science 8 finals :scream:
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
1
New cards
compound
a mix of chemicals that can only be broken down by chemical changes
2
New cards
matter
anything that has mass and volume (takes up space)
3
New cards
physical property
a quality that can be observed without changing chemical identity
4
New cards
chemical property
a quality that can only be observed when changing chemical identity, ability of matter to react with another substance to form a new substance(s)
5
New cards
physical change
a change of matter that does not change the chemical identity
6
New cards
chemical change
change of matter that produces a new substance(s)
7
New cards
difference between a change and a property
a property is a quality, a change is a change idk
8
New cards
density
d = m/v (mass/volume)
9
New cards
three main states of matter
solid, liquid, gas
10
New cards
atoms in a liquid sate
they slip and slide past each other
11
New cards
what happens to liquid particles as it changes to a gas
the atoms gain more energy and they move faster and farther apart
12
New cards
what happens to liquid particles as it changes to a solid
the atoms lose energy and move slower and closer together
13
New cards
units to measure density
g/ml or g/cm^3
14
New cards
sublimation
when solid turns to gas
15
New cards
what does KMT state
all matter has energy and all matter is constantly in motion
16
New cards
what matter is made of
atoms
17
New cards
subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, electrons
18
New cards
where are neutrons
in the nucleus
19
New cards
where are protons
in the nucleus
20
New cards
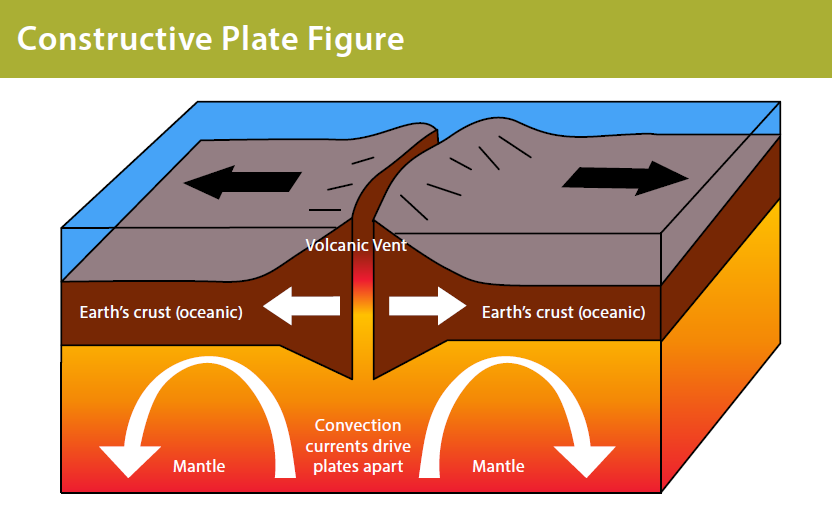
where are electrons
in the energy shells, surrounding the nucleus
21
New cards
what charge does a neutron have
none/neutral
22
New cards
what charge does a proton have
positive
23
New cards
what charge does an electron have
negative
24
New cards

what does the 8 signify
it’s the atomic number, it represents how many protons there are in that element
25
New cards

what does the O signify
it’s the atomic symbol
26
New cards

what does the 15.999 signify
the atomic mass, which is # of protons + # of neutrons
27
New cards

how many protons, electrons, and neutrons are there in a neutral neon atom
10 protons, 10 electrons, 10 neutrons
28
New cards
mixture
a mix of things that can be separated by physical changes
29
New cards
element
a pure substance that cannot be broken down anymore (just trust me bro)
30
New cards
period
a row on the periodic table of elements that have the same number of electron shells
31
New cards
group/family
a column on the periodic table of elements that all have the same number of electrons on the outermost shell
32
New cards
alkali metals
group 1 on the periodic table
33
New cards
alkaline earth metals
group 2 on the periodic table
