OUT Quizes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
A patient mistakenly claims exemption for NHS dental treatment costs during a course of treatment at your Outreach placement. Which action would the NHS BSA take?
A £100 penalty fine plus the cost of the treatment band
A dental Hygienist and Therapist can provide treatment to patients without the prescription of a dentist (Direct Access). What procedures or treatments, even if a patient is being seen under 'Direct Access', would still require a prescription from a dentist?
Tooth whitening
Radiographs
Fissure Sealants
Temporary Re-cement of a crown
Toothwhitening
You are considering an appropriate recall interval for a patient and have consulted the SDCEP guidance to help you record their oral health risk. You have communicated to the patient that they have a medium risk of developing dental caries. What follow up period should be advised?
3mth
12mths
6mths
9mths
6 months
(A patient with a medium risk of developing dental caries should be reviewed every 6 months to monitor their compliance and reinforce all of the oral health advice given, which should help to reduce their risk of developing dental caries.)
A patient completes their PR form but is unsure whether they have to pay for their dental treatment. What should you do?
Ask them to pay the appropriate NHS band charge, and claim it back at a later date
https://www.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/dont-get-caught-out-penalty-charges/check-you-tick
https://www.nhs.uk/using-the-nhs/help-with-health-costs/get-help-with-dental-costs/
When carrying out a Oral Heath Assessment/Dental Examination what modifying factors would you consider using to evaluate a patients level of risk for development of oral diseases, such as periodontal disease.
Please choose the appropriate options.
Diabetes
Poor OH
Smoking habits
Alcohol intake
Occupation
Diabetes
Poor OH
Smoking habits
Concurrent medical factor that is directly affecting the periodontal tissues (e.g. diabetes, stress, certain medication)
Medical history that significantly affects clinical management (e.g. immunocompromised or immunosuppressed, potential drug interaction)
Evidence of gingivitis
Poor level of oral hygiene
Presence of plaque-retaining factors
Regular tobacco smoking
(NOT alcohol intake, check SDCEP OHA)
A newly qualified dentist or therapist would be expected to provide treatment to NHS patients at a Level 2 level of complexity?
True or false
False
You would not be expected to provide a Level 2 procedure in your primary care practice, especially if you didn't have the experience or enhanced skills to safely complete the procedure.
Level 2 - procedures require a clinician with enhanced skills and experience who may or may not be on a specialist register e.g. extraction of retained root fragment following an attempt to extract”
When carrying out a Oral Heath Assessment/Dental Examination what modifying factors would you consider using to evaluate a patients level of risk for development of oral diseases, such as oral cancer.
Please choose the appropriate options?
Occupation
Smoking Habits
Alcohol intake
Absence of fruit and veg in diet
Salivary flow rate
Occupation
Smoking Habits
Alcohol intake
Absence of fruit and veg in diet
Salivary flow rate
Betel quid chewing
Diets low in fruit and vegetables
Excessive alcohol use (>14 units of alcohol per week for men; >14 units alcohol per week for women)
Low saliva flow rate (dry mouth
Outdoor workers1
Tobacco use
You have just completed a dental examination of a patient previously assessed as having a high risk for dental caries. You regard this past disease as being stabilised and none active but are aware of several modifying risk factors that could, over time, significantly increase the patients likely hood of developing more carious lesions.
When would you review this patient again?
Discuss with the patient their risk factors providing a high strength fluoride supplement and review in 3 months.
Ongoing review of the patients oral health will include reviews based on their level of risk. If the patient is still showing risk factors that could significantly increase their oral disease shorter review periods and preventative advice is recommended.
Commissioning in primary care requires dental professionals to provide dental care for differing levels of complexity.
From the options below what bests describes the differences between level 1, level 2, level 3 complexity?
Type of dental setting treatment is provided
Practitioners specialist qualifications
Type of dental contract provider is performing under
Procedural difficulty
Procedural difficulty
(The levels of complexity do not describe contracts, or practitioners or settings. Levels 1, 2 and 3 care descriptors reflect a case in terms of procedural difficulty, patient modifying factors and competence required of a clinician to deliver care of that level of complexity.)
