the palatine bone + the hard palate
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
where is the palatine bone located/what parts does it form
posterior of hard palate
lateral wall of nasal cavity
posterior floor of orbit
medial wall of pterygopalatine fossa
what are the articulations of the palatine bone
maxilla
ethmoid
sphenoid
vomer
inferior turbinate bone (conchae)
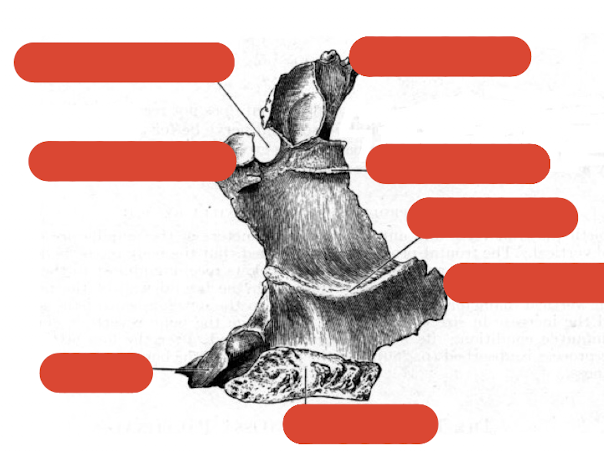
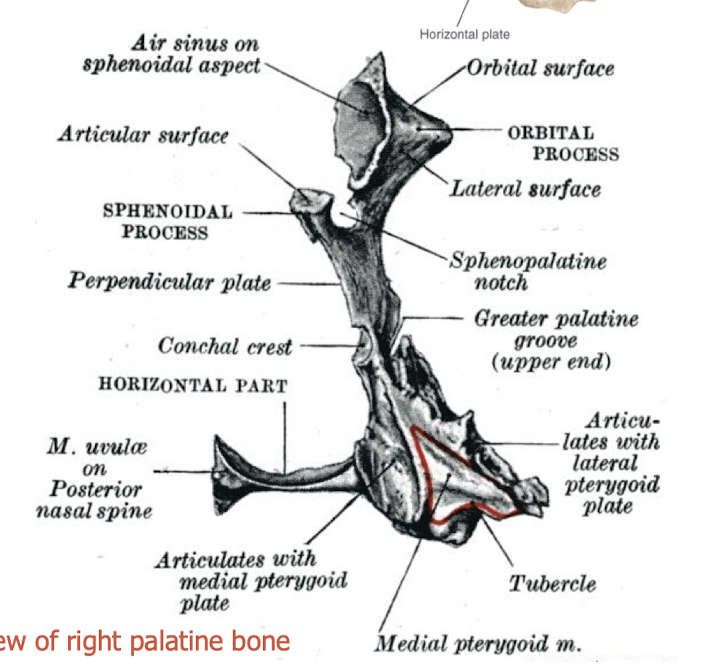
what are the components of the palatine bone
horizontal plate (palatine)
vertical plate (nasal)
tuberosity
orbital process
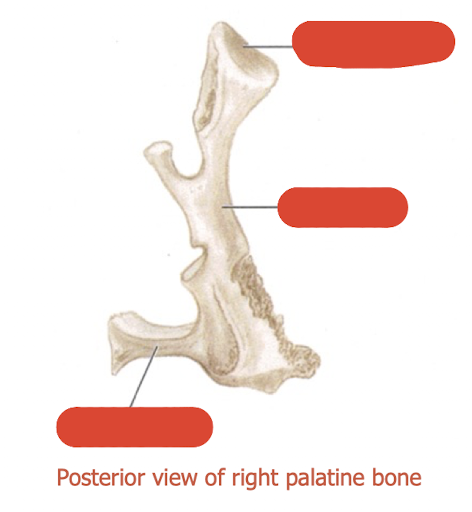
label this diagram
describe the horizontal plate
forms posterior 1/3 of the hard palate
foramina between join of horizontal plate and vertical plate - greater palatine foramen (medial side)
describe the tuberosity of the palatine bone
behind the palatine foramen
occupies the notch between pterygoid plates
completes pterygoid fossa
