AP Human Geography Unit 4 MCQ
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
4.1~ State
Definition; needs defined boundaries, Permanent Population, Sovereignty over domestic and international Affairs, recognized by other states
Nation
Definition; A group of people who have certain things in common~ EX; Hawaiians, Navajo, Catalonia, Basque
Nation-State
Definition; A national group whose borders are nearly identical to the ones of the state in which they reside within~ EX; Slovenia, Italy, Japan
Stateless Nation
Definition; A national group spread throughout 2 or more countries (is NOT a MAJORITY in any country)~ EX; Kurds and Rohingya
Multinational State
Definition; A country with two or more national groups within it's borders~ EX; Ukraine, US, UK, Russia, Canada, Indonesia
Multi-State Nation
Definition; A notional group spread throughout two or more countries (IS the MAJORITY in more than one country) Korea, Germany, Austria
Autonomous Region
Definition; An Area within a State that has a high degree of self Gov and Freedom Typically an Exclave- some regions can be semi Autonomous where they still have more self government then usual but are still mainly controlled by a main country. EX; China (Hong Kong), Nunavut, Greenland, Tibet
Irredentism
Definition; The claim to a section of land because it has "Cultural Value" But really its just for more land~ EX; Ukraine and Russia, Italy
Ethnic Enclave
Definition; A small area occupied but a minority and is SURROUNDED by a majority group~ EX; Lesotho, Vatican city, San Marino
Ethnic Exclave
Definition; A small area occupied but a group that has been SEPARATED from the larger group and is surrounded by another group~ EX; Kaliningrad
4.2~ Prior to 1800's
City-states, empires, Kingdoms, small land areas, are controlled by nobles (People higher in social class)
Nation-State Building
Began in the 1800's in Europe it is done to break up the land into smaller sections and allow each cultural group to have there own way of ruling, there are many countries in Europe because of this.