A dental therapist is providing a restoration for a patient on referral from a dentist. Local Anaesthetic has been given.
During caries removal a small pinhead of pulp horn is exposed. The dentist is away on holiday there is no other dentist on site.
What would you expect the therapist to do, within their scope of practice?
Remove any soft caries with an excavator clearing the ADJ. Pulp cap the exposure and restore or dress. Document and warn patient about symptoms and possible need for RCT. Inform referring dentist.
(It is important that the DCP doesn't go beyond their scope of practice and prevents further exposure of the pulp. The DCP should try to contact a dentist for advice if they are either unsure or concerned that the tooth in question may need further treatment.
Stabilizing the tooth is the most appropriate option until the tooth can be reviewed by a dentist.)
The dental team works together to provide a holistic approach to patient care, including the prevention of oral disease. What members of the dental team may be able to prescribe radiographs without the prescription of a dentist to help in monitoring a patients oral disease?
Dental nurse
Dental receptionist
Dental Therapist
Clinical Dental Technician
Dental Therapist
When working to a Patient Group Direction (PGD) it is important to understand the limitations of your scope of practice.
What are PGDs required for to administer?
PGDs are required for a dental care professional to administer a prescription only medicine, which can be provided without a dentist present in the practice.
PGDs allows a dental care professional to administer and provide a prescription only medicine without the need for a dentist being present in the practice.
The Community Dental Service can offer appointments and treatments to which following patients?
Medically compromised patients
Patients requiring routine extractions
Patients with learning and physical disabilities
Patients requiring routine extractions under sedation
* Medically compromised patients
* Patients with learning and physical disabilities
* Patients requiring routine extractions under sedation
The Community Dental Service is a specialist and specialized service, that can treat a whole range of patients in primary care. It cannot treat patients who require routine treatment such as tooth extraction, which can just as easily be provided in a General Dental Practice setting.
When working in a primary care practice a patient specific direction (PSD) can be used by a dentist to allow a dental care professional such as a therapist to administer and in some instances supply prescription only medicines.
Please select all prescription only medicines that would apply from this statement?
Antimicrobial mouthwash (Chlorhexidine)
Topical Fluoride (Duraphat varnish)
Toothpaste (Duraphat toothpaste)
Local Anaesthetic
Topical Fluoride (Duraphat varnish)
Toothpaste (Duraphat toothpaste)
Local Anaesthetic
A patient specific direction allows a dental care professional to supply or administer a prescription only medicine providing that this is within their scope of practice and they fully understand relevant information about the prescription only medicine.
The dental team works together to provide a holistic approach to patient care for the prevention of oral disease. What members of the dental team may be able to take radiographs without the prescription of a dentist to assist in the monitoring of a patients oral disease?
Dental therapist
Dental Nurse
Dental technician
Clinical Dental Technician
Dental therapist
Please see the scope of practice document to fully understand the differences between treatment that can be carried out direct to a patient compared to treatment that will require a patient specific direction form a dentist.
Generally a dental Nurse can gain additional skills but still requires direction from a dentist and a dental technician would require enhanced clinical training and be qualified as a clinical dental technician before they can take radiographs. A clinical dental technician can only take a radiograph that relates to providing a removable dental appliance, but not to monitor a patients dental disease.
Receptionists numerous duties highlight their important role in a dental practice. Choose all the possible duties a receptionist can undertake during a working day that would assist a dental professional in the monitoring of a patients oral disease?
Ensuring patients are booked in the correct recall period as prescribed by the dental professional
Updating the details of every patient, including contact numbers, email and place of residence
Providing the dental professional with a list of patients that are overdue their recall period
Ensuring the patient charge is collected
* Ensuring patients are booked in the correct recall period as prescribed by the dental professional
* Updating the details of every patient, including contact numbers, email and place of residence
* Providing the dental professional with a list of patients that are overdue their recall period
From the options choose the correct prescription form, used in an NHS primary care GDS practice, that can be used to prescribe prescription only medicines such as fluoride toothpastes.
Form colours purple, green, pink, yellow ?
