Emergency Medicine EOR
1/1766
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1767 Terms
HACEK
HACEK: Haemophilus, Actinobacillus, Cardiobacterium, Eikenella, Kingella (hard to culture)
HACEK organisms in endocarditis present when
native valves in community acquired
tx of HACEK endocarditis
ceftriaxone
MCC of endocarditis, valve, and when it occurs
Streptococcus viridans, *mitral valve
*usually as late complication of valve replacement
MCC of bacterial endocarditis in IVDU and MC valve
- staph aureus - causes smaller vegetations
- tricuspid valve
stroke + fever think
think endocarditis!
patient has vegetation on the aortic or mitral valve the vegetation breaks off goes up to the brain causes the stroke. They will have the fever from the endocarditis and the vegetation in brain causing the stroke.
MCC of bacterial endocarditis in prosthetic valve
Staphylococcus epidermidis (within 60 days) or staph aureus
candida endocarditis
- slow-growing organism
- most common source is a contaminated line
- typically causes large vegetations in endocarditis.
- Large vegetation endocarditis in the early post-valve replacement period (2 months post-surgery) is most likely due to fungus, that is, Candida infection
what causes subacute bacterial endocarditis
Indolent (slow moving) infection of abnormal valves with less virulent organisms (S. viridans)
osler nodes
PAINFUL raised lesions on palms and soles with endocarditis
(O = ouch!)
*result from deposition of immune complexes
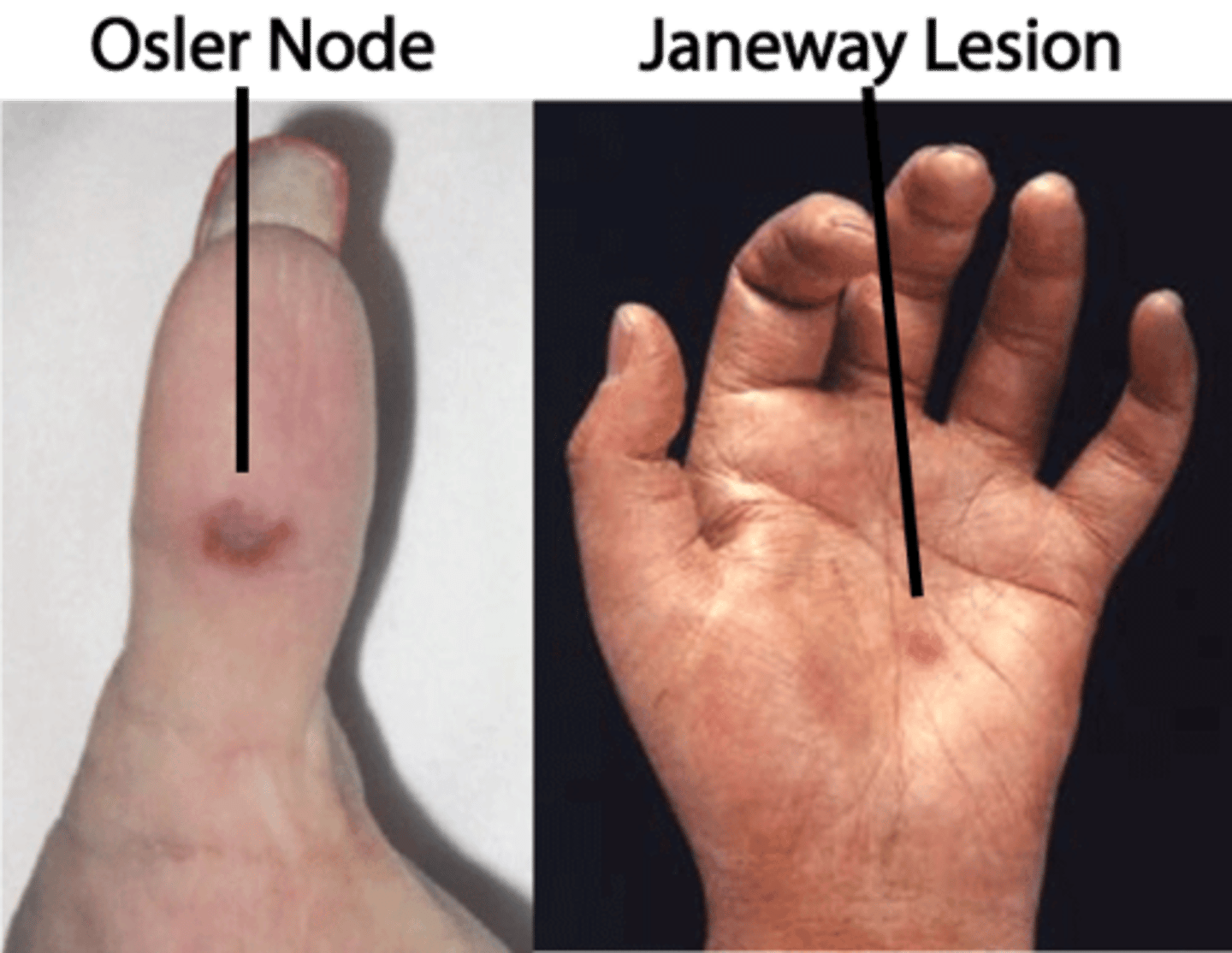
Janeway leisions
PAINLESS macule on palms/soles
what cause Osler nodes and Janeway lesions
emboli that lodge in small blood vessels in the skin.
4 classic peripheral findings of bacterial endocarditis
Janeway lesions, Osler nodes, Roth spots, Splinter hemorrhages
other physical signs of bacterial endocarditis
Petechiae: These are small, flat hemorrhages on the skin. They are caused by bleeding from small blood vessels.
Purpura: These are larger, raised hemorrhages on the skin. They are also caused by bleeding from small blood vessels.
Clubbing: This is a thickening of the fingertips and/or toenails. It is caused by a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the blood.
Splenomegaly: This is an enlargement of the spleen. It is caused by an increased number of white blood cells in the spleen.
Hepatomegaly: This is an enlargement of the liver. It is caused by inflammation or infection of the liver.
Hematuria: Due to emboli or glomerulonephritis.
