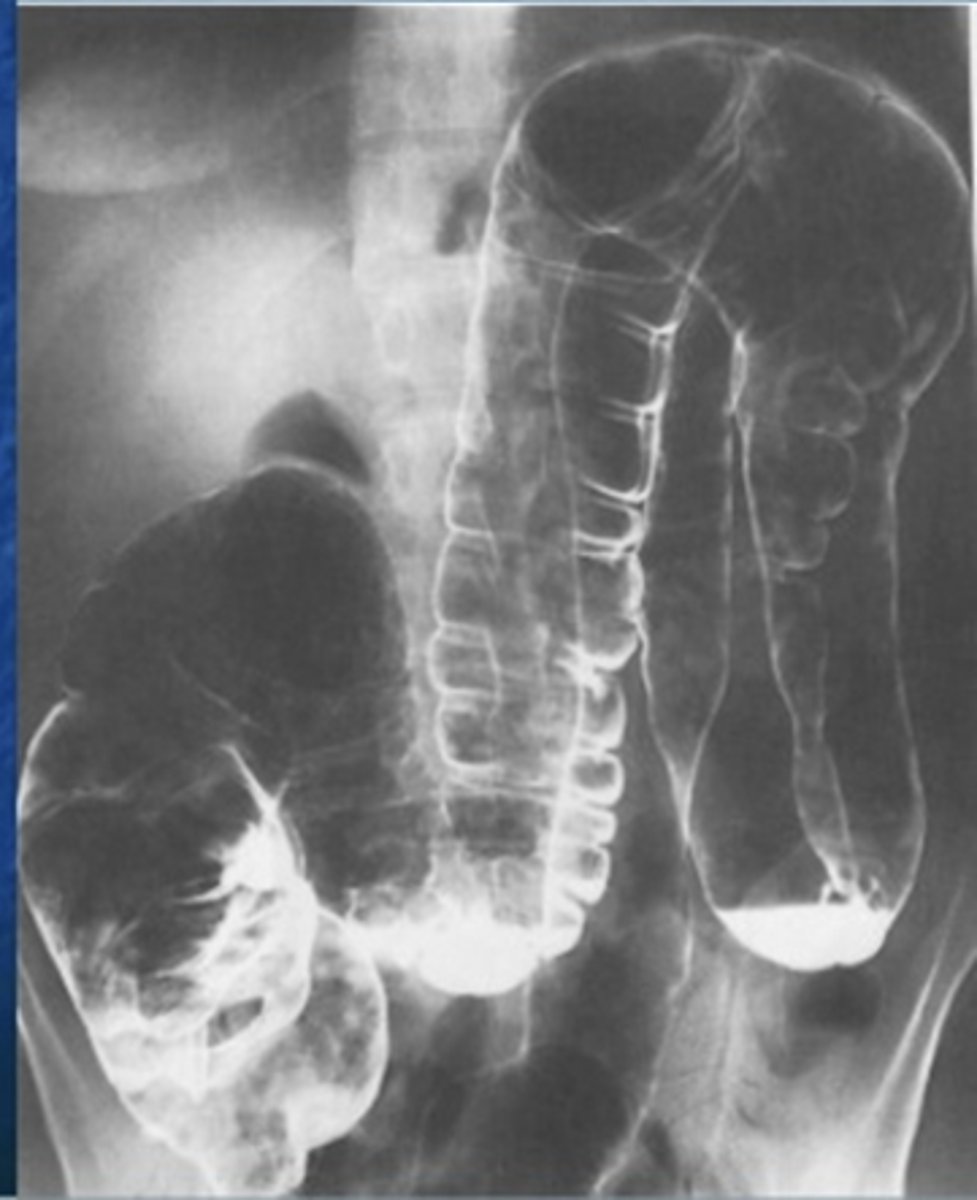
Technique that is typically changed is ______
mAs.
