Untitled
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:58 AM on 9/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
1
New cards
Well-Being
The status of being healthy, happy, and prosperous.

2
New cards
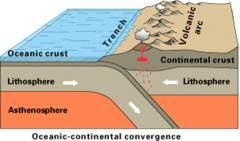
Oceanic Plates
Lie underneath ocean. Dense and rich in iron
3
New cards
environment
the surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal, or plant lives or operates
4
New cards
Economics
How humans as individuals or companies allocate scare resources in the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.

5
New cards
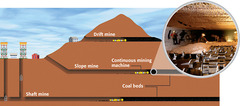
Subsurface Mining
Tunnels within mountain where people go in.
6
New cards
environmental science
branch of science focused on the study of the relationships of the natural world and the relationships between organisms and their environments
7
New cards
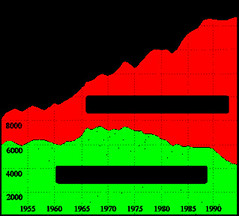
Genuine Progress Indicator
A measurement of the economy that considers personal consumption, income distribution, levels of higher education, resource depletion, pollution, and the health of the population. Over the last 40 years GDP has risen while GPI has remained stable.
8
New cards
Placer Mining
Process of looking for metals and precious stones in river sediments

9
New cards
system
A group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements or parts that function together as a whole to accomplish a goal
10
New cards
Technology Transfer
Less developed countries adopt technological innovations developed in wealthy countries.

11
New cards
Mountaintop Removal
Miners remove entire top of a mountain with explosives

12
New cards
ecosystem
A system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment
13
New cards
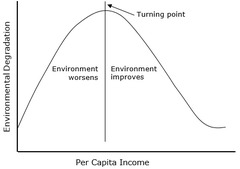
Kuznets Curve
As per capita increases, environmental degradation first increases and then decreases.
14
New cards
Open pit mining
Create large pit or hole in ground to mine

15
New cards
biotic
living things
16
New cards
abiotic
Non-living things
17
New cards
Mining Spoils/Tailings
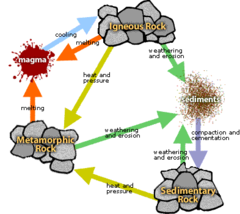
Unwanted waste material created during mining.

18
New cards
Leapfrogging
New technology develops in such a way that makes the older technology obsolete and unnecessary.

19
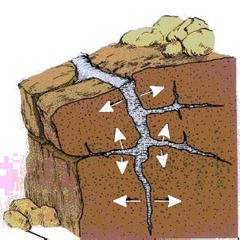
New cards
Microlending
Practice of loaning small amounts of money to people who intend to start a small business in less developed countries. Improves quality of life, increases income, increases confidence, empowers women and sound environmental practices, lowers fertility rate so the population stabilizes, and local markets develop so less fuel is used to transport goods.

20
New cards
Strip Mining
Minerals close to the surface, remove soil and rock to expose them, then return unwanted waste material.

21
New cards
environmentalist
a person who is concerned with or advocates the protection of the environment
22
New cards
Natural Capital
Resources of the planet such as air, water, and minerals.

23
New cards
Metals
Elements with properties that conduct electricity and heat
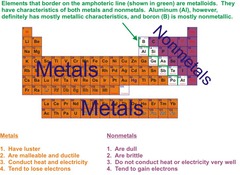
24
New cards
environmental studies
multidisciplinary academic field which systematically studies human interaction with the environment in the interests of solving complex problems
25
New cards
Human Capital
Refers to human knowledge and abilities.

26
New cards
Crustal Abundance
Average Concentration of an element in the crust
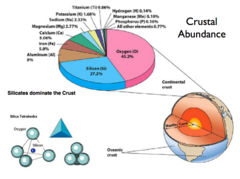
27
New cards
ecosystem services
the many and varied benefits that humans freely gain from the natural environment and from properly-functioning ecosystems
28
New cards
Manufactured capital
All goods and services that humans produce.

29
New cards
Ores
Economically valuable concentrated accumulations of minerals.

30
New cards
environmental indicators
describe the current state of an environmental system
31
New cards
sustainability
the ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level
32
New cards
Soil Degradation
Loss of some or all of the ability of soils to support plant growth.

33
New cards
Market Failure
When an economic system doesn't appropriately account for all costs

34
New cards
biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem
35
New cards
Environmental Economics
Examines the costs and benefits of various policies and regulations that seek to regulate pollution and degradation.

