The 27! Reviewed
1/879
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
880 Terms
Turns Testosterone → Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Used for external male genitalia
What does 5alpha-reductase do?
Hypercapnia: Vasodilates → Increased CBF
Hypocapnia: Vasoconstricts → Decreased CBF
What happens to cerebral blood flow (CBF) under the following conditions?:
Hypercapnia
Hypocapnia
Cryptosporidium!
What bug is causing this?
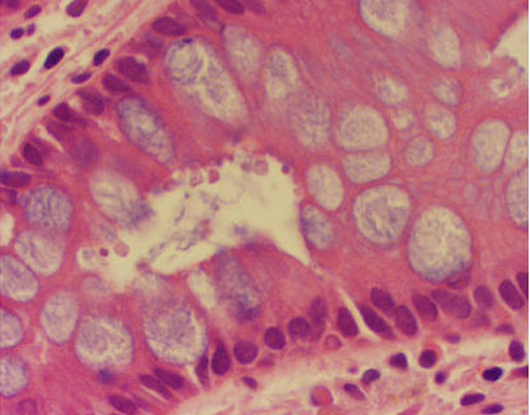
Unopposed estrogen!
What is the strongest predisposing factor for endometrial adenocarcinoma?
Lactic acidosis!
How would someone die from a metformin overdose?
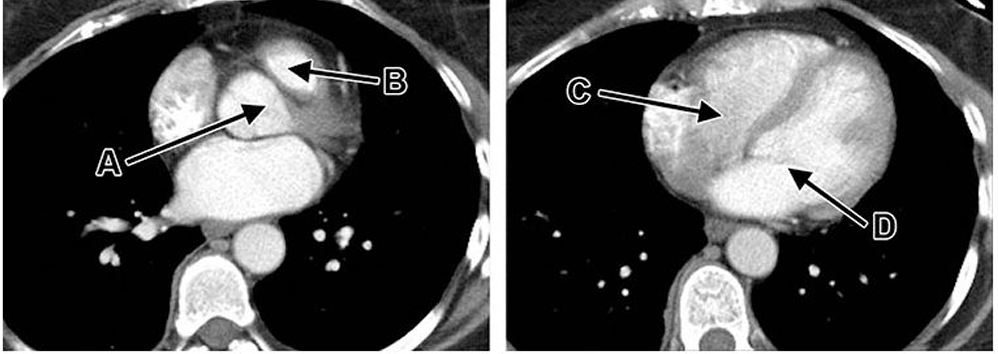
A. Aortic valve
B. Pulmonic valve
C. Tricuspid
D. Mitral
What are these valves?
Monoclonal overproduction of ONE specific Immunoglobulin
What does an M-Protein spike indicate?
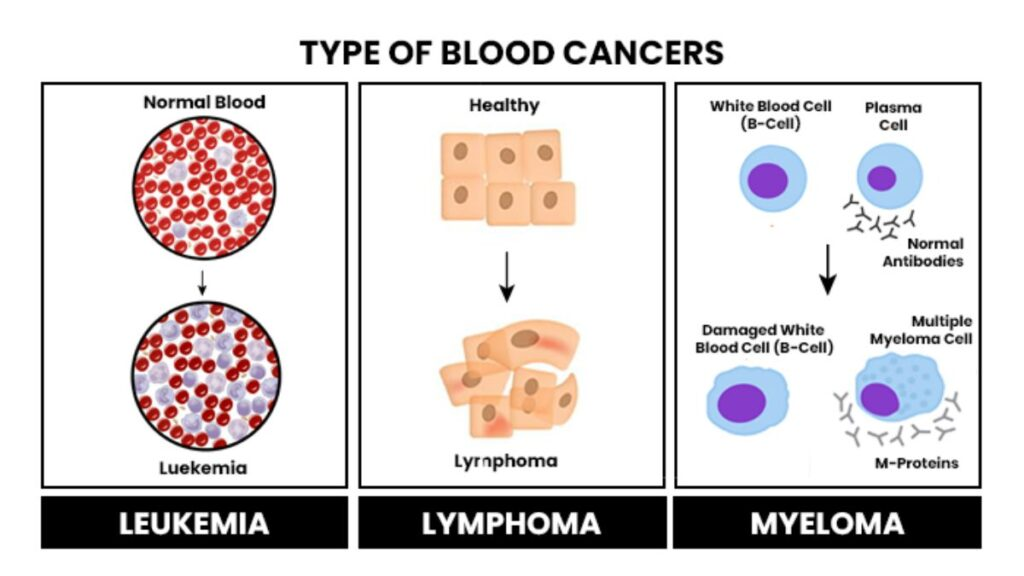
FALSE!:
Multiple Myeloma = cancer of PLASMA CELLS (mature B cells that produce antibodies)
Myelogenous Leukemia: Cancer of myeloid progenitor cells → like neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, RBCs, platelets
True or False: Multiple myeloma and myelogenous leukemia (acute or chronic) are the same thing
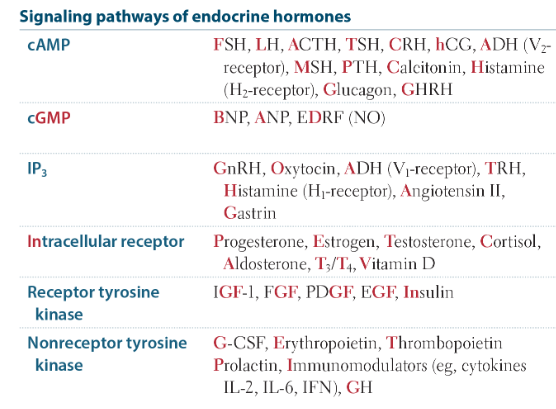
Progesterone, Estrogen, Testosterone, Cortisol, Aldosterone, T3/T4, and Vitamin D
PET CAT in TV
*Intracellular means in the cytoplasm or nucleus
Who has intracellular receptors? What does that even mean?
What are the mnemonics for each?
HHV-1 & 2 = Herpes
HHV-3 = VZV
HHV-4 = EBV
HHV-5 = CMV
HHV-6 & 7 = Roseola
HHV-8 = Kaposi sarcoma
Tell me the names for HHV 1-8
Hyperventilating!!
Which could be induced by breathing in low pO2 gas
What kind of situation would CAUSE someone to go from point Y to point Z?

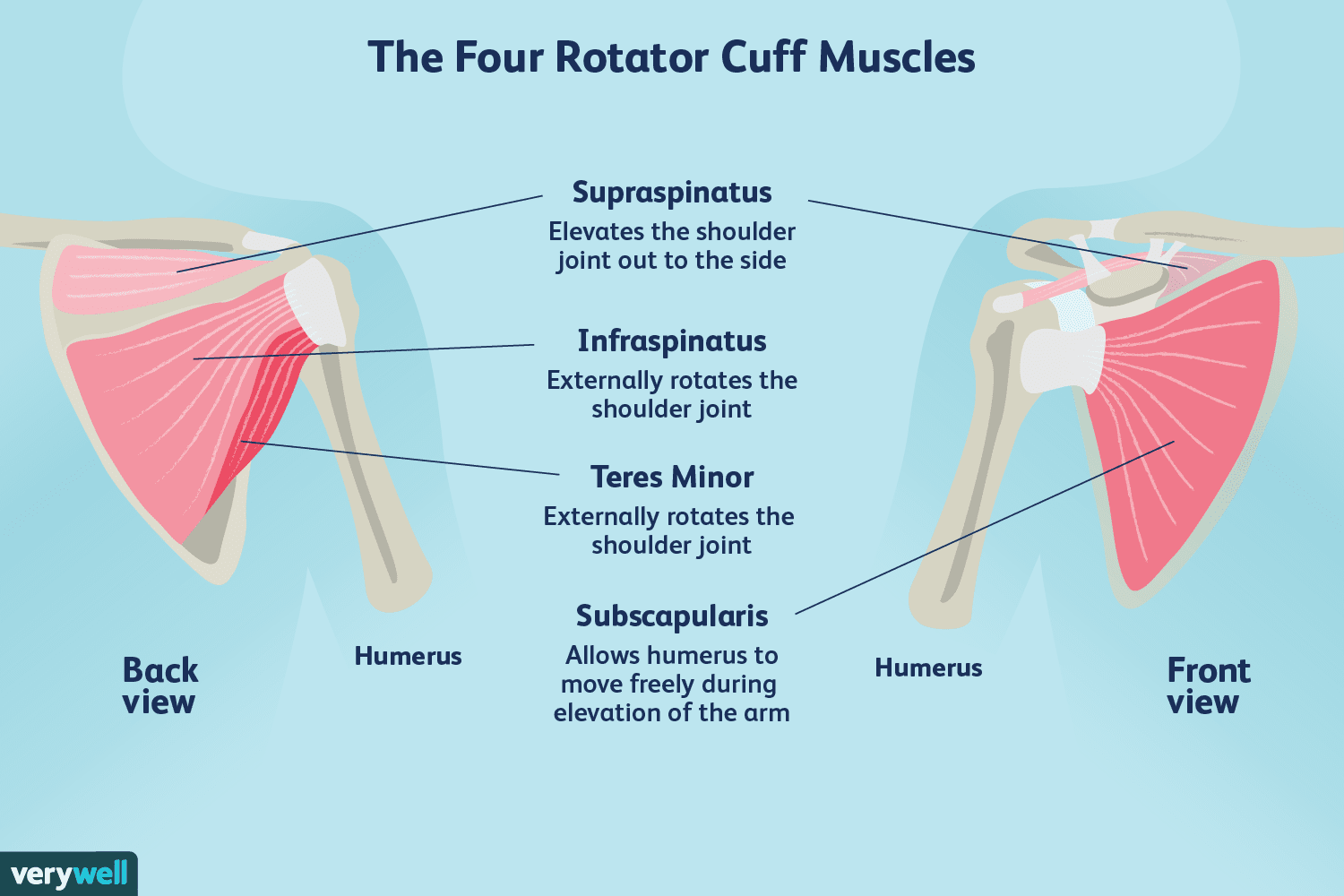
Supraspinatus: Abducts the arm → attaches to the SUPERIOR facet of the greater tubercle
Infraspinatus and teres minor → Externally rotates the arm → attaches to the greater tubercle
Subscapularis → Internally rotates the arm → attaches to the lesser tubercle of the humerus
*Remember the story, the subscapsularis is the superior rich kid, the infraspinatus and teres minor are extraverted friends who always hang out, and the subscapularis is the introverted subdweller
What are the rotator cuffs and their actions?