Grids improve contrast by blocking _______ from reaching the IR
scatter
The higher the grid ratio, the _____________ the patient dose
higher
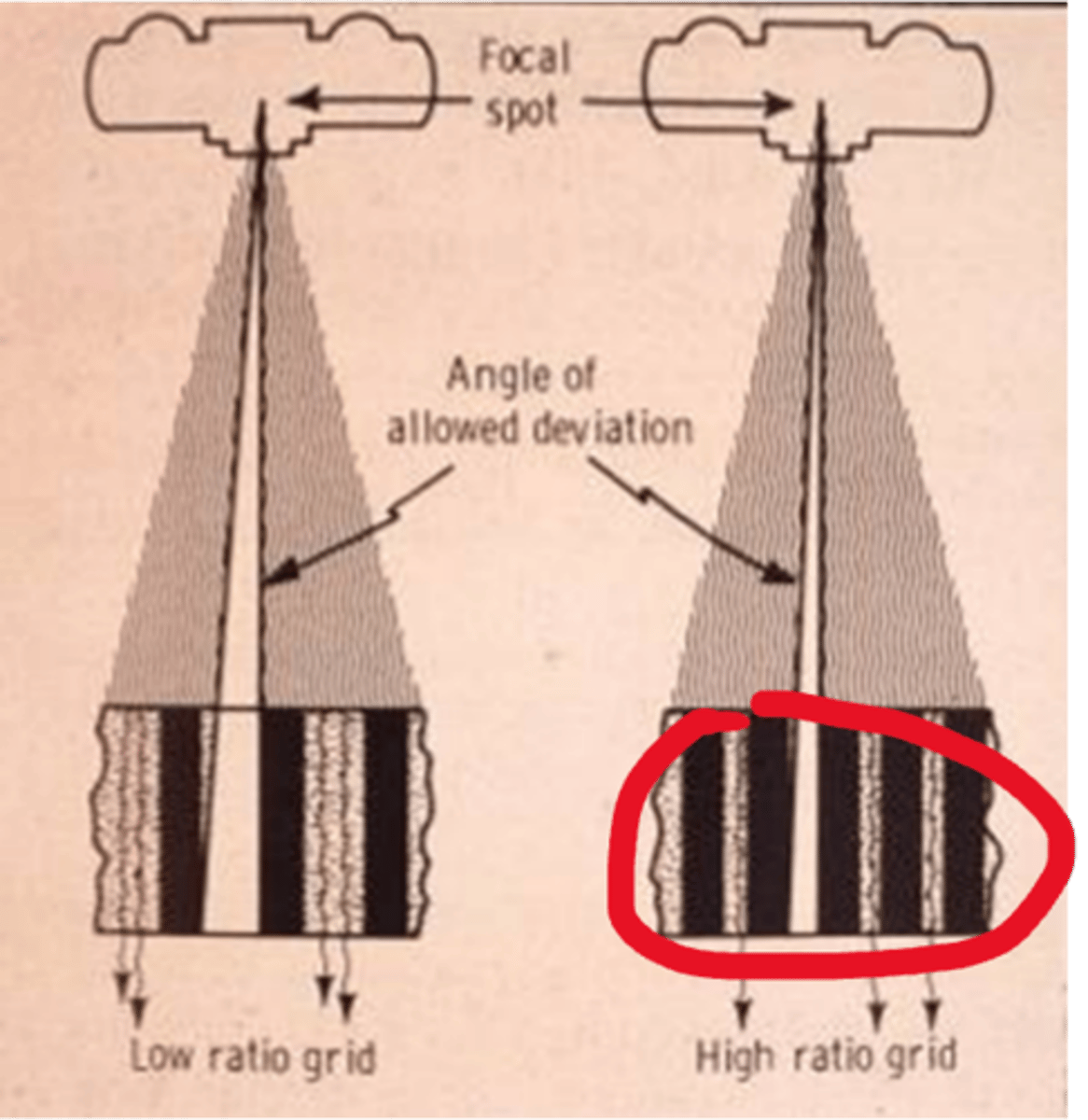
stationary grid
table top or mobile/portable radiography

