FCM: practice questions (week 2)
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
anesthesia monitoring, anesthesia complications + CPR, asepsis + sterility, abdominal ultrasound, materials + needles, bone fractures + disease radiographs, castration + spay procedures, basic anesthetics in different ages
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
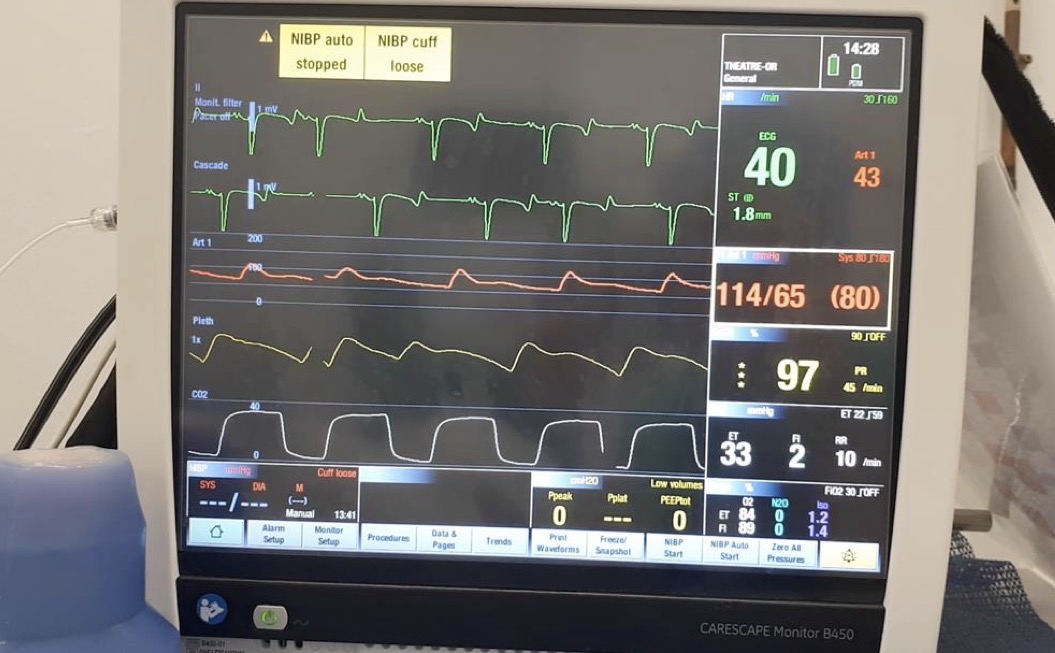
Which species does this ECG most likely represent?
Horse
What are the values we monitor during anesthesia?
SPO2, HR, RR, BP, CO2, temp
What is the normal range for HR in dogs while under anesthesia?
Small dogs (<20kg): 80-120bpm
Lage dogs (>20kg): 70-100bpm
What is the normal range for arterial BP in both cats + dogs while under anesthesia?
SAP: 90-140mmHg
DAP: 40-80mmHg
MAP: 60-100mmHg
What is the normal range for RR in both cats + dogs while under anesthesia?
8-12bpm
What is the normal range for HR in cats while under anesthesia?
130-170bpm
What is the normal Tidal Volume (VT) in both cats + dogs while under anesthesia?
10-15ml/kg
What is the normal Minute Ventilation in both cats + dogs while under anesthesia?
100-300ml/kg/min
What is the normal O2 consumption in both cats + dogs while under anesthesia?
4-10ml/kg/min
What is the normal ETCO2 in cats vs. dogs while under anesthesia?
Cats: 32-37mmHg
Dogs: 35-45mmHg
During a routine ovariectomy, a 3yo female intact cat is maintained on isoflurane anesthesia + spontaneous ventilation. Throughout the procedure, the cat’s eyes remain centrally positioned despite appropriate surgical stimulation & adequate anesthetic depth as confirmed by absent jaw tone, absent pedal withdrawal reflex, & stable cardiovascular parameters.
What is the most likely explanation for the persistent central eye position?
The cat received ketamine as part of the premedication protocol
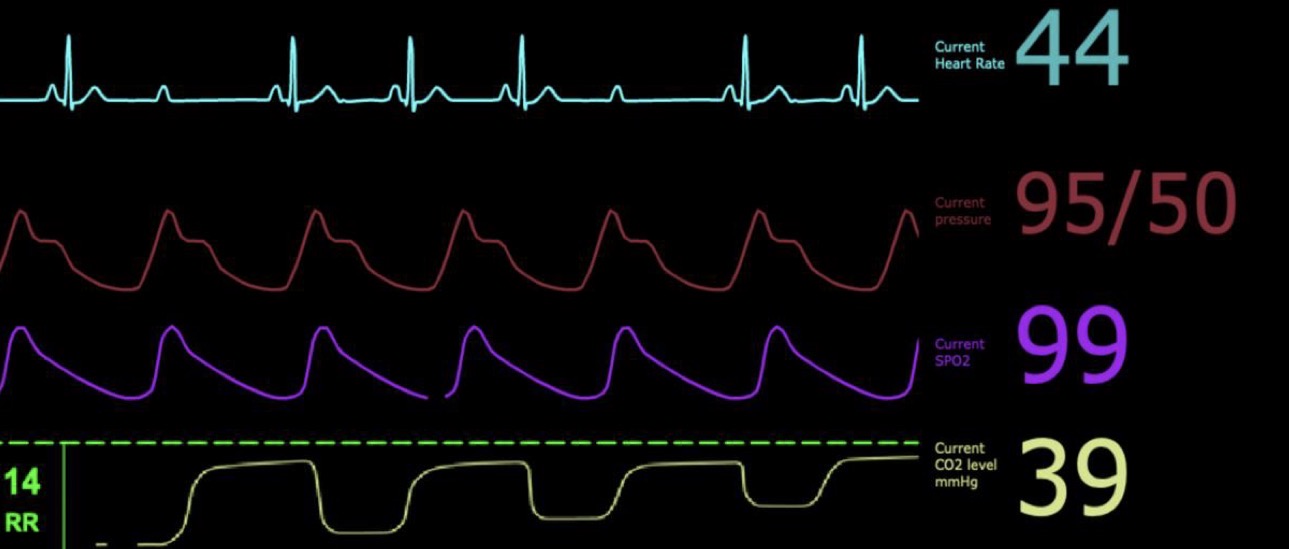
What type of arrhythmia is demonstrated in this case?
