Hematopoiesis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/163
Last updated 9:41 PM on 1/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
1
New cards
G6PD enzyme deficiency
Which of the following can lead to shortened RBC survival?
2
New cards
T
T/F Epinephrine can cause an increased production of EPO
3
New cards
F
T/F Aplastic anemia can cause anemia secondary to increase in RBC destruction
4
New cards
folic acid
Which of the following deficiency can result in a macrocytic type of anemia?
5
New cards
Erythroblastosis fetalis
A condition that cause the mother’s white blood cell to attack the fetus red blood cell usually as result of Rh incompatibility
6
New cards
T
T/F Androgen can cause an increased production of EPO.
7
New cards
T
T/F Thalassemia can cause anemia secondary to increase in RBC destruction
8
New cards
Bone marrow
During the third trimester of pregnancy, where is the predominant site of RBC production?
9
New cards
oxygen
Which of the following is the most important regulator of red cell production?
10
New cards
T
T/F Norepinephrine can cause an increase production of EPO
11
New cards
F
T/F Estrogen can cause an increase production of EPO
12
New cards
yolk sac
What is the major site of erythropoiesis during the **3rd week** gestation
13
New cards
F
T/F Iron deficiency anemia can cause anemia secondary to increase in RBC destruction
14
New cards
F
T/F Thalassemia can cause anemia secondary to increase in RBC production
15
New cards
T
T/F Hypoxia can cause an increase production of EPO
16
New cards
G6PD enzyme deficiency
Which of the following can lead to shortened RBC survival?
17
New cards
Embden-Meyerhof Pathway (Glycolytic Pathway)
What pathway in the RBC accounts for 90% of glycolysis to generate ATP?
18
New cards
Vitamin B12
Which of the following deficiency can result in a macrocytic type of anemia?
19
New cards
blood
Opaque, red liquid consisting of cells suspended in a complex amber fluid called **plasma**
20
New cards
6-8%
blood accounts for what % of the total body weight in a healthy individual
21
New cards
5-6 L
approximate volume of blood in males
22
New cards
4\.5-5 L
approximate volume of blood in females
23
New cards
thrombocytes
Deficiency in this cellular component will result in **bleeding**
24
New cards
plasma
Liquid upper part of the anticoagulated blood – dilute solution of salts, glucose, amino acids, vitamins, urea, proteins, and fats
25
New cards
albumin
Most abundant plasma protein that is important in maintaining **oncotic pressure;** Produced by the **liver**
26
New cards
A
VR: albumin and oncotic pressure
27
New cards
Alpha and beta globulins
transport lipids and fat-soluble vitamins
28
New cards
Gamma globulins
has Antibodies necessary for immune defense
29
New cards
liver
Alpha and beta globulins are produced in the
30
New cards
lymphoid tissues
Gamma globulins are produced in the
31
New cards
fibrinogen
Large molecules synthesized in liver that are important in clotting
32
New cards
cholesterol
Building block for certain hormones
33
New cards
Triglycerides
Transfer of food-derived energy into cells
34
New cards
glucose
Primary source of energy for the body cells and RBCs
35
New cards
serum
Liquid portion left after clotted or coagulated blood is removed out; without fibrinogen and clotting factors
36
New cards
erythrocytes
Major function is to transport hemoglobin which carries oxygen from lungs to tissues
37
New cards
carbonic anhydrase
* Catalyzes reversible reaction between CO2 and water to form **carbonic acid**
* maintains good pH in the blood and homeostasis
* maintains good pH in the blood and homeostasis
38
New cards
7\.8 micrometers
mean diameter of RBCs
39
New cards
2\.5 micrometers
thickness of RBC at the periphery (thickest point)
40
New cards
1 micrometer or less
thickness of RBC at the center
41
New cards
Biconcave shape
Provides RBCs with maximum surface area and minimum diffusion distance in proportion to volume
42
New cards
\~4 months
lifespan of RBCs
43
New cards
1%
what % of body’s erythrocytes that is destroyed and replaced everyday
44
New cards
T
T/F RBCs lack of nuclei, mitochondria or ER for protein synthesis
45
New cards
34g of Hgb/100mL of RBC
metabolic limit of the cell’s hemoglobin-forming mechanism
46
New cards
average of 15g of Hgb/100mL of RBC
normal hemoglobin value in men
47
New cards
average of 14g of Hgb/100mL of RBC
normal hemoglobin value in women
48
New cards
1\.34 mL
Each gram of pure hemoglobin is capable of combining with much of oxygen?
