Block 4: Basic Electricity
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
What is a unit of charge (condition)?
Coulomb.
1 sec of coulomb is…
1 sec is Amp.
What is an “Element”?
Is a type of substance/matter made of one type of atom.
Can an atom be split by chemical means?
Not by any means of a chemical process, instead by physical process.
Is it true that the # of protons is equal to the # of neutron?
True
What is the formula to find the amount of electrons in a element?
2n² (ie: 2(3)² = 18 valence electrons.)
With the following valence electrons they are known as?
1, 2, 3 electrons:
Only 4 electrons:
5,6, and so on electrons:
1, 2, or 3 electrons: Conductors
Only 4 electrons: Semiconductors
5 or more electrons: Insulators
Why is the valence orbit (the last shell in a atom) important?
Tells us if the atom is a Conductor, Semiconductor, or an Insulator.
What is the unit of resistances called?
Ohms (Ω ← omega)
What is the purpose a resistor?
To limit or control the current flow of electricity. To dissipate heat.
(Resistance value → Ohmic value)
What is the formula to determine a resistor’s resistance value?
𝑅=𝜌𝐿/𝐴
R = Resistance - - - - - - - - - - |
𝜌 (Rho)= Resistivity | - Directly proportional
L = Length or wire - - - - - - - - |
(÷)
A = Cross Sectional Area
Define “P.T.C”.
Positive Temperature Coefficient: if temp. increases, then the resistance increases.
Define “N.T.C”.
Negative Temperature Coefficient: if the temperature increases, then the resistance decreases.
What is magnetism?
The ability to attract or repel specifically ferrous metals.
The three aspects that make a magnet are…
Permeability: How magnetic it is. (pull in electrons/protons)
Retentivity: To retain its magnetism.
Reluctantivity: How it resists magnetism (ie: copper)
How to re-magnetize a magnet?
By using a Keeper to maintain contact with the bipolar (South + and North -) fields.
The 5 sources of electricity are?
Hint:
“EETES”
*1) Electro-chemical (batteries)
*2) Electro-Magnetism (generators)
3) Thermocouple (heat produced via 2 types of material connected)
4) Electromagnetic material (pressure) (ie: Quartz/flint)
5) Sun-material (light)
The 2 types of electricity are?
Static: Electro-accumulation
Dynamic: Flow of electricity
The effects of wiring are…
*1) Heat
*2) Magnetism
3) Electrolysis
Electron flow theory states:
Conventional current theory states:
Negative to positive. (From North to South pole - closed loop)
Positive to negative (South to North Pole)
What makes silver special as a conductor?
Has the least amount of resistance to electrical currents. Yet, it can corrode.
Atoms in a neutral position are considered?
They are considered electrically neutral. Thus, cannot produce any electricity at all. (ie: 5 protons, 5 neutrons)
Difference between positive ion and negative ion?
- : Unstable with excessive electrons (anions)
+ : Unstable with excessive protons (Cations)
The 2 ways to artificially create a magnet is to?
By physical means: friction
By electrical means: using electrical currents with copper wires.
What are the 2 ways to find Ohmic value?
Ohmic-meter
Calculating with color codes
What are the 2 types of variable resistor:
Potentiometer: Has 3 terminals and can alter the voltage/ohms.
Rheostat: Has 2 terminals and can control the electrical current.
Define “LDR” or a Photo Cell.
Light Dependent Resistor: a resistor that needs light to alter resistance.
Define “Thermistor”.
A sensor resistor that needs temperature to alter resistance. (as the sensed temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor decreases.)
Define “Varistor”.
A sensor resistor that is sensitive to voltage and can alter resistance based on the amount of voltage it detects. (resistance decreases as voltage increases)
What does an Ohmmeter (Ω) measure?
Either ohmic value or continuity or resistances in parallel (doesn’t need power or polarity)
What does an Voltmeter (V) measure?
Its voltage in parallel (needs power and correct polarity)
What does an Amp-meter (A) measure?
Its Amperage (measured in series)
What is the purpose of ionizing?
To gain or lose specifically electrons and to charge an atom.
What is inside a nucleus?
Protons and Neutrons.
An example of a fixed resistor are…
Carbon composition or wire wound or thick/thin film.
An example of a variable resistor are…
Potentiometer and Rheostat.
How is electricity produced?
By using magnetic fields.
How is magnetic fields produced?
By using electricity.
What is the difference between DC and AC?
Direct Current deals with batteries while Alternating Currents deals with generators.