It inhibits phagolysosome fusion
So macrophages can engulf the TB into a phagosome but the phagosome DOESN’T become a phagolysosome
So basically TB can stay inside the phagosome and even multiply in there
What protects TB from being destroyed by macrophages?
Bacillary angiomatosis
Bartonella = cat scratch disease
What is this?
Remodeling = Matrix metalloproteinases
Scar formation = Transforming growth factor - Beta (TGF-Beta)
Remodelling of a scar is mediated by what? What about the scar formation itself?
It increases!
There is an increased venous return because of decreased SVR → which increases stroke volume
What happens to cardiac output in instances of an AV fistula?
Increased tactile fremitus = there is something increasing the density of lung tissue
Pneumonia
Decreased tactile fremitus = there is something in-between the lung tissue and the chest wall causing there to be a decrease in lung vibrations
Pneumothorax or
Pleural effusion
What does tactile fremitus tell us? Tell me the MCC of increased vs decreased tactile fremitus.
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors:
Drugs like Pioglitazone and Gemfibrozil use them to improve insulin sensitivity and lower triglyceride levels, respectively
What are PPARs?
PPAR-alpha: Found in the liver, muscle, kidney, and heart → increases fatty acid oxidation and LPL activity (increases HDL synthesis)
Fibrates
PPAR-gamma: Found in the adipose tissue → increases insulin sensitivity
-tazones (i.e. pioglitazone and rosiglitazone)
What are the different types of PPAR? Which drugs use them as a MOA?
Fibronectin
Key indicator of ECM production in pathological states
Collagen
The structural protein of the ECM
What are the two main components of extracellular matrix?
Dysdiadokokinesia
What is another way to say “unable to do rapid alternating movements”
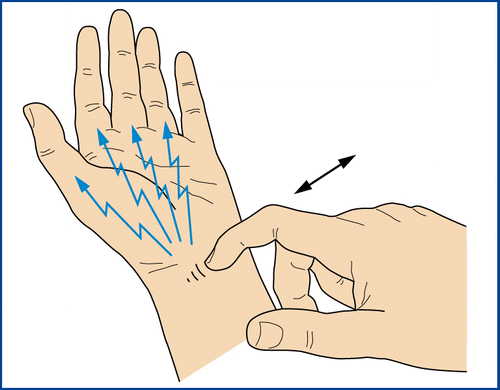
The person has carpal tunnel!
What does a positive Tinel sign tell us?
Hyperopia: Farsightedness
Myopia: Nearsightedness
Nuclear sclerosis: Age-related cataract
Presbyopia: Age-related gradual loss of the eye’s ability to focus on close objects
Give me another name for the following:
Hyperopia
Myopia
Nuclear sclerosis
Presbyopia
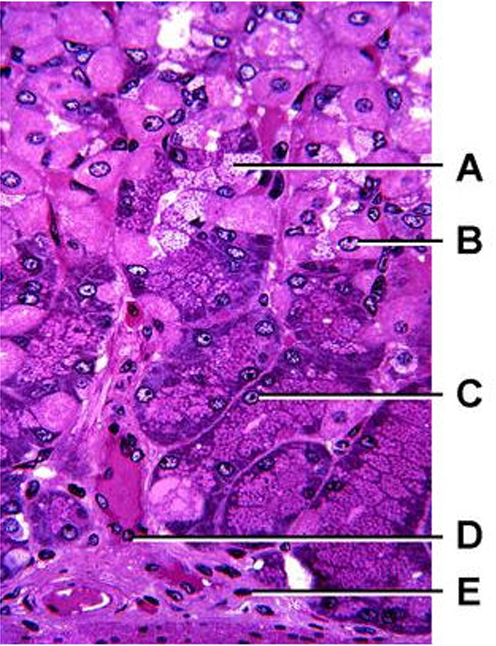
A. Neck cell → produces gastric mucus
B. Parietal cell → produce gastrin (You can tell because of their intensely acidophilic cytoplasm)
C. Chief cell → produce pepsin (have a basophilic cytoplasm)
D. Vascular endothelial cell (it’s literally lining a capillary)
E. Perivascular fibroblast
Glycosaminoglycans!
aka mucopolysaccharides
What is dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate?

Either Hunter syndrome or Hurler syndrome!
An accumulation of mucopolysaccharides is suggestive of what kind of diseases?
Porphobilinogen deaminase
What enzyme mutation causes acute intermittent porphyria?
TRUE!
It presents with acute onset joint pain, erythema, swelling, refusal to bear weight, and the signs/symptoms of sepsis
True or False: Septic arthritis is a common surgical emergency in the pediatric population
A fluoroquinolone!
Inhibits bacterial topoisomerases (i.e. DNA gyrase)
What kind of drug is ciprofloxacin?
Postinfection glomerulonephritis!
“Proliferative glomerulonephritis” is a common way to describe what?
Tremors and arrythmias
What are the side effects of B2 agonists?
Plasminogen -→ plasmin
CLEAVES FIBRIN! ✂
Prothrombin → Thrombin & Fibrinogen → Fibrin
Forms CLOTS ❤
Okay so we know the following:
Plasminogen -→ plasmin
Fibrinogen → Fibrin
Prothrombin → Thrombin
What are their roles?
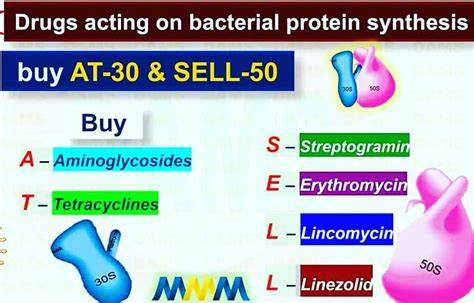
Neisseria gonorrhea, chlamydia, and HSV
Give erythromycin (a macrolide that binds to the 50s subunit)
Neonatal conjunctivitis is most commonly caused by what? What should ALL babies get as a topical prophylaxis?
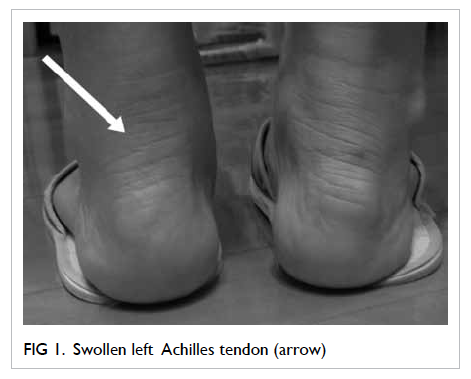
Fluoroquinolones!
“An antibiotic is causing a tendinopathy” what drug are we talking about here?
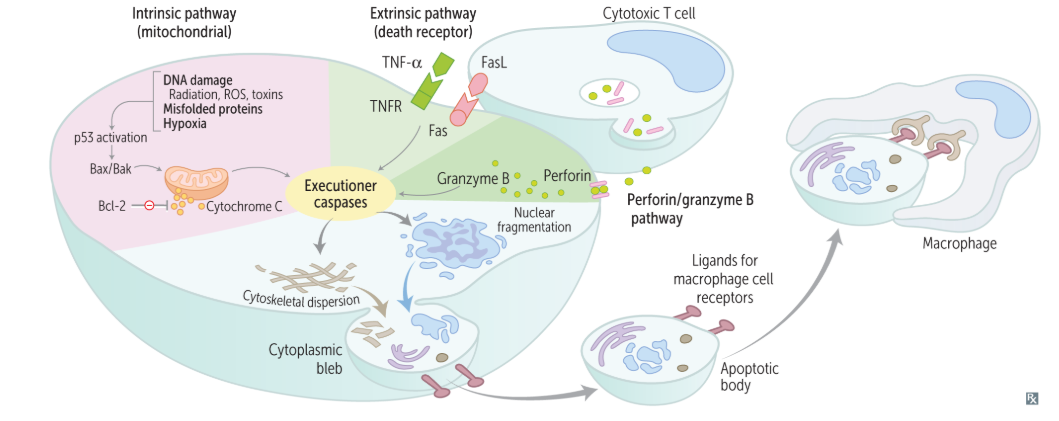
Intrinsic:
p53 → Bax/Bak → Bcl-2 → CYTOCHROME C
Extrinsic:
TNF-alpha/TNFR and FasL/Fas
Who is signaling for apoptosis in the intrinsic pathway? What about the extrinsic pathway?