49
New cards
erythropoiesis
Process by which RBCs are made
50
New cards
Hematopoiesis
Process in which human marrow makes approximately
**10^10** new blood cells, the bulk of them mature erythrocytes
**10^10** new blood cells, the bulk of them mature erythrocytes
51
New cards
yolk sac
Main site of hematopoiesis in 2-4 weeks age of gestation
(AOG)
(AOG)
52
New cards
fetal liver
Main site of \~5 week AOG
53
New cards
bone marrow
Main site of >5th weeks AOG and after birth
54
New cards
sternum
One of the most common site to assess marrow activity
55
New cards
2nd and 3rd trimester
during this time of pregnancy, the main site of hematopoiesis will be **liver, spleen and bone marrow**
56
New cards
1st few months
during this time of pregnancy, there is formation of **mesenchyme**
57
New cards
bone marrow
During the later months of pregnancy this is the main site of hematopoiesis
58
New cards
B
VR: age and hematopoietic activity of bones
59
New cards
decrease
after birth, erythropoiesis will (inc or dec?)
60
New cards
* Erythropoietin
* Vitamin B12
* Folic Acid
* Iron
* Vitamin B12
* Folic Acid
* Iron
factors that influence the production of RBCs
61
New cards
pluripotent stem cell
Single type of cell from which all the cells of the circulating blood are eventually derived
62
New cards
long-term hematopoietic stem cell
Ability to **give rise to new stem cells**; cell renewal
63
New cards
short-term hematopoietic stem cell
Ability to differentiate into any one of the blood cell lines
64
New cards
* Natural Killer Cells (NK cells)
* B-cells
* T-cells
* B-cells
* T-cells
Common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) will give rise to:
65
New cards
* Eosinophil
* Mast cell
* Megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitor (MkEP)
* Granulocyte macrophage progenitor (GMP)
* Mast cell
* Megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitor (MkEP)
* Granulocyte macrophage progenitor (GMP)
Common myeloid progenitor (CMP) will give rise to:
66
New cards
RBCs and Megakaryocyte
Megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitor (MkEP) will give rise to:
67
New cards
Neutrophil and Macrophage
Granulocyte macrophage progenitor (GMP) will give rise to
68
New cards
hematopoietic growth factors
* Hormone-like inducers of growth and differentiation
* Produced by stromal cells of the microenvironment and by the hematopoietic stem cells
* Produced by stromal cells of the microenvironment and by the hematopoietic stem cells
69
New cards
EPO
Stimulates maturation of erythrocytes through the late BFU, CFU, and (pro) normoblasts
70
New cards
A
VR: EPO and reticulocytes
71
New cards
kidney
main organ producing EPO
72
New cards
B
VR: EPO and lung diseases
73
New cards
androgens
* Stimulates EPO production
* Directly induces differentiation of marrow stem
* Directly induces differentiation of marrow stem
74
New cards
Vitamin B12 and folic acid
required for the synthesis of the nucleotide base **thymidine triphosphate and THF**
75
New cards
thymidine triphosphate
essential in the formation of DNA and normal cell division produced by Vitamin B12 and folic acid
76
New cards
B
VR:
* Vit. B12 and folic acid
* immature cells
* Vit. B12 and folic acid
* immature cells
77
New cards
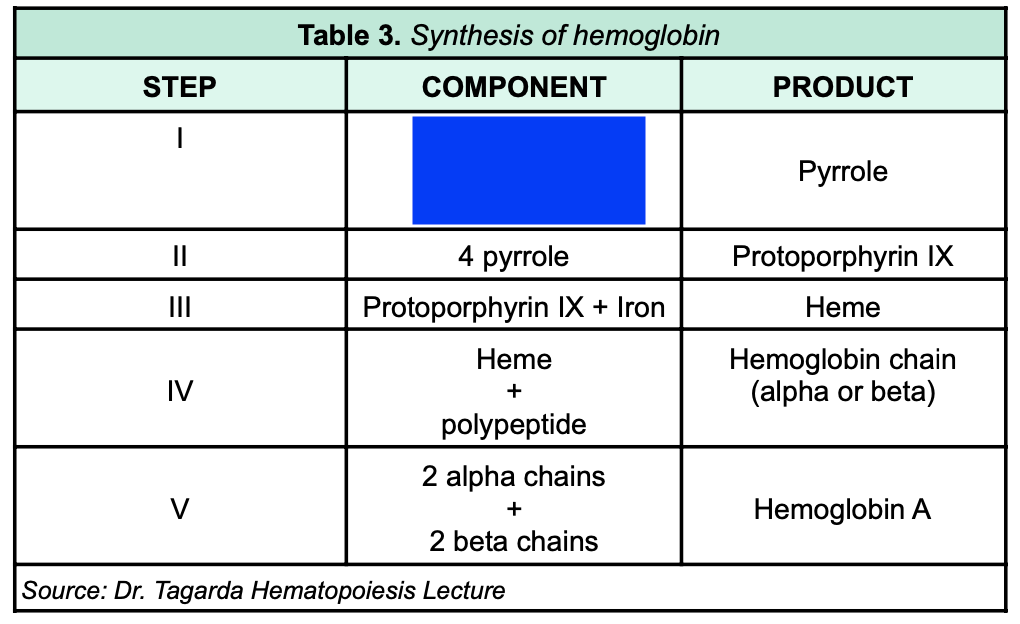
pyrrole
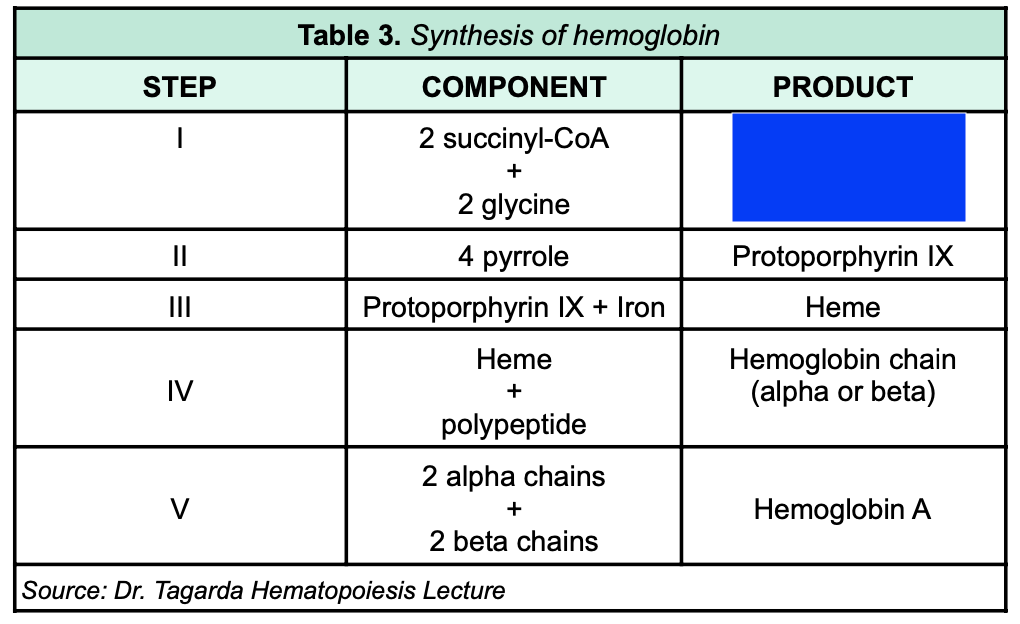