Yellow form
There are multiple different prescriptions being used to administer medicines within the NHS. The colour and code will differ depending on which setting you are working in.
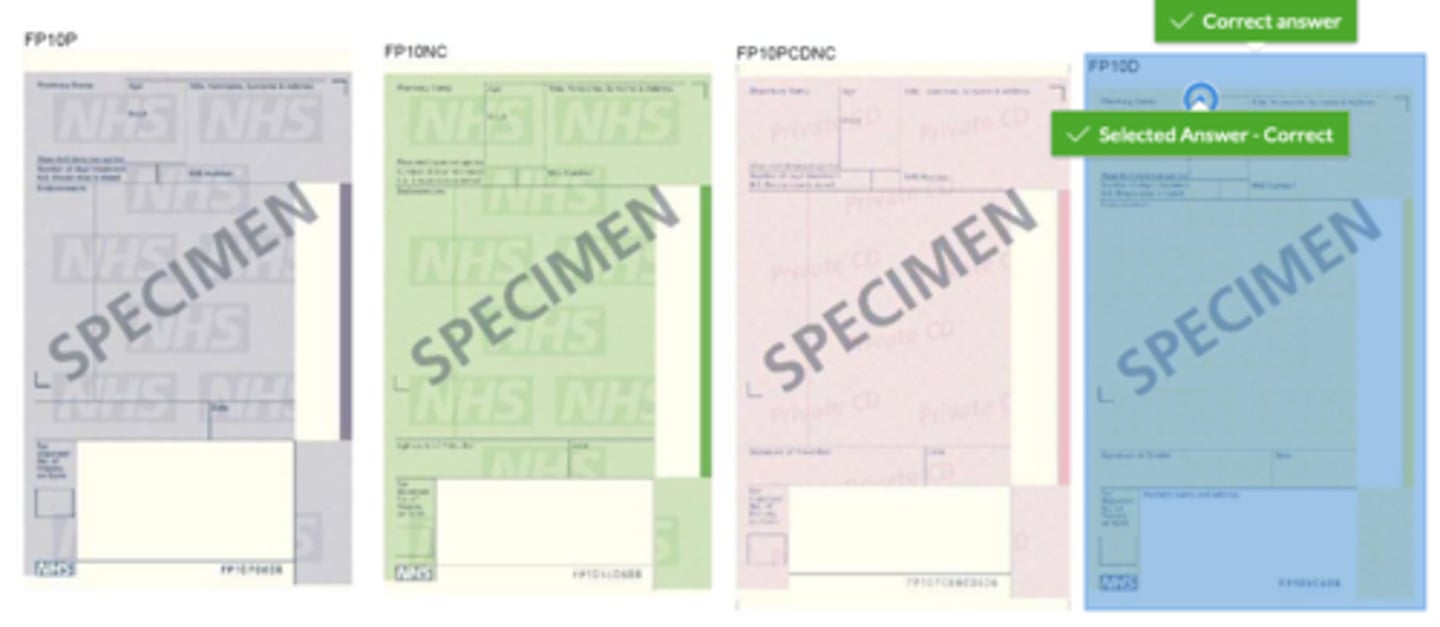
In the Cheshire and Mersey region there are several ways you can refer a dental patient patient to another service provider for advanced services. Select all the appropriate methods of referral that will be accepted by a provider?
Online Dental referral
Phone only referral
Paper proforma referral faxed
Paper proforma referral posted
Online Dental referral
Paper proforma referral posted
Paper proforma referral faxed
Normally all referrals except phone referrals will be accepted. Providers require patient details, medical histories and sometimes the assistance of radiographs and photographs before they can accept a referral, usually with the appropriate proforma completed in full by the referring dentist.
In primary dental care what does the acronym PDS stand for?
Primary Dental Service
Professional Dental Service
Personal Dental Service
Patient Dental Service
Personal Dental Service
this type of contract can provide specialist of specialized services
Usually have a higher UDA value attached to their contract
Contracts are usually time limiting (Can be re-negotiated)
In primary care, which options would you consider as having appropriate referral criteria to send to the Community Dental Service ?
