3. Sub-aerial processes: weathering
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Name 3 types of physical weathering?
Freeze-thaw, pressure release, salt crystalisation
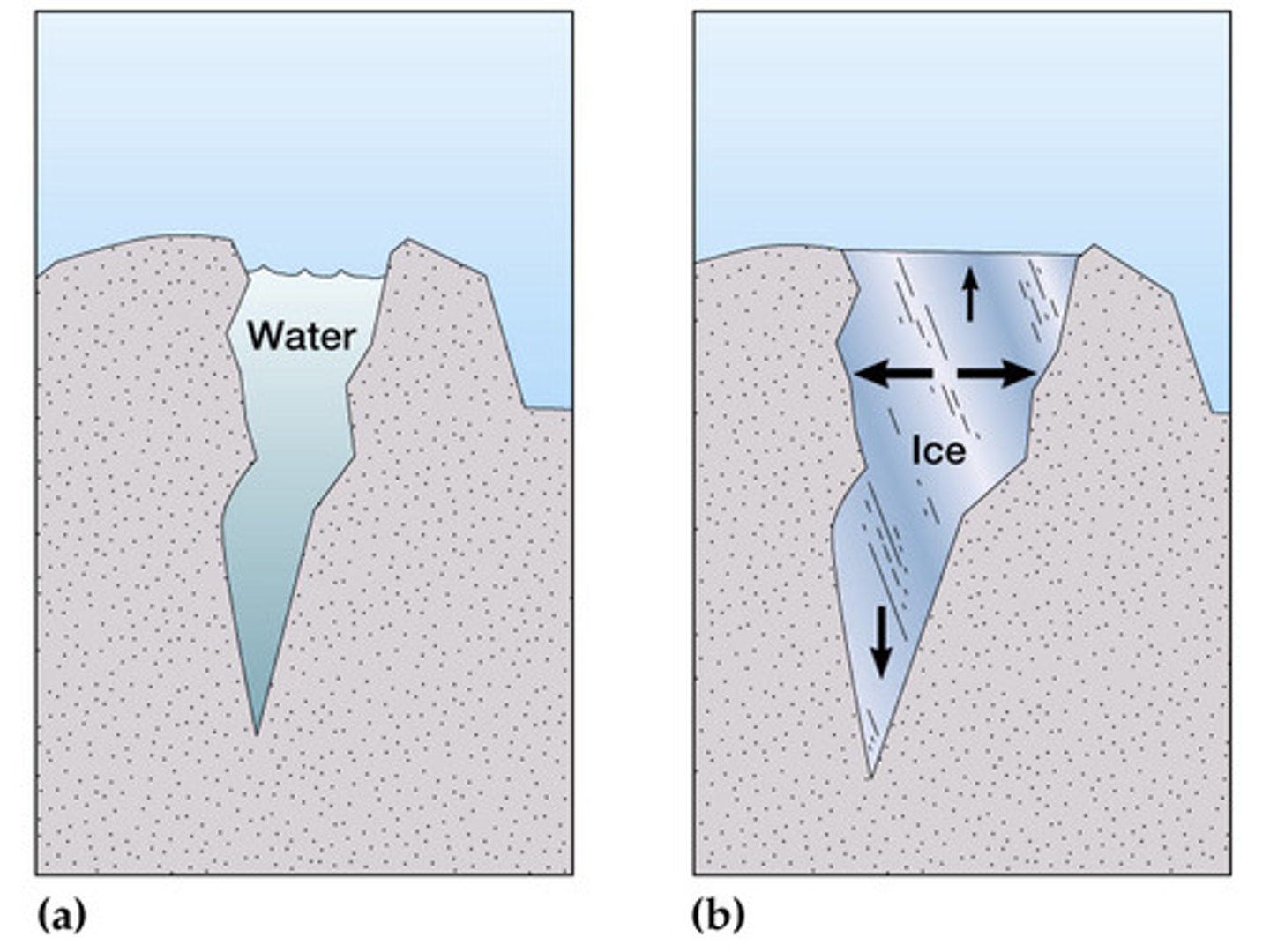
Describe freeze thaw weathering