Second degree AV block
-not every P wave has a QRS
A 3kg 5yo mixed breed dog develops a 2nd degree AV block during general anesthesia for castration. The anesthetic protocol included methadone + dexmedetomidine for premedication, ketamine + propofol for induction, intratesticular lidocaine + SQ carprofen for analgesia, & isoflurane for maintenance.
What is the most likely cause of this arrhythmia?
The combination of drugs inducing bradycardia + vagal stimulation
-pulling on testicles can cause vagal response, dexmed + methadone can cause bradycardia
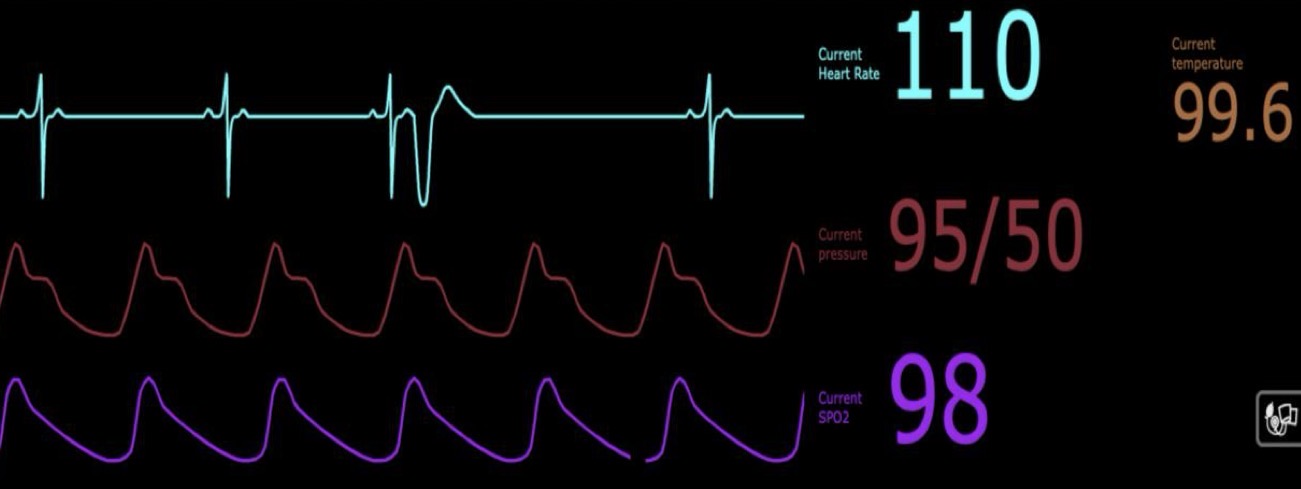
What type of arrhythmia is demonstrated in this case?
Ventricular premature contractions
-bizarre QRS
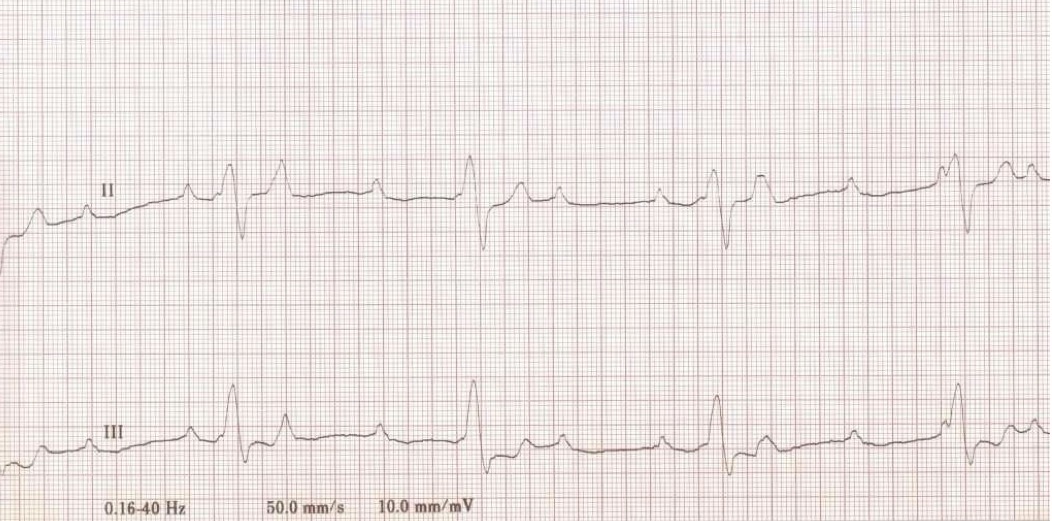
What type of arrhythmia is demonstrated in this case?