34
New cards
halogens
group 17 on the periodic table
35
New cards
nobel gasses
group 18 on the periodic table, and they are the most stable because they have full shells
36
New cards
emr
electromagnetic radiation, light energy
37
New cards
emr spectrum (lowest to highest frequency)
radio waves, micro waves, infrared, visible light, uv rays, x-ray, gamma rays
38
New cards
hertz/frequency
cycle per second, each time the wave passes through the rest position
39
New cards
ray model
shadow model, shows light travels in a straight line and cant bend around objects
40
New cards
wave model
light shining through gaps and making a pattern, shows that light spreads out with wave-like properties
41
New cards
particle model
photons hitting metal, electrons only being given off at certain frequencies shows that light has to interact in packets of certain amounts of energy
42
New cards
ionizing
waves that have the ability to detach electrons from atoms and giving them a charge, exposure can cause tissue and organ damage
43
New cards
reflection
light bounces off something
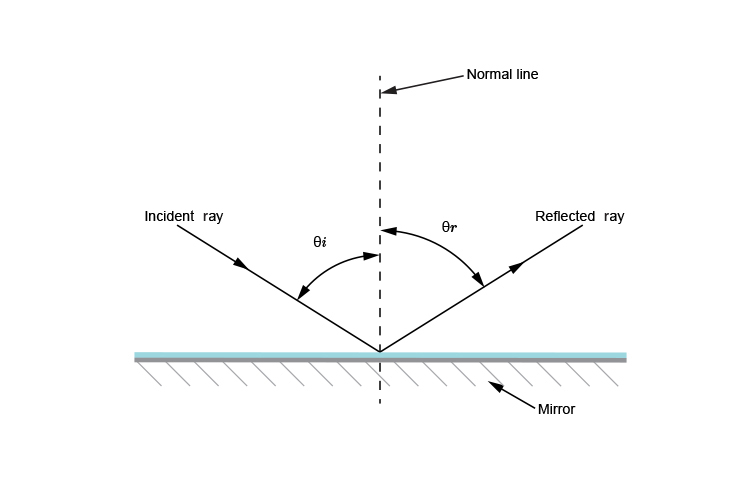
44
New cards
absorption
light energy is trapped
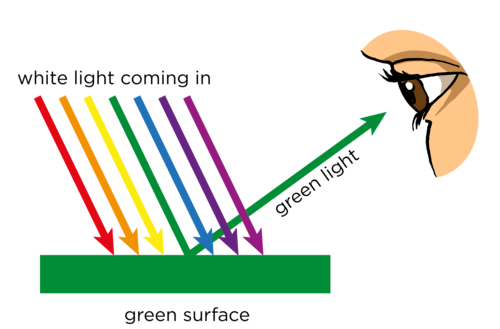
45
New cards
transmission
light passes through
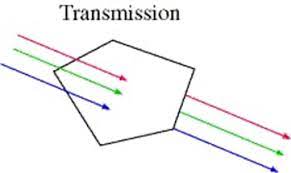
46
New cards
refraction
path of light bends and speed of light changes (light bends towards the normal when moving into denser media and vice versa)
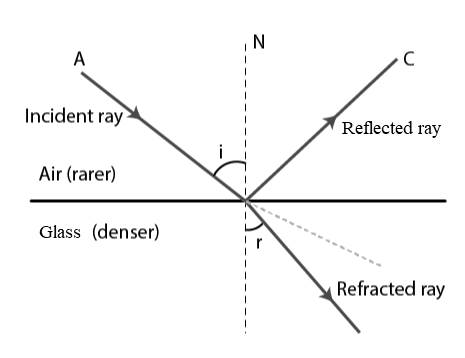
47
New cards
media/medium
matter that light interacts with
48
New cards
opaque
no light is transmitted, light is either reflected or absorbed
49
New cards
translucent
some light is transmitted and scattered, some light is absorbed or reflected
50
New cards
transparent
all light is transmitted, a small amount of light is scattered
51
New cards
plane mirror reflection
same distance, same size, upright, virtual
52
New cards
concave mirror reflection close to fp
farther, larger, inverted, real
53
New cards
concave mirror reflection far from fp
closer, smaller, inverted, real
54
New cards
concave mirror reflection in between mirror & fp
farther, larger, upright, virtual
55
New cards
convex mirror reflection
closer, smaller, upright, virtual
56
New cards
rainbow formation
white light enters the raindrop and refracts, then reflects off the back of the raindrop where it starts to break into colors, then refracts more as light leaves the raindrop and splits fully
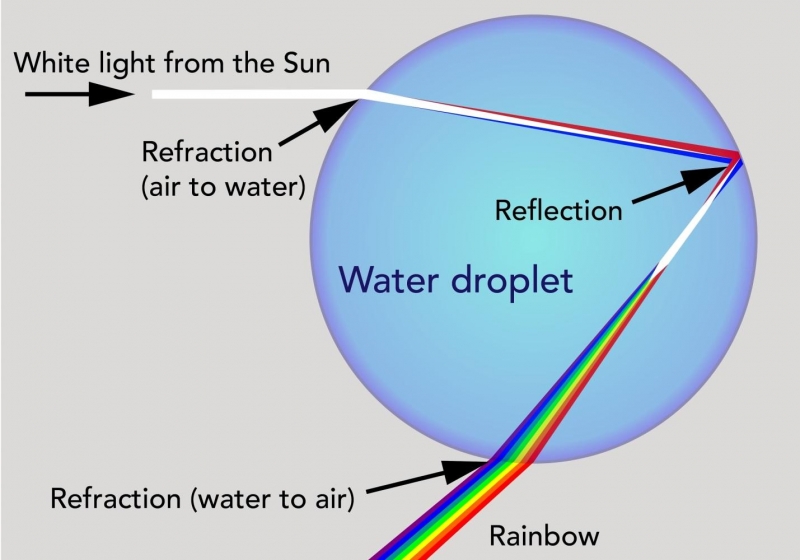
57
New cards
mirage formation
on a really hot day, air splits into layers by heat, with hot air closer to the ground. light refracts more and more at each hotter layer and eventually doesnt touch the ground and travels in a u shape until it hits our eyes. our eyes cant comprehend light bending so we see an image on the ground instead of the ground.