crossed grid
-crosshatch pattern using 2 parallel grids
-used in specials
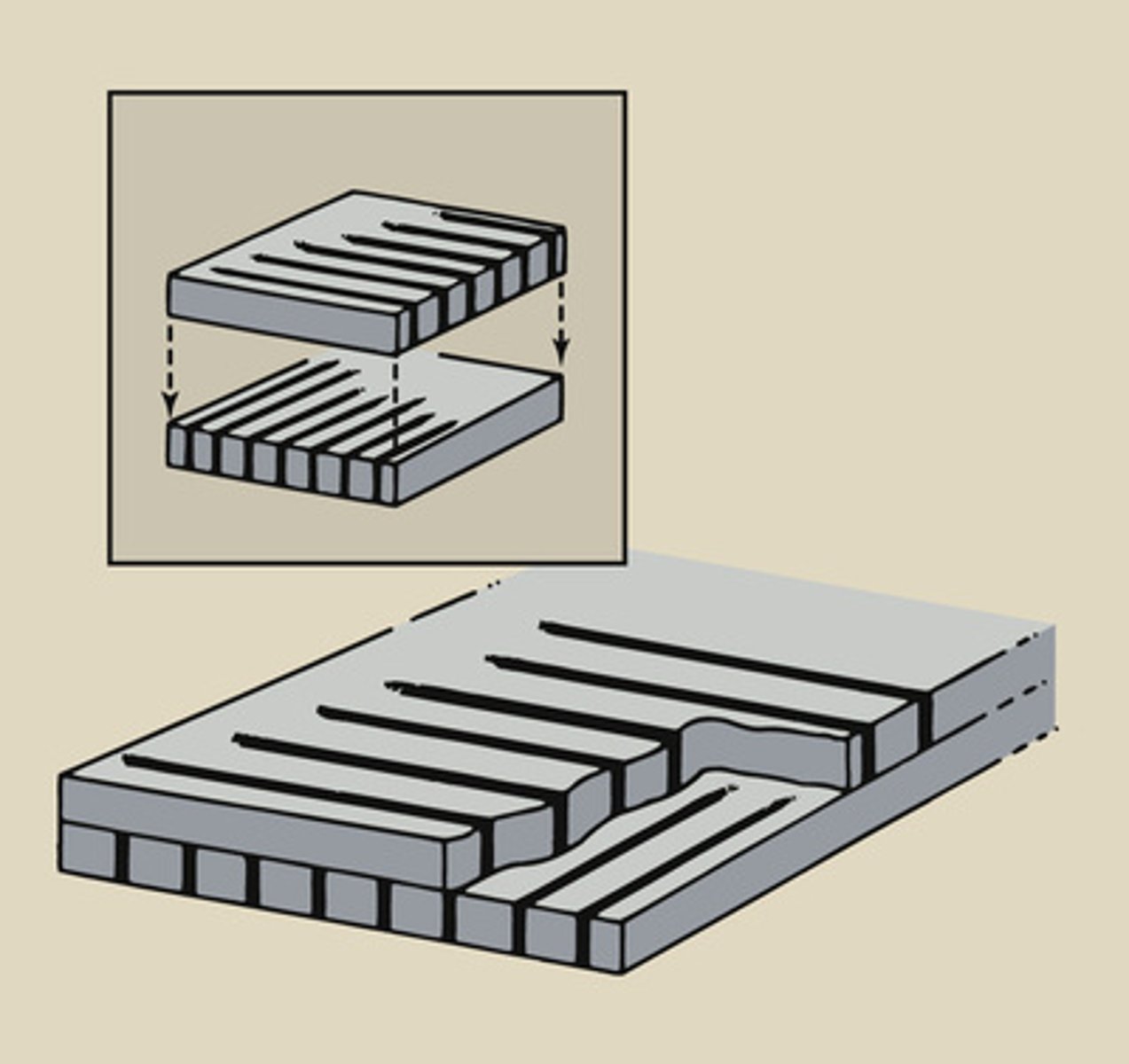
parallel grid
A grid with strips that are parallel to each other, rather than focused.
