Lifespan Final Pt 2 (Disorders)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Oppositional Defiant Disorder
Patterns of _____, ______, or _______ lasting at least____ evidenced by at least ___of the following symptoms from_________ exhibited during an interaction with at least 1 individual who is not _______.
Name the 3 categories.
What is key for this diagnosis?
Distress for the affected person or…or…
A. Pattern of angry/ irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness lasting at least 6 months as evidenced by at least 4 symptoms from any of the following categories, exhibited during interaction with at least 1 individual who is not a sibling.
Angry/ irritable mood
Often loses temper
Is often touchy or easily annoyed
Often angry and resentful
Argumentative/ Defiant Behavior
Often argues with authority figures or, for children and adolescents, with adults.
Often actively defies/ doesn’t comply with rules or requests from authority figures
Often deliberately annoys others
Often blames others for their mistakes/ misbehavior
Vindictiveness
Has been spiteful or vindictive at least twice in the last 6 months.
Note: persistence and frequency of these behaviors is key for diagnosis
For children under 5, behavior should occur on most days for at least 6 months unless otherwise noted
5 years and older: at least once per week, for a period of at least 6 months
Intensity should also be considered: is it outside what is considered normal for the individual’s developmental level, gender, and culture
B. Distress for the individual or those in their immediate context (family and close friends or spouse) or it impacts functioning
Intermittent explosive disorder
A. Recurrent _______ resulting from_______, manifested by either of the following (2, make sure to specify time frame).
B. Magnitude of _____ is…
These outbursts are not _____and are not committed to…
Distress or impairment or are associated with…
At least __ years old.
A. Recurrent behavioral outbursts resulting from a failure to control aggressive impulses, as manifested by either of the following
Verbal or physical aggression, twice weekly on average for a period of 3 months. Physical aggression does not result in destruction or damage of property and does not result in physical injury to animals or other individuals.
Three behavioral outbursts involving damage or destruction of property and/ or physical assault involving physical injury against animals or other people within a 12 month period.
B. Magnitude of aggression is grossly out of proportion to any provocation or stressors.
C. Recurrent aggressive outbursts are not premeditated (impulsive) and are not committed to achieve some tangible objective (power, money, intimidation etc)
D. Distress/ impairment in occupational or interpersonal functioning, or are associated with financial or legal consequences.
E. At least 6 years old (or equivalent developmental level)
F. Outbursts not better explained by another disorder and are not attributable to another medical condition
Conduct Disorder
Repetitive behavior in which…
Manifested by at least ____ of the criteria in the past ____ months, from any of the categories below, with at least one criterion present in the last 6 months.
name the 4 categories.
If the individual is older than ___, criteria for ______ are not met.
A. Repetitive behavior in which the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate social norms are violated, manifested by at least 3 of the 15 criteria in the past 12 months, from any of the categories below, with at least one criterion present in the past 6 months
Aggression to people and Animals
Often bullies, threatens, or intimidates others
Often initiates physical fights
Has a weapon that can cause serious harm to others
Has been physically cruel to people
Has been physically cruel to animals
Has stolen while confronting a victim
Has forced someone into s***** activity
Destruction of property
Has deliberately set a fire with intention of causing damage
Has deliberately destroyed others’ property (other than by fire setting)
Deceitfulness or theft
Has broken into someone else’s house, building or car
Often lies to obtain goods, favors, or to avoid obligations (cons others)
Has stolen items of nontrivial value without confronting a victim (ex. shoplifting without breaking and entering)
Serious violation of rules
Often stays out at night despite parental prohibitions,
Has run away overnight at least twice while living with parent, or run away once without returning for a lengthy period
Often truant from school, beginning before age 13 years
B. Causes clinically significant impairment
C. if the individual is older than 18, criteria are not met for antisocial personality disorder
Brief Psychotic Disorder
Presence of one or more of the following symptoms. At least one of these must be 1, 2, or 3. (4 total).
Do not include a symptom if it is a ______.
Duration of the episode is at least ___ but less than _____, with eventual…
A. Presence of one (or more) of the following symptoms. At least one of these must be 1,2, or 3
Delusions
Hallucinations
Disorganized speech (derailment and incoherence)
Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
Note: Do not include a symptom if it is a culturally sanctioned response
B. Duration of an episode is at least 1 day but less than 1 month, with eventual full return to premorbid level of functioning
Schizophreniform disorder
____ or more of the following criterion, each present for a _______, during a ____ period (or less if successfully treated). At least one of these must be 1,2, or 3. (5total)
B. Episode lasts at least _____ but less than ______.
C. _____ and ______ have been ruled out because either
or
.
A. Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of the time, during a 1 month period (or less if successfully treated). At least one of these must be 1,2, or 3
Delusions
Hallucinations
Disorganized speech
Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
Negative symptoms
B. An episode lasts at least 1 month but less than 6 months. When a diagnosis must be made without waiting for recovery, must be qualified as “provisional”
C. Schizoaffective disorder and depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features have been ruled out because either 1. no major depressive or manic episodes have occurred concurrently with active phase symptoms or 2. If mood episodes have occurred during active phase symptoms, they have been present for a minority of the total duration.
Schizophrenia
____ or more of the following, each present a significant portion of the time during a _____ period. At least one of these must be 1, 2, or 3 (5 total).
For a significant portion of the time since disturbance onset….
If onset was in childhood or adolescence…
Continuous signs of the disturbance persist for at least…
This period must include at least _____ of symptoms (or less if successfully treated) that meet criterion A, and may include prodromal or residual symptoms. During these periods, disturbance may be manifested by…
____ and _____ have been ruled out because either…
or
.
If there is a childhood onset of ___ or ____, additional diagnosis of schizophrenia is made only if…
A. Two or more of the following, each present for a significant portion of the time during a 1-month period (or less if successfully treated). At least one of these must be 1,2, or 3
Delusions
Hallucinations
Disorganized speech
Grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
Negative symptoms (i.e. flat affect, very little speech, avolition, anhedonia, asociality)
B. For a significant portion of the time since disturbance onset, level of functioning in at least one major area is markedly below the level achieved prior to onset (or if onset is in childhood/ adolescence, there is failure to achieve expected level of functioning)
C. Continuous signs of the disturbance persist for at least 6 months. This 6-month period must include at least 1 month of symptoms (or less if successfully treated) that meet criterion A, and may include prodromal or residual symptoms. During these P&R periods, disturbance may be manifested only by negative symptoms or two or more symptoms listed in criterion A in an attenuated form.
D. Schizoaffective disorder and depressive or bipolar disorder with psychotic features have been ruled out because either 1. no major depressive or manic episodes have occurred concurrently with active phase symptoms or 2. If mood episodes have occurred during active phase symptoms, they have been present for a minority of the total duration.
F. If there is childhood onset ASD or communication disorder, the additional diagnosis of schizophrenia is made only if prominent delusions or hallucinations, in addition to other required symptoms, are also present for at least 1 month (or less if successfully treated).
Schizoaffective disorder
A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a ______ (___ or ___), concurrent with ________.
Note
B. ______ or ______ for _____(time period) in the absence of… during the lifetime duration of the illness.
C. Symptoms that meet criteria for ______ are present for…
Can either be ____ or _____ type.
A. An uninterrupted period of illness during which there is a major mood episode (depressive or manic), Concurrent with criterion A of schizophrenia.
Note: the major depressive episode must include Criterion A1: depressed mood.
B. Delusions or hallucinations for 2 or more weeks in the absence of a major mood episode during the lifetime duration of the illness
C. Symptoms that meet criteria for a major mood episode are present for the majority of the total duration of the active and residual portions of the illness.
Can either be bipolar or depressive type.
For confusion about criteria B and C:
Criterion B ensures psychosis is not 100% tied to mood.
There MUST be at least one “pure psychosis” period.
Criterion C ensures mood symptoms dominate the overall course.
Mood symptoms must appear more often than they are absent.
Both can happen simultaneously.
Substance Use Disorder
A. Problematic pattern of substance use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by at least ___ of the following ___ symptoms, occurring within a _____ period.
List the 4 categories of criteria
Then list possible symptoms for each category
At least 2 of the following symptoms, occurring within a 12-month period.
4 Categories of criteria: Impaired control, Social impairment, Risky use, Pharmacological Criteria.
Impaired control
Substance is taken in larger amounts or over a longer period of time than intended
Persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control use
Great deal of time spent obtaining, using, or recovering from the substance
Craving, or a strong desire/ urge to use the substance.