They stimulate endogenous release of insulin from the pancreatic beta cells
Okay so Glipizide is a sulfonylurea… how does it work?
HHV-6 aka ROSEOLA!
What is going on here?
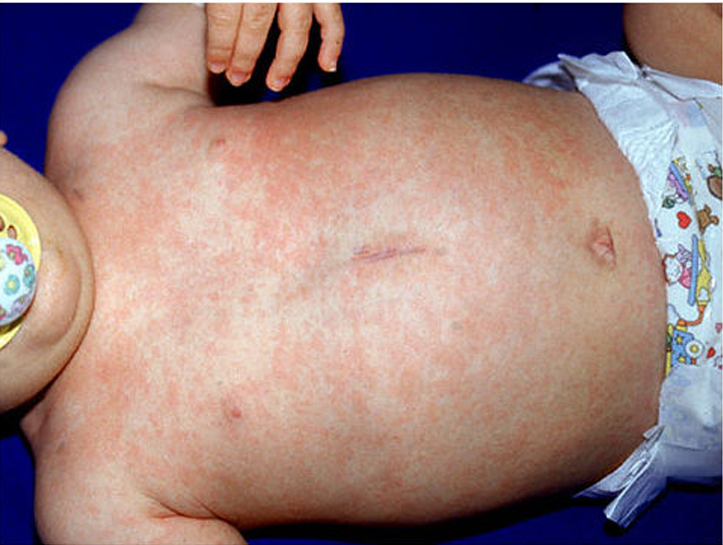

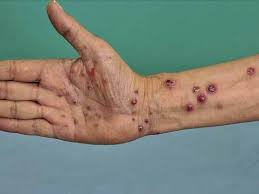
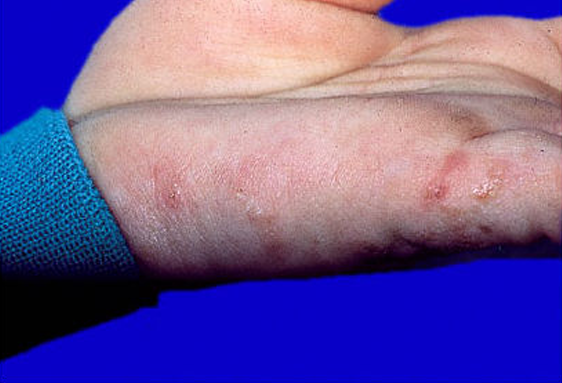
Scabies!
What is going on here? Note: they are on the armpits, both hands and feet, and groin
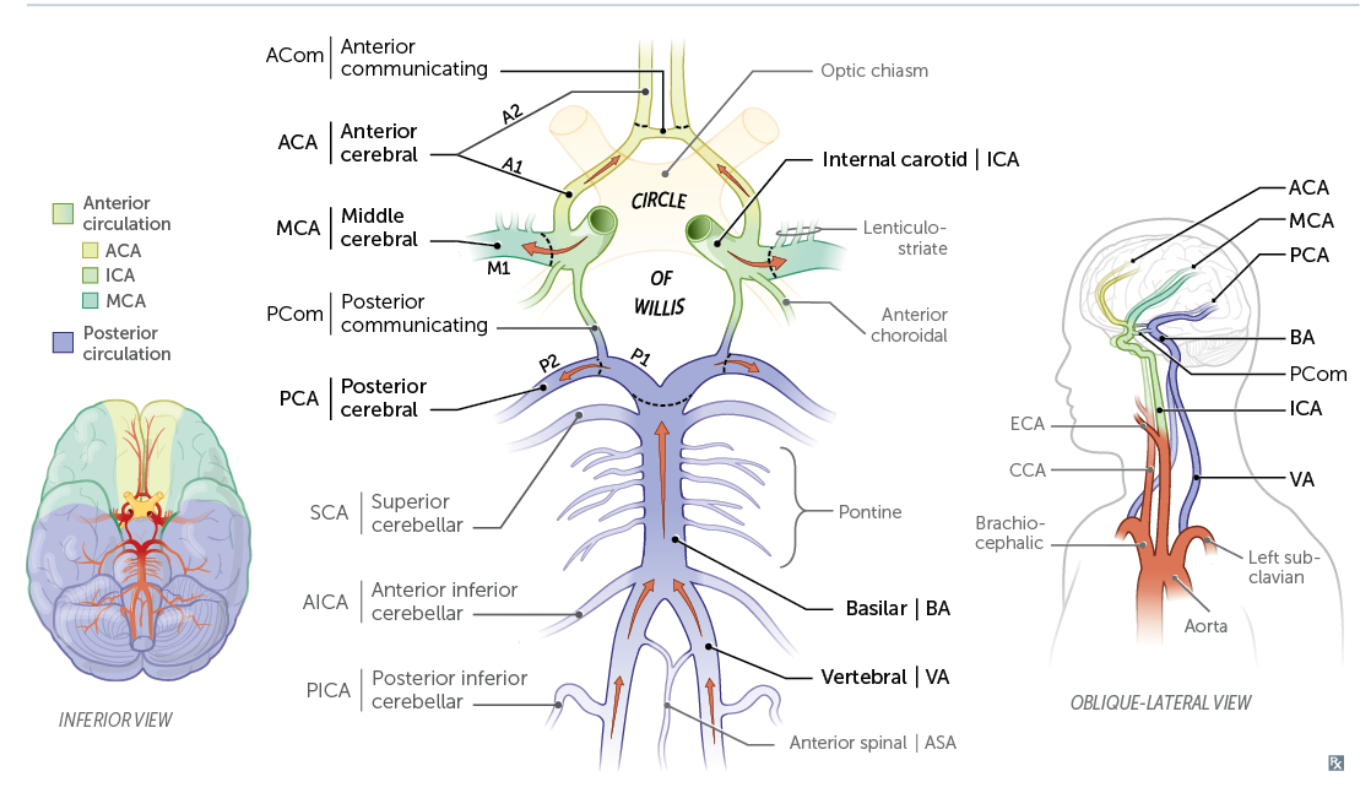
The Posterior cerebral artery
What artery are we pointing at here?
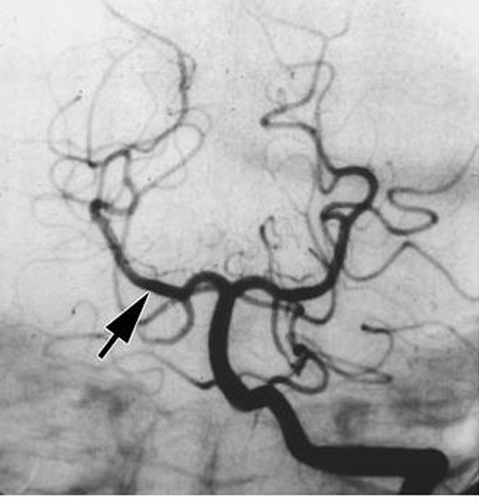
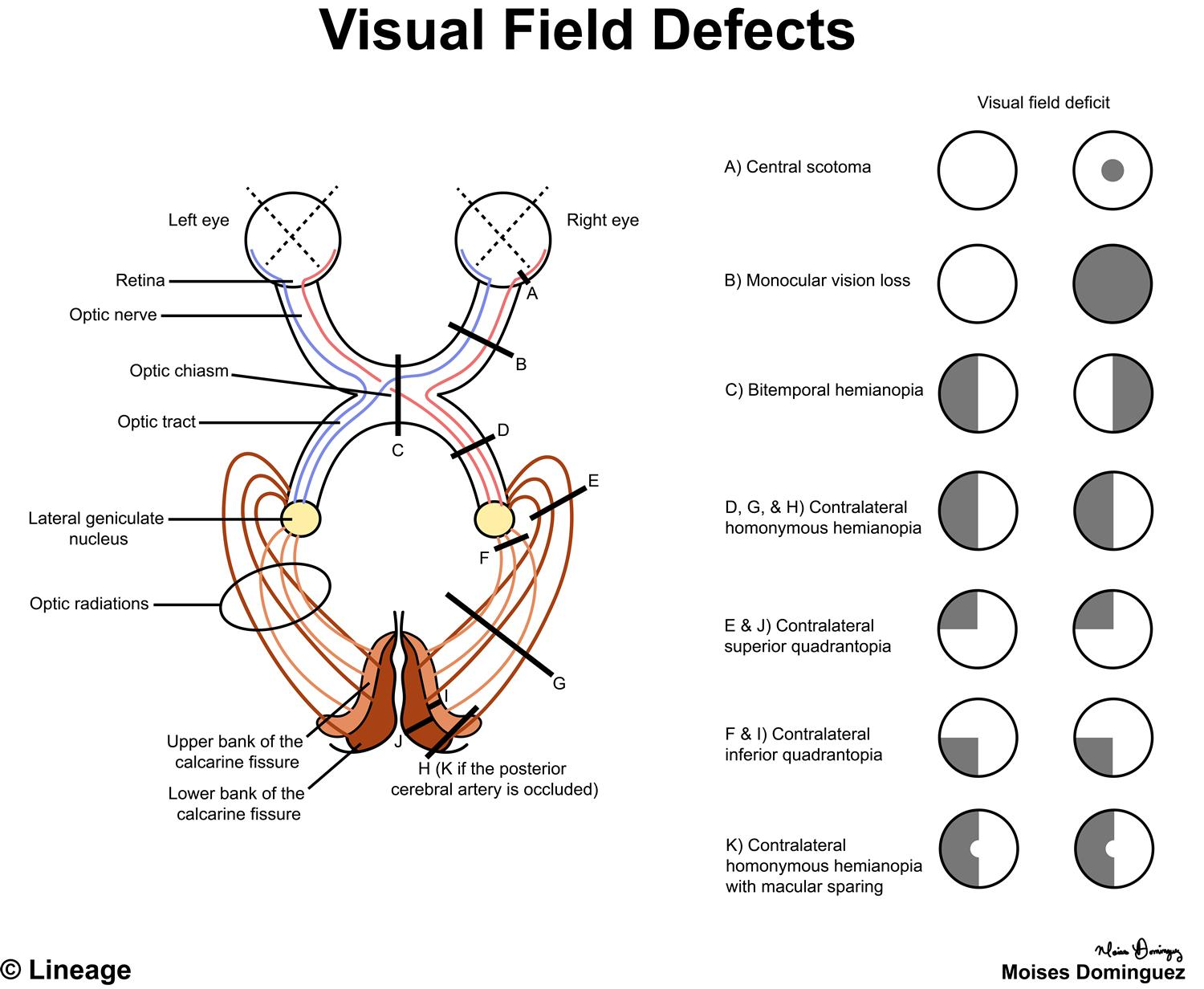
You get contralateral homonymous hemianopsia with macular sparing!