label this diagram
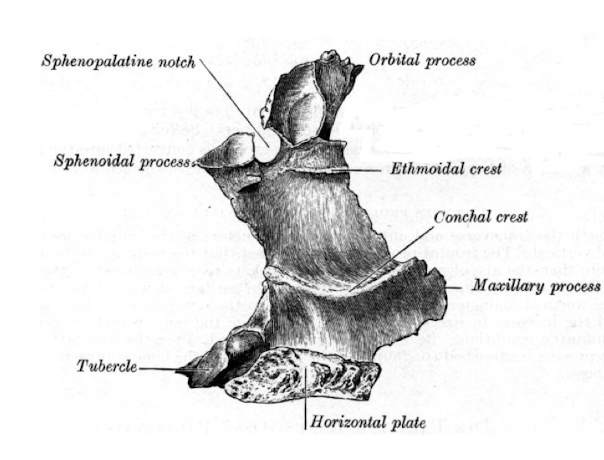
describe the vertical plate of the palatine bone
completes lateral wall of the nasal cavity
anteriorly overlaps back of nasal wall of maxilla
partially covers maxillary antrum
forms medial wall of pterygopalatine fossa
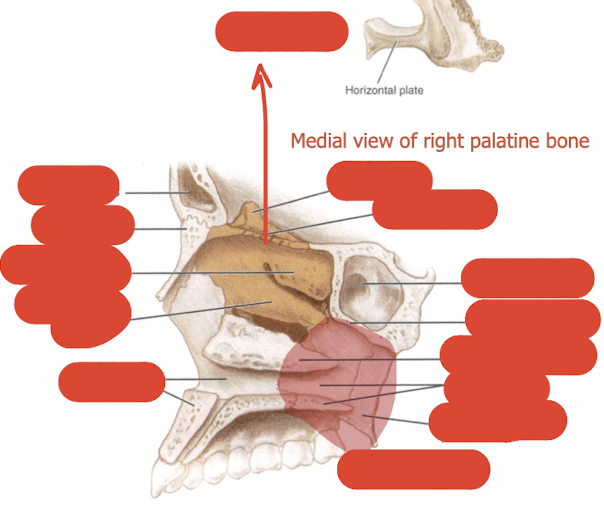
label this diagram
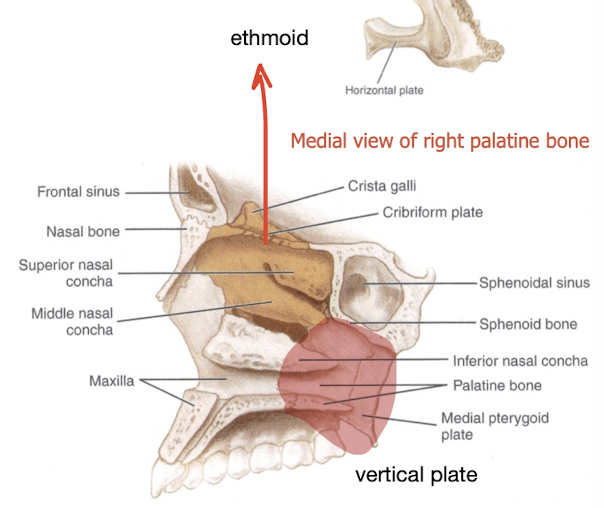
what canal is present in the vertical plate
palatine canal from pterygopalatine fossa to palatine foramina
greater and lesser palatine vessels travel through canal
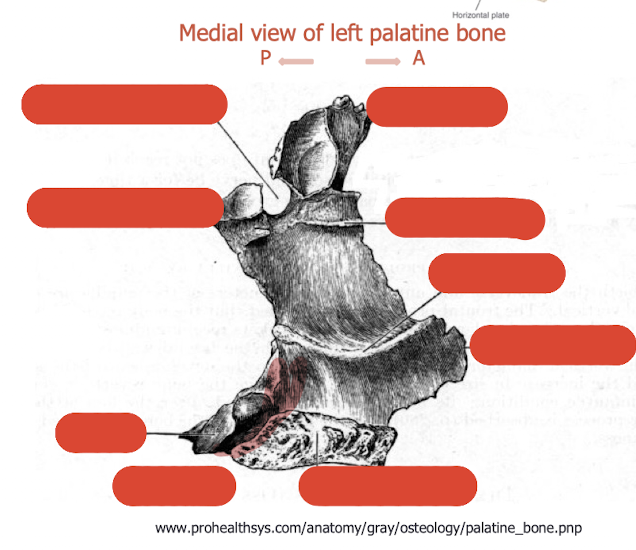
label this diagram
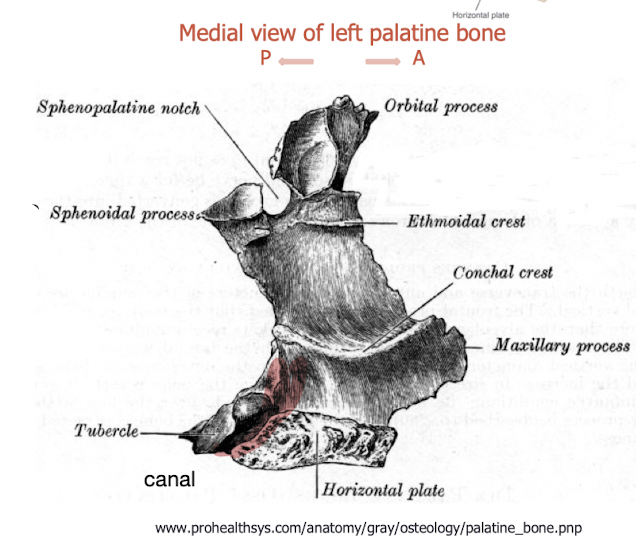
what does the vertical plate articulate with
articulates posteriorly with the medial pterygoid plate
describe the notch in the vertical plate
sphenopalatine notch (in vivo foramen)
becomes a foramina
nerve from outside travels through into nasal cavity
nerve is referred to as sphenopalatine nerve/nasopalatine nerve
