BIOL 208: Lecture 8 - Water constraints
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
High temp = death. Is it the high temp that kills you or something else?
WATER LOSS kills you
can only tolerate 12-14% dehydration
Why is water life?
Most organisms are composed mostly of water
50 - 90 %
Fill in the blanks: Organisms must control ______ levels inside their bodies to keep _____ balance
Solute levels to keep water balance
True or false: Water is limited in MOST environments, everywhere but aquatic.
FALSE
limited even in aquatic environment
depends on conditions of H2O itself
What are Estuaries?
brackish environments
What are brackish environments?
Combo of fresh + salt water
What is the unit for measuring salt concentrations in aquatic environments?
ppt
Parts per Thousand
Fill in the blank: LAKES display a _____ range of salinity and different ____ content (eg. ____ or ____ dominated)
WIDE RANGE of salinity + different ION content (eg. Sodium or sulfate dominated)
Water budget: All organisms regulate their internal water concentration by balancing what?
How much water they take in vs. how much water they let out
*****True or false: these water inputs + outputs = DIFFERENT between plants + animals, and remain CONSTANT between terrestrial + aquatic animals
FALSE
different between terrestrial + aquatic animals as well as between plants + animals
What do all the components of the Water budget equation for AQUATIC ORGANISMS represent?
Wi = Internal water
Wd = water gain through DRINKING
Ws = water loss though SECRETION
Wo = Water loss OR gain through OSMOSIS
Diffusion vs. Osmosis
Diffusion:
movement of particles from areas of high [ ] to low due to random movement
Osmosis:
Movement of water down [ ] gradient through a semipermeable membrane
What is Osmolarity in the context of this course?
Amount of solute/water in an organism in relation to its environment.
How the solute [ ] of the organism relates to the enviornemnt
What are the 3 types of osmolarity?
Isosmotic
Hyperosmotic
Hypoosmotic
Define Each osmolarity term.
Isosmotic: SAME between the 2
Hyperosmotic: Organism has LOWER water and HIGHER solute
Hypoosmotic: Organism has HIGHRE water + LOWER solute than environment
MOST MARINE FISH are What type of osmolarity?
ISOOSMOTIC
****MANY MARINE fish are What type of Osmolarity?
Hypoosmotic
organism has low solute + higher water compared to environment
****What are the RISKS that HYPOOSMOTIC MARINE FISH experience?
WATER LOSS (dehydration)
Surplus salt intake through gills
*****What 3 SOLUTIONS do Hypoosmotic marine fish used to mitigate the RISKS involved with being Hypoosmotic?
DRINK constantly to counteract dehydration
LOW URINATION rates + volumes
Get RID of EXCESS SALT through gills
****Why do hypoosmotic marine fish need to get rid of excess salt if they are already low in solute concentration relative to their environment?
Constant drinking to combat dehydration = SALT WATER
Need to get rid of the salt from drinking
****What part of the GILLS of hypoosmotic marine fish gets rid of the excess salt?
Specialized Chloride Cells
MOST FRESHWATER organisms are What type of osmolarity?
HYPEROSMOTIC
High in solutes + Low in water relative to environment
****What are the RISKS that HYPEROSMOTIC FRESHWATER FISH experience?
Too much water enters
Too many salts leave organism
*****What 3 SOLUTIONS do Hyperosmotic freshwater fish used to mitigate the RISKS involved with being Hypoosmotic?
Do NOT DRINK
Excrete excess internal water via LARGE AMOUNTS OF DILUTE URINE
Replace salts by reabsorbing sodium chloride
What are the 2 ways that hyperosmotic freshwater fish replace salts?
Absorbing sodium chloride in gills
Ingesting Food
****Why do hyperosmotic Freshwater fish need to ingest excess salt if they are already High in solute concentration relative to their environment?
Even though their body fluids are more concentrated than the water, they are constantly losing salts to the environment.
To prevent their internal salt concentration from dropping too low, they must actively replace the lost ions.
Define Anadromous + Catadromous
Both = fish that move between salt + fresh water
Anadromous:
Born in FRESH, Spend most of life at SEA + comeback to FRESH to SPAWN
Catadromous:
Born in SEA, spend most of life in fresh + return to SEA to SPAWN
Give an example of each type of fish that move between salt + fresh water.
