TOPIC 4: Visualization
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
‼️ Based on Lecture Slides, DOES NOT INCLUDE VIDEO CONTENT YET
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Visible light
(Wavelength of Radiation)
___ ___ is part of a spectrum of electromagnetic radiation
Electrons
(Wavelength of Radiation)
___ are charged particles and when moving, act as waves with wavelengths dependent on the voltage of electron beam
smaller wavelengths
(Wavelength of Radiation)
Radiation of ___ ___ results in enhanced microscopy
Magnification
Apparent increase in size of an object and indicated by number and an “x’ (i.e. 1000x)
Magnification
Results when a beam of radiation refracts as it passes through a lens
Brightfield
Darkfield
Phase Contrast
Types of Light Microscopy
Brightfield
(Type of Light Microscopy)
Background is illuminated
Most elementary form of microscope of illumination techniques
Derived from the fact that the specimen is dark and contrasted by the surrounding bright viewing field
Darkfield
(Type of Light Microscopy)
Specimen is made to appear light against a dark background
Phase Contrast
(Type of Light Microscopy)
Use the alignment or misalignment of light waves to achieve the desired contrast between a living specimen and its background
Resolution
This is the ability to distinguish between objects that are close together
(1) wavelength
(2) numerical aperture
Resolution distance is dependent on:
the (1) ___ of the light or electron beam
(2) ___ ___ of the lens
Contrast
Refers to the differences in intensity between two objects or between an object and its background
Stains
What is used to achieve contrast?
Fluorescent Microscopy
Uses invisible UV light to cause specimens to radiate visible light
Fluorochroming
Immunofluorescence or Fluorescent Antibody Technique (FAT)
Categories of Fluorescent Microscopy
Fluorochroming
(Category of Fluorescent Microscopy)
Direct chemical interaction occurs between the fluorescent dye or fluorophore and a component of the bacterial cell
Immunofluorescence or Fluorescent Antibody Technique (FAT)
(Category of Fluorescent Microscopy)
In which an antibody is attached to the dye
Electron Microscopy
Uses a beam of electron instead of light to see the structure of the bacteria
Transmission (TEM)
Scanning (SEM)
Types of Electron Microscopy
Transmission (TEM)
(Type of Electron Microscopy)
Can resolve particles with 0.001 micrometer in size
E.g., x-ray
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
(Type of Electron Microscopy)
Scans a focused electron beam over the surface to create an image - can be in a 3D view
Direct Wet Mount Preparation
Hanging Drop Preparation
Intravital Staining
Techniques in Visualization for Unstained, Living State
Direct Wet Mount Preparation
(Techniques in Visualization for Unstained, Living State)
Used for the examination of motile protozoa and trophozoites
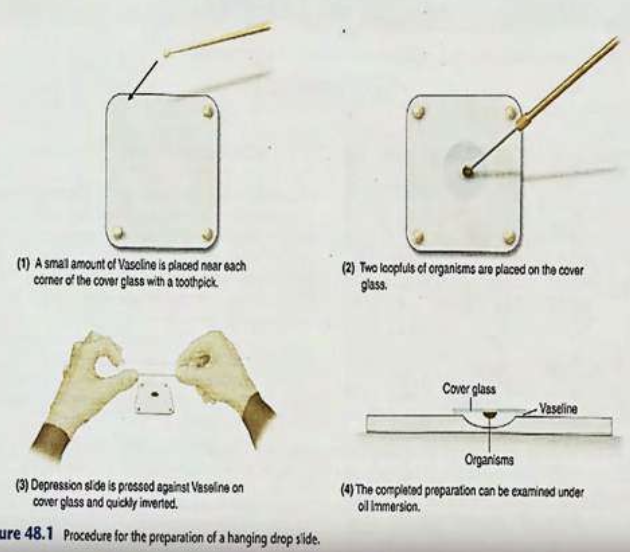
Hanging Drop Preparation
(Techniques in Visualization for Unstained, Living State)
Using concave slides
Intravital Staining
(Techniques in Visualization for Unstained, Living State)
Combination of both direct wet mount preparation and hanging drop preparation
Non-toxic dye is introduced to a microorganism and selectively stains certain cells and tissues
Smear Preparation
Air Drying
Fixation
Techniques in Visualization for Fixed, Stained State
Smear Preparation
(Techniques in Visualization for Fixed, Stained State)
Use a clean glass slide
Air Drying
(Techniques in Visualization for Fixed, Stained State)
Used to preserve the morphology of the organism
Fixation
(Techniques in Visualization for Fixed, Stained State)
Either heat (pass sample 3-5 times under flame) or chemical (immerse in ethanol)
Ethanol
What substance is used for Chemical Fixation?