When water enters a crack/joint and freezes overnight when temperatures are cooler causing it to expand by 10% which exerts pressure on the rock and causes the crack to widen more and parts of rock to break off
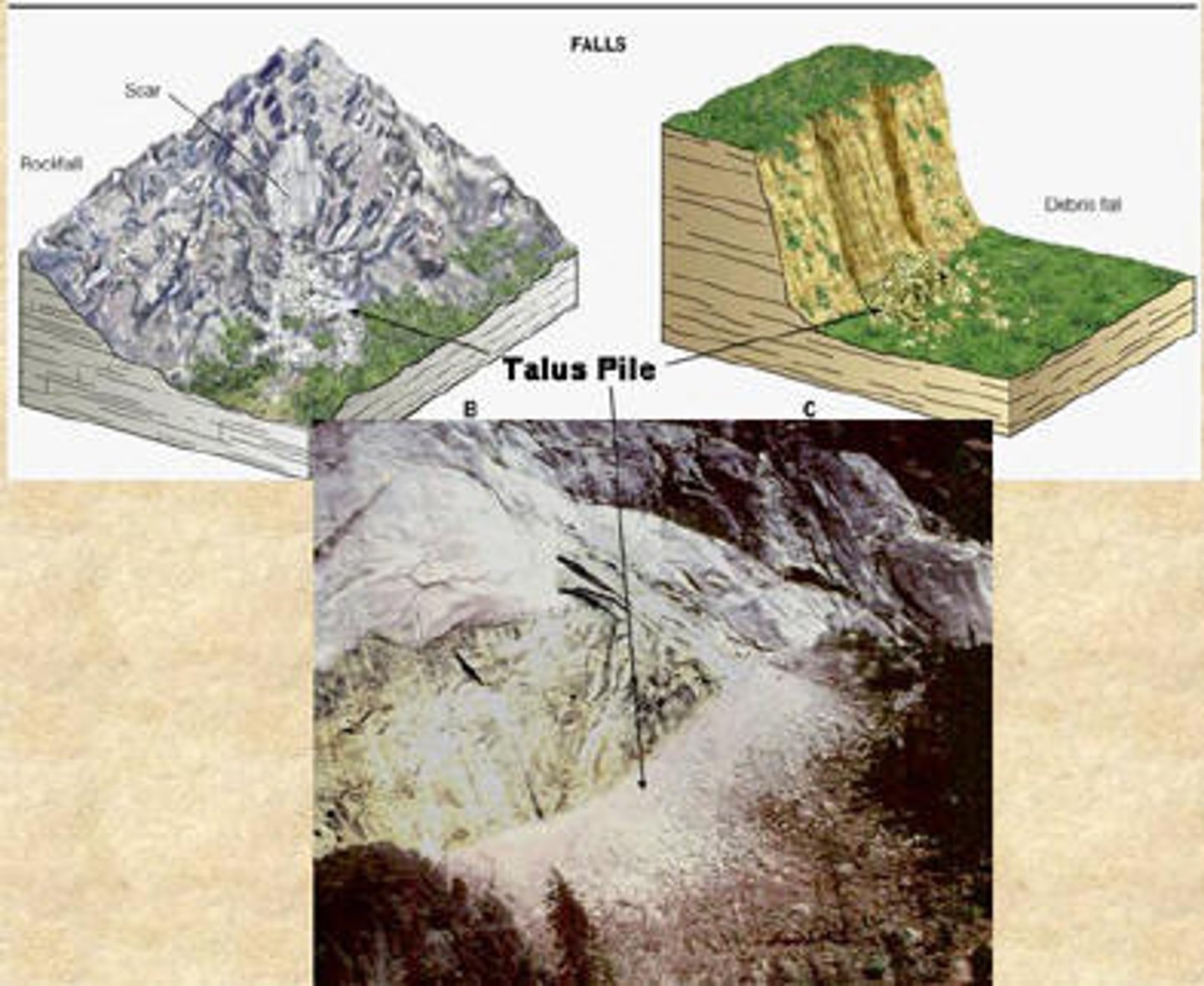
What can freeze-thaw weathering result in?