Anxious adults – for continuing care such as dental examination
Oral surgery – for a single course of treatment
Paediatric exodontia with local anaesthetic and inhalation sedation or general anaesthetic
Special care patients – children or adults for continuing care
* Paediatric exodontia with local anaesthetic and inhalation sedation or general anaesthetic
* Special care patients – children or adults for continuing care
* Oral surgery – for a single course of treatment
Anxious adults – for continuing care such as dental examination can be seen for their continuous care in general practice and then referred for single items of treatment.
Please visit the READING LISTS@Liverpool to look up the community services referral guidance.
Can you identify the correct Course of Treatment to the correct NHS Band?
Examination, Composite Filling, Scale & Polish
Band 2
Band 2 includes band 1 as well as fillings, extractions, RC, denture additions and PDL therapy
A DAC universal Autoclave is used for the disinfection and sterilisation of dental mirror and probes?
True or False
False
DAC is used to disinfect and sterilise dental handpieces
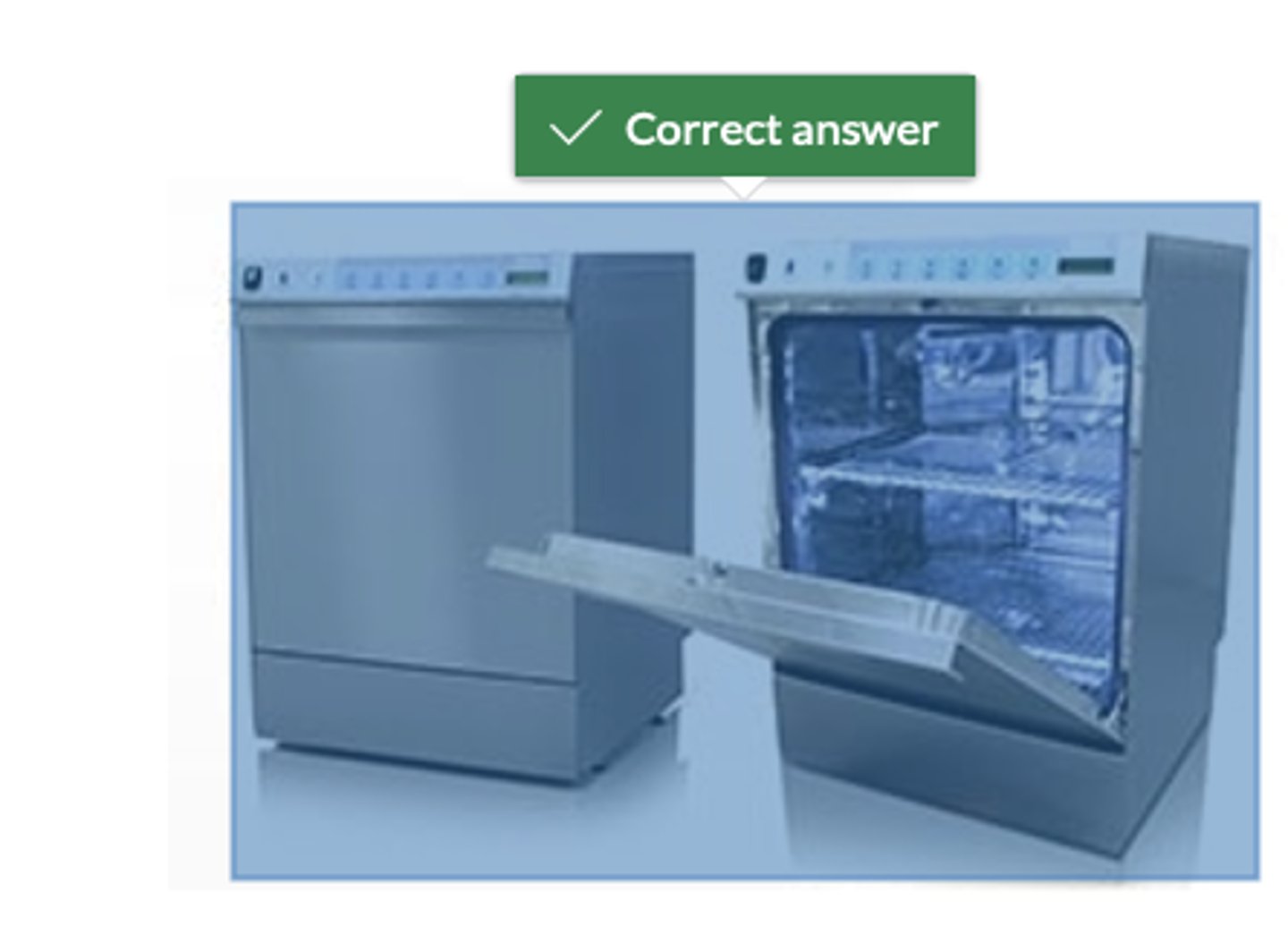
A washer disinfector is a piece of equipment that you may find being used as part of the decontamination process in a primary care dental practice. Can you identify one from the images below?