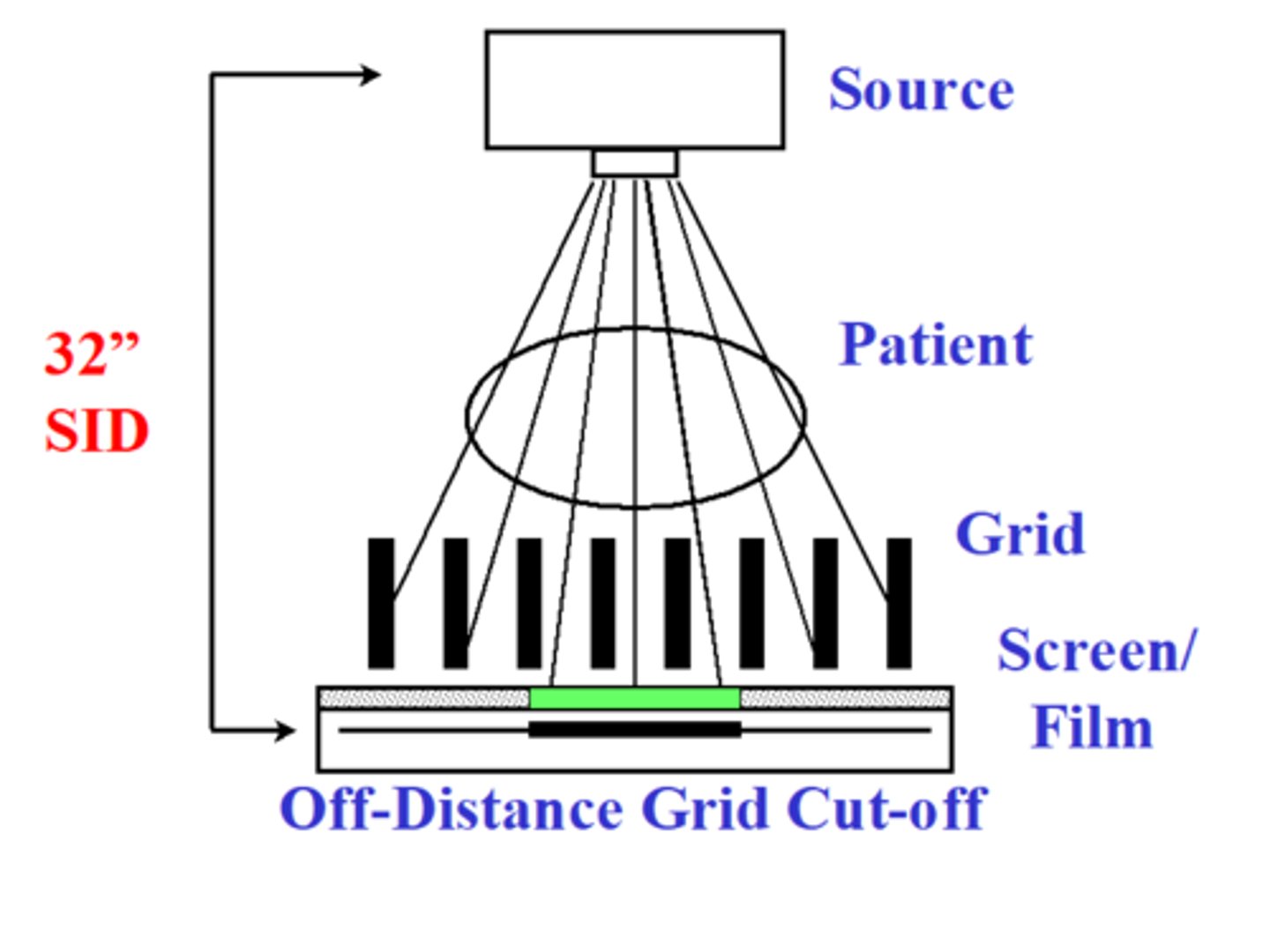
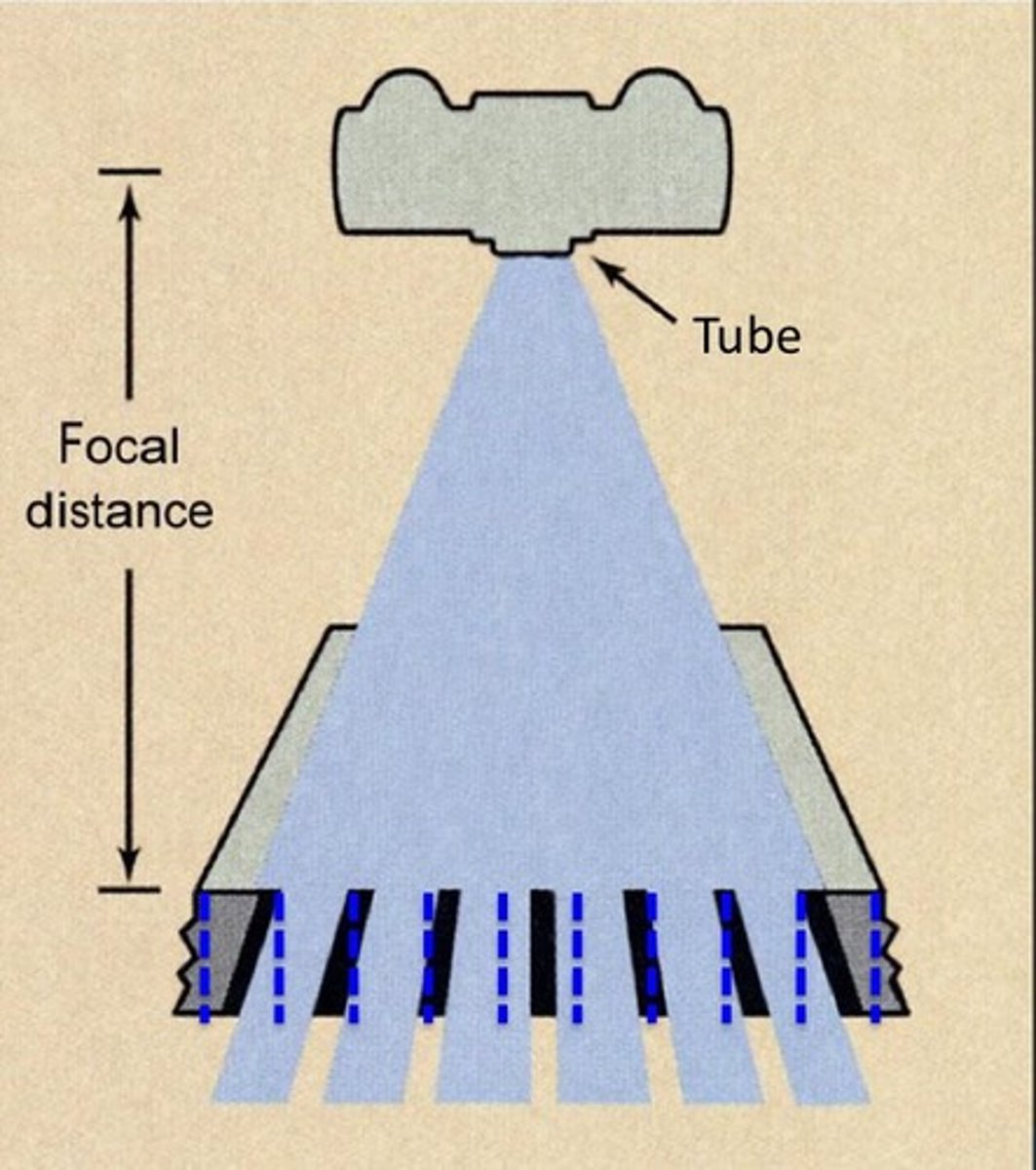
Focused grids
-lead strips angled to coincide w/ divergence of beam
-Focal range - specific SID