Third degree AV block
-QRS is wide + bizarre, some P waves w/o QRS
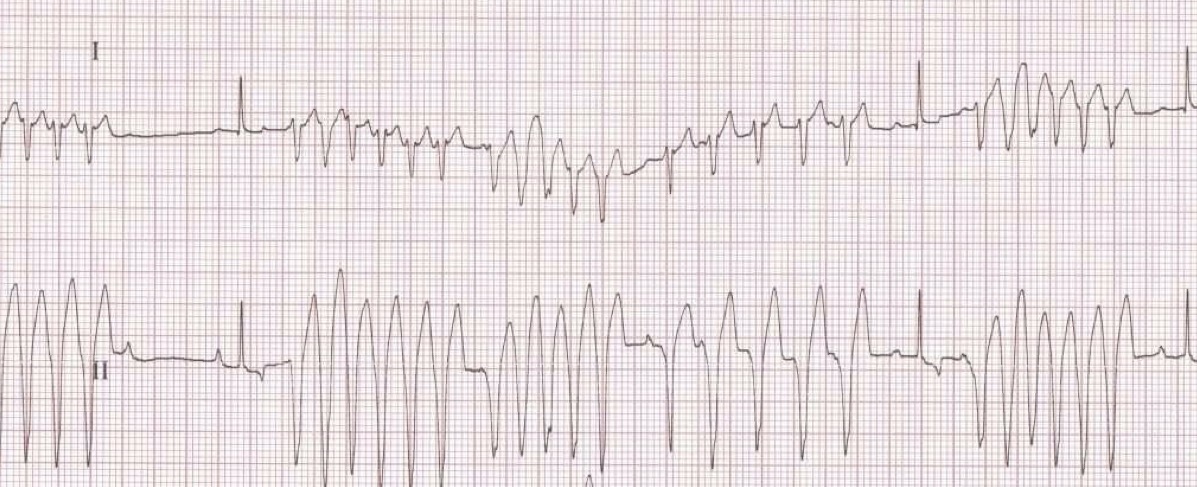
What type of arrhythmia is demonstrated in this case?
Ventricular tachycardia
-still see some QRS
Which blood pressure value is the best indirect clinical indicator of perfusion?
MAP - mean arterial pressure
When utilizing a non-invasive blood pressure cuff during surgery, what may occur if the cuff is too wide for the patient?
Measured pressure will be too low
A vet nurse is preparing to measure blood pressure non-invasively on a dog’s forelimb that has a circumference of 12cm at the measurement site. The available cuffs are 3cm, 5cm, 8cm, & 10cm wide. The nurse selects the 8cm cuff.
What effect will this have on the blood pressure measurement?
The measured BP will be artificially low
-should use ~4-5cm cuff (12 × 40% → 0.4)
Which mechanical monitors assess respiratory function during anesthesia?
Blood gas analysis, pulse oximetry, capnography, spirometry
In what cases will capnography be unreliable?
V/Q mismatch, increase dead space, high FGF, rapid shallow breaths (no alveolar plateau), moisture in sample line or probe, slow deep breaths (alveolar plateau)
A 6yo Cocker Spaniel is undergoing an exploratory laparotomy under isoflurane anesthesia. You notice that the capnograph shows a gradual increase in the alpha angle, with the expiratory upstroke becoming progressively less steep over the past 15 minutes. The dog’s respiratory rate is 8bpm, & end-tidal CO2 is 48mmHg.
What is the most likely cause of this capnogram change?
Increased airway resistance due to bronchospasm or airway obstruction
What most plausibly explains post-operative infections in a surgical setting where autoclaved instruments + chemical indicators confirmed exposure to sterilization conditions?
The chemical indicators confirmed exposure but not microbial kill
If there is a shift to the right on pulse oximetry, what is occurring in the patient?
Low Hb-O2 affinity
If there is a shift to the left on pulse oximetry, what is occurring in the patient?
High Hb-O2 affinity
Which value measures the relative variability of the plethysmogram (PPG) waveform noninvasively detected from a pulse oximetry sensor, calculating the dynamic changes (in the arteries) that occur during the respiratory cycle?
Pleth Variability Index (PVi)
What value measures peripheral perfusion in a patient by non-invasively monitoring the ratio of pulsing to non-pulsing blood?
Perfusion Index
A 1yo male dog receives dexmedetomidine in combination with an opioid for premedication. What is the expected effect of dexmedetomidine on the pulse plethysmograph waveform amplitude?
The waveform amplitude will decrease due to peripheral vasoconstriction
What are the most common anesthetic complications (the 4 hypos) that we may encounter during surgery?
-Hypoventilation (hypercapnia)
-Hypotension
-Hypoxemia
-Hypothermia
-Bradycardia
-Prolonged recovery
What are some of the major causes of hypoventilation during surgical procedures?
-Drug-induced respiratory depression
-Neuromuscular blockade (NMBA) or disease
-Increased abdominal pressure (pregnancy/obesity)
-Positional (dorsal recumbency)
What strategies or interventions can be used to treat hypoventilation during anesthesia?
Manual/mechanical ventilation
What are some of the most common causes of apnea (no EtCO2 reading on monitor) during surgical procedures?
-Equipment failure
-Drugs given too fast (propofol, ketamine)
-Reflex secondary to visceral traction
What are the potential consequences if hypotension is left untreated under anesthesia?