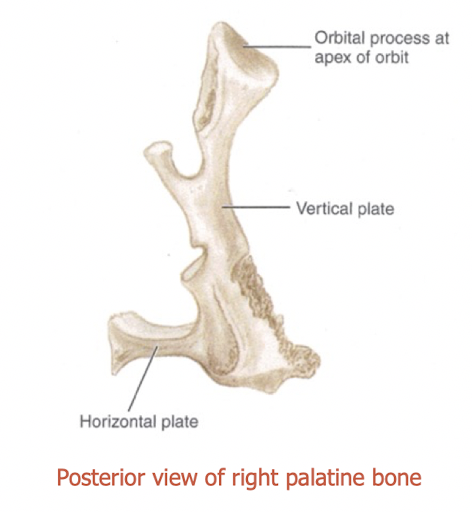
describe the orbital process of the palatine bone
forms posterior floor of the orbit
articulates with maxilla, ethmoid and sphenoid
air sinus for lightness, will get sealed
section of orbital process which creates small portion of orbit
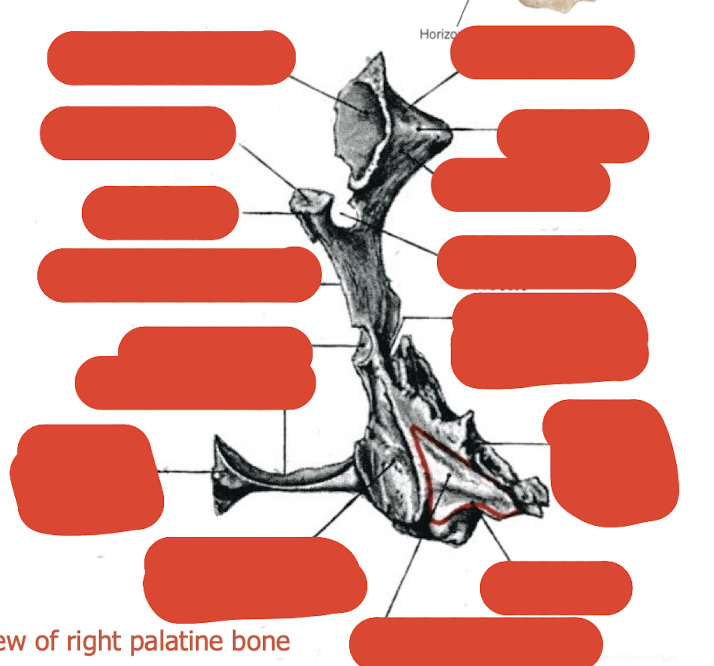
label this diagram
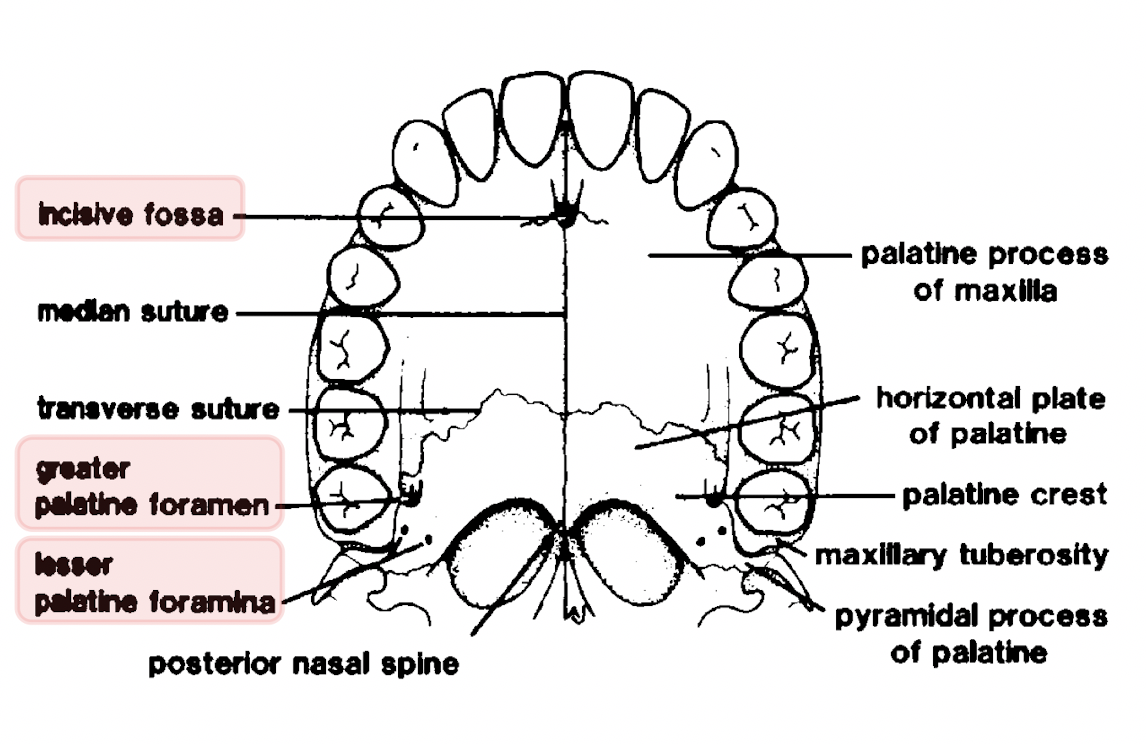
what does the palate separate and what is it divided into
separates the oral and nasal cavities
divided into:-
hard palate
soft palate
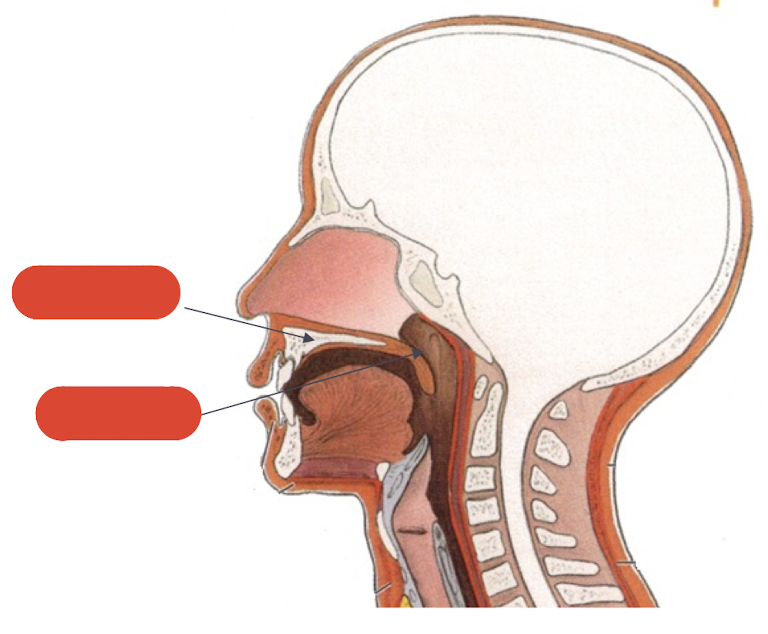
label this diagram
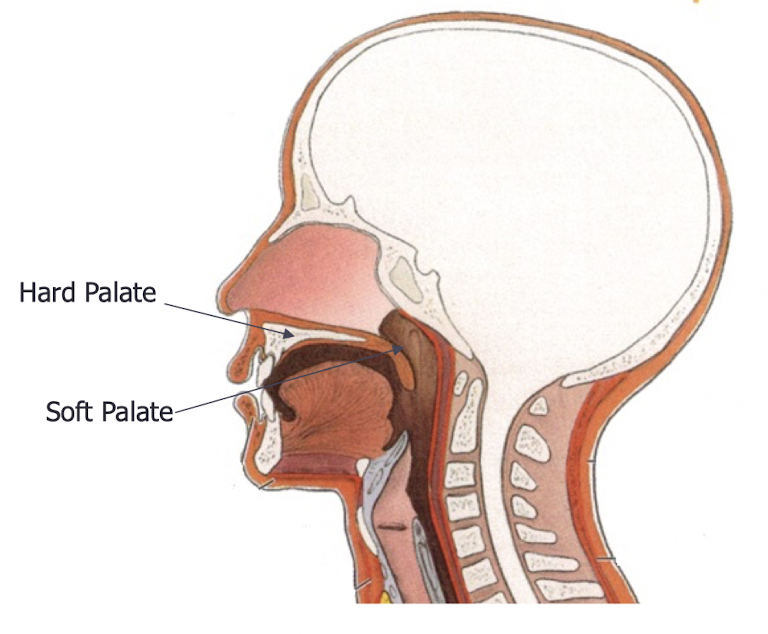
what part of the mouth does the hard palate make up
anterior two thirds of the roof of the mouth
which bones make up the hard palate
palatal processes of the maxillae
horizontal plates of the palatine bones
when is the premaxilla bony part of the hard palate formed
during embryonic life