Grid ratio
the ratio of the height of the lead strips to the distance between them
grid ratio formula=
height/distance between them

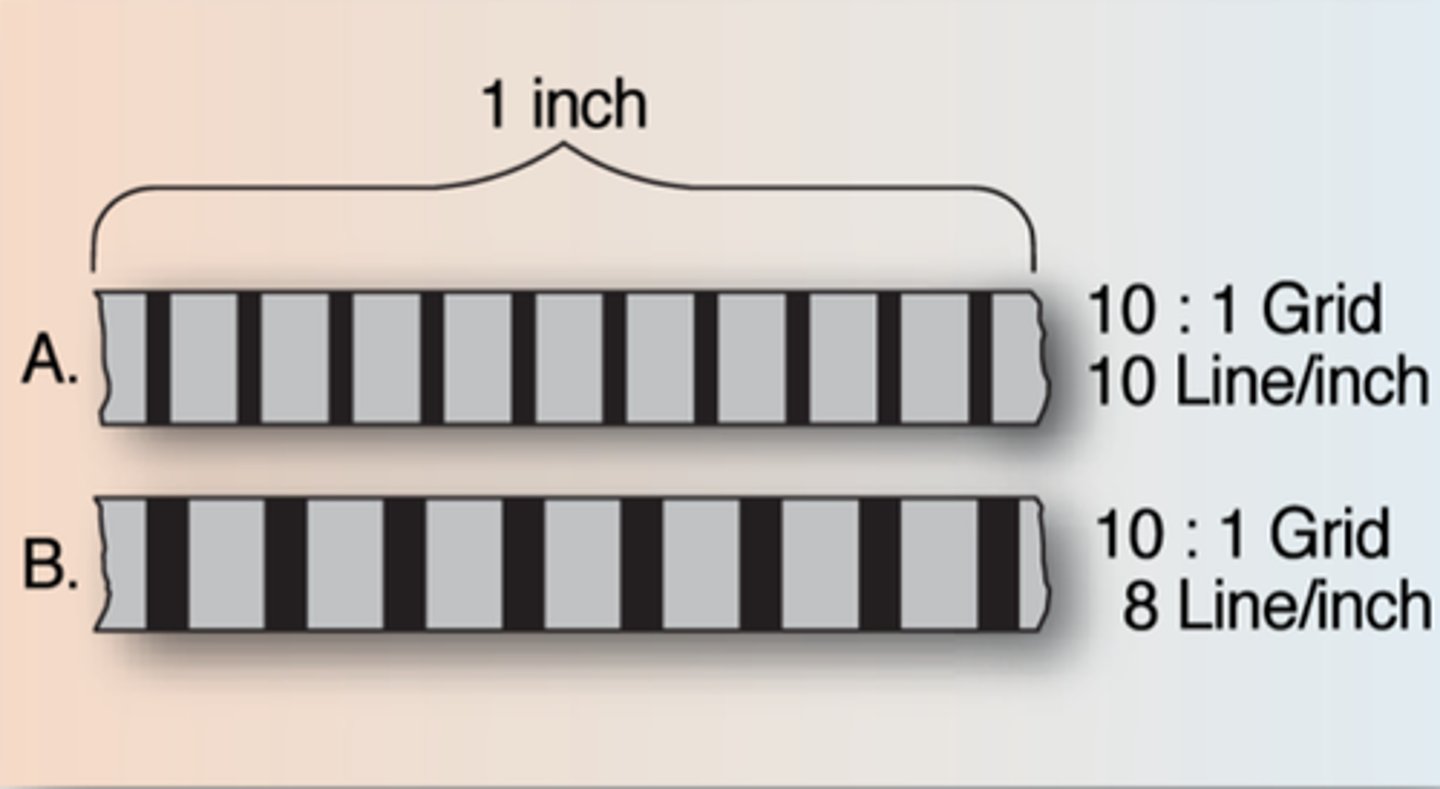