Hypoperfusion to the kidney, brain, heart, & extremities + Inadequate removal of waste products (CO2)
What can we use to treat hypotension under anesthesia?
-Vasopressors (norepinephrine) → increase systemic vascular resistance
-Anticholinergics (atropine) → increase HR if bradycardic
-Fluid bolus → replaces volume if dehydrated/hypovolemic
-Heart meds (pimobendan/dobutamine) → if patient has heart disease
What are some of the clinical consequences of hypothermia while under anesthesia?
-Decreased metabolic rate → prolonged recovery, metabolism of drugs reduced, electrolyte imbalance
-Peripheral vasoconstriction → reduced blood flow + O2 delivery to wounded tissue & drop in BP
-Reduced cardiac output
-Hypoventilation
How can we reduce or prevent heat loss via convection during surgical procedures?
Bairhugger + Blanket/towel over patient
How can we reduce or prevent heat loss via conduction during surgical procedures?
Heated mat between patient & table
At what values should you suspect bradycardia in dogs, cats, & horses under anesthesia?
Dogs: HR <60bpm
Cats: HR <100bpm
Horses: HR <20bpm
How should we treat tachycardia in patients under anesthesia?
-Analgesics if pain response
-Increase iso if surgical depth too light
-Beta-blockers (propanolol, esmolol)
What tumor could cause hypertension in animals under anesthesia?
Pheochromocytoma (on adrenals → releases catecholamines)
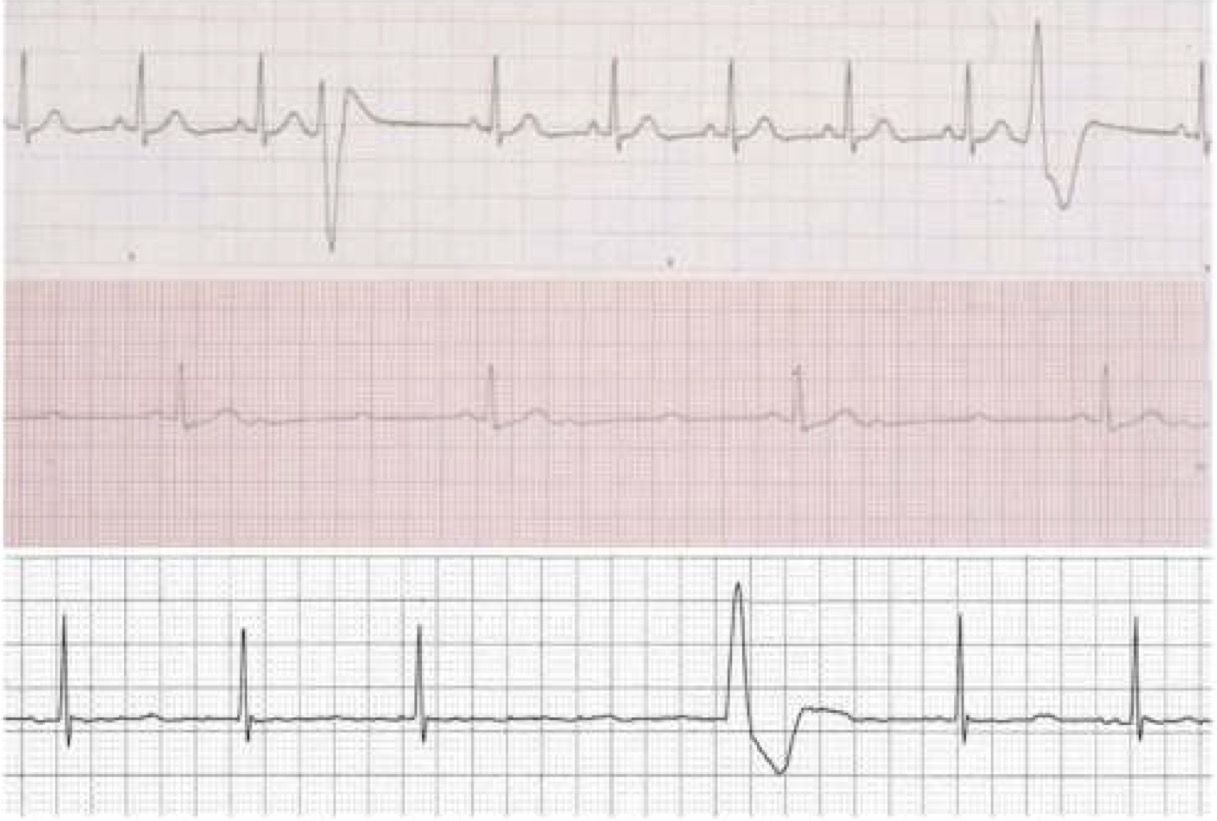
What are these three common arrhythmias seen in animals under anesthesia?
Ventricular premature complexes (VPCs)
High grade, second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block
Sinus bradycardia with a ventricular escape beat
When starting Basic Life Support (BLS) for a patient in CPA, how many chest compressions should be performed per minute & how often should you ventilate?
100-120 chest compressions per minute, ventilate twice every 6 seconds (or every 30 compressions)
-2 minute cycles
What are the non-shockable heart rhythms when performing CPR?
Asystole + Pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
If you encounter a non-shockable heart rhythm such as asystole or PEA, what is the next recommended step after performing BLS?
Administer epinephrine or vasopressin every other cycle → causes vasoconstriction + positive inotropism/chronotropism
-may also give atropine as early as possible
What are the shockable heart rhythms when performing CPR?