Neurologic findings consistent with CVA, such as visual loss, motor weakness, and aphasia
who needs prophylaxis in endocarditis
1. Prosthetic heart valve 2. Heart repair using prosthetic material 3. Prior history of endocarditis 4. Congenital heart disease
diagnostic study of endocarditis
- 3 sets of blood cultures 1 hour apart
- EKG
- echo
- CBC
gold standard diagnosis of bacterial endocarditis
transesophageal echocardiogram
How to qualify for endocarditis based off of Duke criteria
2 major OR 1 major + 3 minor OR 5 minor
Major duke criteria
1. sustained bacteremia (2 positive cultures)
2. endocardial involvement --> positive echo showing vegetations or NEW valvular regurgitation
Minor duke criteria
1. predisposing condition (IVDU)
2. Fever (over 100.4)
3. vascular/embolic phenomena: janeway lesion, septic emboli, ICH
4. Immunologic phenomena: Osler nodes, Roth spots, positive RF, acute glomerulonephritis
5. positive blood culture not meeting major criteria
6. positive echo not meeting major criteria
empiric therapy for native valve bacterial endocarditis
PCN/ampicillin + gentamicin + vanco (in IVDU)
(IV ampicillin+ nafcillin + gentamicin)
empiric therapy for prosthetic valve bacterial endocarditis
Vanco + gentamicin + rifampin
tx of endocarditis in IVDU
IV nafcillin
abx prophylaxis for endocarditis
2 g of Amoxicillin 30-60 minutes before the procedure
tx of fungal endocarditis
Amphotericin B, caspofungin
- if severe --> valve replacement
how long to treat bacterial endocarditis
4-6 weeks
tx of laryngitis
self-limited
- oral and IM steroids for vocal performers to hasten recovery
tx of bacterial laryngitis
erythromycin, cefuroxime, or Augmentin
MC bugs of acute otitis media
strep pneumo, h. flu, moraxella catarrhalis
diagnosis of AOM
1) bulging of the tympanic membrane or 2) other signs of acute inflammation (e.g., marked erythema of the tympanic membrane, fever, ear pain) and middle ear effusion
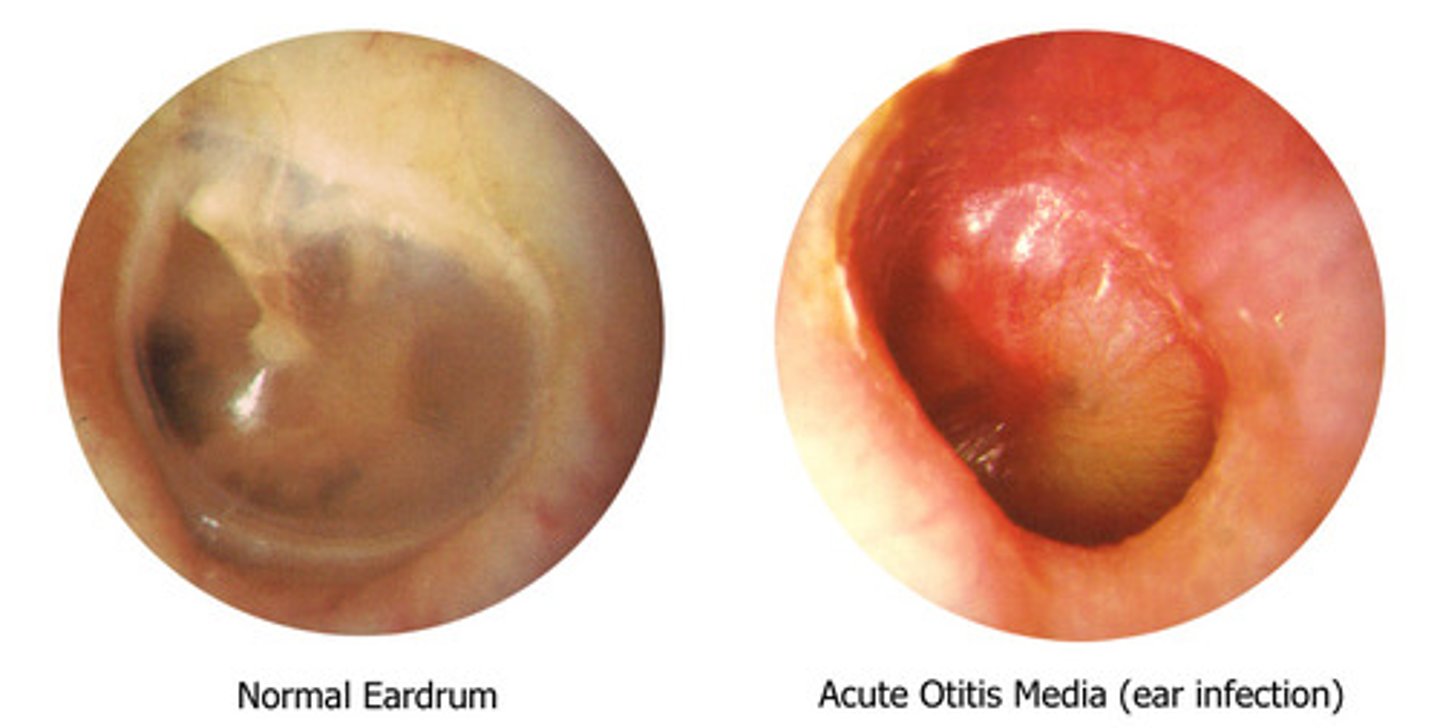
AOM diagnosis for children under 2
limited mobility of the TM with pneumotoscopy
- they will usually be tugging at the ear
what does tuning fork show for AOM
bone conduction > air conduction
acute otitis media timeline
under 3 weeks
tx timeline for AOM
< 2 y for 10 days
> 2 y for 5-7 days
complications of AOM
Mastoiditis and bullous myringitis
tx of AOM
- amoxicillin
- 2nd line= amox-clav
- PCN allergy = azithro, Bactrim
tx of chronic or recurrent otitis media
myringotomy with ventilation tube
tx of auricular hematoma (to prevent cauliflower ear)
- evacuate clot
- cephalexin to prevent infection
centor criteria for strep pharyngitis
1. fever >100.4