dishwasher type

You have recently had your medical emergencies training session and the practice owner has decided the equipment and emergency drugs are most accessible from your room as it is closest to reception and on the ground floor. The lead nurse is in charge of checking the equipment and asks you how often should the emergency equipment be checked?
Weekly
Monthly
Daily
Bi-weekly
Weekly
A weekly check as a minimum will ensure that the practice rarely has equipment missing, which could prevent a medical emergency being managed properly.
A primary care dental practice will need to manage its budget to enable sustainable cashflow throughout a financial year. Identify below the costs that are generally the responsibility of a GDS practice owner.
Uniform for a hygienist who is employed
Uniform for a self employed therapist
Uniform for a associate dentist
Uniform for a dental nurse
Uniform for a hygienist who is employed
Uniform for a dental nurse
An adult patient receives a course of treatment consisting of an examination, bitewing radiographs, preventive advice, scale & polish and 2 fissure sealants. What band should the dentist claim?
Band 1 plus a private fee for the white tooth coloured fissure sealants
Band 2 NHS charge
Band 1 NHS charge
Band 3 NHS charge
Band 1 NHS charge
Correct!
There can be a lot of confusion between fissure sealants, which carry a band 1 charge and sealant restorations, which have a band 2 charge. Sealant restorations involve drilling the tooth so if you don’t drill, claim a band 1. There are 4 different codes for sealants, 3 of which carry a band 2 charge so be careful that you check the UDA value of the course of treatment before you submit it.
A primary care dental practice will need to manage its budget to enable sustainable cashflow throughout a financial year. Generally how would a practice owner raise the funds for a capital purchase such as a dental chair.
Personal finances
NHS capital funding
Credit agreement with supplier
Bank loan
Personal finances
Credit agreement with supplier
Bank loan
There are multiple ways that a dental practice can fund expensive items such as dental chairs. Generally the NHS will not provide capital funding for items such as dental chairs in a GDS setting.
When considering members of the dental team in a typical GDS dental practice, what members of the dental team are currently able to complete items in course of NHS treatment.
Associate dentist
Dental nurse
Foundation dentist
Dental therapist
Associate dentist
Dental nurse
Foundation dentist
Dental therapist
All members listed are able to perform certain items planned in an NHS course of treatment as long as they have a performer number, are on an approved training scheme, or there is a patient specific direction and the member of the dental team is working with their scope of practice.
What band of treatment applies to a course of treatment that generates 3 Units of Dental Activity.
Band 3
Band Urgent
Band 2
Band 1
Band 2
Sorry!
3 UDAs relates to the band 2 Course of treatment
Band 1 attracts 1 UDA
Band 3 attracts 12 UDAs
Band Urgent attracts 1.2 UDAs
When considering members of the dental team in a typical GDS dental practice, what members of the dental team are currently able to plan a course of NHS treatment.
Associate dentist
Foundation dentist
Dental nurse
Dental therapist
Associate dentist
Foundation dentist
Currently the NHS only allows clinicians with either a performer number, or who are in training on an approved foundation training scheme the ability to plan an NHS course of treatment.