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) + Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT)
In intubated patients in CPA, how many breaths per minute should be given?
10bpm
When measuring the efficacy of early CPR with EtCO2, what value should it be above to indicate success?
>18 mmHg
What is the aim of defibrillation during ALS?
Depolarize ventricular myocardial cells, driving them to the refractory period & stop random electrical + uncoordinated mechanical activity (stop ventricles from fibrillating)
-basically just halts heartbeat
What antiseptic is most likely to maintain antimicrobial activity after exposure to blood & organic debris in a comparative study?
Chlorhexidine
What is the most scientifically sound conclusion when microbial growth is observed after incubating biological indicators in a veterinary surgical unit using steam autoclaving?
The sterilization cycle failed to eliminate resistant spores
Why do alcohol-based antiseptic combinations (ex: ChloraPrep) outperform single-agent antiseptics in surgical site preparation?
They combine rapid action with prolonged residual activity
What best distinguishes antisepsis from sterilization in terms of microbial control & application?
Antisepsis reduces microbial load on animate surfaces; sterilization eliminates all microbes on inanimate objects
What best defines the status of “scrubbed” hands in a sterile environment?
They are surgically clean but must not touch sterile items
An autoclave indicator strip turns black after a cycle, but the biological indicator shows growth (positive result) after incubation. How should this be interpreted?
The cycle failed to achieve sterility; the load must be re-processed
What is the primary function of a chemical indicator such as the autoclave tape?
To distinguish between processed vs. unprocessed items
What is the difference between chlorhexidine (CHG) scrub vs. solution?
Scrub is used for surgical prepping healthy skin (2-4%), while solution is used for wound management (0.05%)
What do physical indicators tell us about an item that we have autoclaved?
Physical conditions within the autoclave (temp, pressure, time)
-does not confirm sterility
What do chemical indicators tell us about an item that we have autoclaved?
Changes color in response to heat + pressure
-does not tell us exposure time or confirm sterility
What do biological indicators tell us about an item that we have autoclaved?
Validates sterilization process
Ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization can be very toxic, flammable, & carcinogenic, & it needs aeration so it can take a long time. In what case might we risk this for the sake of sterilization?
For items that cannot withstand steam sterilization (plastics, rubber)
For what type of items might we use ionizing radiation sterilization, which uses low temperatures to sterilize?
Single-use items (surgical gloves, suture, syringes)
What sterilization method do we use for rapid sterilization of endoscopes or as a “cold soak” for items that cannot be autoclaved?
Peracetic acid sterilization
What is the most common bacteria found in infected/contaminated surgical incision sites?
Staph. Pseudintermedius
For a spay procedure, where should you shave the surgical window?
From xiphoid to pubis
What are the cranial & caudal borders of the liver on ultrasound?
Cranial: Diaphragm + lung interface
Caudal: Spleen on left + Right kidney on right
What is the normal appearance of the liver on ultrasound?
Uniformly hypoechoic with coarse echotexture
-caudal tips of liver lobes are pointed
-portal veins have bright echogenic walls
What does a normal gallbladder look like on ultrasound?
Anechoic teardrop structure with a conical extension (cystic duct)
-may have hyperechoic biliary sludge but this is normal
-cats may have bilobed GB but this is normal
How will the liver appear on ultrasound in a case of hepatomegaly?
Tips of liver lobes are rounded + liver will extend beyond right kidney
What are the top differential diagnoses if you see hypoechoic foci on an ultrasound of the liver?
Nodular hyperplasia, EMH, metastatic disease (lymphoma)
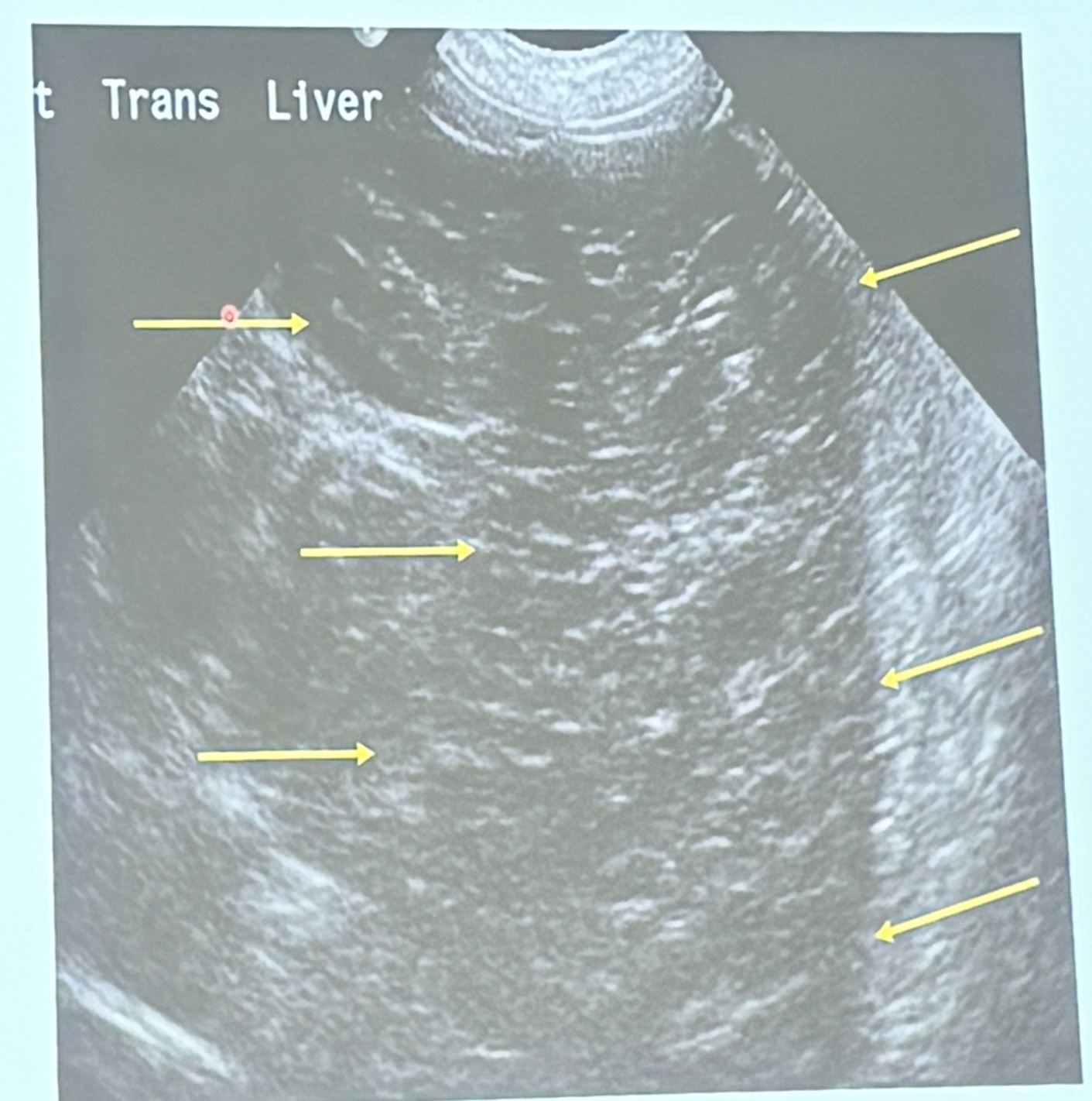
This is a longitudinal scan of the liver from an 8yo MN MBD diagnosed with lymphoma. What are the ultrasonographic findings?
Diffuse hypoechogenicity
How does the normal spleen appear on both the long axis & cross-section on ultrasound?
Long axis: Elongated + tongue-shaped
Cross-section: Triangular or lenticular
What structures does the head of the spleen form a “hook” between on ultrasound?
Gastric fundus + Left kidney
What vasculature can be seen on ultrasound of the spleen as a tubular anechoic structure?
Splenic vein
-cannot see splenic artery
What are the top differentials if multiple hypoechoic nodules are seen on an ultrasound of the spleen (swiss-cheese appearance)?
Lymphoma, infarction, EMH
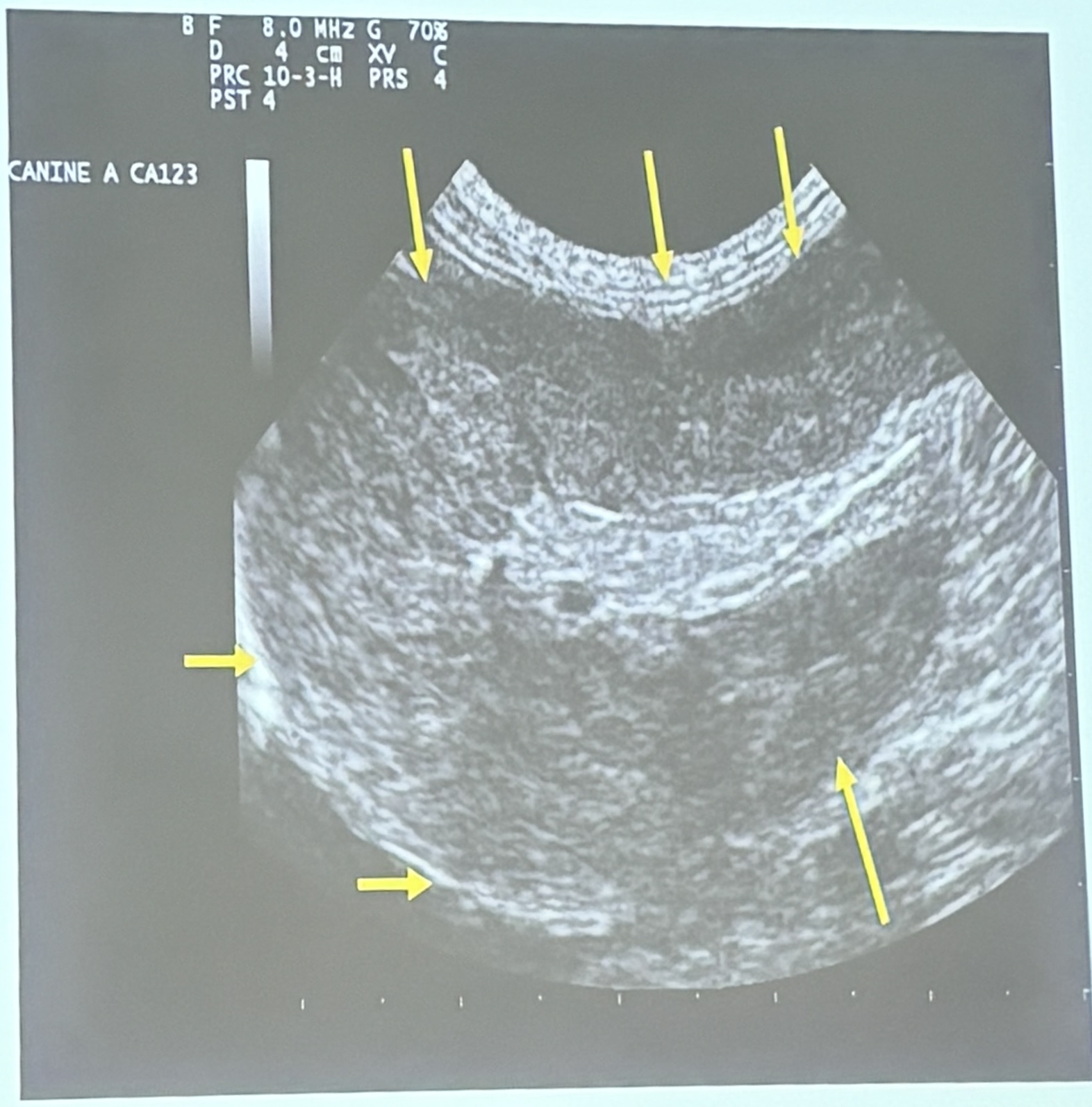
This is a longitudinal scan of the spleen of a 13yo FS Siamese cat presenting with a history of abdominal distension & anorexia. What are the ultrasonographic findings?