Anadromous = Salmon, smelt, shad, striped bass, sturgeon
Catadromous = Eels
*****How do fish that move between salt + fresh water deal with the difference in osmolarity?
they ACCLIMATE to the salinity of their new environment
reversible physiological change
*****What do they(moving fish) use to ACCLIMATE to the changing salinity?
Shifting their secretion cells (SPECIALIZED CHLORIDE CELLS)
*****HOW do they(moving fish) use their specialized chloride cells to ACCLIMATE to the new salinity?
Fresh water = TAKE IN SALT
Ocean = EXCRETE SALT
****Why do they (moving fish) Fresh water = TAKE IN SALT + Ocean = EXCRETE SALT. Shouldn’t it be the other way around?
The key is what direction salts and water are moving passively.
Fish have to counteract those passive movements to stay balanced (homeostasis).
eg. Freshwater, = Gain too much water, lose salts. They’re losing salts by diffusion and need to replace them.
****Is the Water balance equation for TERRESTRIAL systems the same as the one for AQUATIC systems?
NO
****Is the Water balance equation for TERRESTRIAL PLANTS systems the same as the one for ANIMAL systems?
NO
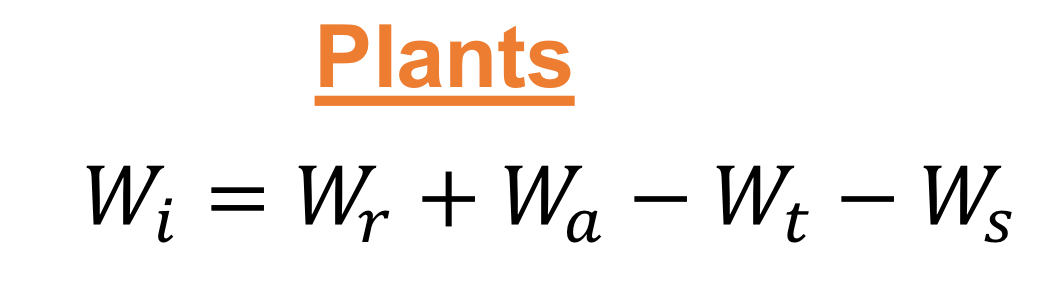
What do each component of the Water budget equation for TERRESTRIAL PLANT systems represent?
Wi = Internal water
Wr = Water gained from ROOTS
Wa = Water gained from AIR
Wt = Water Loss from Transpiration (stomata)
Ws = Water loss from Secretion
What could be some sources of Ws (secretion) for plants?
Nectar
Producing seeds
What are vascular plants?
Plants that have tissue for movement of H2O (XYLEM)
How does Water get from the Roots to the leaves for plants?
Water potential
Define Water Potential
Water’s potential energy/ ability to do WORK
Work = move itself according to [ ] gradient
******Is water potential normally a negative number or a positive number? What numbers does it RANGE between
Negative (0 to -100)
*****Where is it normally 0 and where is it normally -100? How does water potential change in value as you move up the tree/plant?