36
New cards
Base Saturation
Measure of proportion of soil bases to soil acids
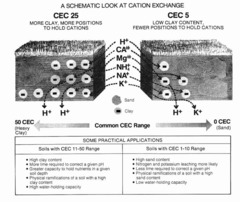
37
New cards
Ecological Economics
Treats economics as a component of ecological systems.
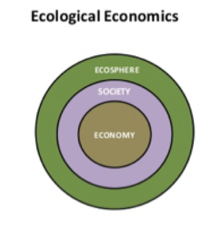
38
New cards
Cation Exchange Capacity
Ability of a soil to absorb and release cations. Determined by clay. Higher is better, but higher decreases porosity, therefore, there's a tradeoff.
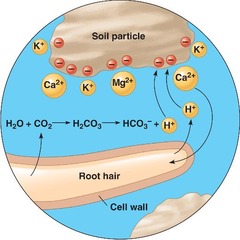
39
New cards
species
a group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes or interbreeding
40
New cards
Vaulation
Assigning monetary value to intangible benefits and natural capital.
41
New cards
Texture of soil
Determined by percentage of sand, silt, and clay
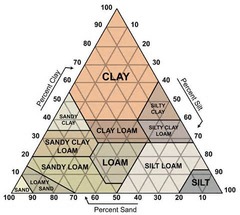
42
New cards
speciation
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution
43
New cards
Environmental worldview
Encompasses how people think the world works, how they view their role in it, and what they believe to be proper behavior regarding the environment.

44
New cards
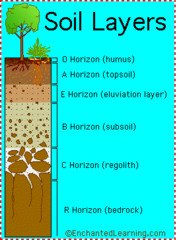
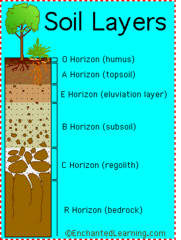
C Horizon
Least weathered. Most similar to parent material
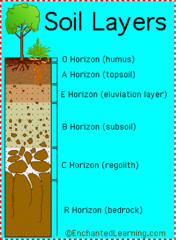
45
New cards
background extinction rate
the standard rate of extinction in earth's geological and biological history before humans became a primary contributor to extinctions
46
New cards
greenhouse gases
a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation, e.g., carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons
47
New cards
B Horizon
Mineral material, little organic matter
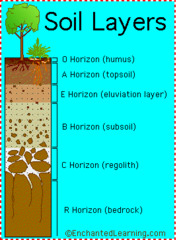
48
New cards
Anthropocentric Worldview
Human centered worldview. Considers that human beings have intrinsic value.
49
New cards
anthropogenic
(chiefly of environmental pollution and pollutants) originating in human activity
50
New cards
E Horizon
Leaches organic acids from above layers to B where they accumulate
51
New cards
Stewardship
Subset of anthropocentric worldview that is the careful and responsible management and care for Earth and its resources.

52
New cards
Biocentric Worldview
Life centered. Humans are one of many species, all of which have intrinsic value.

53
New cards
A Horizon
Topsoil. Organic material and minerals
54
New cards
development
the process of change that occurs during an organism's life to produce a more complex organism
55
New cards
Ecocentric Worldview
Earth centered. Equal value on all living organisms and the ecosystems they live in.
56
New cards
sustainable development
economic development that is conducted without depletion of natural resources
57
New cards
O Horizon
Top layer. Organic horizon and detritus.
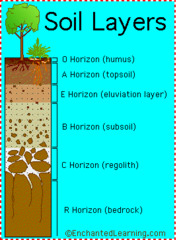
58
New cards
United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP)
A group within the United Nations responsible for gathering environmental info and research and assessing environmental problems.
59
New cards
Parent Material
Rock material underlying a soil
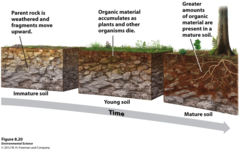
60
New cards
biophilia
an appreciation for life
61
New cards
World Bank
Provides technical and financial assistance to developing countries to reduce poverty and promote growth.

62
New cards
Soil
Mix of geologic and organic components
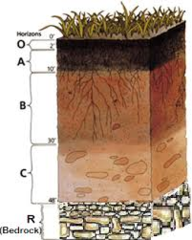
63
New cards
ecological footprint
the impact of a person or community on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resource
64
New cards
scientific method
A series of steps followed to solve problems including collecting data, formulating a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and stating conclusions
65
New cards
World Health Organization (WHO)
A group within the United Nations responsible for human health, including combating the spread of infectious diseases and health issues related to natural disasters.