Imperialism vs. Colonialism
includes a variety of ways of influencing another country or group of people (conquering, economic control, cultural dominance) vs type of imperialism in which people from your home land and settle into another country (Like Texas with the missionaries). Very few colonies left in the world today, but can be identified because they are controlled by another power, and are islands/coastal locations & have a small population.
World War I
Astro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires Collapsed European borders completely redrawn.
World War II
This is the start of the first major refugee crisis, European colonies around the world begin gaining much independence, soviet union and US gain geopolitical power beginning of the cold war.
Independence Movements
Many Colonies gained independence politically but not economically (Neocolonialism- countries are independent but other countries are influencing the new independent countries) so although many countries had self determination (Choose your own political status) they were still being controlled by other countries
Ethnic Cleansing vs Genocide
An ethnic cleansing is not considered a crime under international law, a genocide is a crime
Devolution
In a multi-national states, the transfer of power from the central government to subnational levels of government mostly following regional lines to give more nationalities the power to rule themselves. Mainly centrifugal, but can be good like in the UK
4.3~ Neocolonialism
The continued economic & political dominance of former colonial powers over their former colonies or other countries in the developing world, can be done through Economic dependency, Cultural Domination, Political.
Territoriality
Willingness by a group of people to defend space they claim, Influencing other states, Asserting control over a space~ EX; South China Sea competing territorial Claims, Sunni Saudi Arabia Vs. Shina Iran, Religious and Ethnic Rivals
Shatterbelts
A region with a strategic location, diverse history + groups of people, possibly explicit, stronger outside powers competing to control the area~ EX; The Balkans, Middle East, The Caucasus, Southeast Asia, Ukraine, Turkey Syria and Iraq
Choke Points
They Are strategic narrow passages that connect to larger areas to one another~ EX; Panama Canal, Strait of Gibraltar, Suez Canal, Straits of Hormuz, Bab el-Mandeb
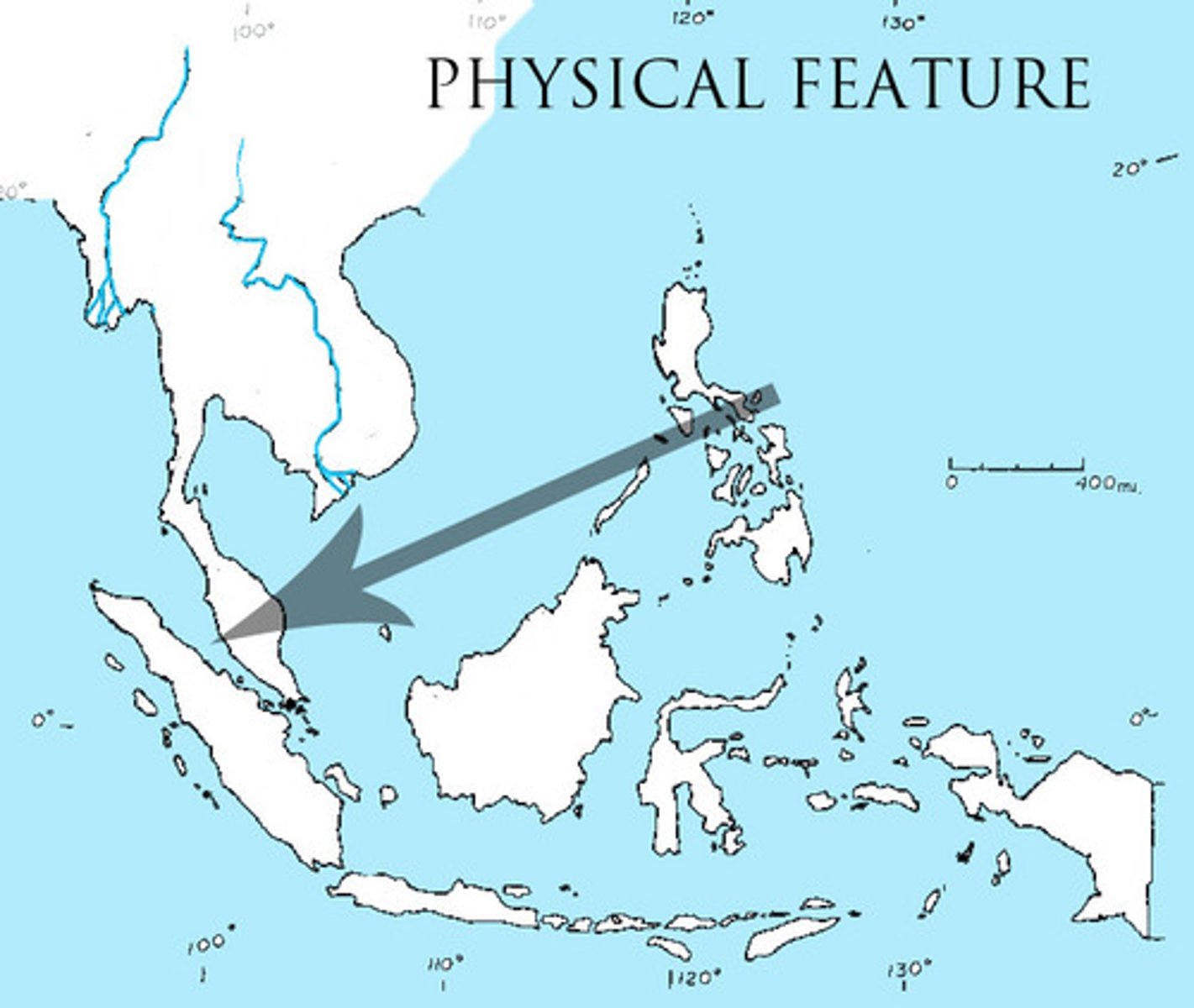
Strait of Malacca
Importance; 25% aka a quarter of all traded goods go through this strait
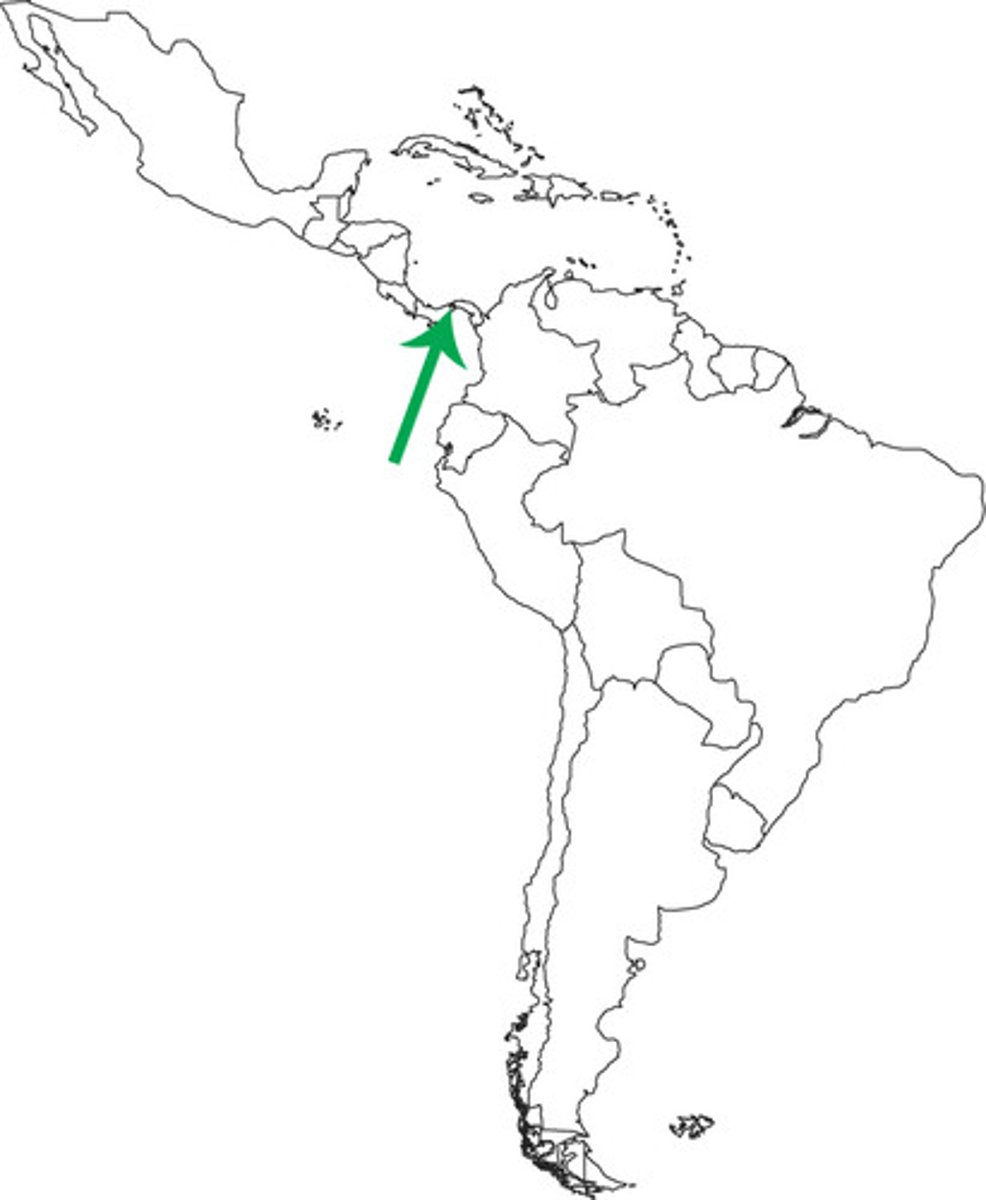
Panama Canal
Importance; connects east and west coast of the US, a lot of agricultural goods go through this Canal
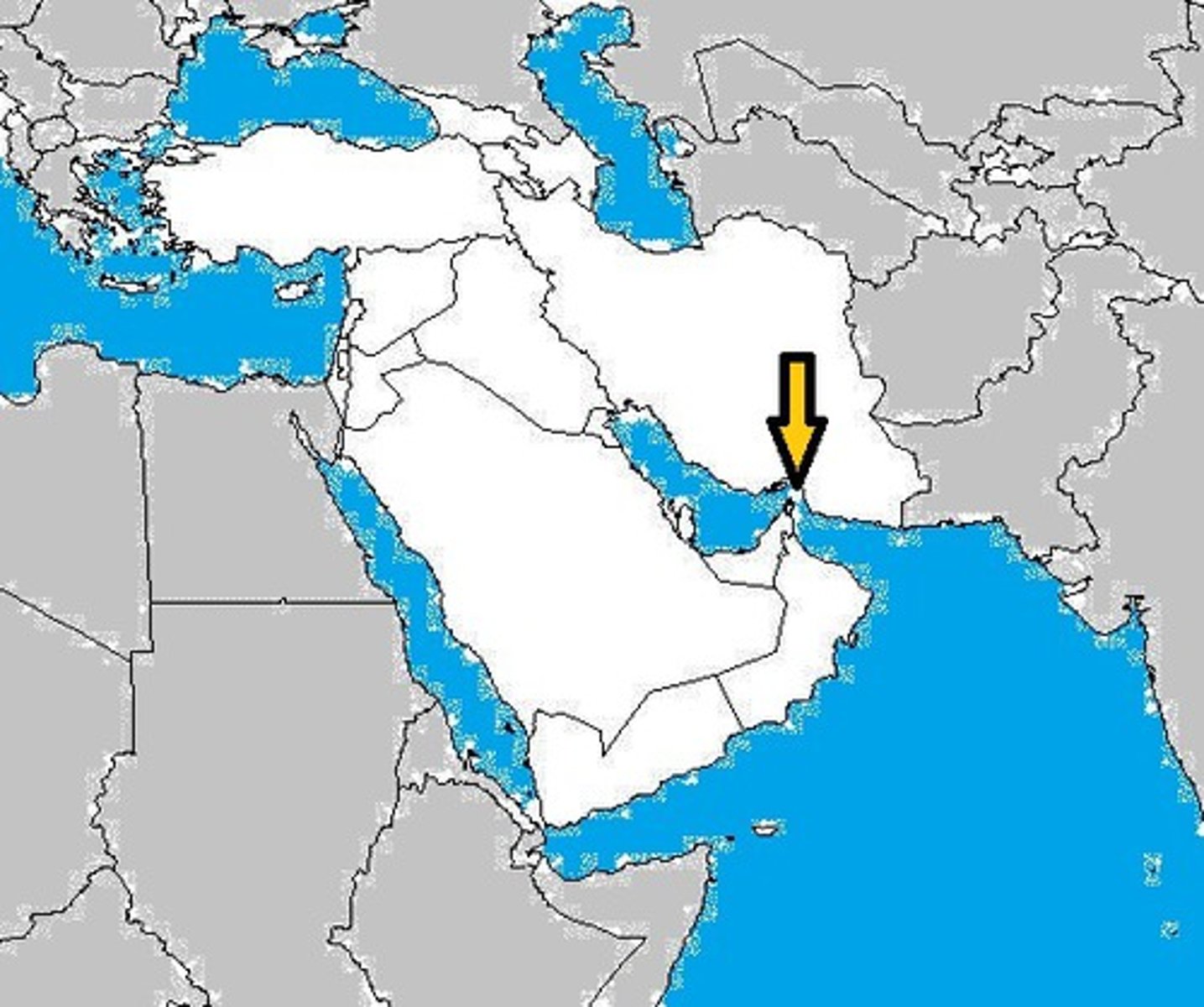
Strait of Hormuz
Importance; Worlds most important Oil Choke point
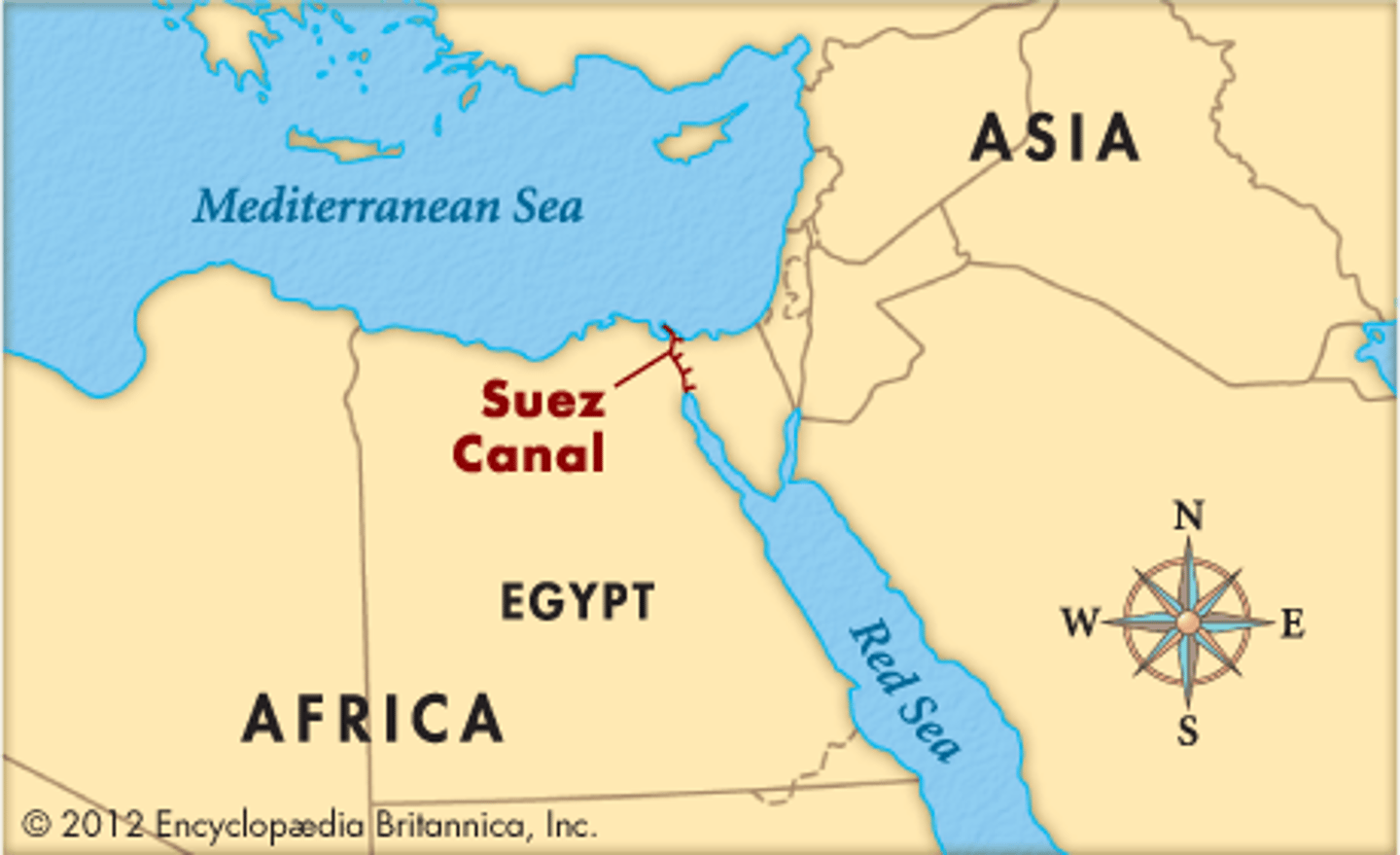