0 = ROOTS
-100 = Hot dry air
Water potential DECREASES in value as you move up the plant/tree
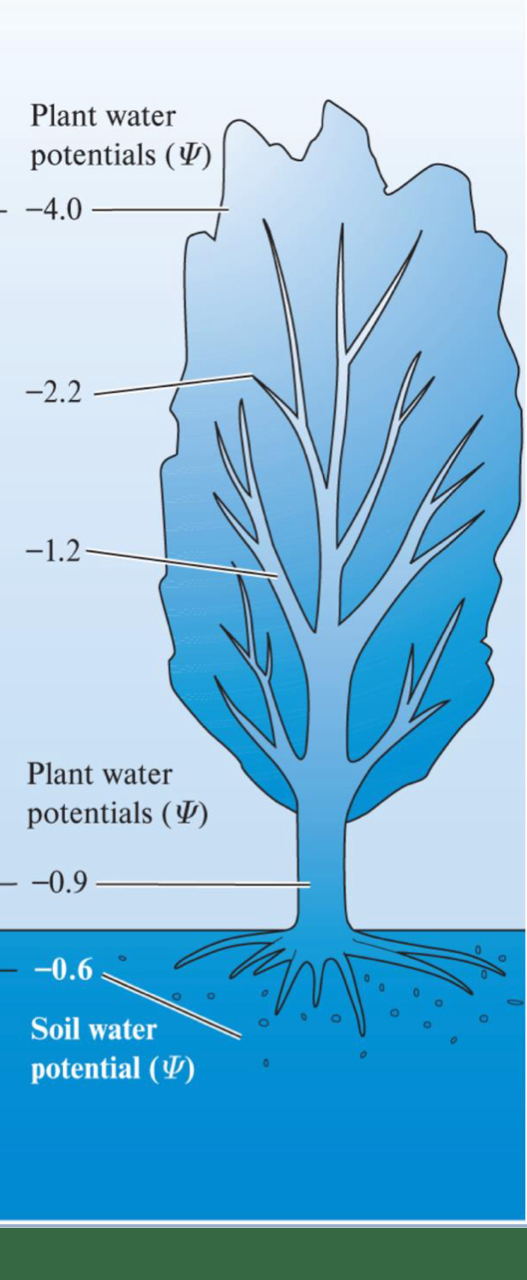
*****Water move from ____ to _____ water potential. If there is a _____ in water potential, water will move.
Move from HIGH to LOW water potential
If there is a difference in water potential, water will move
****What force that move water in Aq. systems vs. terrestrial systems?
Aq. = Diffusion + osmosis
Terrestrial = Water potential
*****How is water potential different than osmosis?
Water potential includes PRESSURE (water vapor pressure)
****How does WATER VAPOUR PRESSURE affect MOVEMENT OF WATER from plants?
EVAPORATION of H2O from leaves = needed to maintain H2O potential for movement of H2O from roots to leaves
Define Water vapor Density
Quantity of Water vapor that Air actually holds
Define Saturation Water vapor Density
MAX quantity of Water vapor that air can potential hold at a given temp
*****Can cold or Warm air hold more water vapor? How does that affect/relate to Saturation water vapor pressure?
Warm air can hold more water vapor
Warm = High Saturation pressure = HIGHER PRESSURE
Cold = Low saturation = LOWER PRESSURE
Hot vs. cold air. How does each affect water movement?
Hot = High sat. water vapor pressure = allow more evaporation = lower water potential
Cold = Low sat. water vapor pressure = less evaporation = Higher water potential
*****How does HOT MOIST air each affect the water movement from roots to leaves. WHY?
Hot Air with High Water vapor = LOW EVAPORATION from leaf because air already has a lot of H2O
*****What type of Air has the most Water movement?
HOT DRY AIR
Hot = High saturation water vapor pressure
Dry = air not already saturated with moisture = allows for evaporation
*****What type of Air has the least Water movement?
Cold moist air
Cold = Low Saturation water vapor pressure
Moist = low evaporation, air already saturated
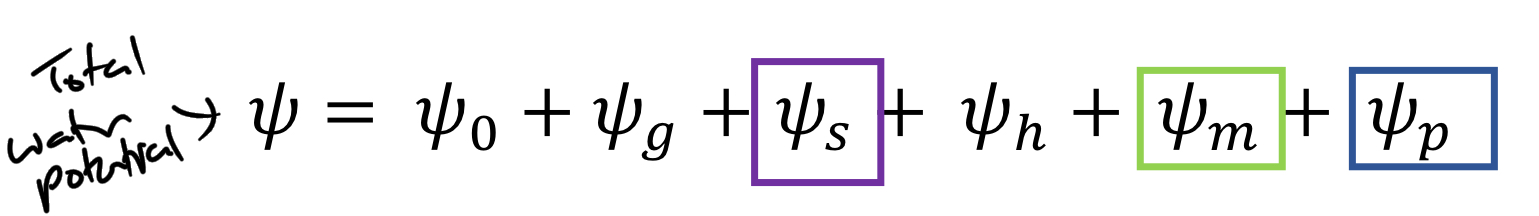
******What does each component of the WATER POTENTIAL equation represent?
0 = water Potential of a REFERENCE SOLUTION (pure water, 0 MPa, highest potential)
g = Force of gravity
s = OSMOTIC pressure
h = Water Vapor Pressure (condition of AIR)
m = Matric pressure
p = Sum of extraneous pressure
****What does it mean by osmotic pressure (s)
Movement in response to different CONCENTRATIONS of SOLUTES
****What does it mean by Matric pressure (m)
Pull through adhesion
adhesive nature of H2O = movement against gravity
****What does it mean by Sum of Extraneous pressure (p)
Anything that is not already in the equation
eg. Evapotranspiration
Evaporation of leaves themselves
Where relative to the Tree has the lowest water potential and which has the highest?