2. pharyngotonsillar exudates
3. tender anterior cervical lymphadenopathy
4. absence of cough
0-1, nothing needed
2-3, throat culture
4-5, give abx (PCN)
tx of strep pharyngitis
PCN *prevent rheumatic fever*
- erythromycin if allergy
most cases of pharyngitis are due to
viral - adenovirus
tx of pharyngitis
- symptomatic = fluids, warm saline, lozenges
- fungal = clotrimazole, nystatin
non-resolving pharyngitis + sexually active, consider
gonorrhea pharyngitis
inhaled steroid use + pharyngitis, consider
fungal pharyngitis
3/4 Centor criteria met ---> get _____ --> if negative, get _____
rapid strep test ---> throat culture (gold standard)
what causes GABHS pharyngitis
S. pyogenes
tx of fungal pharyngitis
clotrimazole, miconazole, or nystatin
tx of Gonococcal pharyngitis
ceftriaxone IM
what can happen if you do not treat strep pharyngitis
scarlet fever, glomerulonephritis, acute rheumatic fever, abscess formation
diagnosis of bullous pemphigoid
skin biopsy with direct immunofluorescence exam shows deposition of IgG and C3 basement membrane
bullous pemphigoid s/s
- Tense pruritic blisters, widespread bullae, usually in lower trunk, itchy, dense, symmetric
- negative Nikolsky sign
- does not effect mucus membranes
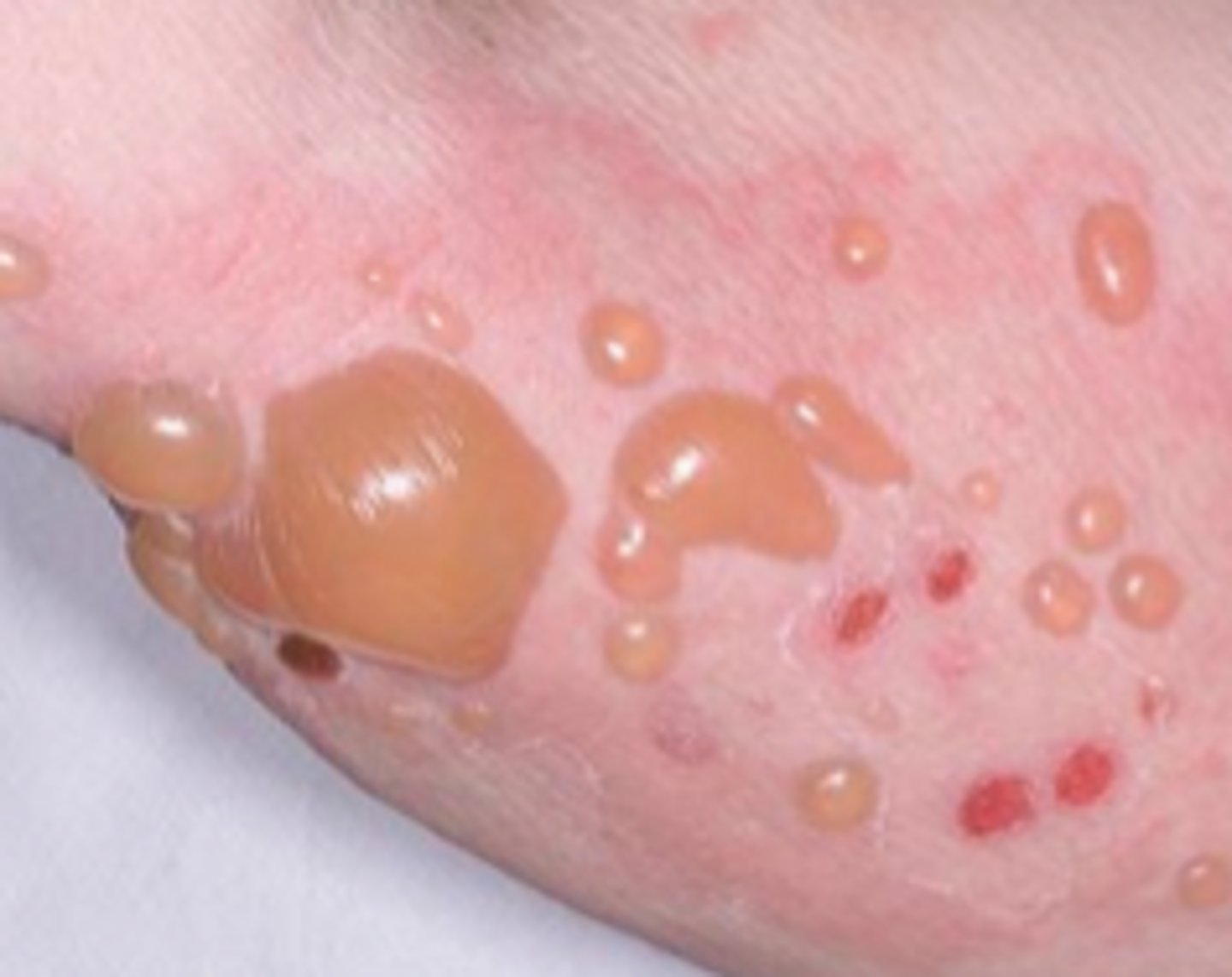
what is bullous pemphigoid
chronic autoimmune condition that is IgG produced, usually in pts over 60
tx of bulls pemphigoid
steroids
major burn characterized as
>25% TBSA adult, >20% young/old, >10% full thickness burn, burns involving face, hands, perineum, feet, cross major joints/circumferential
who needs fluid resuscitation with a burn
children with TBSA over 10%, adults with over 15%
1st degree burn
Erythema of involved tissue, skin blanches with pressure, the skin may be tender
tx of burns
Monitor ABCs, fluid replacement, irrigate chemical burns for 20mins, wrap fingers and toes individually, and sulfadiazine
cervical sprain s/s
stiffness, paarspinal muscle tenderness, spasm, + spurling test
cervical sprain tx
cervical collar for 2-3 days, NSAIDs, ice/heat
muscle relaxant for back strain
cyclobenzaprine, could also use benzodiazepine
back strain caused by
lifting, twisting, or strenuous activity --> is the MCC of back pain
non septic olecranon bursitis
acute trauma or repetitive trauma causes inflammation of the olecranon bursa
olecranon septic bursitis
- infection from microorganisms transferred via trauma to the skin overlying the bursa -- MC = staph aureus
- Pain or fever may suggest an infectious etiology - R/O septic or gout - aspirate
what could be helpful to treat bursitis and tendonitis
steroid injections (not in patellar though!!)