What happens when you infarct the posterior cerebral artery?
Pulmonary blood flow increases!
B/c there is a reversal of the pressure gradient between the pulmonary and systemic circulation
What happens to pulmonary blood flow in the first few minutes after birth?
Leukocyte adhesion!
What is CD18 used for?
Histamine
Prostaglandin-E2
Bradykinin
What are the primary inflammatory mediators?
Neostigmine!
Because succinycholine is an ACh receptor AGONIST! and Neostigmine is a cholinesterase INHIBITOR!
*Basically, we increase the amount of ACh available which competitively binds to the ACh receptors (causing succinylcholine concentrations to decrease)
What drug would reverse the effects of succinylcholine?
Dantrolene!
A ryanodine receptor antagonist → prevents the release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
QUICK! Someone is experiencing malignant hyperthermia. What do we administer? What is its MOA?
Androgens!
We will see Hirsutism
*The effects of a Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor is less dramatic in males though b/c they are already producing these but yeah they occur in the testes of males
What does a Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor produce?
5alpha-Dehydrogenase: Making DHT
1alpha-Hydroxylase: Makes the active form of vitamin D
21-Hydroxylase: Deficiency is seen in CAH
11Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II: Inhibition of this causes excess cortisol
3-Oxosteroid delta4-Dehydrogenase: Seen in bile acid synthesis
Tell me… what processes do you see the following enzymes in?:
5alpha-Dehydrogenase
1alpha-Hydroxylase
21-Hydroxylase
11Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II
3-Oxosteroid delta4-Dehydrogenase
Decreased peak bone accretion!
aka their bones will have low mineral density → increases risk of osteoporosis
What are the immediate effects of low calcium to a pre-pubescent child?
CD18!
LAD = LFA-1 integrin (CD18) deficiency
*Look for late separation of umbilical cord
What is another name for B2 integrin?
Cigarette smoking!
What is the greatest risk factor for pancreatic cancer?
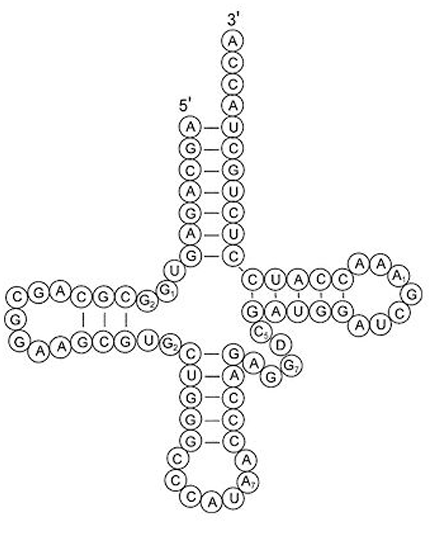
mRNA: AUG → UAC (anticodon)
So we know that mRNA’s start codon is AUG, what would be the matching sequence on tRNA?
Enteropeptidase: Converts trypsinogen → trypsin
Aminopeptidase: an EXOpeptidase → actually snip amino acid chains
Carboxy peptidase A: an EXOpeptidase → actually snip amino acid chains
Chymotrypsin: breaks down amino acids (basics, i.e. Arginine and Lysine)
Trypsin: breaks down amino acids (aromatics)
What do the following do?:
Enteropeptidase:
Aminopeptidase:
Carboxy peptidase A:
Chymotrypsin:
Trypsin:
Scleroderma! → CREST syndrome
Immediately what is this?
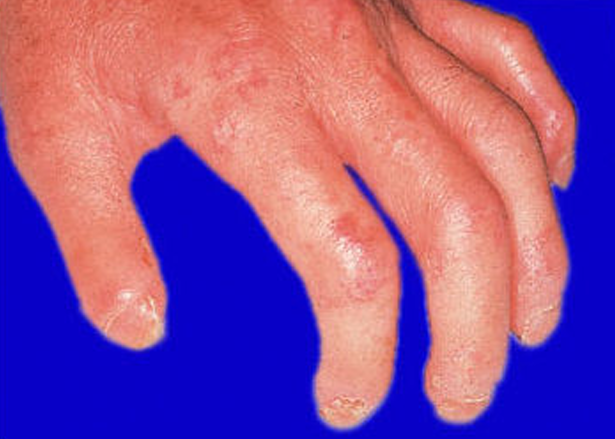
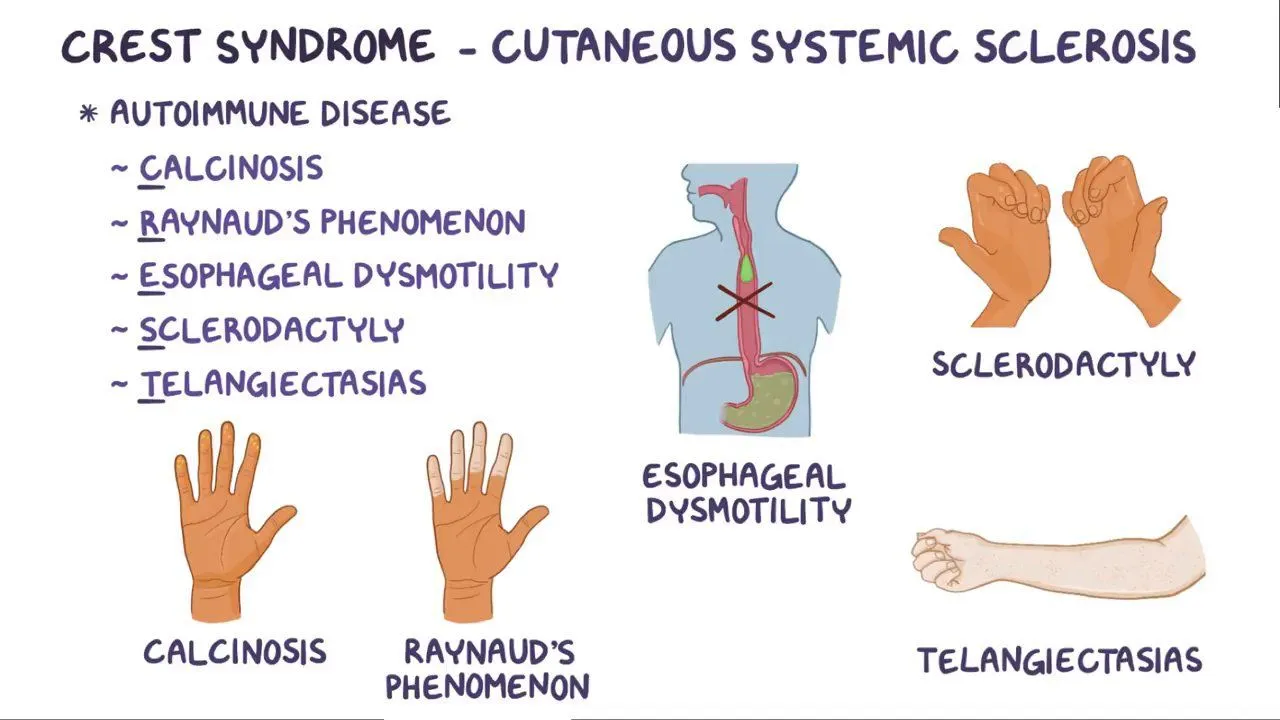
What does CREST syndrome stand for?
TRUE!
The lower esophageal sphinctor is fibrosed which means it’s scarred and can’t contract = decreased tone
True or False: in CREST syndrome LES tone is decreased
A: LE Dorsal column → Fine touch, vibration, proprioception
B: UE Dorsal column → Fine touch, vibration, proprioception
C: Lateral Cortical spinal tract: Voluntary movement (contralateral)
D: Lateral Spinothalamic tract → Pain and temperature (contralateral)
NOTE!!! This is NOT the spinocerebellar which is on the EDGE EDGE
E: Anterior Corticospinal Tract → Voluntary movement (ipsilateral)
What is ABCDE?