Please select the correct statement in relation to the decontamination of reusable dental instruments from the following?
Essential and Best practice only applies to NHS dental practices
There is no difference between Essential practice and Best Practice
Every dental practice should be achieving Best practice
Every dental practice should be achieving Essential practice
Every dental practice should be achieving Essential practice
The guidance can be found in the HTM01-05 document in your reading list
From the list below what are the key areas from the the IPS audit tool a practice will be measuring their compliance against?
Waste Management
Management of medical devices
Prevention of bloodborne virus exposure
Staff PPE
Waste Management
Management of medical devices
Prevention of bloodborne virus exposure
Staff PPE
Read your HTM0105 and IPS audit tool resources for further information
What type of evidence can members of the dental team submit to the GDC that shows they are practising within their scope of practice?
Number of years qualified as a professional
E-Learning certificates
Lecture attendance
Number of UDA's completed in a financial year
Clinical audits
E-Learning certificates
Lecture attendance
Clinical audits
There are several ways to show the GDC that you are practising within your area of expertise. The GDC don't recognise experience and work output alone as a good indicator of maintenance of skills within the profession.
If a patient has a complaint after they have received a course of treatment how long do they generally have to log their complaint to the dental practice?
12 months
3 years
6 months
2 years
12mths
whilst technically within the correct time frame the answer is not the maximum time frame the question is asking for
"If you wish to make a complaint about a dentist or dental practice, try to resolve it directly with them first. Contact the dental surgery's practice manager with details of your complaint. You can complain in writing, by email or by speaking to someone.
Your complaint must be made within 12 months of receiving treatment."
https://www.nhs.uk/common-health-questions/dental-health/how-do-i-complain-about-my-dental-treatment/
A Dental Assurance Framework (DAF) report is produced by the BSA for dental practices how often?
Annually
Quarterly
Bi - Annually
Weekly
Quarterly
The report is released quarterly to allow practices and the AT to get an overview of performance in a timely manner. It allows providers to make any appropriate changes and the frequency of the report is used to help providers reflect on either their own or the whole practices performance.
A dental nurse is able to take dental radiographs, but without any further training what stage of the radiographic process must a be completed by another qualified member of the team.
Reporting
Referral
Justification
Interpretation
Reporting
Referral
Justification
Interpretation
Review the resource in your reading list 'Guidance for the Use of X-Ray Equipment'
From the options below pick the 5 main lines of enquiry the CQC will use to inspect dental services in England.
Clean
Effective
Caring
Compliant
Responsive
Well led
Secure
Safe
Effective
Caring
Responsive
Well -lead
Safe
Visit their site
https://www.cqc.org.uk/what-we-do/how-we-do-our-job/five-key-questions-we-ask
A patient makes a written complaint about treatment you have provided for them on the NHS. What initial steps should you take?
*Acknowledge the complaint as soon as possible but within 3 days
*Inform the patient the should contact the NHS PALs service
*Acknowledge the complaint as soon as possible but within 7 days
*Advise the patient to contact the Dental Complaints Service
*Acknowledge the complaint as soon as possible but within 3 days
Complaints should be acknowledged as quickly as possible 7 days without a response could give the patient no other choice but to escalate further. Giving the patient access to a paper version of the complaints procedure will also help reduce the possibility of the complaint unnecessarily escalating.
Why are clinical audits important in clinical dental practice? Select the most appropriate answer.
Audits help improve a service by constantly reviewing clinical processes
Audits help target neglect in patient care
Audits help reduce costs
Audits show you are complaint to the regulators
Audits help improve a service by constantly reviewing clinical processes
A clinical audit generally will help you identify areas of a clinical practice that may need improvement
A GDS practice will have set roles for the team in relation to the radiation protection regulations. Which of the roles below is linked to a radiation (medical) physics expert?
Radiation Protection Advisor
IRMER Practitioner
Operator
Radiation Protection Supervisor
Radiation Protection Advisor
https://www.hse.gov.uk/radiation/rpnews/rpa.htm
Also visit the reading list resource document 'Guidance for the Safe Use of X-Ray Equipment'