78
New cards
2 succinyl-CoA + 2 glycine
79
New cards
4 pyrrole
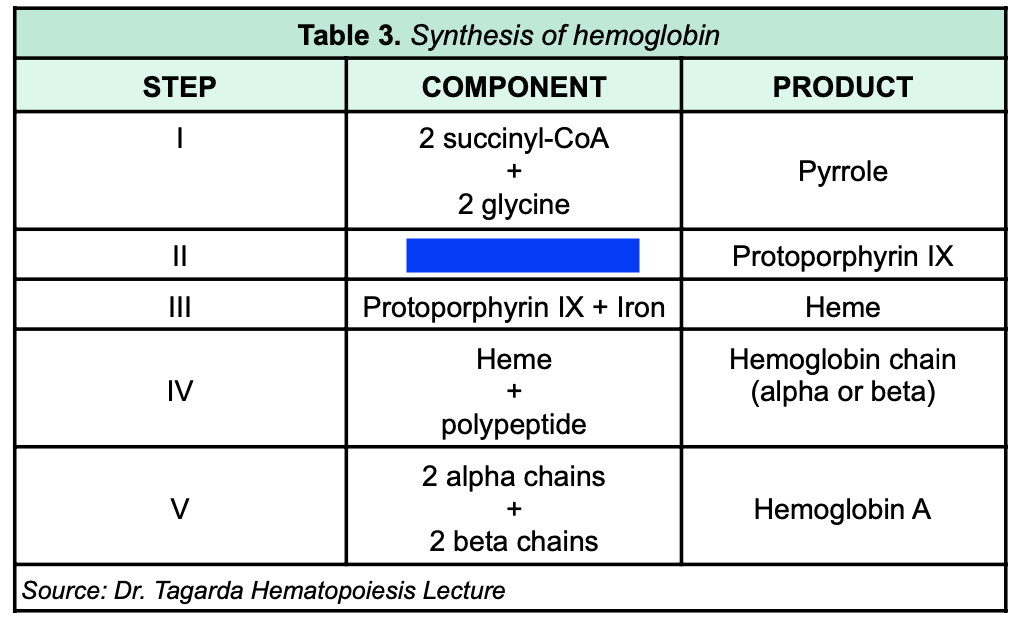
80
New cards
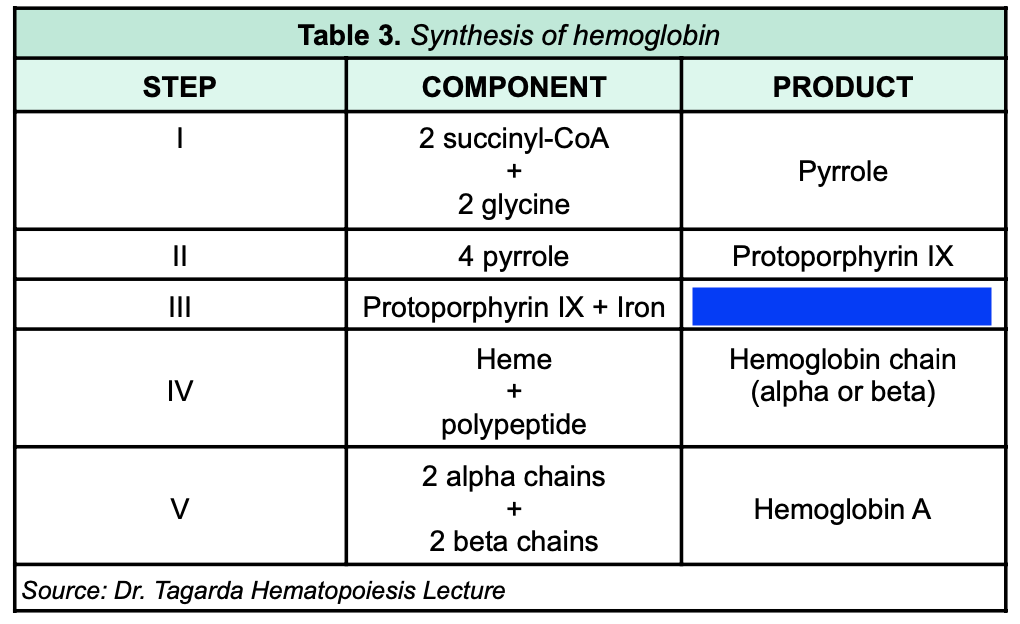
Protoporphyrin IX + Iron
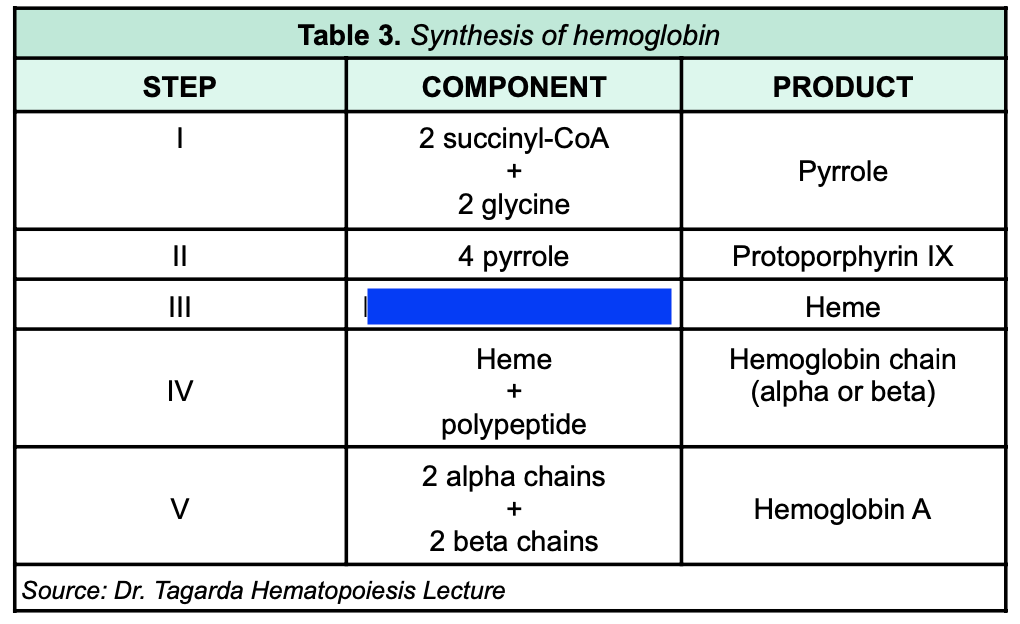
81
New cards
Heme + polypeptide
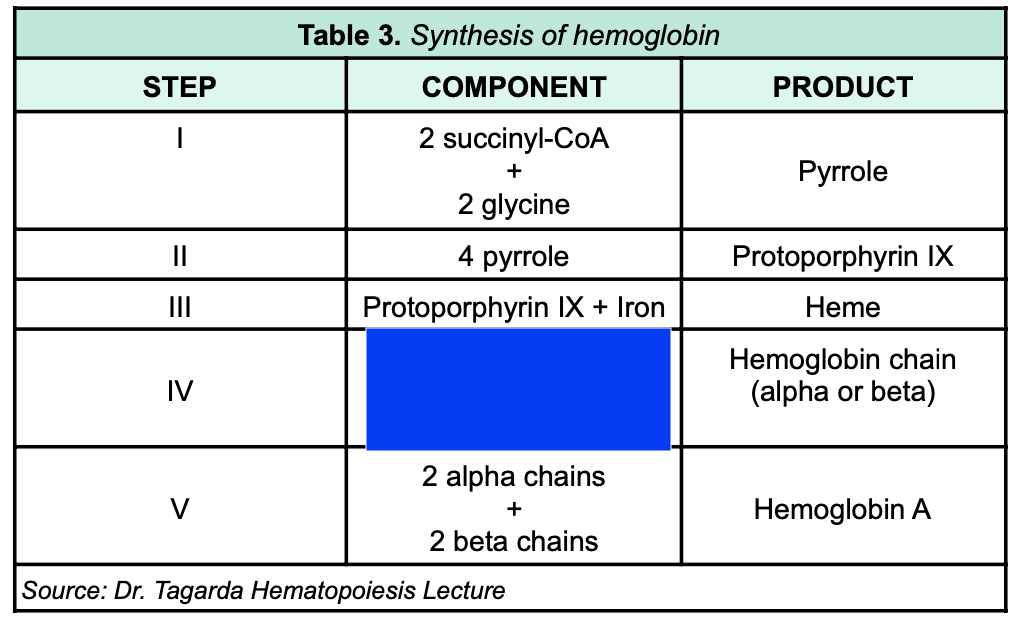
82
New cards
2 alpha chains + 2 beta chains
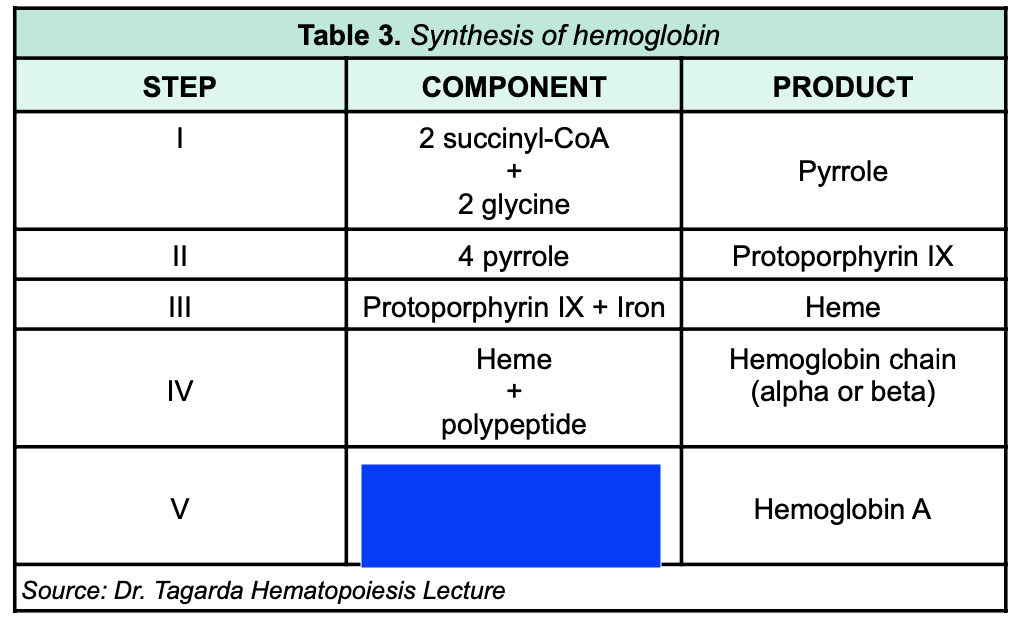
83
New cards
Protoporphyrin IX
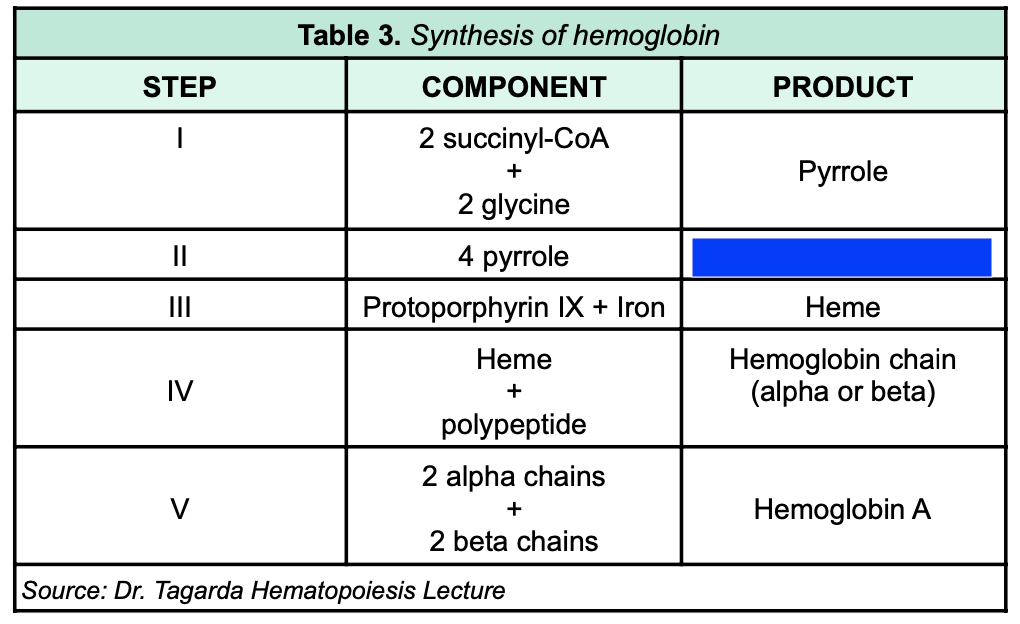
84
New cards
heme
85
New cards
Hemoglobin chain (alpha or beta)
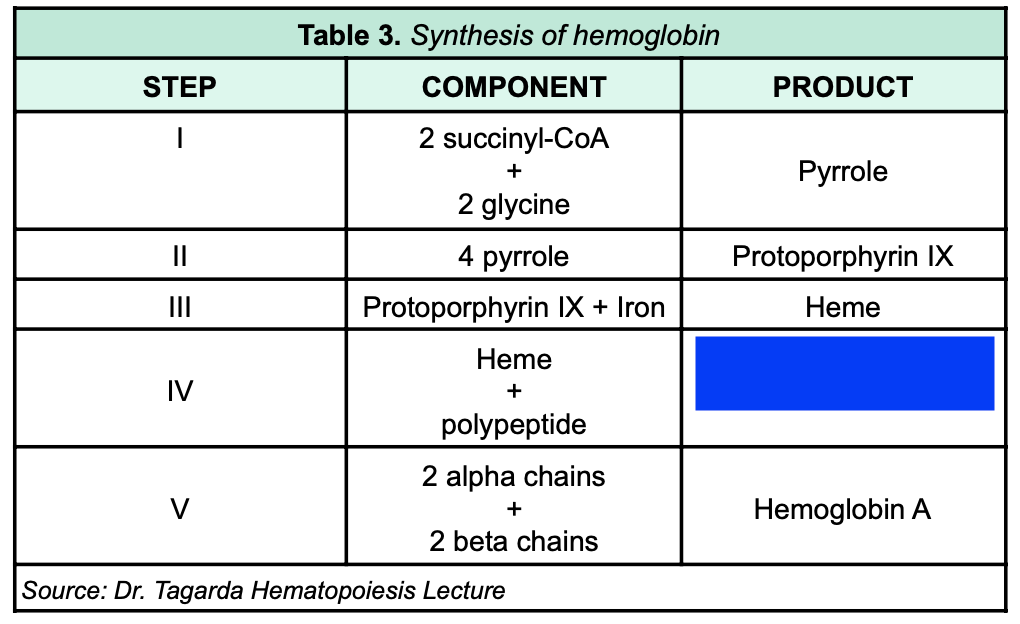
86
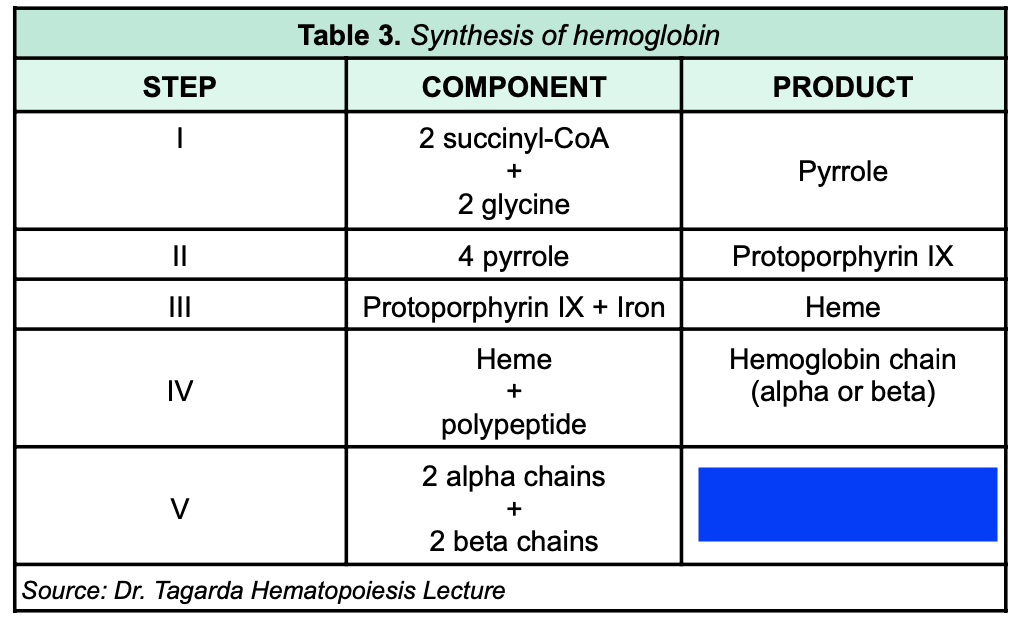
New cards
Hemoglobin A
87
New cards
structural forumla of Gower 1
2 epsilon + 2 zeta
88
New cards
2 alpha + 2 epsilon
structural forumla of Gower 2
89
New cards
2 gamma + 2 zeta
structural forumla of Portland
90
New cards
2 alpha + 2 gamma
structural forumla of Hb-F
91
New cards
2 alpha + 2 beta
structural forumla of Hb-A
92
New cards
2 alpha + 2 delta
structural forumla of Hb-A2
93
New cards
Hb-F
hemoglobin found in fetus
94
New cards
iron
element to which oxygen binds on a Hgb molecule
95
New cards
Transferrin
iron bound to apotransferrin; responsible for transporting iron to different parts of the body
96
New cards
Ferritin and Hemosiderin
Transferrin that attaches to the tissues becomes and is stored as
97
New cards
old/degraded RBC
primary source of iron in the body
98
New cards
lipids
45% of the RBC membrane is composed of
99
New cards
proteins
55% of the RBC membrane is composed of _____ that are important to **maintain the structure** of the RBC
100
New cards
Phospholipids and unesterified cholesterol
predominant lipid in RBC membrane