Ohm’s Law formula states:
E = IR
E
I x R
E = Electro-motive force (voltage pressure)
I = Intensity of the current (Amps)
R = Resistance
1 amp is equal to…
1 ma is equal to…
1000 milli-amp
1/1000 amp
Large unit to smaller unit…
You multiply.
Smaller unit to larger unit, you would multiply or divide?
You divide.
Work formula reads…
W = F x D (Force times Distance)
Power formula reads…
Power = W/T (work over time)
The 2 types of power are…
Mechanical (P = W/T)
Electricity (P = I x E)
Define “Circuit”.
A path to allow electrons to move and be of use.
The minimum requirements states what 3 components?
Some sort of power
Conductor
Load (Resistance: to consume electrical amount)
A practical circuit states what 5 components?
Power source
Conductor
Load
Switch
Protective device
What is Horse Power and Power?
Horse power is the unit for mechanical power while Power is electrical power.
The conversion for HP into P is?
1 HP = 746 W (rounded)
Difference between “Open circuit” and “Short circuit”.
Open is considered non-lethal and can be done intentionally or by fault. (power is off)
Short is considered lethal and can be done intentionally and fault. Bypassing the component’s electrical load. (power is on)
Electricity will take the path with that is the shortest. True or False?
True.

In this resistor, list what each band means:
1st: 1st digit
2nd: 2nd digit
3rd: multiplier

In this resistor, list what each band means:
1st: 1st digit
2nd: 2nd digit
3rd: multiplier
4th: tolerance

In this resistor, list what each band means:
1st: 1st digit
2nd: 2nd digit
3rd: 3rd digit
4th: multiplier
5th: Tolerance
Define “Megger”.
A tool for measuring an extremely high resistance.
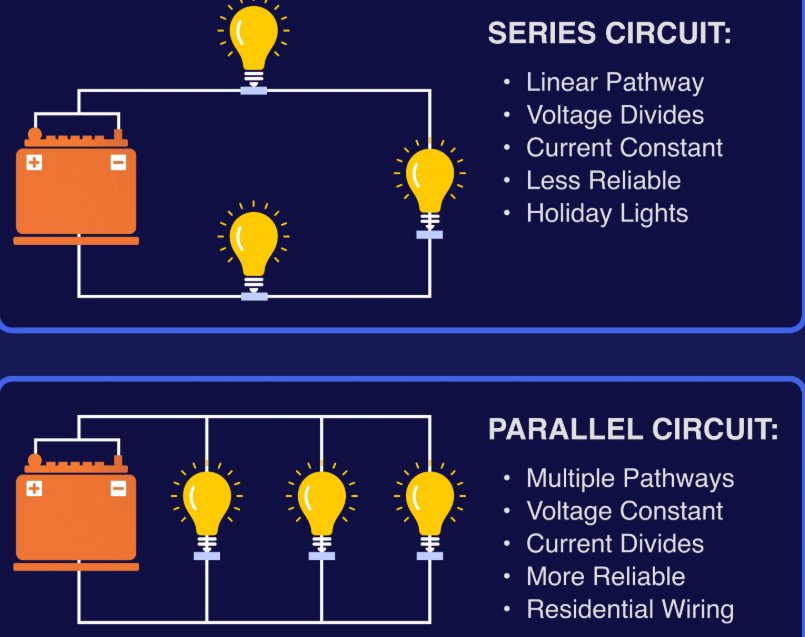
How many types of circuits are there?
Three types:
Series
Parallel
Complex (series, parallel)
What is a series circuit?
A circuit that only have one path for electrons to take.
Kirchoff’s Law states what? And what is the formula for
E = I x R?
The Voltage Law: Algebra sum of all voltage drops must be equal to the source voltage.
E(T) = E(1) + E(2) + E…..
I(T) = I(1) = I(2) = I…..
R(T) = R(1) + R(2) + R…..
The Current Law: The amount of current that enter a node has to come out as the same. (ie: 2 Amps into node = 2 Amps out another node)
E(T) = E(1) = E(2) = E…..
I(T) = I(1) + I(2) + I…..
R(T) = 1/ 1/R(1) + 1/R(2) + 1/R…..
Define “Voltage Drop” and “Voltage Source”?
Voltage Drop: As voltage travels through a circuit and powers components, they lose varying amounts of volts.
Voltage Source: When the voltage comes back around to the source, they should add up back to the original voltage value.
What is the main difference between series and parallel circuits?
Series have linear (single) pathway and have constant currents. Whereas parallel have multiple pathways and the current can divide.
If you have a circuit with only 2 resistors with different value, what formula do you now use?