treat olecranon bursitis
PT, rest and ice, systemic antibiotics based on culture if septic, NSAIDS, injected corticosteroids and joint, operative bursectomy
when to aspirate bursitis?
septic, fever, DM, immunocompromised
tx of septic bursitis (normal and MRSA)
dicloxacillin or cephalexin
MRSA = bactrim or clindamycin
Pre-patellar bursitis (housemaid's knee)
- due to increased pressure on knee
- swelling over the patella
- common in wrestlers - concern for septic bursitis
tx of pre patellar bursitis
compressive wrap, NSAIDs, +/- aspiration, and immobilization
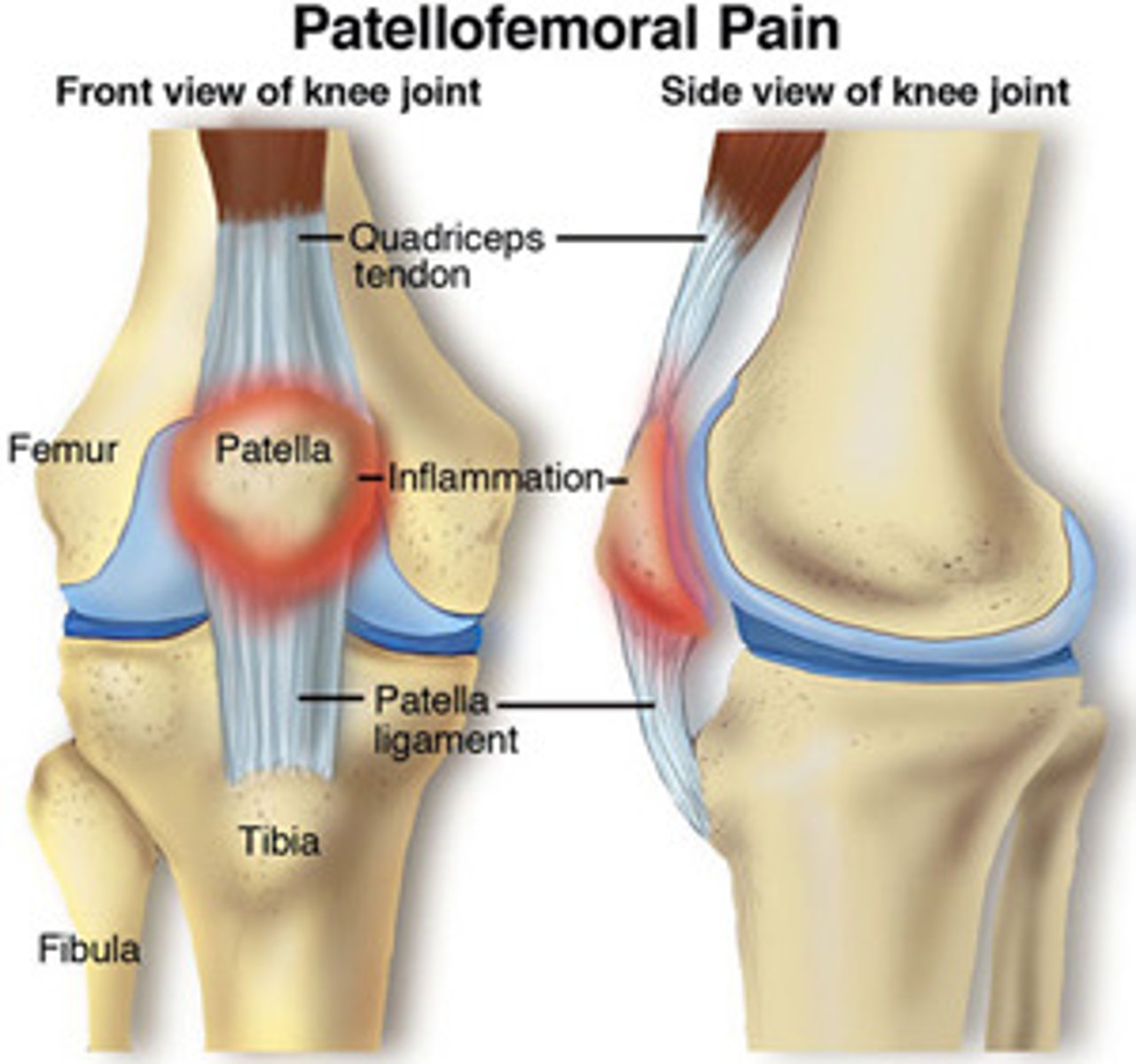
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
"runner's knee", which refers to anterior knee pain that worsens while going up or down stairs, walking hills, or prolonged sitting with knees flexed
*sunrise view on xray
pes anserine bursitis
MEDIAL knee pain; secondary to overuse
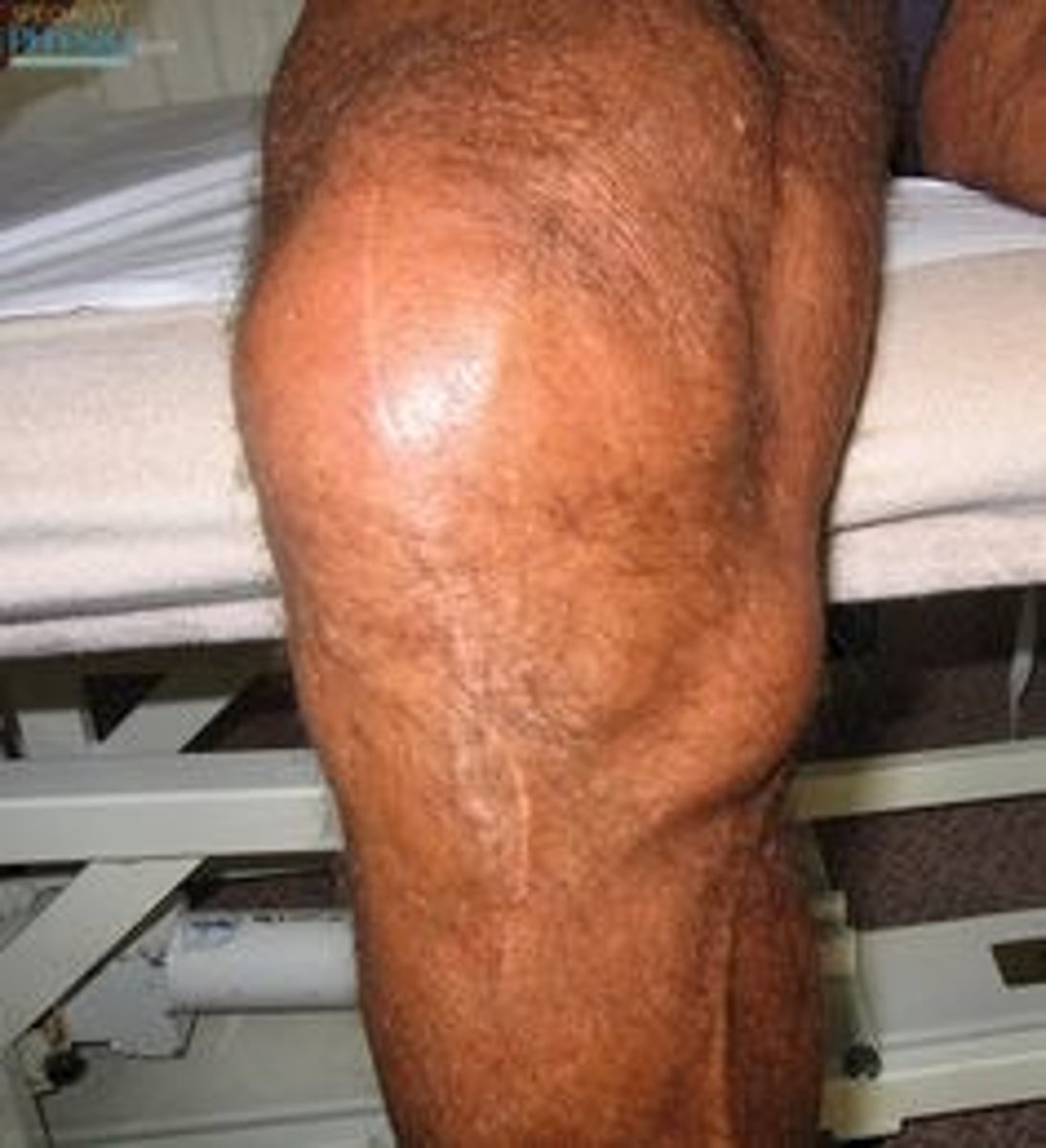
subacromial bursitis
superior surface of the supraspinatus tendon from the overlying coracoacromial ligament, acromion, and coracoid (the acromial arch) and from the deep surface of the deltoid muscle