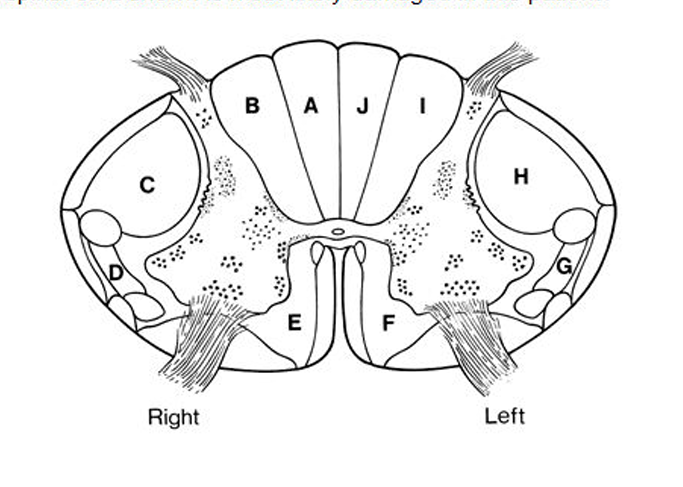
Spinothalamic: Spinal Cord
Dorsal column: Medulla
Lateral corticospinal tract: Medulla
Where do the following decussate?:
Spinothalamic:
Dorsal column:
Lateral corticospinal tract:
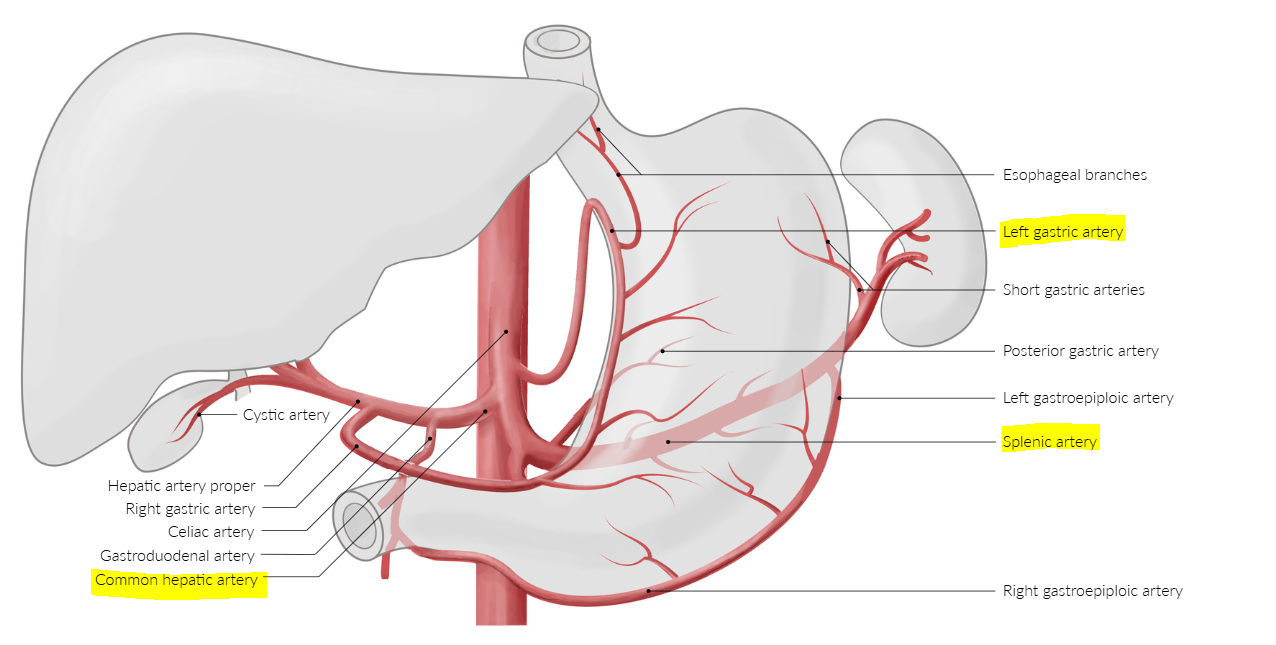
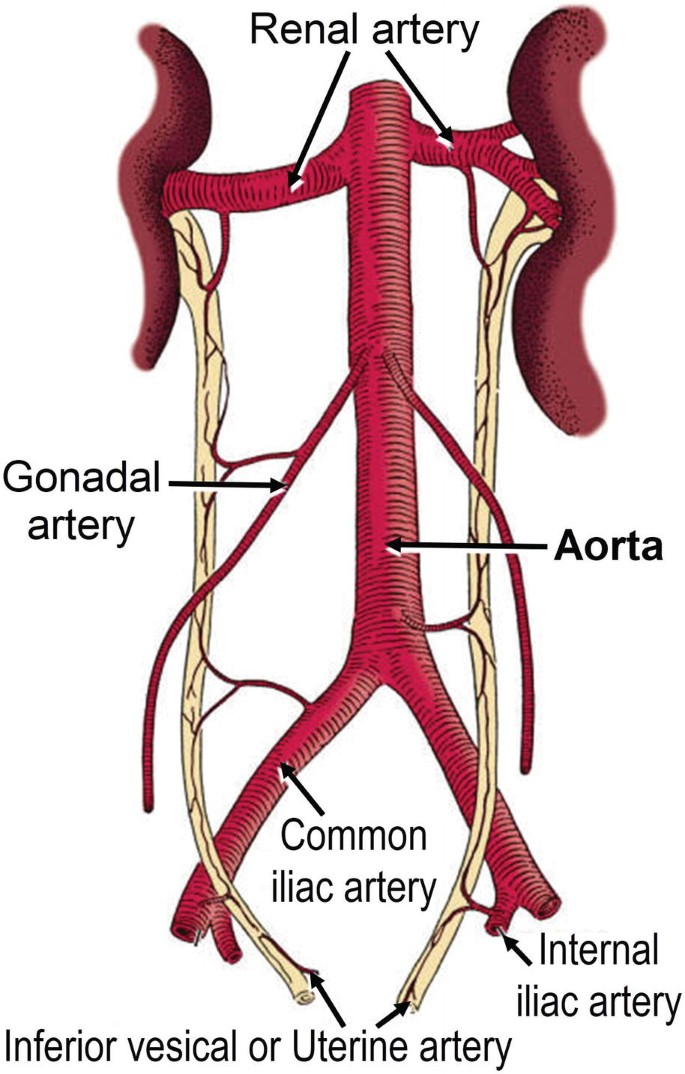
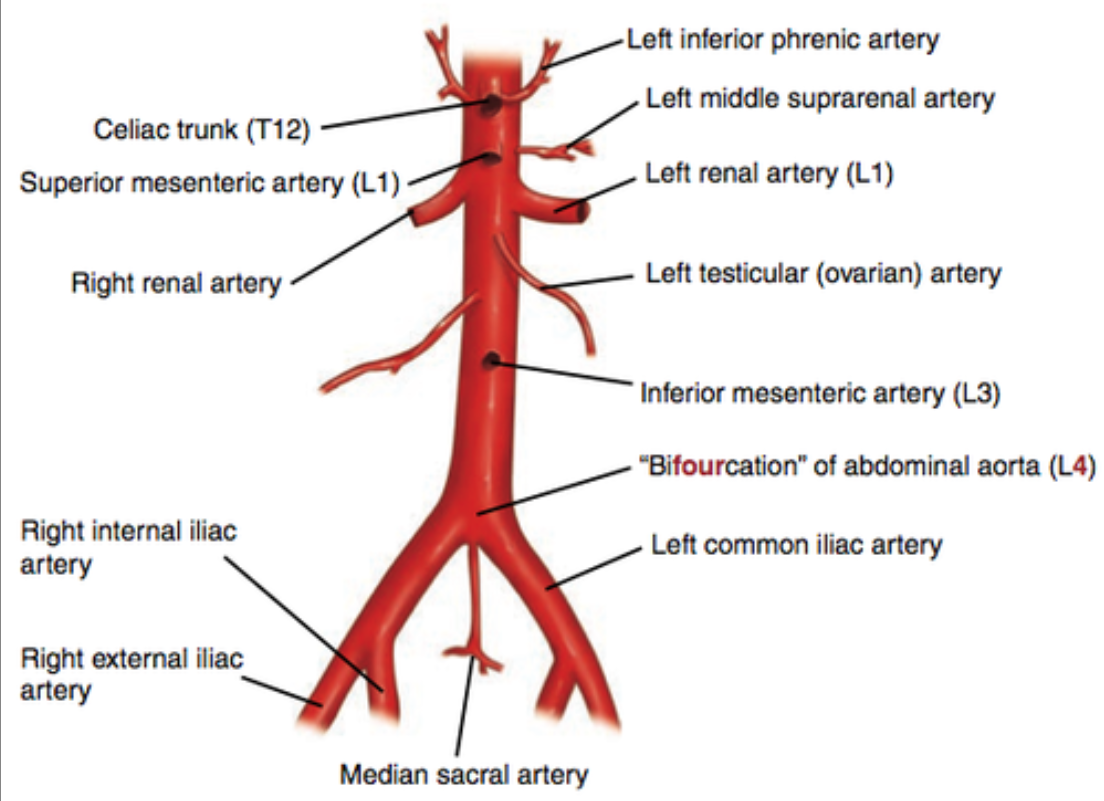
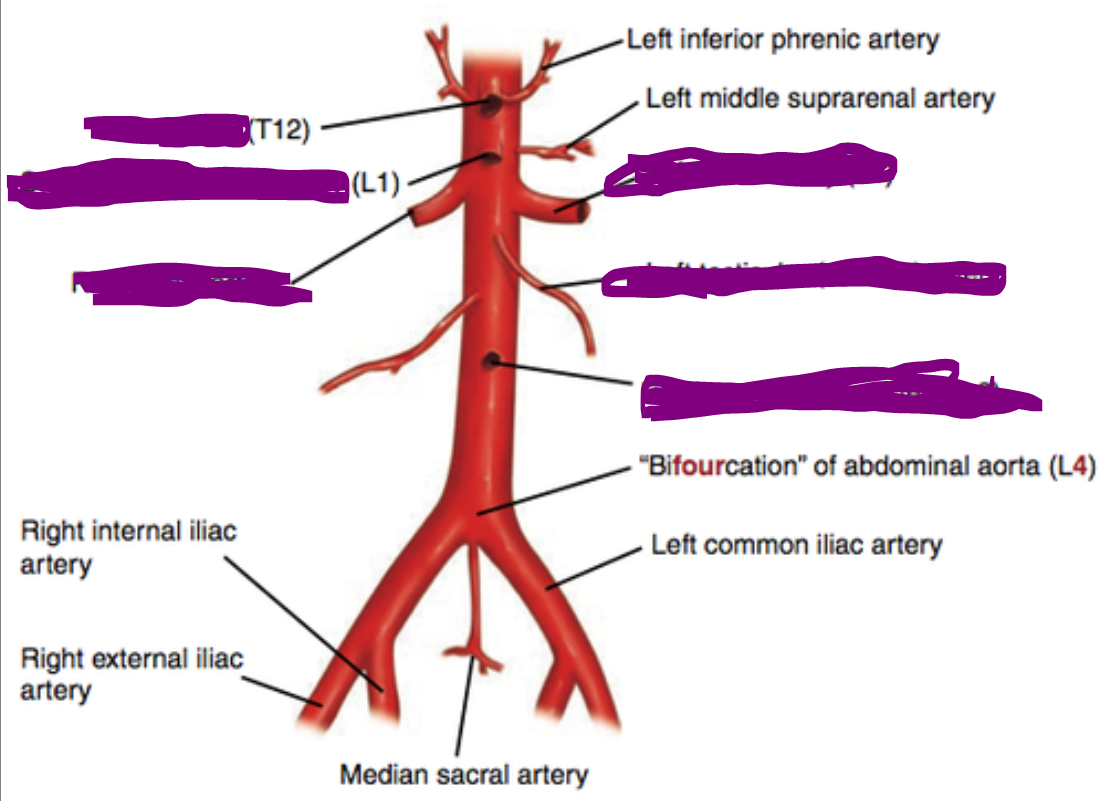
Celiac trunk branches:
Common hepatic
Splenic artery
Left gastric artery