R(T)= product of the 2 resistors/sum of the 2 resistors.
R1 x R2
R1 + R2
If the resistor values all have the same value, what shortcut formula can you use instead of the “Mother Formula”?
R(T) = R/N (#) of resistors
How do you prove a circuit is a series?
Take out a bulb or any sort of path, and if the power deactivates, it has a single pathway.
When solving a complex circuit, it is recommended that you start from the…
Start of the right hand side when solving for a complex circuit.
The purpose of control devices are to?
Control the amount and change the direction of the current.
How are switches rated?
According to the current and the voltage of the circuit.
How do you test a switch?
Simply using a continuity test on a Ohm-meter.
Purpose of a switch guard?
A flap piece that covers the switch which prevents accidental flipping of a switch.
Mechanical control devices include:
Manual: Done by people
Electromagnetically Operated: Done by magnetic fields (magnets)
The abbreviations of NO, NC, and DIP mean?
NO: Normally open (always off until a switch connects)
NC: Normally Closed (always on until a switch connects)
DIP: Dual in line package
What is a “Pole Switch” and a “Throw Switch”?
A “Pole” is physical part that can be pushed or pulled and in an electrical definition is the amount of a separate circuit that a switch can control for.
“Throw” is the number of circuits the current can be done by one action of a pole.
Define the following:
SPST
DPDT
SPST: Single Pole Single Pole (on-off)
DPDT: Double Pole Single Pole (2 circuits and 2 switches)
Difference between relay and solenoid?
Solenoid: Can handle multiple functions (movable core)
Relay: Is an electromagnetic switch for an on and off or activating a single circuit (fixed core)
What happens if a fuse goes out?
There is either a fast blow (if it detects any sort of overload, opens circuit spontaneous) or a slow blow (prolonged overload)
Is it true to install fuses in series?
True, simply because you want the current to go in one path (for now)
What 3 component must be connected in series?
Hint:
2 components and a meter
Fuse
Ammeter
Switch
Difference between circuit breaker and fuse?
when a fuse burns, it must be changed.
Circuit breaker, they “trip” and are able to be reset.
Define “Trip-Free Circuit”.
If the problem exist, the circuit will never transfer until the current load is stable.
Define “Cell”.
Smallest unit of a battery.
Electro-chemical batteries (device) can only produce DC or AC?
Direct Current.
Are primary batteries rechargeable?
No, if attempting to charge, this will result in the battery self destructing. These batteries cannot be recharged due to the zinc will begin to dissolve.
Is it true that the type of the material can hold a certain amount of voltage?
True, simply because of the material’s ability to store electro/chemical energy.
Define a “Secondary battery”.
They are batteries that are rechargeable and it voltage varies depending on the # of cells and type of material.
What 4 components make up a battery?
Positive electrode
Negative electrodes
the container
electrolyte (mediator)
The purpose of a battery is to…?
Provide high current for short period of time to get a device started.
What is the formula of an electrolyte?
H2SO2 + H2O → Sulfuric Acid (Sulphate) + Pure water
(30% acid and 70% water)
Note: Can be a solid, liquid, or gas
Why use pure water in sulfuric acid mixture?
regular tap water will have impurities.
(prevents chemical reaction)
What is the function of electrolyte?
A chemical compound that cause a chemical reaction that releases ion into a system to convert energy.
Define “Specific Gravity”.
A comparison of any material’s density to water’s density.
In general, how do you know if a battery is full?
By measuring its specific gravity of its electrolyte.
By using a hydrometer, would a dead battery freeze more faster than a live battery?
A dead battery would freeze much faster as all that’s left inside is water.
When measuring a battery for its temp, the procedure reads…
If above 80 degree F (standard) 10 degree F increase= add 0.004
If below 80 degree F (standard), every 10 degree = subtract 0.004
What 2 aspects affect a batteries utility?
Active material is equal to its voltage
Plate area (size) is equal to its current
How much does a lead acid-base battery produce voltage?
Per cell of a lead-base battery, produce 2 volts.
PbO2 is a chemical compound for?
Lead dioxide or Lead peroxide.
Insulators are placed in between cells has what purpose?
To prevent shortage of a battery or prevent a chemical reaction.
How do you test for the capacity of a battery?
Measuring its amperage usage per hour
For each hour, divide by that amount.
(ie: 60A/hr = 30A/2hr)
Or using a “Load Tester”
Difference between Deep Cycle and Shallow cycle?
Shallow cycle is always in full charge, while Deep cycle must be drained to be recharged once more.