Rockfall which results in scree or talus slopes
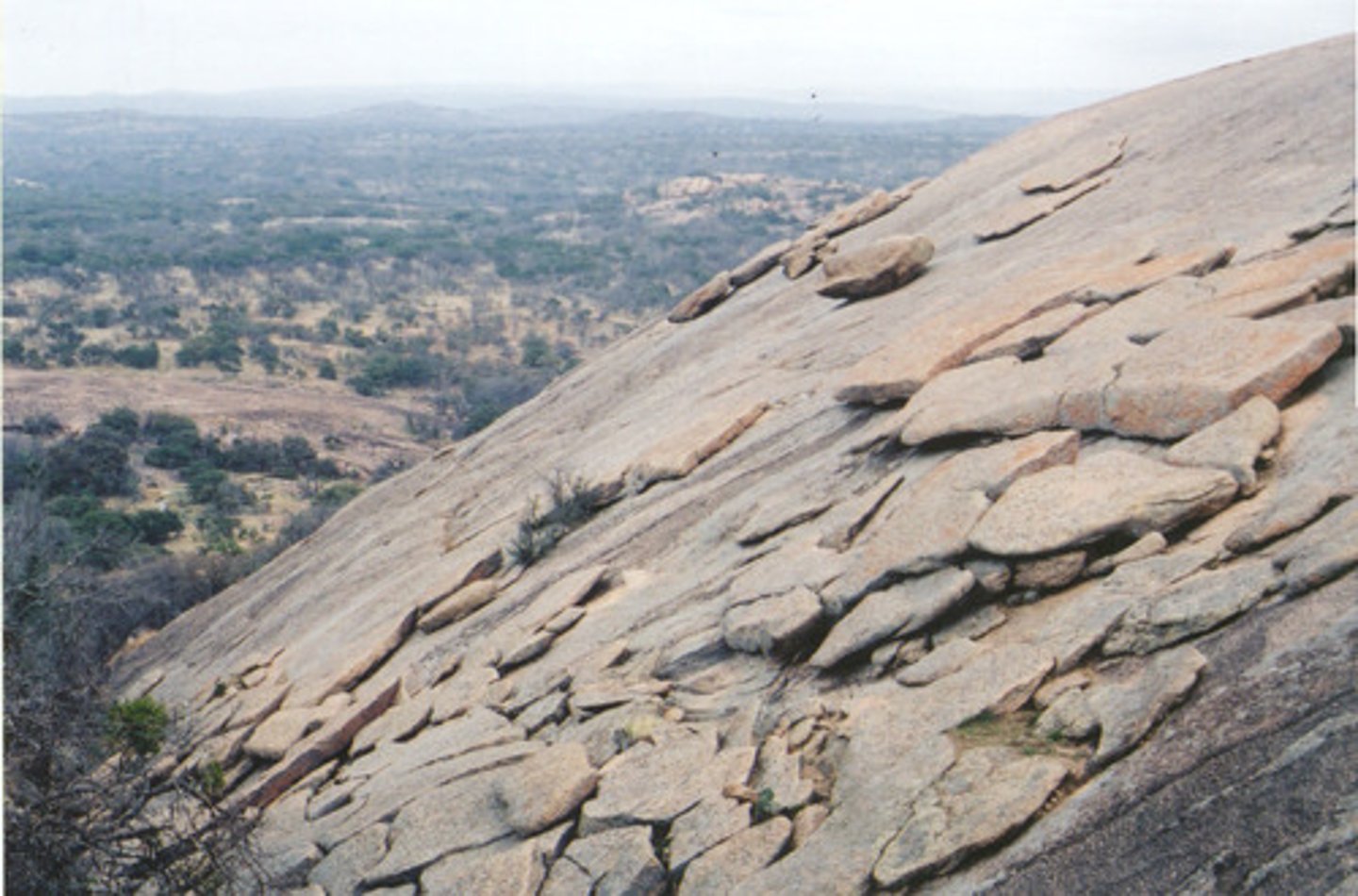
What's pressure release?
Where overlying material is removed by erosional processes there is a release of pressure. This causes outer layers of rock to peel off and slide down the slope

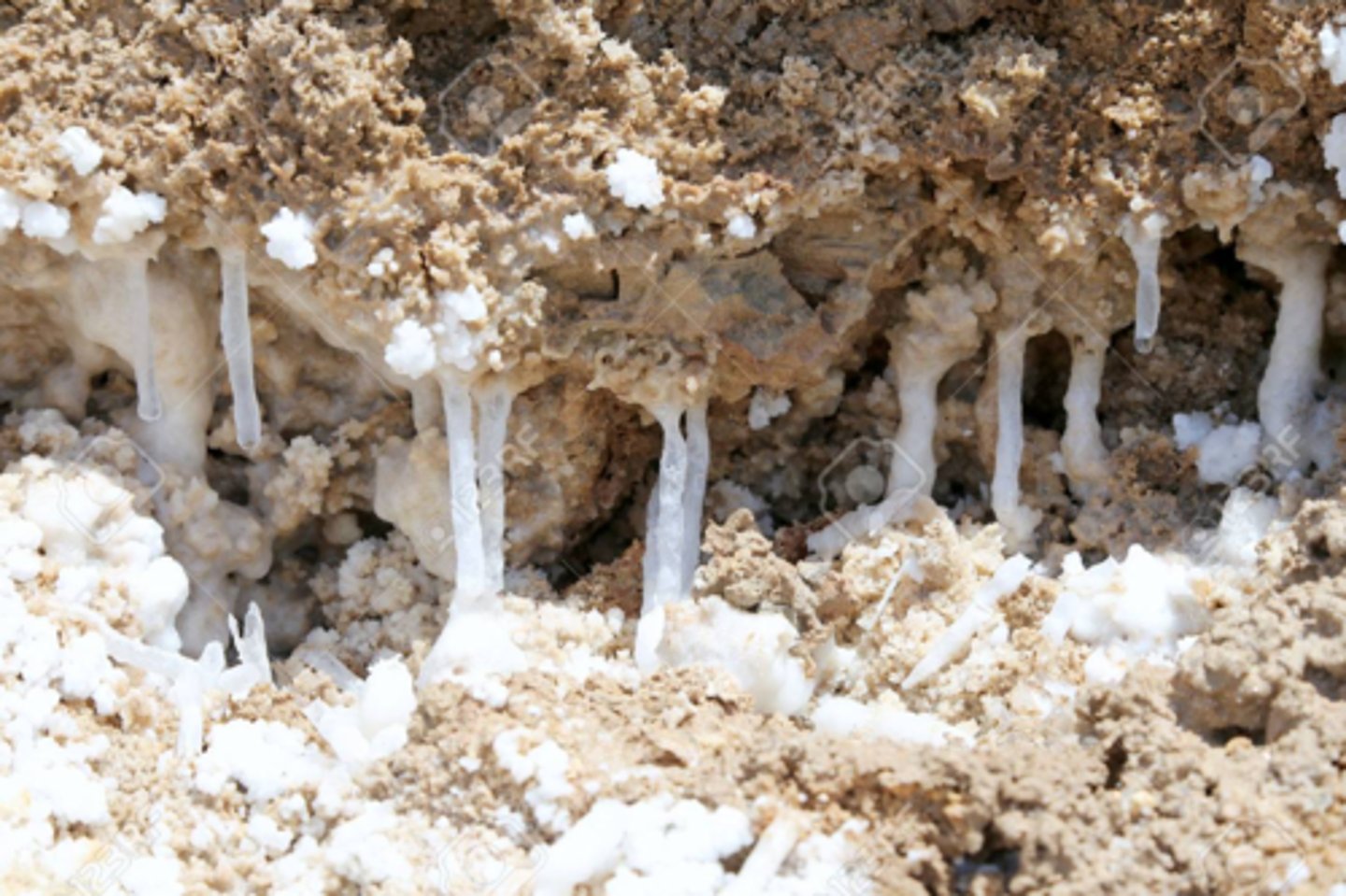
Describe salt crystallisation
Salt water evaporating forming salt crystals which can grow over time and exert a pressure on the rocks (can also corrode some rocks)

Name 3 examples of biological weathering on a coast
1. When a shellfish drills into a rock to keep safe from predators however this makes cracks so the rock is more susceptible to hydraulic action
2. Seaweed attaching to a rock however the movement of water can remove bits of the rock
3. Algae secreting chemicals which can lead to the solution of a rock (only in the intertidal region)
Name 5 types of chemical weathering
Oxidation, hydrolysis, carbonation and acid rain, hydration
Explain oxidation
Reaction of rock materials with oxygen to form a rusty red powder and leave rocks vulnerable to weathering or could disintegrate rocks