Social Impairment
Recurrent use resulting in failure to fulfill major obligations (Work, school, or home)
Continued use despite social/ interpersonal problems caused or worsened by the substance
Important social, occupational, or recreational activities are given up or reduced because of substance use
Risky Use
Recurrent use in physically hazardous situations
Continued use despite knowing it is causing or worsening a physical or psychological problem
Pharmacological criteria
Tolerance
Need for markedly increased amounts to achieve effect
Diminished effect with continued use of the same amount
Withdrawal
Characteristic withdrawal syndrome for the substance
Substance taken to relieve or avoid withdrawal symptoms
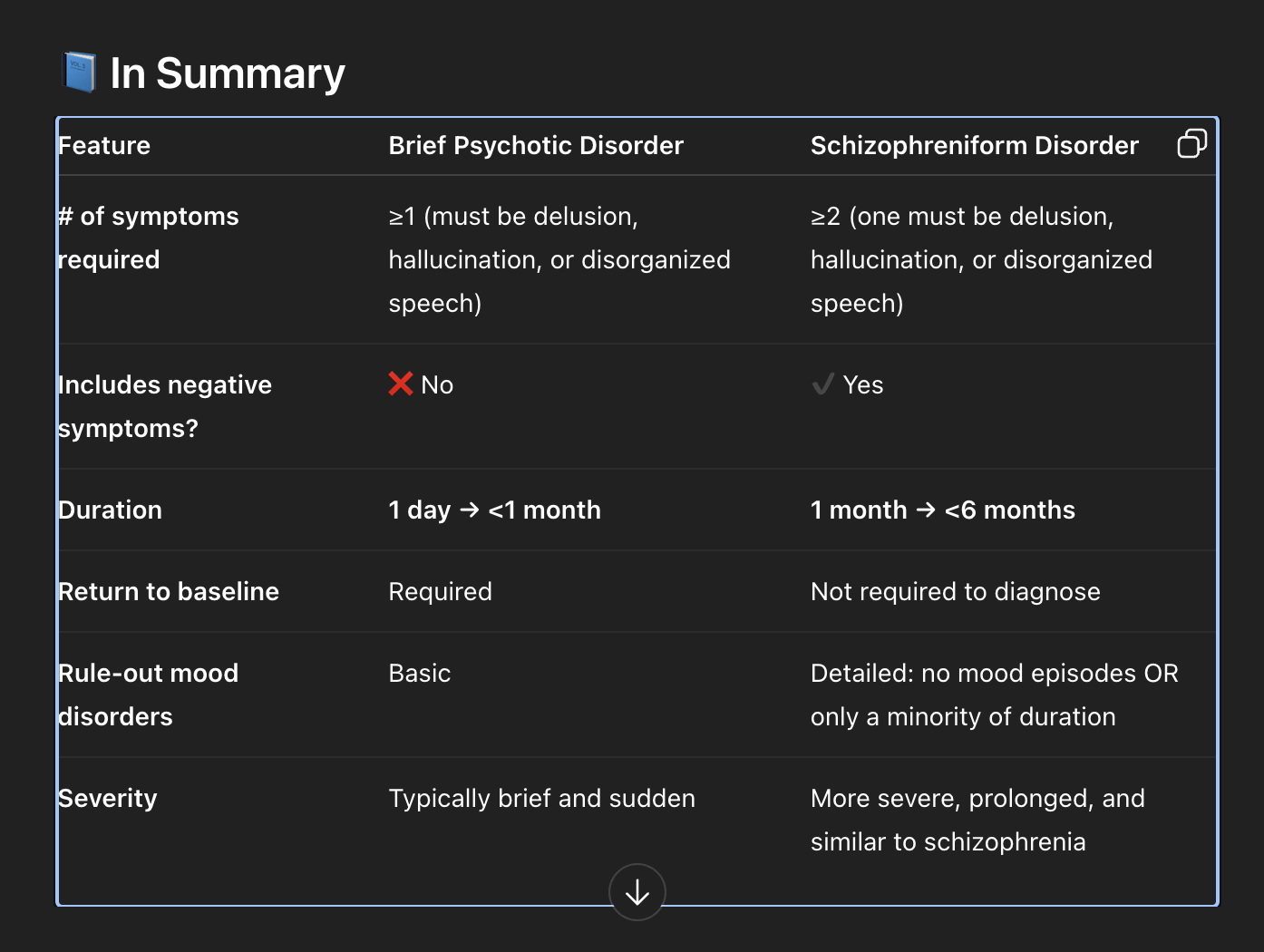
Difference between brief psychotic and schizophreniform disorder?
time frames for each
Symptom # and presentation
Recovery?