Suez Canal
Importance; $9 billion worth of goods goes through this canal every day (52 ships a day)
Strait of Lawrence Seaway
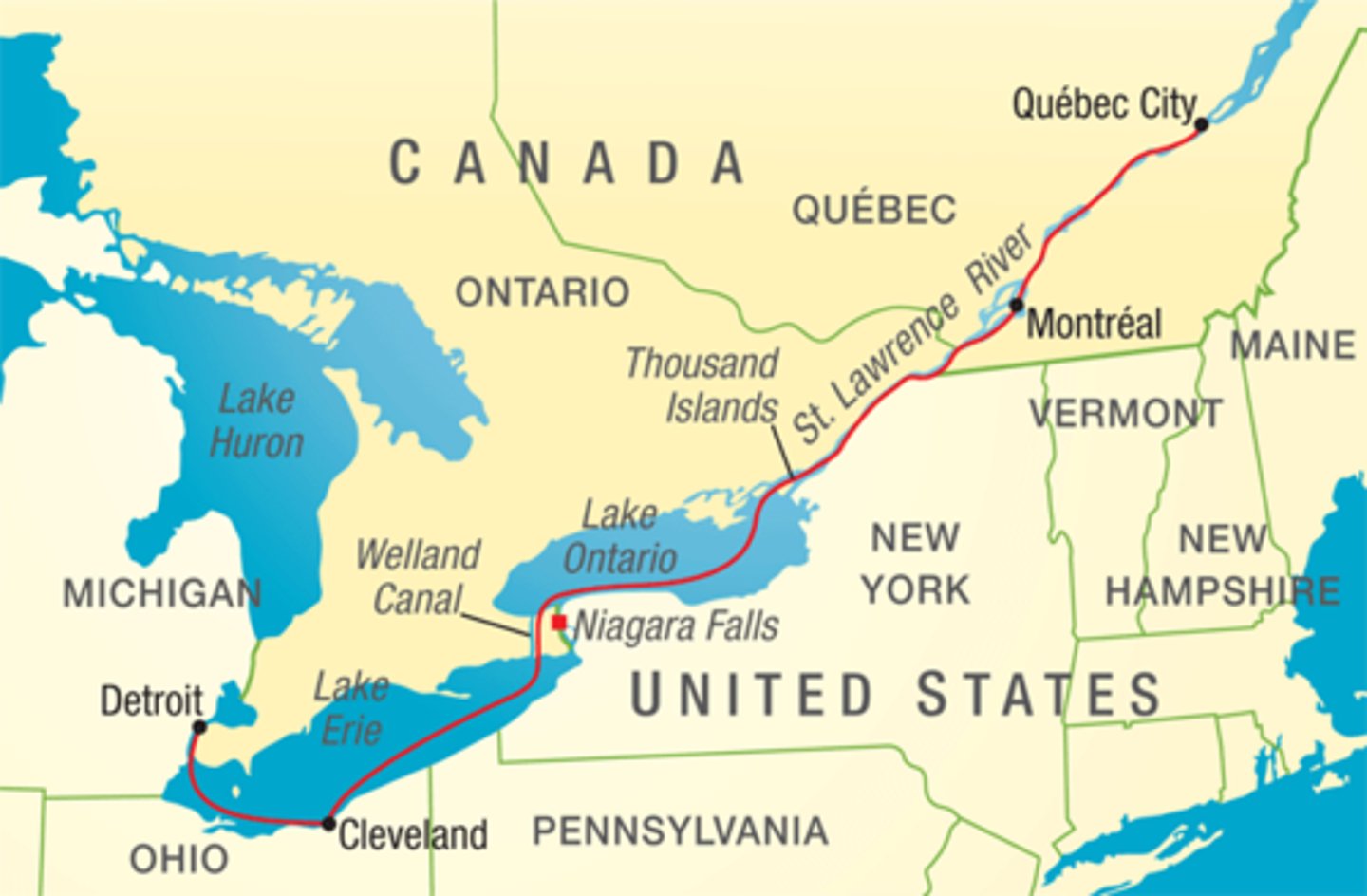
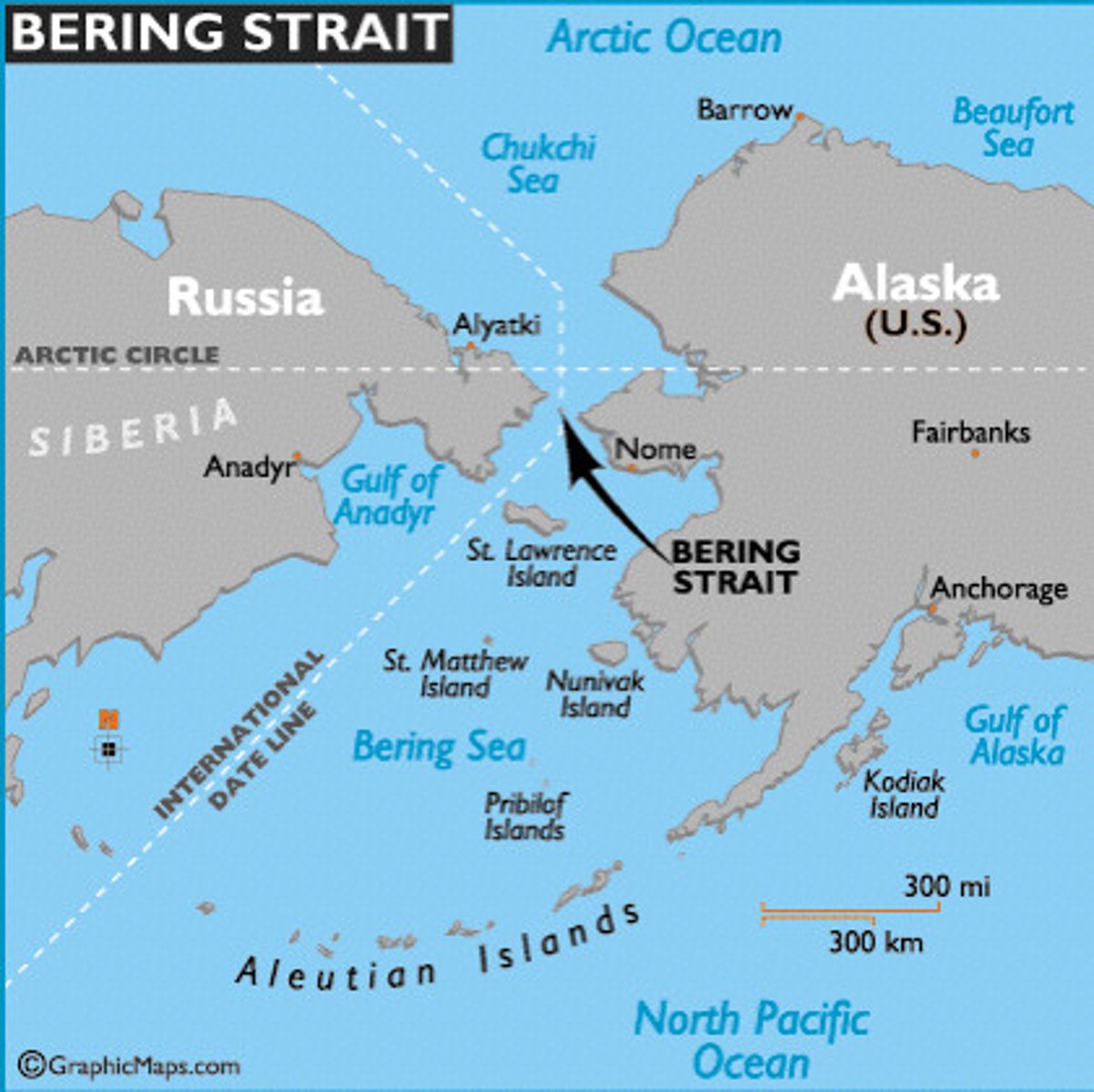
Bering Strait
English Channel
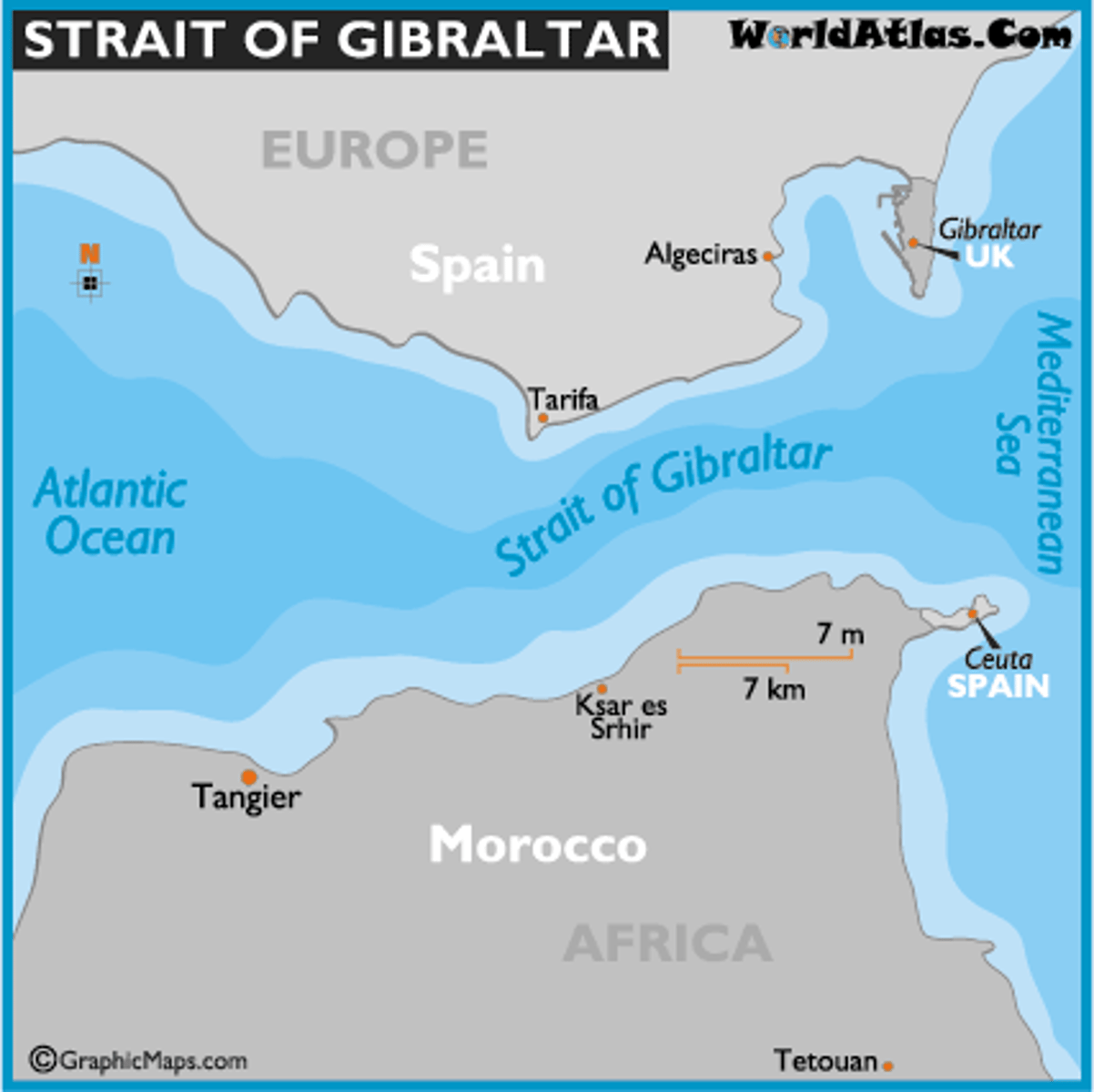
Strait of Gibraltar
Bab el-Mandeb
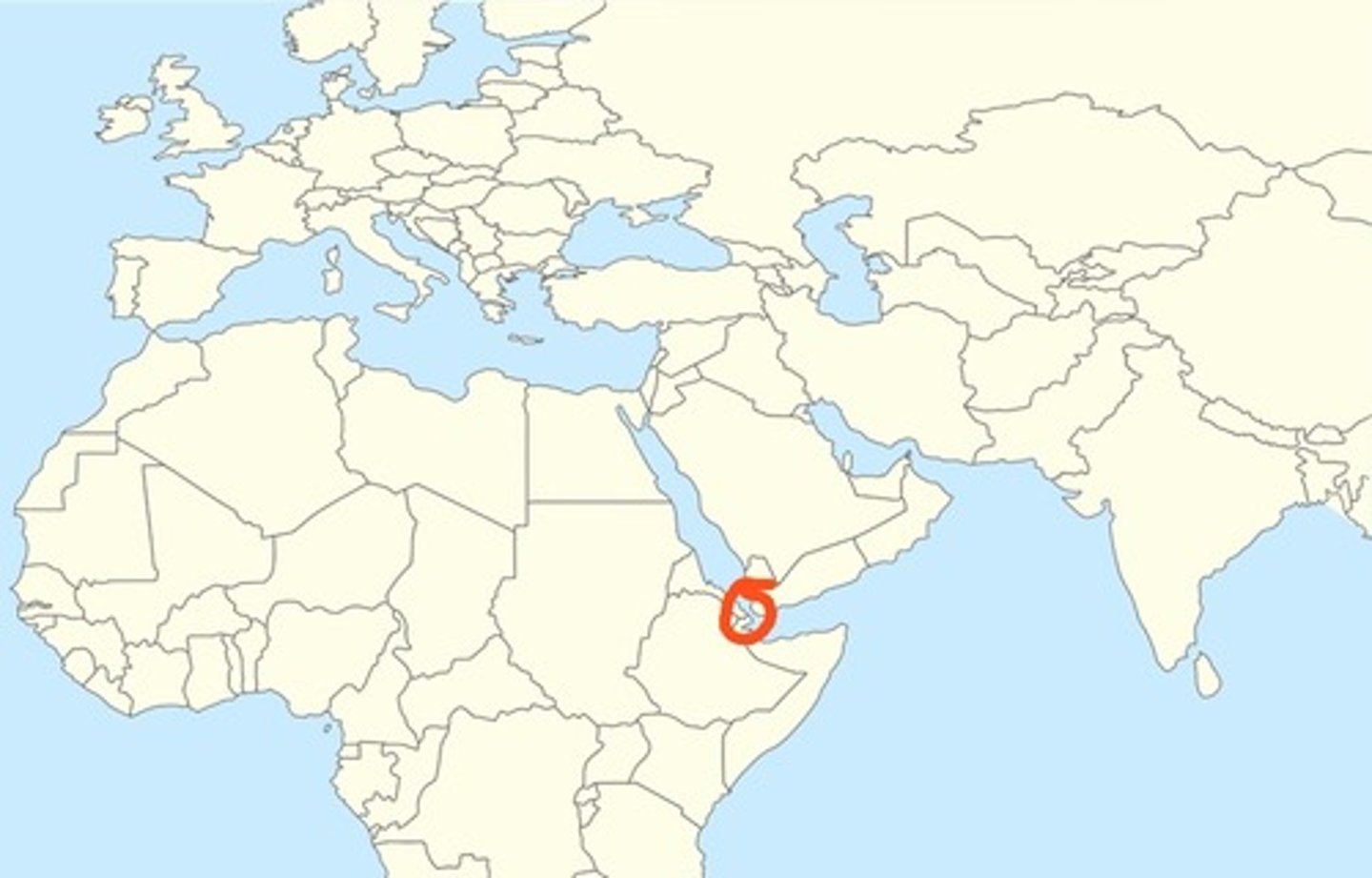
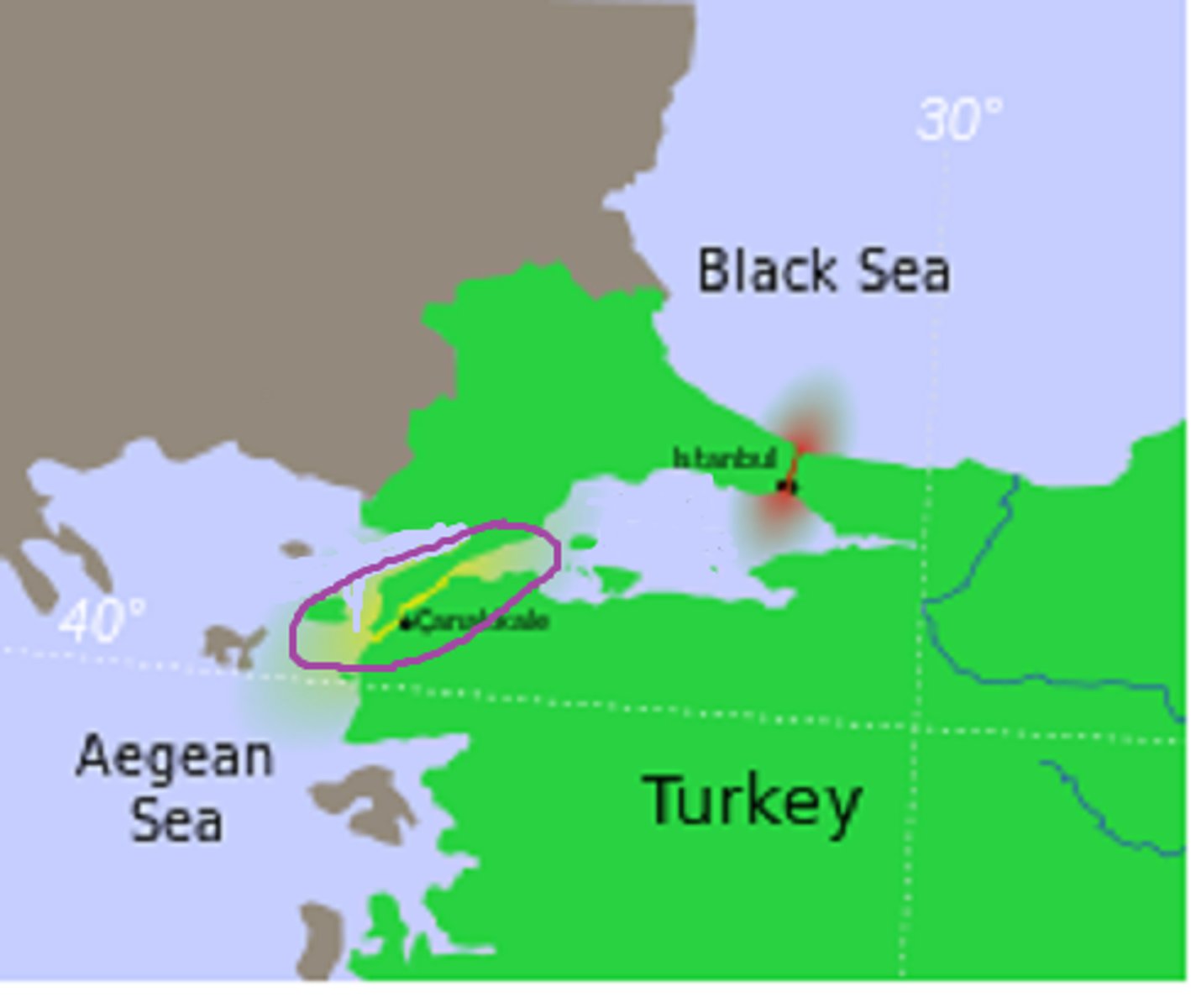
Bosporus Strait
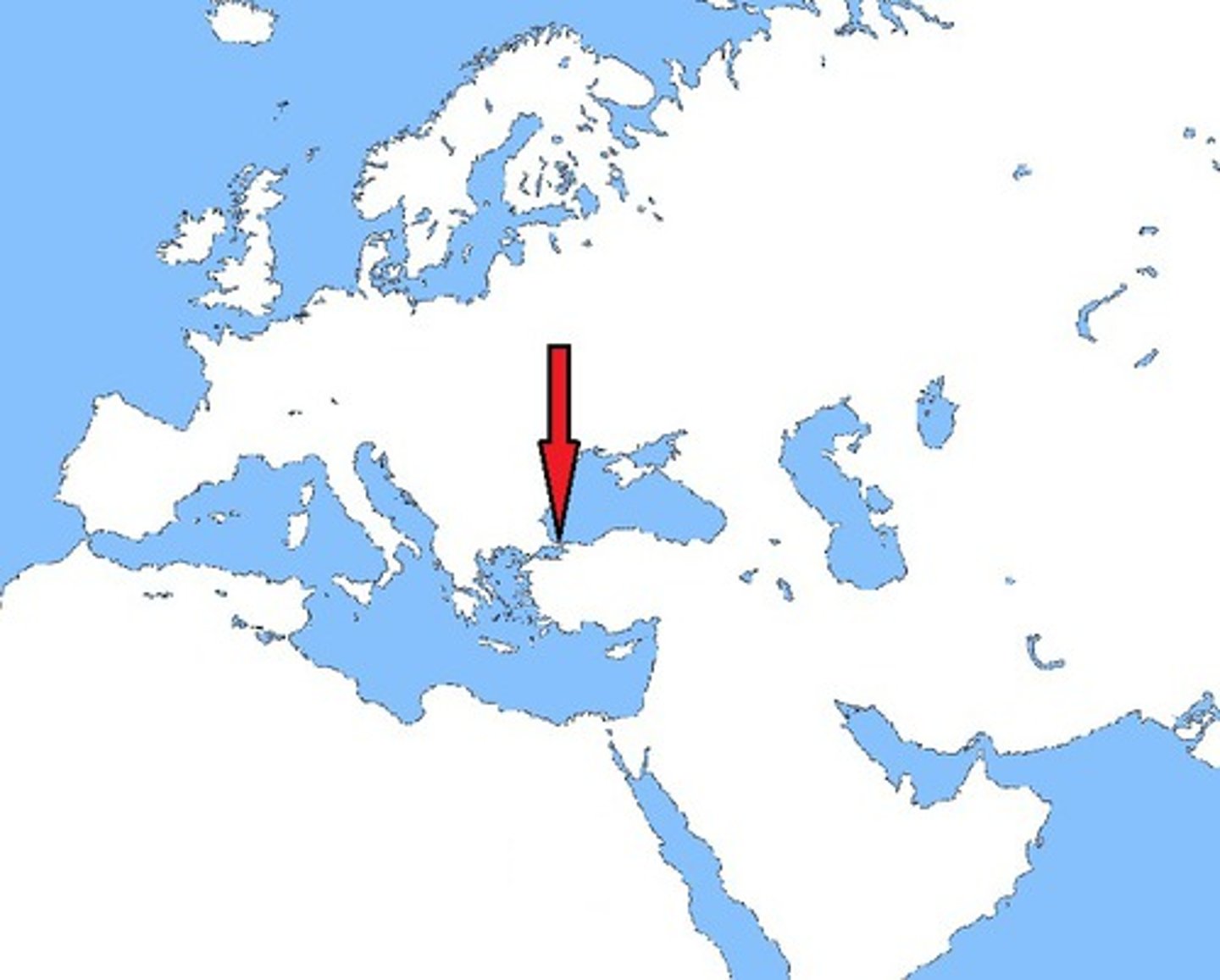
Dardanelles Strait
(The circled one)
4.4/4.5~ Define
First step of boundary process~ establish by a legal document (Treaty), Invisible land
Delimit
Second step of boundary process~ Line drawn on a map
Demarcate
Third step of boundary process~ Identified by physical objects on the landscape EX- Signs, Fences, walls
Administer
Final step of boundary process~ Boundary is enforced
Geometric
Type of boundary~ Strait line boundary, EX; US/ Canada border, many African borders
Physical aka Natural boundary
Type of boundary~ River, crest of a mountain range, or some other physical landmark
Cultural aka Conquest boundary
Type of Boundary~ Language and religion lines sometimes used as a boundary, EX; India/ Pakistan border, Ireland and Northern Ireland border
Antecedent
Evolution Boundaries~ Decided Before an area is largely Populated, EX; Birtish/America and US/Canada
Subsequent
Evolution Boundaries~ Drawn to accommodate for religious, ethnic, linguistic, or economic differences, EX; China/ Vietnam Border
Superimposed
Evolution Boundaries~ Drawn by outside powers, EX; Indonesia/ Papua New Guinea, North/ South Korea, Africa
4.6 Voting Districts
Internal Boundaries hat divide a country's electorate into subnational regions (Aka splitting the stat into smaller sections)
Gerrymandering
giving one political party an advantage over the other can be done by packing-drawing district lines to intentionally pack the opposing sides together or by Cracking- Breaking apart districts into smaller regions.