*pain not associated with trauma usually
s/s of subacromial bursitis
pain with motion and at rest can cause fluid to accumulate. The presentation is very similar to what you would see with subacromial impingement
when to aspirate subacromial bursa
fever, diabetic or immunocompromised
features of tendonitis
pain with movement, swelling, impaired function; resolves over several weeks but recurrence common
patellar tendonitis
- "jumper's knee"
- Activity-related anterior knee pain associated with focal patellar tendon tendernes
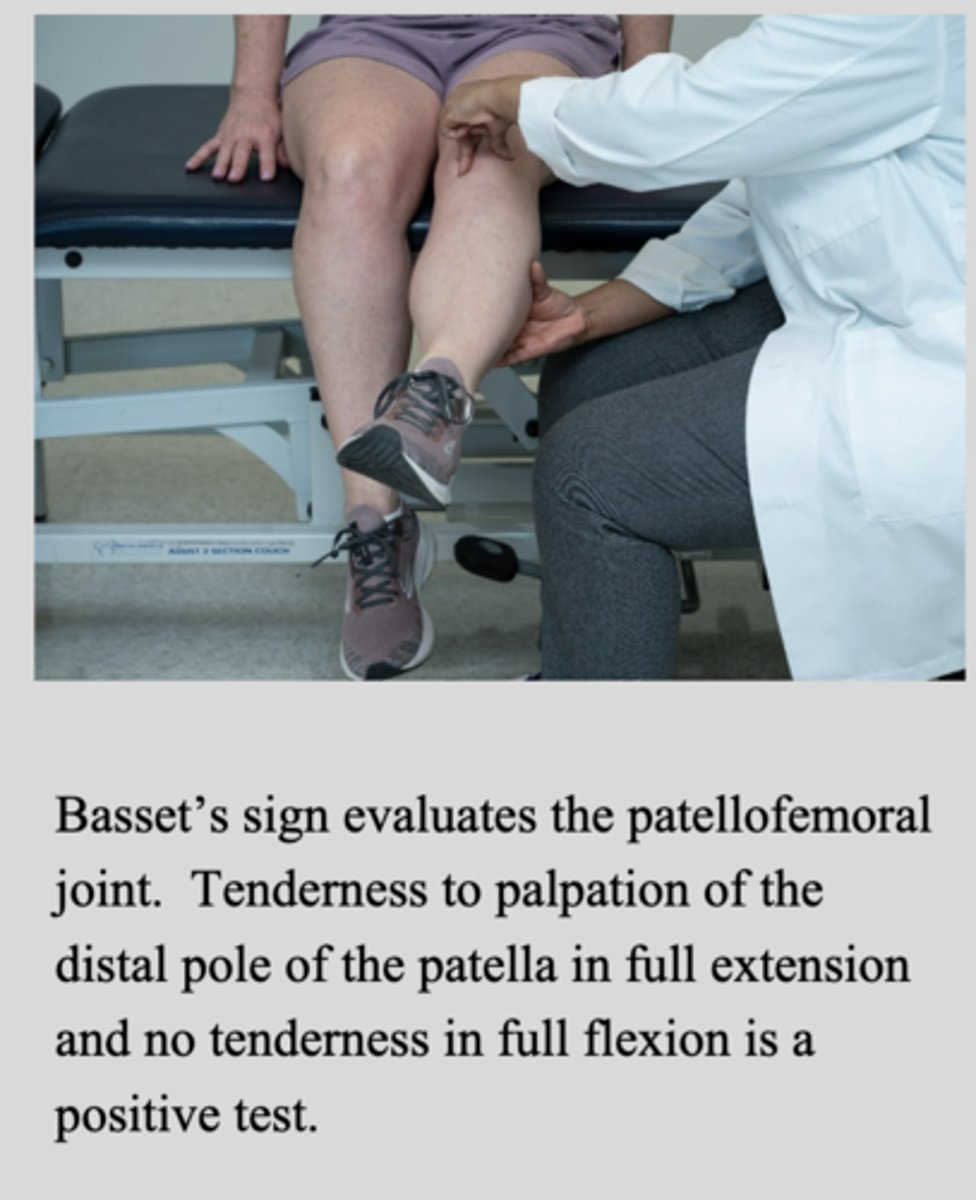
Basset's sign
tenderness to palpation at the distal pole of the patella in full extension and no tenderness to palpation at the distal pole of the patella in full flexion --> patellar tendonitis
tx of patellar tendonitis
Ice, rest, activity modification, followed by physical therapy. Surgical excision and suture repair as needed
diagnosis of patellar tendonitis
History and physical examination are usually sufficient for diagnosis of infrapatellar tendinitis
- MRI can show the extent of the injury
what is C/I in patellar tendonitis care
steroid injections --> risk of tendon rupture!