Splenomegaly / heterogenous echogenicity
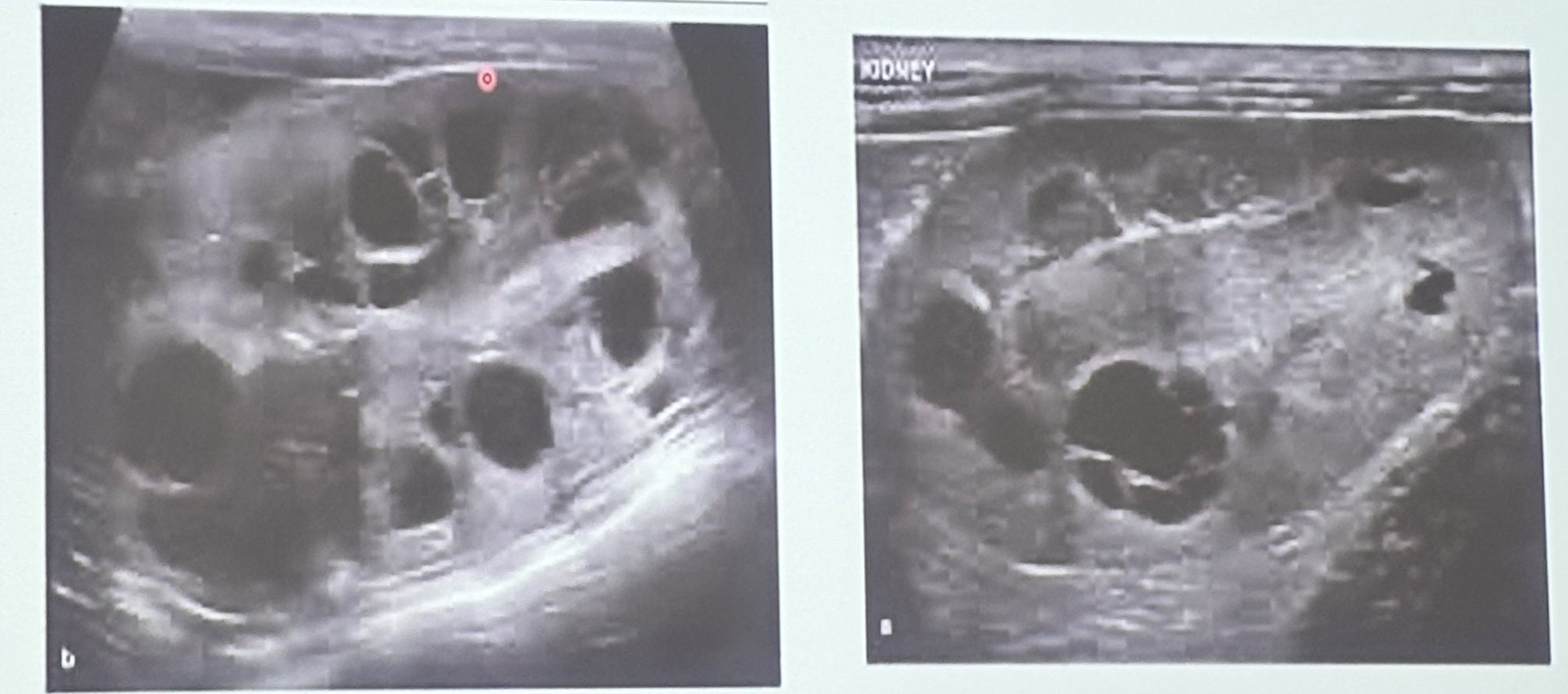
These are long axis scans for the left & right kidneys of a 7yo DSH with a history of azotemia. What are the ultrasonographic findings?
Polycystic kidneys
How can we identify the different segments of the GIT on ultrasound?
Stomach → rugal folds
Small intestine → descending duodenum (thickest segment of small bowel)
Ileocecocolic junction → most commonly gas-filled
Colon→ thin, layered wall often with gas + feces
If you see a bullseye appearance in the region of the small bowel on ultrasound, what is your top differential?
Intussusception
What are the four histological bladder wall layers & how do they appear on ultrasound?
Mucosa → hypoechoic
Submucosa → hyperechoic
Muscularis → hypoechoic
Serosa → hyperechoic
How can you arrange the abdominal organs in order starting from the least to the uppermost echogenicity?