grid frequency
The number of grid lines per inch or centimeter
most common error in the use of grids is
improper positioning
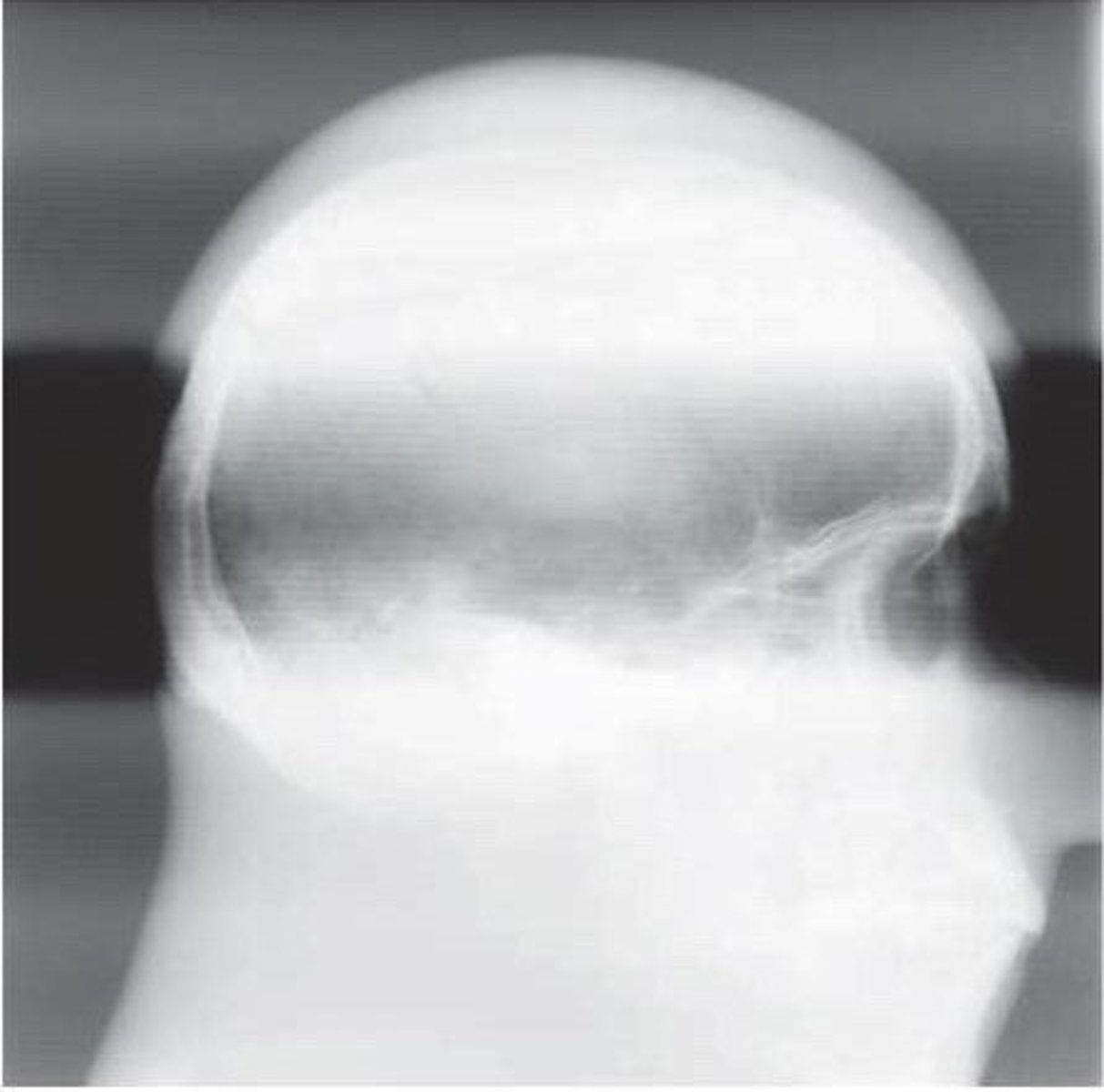
upside down grid error
severe grid cutoff on both sides of the image - usually happens w/ focused grids
which grid error results in grid cut off and loss of exposure on the outside edges of the IR?