58
New cards
converging lens
has at least one convex surface, is thicker in the center, used to correct hyperopia
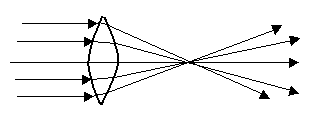
59
New cards
diverging lens
has at least one concave surface, is thinner in the center, used to correct myopia
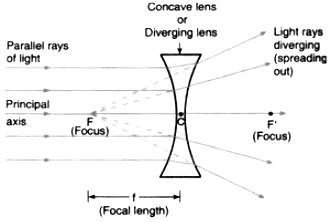
60
New cards
myopia
nearsightedness, caused by long eyeball or curved cornea, can be treated by diverging lens or laser eye surgery
61
New cards
hyperopia
farsightedness, caused by short eyeball or flat cornea, can be treated by converging lens or laser eye surgery
62
New cards
pupil
black part of eyeball on the outside that takes the light into the eye
63
New cards
iris
colored circle of muscle, controls the amount of light entering the eye
64
New cards
cornea
clear film that covers the eye
65
New cards
sclera
the white of the eye
66
New cards
lens
convex lens inside eye that focuses light to the retina
67
New cards
retina
film on the back of the eye where an image is formed
68
New cards
ciliary muscles
controls the shape of the lens to adjust to distance
69
New cards
optic nerve
sends the image formed at the retina to the brain
70
New cards
vitreous humor
clear gell that fills the inside of the eyeball and gives it shape
71
New cards
cataracts
protein buildup in the lens that causes cloudy vision or loss of vision, can only be treated with surgery
72
New cards
astigmatism
elongated cornea, causes images to be blurry at all distances, can be treated by glasses, contact lenses, or laser eye surgery
73
New cards
continental drift hypothesis
theory proposed by alfred wegener that continents used to be connected because they were similar shapes, had similar fossils (ie fern fossils in all southern continents), similar mountains, and glacial striations/fossilized forests
74
New cards
alfred wegener
man who proposed continental drift hypothesis
75
New cards
pangaea
the supercontinent from 200 million years ago when all continents were connected
76
New cards
fixism
the theory that continents had always been where they were, widely regarded as fact until continental drift hypothesis
77
New cards
crust of earth
thin layer of solid rock surrounding the earth, has oceanic crust (made of basalt) and continental crust (made of granite). sometimes contains lithosphere
78
New cards
upper mantle
layer just below crust, very top of the upper mantle is solid and below is softer rock that can flow. contains lithosphere and asthenosphere
79
New cards
lower mantle
below upper mantle, made of denser rock
80
New cards
outer core
below lower mantle, made of iron and nickel, is liquid
81
New cards
inner core
center of the earth, below outer core, is made of iron and some nickel, temp >5000 degrees and is solid from the high pressure of above layers
82
New cards
mid ocean ridges
mountain ridges along the ocean floor, earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur
83
New cards
trenches
long, narrow valleys (depressions) in the ocean floor, can be thousands of km long and deep
84
New cards
sea floor spreading
the process of magma rising to the surface of ridges and forming new ocean crust. magma emerges in the center and pushes older crust to the sides and below other plates. explained how continents were able to move, because the rock and plates were moving beneath them.