What are the branches of the celiac trunk? Which one is associated with esophageal varices?
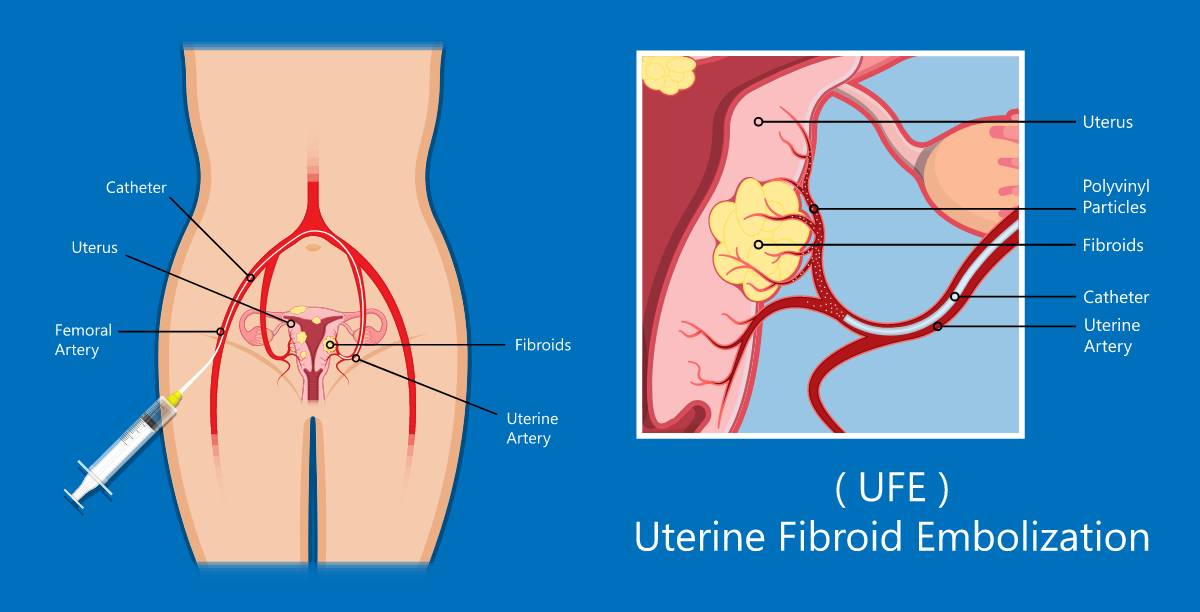
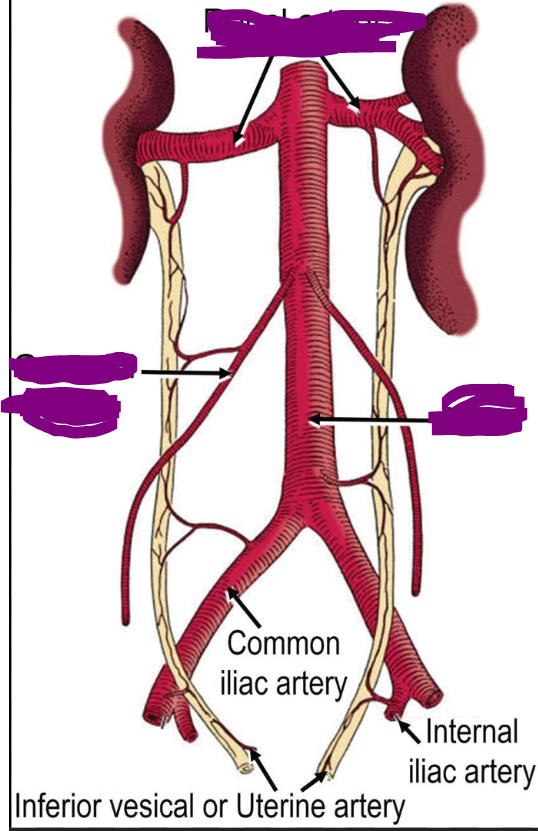
Femoral artery → External iliac → Internal iliac → Uterine Artery
How can you get from the femoral artery to the uterine artery?
Cardiogenic shock: Inability for heart to pump blood
Seen in a MASSIVE MI
Hypovolemic shock: Inadequate tissue perfusion due to critical reduction of bodily volume
Define the following:
Cardiogenic shock:
Hypovolemic shock:
FALSE!