presentation of bicep tendonitis
- pain in the biceps groove
- Anterior shoulder pain - may have pain radiating down the region of the biceps, symptoms may be similar in nature and location to the rotator cuff or subacromial impingement pain
- Pain with resisted supination of the elbow
Popeye deformity
biceps tendon rupture
MRI of biceps tendonitis
thickening and tenosynovitis of proximal biceps tendon - increased T2 signalaround the biceps tendon
tx of bicep tendonitis
NSAIDs, PT strengthening, and steroid injections
special tests for bicep tendonitis
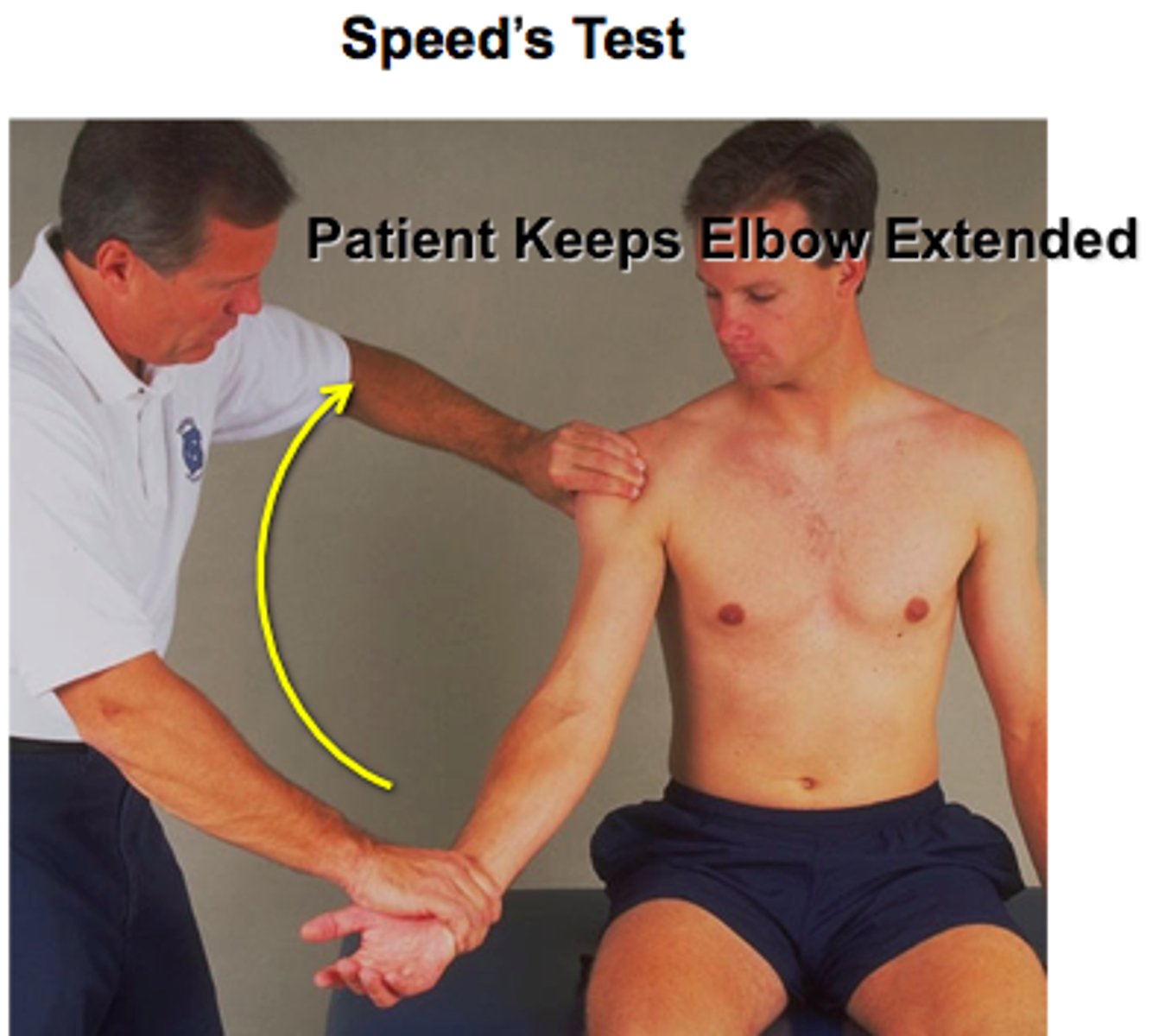
Speed test and Yergason's test
speed test
*biceps tendonitis
- Pain elicited in the bicipital groove when the patient attempts to forward elevate shoulder against examiner resistance while the elbow extended, and forearm supinated
