DCAP Ch 10-11 (Exam 5)
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter that binds at a motor end-plate to trigger depolarization
actin
protein that makes up most of the thin myofilaments in a sarcomere muscle fiber
action potential
change in voltage of a cell membrane in response to a stimulus that results in transmission of an electrical signal; unique to neurons and muscle fibers
aerobic respiration
production of ATP in the presence of oxygen
angiogenesis
formation of blood capillary networks
aponeurosis
broad, tendon-like sheet of connective tissue that attaches a skeletal muscle to another skeletal muscle or to a bone
ATPase
enzyme that hydrolyzes ATP to ADP
atrophy
loss of structural proteins from muscle fibers
autorhythmicity
heart's ability to control its own contractions
calmodulin
regulatory protein that facilitates contraction in smooth muscles
cardiac muscle
striated muscle found in the heart; joined to one another at intercalated discs and under the regulation of pacemaker cells, which contract as one unit to pump blood through the circulatory system. Cardiac muscle is under involuntary control.
concentric contraction
muscle contraction that shortens the muscle to move a load
contractility
ability to shorten (contract) forcibly
contraction phase
twitch contraction phase when tension increases
creatine phosphate
phosphagen used to store energy from ATP and transfer it to muscle
dense body
sarcoplasmic structure that attaches to the sarcolemma and shortens the muscle as thin filaments slide past thick filaments
depolarize
to reduce the voltage difference between the inside and outside of a cell's plasma membrane (the sarcolemma for a muscle fiber), making the inside less negative than at rest
desmosome
cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers to allow contraction to occur
eccentric contraction
muscle contraction that lengthens the muscle as the tension is diminished
elasticity
ability to stretch and rebound
endomysium
loose, and well-hydrated connective tissue covering each muscle fiber in a skeletal muscle
epimysium
outer layer of connective tissue around a skeletal muscle
excitability
ability to undergo neural stimulation
excitation-contraction coupling
sequence of events from motor neuron signaling to a skeletal muscle fiber to contraction of the fiber's sarcomeres
extensibility
ability to lengthen (extend)
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers within a skeletal muscle
fast glycolytic (FG)
muscle fiber that primarily uses anaerobic glycolysis
fast oxidative (FO)
intermediate muscle fiber that is between slow oxidative and fast glycolytic fibers
fibrosis
replacement of muscle fibers by scar tissue
glycolysis
anaerobic breakdown of glucose to ATP
graded muscle response
modification of contraction strength
hyperplasia
process in which one cell splits to produce new cells
hypertonia
abnormally high muscle tone
hypertrophy
addition of structural proteins to muscle fibers
hypotonia
abnormally low muscle tone caused by the absence of low-level contractions
intercalated disc
part of the sarcolemma that connects cardiac tissue, and contains gap junctions and desmosomes
isometric contraction
muscle contraction that occurs with no change in muscle length
isotonic contraction
muscle contraction that involves changes in muscle length
lactic acid
product of anaerobic glycolysis
latch-bridges
subset of a cross-bridge in which actin and myosin remain locked together
latent period
the time when a twitch does not produce contraction
motor end-plate
sarcolemma of muscle fiber at the neuromuscular junction, with receptors for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
motor unit
motor neuron and the group of muscle fibers it innervates
muscle tension
force generated by the contraction of the muscle; tension generated during isotonic contractions and isometric contractions
muscle tone
low levels of muscle contraction that occur when a muscle is not producing movement
myoblast
muscle-forming stem cell
myofibril
long, cylindrical organelle that runs parallel within the muscle fiber and contains the sarcomeres
myogram
instrument used to measure twitch tension
myosin
protein that makes up most of the thick cylindrical myofilament within a sarcomere muscle fiber
myotube
fusion of many myoblast cells
neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
synapse between the axon terminal of a motor neuron and the section of the membrane of a muscle fiber with receptors for the acetylcholine released by the terminal
neurotransmitter
signaling chemical released by nerve terminals that bind to and activate receptors on target cells