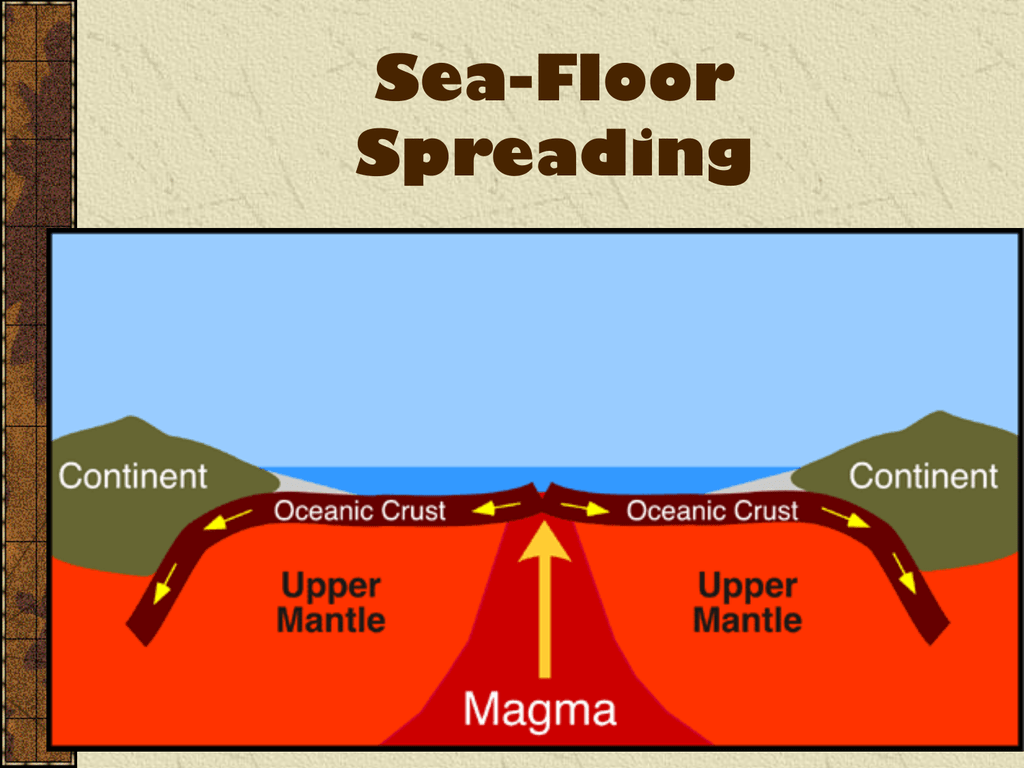
85
New cards
subduction
when denser crust goes below the less dense crust
86
New cards
theory of plate tectonics
earths crust is made of tectonic plates that float ont the fluid rock in the mantle. the plates move very slowly. it explains seafloor spreading/continental drift, earthquakes, volcanoes, and formations of mountains.
87
New cards
lithosphere
outer layer of solid rock and plates composed of crust and part of the upper mantle, when plates interact it causes geological activity
88
New cards
asthenosphere
the soft, flowy part of the upper mantle that is hot and behaves like plastic. this enables plates to move. tectonic plates float on top of it.
89
New cards
divergent plate boundaries
when tectonic plates separate and create new oceanic crust; can also occur in the middle of continents (continental rifting)
90
New cards
convergent plate boundaries
when two plates collide, subduction occurs and causes trenches, often induces earthquakes
91
New cards
oceanic-continental plate convergence
oceanic plate goes beneath continental plate; may form mountains or volcanoes (from the release of pressure from the upper mantle)
92
New cards
oceanic-oceanic plate convergence
subduction with ocean crust occurs, may form volcanic island arc and trenches
93
New cards
volcanic island arc
a belt of volcanoes that occur from plate oceanic plate convergence
94
New cards
continental-continental plate convergence
no subduction occurs, one plate is shoved beneath the edge of the other and creates mountain ranges as the crust goes upwards
95
New cards
transform plate boundaries
when two plates slide past each other; earthquakes are common
96
New cards
mantle convection
warmer, less dense material in the mantle rises as cooler, more dense material sinks; causes currents in the mantle and drags plates with it
97
New cards
ridge push
new material pushes older material aside, causing tectonic plates to move apart (ex. magma hardening in the crust causing plates to move), occurs at diverging plate boundaries; includes seafloor spreading, continental rifting, and new rock formations
98
New cards
slab pull
movement of plates downwards, occurs at converging plate boundaries where subduction may occur; responsible for mountains, volcanoes, earthquakes, and trenches
99
New cards
earthquakes
a natural movement or vibration when earth’s crust shifts. when pressure is applied on a plate too quicky or strongly, the rock will break in the form of an earthquake
100
New cards
focus
the point where the movement in the rock during an earthquake occurs