- Positive if the pain is reproduced
- May also be positive in patients with SLAP lesions
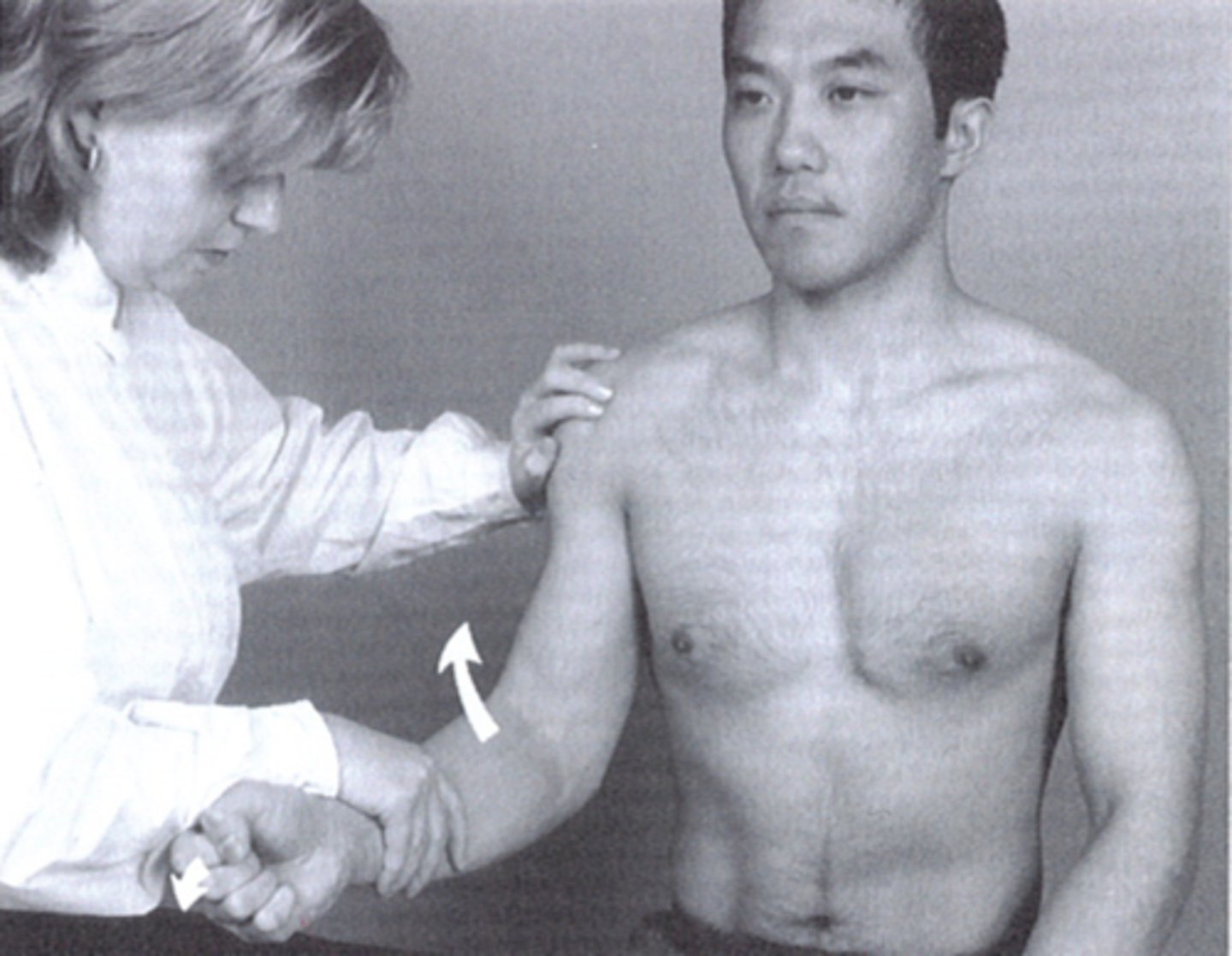
Yergason's test
- Elbow flexed 90 degrees, wrist supination against resistance -Positive if the pain is reproduced.
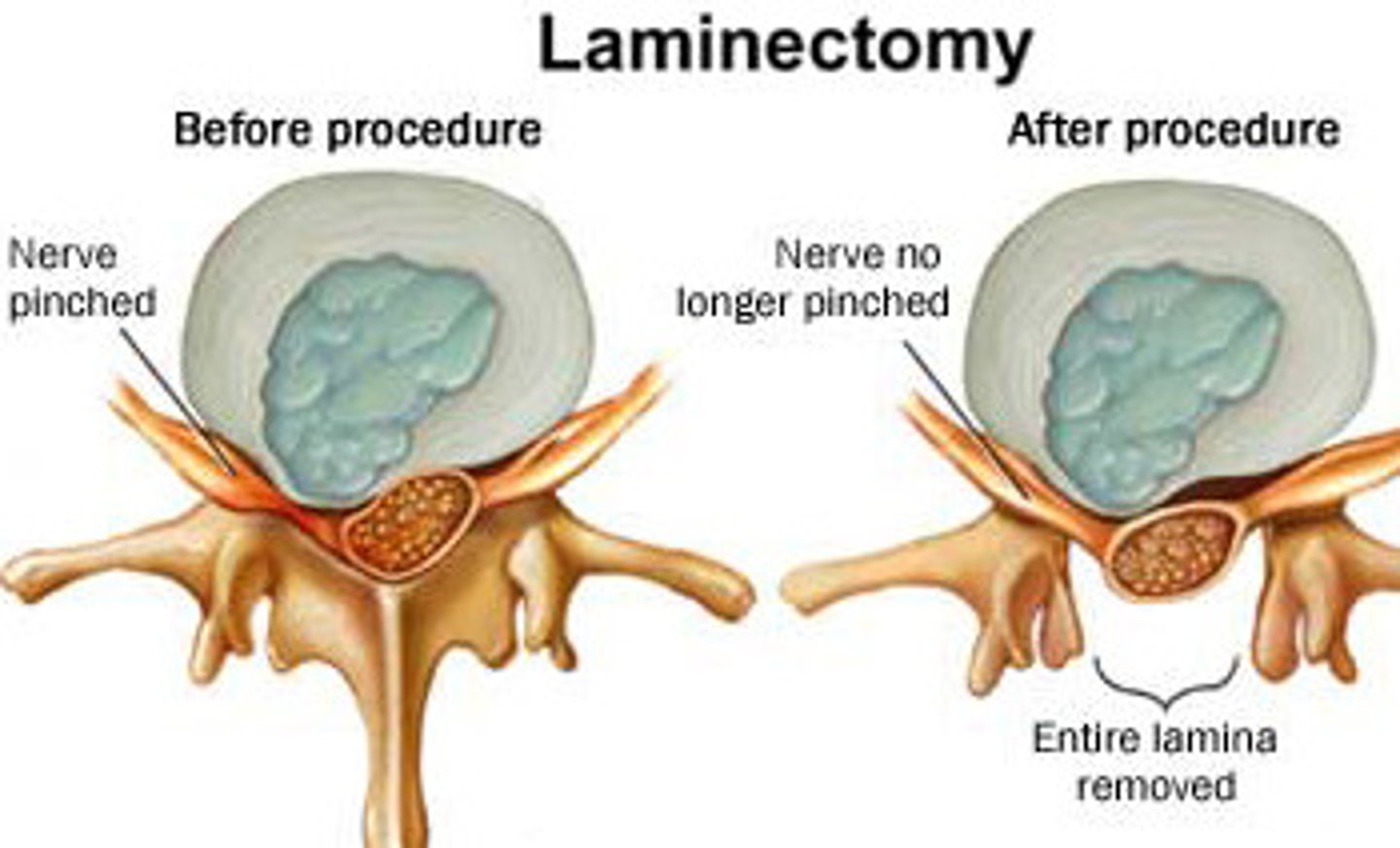
what is cauda equina syndrome
midline disk herniation that compresses nerve roots usually at L4-L5 level
dx of cauda equina
MRI - new onset urinary symptoms with associated back pain/sciatica
tx of cauda equina
urgent surgical referral --> laminectomy to decompress
Costochondritis s/s
pain and tenderness on the breastbone, pain in more than one rib, or pain that gets worse with deep breaths or coughing
risk factors for costochondritis