Redistricting
Redrawing district boundaries so that each district contains roughly the same number of people. Redistricting occurs every 10 years in the United States after the Census to account for population increases and decreases. State legislatures or state committees are in charge of redrawing boundaries- whichever political party is in control tries to redraw boundaries to their benefit.
Reapportionment
Changing the number of representatives granted to each US state so it reflects the state's population
4.7 Federal-Authority of government
Shared between the central government and provincial, state, and local governments (SHARED POWER)
Federal- Hierarchy of Power
Multiple levels of power; power diffused throughout the hierarchy
Federal- type of Country where it is commonly used
Multiple ethnic groups with significant minorities
Federal- Positive Consequences
Power is divided between the government and state and local governments, Power Diversity, Power may be diffused, State or Provincial Governments have some degree of self-rule and have their own legislatures, abuse of power is prevented
Federal- Negative Consequences
Change can come slowly, conflicts between different levels/different areas occur
Federal- Examples
US, Canada, Russia, Australia, Brazil, Sudan + South Sudan, India,
Multi National States
Unitary- Authority of the Government
Held primarily by the central government with very little power given to local governments
Hierarchy of Power
No hierarchy of sovereign powers
Unitary- Type of Country Where Commonly Used
Few cultural differences and small minorities
Unitary- Positive Consequences
National Identity Promoted, Laws are standardized, Efficient
Unitary- Negative Consequence
Very little power diffused, one person holds power, not everyone is represented
Unitary- Examples
Lesotho, Spain, China, Greenland, Denmark, Sweden, Indonesia,
Nation-States
4.8~Devolution
it is- Movement of power form the central government to regional governments within the state
What can cause it- Ethnocultural forces, Economic Forces, Spatial
devolution vs Federal Gov- The devolution could be temporary and reversible, more rights and protection in a federal form of government, could still ne unitary.
EX; Devolution of the soviet union
50 years a Bi-Polar World of Cold War arms race & danger of nuclear war, In 1980s centrifugal forces increased: multi-nationalism & economic troubles, 11/09/1989 the Iron Curtain collapsed, the Berlin Wall was opened, 15 republics became 15 independent states consisting of five groups - Centrifugal
EX; Devolution in Spain
Spain-Basque and Catalonia in 1979 signed autonomy agreements, have their own parliaments, languages have official status, control over education, power of taxation, Basques unsatisfied and continued terrorist attacks, Catalonia Found this Autonomy lovely and wants independence because they have the means to do so and find the money they gain is not giving back to them through taxes.- Centrifugal
EX; Devolution in Nigeria
Religious and Economical differences in the North and South of Nigeria, capital moved to the middle as a more fair location to show the government didn't lean one way or another this is called a forward capital .
EX; Devolution in Italy
Italy-Mezzorgiono (region of the south is poor & agrarian) There is a growing disparity between the industrial North & agricultural South,
Sardinia feels neglected by the mainland, Italy has moved to a federal system due to pressure by the north, Economic divide - Centrifugal
EX; Devolution in Greenland
Greenland is apart of Denmark but is a very autonomous region this is due to spatial, different history, languages, culture reasons- Centripetal because the autonomy allows for space to feel independent but still feel safe by being apart of another country
EX's; Spatial Devolutionary movements- Cultural forces
Quebec and Patri Quebecois in Canada, Belgium-Flemish (Dutch) in north, Walloons (French) in south, Czechoslovakia split in Jan. 1993 in the “Velvet Divorce”, Sudan-Muslim north & Christian south, Sri Lanka-Tamils, a Hindu minority fight for independence from the Sinhalese a Buddhist majority, Hawaii- spatial, taken by force, culture/ language differences, economic issues in Hawaii, history apart from the United States, and a desire to live apart in order to keep traditions alive
4.9~ Supranational Organizations
An international organization, or union, whereby member states transcend national boundaries or interests to share in the decision-making and vote on issues pertaining to the wider grouping.
Types of issues these Organizations address; Transnational and Environmental Challenges, create Economies of scale, Trade Agreements, and Military Alliances
UN ~ United Nations
Political Organization, The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights. The fifteen-member UN Security Council seeks to address threats to international security. Its five permanent members, chosen in the wake of World War II, have veto power. Members ~ 193 total, main UN are in Security council specifically the permanent 5 aka China, France, Russia, UK, US
NATO ~ North Atlantic Treaty Organization
Military Alliance consisting of 32 members- Albania, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Turkey, UK, US
EU ~ European Union
Economic Union between 27 countries, One single market without borders- People, goods, services, and money can move freely, Euro Currency, Removal of border controls between EU countries- Citizen can more easily work, live, and travel abroad Members~ Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden
ASEAN ~ Association of Southeast Asian Nations
Addresses Economic, Security and Political Issues - The bloc’s biggest success has been promoting economic integration among members. - It also helped negotiate the RCEP agreement to create one of the world’s largest free trade blocs. - ASEAN has struggled to form a cohesive response to China’s claims in the South China Sea, which conflict with those of several members. Members~ Myanmar, Laos, Philippines, Vietnam, Brunel (Darussalam), Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Cambodia, Thailand
Arctic Council
Environmental Forum ~ 3 important legally binding agreements among the eight Arctic States, Agreement on Cooperation on Aeronautical and Maritime search and rescue in the Arctic (2011), Agreement on Cooperation on Marine Oil Pollution Preparedness and Response in the Arctic (2013), Agreement on Enhancing International Arctic Scientific Cooperation (2017) Members~ Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden, US
African Union
Political Cooperation & Economic Development~ All 55 countries on the continent of Africa are Members, Main Goals: To promote the unity and Solidarity of the African States; To coordinate and intensify their cooperation and efforts to achieve a better life for the peoples of Africa, To defend their sovereignty, their territorial integrity and independence; To eradicate all forms of colonialism from Africa; To promote international cooperation having due regard to the Charter of the United Nations and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
4.10 ~ Centripetal forces
are things that bind or hold a nation together & promote national unity; Strong leadership, charismatic leader, External threat (can be centrifugal), Education, Ideology, Fascism, Communism or Democracy
Centrifugal forces
are things that divide or tear a state apart; Ethnic or cultural differences (can be centripetal), Religious differences, Linguistic diversity, Economic disparity, Physical geographical differences
Centripetal forces can lead too...
Ethnonationalism, Equitable Infrastructure Development, Increased Cultural Cohesion
Centrifugal forces can lead too...
Failed States (Fragile States), Uneven Development, Stateless Nations, Ethnic Nationalist Movements