Simple
Positive Staining
Negative Staining
Differential
Special
Types of Staining
Simple Staining
(Type of Staining)
Using only one dye
Positive Simple Staining
(Type of Staining)
Bacteria is stained but not the background
E.g. Dilute Carbol Fuchsin
Negative/Relief Staining
(Type of Staining)
Background is stained but not the bacteria
E.g. India Ink Method
Differential Staining
(Type of Staining)
Uses 2 dyes
E.g. gram staining and acid-fast staining
Special Staining
(Type of Staining)
Used for structures that are difficult to visualize under ordinary stain
E.g. spores or capsules or metachromatic granules
Gram Staining
(Staining Reaction)
Differentiates bacteria into two groups
Staining procedure discovered by Danish scientist Hans Christian Joachim Gram (1884)
Hans Christian Joachim Gram
Discovered Gram Staining
All cocci are gram (+) except the Neisseria Group, Moraxella (formerly Branhamella) catarrhalis (and Veillonella)
What bacteria are Gram (+)?
All bacilli are gram (-) except the ACID FAST ORGANISMS (Mycobacterium, Nocardia), SPOREFORMERS (Bacillus, Clostridium), and Corynebacterium species
What bacteria are Gram (-)?
Hocker’s Method
What is the method of Gram Staining used?
Make a smear
Flood smear with crystal violet
Wash with tap water
Cover the slide with gram’s iodine
Wash with tap water
Now forming a Crystal Violet Iodine (CVI) complex
Decolorize with absolute alcohol or mixture of acetone and alcohol
Wash with tap water
Flood the slide with safranin for 30 secs
Wash with tap water
Blot dry and examine stain smear under OIO
Steps in Gram Staining (Hocker’s Method)
Crystal Violet
What is the primary stain in Gram Staining?
Mordant
What is the term for the substance that enhances the color of the primary stain?
Gram’s Iodine
What is the substance that acts as the mordant?
Crystal Violet Iodine (CVI) Complex
What is formed upon the addition of Gram’s Iodine?
Absolute alcohol or mixture of acetone & alcohol
What is used to decolorize in Gram staining?
Safranin
What is the counterstain used in Gram Staining?
Oil Immersion Objective
What lens is used to examine the sample in Gram Staining & Acid Fast Staining?
Purple
What color does Gram (+) bacteria ultimately stain?
Pink
What color does Gram (-) bacteria ultimately stain?
Differential Stain
What can a gram stain be called since it differentiates between gram (+) and (-) bacteria?
Magnesium Ribonucleate
What substance is only found in gram (+) cells, which helps (+) bacteria retain the primary dye?
(1) cell wall integrity
(2) old age
(3) autolytic enzymes
Gram (+) cells stain (-) due to the loss of (1) ___ ___ ___ because of (2) ___ ___ or action of (3) ___ ___
(1) 50-90
(2) mycolic
Acid Fast Stain depends on long chain ((1)___-___ C atoms) fatty ((2)____) acids
France Ziehl & Fredrik Neelsen
Who modified the Acid Fast stain by adding phenol or carbolic acid and basic fuchsin?
Ziehl-Neelsen
What is the name of the Acid Fast stain that uses heat?
Cold Kinyoun
What is another variation of acid-fast staining that unlike the Ziehl-Neelsen, it does not require heating so the concentration of carbol fuchsin is increased?
Steps in Acid Fast Staining
Carbol Fuchsin
What is the primary stain in Acid Fast Stain?
Acid Alcohol (i.e., Sulfuric Acid)
What is the decolorizer in the Acid Fast Stain?
Methylene Blue
What is the counterstain in the Acid Fast Stain?
Red
What color does an acid fast bacteria exhibit?
Blue
What color does a nonacid fast bacteria exhibit?