Protein structure and function II
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
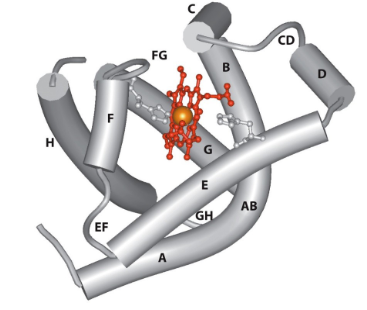
Myoglobin
A monomeric, globular protein in muscle which binds oxygen with high affinity
Haemoglobin
A tetrameric protein in red blood cells which transports oxygen
Bohr effect
An increase of H+ concentrations lowers the pH and CO2 concentration reduces the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen
Tissues with high metabolism produces CO2 and acids which requires oxygen
H+ and CO2 bind to haemoglobin and lowers oxygen affinity
Differences between myoglobin and haemoglobin
Myoglobin is a monomer
Myoglobin stores oxygen
Haemoglobin is a tetramer
Haemoglobin transports oxygen
Haemoglbin binds oxygen cooperativley
Binding of oxygen to haemoglobin can be regulated
Evolution of globin proteins
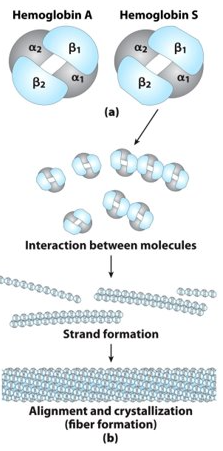
Sickle cell anaemia
Glu6—> Val in the beta chain of haemoglobin
The new valine side chain can bind to a different haemoglobin molecules to form a strand
This will sickle the red blood cell
The sickled blood cells clog small capillaries and impair blood flow because of the long haemoglobin fibres
This will result in painful swellings and a high risk of a stroke
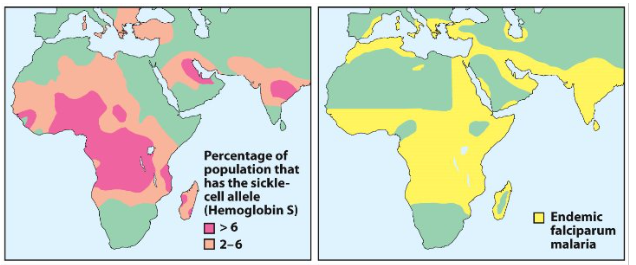
Sickle cell trait and malaria
Untreated homozygous individuals generally die in childhood
Heterozygous individuals exhibit a resistance to malaria
The parasite ‘plasmodium falciparum’ which causes malaria lives within red blood cells at one stage in its life cycle
Fibrous proteins
Provides strenght and flexibility
alpha-keratin is an essential component of hair, skin and feathers
Collagen is the most abundant protein found in mammels. It is am extracellular protein and is a main fibrous component of skin, bone, teeth, tendon and cartilage
What does collagen form
Forms a triple helix
The collagen helix is a unique secondary structure, distinct from the alpha-helix
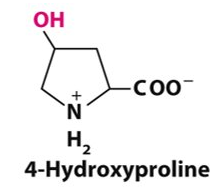
4-hydroxyproline
Contains a hydroxyl group
It is needed for the structure of collagen
Proline is converted to 4-hydroxyproline after collagen has been synthesized
The yellow dashes represent covalent bond forming between the alpha helix