incorrect SID w/ focused grid
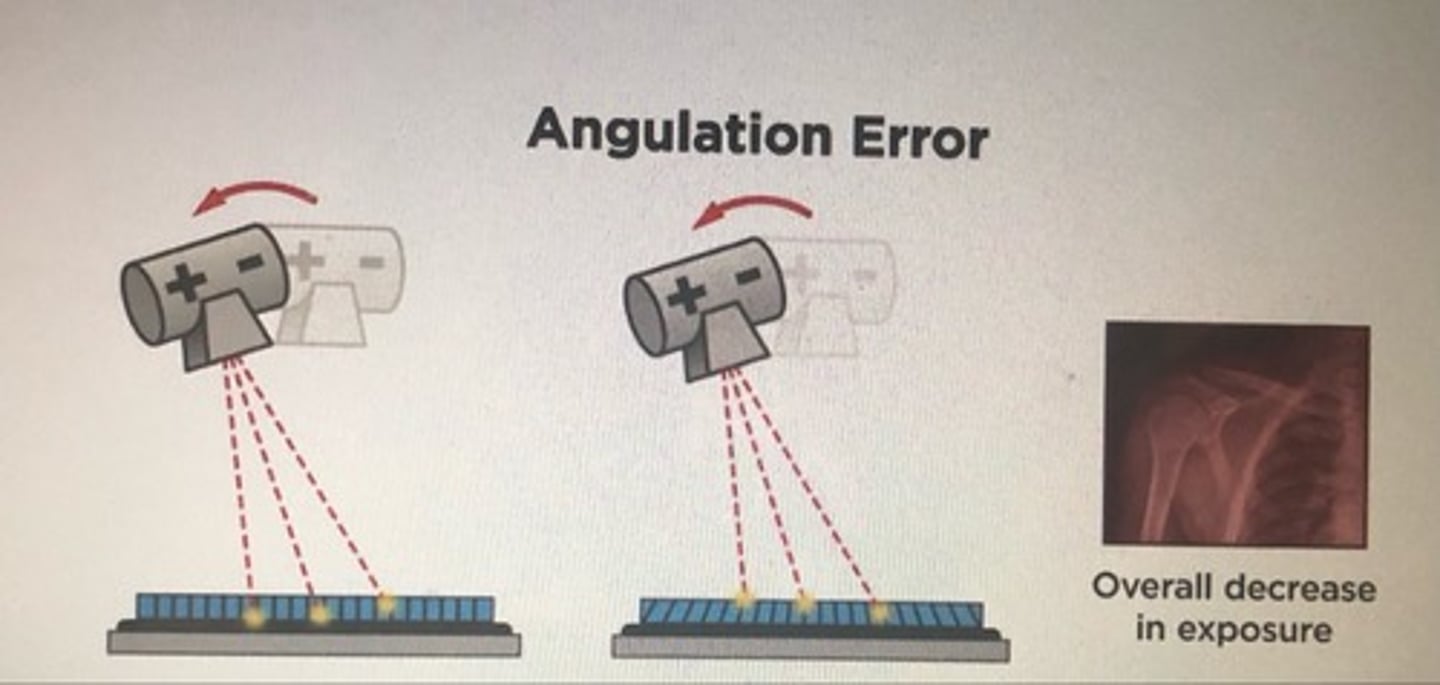
angulation grid error
overall lowering of receptor exposure over the entire image