age >40, high-impact sports, manual labor, allergies, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis
pain with costochondritis
reproduced with palpation of the chest wall area
(if not, think of another diagnosis)
tx of costochondritis
- Tylenol, NSAIDs
- Applying heat
-PT, local steroid injection
what more serious condition may mimic costochondritis
Pulmonary embolism
Tietze syndrome
costochondritis + palpable edema; inflammatory process
tx of proximal humerus fx
sling
splint for distal or shaft humerus fracture
sugar tong splint (distal) and coaptation splint (shaft)
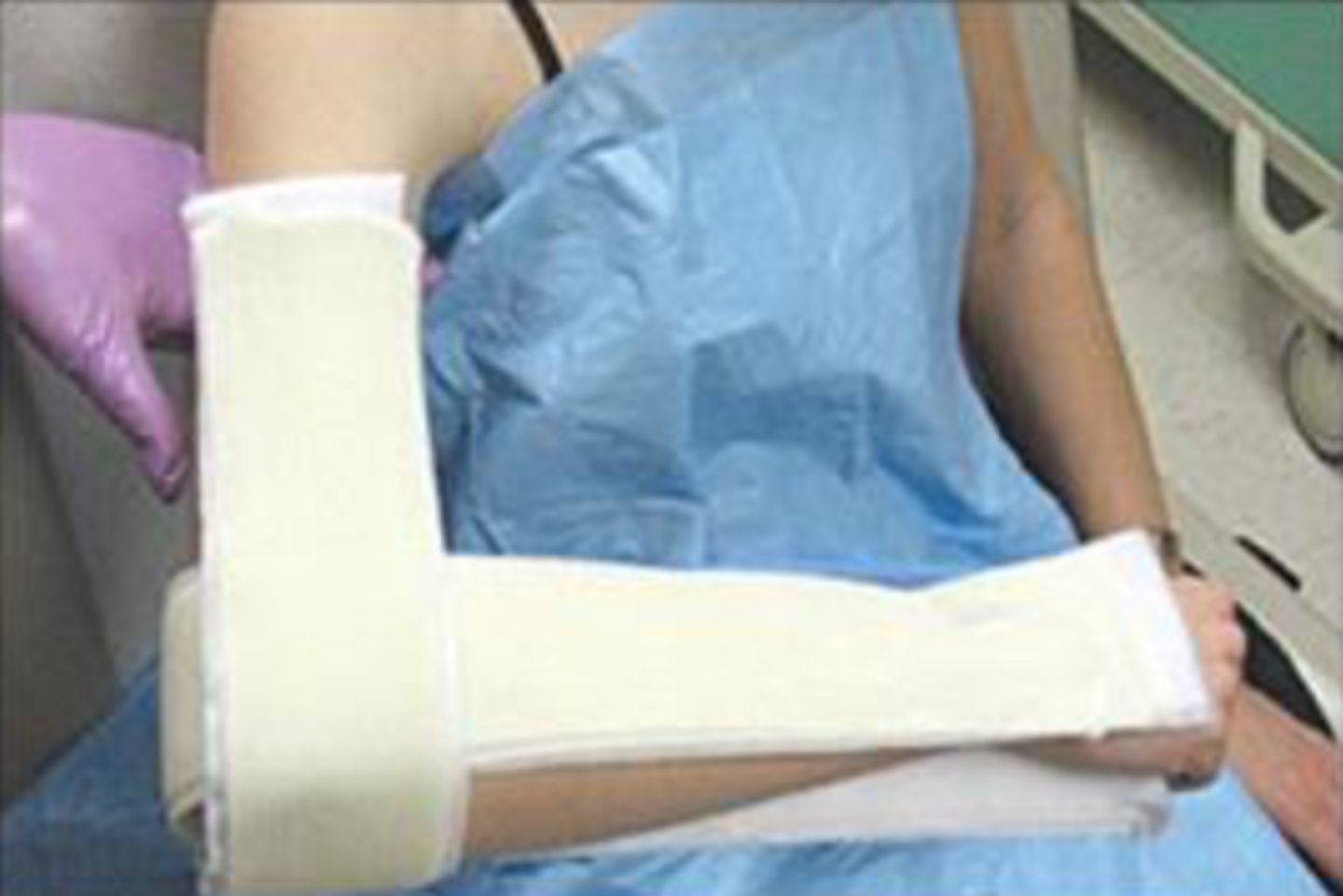
complication of distal/shaft humerus fracture
radial nv injury = wrist drop
complication of proximal humerus fracture
axillary nv injury --> avascular necrosis or deltoid paresthesia