oxygen debt
amount of oxygen needed to compensate for ATP produced without oxygen during muscle contraction
pacesetter cell
cell that triggers action potentials in smooth muscle
pericyte
stem cell that regenerates smooth muscle cells
perimysium
connective tissue that bundles skeletal muscle fibers into fascicles within a skeletal muscle
power stroke
action of myosin pulling actin inward (toward the M line)
pyruvic acid
product of glycolysis that can be used in aerobic respiration or converted to lactic acid
recruitment
increase in the number of motor units involved in contraction
relaxation phase
period after twitch contraction when tension decreases
sarcolemma
plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle fiber
sarcomere
longitudinally, repeating functional unit of skeletal muscle, with all of the contractile and associated proteins involved in contraction
sarcopenia
age-related muscle atrophy
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum, which stores, releases, and retrieves Ca++
satellite cell
stem cell that helps to repair muscle cells
skeletal muscle
striated, multinucleated muscle that requires signaling from the nervous system to trigger contraction; most skeletal muscles are referred to as voluntary muscles that move bones and produce movement
slow oxidative (SO)
muscle fiber that primarily uses aerobic respiration
smooth muscle
nonstriated, mononucleated muscle in the skin that is associated with hair follicles; assists in moving materials in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, and internal passageways
somites
blocks of paraxial mesoderm cells
stress-relaxation response
relaxation of smooth muscle tissue after being stretched
synaptic cleft
space between a nerve (axon) terminal and a motor end-plate
T-tubule
projection of the sarcolemma into the interior of the cell
tetanus
a continuous fused contraction
thick filament
the thick myosin strands and their multiple heads projecting from the center of the sarcomere toward, but not all to way to, the Z-discs
thin filament
thin strands of actin and its troponin-tropomyosin complex projecting from the Z-discs toward the center of the sarcomere
treppe
stepwise increase in contraction tension
triad
the grouping of one T-tubule and two terminal cisternae
tropomyosin
regulatory protein that covers myosin-binding sites to prevent actin from binding to myosin
troponin
regulatory protein that binds to actin, tropomyosin, and calcium
twitch
single contraction produced by one action potential
varicosity
enlargement of neurons that release neurotransmitters into synaptic clefts
visceral muscle
smooth muscle found in the walls of visceral organs
voltage-gated sodium channels
membrane proteins that open sodium channels in response to a sufficient voltage change, and initiate and transmit the action potential as Na+ enters through the channel
wave summation
addition of successive neural stimuli to produce greater contraction
first step of muscle contraction
nerve impulse travels from dendrite to axon end terminal (synaptic bulb)
second step of muscle contraction
ion channels open to receive calcium into synaptic end
third step of muscle contraction
synaptic vesicles release acetylcholine into the synapse
fourth step of muscle contraction
acetylcholine binds to receptors in the sarcolemma, which open to allow sodium ions to enter muscle (depolarization or action potential)
fifth step of muscle contraction
action potential is propagated along the sarcolemma and into T tubules to open calcium channels in sarcoplasmic reticulum
sixth step of muscle contraction
sarcoplasmic reticulum diffuses out of the terminal cisternae into the sarcoplasm
seventh step of muscle contraction
calcium binds to troponin, which moves the troponin-tropomyosin complex to expose myosin binding site on actin
first step of crossbridge cycling
myosin head attaches to exposed binding site on actin, forming a crossbridge
second step of crossbridge cycling
myosin head pivots and pulls the thin filament toward the center of the sarcomere; ADP and Pi are released from the myosin head
third step of cross bridge cycling
ATP binds to myosin head causing it to detach from actin
last step of crossbridge cycling
ATP splits into ADP and Pi; myosin head returns to the cocked position
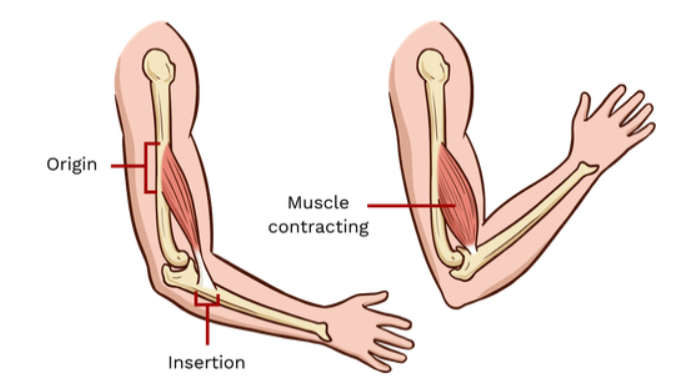
origin
the fixed attachment point for a muscle
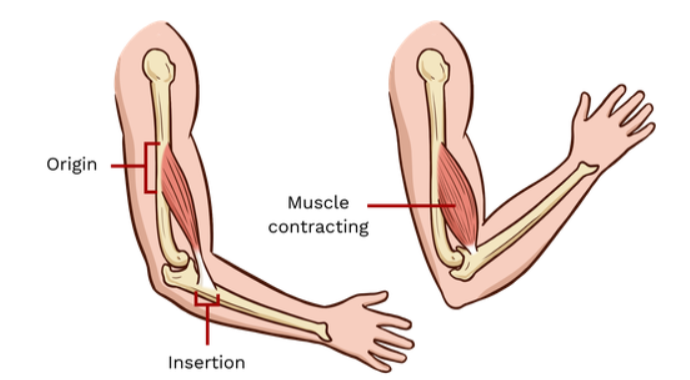
insertion
the moveable attachment point for a muscle
agonist
muscle that provides the major force for producing movement during a particular action
antagonist
muscles that oppose or reverse a movement, working in opposition to the agonist.