Abraham Lincoln had Marfans and was smart enough to become president
This helps differentiate Marfans from Homocystinuria which DOES have intellectual disability
True or False: Marfan’s is associated with intellectual disability
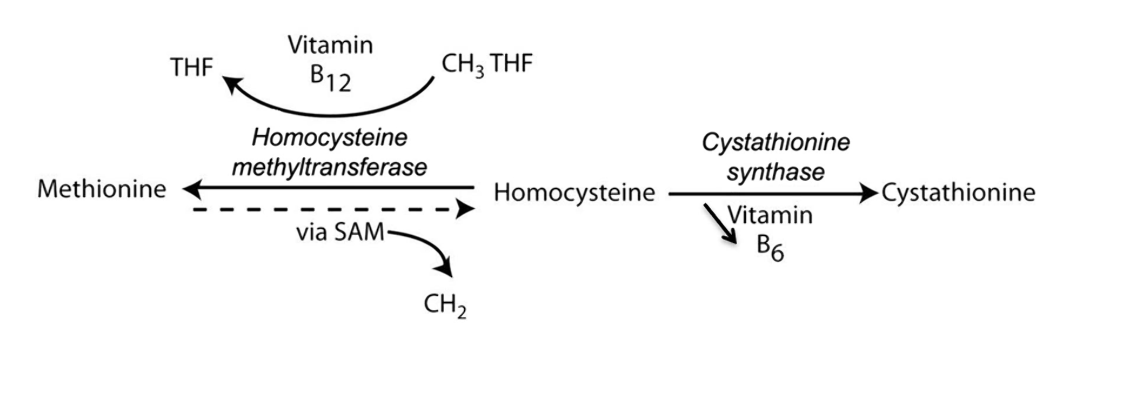
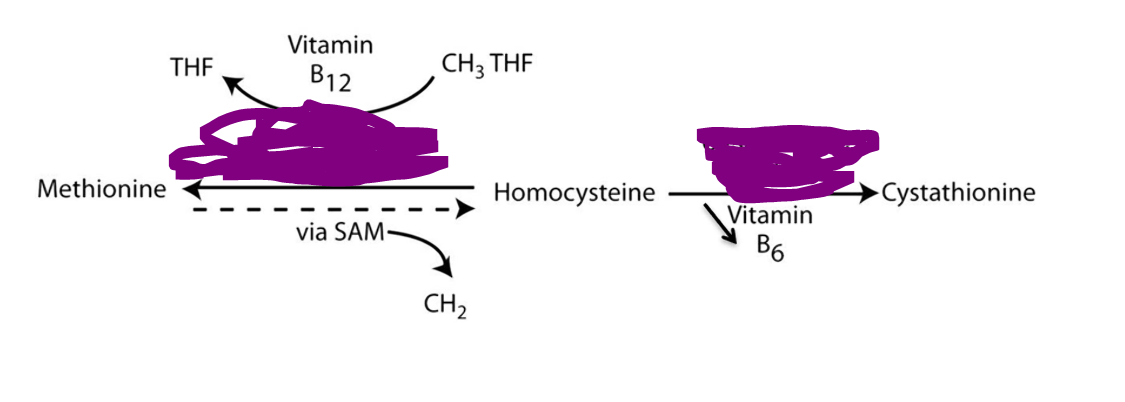
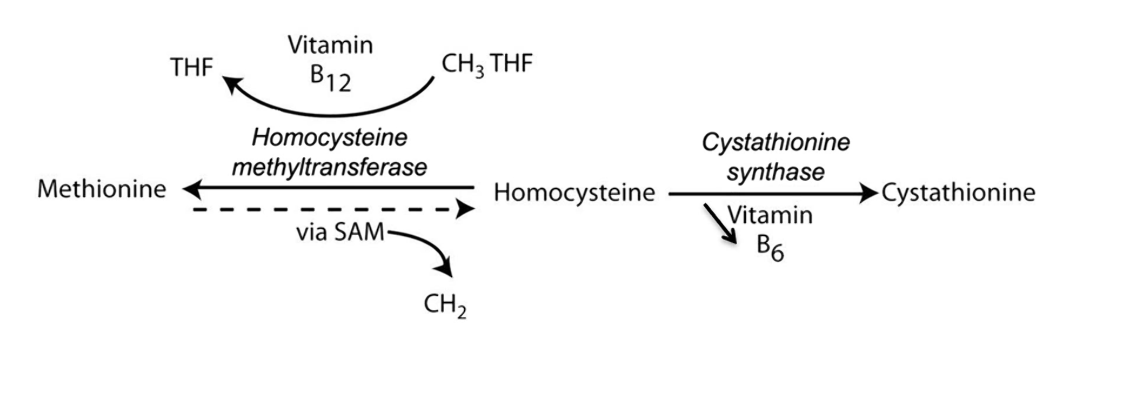
Homocysteine methyltransferase
Cystathionine synthase
What are the two main enzymes that can be effected in Homocystinuria?
NNT = 1/ARR
How do you calculate the NNT?
FALSE! DUH!
Fibrin is the final product of the coagulation cascade (think making a fibrin mash)
Platelets are the primary response to stop bleeding
True or False: Fibrin and platelets are the same thing
TRUE!
Therefore, in von Willebrand disease we will see a moderately suppressed activity of factor VIII with a normal PTT time
True or false: vWF typically stabilizes factor VIII, allowing it to do its job
Glycine
Proline (which gets converted to hydroxyproline)
Lysine (which gets converted to hydroxylysine)
What are the three amino acids you should be thinking about in collagen synthesis?
33%!
Every 1/3 amino acids in collagen is glycine
What is the glycine content in collagen?
Proline → Hydroxyproline
Makes the kinks for triple helix formation
Lysine → hydroxylysine
Formation of cross-links
*Please do not forget that vitamin C is required for hydroxylation!
What is the role of proline in collagen synthesis? What about lysine?
Sudden reduced blood flow to the heart
What is acute coronary syndrome?
Thiazides: Distal tubule
Spironolactone: Collecting ducts
What part of the nephron do the following act on?:
Thiazides:
Aldosterone inhibitors (i.e. spironolactone):
A form of estrogen produced by adipose tissue, ovaries, and adrenal glands
What the heck is “Estrone”
30mL/h
What is normal urine output?
Enteropeptidase
Converts trypsinogen → trypsin
Enterokinase is aka what? What is the function?
ACh: Stimulates M3 receptors on gasdtric parietal cells = gastric acid secretion
Cholecystokinin: produced by duodenal and jejunal I-cells → stimulates pancreatic secretion and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi, contraction of the gallbladder, and delay of further gastric emptying
Enterokinase: converts Trypsinogen → trypsin
Histamine: Produced by enterochromaffin-like cells → stimulates parietal cells to produce gastric acid
Secretin: Produced by duodenal S cells → promotes release of bicarb-rich pancreatic secretions and bile → INHIBITS gastric acid production
What do the following do in GI:
ACh:
Cholecystokinin:
Enterokinase:
Histamine:
Secretin:
FALSE!
p53 is a transcription factor that effects RNA polymerase!
True or False: p53 is a transcription factor that effects DNA polymerase
TRUE!
True or false: The TATA sequence can be found in the promotor region
A fluoroquinolone!
I.e. Levofloxacin (-FLOXACIN)
“After taking an antibiotic, he got an Achilles tendon rupture” What was the antibiotic?
Making the patient hyperventilate
When using a ventilator, if you “increase the frequency at constant tidal volume” you are essentially doing what?
Testosterone: Promotes the speeding up of bone growth during puberty
Estrogen: Promotes the slowing down or stopping of bone growth (epiphyseal plate closures)
How do testosterone and estrogen play a role in bone growth during puberty?
There is a problem with peroxisomes and beta-oxidation
“Serum studies show increased concentrations of very-long-chain fatty acids” What should we immediately be thinking is wrong?
It is a serotoninergic receptor antagonist!
How does Ondansetron work as an anti-emetic?
Mucus production: Increases
Activity of airway cilia: Decreases
Alveolar macrophage function: Decreases
*Smoking disrupts the ability of the lungs to clear mucus and foreign debris!
What does smoking do to the following:
Mucus production
Activity of airway cilia
Alveolar macrophage function
Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
A vasculitis with eosinophilia and granulomas
What is another name for Churgg-Strauss syndrome? How does it present?
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
A vasculitis that has necrotizing granulomas and vasculitis effecting the respiratory tract and kidneys (associated with ANCA → anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies)
What is another name for Wegener granulomatosis?
Urothelial carcinoma!
Highest risk = cigarette smoking
what is this
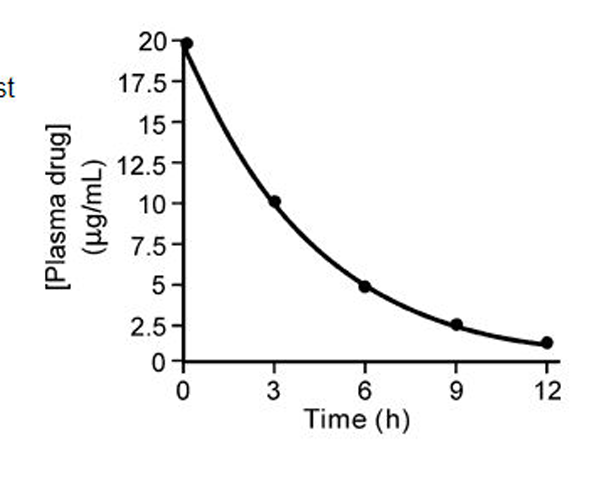
3 hours!
It took 3 hours for the drug to get from [20] to [10]
What is the half-life of this drug?
TRUE!
It is a viral protein produces by the HPV (a VIRUS!)
True or False: the E6 protein seen in HPV 16 is a non-human antigen
Because it is a partial agonist of dopamine receptors
Apriprazole has a decreased chance of causing drug-induced parkinsonism… why?
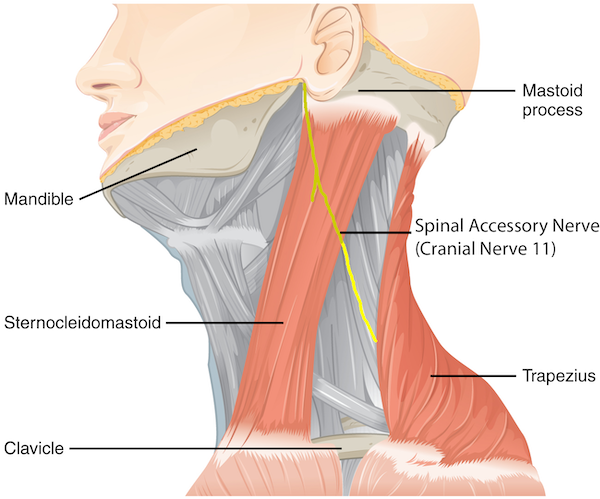
The Trapezius!
Innervation: CN XI
What muscle elevates the shoulder? What is it’s innervation?