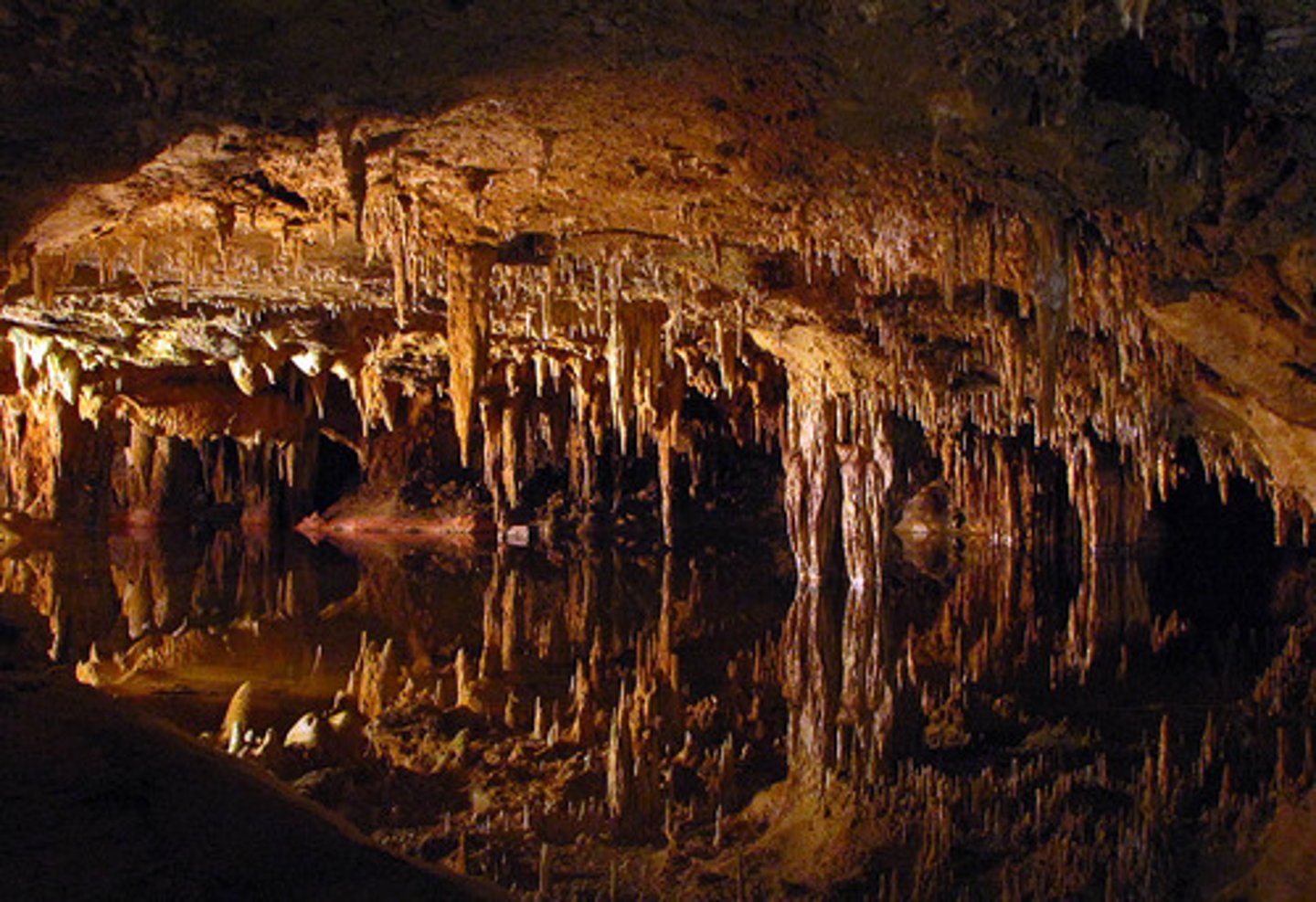
What's carbonation?
Rainwater absorbing CO2 from the air to form weak carbonic acid which reacts with the calcium carbonate in rocks forming a karst landscape

Name 2 types of acid rain?
Sulfur dioxide and nitric oxides and it forms due to fossil fuel emissions
Name 3 effects of acid rain?
Kills plants, pollutes rivers and erodes stonework/cliffs
What's hydration and where is it most effective?
When rocks containing salt absorb water and swell and so when they dry they are more at risk of decomposition.
Most effective in the intertidal zone as there are dry and wet areas due to the tide
What is hydrolysis?
Where mildly acidic water reacts or combines with minerals in the rocks to create clays and dissolvable salts which degrades the rock making it more susceptable to erosion or weathering
Describe 4 forms of marine transportation?
- Traction: large stones and boulders roll along a seabed by moving seawater
- Saltation: small stones bounce along the seabed
- Suspension: very small particles of sand and silt are carried by moving water picked up mainly through turbulence
- Solution: dissolved materials are transported within the mass of moving water
Describe 2 forms of aeolian deposition?
- Surface creep: wind rolls or slides sand grains along the surface
- Saltation: where wind is strong enough to temporarily lift the grains into the airflow for distances up to 30m
Explain the 5 forms of marine erosion?
1. Hydraulic action - waves/water exerting enormous pressure onto the rocks weakening it
2. Wave quarrying/cavitation - a breaking wave trapping air as it hits the cliff face which exerts pressure on the cracks/joints
3. Abrasion/corrasion - The wearing away of the cliff or seabed by material being thrown against it by waves.
4. Attrition - where rocks and pebbles smash into each other and become smaller, smoother, and rounder.
5. Solution/corrosion - Chemical breakdown of rocks (limestone or chalk) by acidic seawater. Minerals in the rock dissolve into the water over time.