Brief Psychotic = Brief and Positive
Short duration (At least 1 day but less than 1 month)
Positive symptoms only
Quick full recovery
1 or more symptoms required
Schizophreniform = Schizophrenia-Lite
Same symptoms as schizophrenia
Same rule-outs
Same structure
But time-limited (1–6 months) (for schizophrenia, time active phase symptoms are more than 1 month, and full illness is more than 6 months)
2 or more symptoms required.
Can include negative symptoms
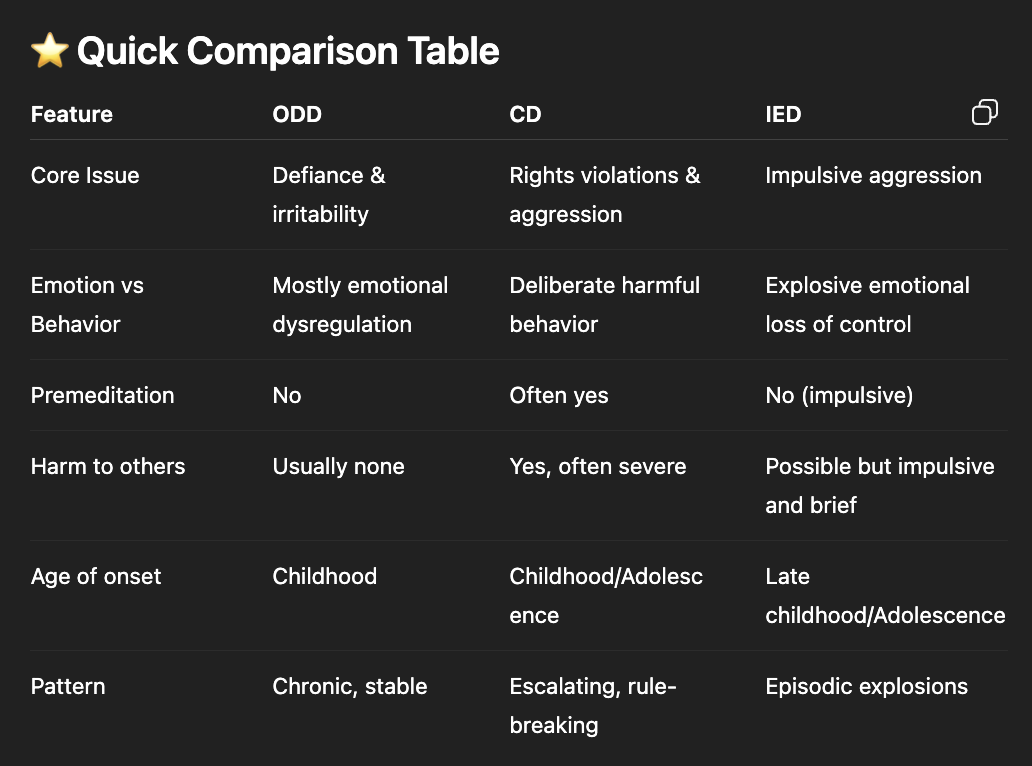
Summarize differences between oppositional defiant, conduct, and intermittent explosive disorder.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder: Think: “Chronic irritation + defiance, but not dangerous.”
Conduct Disorder: Think: “Violation of rights, aggression, crime-like behavior.”
Intermittent Explosive Disorder : Think: “Sudden explosive anger — impulsive, not planned.”
What are prodromal and residual symptoms?
✅ Prodromal symptoms
Occur before the first psychotic episode
Represent early warning signs
Often involve declining functioning, increased odd behaviors, and subtle cognitive changes
✅ Residual symptoms
Occur after a psychotic episode
Represent partial remission
Often involve leftover negative symptoms and mild thought disturbance
Difference between disruptive mood dysregulation disorder and intermittent explosive disorder?
Big-picture difference (one sentence)
DMDD = chronic, pervasive irritability with frequent outbursts (3+ times a week)
IED = episodic impulsive aggression with normal mood between outbursts