66
New cards
Deposition
Accumulation or depositing of eroded material

67
New cards
hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
68
New cards
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
A program of the United Nations that works to improve living conditions through economic development.

69
New cards
Erosion
Physical removal of rock fragments from a landscape or ecosystem

70
New cards
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
A U.S. government agency that creates federal policy and oversees enforcement of regulations related to the environment,including science, research, assessment, and education.

71
New cards
Acid Precipitation
Acid rain. Sulfur Dioxide reacts with water vapor to form sulfuric acid in rain.
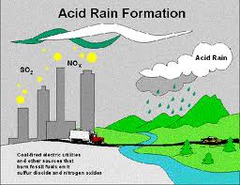
72
New cards
null hypothesis
a statement or idea that can be falsified, or proved wrong
73
New cards
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
A U.S. federal agency responsible for the enforcement of health and safety regulations in the workplace.

74
New cards
Chemical Weathering
Breakdown of rocks and minerals by chemical reactions and dissolving of a rocks chemical elements. Alters newly exposed/primary minerals to make secondary minerals.

75
New cards
replication
the action of copying or reproducing something
76
New cards
Department of Energy (DOE)
A U.S. government agency created in 1977 with the goal of advancing the energy and economic security of the United States.
77
New cards
Physical Weathering
Mechanical breakdown of rocks and minerals. Water, wind, or temp. Plants or burrowing animals can contribute. Exposing more surface area and makes more vulnerable to more erosion.
78
New cards
sample size
The number of subjects used in an experiment or study. Generally, the larger the better.
79
New cards
Human Development Index (HDI)
A measure of economic well-being that combines life expectancy, knowledge, education,and standard of living as shown in GDP per capita and purchasing power.

80
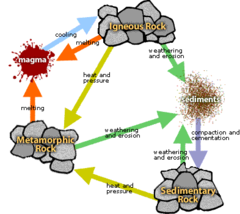
New cards
Metamorphic Rocks
Other rock types subjected to high temps and pressure causing physical and chemical changes. Pressure creates distorted bands called foliation.
81
New cards
accuracy
A description of how close a measurement is to the true value of the quantity measured
82
New cards
precision
a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another
83
New cards
Sedimentary Rocks
Form by sediments like muds, sands, and gravels compressed by overlying sediments. Can be uniform or different. Contains the most fossils.

84
New cards
Human Poverty Index (HPI)
A multidimensional measure of poverty, measuring longevity, knowledge, economic provisioning and social inclusion.

85
New cards
Command and Control Approach
Sets regulations for emissions and controls with fines and punishments

86
New cards
Fractures
Cracks caused by stress after cooling

87
New cards
uncertainty
doubt, the state of being unsure
88
New cards
Incentive Based Approach
Financial benefits and incentives for lowering emissions.

89
New cards
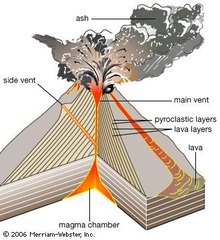
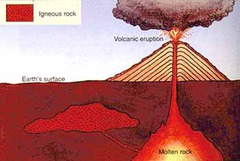
Extrusive Igneous Rock
Magma cools on surface, cools rapidly, minerals don't separate
90
New cards
inductive reasoning
A type of logic in which generalizations are based on a large number of specific observations
91
New cards
Green Tax
Tax places on environmentally harmful activities or emissions.

92
New cards
Intrusive Igneous
Cools inside Earth underground. Many colors, cools slowly, minerals separate.
93
New cards
deductive reasoning
reasoning in which a conclusion is reached by stating a general principle and then applying that principle to a specific case (The sun rises every morning; therefore, the sun will rise on Tuesday morning.)
94
New cards
Triple Bottom Line
Must take into account 3 factors economic, environmental, and social when making decisions.

95
New cards
Igneous Rocks
Forms directly from magma. Classified by composition and mode of formation
96
New cards
critical thinking
the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment
97
New cards
theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data
98
New cards
UN Millennium Declarations
Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger, achieve universal primary education, promote gender equality and empower women, reduce child mortality, improve maternal health, combat HIV, malaria, and other diseases, ensure environmental sustainability, and develop a global partnership for development.
99
New cards
Minerals
Solid, Crystalline, Specific chemical structure, certain formations, uniform

100
New cards
United Nations (UN)
An institution dedicated to promoting dialogue among countries with the goal of maintaining world peace.