Tree canopy = lowest
Trunk
Roots
Soil = Highest
******Why is Tree canopy the lowest water potential? What components of the Water potential equation causes this? (2)
There is the lowest/most negative Evaporation (p) and Water vapor pressure (h)
Leaf surfaces interact with the air = Evaporation + transpiration
******Why is Tree TRUNK moderate to low water potential? What components of the Water potential equation causes this? (2)
Matric pressure (m) and Osmolarity (s) are low very negative/ highly affecting water potential
****Why is Matric pressure Lower/More negative in trunks?
Smaller tubes increase CAPILLARY PULL
****What is the (s) Osmolarity of the ROOTS compared to the SOIL? Why?
Osmolarity (S) = LOWER in roots than in soil
Roots have more solutes = promote water movement in to roots
*****Acquisition of water in roots is essential for water pump to work but WATER = LIMITED in many environments. What is a STRATEGY for plants to acquire water?
Deep roots
acquire water found in deeper soil later or at the ground water level
Roots tend to be DEEPER in ____ climates than in ____ climates
Deeper in dryer than in wetter climates
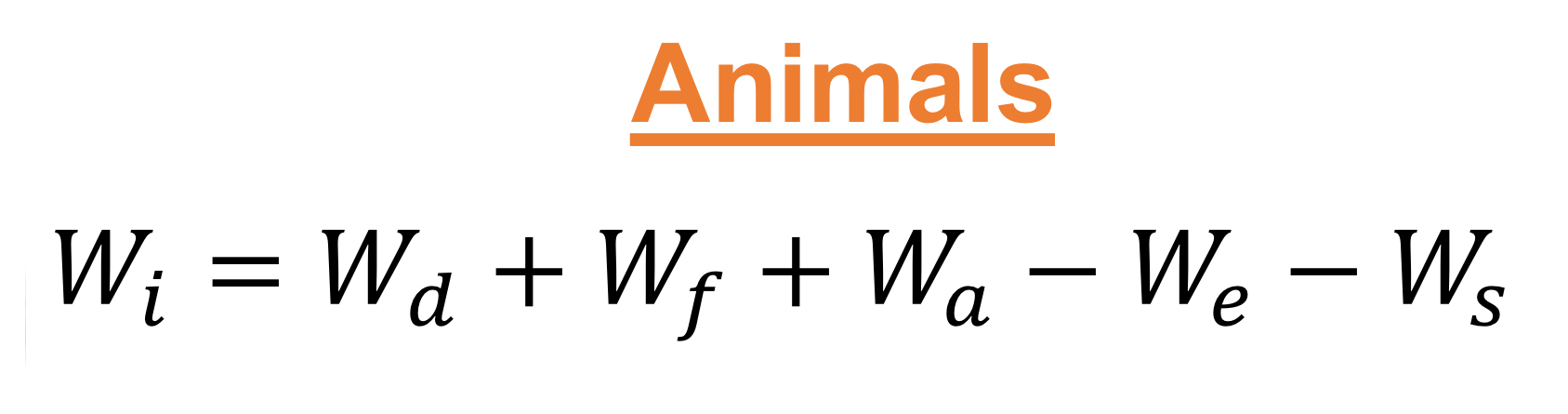
What do each component of the Water budget equation for TERRESTRIAL ANIMAL systems represent?
Wi = internal water
Wd = gain from drinking water
Wf = gain from food water
Wa = gain from air
We = LOSS from evaporation
Ws = LOSS from secretion
What is the main avenue of water loss by animals? What about water gain?
Water loss = EVAPORATION
Gain = FOOD + DRINK
How is Water gained through food?
Liquid in the food
METABOLIC WATER
What is Metabolic water?
Water gained from aerobic respiration
Glucose + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6 H2O
****True or false: Wf is VERY EFFICIENT
True
****What are the 5 methods of Water CONSERVATION mentioned in class? Indicate which specific organisms they each apply to.
Thick waxy cuticles or shells (Invertebrates + Plants)
Store water + release slowly in periods of drought (terrestrial plants + animals)
Conservation of urine, feces + sweat (Terrestrial animals)
Behavioral adaptation (Terrestrial animals of plants)
Wilting (terrestrial plants)
****For the storage of water in ANIMALS: What are the 2 strategies used?
Metabolic water (eg. fat storage in Camels)
Storage in Bloodstream + Tissues
What is an example of a behavioral adaptation done by animals to minimize water loss?
Burrows
microclimate = cooler + transpiration = lower
*****How does Wilting Reduce water loss?
Reduce surface area during prolonged water stress + drop in turgor pressure (decrease in shape integrity due to removal of water)
Wilting _____ transpiration + _______
Wilting reduces transpiration + photosynthesis
Is wilting a long term strategy? Why?
No
Permanent wilting point will occur + plant will not recover even when watered