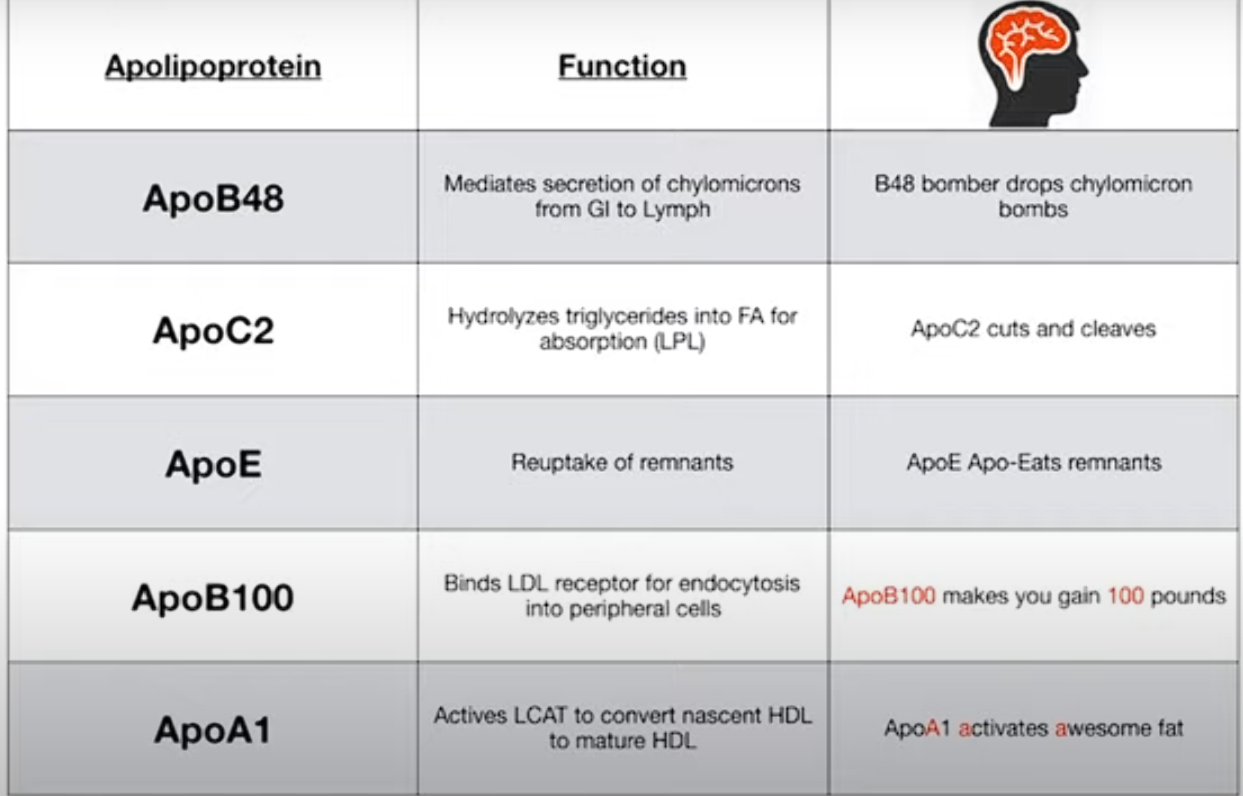
Talk to me about ApoA-E

INGESTION!
What is the route of transmission for toxoplasma gondii?
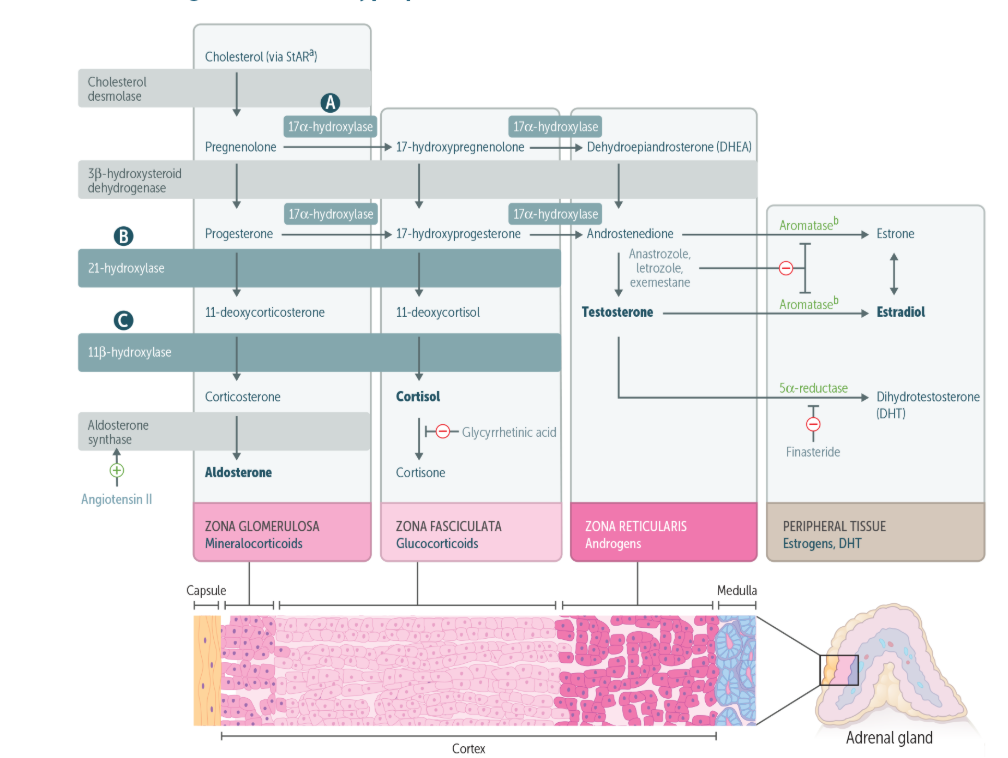
21-hydroxylase deficiency!!
CAH!
“INCREASED concentration of 17-hydroxyprogesterone and androstenedione” is signaling what disease?
Schwann cells and macrophages
During Wallerian degeneration, who clears the debris?
Satellite cells give nutrition and support to astrocytes
What do satellite cells do?
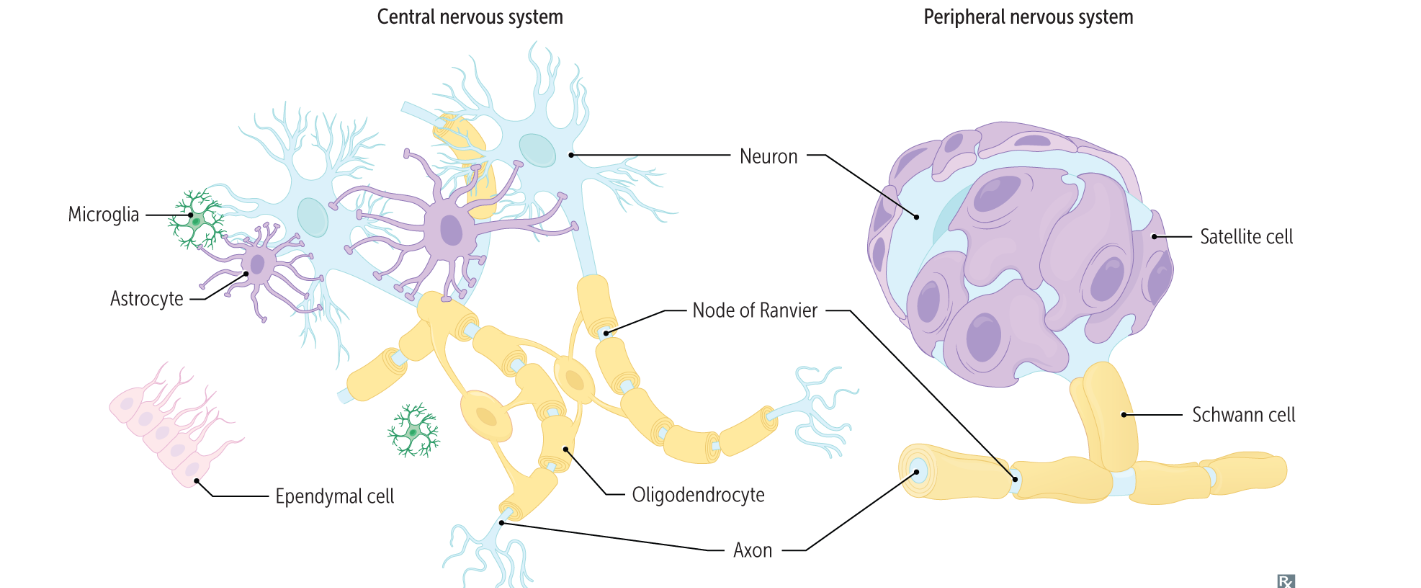
Oligodendrocytes: CNS → Multiple axons
Schwann cells: PNS → ONE axon
How many axons are myelinated with Schwann cells? What about oligodendrocytes?
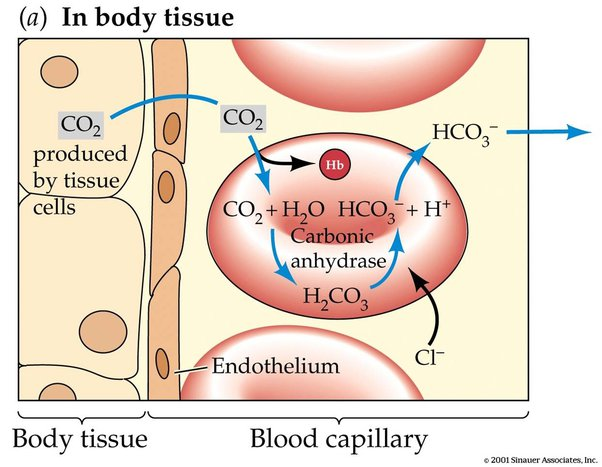
CO2- will accumulate in RBCs
HCO3- will have a decreased concentration in RBCs AND the plasma
Cl- will have a lower concentration in the RBCs and a HIGHER concentration in the plasma (compensating for less bicarb leaving the RBCs)
*RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS!*
If you knock out carbonic anhydrase in RBCs, what will happen?