Renal medulla < Renal cortex < Liver < Spleen < Prostate
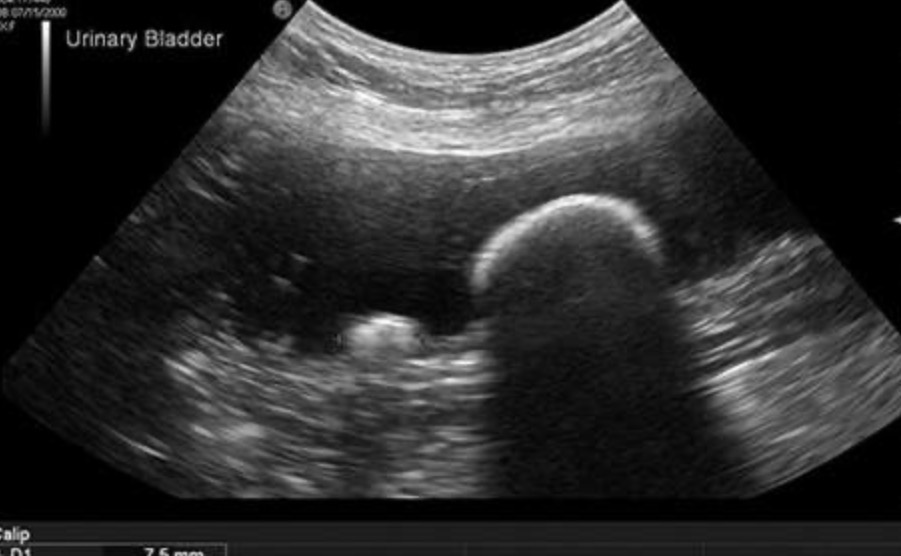
What is the term used to describe the following artefact on this longitudinal scan of the urinary bladder?
Distal acoustic shadowing
What size suture do we typically use in small animals to close up the muscle layer?
2-0 (sometimes 3-0)
What size suture do we typically use in small animals to close up the subcutaneous layer?
3-0 (sometimes 4-0)
What size suture do we typically use in small animals to close up the skin layer?
4-0 (sometimes 5-0)
What is the primary advantage of using a monofilament suture for skin incision closure?
It minimizes the risk of infection due to its smooth design
When selecting suture material, it’s crucial to consider the properties that can negatively impact the patient & avoid them. Among the properties of suture material, which one is most directly responsible for minimizing tissue trauma during insertion?
Surface friction
A surgeon is seeking a suture material that can maintain tensile strength for over 60 days while minimizing tissue reactivity during the repair of a ruptured patella ligament. Which combination of classification + absorption mechanism would be most suitable for this purpose?
Non-absorbable; Hydrolysis
A surgical needle with a triangular tip & upward-facing cutting edge is used in a procedure. What is the most likely consequence compared to a reverse cutting needle?
Increased risk of suture pull-through
Which classification of suture material is single stranded with less tissue drag, has decreased knot security, & is weakened by kinking or crushing by instruments?
Monofilament
Which classification of suture material is braided (so more pliable), has better knot security but more tissue drag, higher infection risk (wicking), & should not be used in infected areas or hollow organ procedures such as a cystotomy?
Multifilament
Which mechanism of absorption attacks collagen structure & breaks down peptide bonds, but causes significant tissue reactivity (edema, redness)?
Enzymatic digestion (natural fibers)
Which mechanism of absorption uses water molecules to cleave/break the polymer chains, & has low inflammatory response leading to less tissue reaction?
Hydrolysis (synthetic fibers)
Which absorbable suture is a synthetic mono or multifilament (typically braided) material that causes minimal tissue reaction, & is commonly used for rapid healing tissues (oral cavity, periocular skin) or soft tissue surgery as it absorbs at a pretty fast rate (56-70 days)?
Polyglactin 910 (Vicryl)
Which absorbable suture is a synthetic monofilament material with very low tissue reactivity that is commonly used in closure of the linea alba, fascia (LA), tendons, or GI surgery as it absorbs slowly (180 days)?
Polydioxanone (PDS)
Which absorbable suture is a synthetic monofilament material with very low tissue reaction that is commonly used in small animal soft tissue surgeries such as castrations for SQ & intradermal closure as it has intermediate absorption times (90-120 days)?
Polyglecaprone 25 (Monocryl)
Which absorbable suture is a synthetic monofilament material with high tensile strength, minimal tissue reactivity, & slow absorption (180 days) & is commonly used for closure of the abdominal wall, fascia, or orthopedic soft tissues?
Polyglyconate (Maxon)
Which absorbable suture is a natural twisted material that utilizes enzymatic digestion (so causes high tissue reactivity) that is not used often today, but can be used for ligatures or in LA if necessary?
Natural Absorbable (Catgut)
What suture material is most appropriate for a 6yo MN DSH with feline odontoclastic resorptive lesions (FORLs)?
Vicryl
Which non-absorbable suture is a synthetic mono/multifilament material with very low tissue reactivity that is highly resistant to degradation, making it a good option for large animal skin closure, ligation of blood vessels, or ophthalmic & neurosurgery, but is contraindicated in hollow organs like the bladder?
Nylon (Polyamide)
Which non-absorbable suture is a synthetic monofilament material that has very low tissue reactivity, excellent tensile strength, & is non-degradable, making it a great option for vascular surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, joint repair, neurosurgery, or long-term skin closure?
Polypropylene