from median nasal processes which fuse with palatal process of the maxilla at the premaxillary suture
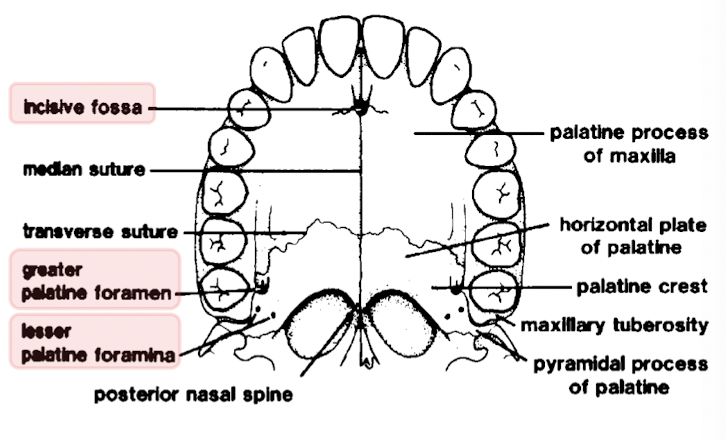
what are the sutures of the hard palate
midline or median palatine suture
transverse palatine suture
what do the suture lines combine to form
the cruciform suture
describe the midline/median palatine suture
runs from posterior nasal spine
down full length of palate
to central incisor teeth
describe the transverse palatine suture
found where palatine bones join the palatal processes of the maxilla
how many main foramina are found in the hard palate and what are they called
three:
incisive - lies immediately behind central incisor teeth
greater palatine - lie anteriorly to tubercle of palatine bone
lesser palatine - lie posteriorly to tubercle of palatine bone
what are the 3 main soft tissue features of the hard palate
incisive papilla
rugae
palatine raphe
describe the incisive papilla
oval prominence found immediately behind central incisor teeth
covers opening of incisive foramen
describe the rugae
irregular branching ridges of dense connective tissue
radiate from incisive papilla and anterior palatine raphe
describe the palatine raphe
flat layer of tissue covering the full length of midline suture
masticatory mucosa covering hard palate is highly keratinised to withstand constant friction
where do the greater palatine nerves and vessels run
run in the submucosal layer
describe the blood supply to the hard palate
posteriorly, greater palatine artery leaves greater palatine foramen
travels forwards within submucosal layer
anteriorly, sphenopalatine artery leaves incisive foramen to supply anterior palatal gingivae
describe the nerve supply to the hard palate
posteriorly, greater palatine nerve leaves greater palatine foramen, travels forwards within mucoperiosteum
anteriorly, sphenopalatine nerve leaves incisive foramen to supply anterior palatal gingivae
label this diagram